1. Introduction
Accessing government services, particularly at the local level, can often be a time-consuming and complex process. The Local Self Government Department (LSGD) of Kerala offers numerous essential services to the public, yet navigating through the procedures to avail these services remains a challenge for many. This can lead to inefficiencies and delayed responses to public needs, particularly in areas such as complaint registration, access to forms, and service updates. With the growing digitalization of public services, there is an opportunity to streamline these processes by incorporating automation and user-friendly interfaces.
The proposed solution is the development of an intelligent chatbot capable of automating basic LSGD services while providing additional features like complaint generation and local language support. The chatbot aims to simplify access to government functions, making it easier for citizens to interact with the system in their preferred language. Furthermore, the chatbot will utilize advanced technologies like Large Language Models (LLM) and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) to adapt quickly to newly introduced government schemes and forms, ensuring that it remains up-to-date with the latest information. This adaptability will enhance the efficiency of service delivery while providing a seamless user experience.
The primary challenge in developing such a system lies in integrating multiple services and ensuring that the chatbot can effectively handle a wide variety of user requests. Additionally, the incorporation of local language support is crucial for expanding the reach of the chatbot to non-English speakers. This paper is organized as follows:
Section 2 provides an overview of the Local Self Government Department and its key services.
Section 3 explores the technologies behind Large Language Models (LLM) and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). In
Section 4, a literature review is presented to understand the existing work in chatbot development for public services.
Section 5 concludes the paper, while
Section 6 discusses the future scope of integrating more advanced features into the chatbot system.
2. Local Self Government Department (LSGD)
The Local Self Government Department (LSGD) in Kerala, India, plays a crucial role in delivering essential services to the public at the local level. The LSGD is responsible for the administration and governance of local bodies, including municipalities and panchayats, which are tasked with implementing various government schemes and services. The department aims to empower local communities by decentralizing governance, allowing for more responsive and accountable service delivery.
In Kerala, the LSGD operates through a structured framework that includes elected representatives at the local level, who are responsible for identifying community needs and implementing development projects. The department facilitates various services, such as Birth, Death and Marriage Certificate Registrations, Social Security Pension Applications, Licenses, Permissions, Building Permits, Complaint Resolution, giving Appeals, Tax Payment and Legal Assistance, ensuring that local governance is aligned with the needs of the citizens.
3. Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is an innovative framework that combines the strengths of information retrieval and generative models to enhance the performance of natural language processing (NLP) tasks. The primary goal of RAG is to improve the accuracy and relevance of generated responses by grounding them in real-world data. This is particularly useful in applications where factual correctness is critical, such as question answering, chatbots, and information retrieval systems.
RAG operates through two main components:
Retriever: The retriever is responsible for fetching relevant documents or pieces of information from a large corpus or database. It uses various techniques, such as keyword matching, semantic search, or vector-based retrieval, to identify the most pertinent data based on the user’s query. The retriever ensures that the information used for generating responses is contextually relevant and factually accurate.
Generator: Once the retriever has gathered the relevant information, the generator takes over to formulate a coherent and contextually appropriate response. This component typically utilizes a Large Language Model (LLM) that has been trained on extensive text data. The generator synthesizes the retrieved information with its understanding of language to produce a response that is not only informative but also human-like in its articulation.
The integration of these two components allows RAG systems to leverage the vast knowledge contained in external databases while maintaining the generative capabilities of LLMs. This hybrid approach mitigates the limitations of LLMs, which can sometimes produce inaccurate or irrelevant information if they rely solely on their training data without grounding in real-time facts.
4. Literature Survey
Many efforts have been introduced to make government services which include complaint management as well as basic services from government more accessible to the public by leveraging emerging technologies.
O. S. Al-Mushayt [
1] presented a comprehensive framework aimed at enhancing e-government systems through the integration of advanced AI techniques. It discussed the current state of e-government globally, identified challenges such as the lack of expertise and resources, and proposed solutions tailored for Arabic-speaking countries. The authors introduced deep learning models for automating various e-government services, including sentiment analysis and handwritten digit recognition. Additionally, the paper outlined a smart platform for the development and implementation of AI in e-government, ultimately aiming to improve trust, transparency, and efficiency in government services.
Papageorgiou G et al. [
2] explored the integration of Large Language Models (LLMs) into e-government applications to improve public service delivery. It proposed a modular and reproducible architecture based on Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) that enhances the efficiency, scalability, and transparency of AI systems in the public sector. Through a comprehensive literature review and real-world case studies, the paper demonstrated how LLMs can facilitate intelligent citizen interactions, improve access to open government data, and automate processes, ultimately leading to more effective and user-friendly government services. The research emphasised the importance of ethical standards and user feedback in the deployment of these advanced technologies.
B. Kurian et al. [
3] proposed an innovative chatbot, GovInfoHub, designed to enhance citizen engagement with government services by providing real-time information on various schemes, including insurance options and scholarships. It emphasised the integration of advanced technologies such as Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN), Natural Language Processing (NLP), Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR), and Text-to-Speech (TTS) to facilitate efficient communication and personalised user experiences. The study highlighted the chatbot’s user-friendly interface, multilingual support, and the importance of data processing techniques for accurate information retrieval. Through rigorous testing and evaluation, the paper demonstrated GovInfoHub’s potential to improve accessibility and transparency in digital governance, ultimately bridging the gap between citizens and essential government services.
M. Alhalabi et al. [
4] presented a novel AI-based conversational mobile application, MGov-Bot, designed to centralise access to a wide range of UAE government services through a user-friendly interface. It employed advanced Natural Language Processing (NLP) techniques to enhance user interaction and satisfaction. The study evaluated the perceived usefulness and satisfaction of the application, incorporating Acceptance of Automation (AOA) as a critical factor within an extended information systems success model. Results from a survey of 200 participants indicate a strong positive reception towards the application, suggesting that it can significantly improve the quality, availability, and accessibility of government services, ultimately revolutionising the user experience in M-Government initiatives.
C. H. Yun et al. [
5] explored the integration of AI technologies within the e-Government framework in Korea. It highlighted the growing trend of utilising AI to enhance governmental operations, drawing comparisons with practices in other regions such as the United States and the European Union. The research employed a quantitative methodology, surveying 128 government officials to assess their attitudes towards AI-based e-Government systems, focusing on factors like social influence, perceived trust, and acceptance. The findings underscored the importance of AI in improving efficiency and responsiveness in civil affairs, while also providing valuable insights for future policy development and implementation of AI technologies in public administration.
Figure 1.
Working Of Naive LLM.
Figure 1.
Working Of Naive LLM.
Figure 2.
Working Of Retrieval-Augmented Generation based LLM.
Figure 2.
Working Of Retrieval-Augmented Generation based LLM.
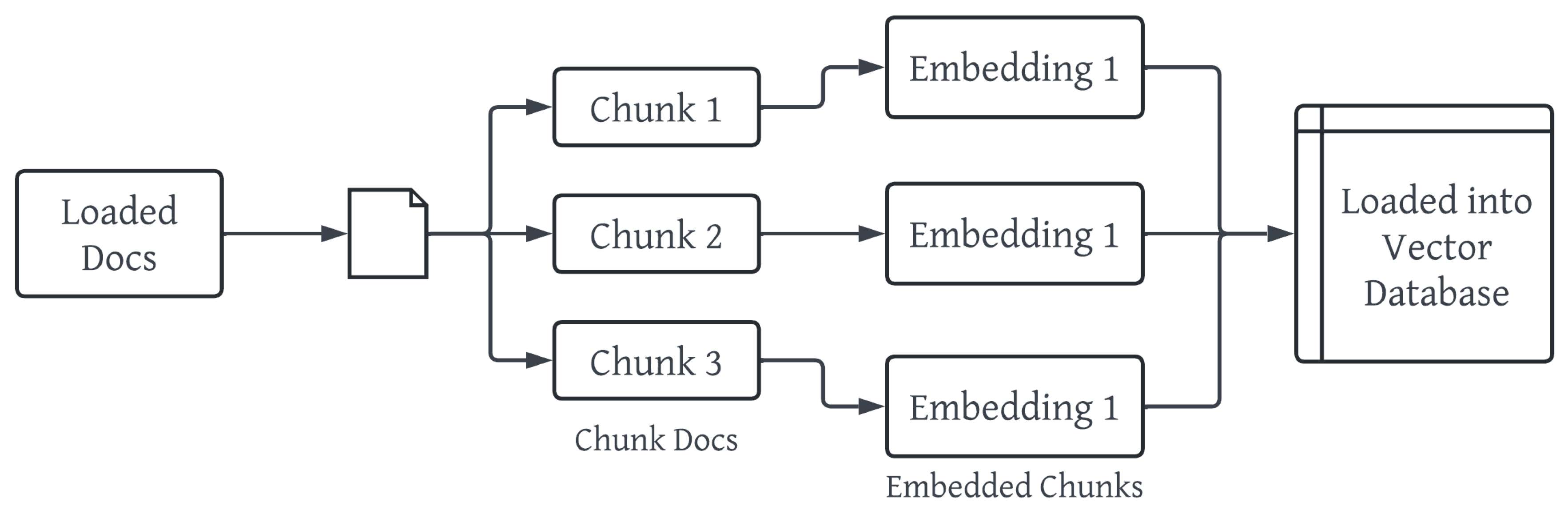
Figure 3.
Architecture of Knowledge Base Of RAG Module.
Figure 3.
Architecture of Knowledge Base Of RAG Module.
Scott Barnett et al, [
6] discussed the integration of semantic search capabilities into applications through Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) systems. It highlighted the advantages of RAG, such as reducing hallucinated responses from large language models (LLMs), linking sources to generated answers, and minimizing the need for document annotation. However, the authors also addressed inherent limitations of information retrieval systems and LLMs, presenting insights from three case studies in research, education, and biomedical domains. The paper identified seven critical failure points to consider during the design of RAG systems and emphasizes that validation occurs during operation, with system robustness evolving over time. Additionally, it outlines potential research directions for further exploration in the field of software engineering related to RAG systems.
Pouria Omrani et al. [
7] presented a novel hybrid Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) approach that integrates two advanced retrieval techniques—Sentence-Window and Parent-Child methods—alongside a re-ranking module to enhance the query response capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs). By leveraging both detailed embeddings and contextual information from parent chunks, the proposed method aimed to improve the relevance, correctness, and faithfulness of generated responses. The study evaluated the effectiveness of this hybrid approach using the Paul Graham Essay Dataset and demonstrates its superiority over existing state-of-the-art RAG methods through comprehensive experimental results and benchmark metrics. Future research directions include refining re-ranking mechanisms and exploring multimodal knowledge integration.
Antonia Šarčević et al. [
8] explored the evaluation and optimization of Large Language Models (LLMs) for educational purposes, detailing a comprehensive assessment methodology that included criteria such as fluency, coherence, relevance, and context understanding. It highlighted the use of Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) for enhancing model performance and discussed the integration of AI-based chatbots into adaptive e-learning environments. The research aimed to share methodologies and findings to facilitate the development of similar AI solutions in education.
Sonia Vakayil et al. [
9] discussed the development of a chatbot powered by the Llama-2 model, designed to assist victims of sexual harassment in India by providing accurate, empathetic, and non-judgmental responses. It details the implementation process, including resource compilation from reputable sources, the use of a transformer architecture for generating responses, and the integration of a Retrieval-Augmented-Generation (RAG) workflow. The study highlights the chatbot’s effectiveness, achieving over 95% accuracy, while also addressing challenges such as limited resources for male victims and the need for further enhancements to improve accessibility and real-time support.
Christoph Hennebold et al. [
10] discussed the current state of complaint management within customer relationship management (CRM) and highlighted the need for a new machine learning (ML) based approach to improve efficiency and accuracy. It detailed the preprocessing of complaint data, the application of active learning (AL) for classification, and the evaluation of the proposed system using real complaint data. The findings emphasised the potential of intelligent approaches, such as natural language processing (NLP), to automate and enhance the complaint management process, ultimately leading to better customer satisfaction and reduced costs.
5. Conclusions
The application of LLMs in automating e-government services has the potential to revolutionize public service delivery by increasing efficiency and enhancing user experience. This literature review highlights the significant advancements made in the field while also pointing out critical areas requiring further research, particularly concerning data privacy, model accuracy, and ethical deployment. While existing studies demonstrate promising results, there remains a need for comprehensive frameworks to ensure that LLM-based systems can operate securely and equitably in public sector environments. Future research should focus on addressing these gaps to fully realize the potential of AI-driven local government service automation.
6. Future Directions
The integration of Large Language Models (LLMs) and advanced technologies in local government service automation offers significant opportunities for enhancement. Future research should focus on local language support to make the app accessible to individuals with less technical expertise and bureaucratic know-how. Incorporating Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) technology will improve chatbot performance by allowing new government schemes to undergo text extraction into JSON or XML formats, which can be appended to RAG’s knowledge base for more robust and accurate responses. Additionally, fine-tuning the LLM will ensure accurate responses when significant changes occur in the local government structure or new departments are added.
It is essential to develop frameworks addressing data privacy and security, ensuring compliance with regulations. Implementing user feedback mechanisms will facilitate continuous improvement of the chatbot’s functionalities. Future work should also explore scalability and interoperability to handle increased user demand and integrate with existing government systems. Ethical considerations in AI deployment must be prioritized, with guidelines established for transparency and accountability. Real-time data feeds will enhance the chatbot’s ability to provide up-to-date information on government services. By addressing these future directions, AI-driven local government service automation can significantly improve public service delivery and citizen engagement.
References
- O. S. Al-Mushayt, "Automating E-Government Services With Artificial Intelligence," in IEEE Access, vol. 7, pp. 146821-146829, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou G, Sarlis V, Maragoudakis M, Tjortjis C, "Enhancing E-Government Services through State-of-the-Art, Modular, and Reproducible Architecture over Large Language Models," in Applied Sciences, 2024, 14(18):8259. [CrossRef]
- B. Kurian, A. Aafreen Fathima, T. Afra Fathima and R. Shahista Begum, "GovInfohub: A Dynamic Government scheme Chatbot for informed Engagement and Accessibility," 2024 International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communication and Applied Informatics (ACCAI), Chennai, India, 2024, pp. 1-6. [CrossRef]
- M. Alhalabi et al., "M-Government Smart Service using AI Chatbots: Evidence from the UAE," 2022 2nd International Mobile, Intelligent, and Ubiquitous Computing Conference (MIUCC), Cairo, Egypt, 2022, pp. [CrossRef]
- C. H. Yun, A. P. Teoh and T. Y. Khaw, "Artificial Intelligence Integration in e-Government: Insights from the Korean Case," 2024 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Electrical Engineering, Big Data and Algorithms (EEBDA), Changchun, China, 2024, pp. 1159-1164. [CrossRef]
- S. Barnett, S. Kurniawan, S. Thudumu, Z. Brannelly and M. Abdelrazek, "Seven Failure Points When Engineering a Retrieval Augmented Generation System," 2024 IEEE/ACM 3rd International Conference on AI Engineering – Software Engineering for AI (CAIN), Lisbon, Portugal, 2024, pp. 194-199.
- P. Omrani, A. Hosseini, K. Hooshanfar, Z. Ebrahimian, R. Toosi and M. Ali Akhaee, "Hybrid Retrieval-Augmented Generation Approach for LLMs Query Response Enhancement," 2024 10th International Conference on Web Research (ICWR), Tehran, Iran, Islamic Republic of, 2024, pp. 22-26. [CrossRef]
- A. Šarčević, I. Tomičić, A. Merlin and M. Horvat, "Enhancing Programming Education with Open-Source Generative AI Chatbots," 2024 47th MIPRO ICT and Electronics Convention (MIPRO), Opatija, Croatia, 2024, pp. 2051-2056. [CrossRef]
- S. Vakayil, D. S. Juliet, A. J and S. Vakayil, "RAG-Based LLM Chatbot Using Llama-2," 2024 7th International Conference on Devices, Circuits and Systems (ICDCS), Coimbatore, India, 2024, pp. 1-5. [CrossRef]
- C. Hennebold, X. Mei, O. Mailahn, M. F. Huber and O. Mannuß, "Cooperation of Human and Active Learning based AI for Fast and Precise Complaint Management," 2022 IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics (SMC), Prague, Czech Republic, 2022, pp. 282-287. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).