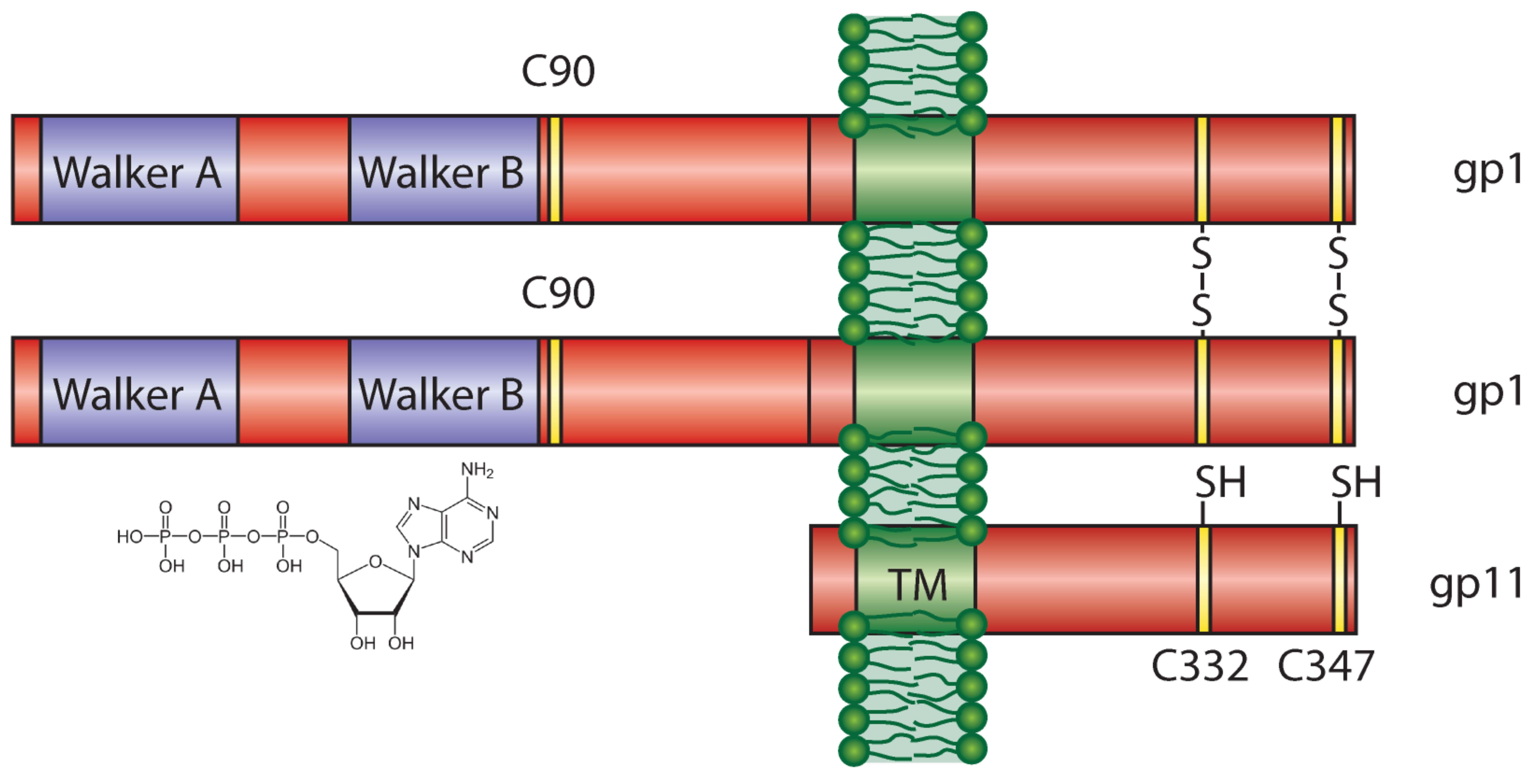
In contrast to lytic phages, filamentous phages are assembled in the inner membrane and secreted across the bacterial envelope without killing the host. For assembly and extrusion of the phage across the host cell wall, filamentous phages code for membrane-embedded morphogenesis proteins. In the outer membrane of E. coli, the protein gp4 forms a pore-like complex, while gp1 and gp11 form a complex in the inner membrane of the host. By comparing sequences with other filamentous phages, we identified putative Walker A and B motifs in gp1 with a conserved lysine in the Walker A motif (K14), and a glutamic and aspartic acid in the Walker B motif (D88, E89). In this work we demonstrate that both, Walker A and Walker B, are essential for phage production. The crucial role of these key residues suggest that gp1 is likely to be a molecular motor driving phage assembly. We further identified essential residues for the function of the assembly complex. Mutations in three out of six cysteine residues abolish phage production. Similarly, two out of six conserved glycine residues are crucial for gp1 function. We hypothesise that the residues represent molecular hinges allowing domain movement for nucleotide binding and phage assembly.