Submitted:
31 July 2025
Posted:
01 August 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
2.2. Extraction of Coffee By-Product Plant Materials
2.3. Preparation of Solutions and of Salmonella Suspension
2.4. 2LabsToGo-Eco Analysis
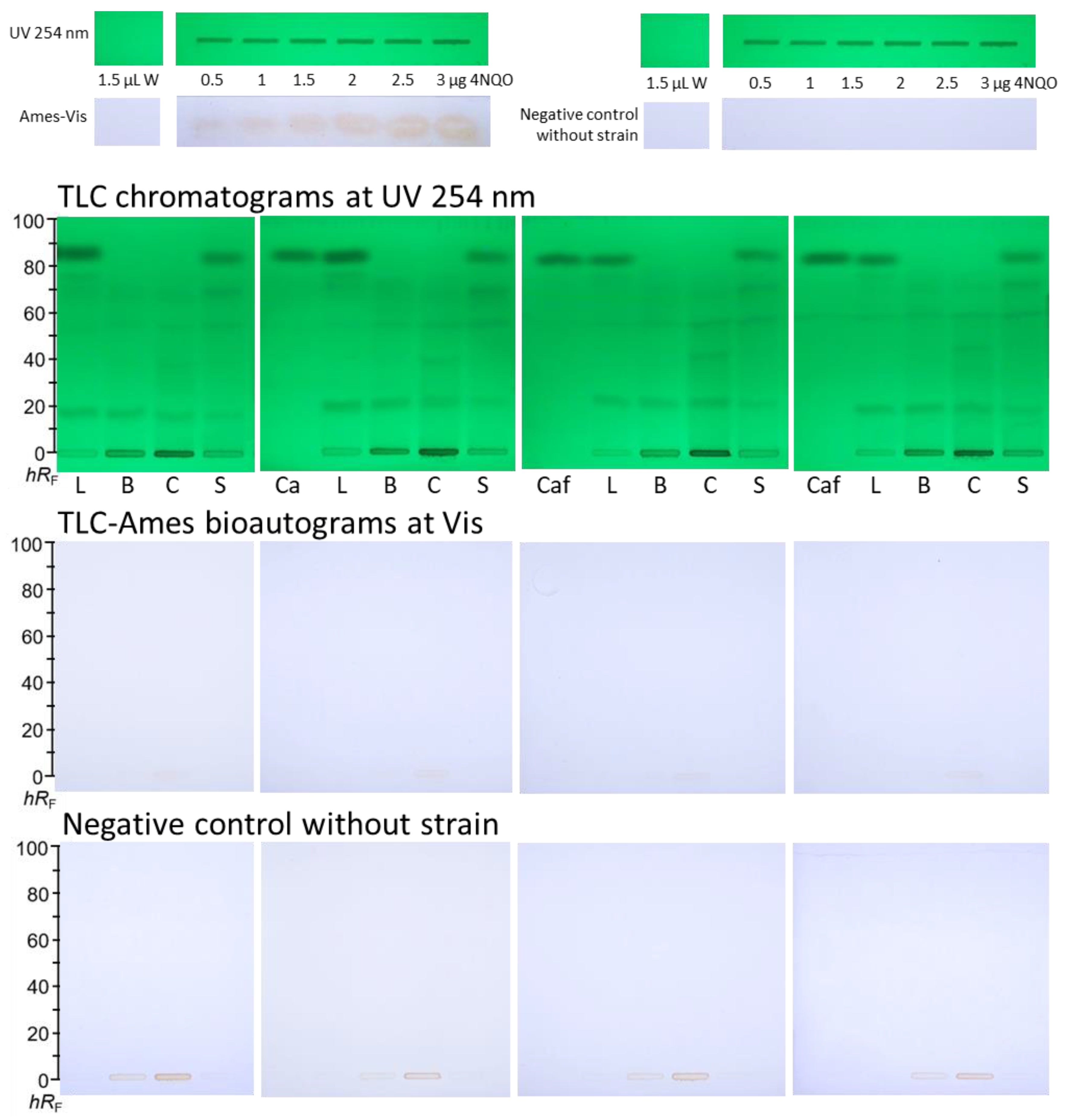
2.5. Planar Ames-Vis bioassay
3. Results
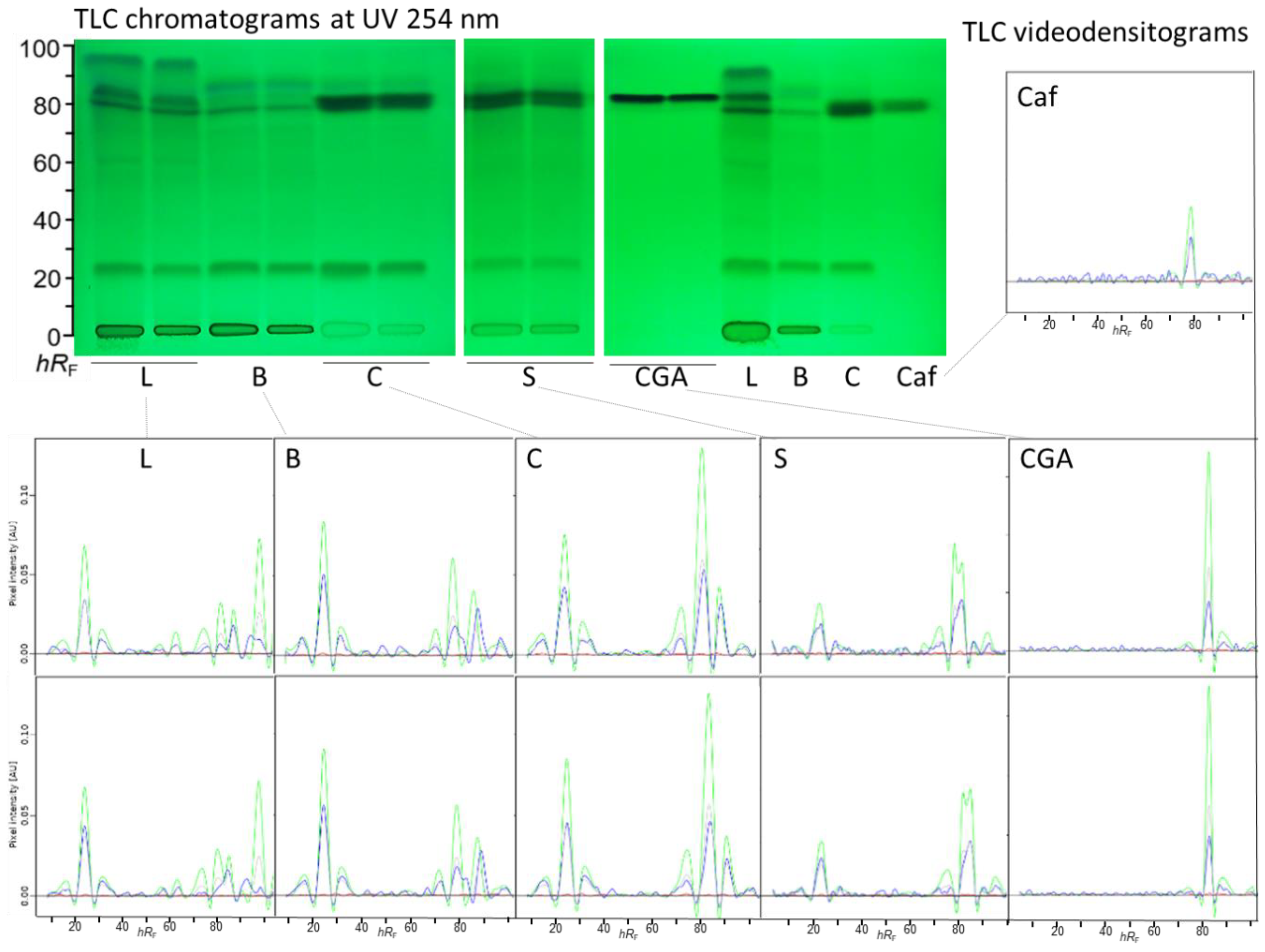
3.1. Optimization of the Extraction and Mobile Phase for TLC Analysis of Coffee By-Products
3.2. Repeatability of the 2LabsToGo-Eco Analysis
3.2. Reproducibility of the TLC-Ames-Vis Bioautograms
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blinová, L.; Sirotiak, M.; Bartošová, A.; Soldán, M. Utilization of Waste from Coffee Production. Vedecké Práce Materiálovotechnologickej Fakulty Slovenskej Technickej Univerzity v Bratislave so Sídlom v Trnave 2017, 25, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, P.S.; Naidu, M.M. Sustainable Management of Coffee Industry By-Products and Value Addition—A Review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2012, 66, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heeger, A.; Kosińska-Cagnazzo, A.; Cantergiani, E.; Andlauer, W. Bioactives of Coffee Cherry Pulp and Its Utilisation for Production of Cascara Beverage. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 969–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, R.C.; Rodrigues, F.; Nunes, M.A.; Vinha, A.F.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P. State of the Art in Coffee Processing By-Products. In Handbook of coffee processing by-products; Galanakis, C.M., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2017; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Carriço, C.; Ribeiro, H.M.; Marto, J. Converting Cork By-Products to Ecofriendly Cork Bioactive Ingredients: Novel Pharmaceutical and Cosmetics Applications. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 125, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kull, A.-K.; Lachenmeier, D.W. Comprehensive Update on European Union Labeling Standards for Coffee and Its By-Products. Proceedings 2024, 109, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, N. and A. (NDA); Turck, D.; Bresson, J.; Burlingame, B.; Dean, T.; Fairweather-Tait, S.; Heinonen, M.; Hirsch-Ernst, K.I.; Mangelsdorf, I.; McArdle, H. Guidance on the Preparation and Presentation of an Application for Authorisation of a Novel Food in the Context of Regulation (EU) 2015/2283. Efsa J. 2016, 14, e04594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) Test No. 487: In Vitro Mammalian Cell Micronucleus Test; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2023; pp. 1–29.
- Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) Test No. 471: Bacterial Reverse Mutation Test; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2020; pp. 1–12.
- Wexler, P.; Anderson, B.D. Encyclopedia of Toxicology; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2005; Vol. 1, ISBN 0127453547. [Google Scholar]
- Kier, L.D. Use of the Ames Test in Toxicology. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 1985, 5, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjørseth, A.; Eidså, G.; Gether, J.; Landmark, L.; Møller, M. Detection of Mutagens in Complex Samples by the Salmonella Assay Applied Directly on Thin-Layer Chromatography Plates. Science (1979) 1982, 215, 87–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schilter, B.; Burnett, K.; Eskes, C.; Geurts, L.; Jacquet, M.; Kirchnawy, C.; Oldring, P.; Pieper, G.; Pinter, E.; Tacker, M. Value and Limitation of in Vitro Bioassays to Support the Application of the Threshold of Toxicological Concern to Prioritise Unidentified Chemicals in Food Contact Materials. Food Addit. Contam.: Part A 2019, 36, 1903–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainer, B.; Mayrhofer, E.; Redl, M.; Dolak, I.; Mislivececk, D.; Czerny, T.; Kirchnawy, C.; Marin-Kuan, M.; Schilter, B.; Tacker, M. Mutagenicity Assessment of Food Contact Material Migrates with the Ames MPF Assay. Food Addi. Contam.: Part A 2019, 36, 1419–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidtmann, K.; Lemme, J.; Morlock, G.E. Ames Assay Transferred from the Microtiter Plate to the Planar Assay Format. J. Xenobiot. 2025, 15, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monazzah, M.; Lachenmeier, D.W. Genotoxicity of Coffee, Coffee By-Products, and Coffee Bioactive Compounds: Contradictory Evidence from In Vitro Studies. Toxics 2025, 13, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albertini, S.; Friederich, U.; Schlatter, C.; Würgler, F.E. The Influence of Roasting Procedure on the Formation of Mutagenic Compounds in Coffee. Food Chem. Toxicol. 1985, 23, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shane, B.S.; Troxclair, A.M.; McMillin, D.J.; Henry, C.B. Comparative Mutagenicity of Nine Brands of Coffee to Salmonella Typhimurium TA100, TA102, and TA104. Environ. Mol. Mutagen 1988, 11, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, Y.; Wakabayashi, K.; Nagao, M.; Sugimura, T. Characteristics of Major Mutagenicity of Instant Coffee. Mutat. Res. Lett. 1985, 142, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.-S.; Chen, P.-W.; Wang, J.-Y.; Kuo, T.-C. Assessment of Cellular Mutagenicity of Americano Coffees from Popular Coffee Chains. J. Food Prot. 2017, 80, 1489–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, M.P.; Laires, A.; Gaspar, J.; Oliveira, J.S.; Rueff, J. Genotoxicity of Instant Coffee and of Some Phenolic Compounds Present in Coffee upon Nitrosation. Teratog. Carcinog. Mutagen 2000, 20, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, T.; Hiramoto, K.; Kikugawa, K. Possible Occurrence of New Mutagens with the DNA Breaking Activity in Coffee. Mutat. Res. Fundam. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 1994, 306, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, J.; Arbillaga, L.; de Peña, M.P.; Cid, C. Antioxidant and Genoprotective Effects of Spent Coffee Extracts in Human Cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 60, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monente, C.; Bravo, J.; Vitas, A.I.; Arbillaga, L.; De Peña, M.P.; Cid, C. Coffee and Spent Coffee Extracts Protect against Cell Mutagens and Inhibit Growth of Food-Borne Pathogen Microorganisms. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 12, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, A.S.; Mello, F.V.C.; Thode Filho, S.; Carpes, R.M.; Honório, J.G.; Marques, M.R.C.; Felzenszwalb, I.; Ferraz, E.R.A. Impacts of Discarded Coffee Waste on Human and Environmental Health. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 141, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimbach, J.T.; Marone, P.A.; Hunter, J.M.; Nemzer, B. V; Stanley, S.M.; Kennepohl, E. Safety Studies on Products from Whole Coffee Fruit. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 2517–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iriondo-DeHond, A.; Haza, A.I.; Ávalos, A.; Del Castillo, M.D.; Morales, P. Validation of Coffee Silverskin Extract as a Food Ingredient by the Analysis of Cytotoxicity and Genotoxicity. Food Res. Int. 2017, 100, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabezudo, I.; Salazar, M.O.; Ramallo, I.A.; Furlan, R.L.E. Effect-Directed Analysis in Food by Thin-Layer Chromatography Assays. Food Chem. 2022, 390, 132937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morlock, G.E. Chemical Safety Screening of Products–Better Proactive. J. Chromatogr A 2025, 1752, 465946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morlock, G.E. Planar Chromatographic Super-Hyphenations for Rapid Dereplication. Phytochem. Rev. 2025, 24, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morlock, G.E.; Heil, J.; Inarejos-Garcia, A.M.; Maeder, J. Effect-Directed Profiling of Powdered Tea Extracts for Catechins, Theaflavins, Flavonols and Caffeine. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inarejos-Garcia, A.M.; Heil, J.; Martorell, P.; Álvarez, B.; Llopis, S.; Helbig, I.; Liu, J.; Quebbeman, B.; Nemeth, T.; Holmgren, D. Effect-Directed, Chemical and Taxonomic Profiling of Peppermint Proprietary Varieties and Corresponding Leaf Extracts. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morlock, G.E.; Heil, J. Fast Unmasking Hazards of Safe Perfumes. J. Chromatogr. A 2025, 1754, 465959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windisch, M.; Kittinger, C.; Heil, J.; Morlock, G.E. Simple Performance of the Planar SOS-Umu-C–FLD Genotoxicity Bioassay Shown for Perfume and Packaging Material Analysis. JPC–J. Planar Chromatogr.–Mod. TLC 2023, 36, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oresanya, I.O.; Orhan, I.E.; Heil, J.; Morlock, G.E. African Under-Utilized Medicinal Leafy Vegetables Studied by Microtiter Plate Assays and High-Performance Thin-Layer Chromatography–Planar Assays. Molecules 2024, 29, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiliotopoulos, D.; Koelbert, C. Assessment of the Miniaturized Liquid Ames Microplate Format (MPFTM) for a Selection of the Test Items from the Recommended List of Genotoxic and Non-Genotoxic Chemicals. Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2020, 856, 503218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, D.; Marin-Kuan, M.; Debon, E.; Serrant, P.; Cottet-Fontannaz, C.; Schilter, B.; Morlock, G.E. Detection of Low Levels of Genotoxic Compounds in Food Contact Materials Using an Alternative HPTLC-SOS-Umu-C Assay. ALTEX 2021, 38, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadniya, E.; Mollergues, J.; Stroheker, T.; Billerbeck, K.; Morlock, G.E. New Incorporation of the S9 Metabolizing System into Methods for Detecting Acetylcholinesterase Inhibition. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2020, 1129, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fichou, D.; Morlock, G.E. Powerful Artificial Neural Network for Planar Chromatographic Image Evaluation, Shown for Denoising and Feature Extraction. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 6984–6991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fichou, D.; Ristivojevic, P.; Morlock, G.E. Proof-of-Principle of RTLC, an Open-Source Software Developed for Image Evaluation and Multivariate Analysis of Planar Chromatograms. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 12494–12501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fichou, D.; Yüce, I.; Morlock, G.E. EicCluster Software, an Open-Source in Silico Tool, and on-Surface Syntheses, an in Situ Concept, Both Exploited for Signal Highlighting in High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry to Ease Structure Elucidation in Planar Chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1577, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sereshti, H.; Poursorkh, Z.; Aliakbarzadeh, G.; Zarre, S. Quality Control of Saffron and Evaluation of Potential Adulteration by Means of Thin Layer Chromatography-Image Analysis and Chemometrics Methods. Food Control 2018, 90, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fichou, D.; Morlock, G.E. QuanTLC, an Online Open-Source Solution for Videodensitometric Quantification. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1560, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingelhöfer, I.; Morlock, G.E. Sharp-Bounded Zones Link to the Effect in Planar Chromatography-Bioassay-Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1360, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azadniya, E.; Goldoni, L.; Bandiera, T.; Morlock, G.E. Same Analytical Method for Both (Bio) Assay and Zone Isolation to Identify/Quantify Bioactive Compounds by Quantitative Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1628, 461434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, C.; Lu, C.; Zhou, S.; Tian, G.; He, L.; Bao, Y.; Fauconnier, M.-L.; Xiao, H.; Zheng, J. Simultaneous Determination of 14 Bioactive Citrus Flavonoids Using Thin-Layer Chromatography Combined with Surface Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2021, 338, 128115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, D.; Marin-Kuan, M.; Debon, E.; Serrant, P.; Cottet-Fontannaz, C.; Schilter, B.; Morlock, G.E. Detection of Low Levels of Genotoxic Compounds in Food Contact Materials Using an Alternative HPTLC-SOS-Umu-C Assay. ALTEX 2021, 38, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morlock, G.E. High-Performance Thin-Layer Chromatography Combined with Effect-Directed Assays and High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry as an Emerging Hyphenated Technology: A Tutorial Review. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2021, 1180, 338644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiner, T.; Ronzheimer, A.; Friz, M.; Morlock, G.E. Multiplex Planar Bioassay with Reduced Diffusion on Normal Phase, Identifying Androgens, Verified Antiandrogens and Synergists in Botanicals via 12D Hyphenation. Food Chem. 2022, 395, 133610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morlock, G.E. Miniaturized Planar Chromatography Using Office Peripherals—Office Chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1382, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, M.C.O.; Jakob, K.; Schmidt, J.; Nimmerfroh, T.; Schwack, W.; Morlock, G.E. Consolidating Two Laboratories into the Most Sustainable Lab of the Future: 2LabsToGo-Eco. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2025, 344103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morlock, G.E.; Koch, J.; Schwack, W. Miniaturized Open-Source 2LabsToGo Screening of Lactose-Free Dairy Products and Saccharide-Containing Foods. J. Chromatogr. A 2023, 1688, 463720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sing, L.; Schwack, W.; Göttsche, R.; Morlock, G.E. 2LabsToGo─ Recipe for Building Your Own Chromatography Equipment Including Biological Assay and Effect Detection. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 14554–14564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakob, K.; Schwack, W.; Morlock, G.E. All-in-One 2LabsToGo System for Analysis of Ergot Alkaloids in Whole Rye. Food Chem. 2024, 453, 139593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schade, F.; Schwack, W.; Demirbas, Y.; Morlock, G.E. Open-Source All-in-One LabToGo Office Chromatography. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2021, 1174, 338702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fichou, D.; Morlock, G.E. Office Chromatography: Miniaturized All-in-One Open-Source System for Planar Chromatography. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 12647–12654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altemimi, A.; Lakhssassi, N.; Baharlouei, A.; Watson, D.G.; Lightfoot, D.A. Phytochemicals: Extraction, Isolation, and Identification of Bioactive Compounds from Plant Extracts. Plants 2017, 6, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maron, D.M.; Ames, B.N. Revised Methods for the Salmonella Mutagenicity Test. Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen 1983, 113, 173–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, P.; Kumar, B.; Kaur, M.; Kaur, G.; Kaur, H. Phytochemical Screening and Extraction: A Review. Int. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 1, 98–106. [Google Scholar]
- Chamyuang, S.; Owatworakit, A.; Intatha, U.; Duangphet, S. Coffee Pectin Production: An Alternative Way for Agricultural Waste Management in Coffee Farms. Sci. Asia 2021, 47, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumenthal, P.; Steger, M.C.; Einfalt, D.; Rieke-Zapp, J.; Quintanilla Bellucci, A.; Sommerfeld, K.; Schwarz, S.; Lachenmeier, D.W. Methanol Mitigation during Manufacturing of Fruit Spirits with Special Consideration of Novel Coffee Cherry Spirits. Molecules 2021, 26, 2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Committee, E.S. Scientific Opinion on Genotoxicity Testing Strategies Applicable to Food and Feed Safety Assessment. EFSA J. 2011, 9, 2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Nutrition, N.F. and F.A. (NDA); Turck, D.; Bohn, T.; Castenmiller, J.; de Henauw, S.; Hirsch-Ernst, K.I.; Maciuk, A.; Mangelsdorf, I.; McArdle, H.J.; Naska, A. Guidance on the Scientific Requirements for an Application for Authorisation of a Novel Food in the Context of Regulation (EU) 2015/2283. EFSA J. 2024, 22, e8961. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




