Submitted:
21 February 2025
Posted:
28 February 2025
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Notions of Computation
2.1. the Fundamental Task
- input operand(s) need to be delivered to the processing element
- processing must be wholly performed
- output operand(s) must be delivered to their destination
2.2. Modeling Computation
2.3. Time Windows
2.4. Three-Stage Computing
2.5. Issues in Formulating Efficiency
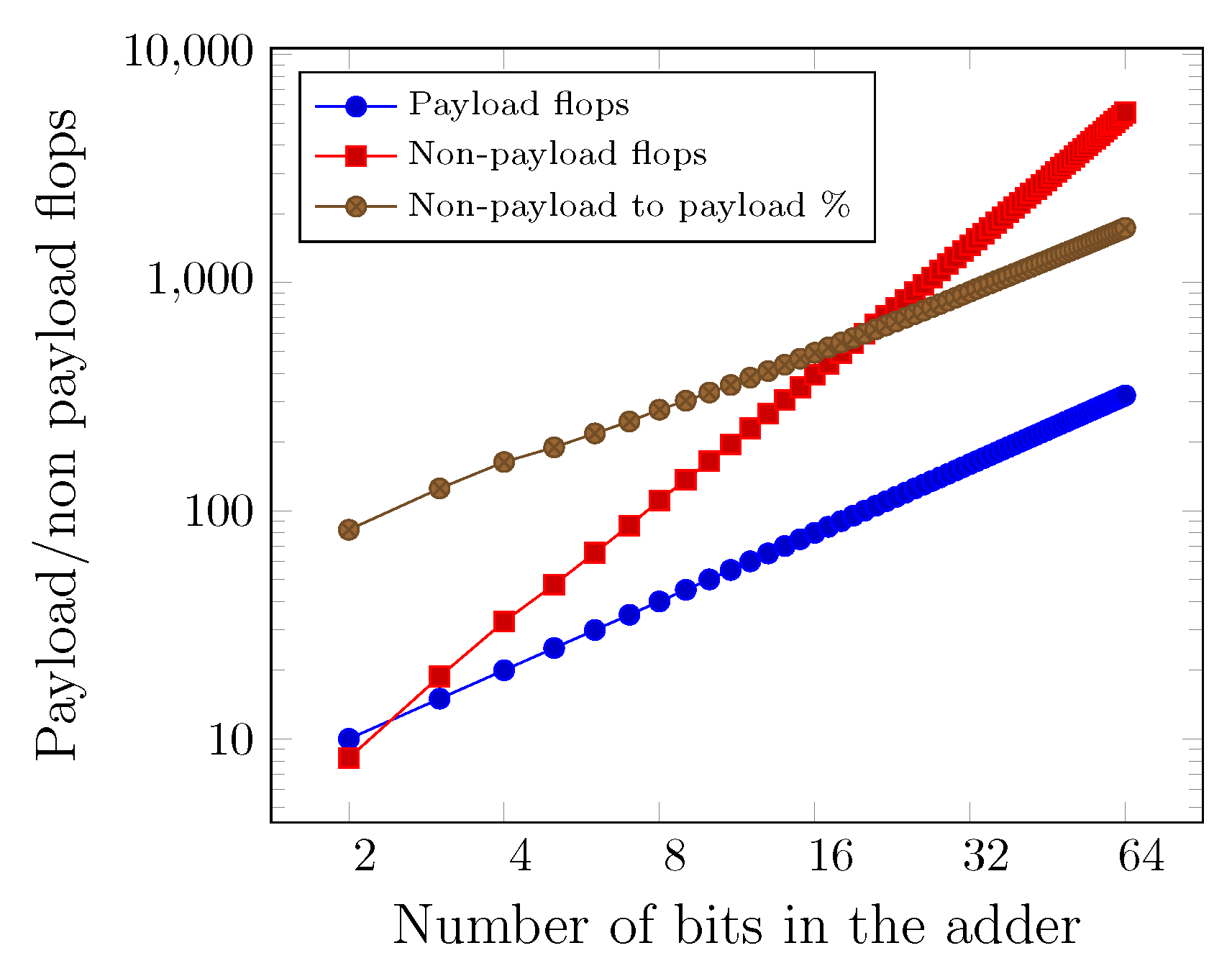
2.6. Payload Vs. Theoretical Efficiency
2.7. Instruction- and Data-Driven Modes
2.8. Connecting Elemental Units
2.9. Proper Sequencing
2.10. Looping Circuits
3. Technical Computing
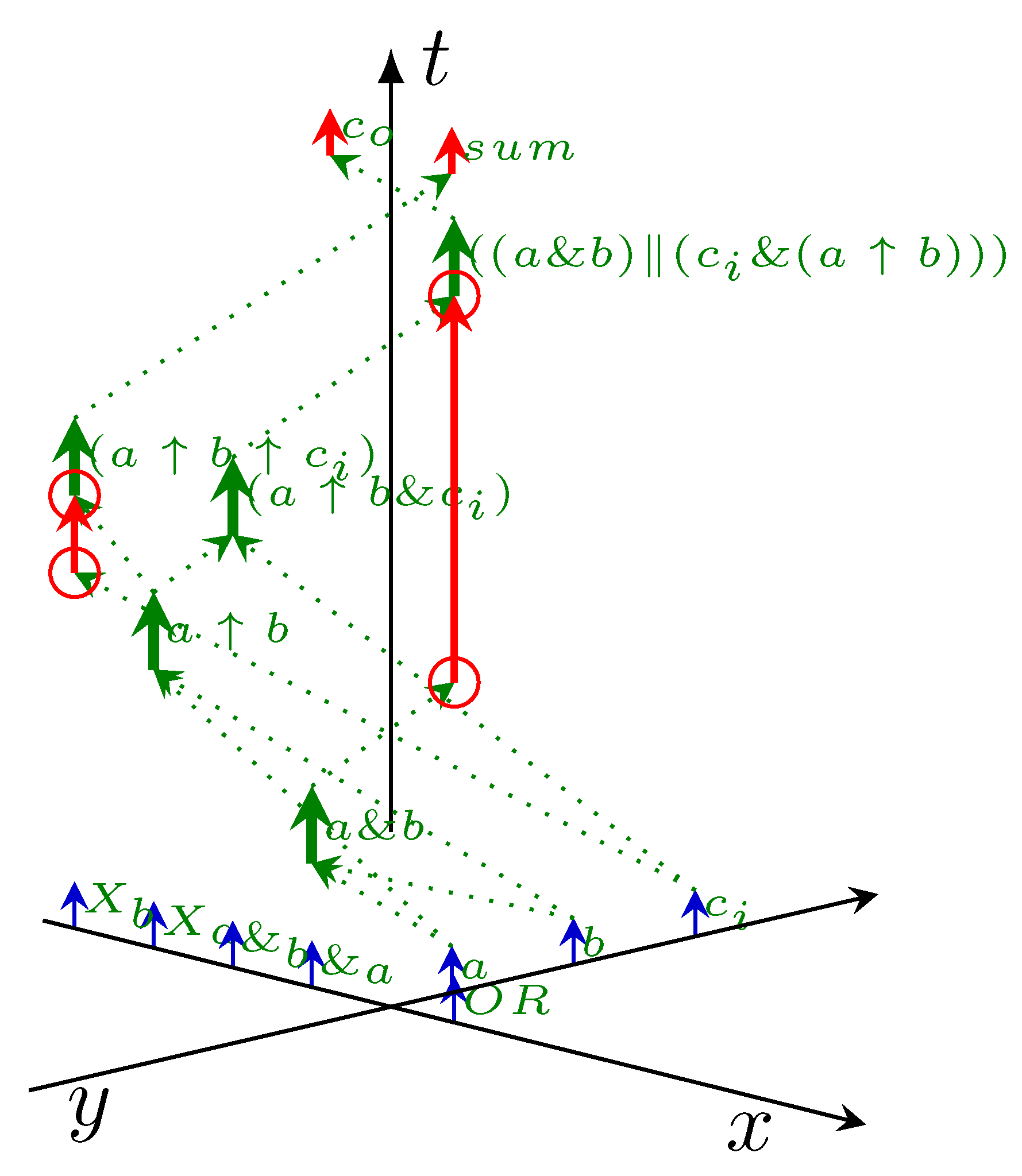
3.1. Cost Function
3.1.1. Thermal Limit
3.1.2. Word Length
3.1.3. Wrong Execution Time
3.1.4. Central Clock Signal
3.1.5. Dispersion
3.1.6. Generating Square Waves
3.1.7. Resource Utilization
3.2. Hardware/Software Cooperation
3.2.1. Single-Thread View
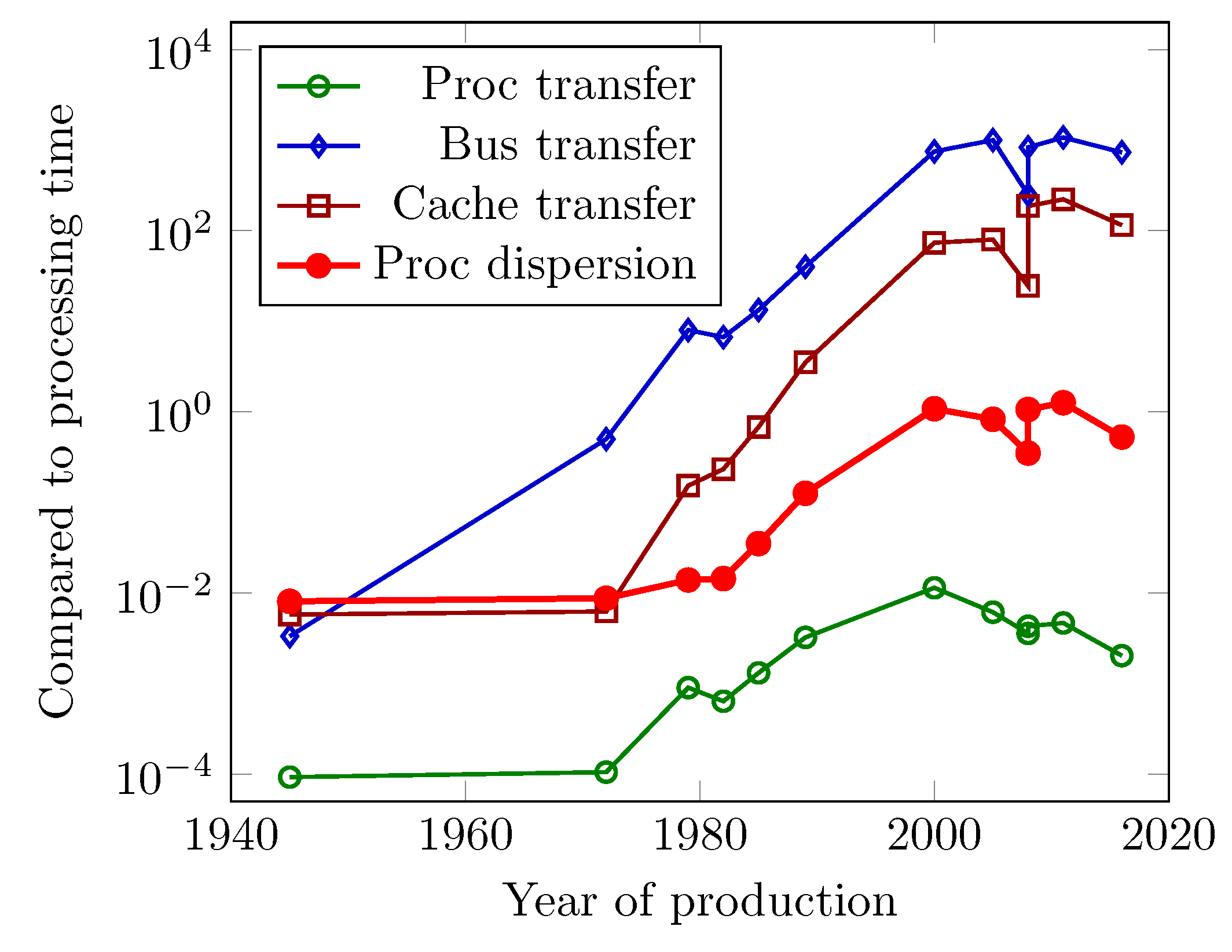
3.2.2. Communication
3.2.3. Wiring
3.3. Structure Vs. Architecture
3.3.1. Single-Processor Performance
3.3.2. Multi- and Many-Core Processors
3.3.3. Memory
3.3.4. Bus

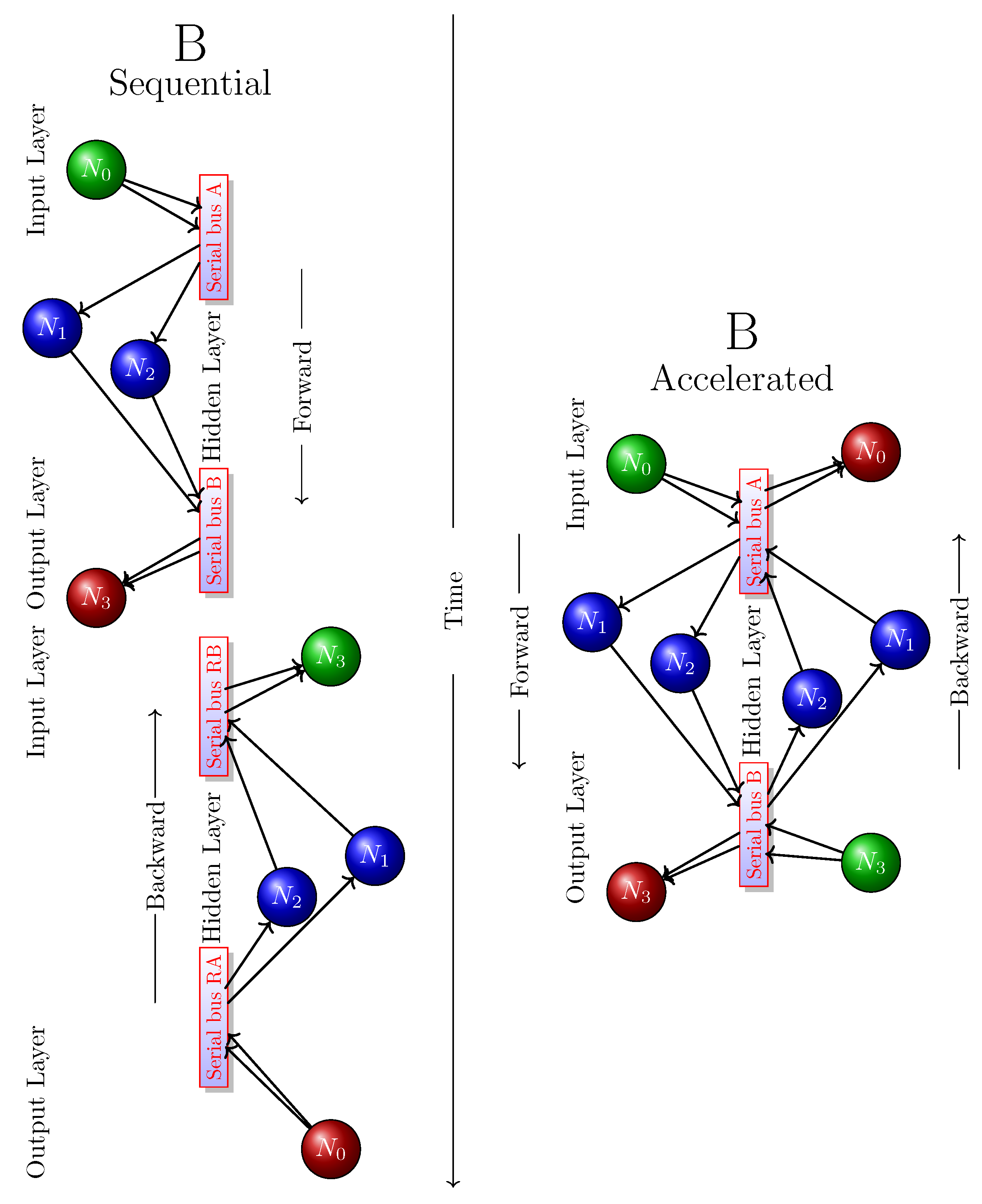
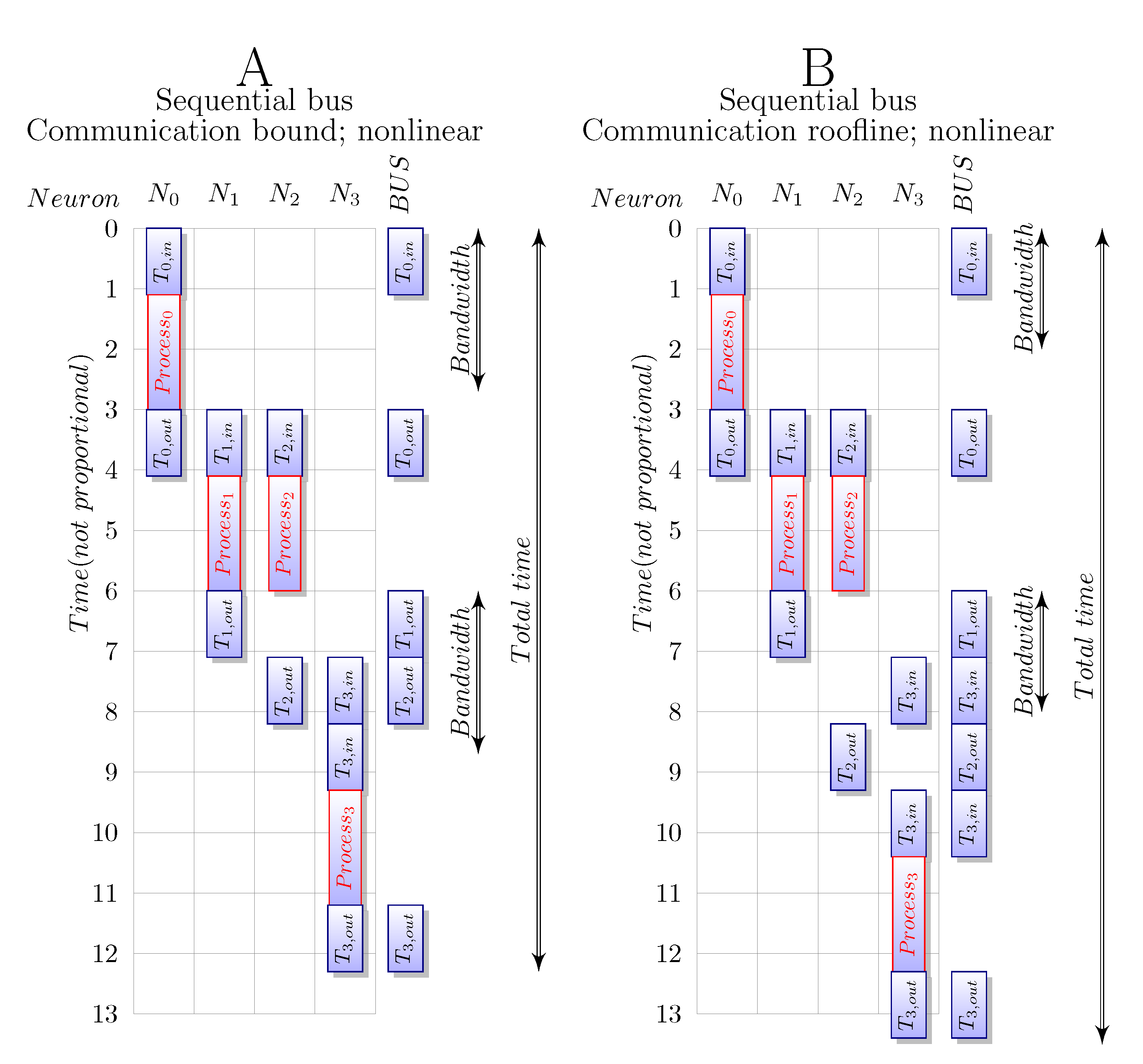
3.4. Accelerating Computing
3.4.1. ’Multiple Data’ Computing
3.4.2. New Materials/Technologies for Data Storing
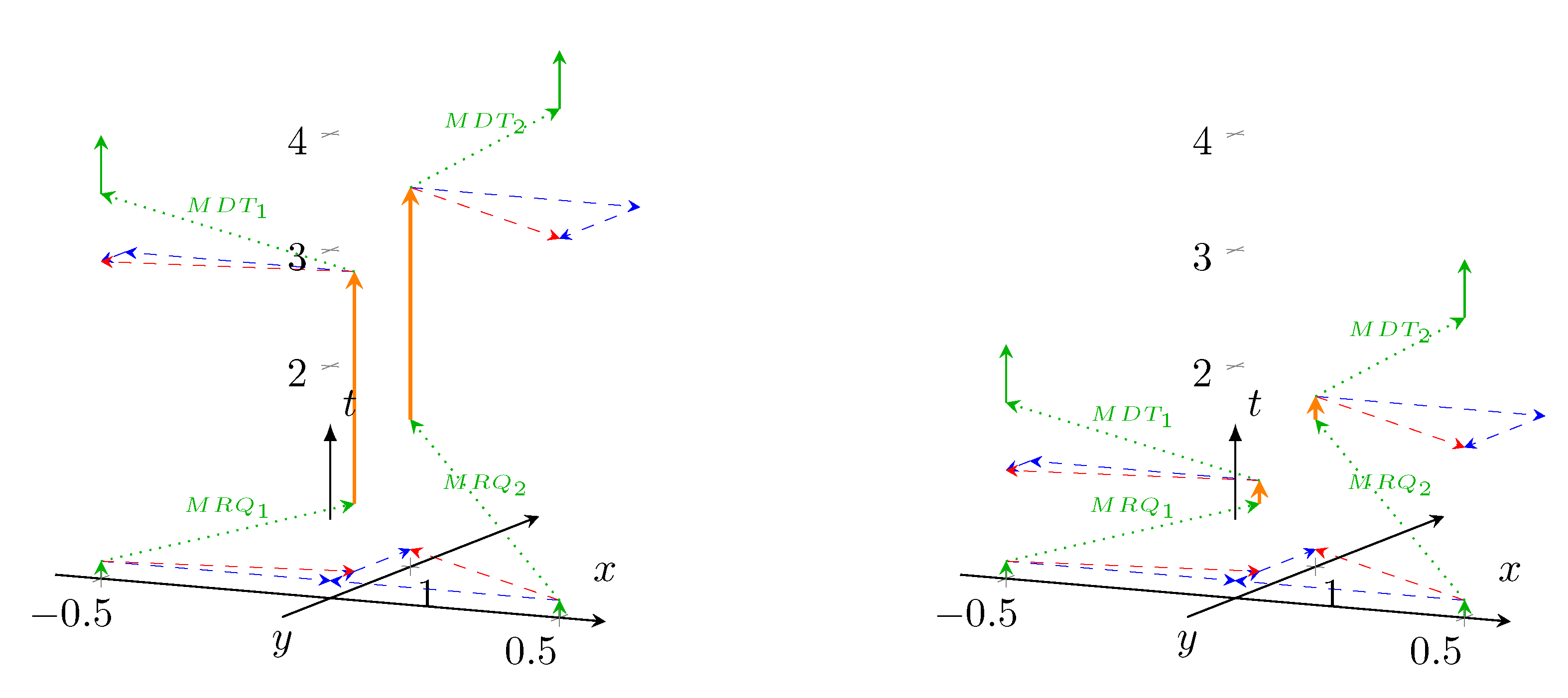
3.4.3. Using Memristors for Processing
3.4.4. Using Mixed-Length Operands
3.5. Mitigating Communication
4. Biological Computing
4.1. State Machine
4.2. Conceptual Operation
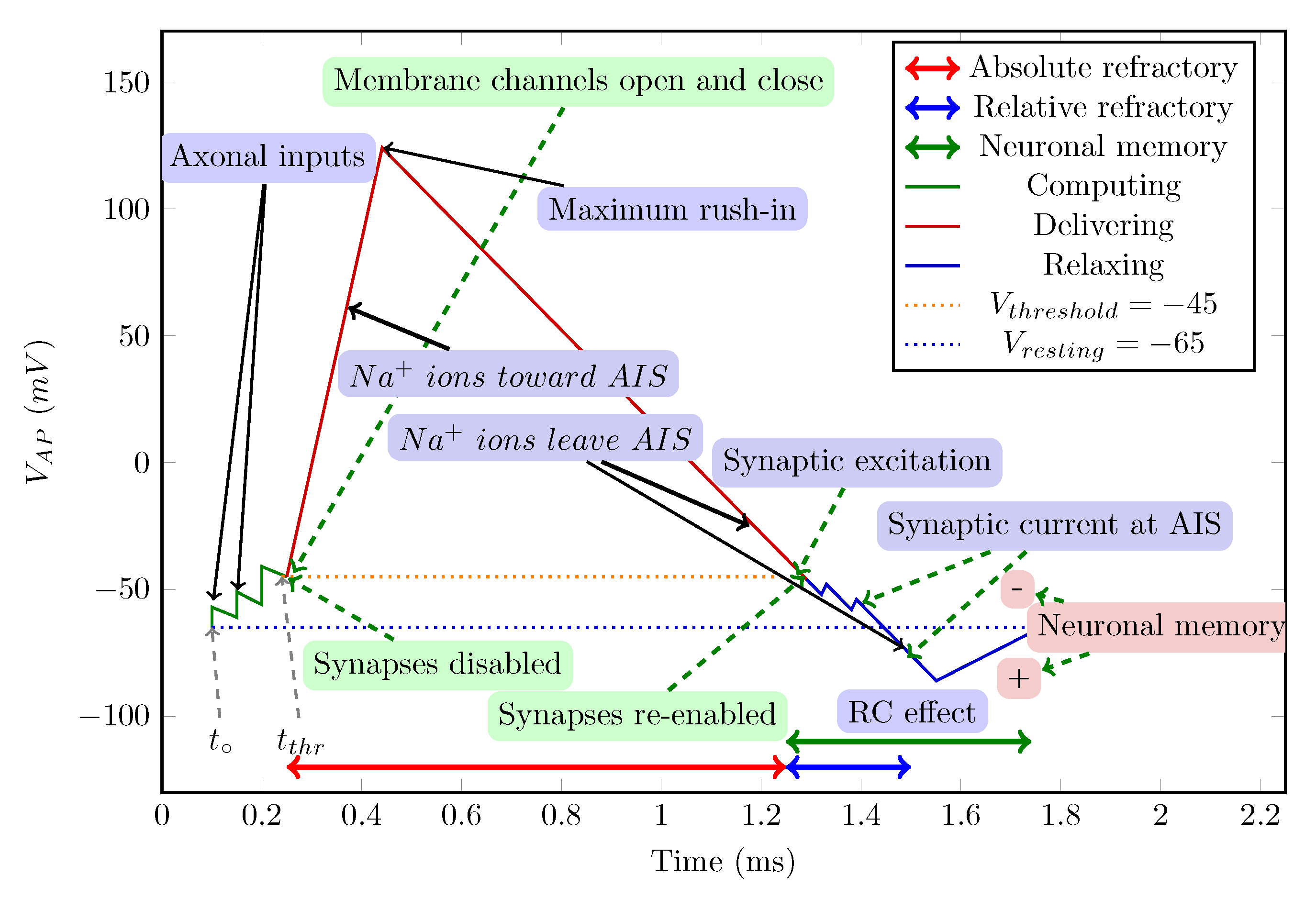
4.2.1. Stage ’Computing’
4.2.2. Stage ’Delivering’
4.2.3. Stage ’Relaxing’
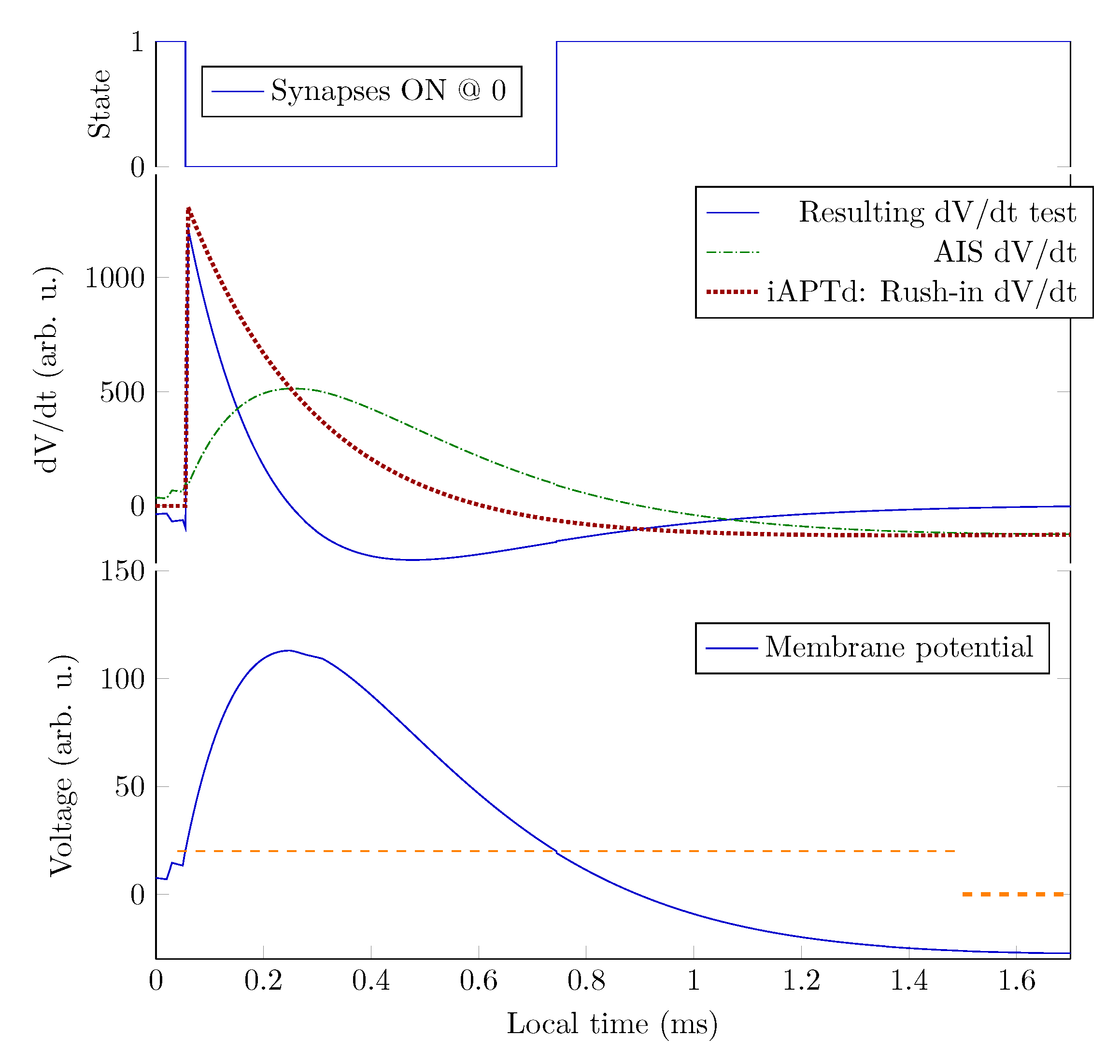
4.2.4. Synaptic Control
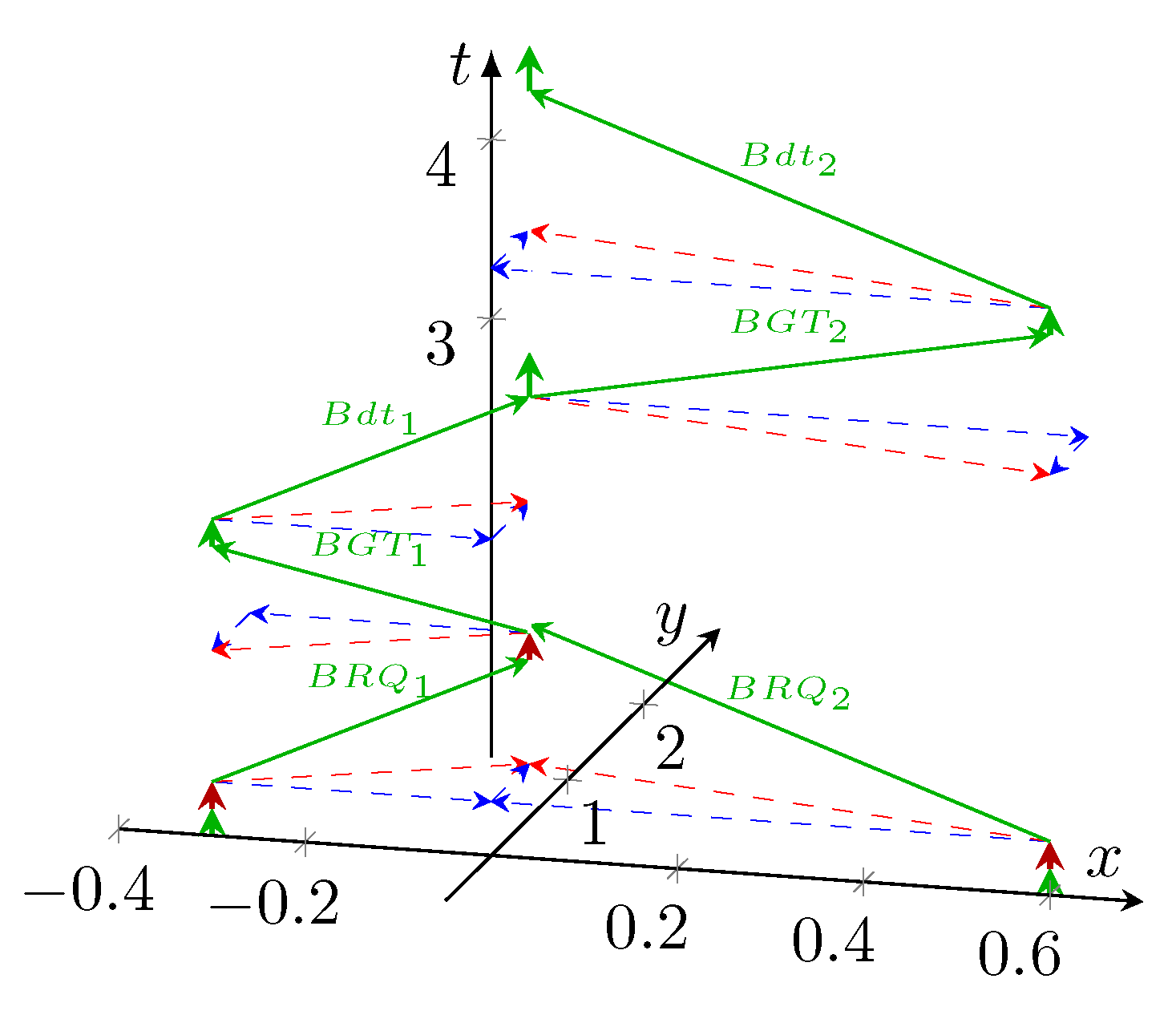
4.2.5. Operating Diagrams
4.2.6. Classic Stages
4.3. Electrical Description
4.3.1. Hodgkin-Huxley Model
4.3.2. Electrotonic Model
4.3.3. Physical Model
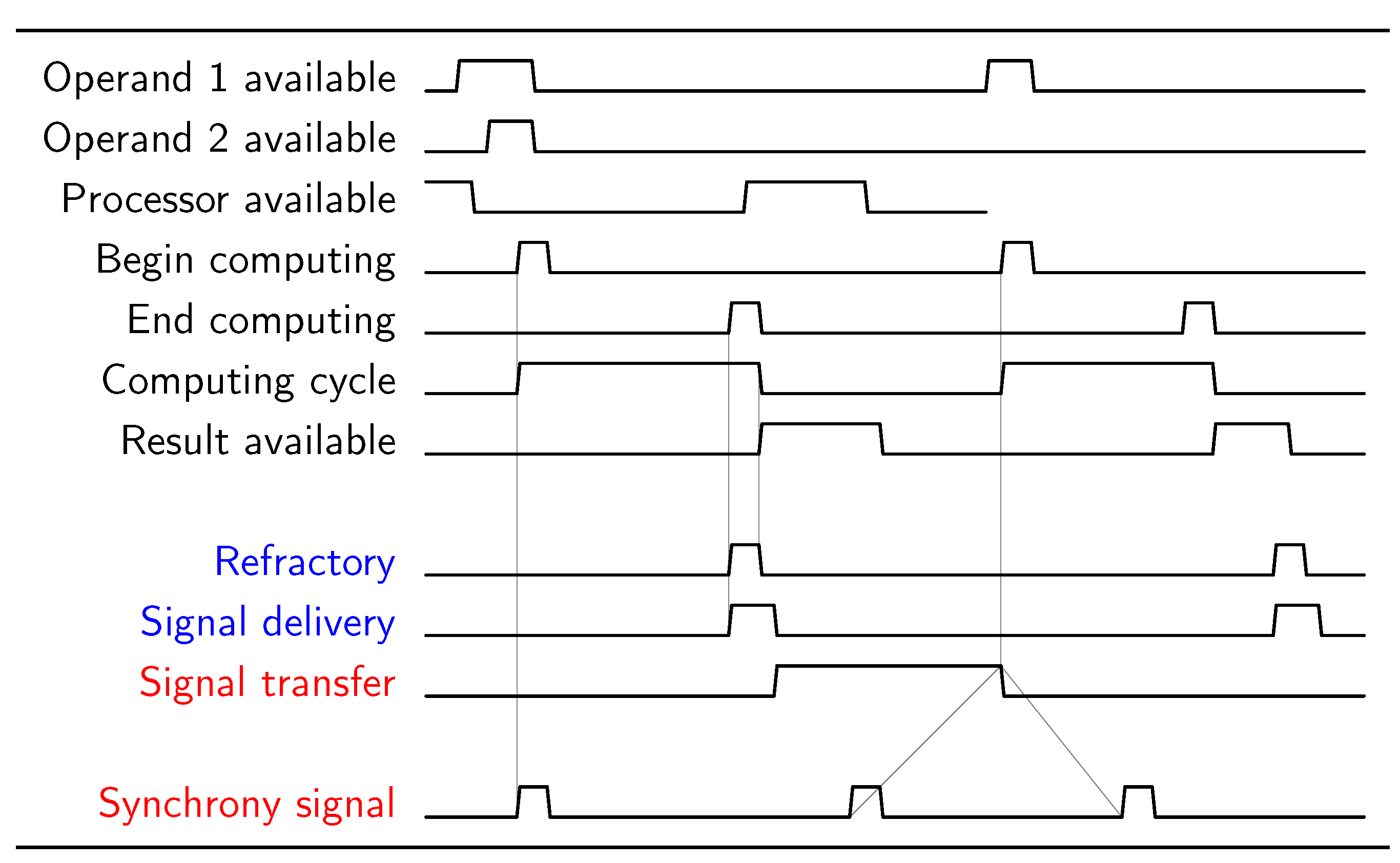
Timing relations
5. Biological Learning Vs Machine Learning
5.1. Biological Learning
5.2. Machine Learning
5.3. Comparing Learnings and Intelligences
5.4. Imitating Neural Computations
5.4.1. Using Accelerators
5.4.2. Training Anns
6. Tendency of Computing Performance
6.1. Energy Consumption
6.2. Computing Efficiency
7. Conclusions
Glossary
| ACM | Association for Computing Machinery |
| ANN | Artificial Neural Newtwork |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| AIS | Axon Initial Segment |
| AP | Action Potential |
| APTD | Action Potential Time Derivative |
| ChatGPT | ChatGPT |
| CNN | Computer Neural Network |
| CPU | Central Processing Unit |
| CSTB | Computer Science and Telecommunications Board |
| EM | electromagnetic |
| FPGA | Field Programmable Gate Array |
| GPU | Graphic Processing Unit |
| HPC | High Performance Computing |
| HPL | High Performance Linpack |
| HPCG | High-Performance Conjugate Gradients |
| HT | hyper-thread |
| HW | hardware |
| I/O | Input/Output |
| ISA | Instruction Set Architecture |
| ISI | Inter-Spike Interval |
| LLM | Large Language Model |
| MCP | Multi-Core Processor |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| OPS | Operations Per Second |
| OS | Operating System |
| PFS | Precise Firing Sequence |
| PU | Processing Unit |
| RC | Reconfigurable Computing |
| SPA | Single Processor Approach |
| PSP | Post-Synaptic Potential |
| SNN | Spiking Neural Network |
| SIMDA | Single Instruction Multiple Data |
| SOPS | Synaptic Operations Per Second |
| SW | software |
References
- Ngai, J. BRAIN @ 10: A decade of innovation. Neuron 2024, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.H. , Information theory and neuroscience: Why is the intersection so small? In 2008 IEEE Information Theory Workshop; IEEE, 2008; pp. 104–108. [CrossRef]
- Human Brain Project, E. Human Brain Project. https://www.humanbrainproject.eu/en/, 2018.
- Chu, D.; Prokopenko, M.; Ray, J.C. Computation by natural systems. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/328398755_Computation_by_natural_systems, 2018. Accessed: 2024-03-30. [CrossRef]
- Almog, M.; Korngreen, A. Is realistic neuronal modeling realistic? J Neurophysiol. 2016, 5, 2180–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, C.E. A mathematical theory of communication. The Bell System Technical Journal 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Végh, J.; Berki, Á.J. Towards generalizing the information theory for neural communication. Entropy 2022, 24, 1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, C.E. The Bandwagon. IRE Transactions in Information Theory 1956, 2, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Nizami, L. Information theory is abused in neuroscience. Cybernetics & Human Knowing 2019, 26, 47–97. [Google Scholar]
- Brette, R. Is coding a relevant metaphor for the brain? The Behavioral and brain sciences 2018, 42, e215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuman, C.D.; Potok, T.E.; Patton, R.M.; Birdwell, J.D.; Dean, M.E.; Rose, G.S.; Plank, J.S. A Survey of Neuromorphic Computing and Neural Networks in Hardware. https://arxiv.org/abs/1705.06963 (Accessed on Sep 10, 2022), 2017.
- Kandel, E.R.; Schwartz, J.H.; Jessell, T.M.; abd A. J. Hudspeth, S.A.S. Principles of Neural Science, 5 ed.; The McGraw-Hill, 2013.
- Young, A.R.; Dean, M.E.; Plank, J.S.; S. Rose, G. A Review of Spiking Neuromorphic Hardware Communication Systems. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 135606–135620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Albada, S.J.; Rowley, A.G.; Senk, J.; Hopkins, M.; Schmidt, M.; Stokes, A.B.; Lester, D.R.; Diesmann, M.; Furber, S.B. Performance Comparison of the Digital Neuromorphic Hardware SpiNNaker and the Neural Network Simulation Software NEST for a Full-Scale Cortical Microcircuit Model. Frontiers in Neuroscience 2018, 12, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, S.; Manohar, R. The impact of on-chip communication on memory technologies for neuromorphic systems. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics 2018, 52, 014003. [Google Scholar]
- Carbone, J.N.; Crowder, J.A. THE GREAT MIGRATION: INFORMATION CONTENT TO KNOWLEDGE USING COGNITION BASED FRAMEWORKS. In Proceedings of the Biomedical Engineering; Suh, S.C.; Gurupur, V.P.; Tanik, M.M., Eds., New York, NY, 2011; pp. 17–46.
- Europe spent €600 million to recreate the human brain in a computer. How did it go? Nature 2023, 620, 718–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Végh, J. von Neumann’s missing "Second Draft": what it should contain. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Computational Science and Computational Intelligence (CSCI’20: December 16-18, 2020, Las Vegas, Nevada, USA. IEEE Computer Society, 2020, pp. 1260–1264. [CrossRef]
- Backus, J. Can Programming Languages Be liberated from the von Neumann Style? A Functional Style and its Algebra of Programs. Communications of the ACM 1978, 21, 613–641. [Google Scholar]
- János Végh. Why does von Neumann obstruct deep learning? In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 23rd International Symposium on Computational Intelligence and Informatics (CINTI), Budapest, Hungary, 2023, pp. 000165–000170. [CrossRef]
- Végh, J. Revising the Classic Computing Paradigm and Its Technological Implementations. Informatics 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waser, R., Ed. Advanced Electronics Materials and Novel Devices; Nanoelectronics and Information Technology, Wiley-VCH, 2012.
- Buzsáki, G. Neural syntax: cell assemblies, synapsembles, and readers. Neuron 2010, 68, 362–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buzsáki, G.; Mizuseki, K. The log-dynamic brain: how skewed distributions affect network operations. Nature Reviews Neuroscience 2014, 15, 264–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporale, N.; Dan, Y. Spike Timing–Dependent Plasticity: A Hebbian Learning Rule. Annual Review of Neuroscience 2008, 31, 25–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madl T, Baars BJ, F. S. The timing of the cognitive cycle. PLoS One 2011, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Demmans Epp, C. Exploring the Optimal Time Window for Predicting Cognitive Load Using Physiological Sensor Data 2024. [CrossRef]
- Linder, B.; Garcia-Ojalvo, J.; Neiman, A.; Schimansky-Geier, L. Effects of noise in excitable systems. Physics reports 2004, 392, 321–424. [Google Scholar]
- Perkel, D.; B. , M. Electrotonic properties of neurons: steady-state compartmental model. J Neurophysiol. 1978, 41, 621–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnova, L.e.a. Organoid intelligence (OI): the new frontier in biocomputing and intelligence-in-a-dish. Frontiers in Science 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunkel, S.; Schmidt, M.; Eppler, J.M.; Plesser, H.E.; Masumoto, G.; Igarashi, J.; Ishii, S.; Fukai, T.; Morrison, A.; Diesmann, M.; et al. Spiking network simulation code for petascale computers. Frontiers in Neuroinformatics 2014, 8, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Végh, J. How Amdahl’s Law limits performance of large artificial neural networks. Brain Informatics 2019, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US DOE Office of Science. Report of a Roundtable Convened to Consider Neuromorphic Computing Basic Research Needs. https://science.osti.gov/-/media/ascr/pdf/programdocuments/docs/Neuromorphic-Computing-Report_FNLBLP.pdf, 2015.
- Markovic, D.; Mizrahi, A.; Querlioz, D.; Grollier, J. Physics for neuromorphic computing. Nature Reviews Physics 2020, 2, 499–510. [Google Scholar]
- Mehonic, A.; Kenyon, A.J. Brain-inspired computing needs a master plan. Nature 2022, 604, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Neumann, John. John von Neumann and the Origins of Modern Computing; Yale University Press, 2012.
- Koch, C. Biophysics of Computation; Oxford University Press: New York, Oxford, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Abbott, L.; Sejnowski, T.J. Neural Codes and Distributed Representations; Cambridge, MA: MIT Press, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Lytton, W.W. From Computer to Brain; Springer, 2002.
- Sejnowski, T.J. The Computer and the Brain Revisited. IEEE Annals of the History of Computing 1989, 11, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsafrir, D. The Context-switch Overhead Inflicted by Hardware Interrupts (and the Enigma of Do-nothing Loops). In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 2007 Workshop on Experimental Computer Science, San Diego, California, New York, NY, USA, 2007.
- David, F.M.; Carlyle, J.C.; Campbell, R.H. Context Switch Overheads for Linux on ARM Platforms. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 2007 Workshop on Experimental Computer Science, San Diego, California, New York, NY, USA, 2007. [CrossRef]
- nextplatform.com. CRAY revamps clusterstor for the exascale era. https://www.nextplatform.com/2019/10/30/cray-revamps-clusterstor-for-the-exascale-era/, 2019. Accessed: 2023-09-10.
- Kendall, J.D.; Kumar, S. The building blocks of a brain-inspired computer. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2020, 7, 011305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Végh, J.; Berki, Á.J. On the Role of Speed in Technological and Biological Information Transfer for Computations. Acta Biotheoretica 2022, 70, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, T.; Levy, W.B. A Mathematical Theory of Energy Efficient Neural Computation and Communication. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory 2010, 56, 852–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrödinger, E. , IS LIFE BASED ON THE LAWS OF PHYSICS? In What is Life?: With Mind and Matter and Autobiographical Sketches; Canto, Cambridge University Press, 1992; p. 76–85.
- Végh, J. The non-ordinary laws of physics describing life. Foundations of Physics 2025, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Quirion, R. Brain organoids: are they for real? https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/science/articles/10.3389/fsci.2023.1148127/full, 2023. [CrossRef]
- von Neumann, J. First draft of a report on the EDVAC. IEEE Annals of the History of Computing 1993, 15, 27–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, G.; Bailey, D.H.; Dongarra, J.; Karp, A.H.; Walsh, K. A look back on 30 years of the Gordon Bell Prize. The International Journal of High Performance Computing Applications 2017, 31, 469–484. [Google Scholar]
- IEEE. IEEE Rebooting Computing. http://rebootingcomputing.ieee.org/, 2013.
- Cadareanu, P.; Reddy C, N.; Almudever, C.G.; Khanna, A.; Raychowdhury, A.; Datta, S.; Bertels, K.; Narayanan, V.; Ventra, M.D.; Gaillardon, P.E. Rebooting Our Computing Models. In Proceedings of the 2019 Design, Automation Test in Europe Conference Exhibition (DATE) Florence, Italy; 25-29 March 2019, 2019, pp. 1469–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Végh, J. Finally, how many efficiencies the supercomputers have? The Journal of Supercomputing 2020, 76, 9430–9455. [Google Scholar]
- Levy, W.B.; Calvert, V.G. Communication consumes 35 times more energy than computation in the human cortex, but both costs are needed to predict synapse number. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2021, 118, e2008173118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, R.; Qadeer, W.; Wachs, M.; Azizi, O.; Solomatnikov, A.; Lee, B.C.; Richardson, S.; Kozyrakis, C.; Horowitz, M. Understanding Sources of Inefficiency in General-purpose Chips. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 37th Annual International Symposium on Computer Architecture, Saint-Malo, France, New York, NY, USA, 2010. [CrossRef]
- Végh, J. Introducing the Explicitly Many-Processor Approach. Parallel Computing 2018, 75, 28–40. [Google Scholar]
- Végh, J. How to Extend Single-Processor Approach to Explicitly Many-Processor Approach. In Proceedings of the Advances in Software Engineering, Education, and e-Learning; Arabnia, H.R.; Deligiannidis, L.; Tinetti, F.G.; Tran, Q.N., Eds. Springer International Publishing; 2021; pp. 435–458. [Google Scholar]
- Birkhoff, G. and Von Neumann, J.. The logic of quantum mechanics. Annals of mathematics 1936, pp. 823–843.
- Cho, A. Tests measure progress of quantum computers. Science 2018, 364, 1218–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Perez, L.; Garcia-Escartin, J.C. Quantum arithmetic with the quantum Fourier transform. Quantum Information Processing 2017, 16, 152. [Google Scholar]
- Goychuk, I.; Hänggi, P.; Vega, J.L.; Miret-Artés, S. Non-Markovian stochastic resonance: Three-state model of ion channel gating. Phys. Rev. E 2005, 71, 061906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feynman, R.P. Feynman Lectures on Computation; CRC Press, 2018.
- Asanovic, K.; Bodik, R.; Demmel, J.; Keaveny, T.; Keutzer, K.; Kubiatowicz, J.; Morgan, N.; Patterson, D.; Sen, K.; Wawrzynek, J.; et al. A View of the Parallel Computing Landscape. Comm. ACM 2009, 52, 56–67. [Google Scholar]
- Esmaeilzadeh, H.; Blem, E.; St. Amant, R.; Sankaralingam, K.; Burger, D. Dark Silicon and the End of Multicore Scaling. IEEE Micro 2012, 32, 122–134. [Google Scholar]
- Shafique, M.; Garg, S. Computing in the dark silicon era: Current trends and research challenges. IEEE Design and Test 2017, 34, 8–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenhunen, M.H.H. .A.M.R..P.L..A.J..A.M..C.B..H. Can Dark Silicon Be Exploited to Prolong System Lifetime? IEEE Design and Test 2017, 34, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markov, I. Limits on fundamental limits to computation. Nature 2014, 512, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bourzac, K. Streching supercomputers to the limit. Nature 2017, 551, 554–556. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Service, R.F. Design for U.S. exascale computer takes shape. Science 2018, 359, 617–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S. Furber and S. Temple. Neural systems engineering. J. R. Soc. Interface 2007, 4, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liang, S.J.; Wang, C.Y.; Yang, Z.Z.; Ge, Y.; Pan, C.; Shen, X.; Wei, W.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Beyond von Neumann. Nature Nanotechnology 2020, p. 507. [CrossRef]
- J. P. Eckert, J.; Mauchly, J.W. Automatic High-Speed Computing: A Progress Report on the EDVAC. Technical Report of Work under Contract No. W-670-ORD-4926, Supplement No 4, Moore School Library, University of Pennsylvania, Philadephia, 1945.
- Schlansker, M.; Rau, B. EPIC: Explicitly Parallel Instruction Computing. Computer 2000, 33, 37–45. [Google Scholar]
- Fuller, S.H.; Millett, L.I. Computing Performance: Game Over or Next Level? Computer 2011, 44, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ousterhout, J.K. Why Aren’t Operating Systems Getting Faster As Fast As Hardware? http://www.stanford.edu/~ouster/cgi-bin/papers/osfaster.pdf, 1990. Accessed: 2023-09-10.
- L. Sha and R. Rajkumar and J.P. Lehoczky. Priority inheritance protocols: an approach to real-time synchronization. IEEE Transactions on Computers 1990, 39, 1175–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaoglu, O.; Marzullo, K.; Schneider, F.B. A formalization of priority inversion. Real-Time Systems 1993, 5, 285–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amdahl, G.M. Validity of the Single Processor Approach to Achieving Large-Scale Computing Capabilities. In Proceedings of the AFIPS Conference Proceedings, Vol. 30; 1967; pp. 483–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ARM. big.LITTLE technology, 2011.
- Ao, Y.; Yang, C.; Liu, F.; Yin, W.; Jiang, L.; Sun, Q. Performance Optimization of the HPCG Benchmark on the Sunway TaihuLight Supercomputer. ACM Trans. Archit. Code Optim. 2018, 15, 11–1. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, S., Ed. The Synaptic Organization of the Brain, 5 ed.; Oxford Academic, New York, 2006.
- Singh, J.P.; Hennessy, J.L.; Gupta, A. Scaling Parallel Programs for Multiprocessors: Methodology and Examples. Computer 1993, 26, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelo, G.; Rampone, S. Towards a HPC-oriented parallel implementation of a learning algorithm for bioinformatics applications. BMC Bioinformatics 2014, 15. [Google Scholar]
- Keuper, J.; Pfreundt, F.J. Distributed Training of Deep Neural Networks: Theoretical and Practical Limits of Parallel Scalability. In Proceedings of the 2nd Workshop on Machine Learning in HPC Environments (MLHPC). IEEE; 2016; pp. 1469–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Végh, J. Which scaling rule applies to Artificial Neural Networks. Neural Computing and Applications 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luccioni, A.S.; Viguier, S.; A-N, L. Estimating the Carbon Footprint of BLOOM, a 176B Parameter Language Model. J. Machine Learning Research 2023, 24, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Matheou, G.; Evripidou, P. Architectural Support for Data-Driven Execution. ACM Trans. Archit. Code Optim. 2015, 11, 52–1. [Google Scholar]
- Denning, P.J.; Lewis, T. Exponential Laws of Computing Growth. Communications of the ACM 2017, pp. 54–65.
- Vetter, J.S.; DeBenedictis, E.P.; Conte, T.M. Architectures for the Post-Moore Era. IEEE Micro 2017, 37, 6–8. [Google Scholar]
- Nature. In AI, is bigger always better? Nature 2023, 615, 2023-09–10. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, B. Reinventing computing. In Proceedings of the International Supercomputing Conference; 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, V.W.; Kim, C.; Chhugani, J.; Deisher, M.; Kim, D.; Nguyen, A.D.; Satish, N.; Smelyanskiy, M.; Chennupaty, S.; Hammarlund, P.; et al. Debunking the 100X GPU vs. CPU Myth: An Evaluation of Throughput Computing on CPU and GPU. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 37th Annual International Symposium on Computer Architecture, New York, NY, USA, 2010; ISCA’10, Saint-Malo, France, pp. 451–460. [CrossRef]
- cortical.io. Third AI Winter ahead? Why OpenAI, Google et Co are heading towards a dead-end. https://www.cortical.io/blog/third-ai-winter-ahead-why-openai-google-co-are-heading-towards-a-dead-end/, 2022.
- de Macedo Mourelle, L.; Nedjah, N.; Pessanha, F.G., Reconfigurable and Adaptive Computing: Theory and Applications; CRC press, 2016; chapter 5: Interprocess Communication via Crossbar for Shared Memory Systems-on-chip. [CrossRef]
- Beggs, J.M.; Plenz, D. Neuronal Avalanches in Neocortical Circuits. Journal of Neuroscience 2003, 23, 11167–11177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Végh, J. Introducing Temporal Behavior to Computing Science. In Proceedings of the Advances in Software Engineering, Education, and e-Learning; Arabnia, H.R.; Deligiannidis, L.; Tinetti, F.G.; Tran, Q.N., Eds. Springer International Publishing, 2021, pp. 471–49.
- Végh, J. A configurable accelerator for manycores:the Explicitly Many-Processor Approach. ArXiv e-prints 2016.
- Mahlke, S.; Chen, W.; Chang, P.; Hwu, W.M. Scalar program performance on multiple-instruction-issue processors with a limited number of registers. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the Twenty-Fifth Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, 1992, Vol. 1, pp. 34–44. [CrossRef]
- Chicca, E.; Indiveri, G. A recipe for creating ideal hybrid memristive-CMOS neuromorphic processing systems. Applied Physics Letters 2020, 116, 120501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strukov, D.; Indiveri, G.; Grollier, J.; Fusi, S. Building brain-inspired computing. Nature Communications 2019, 10, 4838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liang, S.J.; Wang, C.Y.; Yang, Z.Z.; Ge, Y.; Pan, C.; Shen, X.; Wei, W.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Scalable massively parallel computing using continuous-time data representation in nanoscale crossbar array. Nature Nanotechnology 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Shi, J.; Wang, P.; Wang, S.; Pan, C.; Yu, W.; Cheng, B.; Liang, S.J.; Miao, F. Parallel perception of visual motion using light-tunable memory matrix. Science Advances 2023, 9, eadi4083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Pool, J.; Tran, J.; Dally, W.J. Learning both Weights and Connections for Efficient Neural Networks. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1506.02626.pdf, 2015.
- Bengio, E.; Bacon, P.L.; Pineau, J.; Precu, D. Conditional Computation in Neural Networks for faster models. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1511.06297, 2016, [arXiv:cs.LG/1511.06297]. Accessed: 2023-08-30. arXiv:cs.LG/1511.06297]. Accessed: 2023-08-30.
- Johnston, D.; sin Wu, S.M. Foundations of Cellular Neurophysiology; Massachusetts Institute of Technology: Cambridge, Massachusetts and London, England, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Végh, J.; Berki, A.J. Revisiting neural information, computing and linking capacity. Mathematical Biology and Engineering 2023, 20, 12380–12403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somjen, G. SENSORY CODING in the mammalian nervous system; New York, MEREDITH CORPORATION, 1972. [CrossRef]
- Susi, G.; Garcés, P.; Paracone, E.; Cristini, A.; Salerno, M.; Maestú, F.; Pereda, E. FNS allows efficient event-driven spiking neural network simulations based on a neuron model supporting spike latency. Nature Scientific Reports 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschanz, J.W.; Narendra, S.; Ye, Y.; Bloechel, B.; Borkar, S.; De, V. Dynamic sleep transistor and body bias for active leakage power control of microprocessors. IEEE Journal of Solid State Circuits 2003, 38, 1838–1845. [Google Scholar]
- Onen, M.; Emond, N.; Wang, B.; Zhang, D.; Ross, F.M.; Li, J.; Yildiz, B.; del Alamo, J.A. Nanosecond protonic programmable resistors for analog deep learning. Science 2022, 377, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgkin, A.L.; Huxley, A.F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J. Physiol. 1952, 117, 500–544. [Google Scholar]
- Losonczy, A.; Magee, J. Integrative properties of radial oblique dendrites in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons. Neuron 2006, 50, 291–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leterrier, C. The Axon Initial Segment: An Updated Viewpoint. Journal of Neuroscience 2018, 38, 2135–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goikolea-Vives, A.; Stolp, H. Connecting the Neurobiology of Developmental Brain Injury: Neuronal Arborisation as a Regulator of Dysfunction and Potential Therapeutic Target. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, K.; ichiro Kuwako, K. Molecular mechanisms regulating the spatial configuration of neurites. Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology 2022, 129, 103–114, Special Issue: Molecular dissection of cognition, emotion and thought by Akira Sawa & Takeshi Sakurai/Special Issue: Emergingbiology of cellular protrusions in 3D architecture by Mayu Inabaand Mark Terasaki. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Végh, J. Dynamic Abstract Neural Computing with Electronic Simulation. https://jvegh.github.io/DynamicAbstractNeuralComputing/ (Accessed on Feb 6, 2025), 2025.
- Forcella, D.; Zaanen, J.; Valentinis, D.; van der Marel, D. Electromagnetic properties of viscous charged fluids. Phys. Rev. B 2014, 90, 035143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, T.; Davis, J.; Zornetzer, S. Single Neuron Computation; Neural Networks: Foundations to Applications, Academic Press, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.Y.M.; Rasband, M.N. Axon initial segments: structure, function, and disease. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 2018, 1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso1, L.M.; Magnasco, M.O. Complex spatiotemporal behavior and coherent excitations in critically-coupled chains of neural circuits. Chaos: An Interdisciplinary Journal of Nonlinear Science 2018, 28, 093102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Tsien, J.Z. Neural Code-Neural Self-information Theory on How Cell-Assembly Code Rises from Spike Time and Neuronal Variability. Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience 2017, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Tsien, J. Neural Code-Neural Self-information Theory on How Cell-Assembly Code Rises from Spike Time and Neuronal Variability. Frontiers in Cell Neuroscience 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelo, G.; Palmieri, F. Network traffic classification using deep convolutional recurrent autoencoder neural networks for spatial–temporal features extraction. Journal of Network and Computer Applications 2021, 173, 102890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TOP500. Top500 list of supercomputers. https://www.top500.org/lists/top500/ (Accessed on Oct 24, 2021), 2021.
- Aspray, W. , John von Neumann and the Origins of Modern Computing. In John von Neumann and the Origins of Modern Computing; Cohen, B.; Aspray, W., Eds.; MIT Press, Cambridge, 1990; pp. 34–48.
- Sterling, P.; Laughlin, S. Principles of Neural Design, 1 ed.; The MIT Press: Cambridge, Massachusetts and London, England, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Antle, M. C. and Silver, R.. Orchestrating time: arrangements of the brain circadian clock. Trends Neurosci. 2005, 28, 145–151. [Google Scholar]
- Végh, J.; Ádám József Berki. Storing and Processing Information in Technological and Biological Computing Systems. In Proceedings of the The 2021 international conference on computational science and computational intelligence; foundations of computer science FCS. IEEE, 2021, Vol. 21, p. FCS4378.
- Stone, J.V. Principles of Neural Information Theory; Sebtel Press, Sheffield, UK, 2018.
- McKenzie, S.; Huszár, R.; English, D.F.; Kim, K.; Yoon, E.; Buzsáki, G. Preexisting hippocampal network dynamics constrain optogenetically induced place fields. Neuron 2021, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, M.I. Artificial Intelligence—The Revolution Hasn’t Happened Yet. https://hdsr.mitpress.mit.edu/pub/wot7mkc1/release/10, 2019.
- Science. Core progress in AI has stalled in some fields. Science 2020, 368, 6494–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouleau, N.; Levin, M. Discussions of machine versus living intelligence need more clarity. Nat Mach Intell 2024, 6, 1424–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Editorial. Seeking clarity rather than strong opinions on intelligence. Nat Mach Intell 2024, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Végh, J.; Berki, A.J. Why learning and machine learning are different. Advances in Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning 2021, 1, 131–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luk, W. Imperial College London, textbook. http://www.imperial.ac.uk/~wl/teachlocal/cuscomp/notes/chapter2.pdf (Accessed on Dec 14, 2020), 2019.
- Black, C.D.; Donovan, J.; Bunton, B.; Keist, A. SystemC: From the Ground Up, second ed.; Springer: New York, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- IEEE/Accellera. Systems initiative. http://www.accellera.org/downloads/standards/systemc, 2017.
- Mitra, P. Fitting elephants in modern machine learning by statistically consistent interpolation. Nature Machine Intelligence 2021, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- axios.com. Artificial intelligence pioneer says we need to start over. https://www.axios.com/2017/12/15/artificial-intelligence-pioneer-says-we-need-to-start-over-1513305524.
- Marcus, G. Deep Learning: A Critical Appraisal. https://arxiv.org/ftp/arxiv/papers/1801/1801.00631.pdf.
- Cremer, C.Z. Deep limitations? Examining expert disagreement over deep learning. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- semiengineering.com. AI Power Consumption Exploding. https://semiengineering.com/ai-power-consumption-exploding/, 2022. Accessed: 2023-09-10.
- Xie, S.; Sun, C.; Huang, J.; Tu, Z.; Murphy, K. Rethinking Spatiotemporal Feature Learning: Speed-Accuracy Trade-offs in Video Classification. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision – ECCV 2018; Ferrari, V.; Hebert, M.; Sminchisescu, C.; Weiss, Y., Eds., Cham; 2018; pp. 318–335. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, K.; Qin, M.; Sun, F.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.K.; Ren, F. Learning in the Frequency Domain. https://arxiv.org/abs/2002.12416, 2020. Accessed: 2025-02-08. [CrossRef]
- Simon, H. Why we need Exascale and why we won’t get there by 2020. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/261879110_Why_we_need_Exascale_and_why_we_won’t_get _there_by_2020, 2014. Accessed: 2023-09-10.
- János Végh. How Science and Technology Limit the Performance of AI Networks. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Advances in Signal Processing and Artificial Intelligence (ASPAI’ 2023), 7-9 June 2023, Tenerife (Canary Islands), Spain . International Frequency Sensor Association (IFSA) Publishing, 2023, pp. 90–92.
- nature.com. Solving the big computing problems in the twenty-first century. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41928-023-00985-1.epdf, 2023. Accessed: 2023-09-10.
- Fuller, S.H.; Millett, L.I. , The Future of Computing Performance: Game Over or Next Level?; National Academies Press, Washington, 2011. [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




