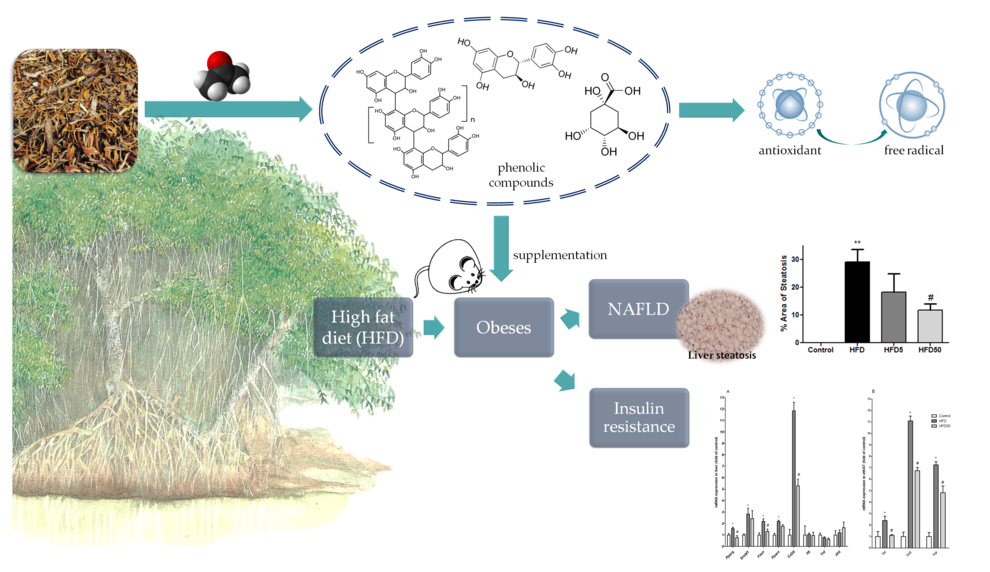
Rhizophora mangle L. is a well-known medicinal plant found in mangroves worldwide used to treatment diabetes. This study evaluated the chemical composition of the acetonic extract from Rhizophora mangle barks (AERM), by HPLC-PDA and FIA-ESI-IT-MS/MS and the effects on high-fat diet induced obesity in mice and its mechanism of action by gene expression of inflammatory markers (Pparg, Ppara, Srebf1, Cd36, Tnf, Ccl2, Lep, Il10, Il6, Fasn, 18s). High-fat diet fed mice during 12 weeks was used as model of obesity and associated alterations. The results were very satisfactory, the extract, rich in polyphenolic compounds, flavonoids and phenolic acids, displayed intense antioxidant activity in vitro (608 µmol Trolox/g), and showed excellent activity against non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and reverse insulin resistance in a model of diet-induced obesity. We can registered a modulatory effect of AERM in liver PPAR-γ mRNA expression associated to an important inhibition of CD36 mRNA expression suggesting that AERM induces the down regulation of CD36 mRNA via PPAR-gamma inhibition. These results support the traditional knowledge about the use of R. mangle for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and reveal the potential of AERM for the treatment of NAFLD and management of obesity and comorbidities.