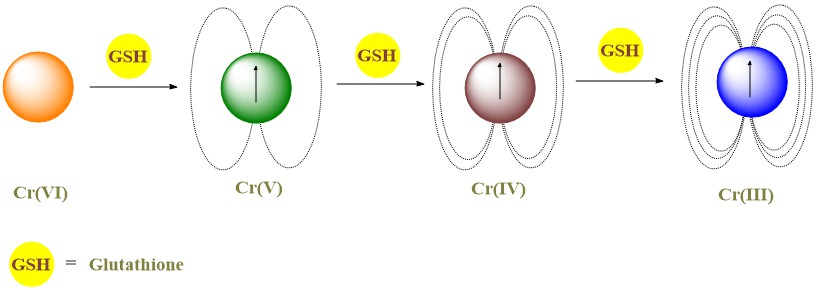
Chromium (VI) is carcinogenic through intermediates formed in the cellular milieu by reduction with small reductants like glutathione (GSH), ascorbate (As), cysteine (Cys) and NADPH. Although the reduction of chromate by thiols have been investigated, the participation of Cr(IV) intermediates has been inferred only indirectly due to its refractive behavior towards EPR spectroscopy and the lack of true chromium (IV) complexes for comparative studies. Biological data from numerous reports indicate that Cr(IV) is the species most likely responsible for the carcinogenicity of Cr(VI). Our kinetic studies suggested that in acidic solutions the reduction of chromate with GSH affords mostly a chromium(IV) intermediate. As a step towards the full characterization of the paramagnetic species involved in the reduction of chromate by thiols at neutral pH, we embarked in the investigation of this reaction using the Superconducting QUantum Interference Device (SQUID) Magnetic Property Measuring System®. Our results indicate a strong influence of the temperature. At 2K, the saturation magnetization method was applied to the frozen reaction when it reached the peak of formation of intermediates. Contrary to our expectations, the contributions were calculated to be 30 % of Cr(IV) and 69 % of Cr(V) at this pH. When the Curie-Weiss method was utilized, the effective magnetic moment was dependent on the portion of the data utilized and generally higher proportion of Cr(IV) was found when the fitting is performed with data from higher temperature.