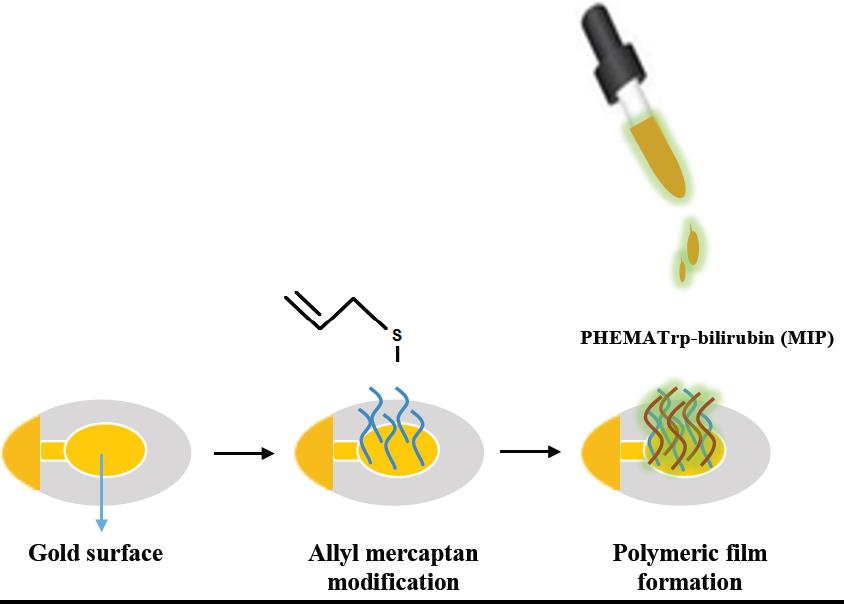
This study aims the preparation of QCM sensor for the detection of bilirubin in human plasma. Bilirubin imprinted poly-(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate-N-methacryloyl-L-tryptophan methyl ester) (PHEMATrp) nanofilm (MIP) on the gold surface of QCM chip was synthesized by molecular imprinting technique. Meanwhile, the non-imprinted PHEMATrp (NIP) nanofilm was synthesized by the same experimental technique to examine the imprinting effect. Characterization of MIP and NIP nanofilms on the QCM chip surface was achieved by atomic force microscopy (AFM), ellipsometry, fourier transform infrared spectrophotometry-attenuated total reflectance (FTIR-ATR) and contact angle measurements (CA). The observations indicated that the nanofilm was almost monolayer. Thereinafter, the imprinted and the non-imprinted QCM chipss were connected to QCM system to investigate kinetic and affinity properties. In order to examine the selectivity of the MIP-PHEMATrp nanofilm, competitive adsorption of bilirubin, cholesterol and estradiol was performed. Limit of detection (LOD) and limit of quantitation (LOQ) values were calculated as 0.45 μg/mL and 0.9 μg/mL, respectively.