Submitted:
10 November 2025
Posted:
11 November 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
MSC: 65C05
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Algorithms
2.1. Hierarchical GP Models and Their Approximate Representations
2.2. RMHMC with a Soft-Absolute Hessian Metric
| Algorithm 1 (RM)HMC |
|
2.3. Structure-Dependent Removal of Redundancy
2.4. Dynamically Programmed Eigendecomposition
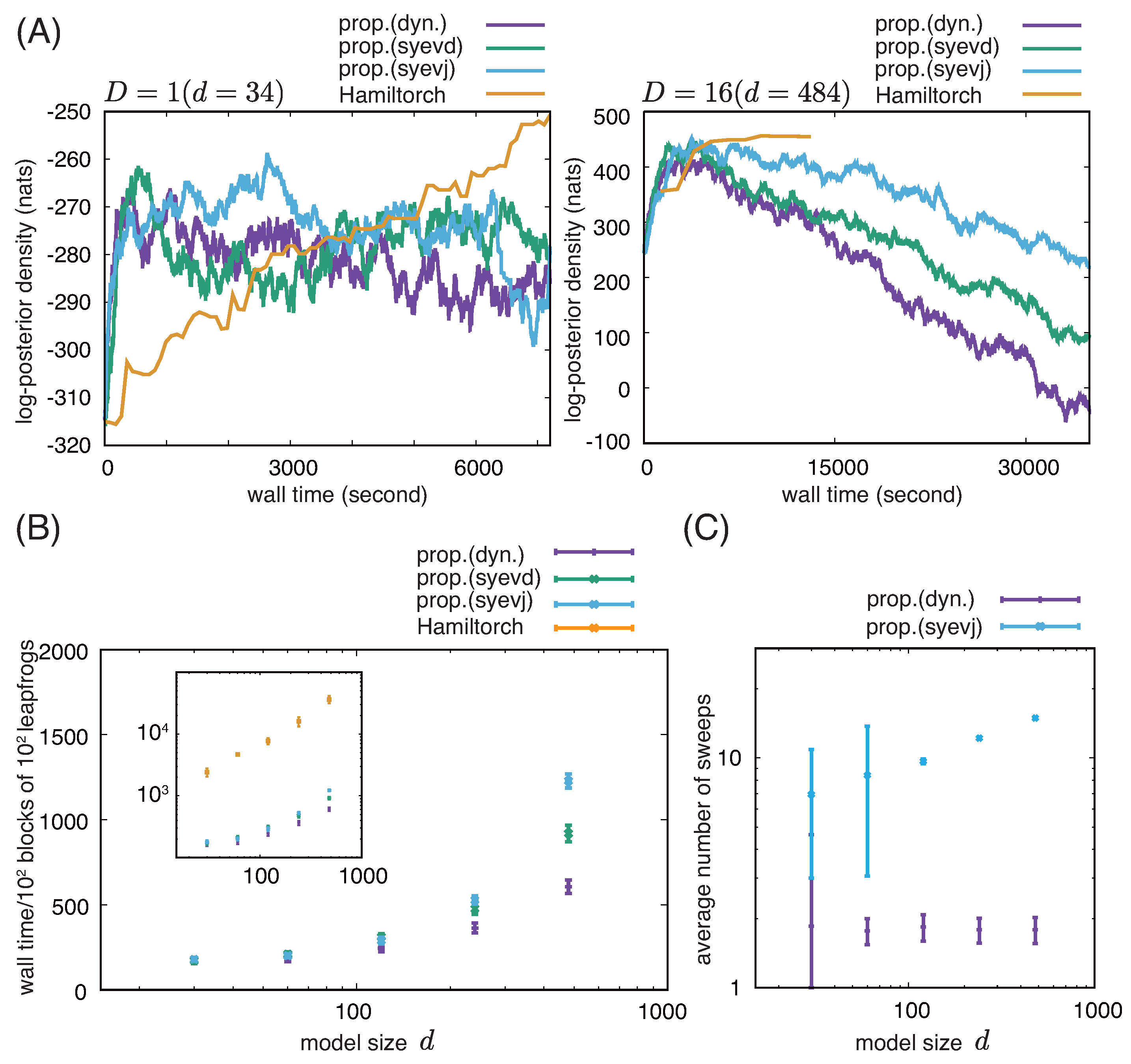
2.5. Numerical Experiments on Computational Complexity
2.6. Analysis of 1987 National Medical Expenditure Survey (NMES)
3. Results
3.1. Comparison Among Different Implementations of RMHMC with a Soft-Absolute Hessian Metric
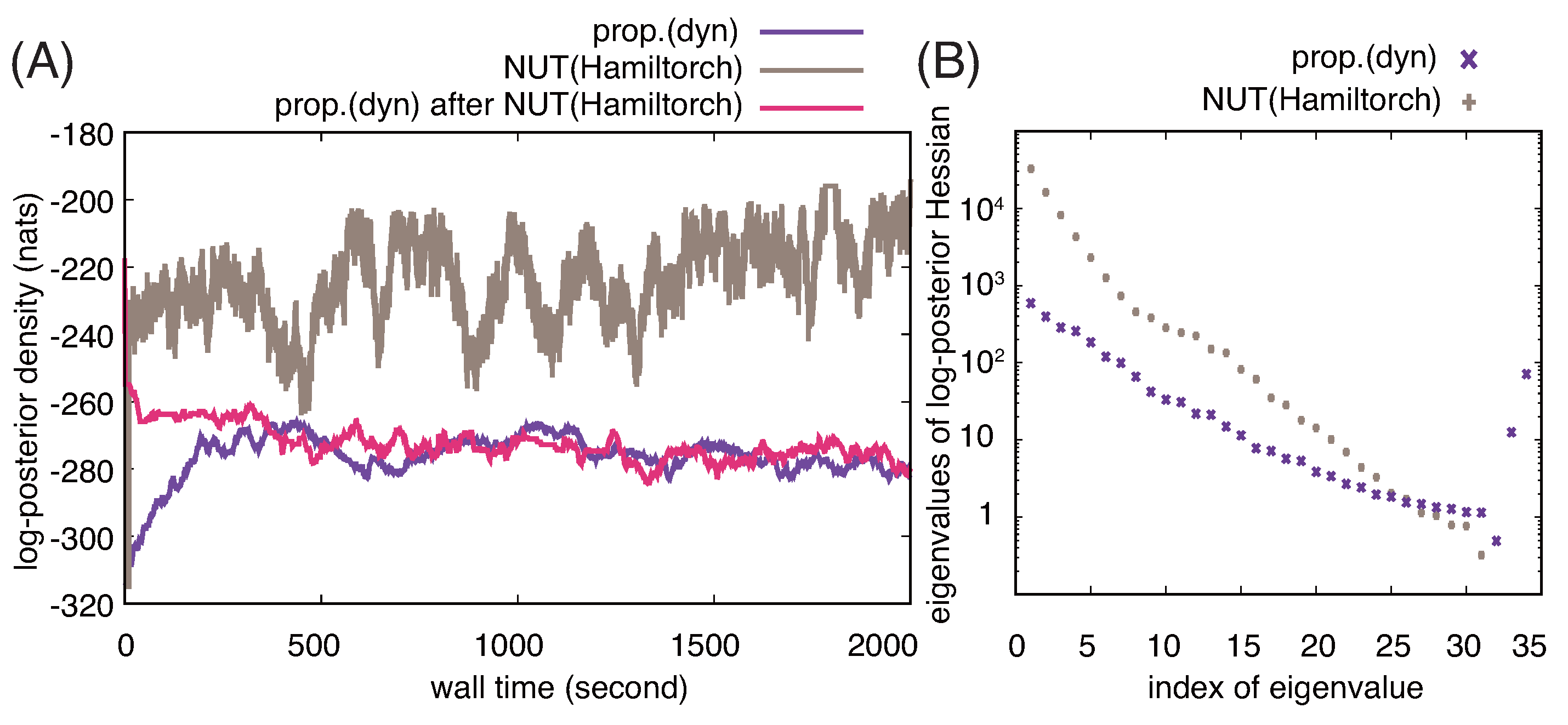
3.2. Comparison with NUT-HMC Sampler
3.3. Calculation of BME beyond the Laplace approximation with simulated data and NMES data
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Reduced-Rank Representation of GPs (Svensson et al. and Solin and Särkkä
| Symbols | Description |
|---|---|
| The sets of real numbers and d-dimensional Euclidean space | |
| The smallest integer that is greater than or equals a | |
| , | Transposition of vector v and matrix A |
| The i-th element of vector v | |
| The element of matrix A in the i-th row of the j-th column | |
| 1ometimes a combinatorial index such as is used. In this example, the index runs through all possible values for the combination . | Vector whose i-th element is |
| 2he first and second subscripts of the bracket specify the indices for the row and column, respectively. | Matrix whose i-th row of the j-th column is |
| Diagonal matrix whose i-th element is | |
| the trace of matrix A | |
| Element a of a set | |
| The Hadamard product of A and B | |
| The number of elements in a set | |
| () | Expectation of the argument random variable (for the specified distribution) |
| Variance of the argument random variable | |
| Empirical standard deviation of the argument variable | |
| Equation defining the object on the left-hand side | |
| , () | Independently and identically distributed (objects drawn from the right-hand side) |
| Uniform probability distribution over the open interval | |
| Gaussian probability distribution with mean and (co)variance | |
| Inverse Gamma probability distribution with shape and scale parameters | |
| Bernoulli probability distribution (value 1 with probability p, or 0 otherwise) |
Appendix B. MC Integration for the Calculation of BME (Calderhead and Girolami)
References
- Williams, C.K.; Rasmussen, C.E. Gaussian processes for machine learning; Vol. 2, MIT press Cambridge, MA, 2006.
- van der Vaart, A.W.; van Zanten, J.H. Rates of contraction of posterior distributions based on Gaussian process priors. The Annals of Statistics 2008, 36, 1435 – 1463. [CrossRef]
- van der Vaart, A.; van Zanten, H. Information Rates of Nonparametric Gaussian Process Methods. Journal of Machine Learning Research 2011, 12, 2095–2119.
- Suzuki, T. PAC-Bayesian Bound for Gaussian Process Regression and Multiple Kernel Additive Model. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 25th Annual Conference on Learning Theory; Mannor, S.; Srebro, N.; Williamson, R.C., Eds., Edinburgh, Scotland, 25–27 Jun 2012; Vol. 23, Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, pp. 8.1–8.20.
- Frigola, R.; Lindsten, F.; Schön, T.B.; Rasmussen, C.E. Bayesian Inference and Learning in Gaussian Process State-Space Models with Particle MCMC. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Burges, C.; Bottou, L.; Welling, M.; Ghahramani, Z.; Weinberger, K., Eds. Curran Associates, Inc., 2013, Vol. 26.
- Svensson, A.; Solin, A.; Särkkä, S.; Schön, T. Computationally Efficient Bayesian Learning of Gaussian Process State Space Models. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics; Gretton, A.; Robert, C.C., Eds., Cadiz, Spain, 09–11 May 2016; Vol. 51, Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, pp. 213–221.
- Yerramilli, S.; Iyer, A.; Chen, W.; Apley, D.W. Fully Bayesian Inference for Latent Variable Gaussian Process Models. SIAM/ASA Journal on Uncertainty Quantification 2023, 11, 1357–1381, [https://. [CrossRef]
- Finocchio, G.; Schmidt-Hieber, J. Posterior Contraction for Deep Gaussian Process Priors. Journal of Machine Learning Research 2023, 24, 1–49.
- Bishop, C.M. Pattern recognition and machine learning; Vol. 4, Springer, 2006.
- Paquet, U.; Fraccaro, M. An Efficient Implementation of Riemannian Manifold Hamiltonian Monte Carlo for Gaussian Process Models. ArXiv 2018, abs/1810.11893.
- Pandita, P.; Tsilifis, P.; Ghosh, S.; Wang, L. Scalable Fully Bayesian Gaussian Process Modeling and Calibration With Adaptive Sequential Monte Carlo for Industrial Applications. Journal of Mechanical Design 2021, 143, 074502. [CrossRef]
- Hensman, J.; Matthews, A.G.d.G.; Filippone, M.; Ghahramani, Z. MCMC for variationally sparse Gaussian processes. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 29th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems - Volume 1, Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015; NIPS’15, p. 1648–1656.
- Betancourt, M.J. A general metric for Riemannian manifold Hamiltonian Monte Carlo. International Conference on Geometric Science of Information 2013, pp. 327–334.
- Cobb, A.D.; Baydin, A.G.; Markham, A.; Roberts, S.J. Introducing an Explicit Symplectic Integration Scheme for Riemannian Manifold Hamiltonian Monte Carlo. arXiv preprint arXiv:1910.06243 2019.
- Paszke, A.; Gross, S.; Massa, F.; Lerer, A.; Bradbury, J.; Chanan, G.; Killeen, T.; Lin, Z.; Gimelshein, N.; Antiga, L.; et al., PyTorch: an imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. In Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems; Curran Associates Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2019.
- Solin, A.; Särkkä, S. Hilbert space methods for reduced-rank Gaussian process regression. Statistics and Computing 2020, 30, 419–446. [CrossRef]
- Bach, F.; Jordan, M. Kernel independent component analysis. Journal of Machine Learning Research 2003.
- Duane, S.; Kennedy, A.; Pendleton, B.J.; Roweth, D. Hybrid Monte Carlo. Physics Letters B 1987, 195, 216–222. [CrossRef]
- Neal, R.M. Probabilistic inference using Markov chain Monte Carlo methods 1993.
- Neal, R.M. Bayesian learning for neural networks; Vol. 118, Springer Science & Business Media, 2012.
- Girolami, M.; Calderhead, B. Riemann manifold Langevin and Hamiltonian Monte Carlo methods. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B (Statistical Methodology) 2011, 73, 123–214, [https://rss.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi//pdf/10.1111/j.1467-9868.2010.00765.x]. [CrossRef]
- Gall, F.L.; Urrutia, F. Improved rectangular matrix multiplication using powers of the coppersmith-winograd tensor. Proceedings of the Twenty-Ninth Annual ACM-SIAM Symposium on Discrete Algorithms 2018, p. 1029–1046.
- van Kempen, H.P.M. On the quadratic convergence of the special cyclic Jacobi method. Numerische Mathematik 1966, 9, 19–22. [CrossRef]
- Golub, G.H.; Van Loan, C.F. Matrix computations; JHU press, 2013.
- Inc., N. NVIDA HPC SDK Version 23.1 Documentation. https://docs.nvidia.com/hpc-sdk/archive/23.1/index.html, 2023. accessed on 5th Nov. 2025.
- Johnson, E.; Dominici, F.; Griswold, M.; Zeger, S.L. Disease cases and their medical costs attributable to smoking: an analysis of the national medical expenditure survey. Journal of Econometrics 2003, 112, 135–151.
- Imai, K.; Van Dyk, D.A. Causal inference with general treatment regimes: Generalizing the propensity score. Journal of the American Statistical Association 2004, 99, 854–866.
- Galagate, D.; Schafer, J.L. Causal inference with a continuous treatment and outcome: Alternative estimators for parametric dose-response functions with applications. Digital repository at the University of Maryland 2016. [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, S. Algebraic geometry and statistical learning theory; Vol. 25, Cambridge university press, 2009.
- Inc., N. NVIDIA Developer Forum: CUBLAS dgemm performance query. https://forums.developer.nvidia.com/t/reasonable-timing-with-cublas-dgemm-and-sgemm/14261, 2012. accessed on 5th Nov. 2025.
- Lung-Sheng, C. Jacobi-Based Eigenvalue Solver on GPU. A shared slide presented in GPU technology conference: https://on-demand.gputechconf.com/gtc/2017/presentation/s7121-lung-sheng-chien-jacobi-based-eigenvalue-solver.pdf, 2017. accessed on 1st June 2022.
- Fawzi, H.; Goulbourne, H. Faster proximal algorithms for matrix optimization using Jacobi-based eigenvalue methods. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Ranzato, M.; Beygelzimer, A.; Dauphin, Y.; Liang, P.; Vaughan, J.W., Eds. Curran Associates, Inc., 2021, Vol. 34, pp. 11397–11408.
- Hoffman, M.D.; Gelman, A. The No-U-Turn Sampler: Adaptively Setting Path Lengths in Hamiltonian Monte Carlo. Journal of Machine Learning Research 2014, 15, 1593–1623.
- Betancourt, M.J. Generalizing the No-U-Turn Sampler to Riemannian Manifolds, 2013, [arXiv:stat.ME/1304.1920].
- Cheng, X.; Chatterji, N.S.; Bartlett, P.L.; Jordan, M.I. Underdamped Langevin MCMC: A non-asymptotic analysis. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 31st Conference On Learning Theory; Bubeck, S.; Perchet, V.; Rigollet, P., Eds. PMLR, 06–09 Jul 2018, Vol. 75, Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, pp. 300–323.
- Dalalyan, A.S.; Riou-Durand, L. On sampling from a log-concave density using kinetic Langevin diffusions. Bernoulli 2020, 26, 1956 – 1988. [CrossRef]
- GREEN, P.J. Reversible jump Markov chain Monte Carlo computation and Bayesian model determination. Biometrika 1995, 82, 711–732, [https://academic.oup.com/biomet/article-pdf/82/4/711/699533/82-4-711.pdf]. [CrossRef]
- Karagiannis, G.; Andrieu, C. Annealed Importance Sampling Reversible Jump MCMC Algorithms. Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics 2013, 22, 623–648, [https://. [CrossRef]
- Moral, P. Feynman-Kac formulae: genealogical and interacting particle systems with applications; Springer, 2004.
- Chopin, N.; Papaspiliopoulos, O.; et al. An introduction to sequential Monte Carlo; Vol. 4, Springer, 2020.
- Chernozhukov, V.; Chetverikov, D.; Demirer, M.; Duflo, E.; Hansen, C.; Newey, W.; Robins, J. Double/debiased machine learning for treatment and structural parameters. The Econometrics Journal 2018, 21, C1–C68, [https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/. [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, T.; Asai, S. Debiased Maximum Likelihood Estimators of Hazard Ratios Under Kernel-Based Machine Learning Adjustment. Mathematics 2025, 13. [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, S. A widely applicable Bayesian information criterion. Journal of Machine Learning Research 2013, 14, 867–897.
- Drton, M.; Plummer, M. A Bayesian Information Criterion for Singular Models. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Series B: Statistical Methodology 2017, 79, 323–380. [CrossRef]
- Calderhead, B.; Girolami, M. Estimating Bayes factors via thermodynamic integration and population MCMC. Computational Statistics and Data Analysis 2009, 53, 4028–4045. [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.C.; Nocedal, J. On the limited memory BFGS method for large scale optimization. Mathematical Programming 1989, 45, 503–528.
| 1 | S |
| 2 | T |
| Data | Model | Estimated BME | Laplace Approx. | Wall time (sec) | # MC (Z) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simulation | NL-logistic | 50 | |||
| NMES | L-mean | — | 10 | ||
| NMES | NL-mean | — | 10 | ||
| NMES | L-mean/var | — | 10 | ||
| NMES | NL-mean/var | — | 10 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





