Submitted:
04 July 2025
Posted:
07 July 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Background
2. Materials and Methods
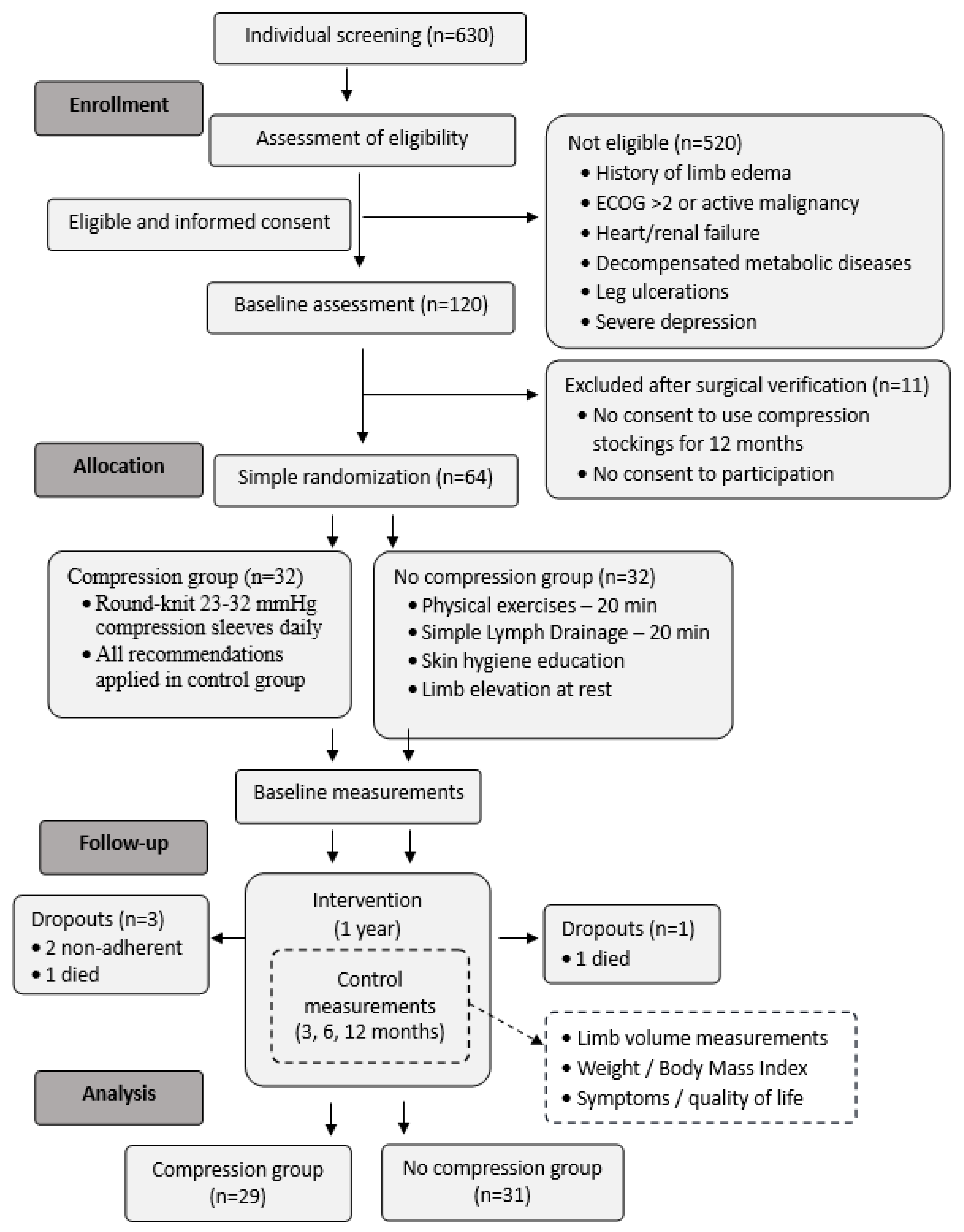
2.1. Participants
2.2. Intervention
2.3. Measurements
- Grade 1 = 2 mm
- Grade 2 = 3–4 mm
- Grade 3 = 5–6 mm
- Grade 4 = ≥8 mm
2.4. Statistics
2.5. The Sample Size
3. Results
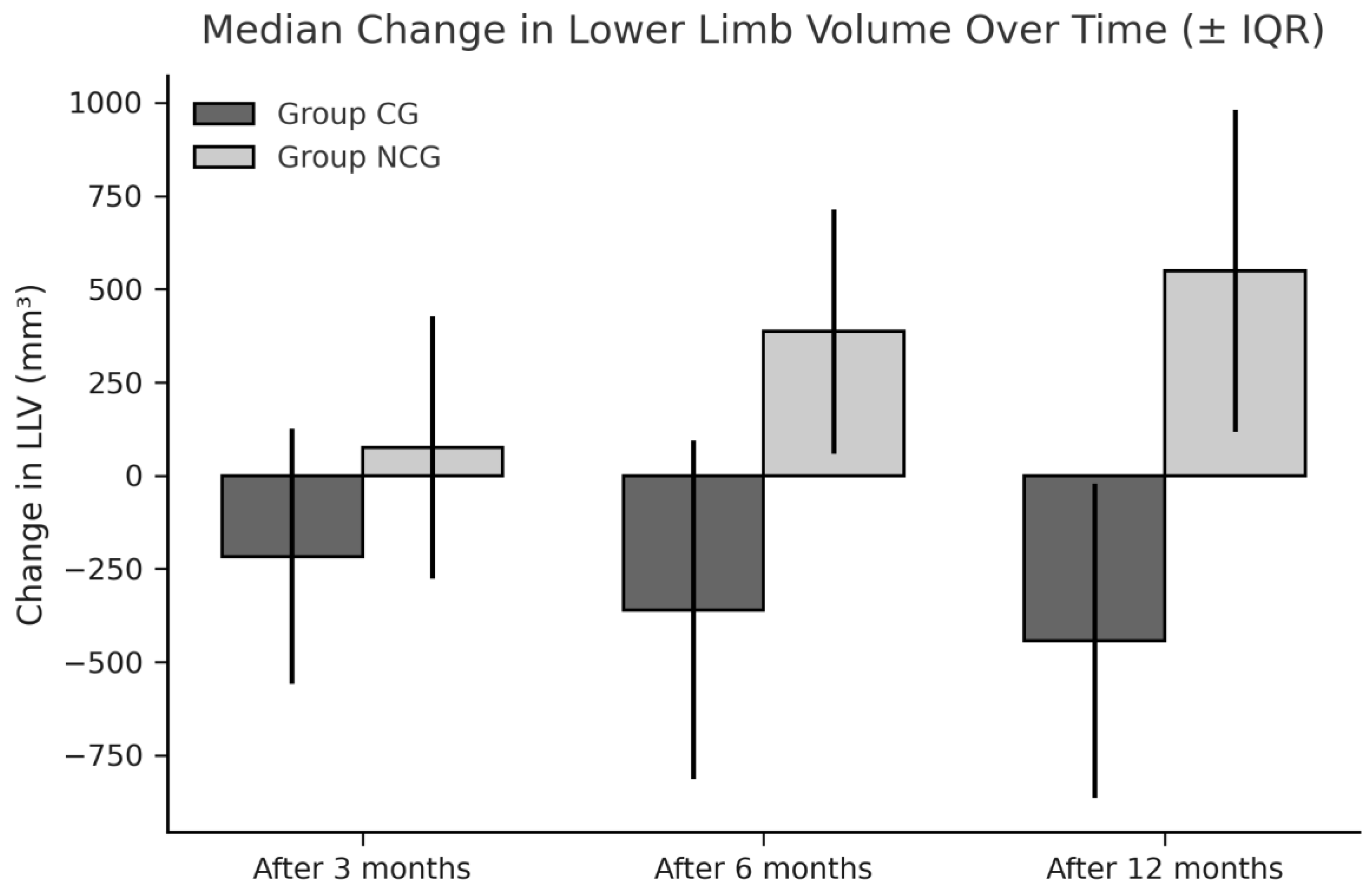
3.1. Limb Volumes and WAC
3.2. The Pitting Test
3.3. Compliance
- walking more than 1 km per day (n = 27),
- Nordic walking (n = 17),
- cycling (n = 11),
- and gymnastic exercises (n = 9).
- rubber gloves (n = 24),
- slippery socks or foot aids (n = 15),
- or assistance from another person (n = 15).
- 8.4/10 immediately after donning, and
- 8.6/10 later in the day.
3.4. Health-Related Quality of Life and Disease - Related Symptoms
4. Discussion
Limitations and Strengths
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Registered ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT06873984
References
- Wu, X. , Liu Y., Zhu D., Wang F., Ji J., Yan H. Early prevention of complex decongestive therapy and rehabilitation exercise for prevention of lower extremity lymphedema after operation of gynecologic cancer. Asian J. Surg. 2021, 44, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, S.C. , Janda M., Ward L.C., et al. Lymphedema following gynecological cancer: Results from a prospective, longitudinal cohort study on prevalence, incidence and risk factors. Gynecol. Oncol. 2017, 146, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshihara, M. , Shimono R., Tsuru S., et al. Risk factors for late-onset lower limb lymphedema after gynecological cancer treatment: A multi-institutional retrospective study. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 46, 1334–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J. , Yu N., Wang X., Long X. Incidence of lower limb lymphedema after vulvar cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2017, 96, e8722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, L.C. , Covens A., Thomas E.J., Armer J.M. Lymphedema measurements and associated patient outcomes: Toward standardization. Gynecol. Oncol. 2022, 160, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.Y. , Liu C.Y., Ho C.L., Hsu K.F. Determinants of quality of life related to lower limb lymphedema in women with gynecological cancer surgery. Asia-Pac. J. Oncol. Nurs. 2023, 10, 100153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, C. , Piedalue K.A., Baydoun M., Carlson L.E. The quality of life and psychosocial implications of cancer-related lower-extremity lymphedema: A systematic review of the literature. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tümkaya M.N., Seven M. Interventions for prevention and management of gynecological cancer-related lower limb lymphedema: A systematic scoping review. Semin. Oncol. Nurs. 2024, in press. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X. , Ding Y., Cai H.Y., et al. Effectiveness of modified complex decongestive physiotherapy for preventing lower extremity lymphedema after radical surgery for cervical cancer: A randomized controlled trial. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2020, 30, 757–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daggez, M. , Koyuncu E.G., Kocabaş R., Yener C. Prophylactic complex physiotherapy in gynecologic cancer survivors: Patient-reported outcomes based on a lymphedema questionnaire. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2023, 33, 1928–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawan, S. , Mugnai R., de Barros Lopes A., Hughes A., Edmondson R.J. Lower-limb lymphedema and vulval cancer: Feasibility of prophylactic compression garments and validation of leg volume measurement. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2009, 19, 1649–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shallwani, S.M. , Towers A., Newman A., et al. Feasibility of a pilot randomized controlled trial examining a multidimensional intervention in women with gynecological cancer at risk of lymphedema. Curr. Oncol. 2021, 28, 455–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuiver, M.M. , de Rooij J.D., Lucas C., et al. No evidence of benefit from class-II compression stockings in the prevention of lower-limb lymphedema after inguinal lymph node dissection: Results of a randomized controlled trial. Lymphology 2013, 46, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sitzia, J. Volume measurement in lymphoedema treatment: Examination of formulae. Eur. J. Cancer Care (Engl.) 1995, 4, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, C.L. , Specht M.C., Horick N., et al. A novel, validated method to quantify breast cancer-related lymphedema (BCRL) following bilateral breast surgery. Lymphology 2013, 46, 64–74. [Google Scholar]
- International Society of Lymphology. The diagnosis and treatment of peripheral lymphedema: 2023 Consensus document of the International Society of Lymphology. Lymphology 2023, 56, 1–25.
- Liu, F. , Liu N.F., Wang L., et al. Treatment of secondary lower limb lymphedema after gynecologic cancer with complex decongestive therapy. Lymphology 2021, 54, 122–132. [Google Scholar]
- Webb, E. , Bissett B., Neeman T., et al. Compression therapy is cost-saving in the prevention of lower limb recurrent cellulitis in patients with chronic edema. Lymphat. Res. Biol. 2023, 21, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavezzi, A. , Cornu-Thenard A., Bergan J.J., et al. Compression therapy, autonomic nervous system, and heart rate variability: A narrative review and our preliminary personal experience. Phlebology 2022, 37, 739–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partsch, H. Compression therapy: Clinical and experimental evidence. Ann. Vasc. Dis. 2012, 5, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, M. , Deveaux A., White H., Rayson D. Compression garments versus compression bandaging in decongestive lymphatic therapy for breast cancer-related lymphedema: A randomized controlled trial. Support Care Cancer 2012, 20, 1031–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabe, E. , Partsch H., Hafner J., et al. Indications for medical compression stockings in venous and lymphatic disorders: An evidence-based consensus statement. Phlebology 2018, 33, 163–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeley, V. The early detection of breast cancer treatment-related lymphedema of the arm. Lymphat. Res. Biol. 2020, 19, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, C. , Levenhagen K., Ryans K., Perdomo M., Gilchrist L. Interventions for breast cancer-related lymphedema: Clinical practice guideline from the academy of oncologic physical therapy of APTA. Phys. Ther. 2020, 100, 1163–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochalek, K. , Gradalski T., Partsch H. Preventing early postoperative arm swelling and lymphedema manifestation by compression sleeves after axillary lymph node interventions in breast cancer patients: A randomized controlled trial. J. Pain Symptom Manage. 2017, 54, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J. , Zhou C., Ma Q., Zhang Y., Zhang X. Preventing lower limb lymphedema after pelvic lymphadenectomy with progressive resistance exercise training: A randomized controlled trial. Asia-Pac. J. Oncol. Nurs. 2024, 11, 100333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, M. , Ruddell S., Sandsund C., Thomas K., Shaw C. A service development evaluation of retrospective data exploring prophylactic risk-reducing advice for patients with gynecological cancers. J. Gynecol. Surg. 2020, 36, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayegh, H.E. , Asdourian M.S., Swaroop M.N., et al. Diagnostic methods, risk factors, prevention, and management of breast cancer-related lymphedema: Past, present, and future directions. Curr. Breast Cancer Rep. 2017, 9, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugisawa, R. , Unno N., Saito T., et al. Effects of compression stockings on elevation of leg lymph pumping pressure and improvement of quality of life in healthy female volunteers: A randomized controlled trial. Lymphat. Res. Biol. 2016, 14, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stout, N. , Partsch H., Szolnoky G., et al. Chronic edema of the lower extremities: International consensus recommendations for compression therapy clinical research trials. Int. Angiol. 2012, 31, 316–329. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, Y.Y. , Nguyen T.T., Chou Y.J., Ho C.L. Effects of exercise on lower limb lymphedema in gynecologic cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Oncol. Nurs. 2024, 70, 102550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, K.H. , Courneya K.S., Matthews C., et al. American college of sports medicine roundtable on exercise guidelines for cancer survivors. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2010, 42, 1409–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, S.C. , Singh B., Reul-Hirche H., et al. The effect of exercise for the prevention and treatment of cancer-related lymphedema: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2022, 54, 2136–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, T. , Tsuji T., Sano Y., et al. Immediate effects of active exercise with compression therapy on lower-limb lymphedema. Support Care Cancer 2017, 25, 2603–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, K. , Tsuji T., Oka A., et al. Postural differences in the immediate effects of active exercise with compression therapy on lower limb lymphedema. Support Care Cancer 2021, 29, 6535–6543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, X. , Cao G., Yang L., Wang C., Tian C. Postoperative effectiveness of comprehensive nursing intervention for lymphedema in gynecological cancer: A controlled study. Altern. Ther. Health Med. 2023, 29, 242–247. [Google Scholar]
| Parameter (n or median, IQR) | CG (n=29) | NCG group (n=31) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 53.5 (15.25) | 58 (14.0) | 0.06* |
| Height (m) | 1.61 (0.11) | 1.58 (0.09) | 0.3* |
| Weight (kg) | 70.0 (16.5) | 75.0 (19.0) | 0.9* |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 26.9 (4.6) | 28.0 (8.6) | 0.5* |
| Professionally active | 19 | 16 | |
| Tumor localization (n) | |||
| Ovaries | 7 | 7 | 0.6** |
| Cervix uteri | 8 | 8 | |
| Corpus uteri | 12 | 15 | |
| Vulva | 2 | 1 | |
| Complementary therapy (n) | |||
| Lymphadenectomy | 29 | 31 | |
| Radiotherapy | 26 | 26 | 0.7** |
| Limb volumes (L) | |||
| ...Right | 8.13 (1.36) | 7.82 (2.28) | 0.8* |
| Left | 8.30 (1.93) | 7.90 (2.17) | 0.9* |
| ...Right and left | 16.60 (3.58) | 15.95 (4.38) | 0.9* |
| Parameter (n or median, IQR) | CG (n=29) | NCG (n=31) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Edema occurrence (n) | 1 | 12 | 0.003* |
| Limb volume changes | |||
| Right limb | |||
| Within 3 months | -86.13 (349.40) | 97.05 (315.27) | 0.049** |
| Within 6 months | -157.33 (480.43) | 193 (836.04) | 0.022** |
| Within 12 months | -259.33 (540.99) | 250.05 (546.81) | 0.001** |
| P-value | 0.01*** | 0.07*** | |
| Left limb | |||
| Within 3 months | -155.66 (285.45) | 36.80 (388.09) | 0.051** |
| Within 6 months | -198.42 (94.43) | 151.37 (384.09) | 0.019** |
| Within 12 months | -137.10 (497.68) | 250.51 (366.36) | 0.002** |
| P-value | 0.011*** | 0.06*** | |
| Right and left limb | |||
| Within 3 months | -216.88 (684.90) | 75.34 (162.36) | 0.032** |
| Within 6 months | -359.81 (375.47) | 386.96 (655.08) | 0.004** |
| Within 12 months | -443.01 (841.88) | 549.07 (861.70) | 0.001** |
| P-value | 0.011*** | 0.011*** | |
| WAC | |||
| Right limb | |||
| Within 3 months | -0.01 (0.04) | 0.02 (0.06) | 0.004** |
| Within 6 months | -0.03 (0.06) | 0.03 (0.02) | 0.003** |
| Within 12 months | -0.06 (0.08) | 0.02 (0.05) | 0.001** |
| P-value | 0.001*** | 0.9*** | |
| Left limb | |||
| Within 3 months | -0.02 (0.05) | 0.01 (0.05) | 0.002** |
| Within 6 months | -0.03 (0.07) | 0.02 (0.05) | 0.003** |
| Within 12 months | -0.05 (0.07) | 0.02 (0.05) | 0.001** |
| P-value | 0.001*** | 0.3*** | |
| Right and left limb | |||
| Within 3 months | -0.02 (0.03) | 0.02 (0.03) | 0.001** |
| Within 6 months | -0.03 (0.05) | 0.02 (0.03) | <0.001** |
| Within 12 months | -0.05 (0.06) | 0.02 (0.04) | <0.001** |
| P-value | 0.001*** | 0.4*** |
| Problem mean±SD and median(IQR) |
CG (n=29) |
P-value within group** |
NCG (n=31) |
P-value within group** |
P-value between groups* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pain within the limbs | |||||
| At baseline | 1.39±0.57 1.0(1.0) | 1.33±0.61 1.0(0.75) | 0.049 | ||
| After 3 months | 1.41±0.57 1.0(1.0) | 1.0 | 1.50±0.63 1.0(1.0) | 0.07 | 0.6 |
| After 6 months | 1.29±0.53 1.0(0.25) | 0.2 | 1.57±0.63 1.5(1.0) | 0.04 | 0.6 |
| After 12 months | 1.32±0.55 1.0(1.0) | 0.5 | 1.59±0.68 1.0 (1.0) | 0.05 | 0.1 |
| Limb heaviness | |||||
| At baseline | 1.26±0.39 1.0(0.5) | 1.23±0.43 1.0 (0.0) | 0.8 | ||
| After 3 months | 1.33±0.48 1.0(1.0) | 0.5 | 1.27±0.52 1.0(0.0) | 0.8 | 0.5 |
| After 6 months | 1.33±0.48 1.0(1.0) | 0.5 | 1.73±0.74 2.0 (1.0) | 0.004 | 0.036 |
| After 12 months | 1.54±0.58 1.5(1.0) | 0.06 | 1.62±0.68 2.0(1.0) | 0.003 | 0.7 |
| Skin tension | |||||
| At baseline | 1.18±0.41 1.0(0.0) | 1.23±0.43 1.0(0.0) | 0.7 | ||
| After 3 months | 1.28±0.46 1.0(1.0) | 0.5 | 1.43±0.50 1.0 (1.0) | 0.04 | 0.3 |
| After 6 months | 1.43±0.57 1.0(1.0) | 0.2 | 1.60±0.67 1.0(1.0) | 0.003 | 0.1 |
| After 12 months | 1.43±0.57 1.0(1.0) | 0.008 | 1.48±0.63 1.0(1.0) | 0.04 | 0.8 |
| Limb numbness | |||||
| At baseline | 1.64±0.68 1.0(1.0) | 1.47±0.5 1.0(1.0) | 0.3 | ||
| After 3 months | 1.46±0.58 1.0(1.0) | 0.09 | 1.70±0.65 2.0(1.0) | 0.02 | 0.2 |
| After 6 months | 1.43±0.50 1.0(1.0) | 0.01 | 1.73±0.64 2.0(1.0) | 0.04 | 0.04 |
| After 12 months | 1.43±0.50 1.0(1.0) | 0.09 | 1.69±0,60 2.0(1.0) | 0.08 | |
| Genital edema | |||||
| At baseline | 1.0±0 1.0(0.0) | 1.0±0.0 1.0(0.0) | 1.0 | ||
| After 3 months | 1.08±0.27 1.0(0.0) | 0.3 | 1.07±0.25 1.0(0.0) | 0.3 | 0.9 |
| After 6 months | 1.0±0 1.0(0.0) | 1.0 | 1.17±-.46 1.0(1.0) | 0.09 | 0.049 |
| After 12 months | 1.0±0 1.0(0.0) | 1.0 | 1.07±0.26 1.0(0.0) | 0.4 | 0.1 |
| Lymphorrhea | |||||
| At baseline | 1.0±0 1.0(0.0) | 1.0±0 1.0(0.0) | 1.0 | ||
| After 3 months | 1.0±0 1.0(0.0) | 1.0 | 1.03±0.18 1.0(0.0) | 1.0 | 0.4 |
| After 6 months | 1.0±0 1.0(0.0) | 1.0 | 1.13±0.43 1.0(0.0) | 0.2 | 0.09 |
| After 12 months | 1.0±0 1.0(0.0) | 1.0 | 1.00±0.00 1.0 (0.0) | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Parameter median (IQR) |
CG (n=29) |
NCG (n=31) |
P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Global health status | 75 (25.0) | 66.67 (16.67) | 0.3 |
| Physical functioning | 93.33 (13.33) | 86.67 (20.0) | 0.03 |
| Role functioning | 100 (20.83) | 83.33 (16.67) | 0.8 |
| Emotional functioning | 83.33 (25.0) | 75.0 (25.0) | 0.9 |
| Cognitive functioning | 91.67 (33.33) | 83.33 (16.67) | 0.5 |
| Social functioning | 100 (16.67) | 100 (16.67) | 0.9 |
| Fatigue | 22.22 (33.33) | 22.22 (22.22) | 0.5 |
| Nausea and vomiting | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (12.5) | 0.8 |
| Pain | 16.67 (33.3) | 25.0 (33.33) | 0.3 |
| Dyspnea | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (33.33) | 0.2 |
| Insomnia | 33.33 (33.33) | 33.33 (33.33) | 0.9 |
| Appetite loss | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (33.33) | 0.4 |
| Constipation | 16.67 (33.33) | 0.0 (33.33) | 0.4 |
| Diarrhea | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | 0.4 |
| Financial difficulties | 0.0 (33.3) | 0.0 (33.3) | 0.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





