1. Introduction
Recently, circular RNA (circRNA) is considered a promising alternative to linear mRNA for various biomedical applications [
1,
2] such as mRNA vaccine [
3,
4,
5,
6,
7]. Therefore, efficient in vitro circRNA preparation methods are of great interests in this area [
8]. Considering pros and cons of in vitro methods for circRNA preparation, self-splicing ribozyme-based self-circularization methods would be the most simple and efficient, and thus more practical for commercial and biomedical applications than chemical- and ligase-based methods [
9,
10,
11].
As a representative self-splicing ribozyme-based method developed about 30 years ago [
12], permuted intron-exon (PIE) method using group I intron has been improved by rationally designing the construct [
2,
13,
14]. Although the PIE method can provide circRNAs in vitro with good efficiency for gene of interest (GOI) that is not too long, it has intrinsic issues to be overcome. For example, it generally leaves extraneous sequences such as E1/E2 fragments or spacer in the generated circRNA, which may trigger unwanted innate immune responses in cells [
15]. Those remnant fragments probably tend to form stable RNA duplexes, which may lead to unwanted immune responses. Therefore, improved versions of group I intron-based PIE method [
16], a group II intron ribozyme-based PIE approach [
17], and a new group I intron ribozyme-based strategy [
18,
19] have been designed to overcome shortcomings of the conventional PIE method.
This review introduces recent updates on in vitro self-circularization methods based on self-splicing ribozyme to overcome the conventional PIE method’s shortcomings. It then discusses advantages and disadvantages of these methods as well as future directions in terms of efficient in vitro circRNA production and engineering.
2. Group I intron PIE-Based Methods
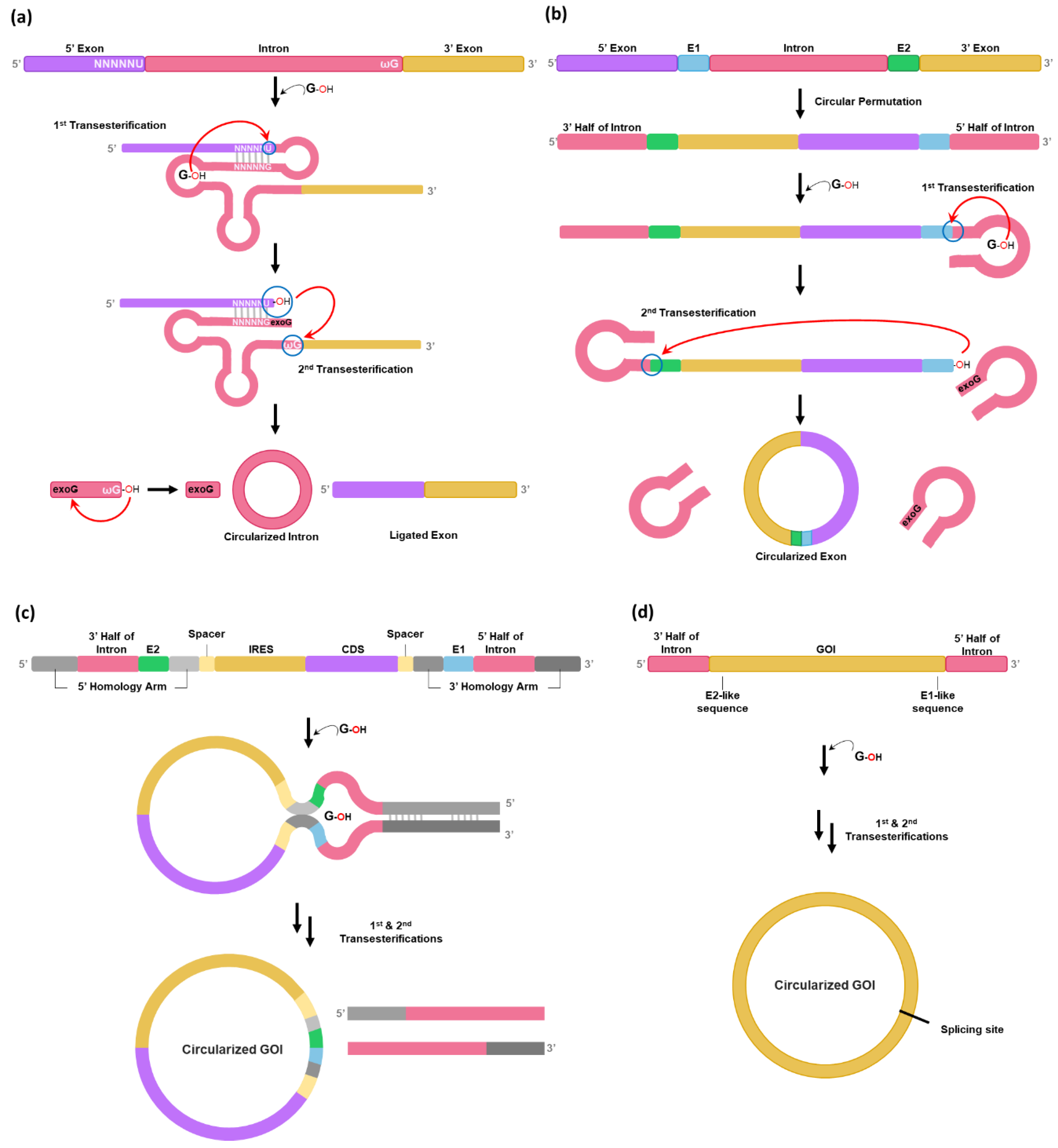
It is known that circular intron can be generated as a by-product after two consecutive transesterification reactions for self-splicing reaction of group I intron precursor RNAs [
20] (
Figure 1a). To generate circular exon instead of circular intron, the PIE method was developed in 1992 from hypothesis that circularly permuted forms of group I intron interrupted by exon could fold into an active conformation for self-splicing to generate circular form of exon [
12] (
Figure 1b). However, the PIE method has only been applied for self-circularization of shorter RNAs such as short exon sequences (100-nt) [
21] or aptamer [
22] as longer GOI between splice sites might reduce the ability of splice sites to interact with one another, thus reducing the self-circularization efficiency [
2].
Therefore, the PIE method has been optimized by rationally designing the PIE construct to be used for longer GOIs [
2,
13,
14]. In 2018, Wesselhoeft et al. optimized the PIE reaction using group I introns present in thymidylate synthase (Td) gene of bacteriophage T4 or in
Anabaena pre-tRNA for longer RNA circularization by introducing homology arms and spacer sequence [
2] (
Figure 1c). Homology arms placed at the 5′ and 3′ ends of the precursor RNA are able to bring the 5′ and 3′ splice sites into proximity of one another, resulting in the increased self-splicing efficiency for longer GOIs [
2]. Spacer sequences can also improve circularization efficiency by separating IRES (Internal ribosome entry site) and 3′ PIE splice site for correct folding of group I intron [
2]. The formation of a sheltered splicing bubble can also be promoted by introducing homology arms in the spacer regions (
Figure 1c), which can increase self-circularization efficiency. Although self-circularization can be completed during in vitro transcription (IVT), additional reaction (55°C incubation for 15 min with 2 mM GTP) after DNase treatment is required in some cases. Notably, utilization of
Anabaena catalytic intron resulted in a 37% reduction in circRNA nicking compared to T4 catalytic intron [
2]. Nicking is a common issue during circRNA production and purification.
However, the PIE method generally leaves extraneous sequences such as E1/E2 fragments essential for catalytic activity that determine the 5′ and 3′ splice sites by the interaction with internal guide sequence (IGS) and neighboring loop structure [
23] or spacer sequences in the circRNA, which can form stable intramolecular RNA duplexes and may trigger unwanted innate immune responses in cells [
15]. Furthermore, obligatory incorporation of E1/E2 and spacer sequences are not appropriate to generate small circRNAs and/or circRNAs that must have exactly the same sequences to their native ones.
To avoid an issue of leaving extraneous sequences, Qiu et al. have developed a Clean-PIE method using Td group I intron of T4 phage [
16] (
Figure 1d). In this strategy, minimal-sized E1/E2 fragments-like sequences are screened from GOI sequences as Rausch et al. have reported that self-circularization efficiency for Td group I intron can be affected by variations on E1 and E2 sequences generated by serial mutagenesis and in vitro selection studies [
23], suggesting that sequence restriction such as E1/E2 requirement can be circumvented. In other words, sequences/structures that function like E1/E2 can be concealed in open reading frame (ORF) or in IRES instead of using natural E1/E2 sequences in exon.
As a previous screening strategy to select E1/E2-like sequences [
23] was inefficient for self-circularization of larger circRNAs, a design principle was further improved for the Clean-PIE method [
16]. Qiu et al. have found that UUGGGUCU (TTGGGTCT in DNA), which can form P1 and part of P9 with IGS in Td group I intron, are the most effective E1/E2 sequences for the PIE method [
16]. Thus, these short sequences can be concealed in the GOI region by modifying codon sequences without changing amino acid sequences. For example,
GATGGATCA sequences (codons for Asp, Gly, Ser) in the coding sequence (CDS) region of EGFP gene can be changed to
GATGGGTCT (Codons for Asp, Gly, Ser) which are almost identical to ideal TTGGGTCT sequences. To design Clean-PIE construct efficiently, Qiu et al. have developed an algorithm for assisting the nucleotide-replacement method with a scoring system to optimize potential E1/E2 fragments in the GOI region [
16].
Clean-PIE strategy would be ideal for group I introns such as Td group I intron which has relatively short E1/E2 fragments for base pairing with IGS for catalytic activity due to ease of prediction/screening of E1/E2-like sequences [
23]. As 99.9% of genes with sizes > 500 bp contain at least one E1/E2-like segment scoring 13 points (score ranges from 0 to 16, with a higher score predicting higher circularization efficiency), the strategy is generally applicable for circularization of most GOIs [
16]. In addition, 82.9% of
Homo sapiens genes with a size >1000 bp contain more than one ideal TTGGGTCT sequences with the highest efficiency [
16].
3. Group II intron PIE-Based Methods
As an alternative strategy, group II intron of
Clostridium tetani [
24] with structure engineering can be used instead of using group I intron for PIE-based method [
25] to generate scarless circRNA [
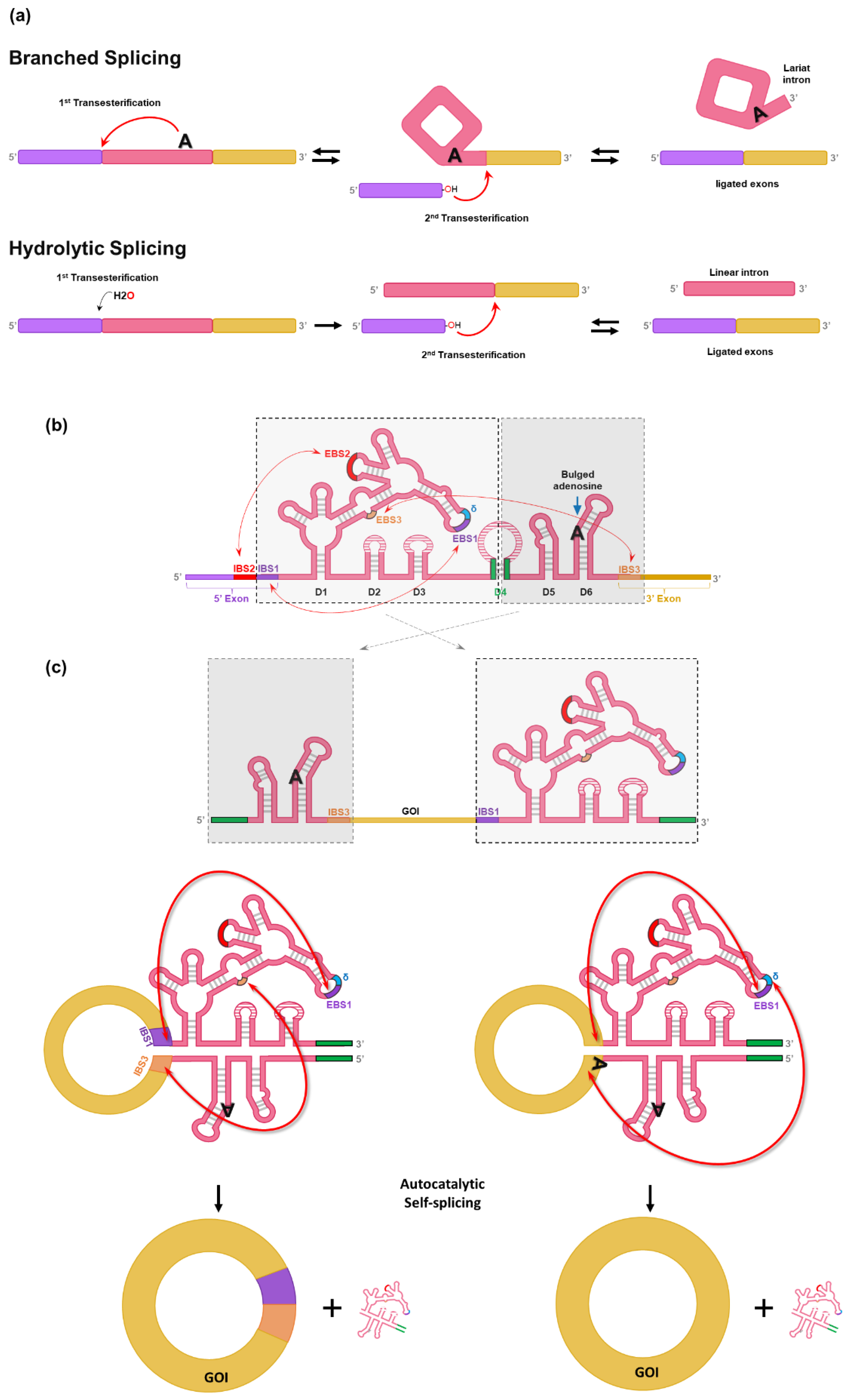
17]. Generally, self-splicing by group II intron occurs through one of two pathways in parallel (branched splicing or hydrolytic splicing) (
Figure 2a) [
26,
27,
28]. In the branched splicing pathway, the 2′-OH group of the intron branchpoint (bulged adenosine) performs the nucleophilic attack on the 5′ splice site (1
st transesterification), which yields a free 5′ exon and a lariat-3′ exon intermediate. Then, the free 5′ exon attack the 3′ splice site (2
nd transesterification), resulting in the formation of ligated exons and lariat intron. Both transesterifications are reversible, enabling reverse splicing that allows group II introns to reverse-splice into new target sites [
26,
27,
28]. In the hydrolytic splicing pathway, a water molecule or hydroxide ion works as a nucleophile for 1
st transesterification. 2
nd transesterification occurs the same as in branched splicing reaction, but the products are ligated exons and a linear intron, instead of lariat intron [
26,
27,
28].
Group II introns are characterized by conserved secondary structures and have six structural domains (D1 to D6) (
Figure 2b). Although group II introns have similar overall secondary structures, three major groups (IIA, IIB, and IIC) distinguished by specific variations in peripheral structures are critical for self-splicing reaction [
26,
27].
D1 contains several short exon binding sites (EBS) to determine the specificity of self-splicing (
Figure 2b) [
26,
27]. Specifically, the EBS1 in D1 binds with the intron binding site (IBS1) to determine the 5′ splicing junction. Moreover, the interaction between IBS3 and EBS3 (for IIB and IIC introns) or the δ base (for IIA intron) in D1 determines the 3′ splicing junction. D2 and D3 stabilize interactions between other domains and increase the catalytic activity for self-splicing. D4 is not essential for self-splicing activity, but it contains ORF encoding an intron-encoded protein (IEP) known as a maturase that is required for in vivo reaction. In contrast, group II self-splicing requires only correct folding of ribozyme structure and Mg
2+ for in vitro reaction [
28]. The highly conserved D5 interacts with D1 to form the catalytic core that binds two divalent metal ions essential for self-splicing reaction [
28]. D6 harbors the bulged adenosine nucleotide that acts as a nucleophile in the 1
st transesterification reaction for self-splicing [
28].
Chen et al. have designed a split-intron system (CirCode system) which contains GOI flanked by the two half-introns like PIE (
Figure 2b amd 2c) [
17]. To generate circRNA without extraneous sequences (12-nt for group II intron of
C. tetani), exon binding sites were engineered so that scarless circRNA could be generated in vitro [
17]. At first, group II intron of
C. tetani was split like the PIE method (
Figure 2c). The stem region of D4 was separated and placed into each end of the designed RNA construct, thus forming a stem structure by complementary binding that helps the folding of the active conformation of group II intron (green lines in
Figure 2c). However, initial design of group II intron-based PIE still leaves a short scar of 12-nt (6-nt sequences of IBS1 and IBS3) (
Figure 2c, left).
The design was further modified to generate scarless circRNA by changing the EBSs in D1. As a result, EBS1 and sequence upstream of EBS1 can form base pairs with the 3′ and 5′ end of GOI, respectively (
Figure 2c, right). Therefore, the CircCode system enabled the generation of circRNA without intronic scar [
17].
Self-circularization can be observed during IVT and the purified RNAs can be further circularized by additional reaction as an option (incubation at 53 °C in the presence of 50 mM Tris-HCl at pH 7.5, 50–100 mM NaCl, and 10–20 mM MgCl
2 after 5 min heating at 75 °C and cooling down to 45°C) [
17].
However, due to the close proximity of intron structure and IRES structure in PIE-based system, spacer sequences are still required because how far apart the two structures are can affect circularization efficiency [
2,
17]. In addition, the formation of 2′,5′-phosphodiester bonds at the ligation site could be an issue, although it remains controversial as the precise mechanism is unclear [
9,
11,
29,
30].
4. Group I intron Self-Targeting and Splicing-Based Methods
Recently, two research groups including our team have reported self-targeting and splicing (STS)-based self-circularization methods based on
Tetrahymena group I intron ribozyme [
18,
19].
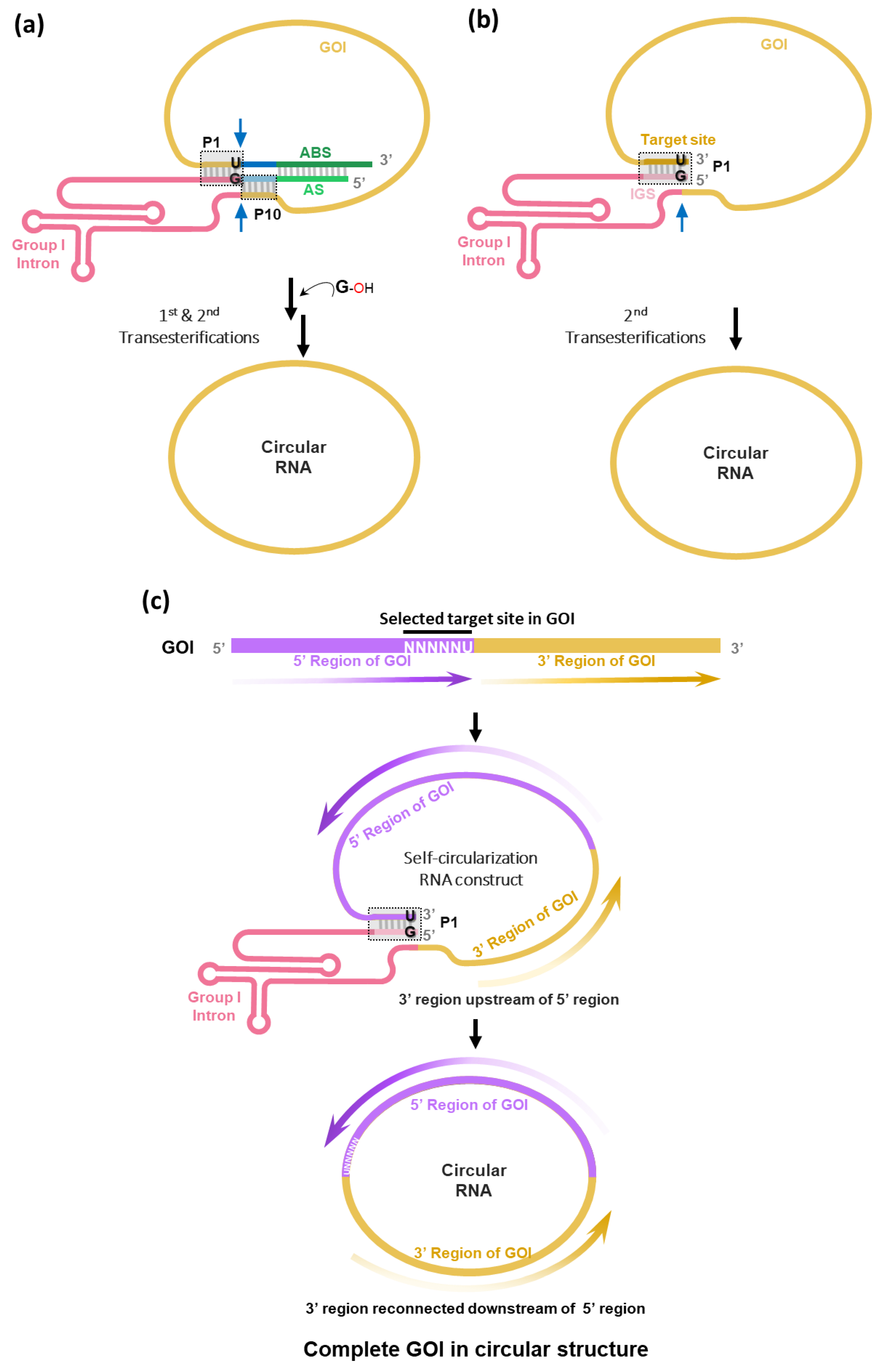
To generate circRNA without extraneous sequences (i.e., intronic scar) such as E1/E2 fragments of PIE construct, we have rationally designed RNA construct using
Tetrahymena group I intron trans-splicing ribozyme [
31] to enable self-circularization through end-to-end STS reaction [
18] (
Figure 3a). In this strategy, the STS reaction cleaves the 3′ end of GOI and then links the 5′ end of GOI, which generates scarless circRNAs and releases group I intron ribozyme. Of note, we found that only the simple P1 helix structure formation (complementary base pairing between target site with 5′-NNNNNU-3′ and IGS with 5′-GN′N′N′N′N′-3′) at the 3′ and 5′ ends of the self-circularizable group I intron RNA construct was sufficient to generate circRNA in vitro (
Figure 3b). In the report by Cui et al. [
19], only full construct with antisense interaction was used for self-circularization (
Figure 3a).
In terms of circRNA engineering, any sequences with 5′-NNNNNU-3′, preferably AU-rich sequences, in GOI can be targeted if only one specific target sequence is present in GOI. When the target site is selected, GOI region following the target site can be sent to the next position of group I intron in the self-circularization construct. Therefore, after self-circularization, GOI regions can be reconnected with each other, generating the circRNA with complete GOI in the correct order (
Figure 3c).
Self-circularization can be completed during IVT efficiently without additional reaction [
2,
7] (additional reaction is optional for STS reaction [
19]). Its efficiency is comparable to that of the PIE method. As STS-based method avoids leaving unwanted sequences, Cui et al. have perfectly mimicked the native sequence of circRNA and the prepared circRNAs performed their original biological functions in cell-based assays [
19]. In this study, circRNA expression vector was used for cell-based assays, instead of directly using in vitro self-circularized circRNAs. Regardless of using in vitro-prepared circRNAs [
18] or circRNA expression vector system [
19], higher protein expression levels as well as longer-lasting expression were observed compared to the use of linear RNAs in cells [
18]. These results are consistent with previous reports [
2,
13] using circRNAs prepared by the PIE method.
In addition, we have developed an ion pair-reverse phase (IP-RP) HPLC method [
18] that can lead to much purer circRNAs than a size exclusion chromatography (SEC) method [
2,
13,
15,
16,
17] commonly used to purify circRNAs prepared by the PIE method.
5. Discussions
Recently, practical self-splicing ribozyme-based in vitro circRNA preparation methods have been receiving great attention. Here, we reviewed recent updates on those methods such as PIE-based and STS-based methods. Based on our opinions on each method and related reports, pros and cons of each method are summarized in
Table 1.
Generally, the PIE method using group I intron has been widely used to prepare circRNA in vitro. However, the conventional PIE method generally leaves extraneous sequences such as E1/E2 fragments and spacer sequences in the generated circRNAs. For example, in the circRNAs generated by
Anabaena group I intron-based PIE, scar sequences consist of 62-nt of intronic scar (15-nt of E1 plus 52-nt of E2) and 108-nt of spacers (69-nt and 39-nt of two spacer regions) with internal homology arms, which can limit the flexibility of design/engineering for circRNAs and may introduce some unwanted side effects [
19] such as innate immune response [
15].
With the Clean-PIE method, sequences/structures that function like E1/E2 can be concealed in the GOI region. Although 99.9% of the genes with sizes >500 bp contain at least one E1/E2-like sequences with a prediction of good efficiency [
16], genes with sizes <500 bp do not. The optimized codon usage in the original CDS should also be changed to use better E1/E2-like function, if required.
PIE using group II intron avoids leaving E1/E2 fragments in the generated circRNAs. However, PIE-based methods require spacer sequence between IRES and intron structures as a close proximity of the two structures can affect circularization efficacy [
2,
17]. Moreover, the exon binding site in the D1 domain of group II intron that was modified to bind to the GOI for scarless circRNA generation is not universally applicable as the GOI sequences are different for each GOI. Therefore, the D1 sequence should be modified for each specific GOI [
32].
The STS method, which has a distinct mechanism from PIE, avoids leaving unwanted sequences/structures in the generated circRNA. Ideally, even spacer sequences are not required as target site can be selected to separate IRES and ribozyme structures in the designed self-circularization RNA construct (K.H. Lee and S.-W. Lee, unpublished data). However, the introduction of spacers such as polyAC could improve the translation efficiency probably due to binding of some intracellular factors such as polyA binding proteins [
14,
16].
With the STS method, P1/P10 and AS/ABS can be optimized to increase the self-circularization efficiency [
18]. In addition, as a target site also affects the self-circularization efficiency, a target site with good self-circularization efficiency can be selected to design the optimal self-circularization construct. Therefore, in addition to the strategy of using AU-rich target sites [
18], an efficient target site selection strategy needs to be established to reduce the laborious design/test cycles.
Self-circularization based on self-splicing ribozyme-based methods can be completed during IVT, although additional incubation reaction would increase the self-circularization efficiency, suggesting that an extra ligation reaction using ligase is not needed for the circularization. Therefore, circRNA production yields would be proportional to IVT scale, suggesting that these methods would be more practical than other in vitro circRNA preparation methods.
However, there are still some shortcomings for self-splicing ribozyme-based in vitro circRNA preparation methods. For example, appropriated purification method for large scale production with higher purity and negligible nick formation should be validated.
Both PIE- or STS-based methods are expected to be further optimized rapidly to overcome their shortcomings for various biomedical applications with unmet needs.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.H.L and S.-W.L.; Writing—original draft preparation, K.H.L. and N.-E.L.; Writing—review and editing, K.H.L. and S.-W.L.; Funding acquisition, K.H.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program of the National Research Foundation (NRF), funded by the Korean government (MSIT) (No. 2022M3E5F1017657).
Conflicts of Interest
K.H.L and N.-E.L. are employees of Rznomics Inc. S.-W.L. is the CEO of Rznomics Inc. Funders had no role in the study design; data collection, data analyses, interpretation of data, writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish study results.
References
- Liu, C.-X.; Chen, L.-L. Circular RNAs: Characterization, Cellular Roles, and Applications. Cell 2022, 185, 2016–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wesselhoeft, R.A.; Kowalski, P.S.; Anderson, D.G. Engineering Circular RNA for Potent and Stable Translation in Eukaryotic Cells. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, D.; Wu, Y.; Lian, J. Circular RNA Vaccine in Disease Prevention and Treatment. Sig. Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaya, L.; Grigoryan, L.; Li, Z.; Lee, A.; Wender, P.A.; Pulendran, B.; Chang, H.Y. Circular RNA Vaccine Induces Potent T Cell Responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2023, 120, e2302191120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Wu, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, M.; Fu, Z.F.; Zhao, L. Circular RNA Vaccines with Long-Term Lymph Node-Targeting Delivery Stability After Lyophilization Induce Potent and Persistent Immune Responses. mBio 2024, 15, e01775-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seephetdee, C.; Bhukhai, K.; Buasri, N.; Leekukkanaveera, P.; Lerdwattanasombat, P.; Manopwisedjaroen, S.; Phueakphud, N.; Kuhaudomlarp, S.; Olmedillas, E.; Saphire, E.O.; Thitithanyanont, A.; Hongeng, S.; Wongtrakoongate, P. A Circular mRNA Vaccine Prototype Producing VFLIP-X Spike Confers a Broad Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 Variants by Mouse Sera. Antiviral Res. 2022, 204, 105370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, L.; Yi, Z.; Shen, Y.; Lin, L.; Chen, F.; Xu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Tang, H.; Zhang, X.; Tian, F.; Wang, C.; Xiao, X.; Dong, X.; Guo, L.; Lu, S.; Yang, C.; Tang, C.; Yang, Y.; Yu, W.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, Q.; Yisimayi, A.; Liu, S.; Huang, W.; Cao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Peng, X.; Wang, J.; Xie, X.S.; Wei, W. Circular RNA Vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 and Emerging Variants. Cell 2022, 185, 1728–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongin, E. Why Rings of RNA Could Be The Next Blockbuster Drug. Nature 2023, 622, 22–24. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, S.; Appel, B. In Vitro Circularization of RNA. RNA Biol. 2017, 14, 1018–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Lu, Y. Circular RNA: Biosynthesis In Vitro. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 787881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.-W. Pros and Cons of In Vitro Methods for Circular RNA Preparation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puttaraju, M.; Been, M.D. Group I Permuted Intron-Exon (PIE) Sequences Self-Splice to Produce Circular Exons. Nucleic Acid Res. 1992, 20, 5357–5364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wesselhoeft, R.A.; Kowalski, P.S.; Parker-Hale, F.C.; Huang, Y.; Bisaria, N.; Anderson, D.G. RNA Circularization Diminishes Immunogenicity and Can Extend Translation Duration In Vivo. Mol. Cell 2019, 74, 508–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Wang, S.K.; Belk, J.A.; Amaya, L.; Li, Z.; Cardenas, A.; Abe, B.T.; Chen, C.-K.; Wender, P.A.; Chang, H.Y. Engineering Circular RNA for Enhanced Protein Production. Nat. Biotechnol. 2023, 41, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.-X.; Guo, S.-K.; Nan, F.; Xu, Y.-F.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.-L. RNA Circles with Minimized Immunogenicity as Potent PKR Inhibitors. Mol. Cell 2022, 82, 420–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Z.; Hou, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, J.; Zhai, M.; Li, D.; Li, Y.; Liu, C.; Li, N.; Cao, Y.; Yang, J.; Sun, Z.; Zuo, C. Clean-PIE: A Novel Strategy for Efficiently Constructing Precise circRNA with Thoroughly Minimized Immunogenicity to Direct Potent and Durable Protein Expression. bioRxiv. 2022, 496777. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Wei, H.; Zhang, K.; Li, Z.; Wei, T.; Tang, C.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z. A Flexible, Efficient, and Scalable Platform to Produce Circular RNAs as New Therapeutics. bioRxiv. 2022, 494115. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.H.; Kim, S.; Song, J.; Han, S.R.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.-W. Efficient Circular RNA Engineering by End-to-End Self-Targeting and Splicing Reaction Using Tetrahymena Group I Intron Ribozyme. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2023, 33, 587–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, C.; Huang, W.; Zou, L.; Yu, X.; Xiao, F. A Precise and Efficient Circular RNA Synthesis System Based on a Ribozyme Derived from Tetrahymena Thermophila. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, e78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cech, T.R. Self-Splicing of Group I Introns. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1990, 59, 543–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, E.; Ares, M.Jr. Synthesis of Circular RNA in Bacteria and Yeast Using RNA Cyclase Ribozymes Derived from a Group I Intron of Phage T4. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 3117–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umekage, S.; Kikuchi, Y. In Vitro and In Vivo Production and Purification of Circular RNA Aptamer. J. Biotechnol. 2009, 139, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rausch, J.W.; Heinz, W.F.; Payea, M.J.; Sherpa, C.; Gorospe, M.; Le Grice, S.F.J. Characterizing and Circumventing Sequence Restrictions for Synthesis of Circular RNA In Vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, e35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeil, B.A.; Simon, D.M.; Zimmerly, S. Alternative Splicing of a Group II Intron in a Surface Layer Protein Gene in Clostridium Tetani. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 1959–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarrell, K.A. Inverse Splicing of a Group II Intron. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 8624–8627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambowitz, A.M.; Zimmerly, S. Group II Introns: Mobile Ribozymes That Invade DNA. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a003616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smathers, C.M.; Robart, A.R. The Mechanism of Splicing as Told by Group II Introns: Ancestors of the Spliceosome. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gene Regul. Mech. 2019, 1862, 194390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyle, A.M. Group II Intron Self-Splicing. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2016, 45, 183–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petkovic, S.; Müller, S. RNA Circularization Strategies In Vivo and In Vitro. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 2454–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obi, P.; Chen, G. The Design and Synthesis of Circular RNAs. Methods 2021, 196, 85–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Han, S.R.; Lee, S.-W. Therapeutic applications of group I intron-based trans-splicing ribozymes. WIREs RNA 2018, 9, e1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.-W.; Nam, J.-W. Optimal Design of Synthetic Circular RNAs. Exp. Mol. Med. 2024, 56, 1281–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).