Submitted:
30 April 2025
Posted:
02 May 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
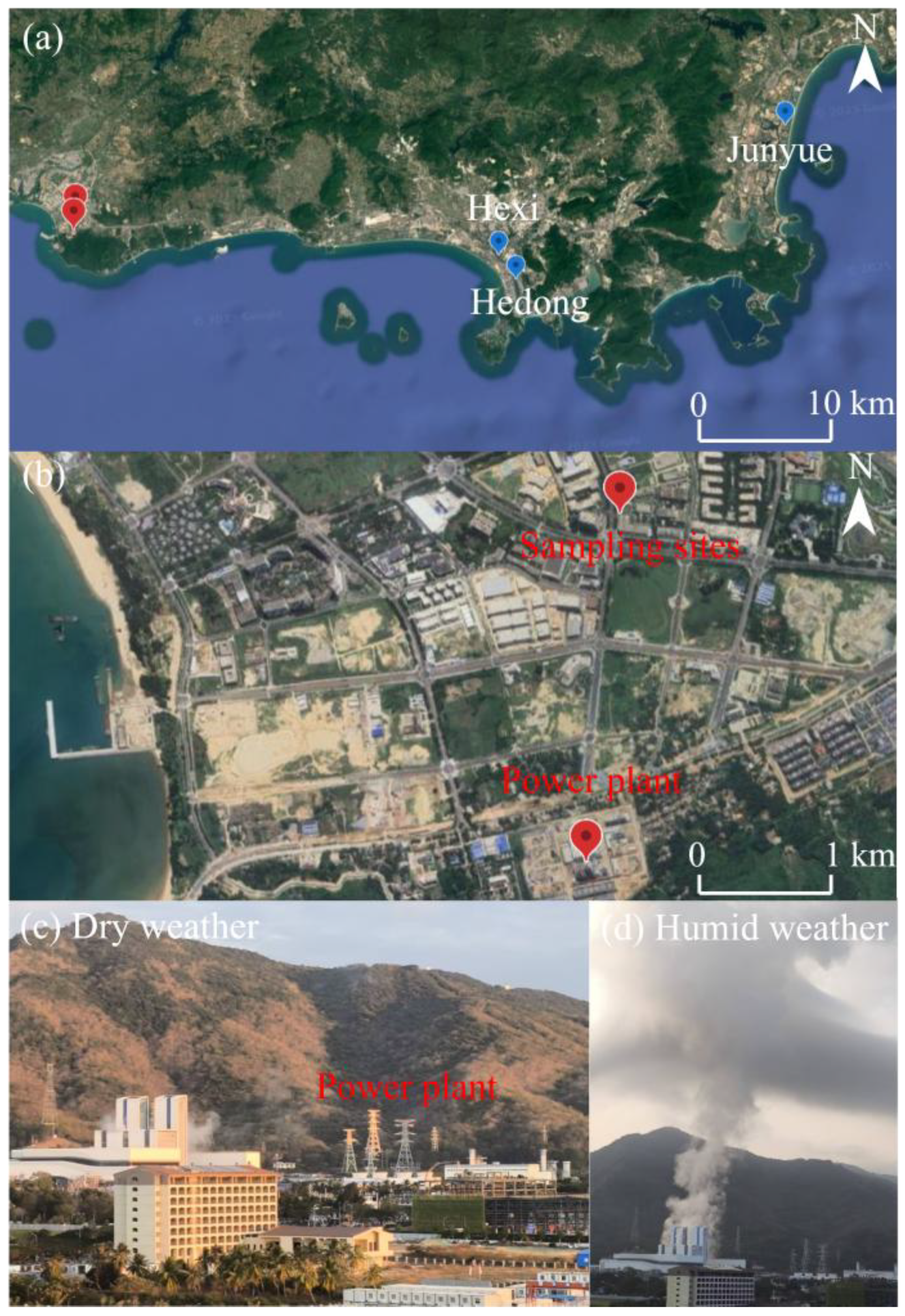
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
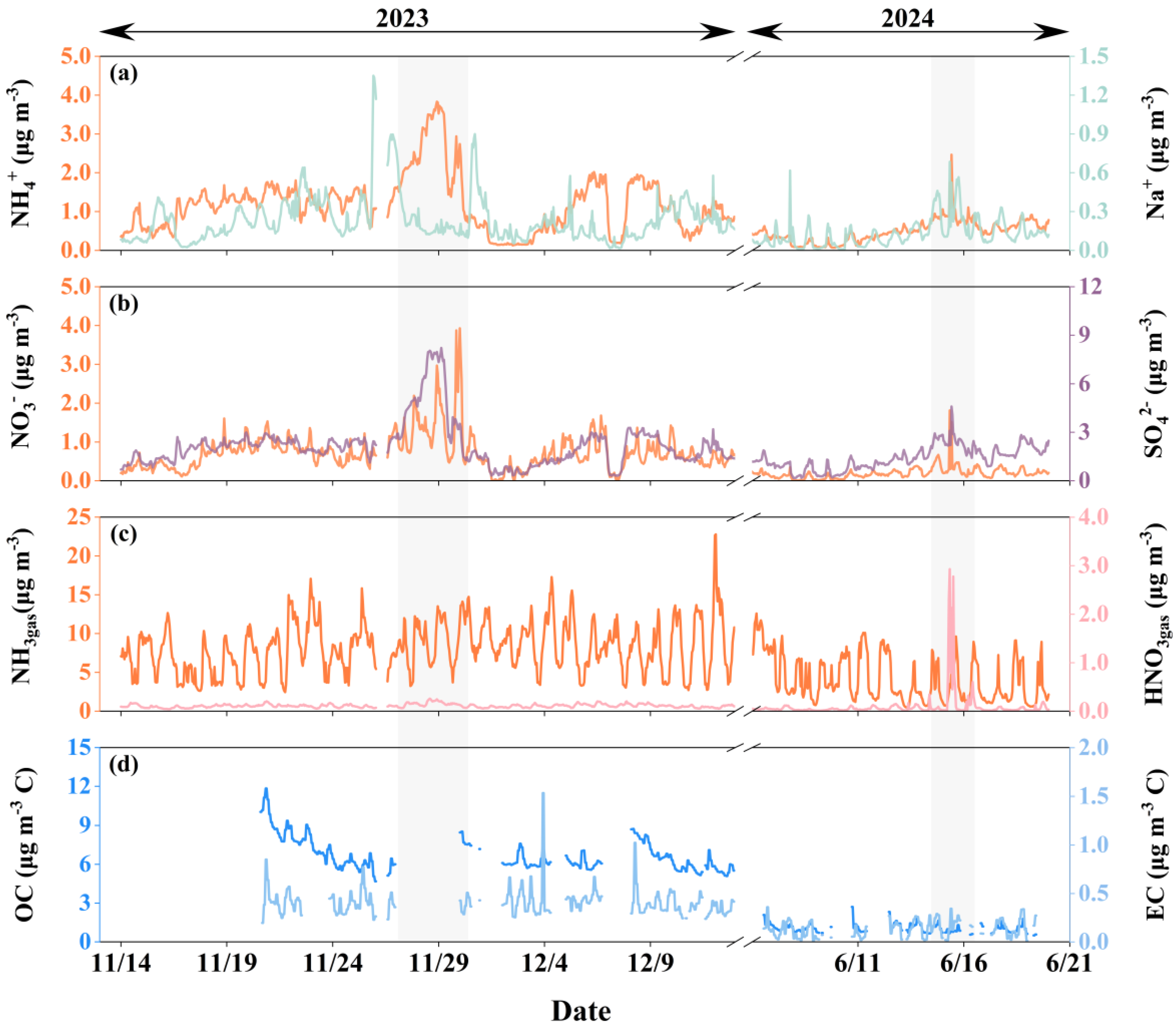
3.1. Overview of Observational Results at the Coastal Site
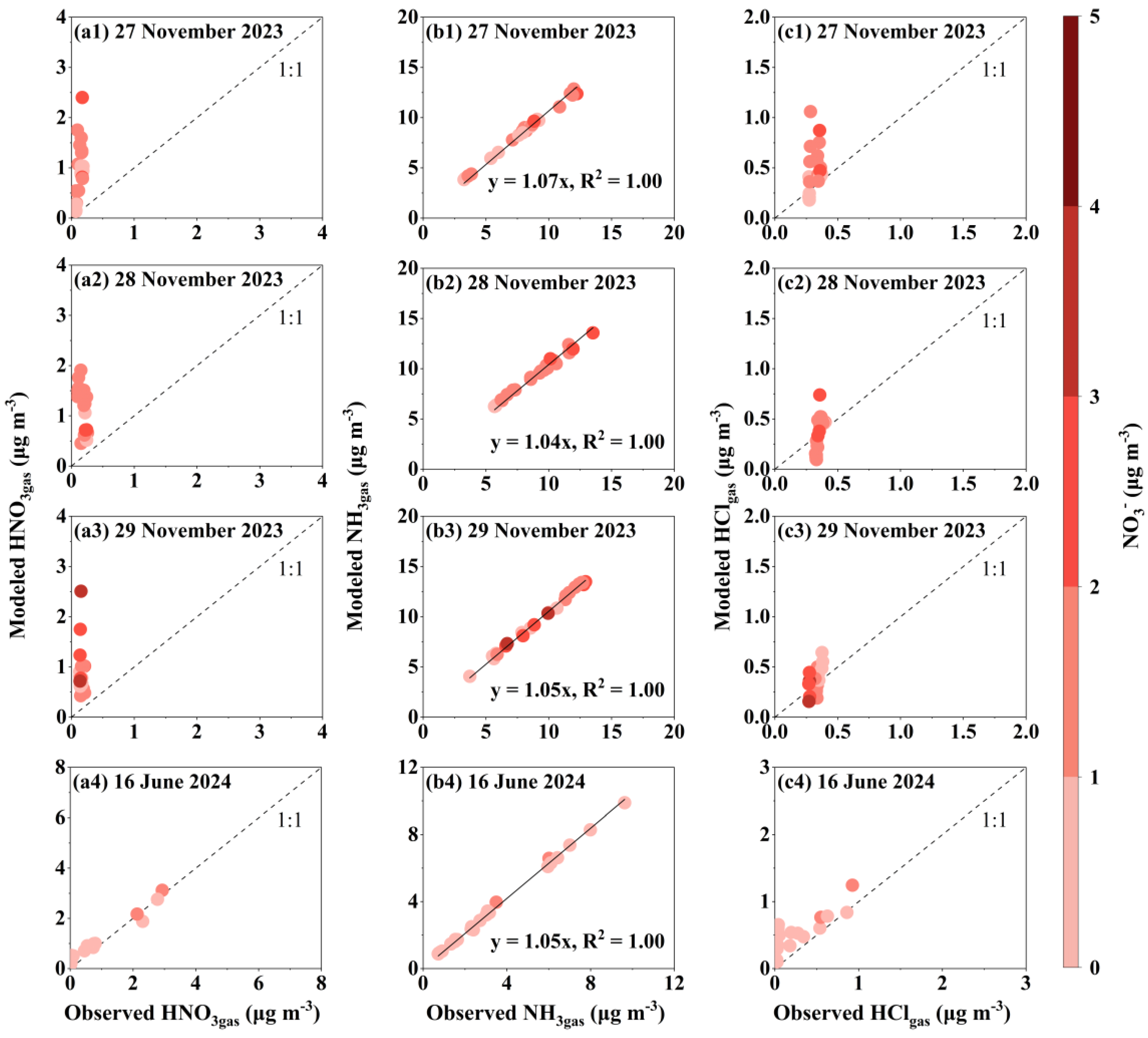
3.2. Thermodynamic Equilibrium Simulations for the Four Cases
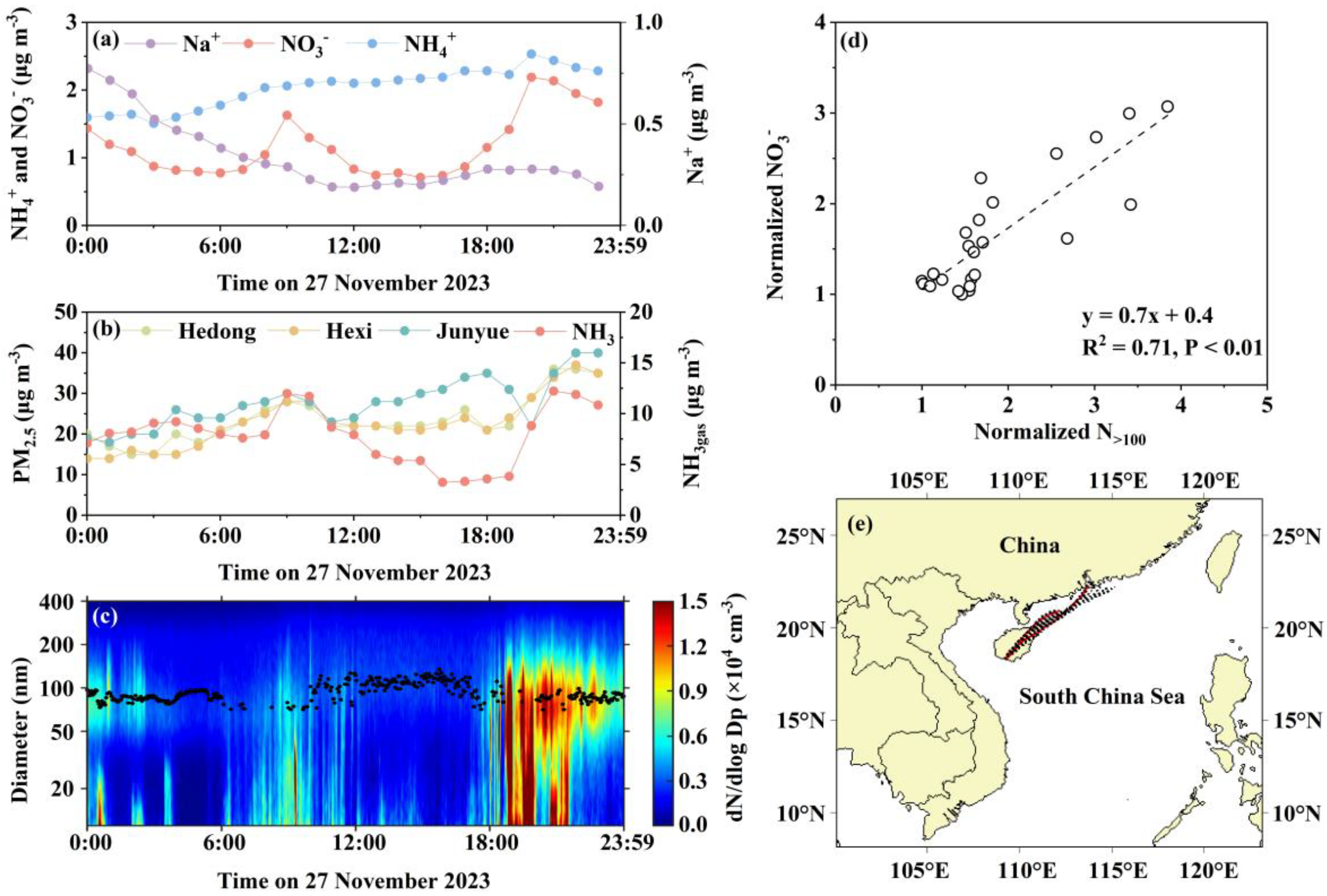
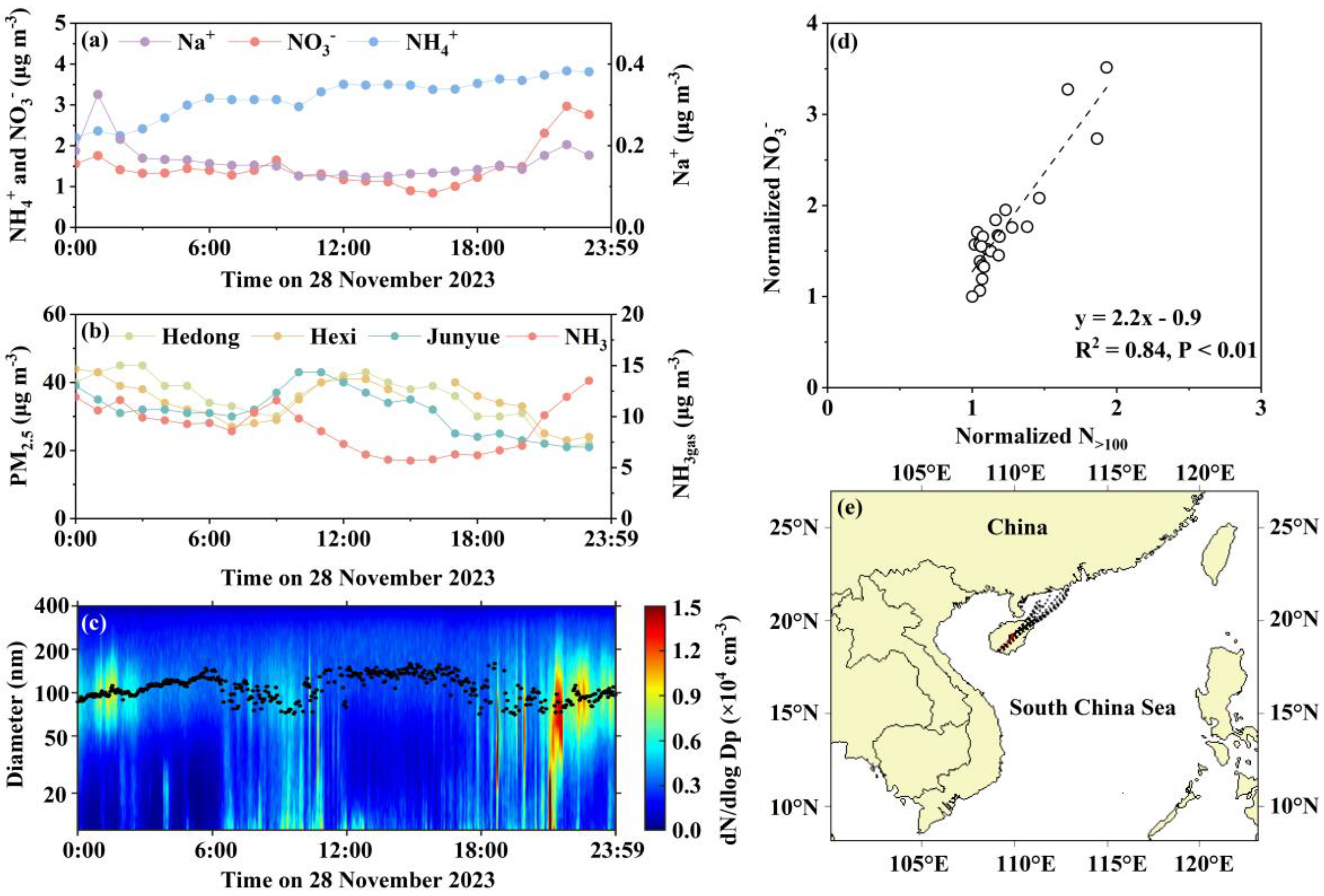
3.3. Case 1: Synergistic Effects of Primary Emissions and Meteorological Conditions on the Rapid In-Plume Formation and Subsequent Volatilization of Fresh Ammonium Nitrate
3.4. Case 2: Biomass-Burning-Derived Potassium Salts and Cloud-Processing of KNO₃ and NH4NO3 by Mixing with Additional Anthropocentric Sources, Followed by NH4NO3 Volatilization
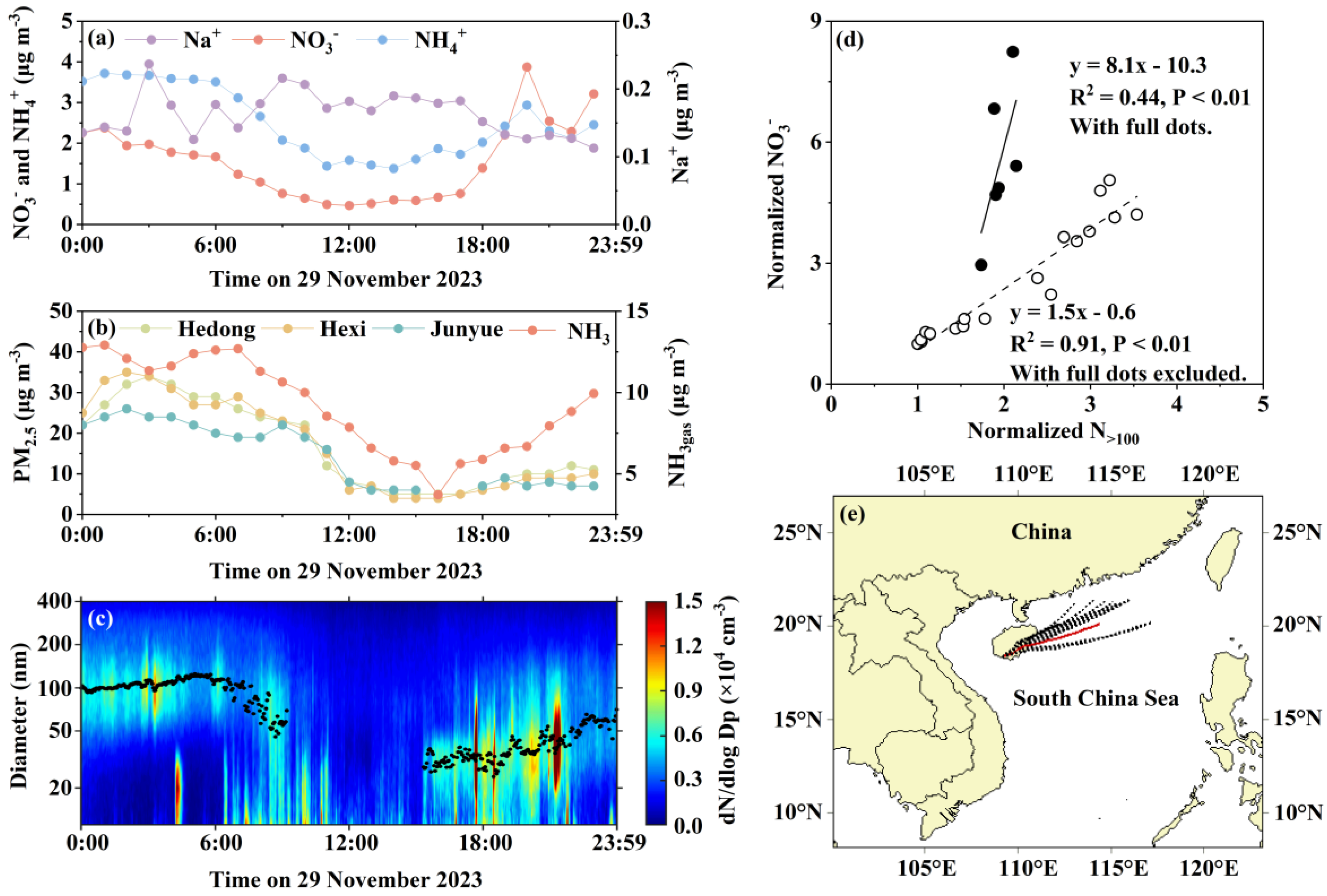
3.5. Case 3: Transition from Regional Transport to Local Combustion Sources Induces Strong Phase Instability and NH₄NO₃ Volatilization
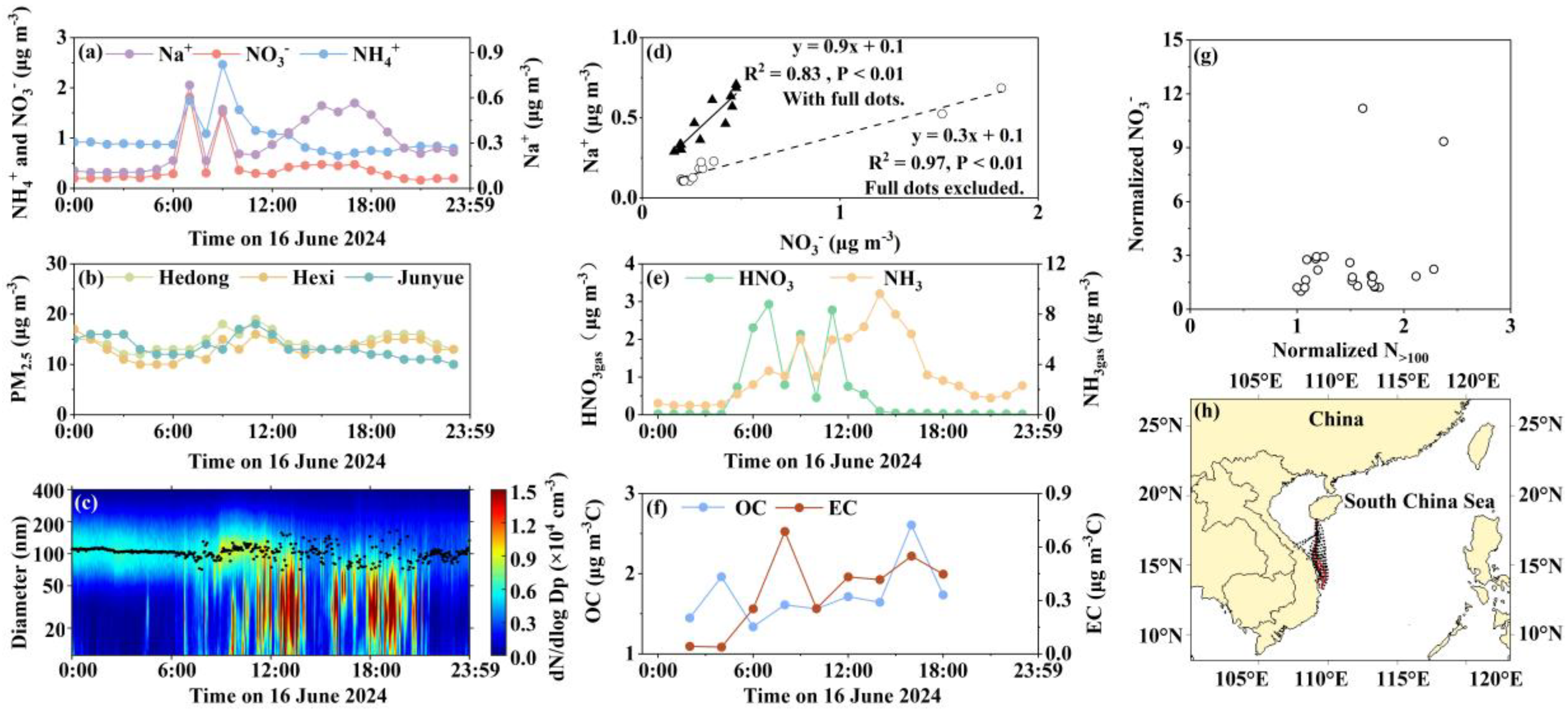
3.6. Case 4: Primary Emissions and Marine Aerosol Interactions Drive Diurnal Sea-Salt-Restricted Nitrate Formation Under Southeast Monsoon Influence
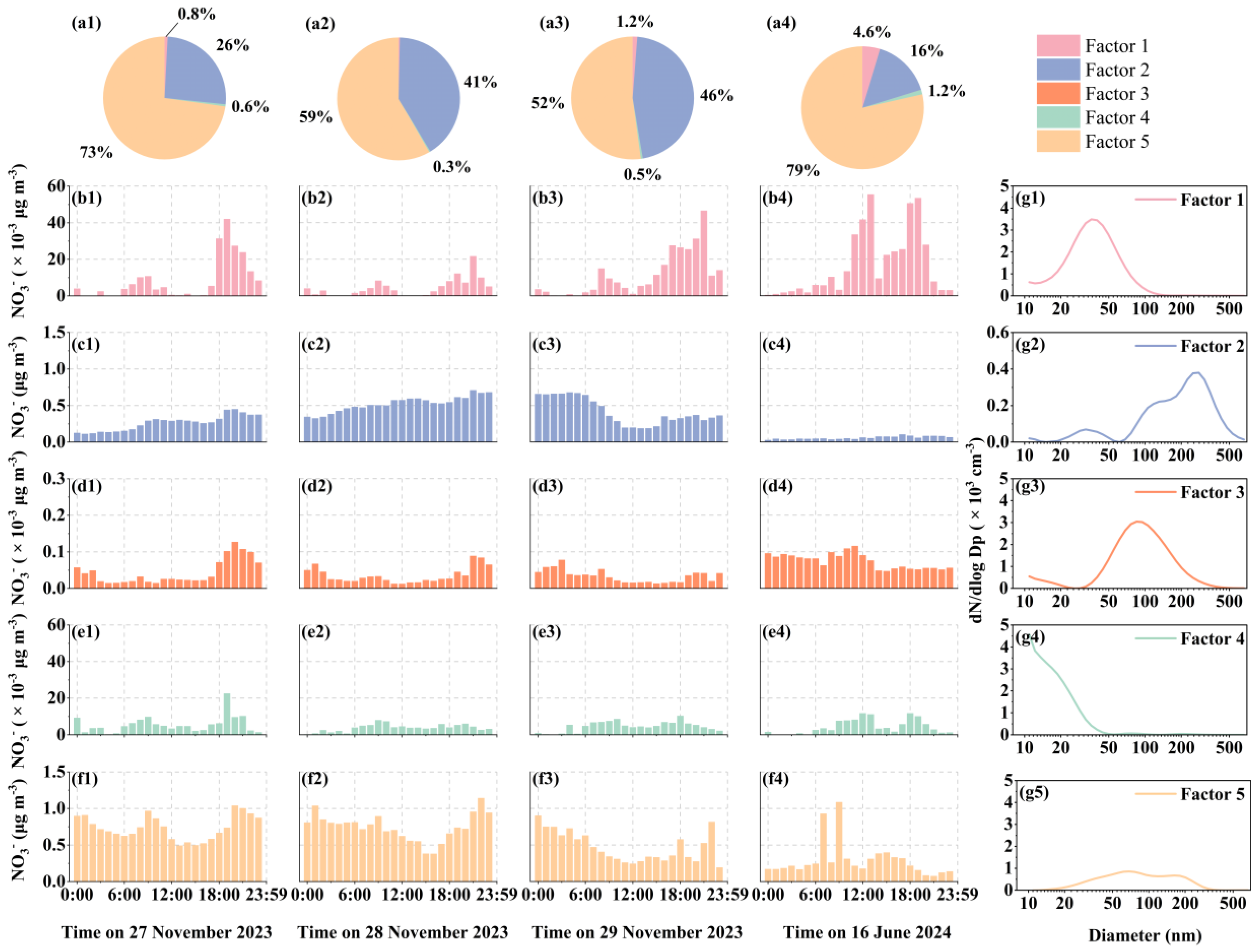
3.7. Source Apportionment of NO3- in PM2.5 During the Four Cases
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Barthelmie, R.J.; Pryor, S.C. Implications of ammonia emissions for fine aerosol formation and visibility impairment: A case study from the Lower Fraser Valley, British Columbia. Atmos. Environ. 1998, 32(3), 345-352. [CrossRef]
- Pathak, R.K.; Wu, W.S.; Wang, T. Summertime PM2.5 ionic species in four major cities of China: Nitrate formation in an ammonia-deficient atmosphere. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 1711-1722. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ding, X.; Fu, X.; He, Q.; Wang, S.; Bernard, F.; Zhao, X.; Wu, D. Aerosol scattering coefficients and major chemical compositions of fine particles observed at a rural site in the Central Pearl River Delta, South China. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 24, 72-77. [CrossRef]
- Park, R.S.; Lee, S.; Shin, S.-K.; Song, C.H. Contribution of ammonium nitrate to aerosol optical depth and direct radiative forcing by aerosols over East Asia. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 2185-2201. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Wang, G.; Guo, S.; Zamora, M.L.; Ying, Q.; Lin, Y.; Wang, W.; Hu, M.; Wang, Y. Formation of urban fine particulate matter. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 3803-3855. [CrossRef]
- Höpfner, M.; Ungermann, J.; Borrmann, S.; Wagner, R.; Spang, R.; Riese, M.; Stiller, G.; Appel, O.; Batenburg, A.M.; Bucci, S.; et al. Ammonium nitrate particles formed in upper troposphere from ground ammonia sources during Asian monsoons. Nat. Geosci. 2019, 12, 608-612. [CrossRef]
- An, Z.; Huang, R.-J.; Zhang, R.; Tie, X.; Li, G.; Cao, J.; Zhou, W.; Shi, Z.; Han, Y.; Gu, Z.; et al. Severe haze in northern China: A synergy of anthropogenic emissions and atmospheric processes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 8657-8666. [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Nie, W.; Chi, X.; Xu, Z.; Ge, D.; Ren, C.; Zhu, C.; Huang, X.; et al. Enhanced particulate nitrate formation in residual layer exacerbates near-surface pollution: Insights from tethered airship and long-term ground measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmospheres 2025, 130, e2024JD042672. [CrossRef]
- Pitchford, M.L.; Poirot, R.L.; Schichtel, B.A.; Malm, W.C. Characterization of the winter Midwestern particulate nitrate bulge. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2009, 59, 1061-1069. [CrossRef]
- Shon, Z.-H.; Kim, K.-H.; Song, S.-K.; Jung, K.; Kim, N.-J.; Lee, J.-B. Relationship between water-soluble ions in PM2.5 and their precursor gases in Seoul megacity. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 59, 540-550. [CrossRef]
- Shah, V.; Jaeglé, L.; Thornton, J.A.; Lopez-Hilfiker, F.D.; Lee, B.H.; Schroder, J.C.; Campuzano-Jost, P.; Jimenez, J.L.; Guo, H.; Sullivan, A.P.; et al. Chemical feedbacks weaken the wintertime response of particulate sulfate and nitrate to emissions reductions over the eastern United States. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 8110-8115. [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Sullivan, A.P.; Campuzano-Jost, P.; Schroder, J.C.; Lopez-Hilfiker, F.D.; Dibb, J.E.; Jimenez, J.L.; Thornton, J.A.; Brown, S.S.; Nenes, A.; et al. Fine particle pH and the partitioning of nitric acid during winter in the northeastern United States. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121. 10355-10376 . [CrossRef]
- Seinfeld, J.H.; Pandis, S.N. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics: From Air Pollution to Climate Change, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, New Jersey, 2016; ISBN 978-1-119-22116-6.
- Li, Y.; Schwandner, F.M.; Sewell, H.J.; Zivkovich, A.; Tigges, M.; Raja, S.; Holcomb, S.; Molenar, J.V.; Sherman, L.; Archuleta, C.; et al. Observations of ammonia, nitric acid, and fine particles in a rural gas production region. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 83, 80-89. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Ma, Z.; Ge, B.; Xie, C.; Zhou, W.; Zhao, J.; Xu, W.; Du, W.; Fu, P.; et al. Temporal characteristics and vertical distribution of atmospheric ammonia and ammonium in winter in Beijing. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 681, 226-234. [CrossRef]
- Watson, J.G.; Chow, J.C.; Lurmann, F.W.; Musarra, S.P. Ammonium nitrate, nitric acid, and ammonia equilibrium in wintertime Phoenix, Arizona. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 1994, 44, 405-412. [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Kishore, S.; Tripathi, S.N.; Behera, S.N. Role of atmospheric ammonia in the formation of inorganic secondary particulate matter: A study at Kanpur, India. J. Atmos. Chem. 2007, 58, 1-17. [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Yao, X.; Chan, C.K.; Tian, X.; Chu, Y.; Clegg, S.L.; Shen, Y.; Gao, Y.; Gao, H. Competitive uptake of dimethylamine and trimethylamine against ammonia on acidic particles in marine atmospheres. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 5430-5439. [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Liu, M.; Zhang, M.; Song, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, L.; Xu, T.; Wang, T.; Yan, C.; Zhou, T.; et al. High efficiency of livestock ammonia emission controls in alleviating particulate nitrate during a severe winter haze episode in northern China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 5605-5613. [CrossRef]
- Saraswati; Sharma, S.K.; Saxena, M.; Mandal, T.K. Characteristics of gaseous and particulate ammonia and their role in the formation of secondary inorganic particulate matter at Delhi, India. Atmos. Res. 2019, 218, 34-49. [CrossRef]
- Franchin, A.; Fibiger, D.L.; Goldberger, L.; McDuffie, E.E.; Moravek, A.; Womack, C.C.; Crosman, E.T.; Docherty, K.S.; Dube, W.P.; Hoch, S.W.; et al. Airborne and ground-based observations of ammonium-nitrate-dominated aerosols in a shallow boundary layer during intense winter pollution episodes in northern Utah. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 17259-17276. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Guan, H.; Luo, L.; Zheng, N.; Xiao, H.; Liang, Y.; Xiao, H. Sources and transformation of nitrate aerosol in winter 2017-2018 of megacity Beijing: Insights from an alternative approach. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 241, 117842. [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Meng, H.; Yao, X.; Peng, Z.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; Gao, Y.; Feng, L.; Liu, X.; Gao, H. Does ambient secondary conversion or the prolonged fast conversion in combustion plumes cause severe PM2.5 air pollution in China? Atmosphere 2022, 13, 673. [CrossRef]
- Dang, R.; Jacob, D.J.; Zhai, S.; Yang, L.H.; Pendergrass, D.C.; Coheur, P.; Clarisse, L.; Van Damme, M.; Choi, J.; Park, J.; et al. A satellite-based indicator for diagnosing particulate nitrate sensitivity to precursor emissions: Application to East Asia, Europe, and North America. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 20101-20113. [CrossRef]
- Tsimpidi, A.P.; Karydis, V.A.; Pandis, S.N. Response of inorganic fine particulate matter to emission changes of sulfur dioxide and ammonia: The eastern United States as a case study. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2007, 57, 1489-1498. [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Xue, L.; Wang, X.; Xu, C.; Chen, T.; Yang, L.; Wang, T.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, W. Summertime fine particulate nitrate pollution in the North China Plain: Increasing trends, formation mechanisms and implications for control policy. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 11261-11275. [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.K.; Kim, Y.P.; Ghim, Y.S.; Song, M.J.; Kim, C.H.; Jang, K.S.; Lee, K.Y.; Shin, H.J.; Jung, J.S.; Wu, Z.; et al. Spatial distribution of PM2.5 chemical components during winter at five sites in Northeast Asia: High temporal resolution measurement study. Atmos. Environ. 2022, 290, 119359. [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.T.; Whitall, D.R.; Robarge, W.; Paerl, H.W. Ambient ammonia and ammonium aerosol across a region of variable ammonia emission density. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 1235-1246. [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, J.; Du, H.; Chen, J.; Chen, H.; Yang, X.; Gao, W.; Geng, F. Important role of ammonia on haze formation in Shanghai. Environ. Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 024019. [CrossRef]
- Weber, R.J.; Guo, H.; Russell, A.G.; Nenes, A. High aerosol acidity despite declining atmospheric sulfate concentrations over the past 15 years. Nature Geosci. 2016, 9, 282-285. [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Lu, K.; Chen, X.; Zhu, Q.; Wu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Sun, K. Fast particulate nitrate formation via N2O5 uptake aloft in winter in Beijing. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 10483-10495. [CrossRef]
- Jo, H.-Y.; Lee, H.-J.; Jo, Y.-J.; Lee, J.-J.; Ban, S.; Lee, J.-J.; Chang, L.-S.; Heo, G.; Kim, C.-H. Nocturnal fine particulate nitrate formation by N2O5 heterogeneous chemistry in Seoul metropolitan area, Korea. Atmos. Res. 2019, 225, 58-69. [CrossRef]
- Bertram, T.H.; Thornton, J.A.; Riedel, T.P.; Middlebrook, A.M.; Bahreini, R.; Bates, T.S.; Quinn, P.K.; Coffman, D.J. Direct observations of N2O5 reactivity on ambient aerosol particles. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, 2009GL040248. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Nie, W.; Qiao, L.; Huang, D.D.; Zhu, S.; Lou, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, Q.; Tao, S.; Sun, P.; et al. Elevated formation of particulate nitrate from N2O5 hydrolysis in the Yangtze River Delta region from 2011 to 2019. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2022, 49, e2021GL097393. [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Tham, Y.J.; Nie, W.; Xia, M.; Wang, H.; Guo, Y.; Ma, W.; Zhan, J.; Hua, C.; Li, Y.; et al. Increasing contribution of nighttime nitrogen chemistry to wintertime haze formation in Beijing observed during COVID-19 lockdowns. Nat. Geosci. 2023, 16, 975-981. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhao, X.; Liu, P.; Chen, D.; Zhang, C.; Xue, C.; Liu, J.; Xu, J.; Mu, Y. Transport pathways of nitrate formed from nocturnal N2O5 hydrolysis aloft to the ground level in winter North China Plain. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 2715-2725. [CrossRef]
- Behera, S.N.; Sharma, M.; Aneja, V.P.; Balasubramanian, R. Ammonia in the atmosphere: A review on emission sources, atmospheric chemistry and deposition on terrestrial bodies. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 8092-8131. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Henze, D.K.; Bash, J.O.; Cady-Pereira, K.E.; Shephard, M.W.; Luo, M.; Capps, S.L. Sources and impacts of atmospheric NH3: Current understanding and frontiers for modeling, measurements, and remote sensing in North America. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2015, 1, 95-116. [CrossRef]
- Dammers, E.; Shephard, M.W.; Palm, M.; Cady-Pereira, K.; Capps, S.; Lutsch, E.; Strong, K.; Hannigan, J.W.; Ortega, I.; Toon, G.C.; et al. Validation of the CrIS fast physical NH3 retrieval with ground-based FTIR. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 2645-2667. [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Ren, H.; Wang, P.; Chen, J.; Fang, Y.; Hu, W.; Ren, L.; Deng, J.; Song, Y.; Li, J.; et al. Aerosol ammonium in the urban boundary layer in Beijing: Insights from nitrogen isotope ratios and simulations in summer 2015. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2019, 6, 389-395. [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Henze, D.K.; Shephard, M.W.; Dammers, E.; Cady-Pereira, K.; Alvarado, M.; Lonsdale, C.; Luo, G.; Yu, F.; Zhu, L.; et al. Inverse modeling of NH3 sources using CrIS remote sensing measurements. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 104082. [CrossRef]
- Van Damme, M.; Clarisse, L.; Franco, B.; Sutton, M.A.; Erisman, J.W.; Wichink Kruit, R.; Van Zanten, M.; Whitburn, S.; Hadji-Lazaro, J.; Hurtmans, D.; et al. Global, regional and national trends of atmospheric ammonia derived from a decadal (2008-2018) satellite record. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 055017. [CrossRef]
- Wyer, K.E.; Kelleghan, D.B.; Blanes-Vidal, V.; Schauberger, G.; Curran, T.P. Ammonia emissions from agriculture and their contribution to fine particulate matter: A review of implications for human health. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 323, 116285. [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Li, H.; Xu, W.; Song, Y.; Xu, L.; Wang, H.; Wang, F.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Z.; Fu, P. Strong impacts of regional atmospheric transport on the vertical distribution of aerosol ammonium over Beijing. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2024, 11, 29-34. [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Otjes, R.; Schlag, P.; Kiendler-Scharr, A.; Nenes, A.; Weber, R.J. Effectiveness of ammonia reduction on control of fine particle nitrate. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 12241-12256. [CrossRef]
- Roig Rodelas, R.; Perdrix, E.; Herbin, B.; Riffault, V. Characterization and variability of inorganic aerosols and their gaseous precursors at a suburban site in northern France over one year (2015-2016). Atmos. Environ. 2019, 200, 142-157. [CrossRef]
- Dang, R.; Jacob, D.J.; Zhai, S.; Coheur, P.; Clarisse, L.; Van Damme, M.; Pendergrass, D.C.; Choi, J.; Park, J.; Liu, Z.; et al. Diagnosing the sensitivity of particulate nitrate to precursor emissions using satellite observations of ammonia and nitrogen dioxide. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2023, 50, e2023GL105761. [CrossRef]
- Pinder, R.W.; Dennis, R.L.; Bhave, P.V. Observable indicators of the sensitivity of PM2.5 nitrate to emission reductions—Part I: Derivation of the adjusted gas ratio and applicability at regulatory-relevant time scales. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 1275-1286. [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Xu, X.; Lin, W.; Ge, B.; Xie, Y.; Song, B.; Jia, S.; Zhang, R.; Peng, W.; Wang, Y.; et al. Role of ambient ammonia in particulate ammonium formation at a rural site in the North China Plain. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 167-184. [CrossRef]
- Ge, B.; Xu, X.; Ma, Z.; Pan, X.; Wang, Z.; Lin, W.; Ouyang, B.; Xu, D.; Lee, J.; Zheng, M.; et al. Role of ammonia on the feedback between AWC and inorganic aerosol formation during heavy pollution in the North China Plain. Earth Space Sci. 2019, 6, 1675-1693. [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-C.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Fan, M.-Y.; Bao, M. Heterogeneous formation of particulate nitrate under ammonium-rich regimes during the high-PM2.5 events in Nanjing, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 3999-4011. [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Qiu, R.; Chan, C.K.; Ravi Kant, P. Evidence of high PM2.5 strong acidity in ammonia-rich atmosphere of Guangzhou, China: Transition in pathways of ambient ammonia to form aerosol ammonium at [NH4+]/[SO42-] = 1.5. Atmos. Res. 2011, 99, 488-495. [CrossRef]
- Schiferl, L.D.; Heald, C.L.; Nowak, J.B.; Holloway, J.S.; Neuman, J.A.; Bahreini, R.; Pollack, I.B.; Ryerson, T.B.; Wiedinmyer, C.; Murphy, J.G. An investigation of ammonia and inorganic particulate matter in California during the CalNex campaign: CALNEX ammonia and inorganic fine PM. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 1883-1902. [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Xiao, H.-W.; Xu, Y.; Zheng, N.-J.; Xiao, H.-Y. Combustion-driven inorganic nitrogen in PM2.5 from a city in central China has the potential to enhance the nitrogen load of North China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 483, 136620. [CrossRef]
- Ianniello, A.; Spataro, F.; Esposito, G.; Allegrini, I.; Hu, M.; Zhu, T. Chemical characteristics of inorganic ammonium salts in PM2.5 in the atmosphere of Beijing (China). Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 10803-10822. [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Zhu, B.; Kang, H.; Chen, K.; Lu, W.; Lu, C.; Kang, N.; Hu, J.; Chen, H.; Liao, H. Inconsistent 3-D structures and sources of sulfate ammonium and nitrate ammonium aerosols during cold front episodes. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2024, 129, e2023JD039958. [CrossRef]
- Chow, J.C.; Watson, J.G.; Lowenthal, D.H.; Magliano, K.L. Loss of PM2.5 nitrate from filter samples in central California. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2005, 55, 1158-1168. [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Gao, Y.; Chen, D.; Sun, L.; Gao, Y.; Gao, H.; Yao, X. Seasonally dependent daytime and nighttime formation of oxalic acid vapor and particulate oxalate in tropical coastal and marine atmospheres. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 98. [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Shen, Y.; Wang, J.; Gao, Y.; Gao, H.; Yao, X. Mapping gaseous dimethylamine, trimethylamine, ammonia, and their particulate counterparts in marine atmospheres of China’s marginal seas – Part 1: Differentiating marine emission from continental transport. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 16413-16425. [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Cui, W.; Ma, N.; Hong, J.; Zhu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Gao, H.; Yao, X. Variations in cloud concentration nuclei related to continental air pollution control and maritime fuel regulation over the Northwest Pacific Ocean. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 972. [CrossRef]
- Pikmann, J.; Drewnick, F.; Fachinger, F.; Borrmann, S. Particulate emissions from cooking: Emission factors, emission dynamics, and mass spectrometric analysis for different cooking methods. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2024, 24, 12295-12321. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Alapaty, K.; Arunachalam, S. Spatiotemporal trends in PM2.5 chemical composition in the conterminous U.S. during 2006-2020. Atmos. Environ. 2024, 316, 120188. [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Wang, T.; Wang, W.; Ravishankara, A.R.; George, C.; Xia, M.; Cai, M.; Li, Q.; Salvador, C.M.; Lau, C.; et al. Photodissociation of particulate nitrate as a source of daytime tropospheric Cl2. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 939. [CrossRef]
- Wexler, A.S.; Seinfeld, J.H. The distribution of ammonium salts among a size and composition dispersed aerosol. Atmos. Environ. Part A Gen. Topics 1990, 24, 1231-1246. [CrossRef]
- Shiraiwa, M.; Seinfeld, J.H. Equilibration timescale of atmospheric secondary organic aerosol partitioning. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, 2012GL054008. [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Zheng, M.; Yan, C.-Q.; Fu, H.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Li, M.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, Y.-H. Application and progress of single particle aerosol time-of-flight mass spectrometry in fine particulate matter research. Chinese J. Anal. Chem. 2015, 43, 765-774. [CrossRef]
- Gunsch, M.J.; Liu, J.; Moffett, C.E.; Sheesley, R.J.; Wang, N.; Zhang, Q.; Watson, T.B.; Pratt, K.A. Diesel soot and amine-containing organic sulfate aerosols in an Arctic oil field. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 92-101. [CrossRef]
- Silvern, R.F.; Jacob, D.J.; Kim, P.S.; Marais, E.A.; Turner, J.R.; Campuzano-Jost, P.; Jimenez, J.L. Inconsistency of ammonium-sulfate aerosol ratios with thermodynamic models in the eastern US: A possible role of organic aerosol. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 5107-5118. [CrossRef]
- Hecobian, A.; Liu, Z.; Hennigan, C.J.; Huey, L.G.; Jimenez, J.L.; Cubison, M.J.; Vay, S.; Diskin, G.S.; Sachse, G.W.; Wisthaler, A.; et al. Comparison of chemical characteristics of biomass burning plumes intercepted by the NASADC-8 aircraft during the ARCTAS/CARB-2008 field campaign. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 13325-13337. [CrossRef]
- Allen, A.G.; Miguel, A.H. Biomass burning in the Amazon: Characterization of the ionic component of aerosols generated from flaming and smoldering rainforest and savannah. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1995, 29, 486-493. [CrossRef]
- Teng, X.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Qi, J.; Shi, J.; Xie, H.; Gao, H.; Yao, X. Identification of major sources of atmospheric NH₃ in an urban environment in northern China during wintertime. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 6839-6848. [CrossRef]
- Vu, T.V.; Delgado-Saborit, J.M.; Harrison, R.M. Review: Particle number size distributions from seven major sources and implications for source apportionment studies. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 122, 114-132. [CrossRef]
- Hopke, P.K.; Feng, Y.; Dai, Q. Source apportionment of particle number concentrations: A global review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 819, 153104. [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Fang, M.; Chan, C.K. Experimental study of the sampling artifact of chloride depletion from collected sea salt aerosols. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 600-605. [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Dennis, R.L.; Bhave, P.V.; Eder, B.K. Primary and secondary organic aerosols over the United States: Estimates on the basis of observed organic carbon (OC) and elemental carbon (EC), and air quality modeled primary OC/EC ratios. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 5257-5268. [CrossRef]
- Ridolfo, S.; Amato, F.; Querol, X. Particle number size distributions and concentrations in transportation environments: A review. Environ. Int. 2024, 187, 108696. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Shen, Y.; Li, K.; Meng, H.; Sun, Y.; Yao, X.; Gao, H.; Xue, L.; Wang, W. Investigation of particle number concentrations and new particle formation with largely reduced air pollutant emissions at a coastal semi-urban site in northern China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2021, 126, e2021JD035419. [CrossRef]
- Ueda, S.; Miura, K.; Kawata, R.; Furutani, H.; Uematsu, M.; Omori, Y.; Tanimoto, H. Number-size distribution of aerosol particles and new particle formation events in tropical and subtropical Pacific Oceans. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 142, 324-339. [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Wang, J.; Gao, Y.; Chan, C.K.; Zhu, Y.; Gao, H.; Petäjä, T.; Yao, X. Sources and formation of nucleation mode particles in remote tropical marine atmospheres over the South China Sea and the northwest Pacific Ocean. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 735, 139302. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




