Submitted:
03 June 2025
Posted:
04 June 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- Can CoT prompting alone improve performance in biomedical QA under zero-shot conditions?
- How does instruction fine-tuning interact with CoT prompts?
- Are gains from CoT consistent across different model families and sizes?
2. Data Collection and Preprocessing
 |
3. Method
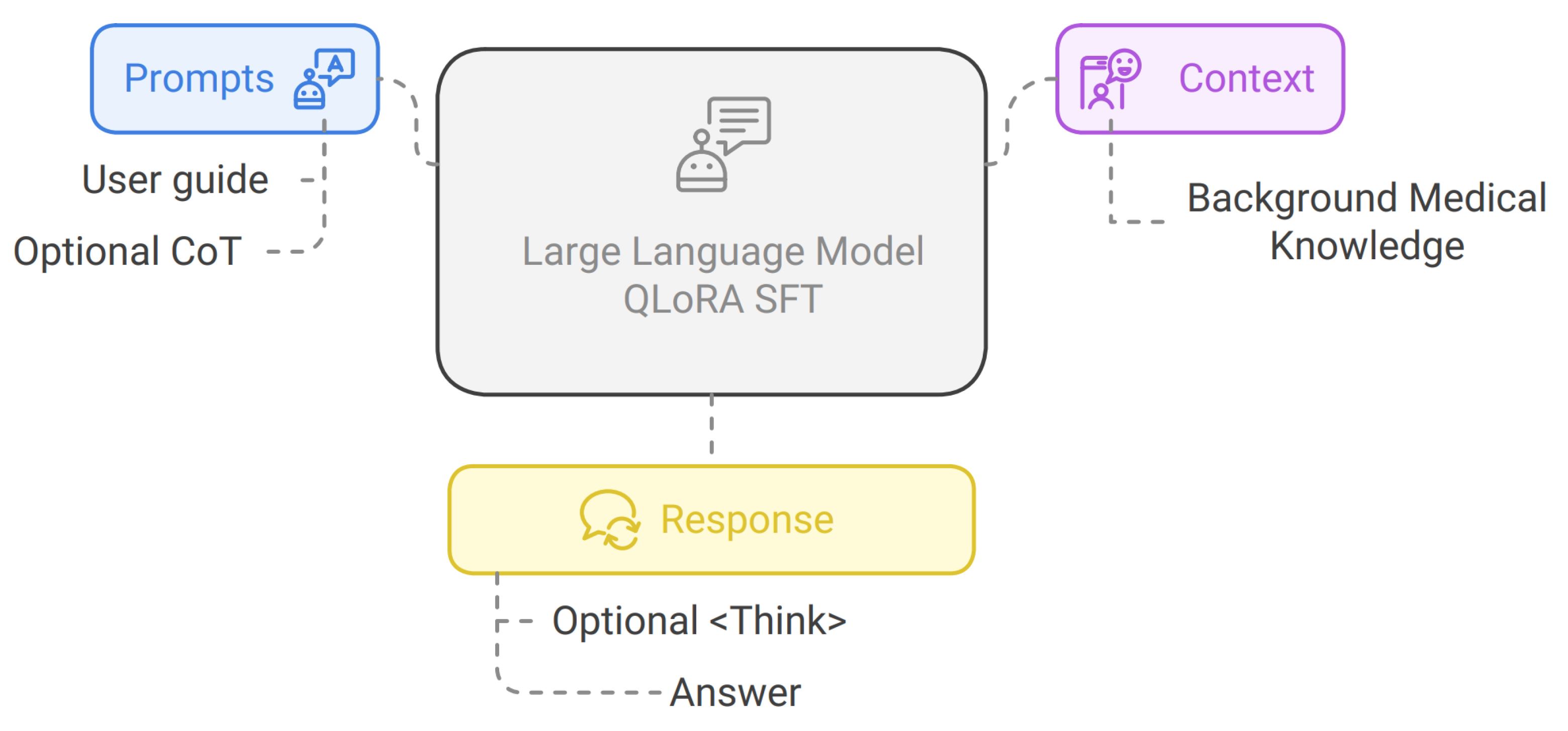
3.1. Framework
3.2. Instruction Fine Tuning
3.3. Chain of Thought Prompting
3.4. QLoRA
3.5. Models and Settings
- Base (Zero-shot): Direct inference using the pre-trained checkpoint.
- Instruction Finetuned (SFT): Models fine-tuned on formatted PubMedQA data using QLoRA.
3.6. Prompting Strategies
- Default Prompt: A concise instruction asking the model to select one of the three options.
- CoT Prompt: Same as Default but with an explicit Think: section encouraging step-by-step reasoning.
4. Experiments
4.1. Training Configuration
4.2. Metrics
- Accuracy: The proportion of correct predictions overall test instances.
- Weighted F1 Score: An F1 score weighted by class distribution is particularly important for PubMedQA due to its imbalanced answer types.
4.3. Comparative Analysis of Model Performance
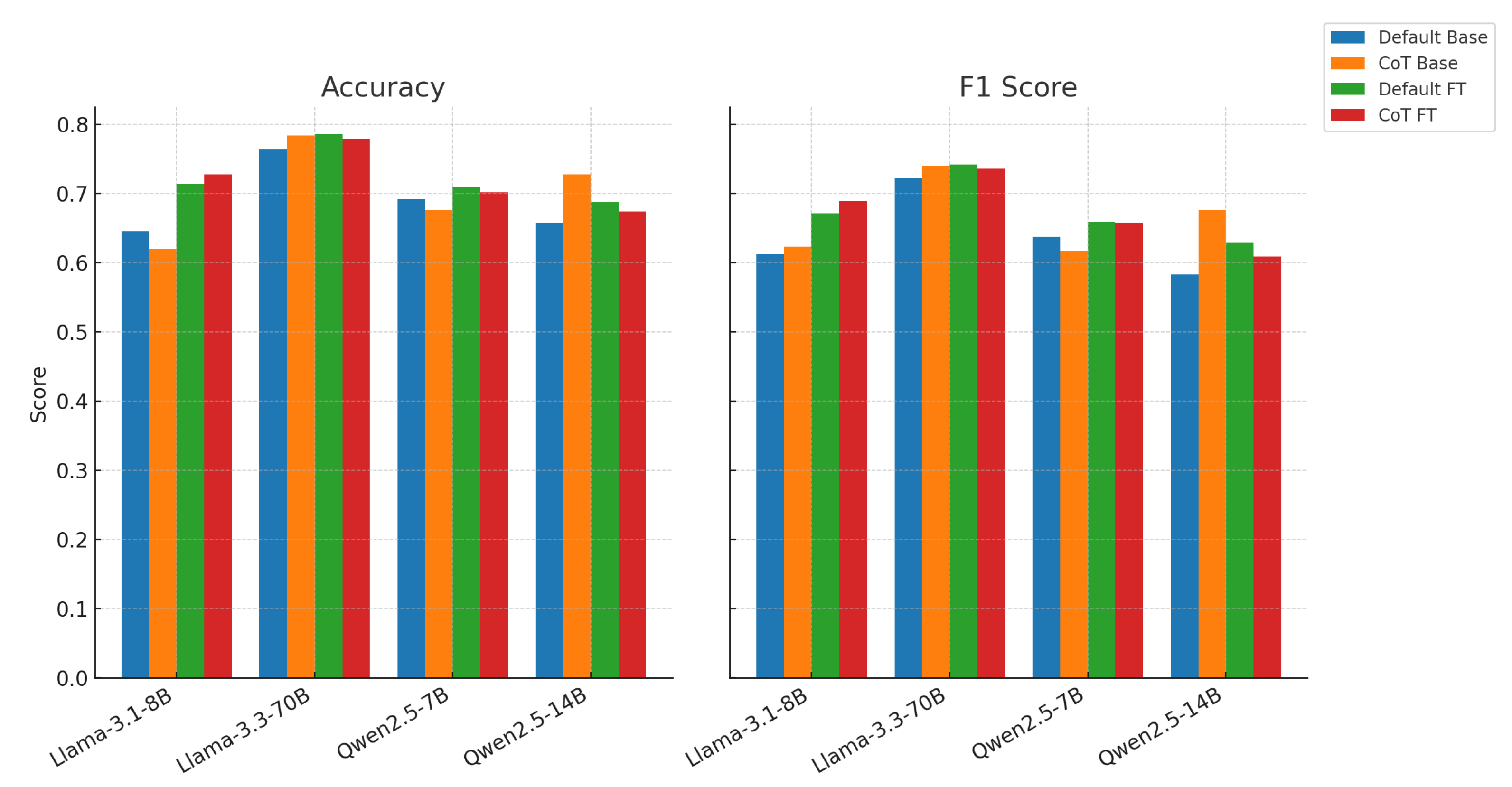
- Instruction fine-tuning leads to consistent improvements. All models show performance gains after SFT, with accuracy increases ranging from +1.0% (Qwen2.5-7B CoT) to +8.0% (Llama-3.1-8B Default). This trend is especially notable under default prompting, where fine-tuning provides clearer gains than CoT.
- CoT prompting improves F1 in base models. In 3 out of 4 models (Llama-3.1-8B, Llama-3.3-70B, Qwen2.5-14B), adding CoT to base models increases F1, suggesting that CoT can help models handle ambiguous or nuanced biomedical questions. For instance, Llama-3.3-70B shows an F1 increase from 0.7224 (Default) to 0.7399 (CoT) in the base setting.
- CoT + SFT is not always beneficial. While CoT SFT gives the highest F1 in some settings (e.g., 0.6891 for Llama-3.1-8B), it can hurt performance in others. Notably, Qwen2.5-14B shows a drop in F1 from 0.6760 (Base CoT) to 0.6087 (CoT + SFT), indicating potential misalignment between CoT-style reasoning and instruction-tuned representations for larger models.
4.4. Model-Specific Insights
Llama-3.1-8B.
Llama-3.3-70B.
Qwen2.5-7B.
Qwen2.5-14B.
4.5. CoT: Help or Hurdle?
5. Conclusion and Future Work
- Multi-stage training with CoT pretraining before full instruction tuning;
- Faithfulness and reasoning quality evaluation for Think: outputs;
- Expansion to real-world clinical tasks with explainability constraints;
- Combining retrieval-based methods (RAG) with CoT prompting for grounded biomedical QA.
References
- Bian, W.; et al. A Review of Electromagnetic Elimination Methods for low-field portable MRI scanner. In Proceedings of the 2024 5th International Conference on Machine Learning and Computer Application (ICMLCA). IEEE, 2024, pp. 614–618. [CrossRef]
- Ni, H.; Meng, S.; et al. Time Series Modeling for Heart Rate Prediction: From ARIMA to Transformers. In Proceedings of the 2024 6th International Conference on Electronic Engineering and Informatics (EEI). IEEE, 2024, pp. 584–589. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Xu, X. Research on Large Language Model Cross-Cloud Privacy Protection and Collaborative Training based on Federated Learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:2503.12226 2025.
- Zhang, Z.; Qin, W.; Plummer, B.A. Machine-generated text localization. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.11744 2024.
- Yang, Z.; Jin, Y.; Xu, X. HADES: Hardware Accelerated Decoding for Efficient Speculation in Large Language Models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2412.19925 2024.
- Zhang, Z.; Zheng, J.; Fang, Z.; Plummer, B.A. Text-to-image editing by image information removal. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF winter conference on applications of computer vision, 2024, pp. 5232–5241.
- Jin, Y.; Yang, Z.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, S. Adaptive Fault Tolerance Mechanisms of Large Language Models in Cloud Computing Environments. arXiv preprint arXiv:2503.12228 2025.
- Lee, J.; et al. BioBERT: a pre-trained biomedical language representation model for biomedical text mining. Bioinformatics 2020.
- Ding, Z.; et al. Enhance Image-to-Image Generation with LLaVA-generated Prompts. In Proceedings of the 2024 5th International Conference on Information Science, Parallel and Distributed Systems (ISPDS). IEEE, 2024, pp. 77–81. [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Yang, Q.; Geng, X.; et al. Exploring Diverse Methods in Visual Question Answering. In Proceedings of the 2024 5th International Conference on Electronic Communication and Artificial Intelligence (ICECAI). IEEE, 2024, pp. 681–685. [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Abouelenien, M.; Mihalcea, R.; et al. Deception Detection from Linguistic and Physiological Data Streams Using Bimodal Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2024 5th International Conference on Information Science, Parallel and Distributed Systems (ISPDS). IEEE, 2024, pp. 263–267. [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Wang, Y.; Ke, Z.; Shen, Q.; Li, Z.; Zhang, R.; Ouyang, K. A Generative Adversarial Network-Based Investor Sentiment Indicator: Superior Predictability for the Stock Market. Mathematics 2025, 13, 1476.
- Li, P.; Lin, Y.; Schultz-Fellenz, E. Contextual Hourglass Network for Semantic Segmentation of High Resolution Aerial Imagery. In Proceedings of the 2024 5th International Conference on Electronic Communication and Artificial Intelligence (ICECAI). IEEE, 2024, pp. 15–18. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Fan, R.; Wang, S.; Shen, L.; Zhang, Q.; Ke, Z.; Zheng, T. Contextual Bandits for Unbounded Context Distributions. arXiv preprint arXiv:2408.09655 2024.
- Ni, H.; Meng, S.; Chen, X.; Zhao, Z.; et al. Harnessing Earnings Reports for Stock Predictions: A QLoRA-Enhanced LLM Approach. In Proceedings of the 2024 6th International Conference on Data-driven Optimization of Complex Systems (DOCS). IEEE, 2024, pp. 909–915. [CrossRef]
- Meng, S.; Chen, A.; Wang, C.; Zheng, M.; Wu, F.; Chen, X.; Ni, H.; Li, P. Enhancing Exchange Rate Forecasting with Explainable Deep Learning Models. In Proceedings of the 2024 4th International Conference on Electronic Information Engineering and Computer Science (EIECS). IEEE, 2024, pp. 892–896. [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; et al. Regional Style and Color Transfer. In Proceedings of the 2024 5th International Conference on Computer Vision, Image and Deep Learning (CVIDL). IEEE, 2024, pp. 593–597. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; He, H.; Plummer, B.A.; Liao, Z.; Wang, H. Complex scene image editing by scene graph comprehension. arXiv preprint arXiv:2203.12849 2022.
- Shree, A.; Jia, K.; Xiong, Z.; Chow, S.F.; Phan, R.; Li, P.; Curro, D. Image analysis. US Patent App. 17/638,773 2022.
- Luo, H.; Ji, C. Cross-Cloud Data Privacy Protection: Optimizing Collaborative Mechanisms of AI Systems by Integrating Federated Learning and LLMs. arXiv preprint arXiv:2505.13292 2025.
- Ji, C.; Luo, H. Cloud-Based AI Systems: Leveraging Large Language Models for Intelligent Fault Detection and Autonomous Self-Healing. arXiv preprint arXiv:2505.11743 2025.
- Ding, Z.; Lai, Z.; Li, S.; et al. Confidence Trigger Detection: Accelerating Real-Time Tracking-by-Detection Systems. In Proceedings of the 2024 5th International Conference on Electronic Communication and Artificial Intelligence (ICECAI). IEEE, 2024, pp. 587–592. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Ji, C.; Luo, H.; et al. Data Augmentation Through Random Style Replacement. In Proceedings of the 2025 6th International Conference on Computer Vision, Image and Deep Learning (CVIDL). IEEE, 2025.
- Xu, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xu, Z.; Zhao, M.; Luo, H. Style Transfer: From Stitching to Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2024 5th International Conference on Big Data & Artificial Intelligence & Software Engineering (ICBASE). IEEE, 2024, pp. 526–530.
- Yang, Q.; et al. A comparative study on enhancing prediction in social network advertisement through data augmentation. In Proceedings of the 2024 4th International Conference on Machine Learning and Intelligent Systems Engineering (MLISE). IEEE, 2024, pp. 214–218. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Chen, A.; Zhou, X.; Ni, H.; Zhang, S.; et al. Evaluating Modern Approaches in 3D Scene Reconstruction: NeRF vs Gaussian-Based Methods. In Proceedings of the 2024 6th International Conference on Data-driven Optimization of Complex Systems (DOCS). IEEE, 2024, pp. 926–931. [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ke, Z.; Li, Z. Convex Optimization of Markov Decision Processes Based on Z Transform: A Theoretical Framework for Two-Space Decomposition and Linear Programming Reconstruction. Mathematics 2025, 13. [CrossRef]
- Langerman, J.M.; Endres, I.; Rethage, D.; Li, P. Three-dimensional building model generation based on classification of image elements. US Patent App. 18/703,608 2025.
- Bolton, E.; et al. Biomedlm: A 2.7 b parameter language model trained on biomedical text. arXiv 2024.
- Achiam, J.; et al. Gpt-4 technical report. arXiv preprint arXiv:2303.08774 2023.
- Grattafiori, A.; et al. The llama 3 herd of models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2407.21783 2024.
- Yang, A.; et al. Qwen2. 5 technical report. arXiv preprint arXiv:2412.15115 2024.
- Wei, J.; et al. Chain-of-thought prompting elicits reasoning in large language models. Advances in neural information processing systems 2022.
- Singhal, K.; et al. Toward expert-level medical question answering with large language models. Nature Medicine 2025.
- Dettmers, T.; et al. QLoRA: Efficient Finetuning of Quantized LLMs. arXiv preprint arXiv:2305.14314 2023.
- Jin, Q.; et al. Pubmedqa: A dataset for biomedical research question answering. arXiv:1909.06146 2019.
- Zhang, S.; et al. Instruction tuning for large language models: A survey. arXiv:2308.10792 2023.
- Loshchilov, I.; Hutter, F. Decoupled weight decay regularization. arXiv preprint arXiv:1711.05101 2017.
| Model | Base | Finetune | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acc | F1 | Acc | F1 | |
| Llama-3.1-8B (Default) | 0.6460 | 0.6130 | 0.7140 | 0.6716 |
| Llama-3.1-8B (CoT) | 0.6200 | 0.6236 | 0.7280 | 0.6891 |
| Llama-3.3-70B (Default) | 0.7640 | 0.7224 | 0.7860 | 0.7420 |
| Llama-3.3-70B (CoT) | 0.7840 | 0.7399 | 0.7800 | 0.7366 |
| Qwen2.5-7B (Default) | 0.6920 | 0.6372 | 0.7100 | 0.6589 |
| Qwen2.5-7B (CoT) | 0.6760 | 0.6173 | 0.7020 | 0.6577 |
| Qwen2.5-14B (Default) | 0.6580 | 0.5834 | 0.6880 | 0.6298 |
| Qwen2.5-14B (CoT) | 0.7280 | 0.6760 | 0.6740 | 0.6087 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





