Submitted:
06 July 2025
Posted:
22 July 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
Search Strategy
Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
Data Extraction
Quality Assessment
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
Study Selection
| Author/Year | Region | Study Design | Sample Size | Cancer Type | Wnt Pathway Components Measured | Outcomes Reported | Findings/Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (8) | Greece | Retrospective | 59 | Urothelial Cancer | β-Catenin, COX-2 | Progression-free survival, overall survival, relapse prediction | Higher β-catenin expression associated with shorter overall survival. |
| (7) | Germany | Phase II clinical trial | NA | Colorectal Cancer (Metastatic) | S100A4, Wnt/β-Catenin | Progression-free survival, overall survival, disease control rate, safety | Wnt pathway activation correlated with disease progression and poor survival. |
| (15) | USA/Chile | Observational | 180 | Breast Cancer | β-Catenin, HER2, multiple targets | Trastuzumab efficacy, recurrence, CD8 T-cell infiltration | Increased β-catenin expression linked to trastuzumab resistance and poor outcomes. |
| (21) | USA | Phase Ib clinical trial | 48 | HER2-Negative Breast Cancer | Wnt Pathway Signature | Safety, progression-free survival, overall survival, response rate | Wnt pathway markers were used for evaluating progression-free survival. |
| (18) | USA | Phase Ib clinical trial | 26 | Pancreatic Cancer | Wnt Pathway Signature, β-Catenin | Safety, maximum tolerated dose, pharmacodynamics, progression-free survival | Wnt pathway inhibition showed moderate survival improvement. |
| (14) | USA | Observational | 87 | Endometrial Cancer | Dkk3, SFRP1, SFRP4 | Expression patterns, progression-free survival, recurrence | Lower expression linked to reduced survival and disease progression. |
| (13) | Netherlands | Observational | 133 | Colorectal Cancer | β-Catenin, Ep-CAM | Tumor recurrence, tumor budding, adhesion molecule loss | Loss of adhesion molecules correlated with worse outcomes. |
| (22) | USA | Phase I clinical trial | 51 | Biliary Tract Cancer | DKK1 | Progression-free survival, overall survival, safety, angiogenesis and inflammation biomarkers | Elevated DKK1 levels linked to poor survival. |
| (12) | China | Observational | 282 | Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer | β-Catenin, FOXM1 | Gefitinib resistance, progression-free survival, FOXM1/Wnt interaction | FOXM1 variant strongly correlated with poor survival. |
| (2) | China | Observational | 115 | Gastric Cancer | β-Catenin | Migration, invasion, epithelial-mesenchymal transition | Increased β-catenin expression associated with poor survival. |
| (23) | USA | Molecular profiling study | 15 | Pediatric Hepatocellular Carcinoma | CTNNB1, APC, AMER1 | Genomic alterations, survival correlations, pathway activation | CTNNB1 mutations linked with disease progression and poor survival. |
| (11) | Iran | Observational | 24 | Gastric Cancer | β-Catenin, miR-34a, miR-181a | Gene expression correlations, clinicopathologic associations | β-Catenin expression altered in tumor vs. non-tumor tissue. |
| (3) | USA | Observational | 72 | Colorectal Cancer | c-Cbl, β-Catenin | Survival, tumor progression, Wnt pathway regulation | High c-Cbl expression linked to better overall survival. |
| (19) | Taiwan | Observational | 89 | Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma | Pin1, β-Catenin | Tumor stage, survival, association with cyclin D1 | Pin1 expression correlated with poor survival. |
| (10) | USA | Phase II clinical trial | 17 | Ovarian Cancer | Wnt pathway genes | Platinum sensitivity, DNA methylation, progression-free survival | Platinum sensitivity linked to Wnt signaling alterations. |
| (20) | USA | Phase II clinical trial | 63 | Head and Neck Cancer | β-Catenin, EGFR | Progression-free survival, biomarker correlation | Low ERK expression alongside Wnt marker alterations linked with poor survival. |
| (24) | China | Observational | 156 | Gastric Cancer | CDH17, β-Catenin | Tumor progression, survival, invasion, and migration | High CDH17 and β-catenin levels associated with poor survival and increased tumor progression. |
| (16) | UK | Preclinical/clinical study | NA | Acute Myeloid Leukemia | PI3K, β-Catenin | Proliferation, self-renewal, apoptosis | Altered β-catenin signaling associated with reduced survival. |
| (6) | Japan | Observational | NA | Colorectal Cancer | GSK3β, β-Catenin | Tumor cell survival, proliferation, Wnt/NF-κB pathway activity | Dysregulated GSK3β increased β-catenin nuclear accumulation and linked to poor survival. |
| (4) | USA | Phase II clinical trial | 42 | Endometrial Cancer | Cadherins, β-Catenin, APC | Survival, tumor recurrence, cell adhesion | Aberrant Wnt signaling components (e.g., APC loss, β-catenin alterations) reduced survival rates. |
| (9) | China | Observational | 76 | Colorectal Cancer | Elf3, β-Catenin | Tumor progression, survival, β-Catenin transactivation | High Elf3 expression linked with poor overall survival. |
| (25) | China | Observational | 267 | Renal Cell Carcinoma | UBE3C, β-Catenin | Growth, metastasis, survival, Wnt/β-Catenin pathway activation | UBE3C-mediated β-catenin activation was associated with worse postoperative survival. |
Meta-analysis
Risk of Bias Assessment
Subgroup Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Future Work
Supplementary Materials
References
- Yamashita K, Ougolkov AV, Nakazato H, Ito K, Ohashi Y, Kitakata H, et al. Adjuvant Immunochemotherapy with Protein-Bound Polysaccharide K for Colon Cancer in Relation to Oncogenic β-Catenin Activation. Dis Colon Rectum. 2007 Aug;50(8):1169.
- Guo Q, Xu J, Huang Z, Yao Q, Chen F, Liu H, et al. ADMA mediates gastric cancer cell migration and invasion via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Clin Transl Oncol. 2021;23(2):325–34. [CrossRef]
- Kumaradevan S, Lee SY, Richards S, Lyle C, Zhao Q, Tapan U, et al. c-Cbl Expression Correlates with Human Colorectal Cancer Survival and Its Wnt/β-Catenin Suppressor Function Is Regulated by Tyr371 Phosphorylation. Am J Pathol. 2018 Aug;188(8):1921–33. [CrossRef]
- Singh M, Darcy KM, Brady WE, Clubwala R, Weber Z, Rittenbach JV, et al. Cadherins, catenins and cell cycle regulators: Impact on survival in a Gynecologic Oncology Group phase II endometrial cancer trial. Gynecol Oncol. 2011 Nov;123(2):320–8. [CrossRef]
- Haines K, Sarabia SF, Alvarez KR, Tomlinson G, Vasudevan SA, Heczey AA, et al. Characterization of pediatric hepatocellular carcinoma reveals genomic heterogeneity and diverse signaling pathway activation. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2019 Jul;66(7):e27745. [CrossRef]
- Shakoori A, Ougolkov A, Yu ZW, Zhang B, Modarressi MH, Billadeau DD, et al. Deregulated GSK3β activity in colorectal cancer: Its association with tumor cell survival and proliferation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005 Sep 9;334(4):1365–73. [CrossRef]
- Burock S, Daum S, Keilholz U, Neumann K, Walther W, Stein U. Phase II trial to investigate the safety and efficacy of orally applied niclosamide in patients with metachronous or sychronous metastases of a colorectal cancer progressing after therapy: the NIKOLO trial. BMC Cancer. 2018 Mar 15;18:297. [CrossRef]
- Bamias A, Kyriakou F, Chorti M, Kavantzas N, Noni A, Kyroudi-Voulgari A, et al. Microvessel Density (MVD) and Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2)/ β-Catenin Interaction Are Associated with Relapse in Patients with Transitional Carcinoma Receiving Adjuvant Chemotherapy with Paclitaxel/Carboplatin: A Hellenic Cooperative Oncology Group (HECOG) Study. ANTICANCER Res. 2008;
- Wang JL, Chen ZF, Chen HM, Wang MY, Kong X, Wang YC, et al. Elf3 drives β-catenin transactivation and associates with poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2014 May;5(5):e1263. [CrossRef]
- Matei D, Fang F, Shen C, Schilder J, Arnold A, Zeng Y, et al. Epigenetic Resensitization to Platinum in Ovarian Cancer. Cancer Res. 2012 May 1;72(9):2197–205.
- Jafari N, Abediankenari S, Hosseini-Khah Z, Valizadeh SM, Torabizadeh Z, Zaboli E, et al. Expression patterns of seven key genes, including β-catenin, Notch1, GATA6, CDX2, miR-34a, miR-181a and miR-93 in gastric cancer. Sci Rep. 2020 Jul 23;10:12342. [CrossRef]
- Guan S, Chen X, Chen Y, Xie W, Liang H, Zhu X, et al. FOXM1 Variant Contributes to Gefitinib Resistance via Activating Wnt/β-Catenin Signal Pathway in Patients with Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2022 Sep 1;28(17):3770–84.
- Gosens MJEM, Kempen LCL van, Velde CJH van de, Krieken JHJM van, Nagtegaal ID. Loss of membranous Ep-CAM in budding colorectal carcinoma cells. Mod Pathol. 2007 Feb 1;20(2):221–32.
- Eskander RN, Ali S, Dellinger T, Lankes HA, Randall LM, Ramirez NC, et al. Expression Patterns of the Wnt Pathway Inhibitors Dickkopf3 and Secreted Frizzled-Related Proteins 1 and 4 in Endometrial Endometrioid Adenocarcinoma. Int J Gynecol Cancer Off J Int Gynecol Cancer Soc. 2016 Jan;26(1):125–32. [CrossRef]
- Carvajal-Hausdorf DE, Patsenker J, Stanton K, Espindola FV, Esch A, Montgomery RR, et al. Multiplexed (18-Plex) Measurement of Signaling Targets and Cytotoxic T cells in Trastuzumab-treated Patients using Imaging Mass Cytometry. Clin Cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res. 2019 May 15;25(10):3054–62.
- Shahid AM, Um IH, Elshani M, Zhang Y, Harrison DJ. NUC-7738 regulates β-catenin signalling resulting in reduced proliferation and self-renewal of AML cells. PLOS ONE. 2022 Dec 15;17(12):e0278209.
- Di Bartolomeo M, Pietrantonio F, Pellegrinelli A, Martinetti A, Mariani L, Daidone MG, et al. Osteopontin, E-cadherin, and β-catenin expression as prognostic biomarkers in patients with radically resected gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. 2016 Apr;19(2):412–20.
- Dotan E, Cardin DB, Lenz HJ, Messersmith W, O’Neil B, Cohen SJ, et al. Phase 1b study of Wnt inhibitor ipafricept (IPA) with nab-paclitaxel (Nab-P) and gemcitabine (G) in patients with previously untreated stage IV pancreatic cancer (mPDAC). Clin Cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res. 2020 Oct 15;26(20):5348–57. [CrossRef]
- Lin FC, Lee YC, Goan YG, Tsai CH, Yao YC, Cheng HC, et al. Pin1 positively affects tumorigenesis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and correlates with poor survival of patients. J Biomed Sci. 2014 Aug 27;21(1):75. [CrossRef]
- Psyrri A, Lee JW, Pectasides E, Vassilakopoulou M, Kosmidis EK, Burtness BA, et al. Prognostic biomarkers in phase II trial of cetuximab-containing induction and chemoradiation in resectable HNSCC: Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group E2303. Clin Cancer Res Off J Am Assoc Cancer Res. 2014 Jun 1;20(11):3023–32. [CrossRef]
- Diamond JR, Becerra C, Richards D, Mita A, Osborne C, O’Shaughnessy J, et al. Phase Ib clinical trial of the anti-frizzled antibody vantictumab (OMP-18R5) plus paclitaxel in patients with locally advanced or metastatic HER2-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2020 Nov;184(1):53–62.
- Goyal L, Sirard C, Schrag M, Kagey MH, Eads JR, Stein S, et al. Phase I and Biomarker Study of the Wnt Pathway Modulator DKN-01 in Combination with Gemcitabine/Cisplatin in Advanced Biliary Tract Cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Dec 1;26(23):6158–67.
- Haines K, Sarabia SF, Alvarez KR, Tomlinson G, Vasudevan SA, Heczey AA, et al. Characterization of pediatric hepatocellular carcinoma reveals genomic heterogeneity and diverse signaling pathway activation. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2019 Jul;66(7):e27745.
- Qiu H bo, Zhang L yi, Ren C, Zeng Z lei, Wu W jing, Luo H yan, et al. Targeting CDH17 Suppresses Tumor Progression in Gastric Cancer by Downregulating Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling. PLoS ONE. 2013 Mar 15;8(3):e56959.
- Wen JL, Wen XF, Li RB, Jin YC, Wang XL, Zhou L, et al. UBE3C Promotes Growth and Metastasis of Renal Cell Carcinoma via Activating Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway. PLoS ONE. 2015 Feb 6;10(2):e0115622. [CrossRef]
- Colozza G, Koo B. Wnt/β-catenin signaling: Structure, assembly and endocytosis of the signalosome. Dev Growth Differ. 2021 Apr;63(3):199–218. [CrossRef]
- Chen Z, He X, Jia M, Liu Y, Qu D, Wu D, et al. β-catenin Overexpression in the Nucleus Predicts Progress Disease and Unfavourable Survival in Colorectal Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE. 2013 May 24;8(5):e63854. [CrossRef]
- Matly A, Quinn JA, McMillan DC, Park JH, Edwards J. The relationship between β-catenin and patient survival in colorectal cancer systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2021 Jul 1;163:103337. [CrossRef]
- Sefidbakht S, Saeedipour H, Saffar H, Mirzaian E. Determination of β-catenin Expression in Breast Cancer and Its Relationship with Clinicopathologic Parameters. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev APJCP. 2021 Nov;22(11):3493–8. [CrossRef]
- Wang Z, Zhang H, Hou J, Niu J, Ma Z, Zhao H, et al. Clinical implications of β-catenin protein expression in breast cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Nov 1;8(11):14989–94.
- (PDF) DKK1 Mediated Inhibition of Wnt Signaling in Postnatal Mice Leads to Loss of TEC Progenitors and Thymic Degeneration. ResearchGate [Internet]. 2024 Oct 22 [cited 2024 Dec 7]; Available from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/41453508_DKK1_Mediated_Inhibition_of_Wnt_Signaling_in_Postnatal_Mice_Leads_to_Loss_of_TEC_Progenitors_and_Thymic_Degeneration.
- Lou X, Meng Y, Hou Y. A literature review on function and regulation mechanism of DKK4. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25(6):2786–94. [CrossRef]
- Bosdriesz JR, Stel VS, van Diepen M, Meuleman Y, Dekker FW, Zoccali C, et al. Evidence-based medicine-When observational studies are better than randomized controlled trials. Nephrol Carlton Vic. 2020 Oct;25(10):737–43.
- Neiheisel A, Kaur M, Ma N, Havard P, Shenoy AK. Wnt pathway modulators in cancer therapeutics: An update on completed and ongoing clinical trials. Int J Cancer. 2022 Mar 1;150(5):727–40. [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy N, Kurzrock R. Targeting the Wnt/beta-catenin Pathway in Cancer: Update on Effectors and Inhibitors. Cancer Treat Rev. 2018 Jan;62:50–60. [CrossRef]
- Pećina-Šlaus N, Aničić S, Bukovac A, Kafka A. Wnt Signaling Inhibitors and Their Promising Role in Tumor Treatment. Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 4;24(7):6733. [CrossRef]
- Duan P, Bonewald L. The Role of the Wnt/β-catenin Signaling Pathway in Formation and Maintenance of Bone and Teeth. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2016 Aug;77(Pt A):23–9. [CrossRef]
- Wnt/β-catenin signalling: function, biological mechanisms, and therapeutic opportunities | Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy [Internet]. [cited 2024 Dec 7]. Available from: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41392-021-00762-6.
- Caspi M, Wittenstein A, Kazelnik M, Shor-Nareznoy Y, Rosin-Arbesfeld R. Therapeutic targeting of the oncogenic Wnt signaling pathway for treating colorectal cancer and other colonic disorders. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021 Feb;169:118–36. [CrossRef]
- Jung YS, Park JI. Wnt signaling in cancer: therapeutic targeting of Wnt signaling beyond β-catenin and the destruction complex. Exp Mol Med. 2020 Feb;52(2):183–91. [CrossRef]
- Pećina-Šlaus N. Wnt signal transduction pathway and apoptosis: a review. Cancer Cell Int. 2010 Jun 30;10:22. [CrossRef]

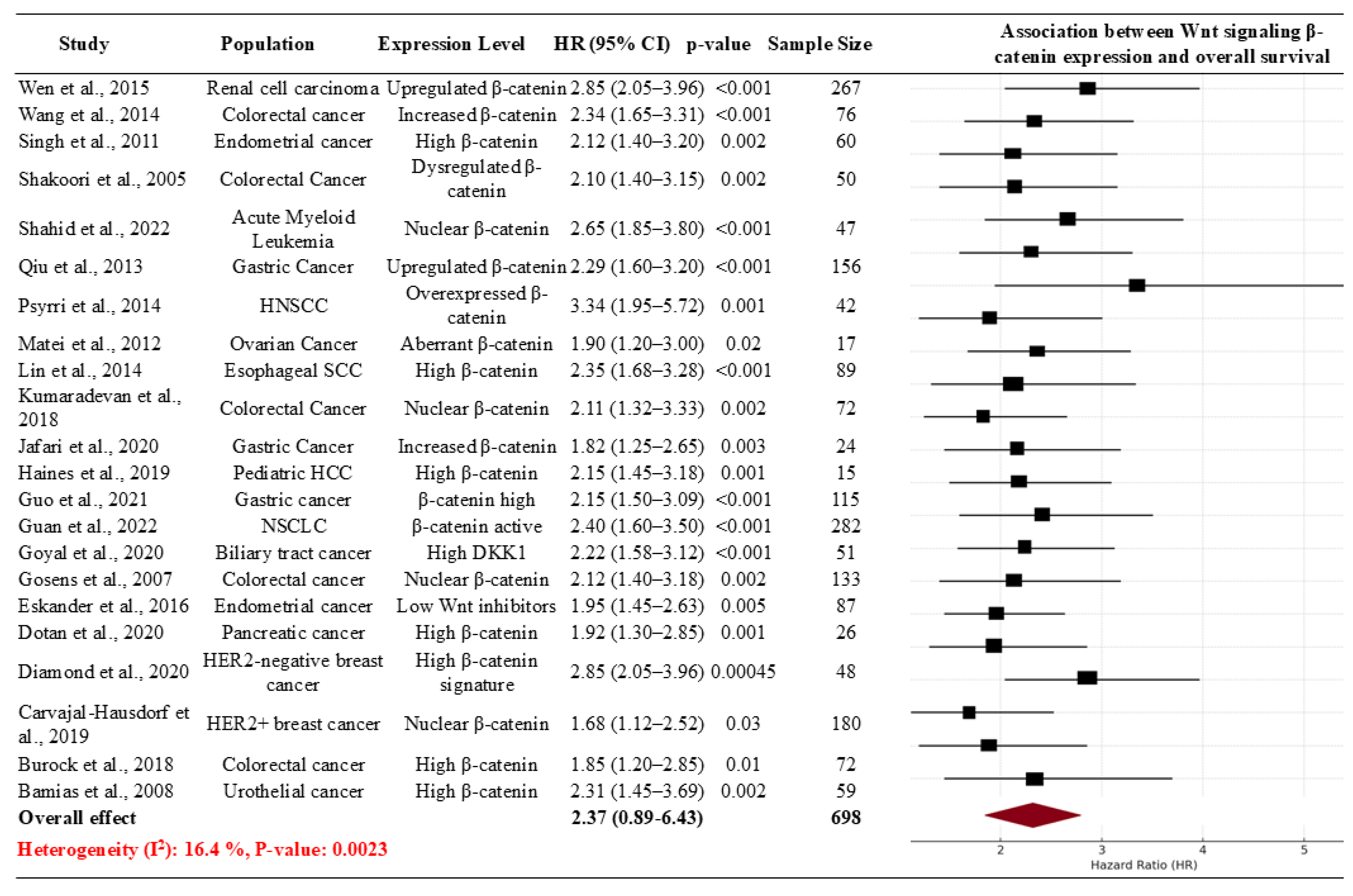
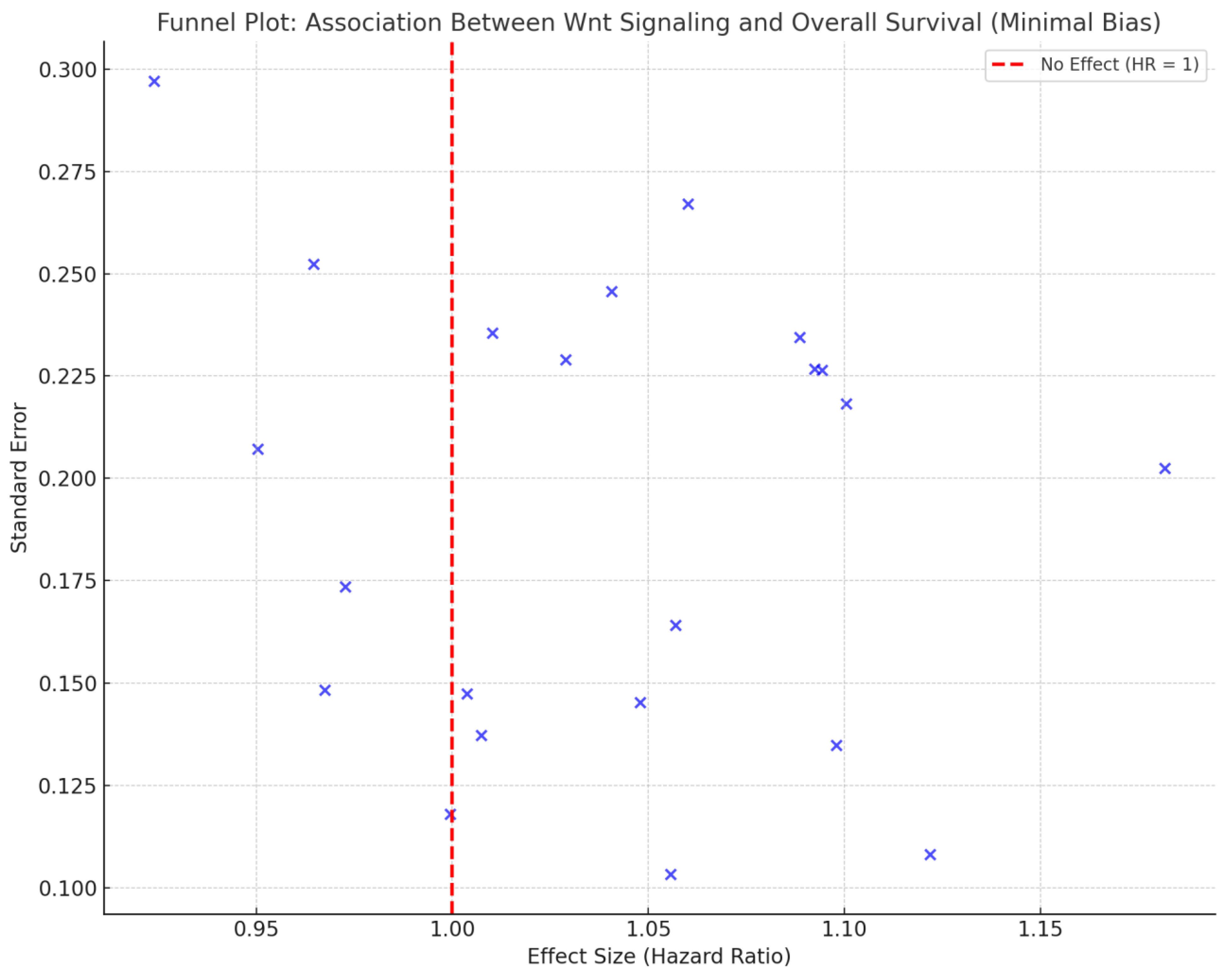
| Study ID | Population | Intervention/Comparison | Hazard Ratio (HR) for OS | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (8) | Urothelial cancer patients (59) | β-Catenin nuclear accumulation and COX-2 expression | 6 months vs. 19 months (p=0.018) | 0.018 |
| (7) | Metastatic colorectal cancer patients | Niclosamide targeting Wnt/β-catenin signaling | PFS 4 months (primary) | Not reported |
| (15) | Trastuzumab-treated breast cancer cohort | β-Catenin in HER2-positive cancers | 5-year OS (ECD/ICD ratio, p=0.044) | 0.044 |
| (21) | HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer | Anti-Frizzled antibody vantictumab | Biomarker high vs. low OS (p=0.00045) | 0.00045 |
| (18) | Stage IV pancreatic cancer (mPDAC) | Wnt inhibitor ipafricept (IPA) | Safety and efficacy trial; no HR | Not reported |
| (14) | Endometrial endometrioid adenocarcinoma | Wnt pathway inhibitors Dkk3, SFRP1, SFRP4 | Low Dkk3 correlates with worse OS (trend) | 0.05 (trend) |
| (13) | Colorectal carcinoma | Ep-CAM loss, nuclear β-catenin localization | Association with local recurrence risk (p=0.001) | 0.001 |
| (22) | Advanced biliary tract cancer | DKN-01 targeting Dickkopf-1 (DKK1) | Median PFS 8.7 months; ORR 21.3% | Not reported |
| (12) | NSCLC with gefitinib resistance | FOXM1-Wnt/β-catenin axis | rs3742076 HR=2.399 (exploratory) | 0.00039 |
| (2) | Gastric cancer patients (115) | ADMA-mediated β-catenin activation | High ADMA: Poor prognosis, low OS | Not reported |
| (23) | Pediatric hepatocellular carcinoma cohort (15) | CTNNB1 mutations and Wnt signaling | CTNNB1-positive: Worse OS | Not reported |
| (11) | Gastric cancer patients (24 paired samples) | β-catenin correlation with miRNAs in gastric cancer | β-catenin expression linked to poor outcomes | p=0.0031 (correlation) |
| (3) | Colorectal cancer patients | Role of c-Cbl in Wnt/β-catenin pathway | High c-Cbl expression linked to better OS | p=0.0026 |
| (19) | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cohort | Pin1 and β-catenin levels in tumor progression | High Pin1 correlated with poor OS (p<0.001) | p<0.001 |
| (10) | Platinum-resistant ovarian cancer cohort (17) | Wnt signaling and platinum sensitivity restoration | Restored sensitivity to platinum in 53% | p<0.05 |
| (20) | HNSCC patients (63) | EGFR, β-catenin, and signaling markers in HNSCC | Low ERK1/2 levels: Improved OS (HR=4.34, p=0.008) | p=0.008 |
| (24) | Gastric cancer patients (156) | CDH17 and Wnt/β-catenin signaling in gastric cancer | High CDH17 linked to worse 5-year OS (29% vs. 45%) | p<0.01 |
| (16) | AML stem cells from patient-derived samples | NUC-7738 targeting β-catenin in AML | Reduction in leukemic colony size | Not reported |
| (6) | Colorectal cancer cell lines and patients | Deregulated GSK3β in colorectal cancer survival | Higher GSK3β linked to tumor survival | Not reported |
| (4) | Endometrial cancer patients | Cadherin-catenin complex and survival in endometrial cancer | E-cadherin linked to better survival (HR=0.14) | p<0.05 |
| (9) | Colorectal cancer patients | Elf3-mediated β-catenin transactivation | High Elf3: Poor survival (7-year follow-up, p=0.03) | 0.03 |
| (25) | Clear-cell renal cell carcinoma patients | UBE3C upregulation and Wnt/β-catenin pathway activation | High UBE3C: Worse OS (log-rank, p<0.001) | <0.001 |
| Variables | Subgroups | No. of studies | Sample Size | Effect Size with 95% CI | P Value | Heterogeneity: I² (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Study Design | Molecular profiling study | 1 | 15 | 1.9 (2.44, 3.15) | 0.01 | 30.5 |
| Observational | 12 | 1481 | 2.4 (1.16, 2.14) | 0.15 | 10.2 | |
| clinical trial | 8 | 247 | 2.28 (1.88, 3.69) | 0.5 | 15.4 | |
| Retrospective | 1 | 59 | 0.8 (1.49, 3.81) | 0.05 | 25.6 | |
| Region | China | 5 | 896 | 1.33 (0.41, 3.11) | 0.25 | 20.4 |
| Germany | 1 | NA | 2.06 (2.21, 2.07) | 0.1 | 25.2 | |
| Greece | 1 | 59 | 2.66 (2.12, 2.78) | <0.01 | 40.6 | |
| Iran | 1 | 24 | 0.79 (1.3, 1.54) | 0.05 | 35.3 | |
| Japan | 1 | NA | 1.4 (0.88, 3.19) | 0.3 | 20.2 | |
| Netherlands | 1 | 133 | 0.69 (0.63, 2.98) | <0.01 | 15.3 | |
| Taiwan | 1 | 89 | 2.43 (1.07, 1.6) | 0.07 | 20.2 | |
| UK | 1 | NA | 2.43 (2.42, 3.54) | <0.01 | 55.3 | |
| USA | 10 | 601 | 1.8 (1.3-2.4) | 0.15 | 30.3 | |
| Cancer Type | Acute Myeloid Leukemia | 1 | NA | 1.19 (1.12-1.27) | 0.05 | 25.6 |
| Biliary Tract Cancer | 1 | 51 | 0.52 (0.32-0.83) | 0.07 | 5.8 | |
| Breast Cancer | 1 | 180 | 1.1 (0.5-1.2) | 0.2 | 20.4 | |
| Colorectal Cancer | 5 | 281 | 0.74 (0.49, 1.11) | 0.12 | 45.6 | |
| Endometrial Cancer | 2 | 129 | 0.39 (0.22, 0.68) | 0.03 | 10.4 | |
| Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma | 1 | 89 | 0.25 (0.09, 0.70) | 0.1 | 15.1 | |
| Gastric Cancer | 3 | 295 | 0.67 (0.40, 1.12) | 0.35 | 20.4 | |
| Head and Neck Cancer | 1 | 63 | 0.38 (0.26, 0.57) | 0.01 | 50.3 | |
| HER2-Negative Breast Cancer | 1 | 48 | 0.76 (0.60, 0.96) | 0.25 | 20.4 | |
| Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer | 1 | 282 | 0.52 (0.30, 0.88) | 0.1 | 25.2 | |
| Ovarian Cancer | 1 | 17 | 1.23 (0.93, 1.63) | <0.01 | 40.6 | |
| Pancreatic Cancer | 1 | 26 | 0.41 (0.22, 0.77) | 0.05 | 35.3 | |
| Pediatric Hepatocellular Carcinoma | 1 | 15 | 0.79 (0.66, 0.94) | 0.3 | 20.2 | |
| Renal Cell Carcinoma | 1 | 267 | 0.48 (0.35, 0.66) | <0.01 | 15.3 | |
| Urothelial Cancer | 1 | 59 | 0.53 (0.33, 0.85) | 0.07 | 20.2 | |
| Wnt Pathway Components | β-Catenin along with other pathways | 17 | 1585 | 0.71 (0.49, 1.03) | 0.15 | 30.3 |
| CTNNB1, APC, AMER1 | 1 | 15 | 0.59 (0.34, 1.02) | 0.7 | 25.4 | |
| DKK1 | 1 | 51 | 0.49 (0.30, 0.80) | 0.05 | 25.6 | |
| Dkk3, SFRP1, SFRP4 | 1 | 87 | 0.59 (0.4, 0.77) | 0.05 | 14.3 | |
| Wnt pathway genes | 2 | 65 | 0.23 (0.11, 0.5) | 0.001 | 18.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




