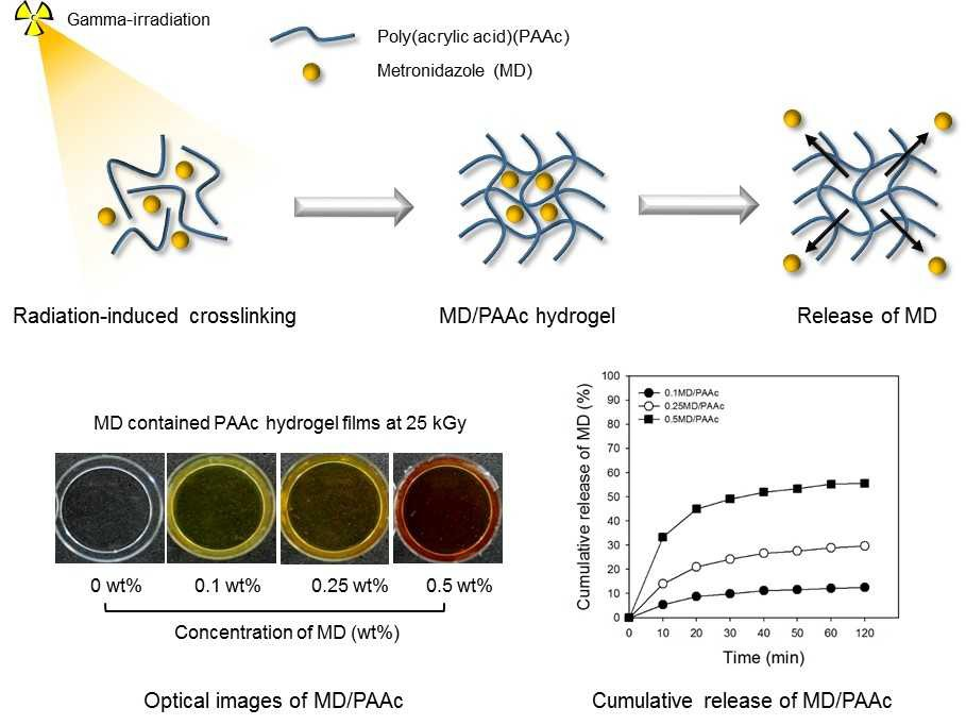
Poly(acrylic acid) (PAAc) hydrogels possess good bioadhesive properties and allow enhanced penetration of drugs. In addition, it is possible to localize the absorption site of the drug in the hydrogel and increase the drug residence time. As opposed to other cross-linking processes radiation-induced polymer cross-linking can be easily and rapidly carried out without the use of cross-linking agents and other chemical additives. In this study, we fabricated metronidazole (MD) containing PAAc hydrogel (MD/PAAc) with different MD contents (0.1, 0.25, 0.5 wt%) using varying radiation doses (25, 50, 75 kGy) by gamma-irradiation. The physical and thermal properties were determined by gel content analysis, swelling ratio measurements, compressive strength measurements, differential scanning calorimetery, and thermogravimetric analysis. The properties of the hydrogel degraded due to the crystalline nature of MD. The properties of the hydrogel degraded due to the crystalline nature of MD. Cumulative release observed after 50 min in the case of 0.5MD/PAAc and 0.1MD/PAAc was 50% and 10%, respectively. Our findings suggest that MD/PAAc could be a suitable drug delivery carrier for use with radiation-based techniques.