Submitted:
01 August 2024
Posted:
04 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Physiology of the Placenta
2.1. Maternal Placental Circulation and Immunity
2.2. Hormonal Secretion
2.3. Placental Barrier
3. Pathophysiology of the Placenta
3.1. Molecular Approach to Placental Disorders
3.2. Biogenesis and Biological Function of miRNAs
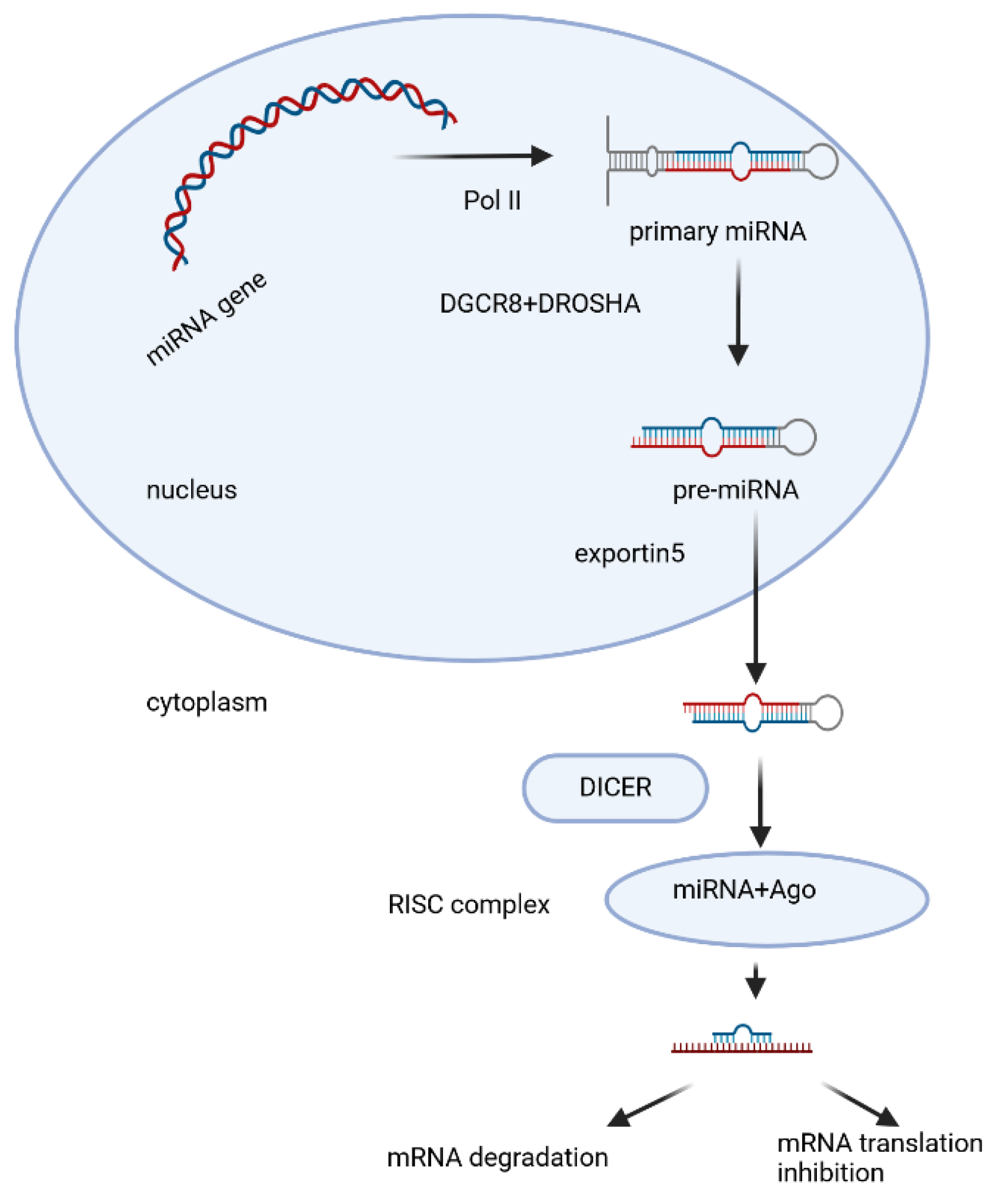
3.3. Expression of miRNAs in Human Placenta
3.4. Micro-RNAs and Human Gestational Disorders
3.5. Preeclampsia (PE) and miRNAs
| Up-Regulated miRNAs | Affected Biological Process |
|---|---|
| miR-155 [128], miR-20a [129], miR-16 [130], miR-142-3p [131], miR-200p-3b [132], miR-137 [133], miR-146a [134] |
proliferation↓ |
| miR-155 [128], miR-431 [135], miR-20b [136], miR-16 [130], miR-125b [139], miR-200p-3b [129], miR-137 [133], miR-146a [140] |
migration↓ |
| miR-431 [135], miR-30a-3p [136], miR-20a [129], miR-20b [136], miR-141 [139], miR-142-3p [131], miR-125b [137], miR-146a [140], miR-517a/b [142], miR-517c [142] |
invasion↓ |
| miR-30a-3p [117], miR-29b [134], miR-16 [135], miR-200p-3b [140] | apoptosis↑ |
| miR-17-92 clusters [143], miR-106a0363 clusters [143] | differntiation↓ |
| 17 [144], miR-206 [145], miR-210 [146], miR-202-3p [147], miR-155p [149] |
other/targets↓ |
| miR-222-3p [149], miR-486-1-5p [150], miR-486-2-5p [150], miR-155 [151], miR-136 [152], miR-494 [152], miR-495 [152] |
in exosomes |
| Down-Regulated miRNAs | Affected Biological Process |
|---|---|
| miR-378a-5p [153], miR-376c [154], miR-335 [155], miR-126 [156] | proliferation↑ |
| miR-378a-5p [153], miR-3935 [157], miR-376 [154], miR-126 [156] | migration↑ |
| miR-378a-5p [153], miR-3935 [157] | invasion↑ |
| miR-335 [155], miR-125a [158] | apoptosis↓ |
| miR-126 [156] | differntiation↑ |
| miR-195 [159] | other/targets↑ |
| miR-153-3p [149], miR-653-5p [149], miR-325 [149] | in exosomes |
3.6. Preeclampsia and Piwi-Interacting RNAs (piRNAs)
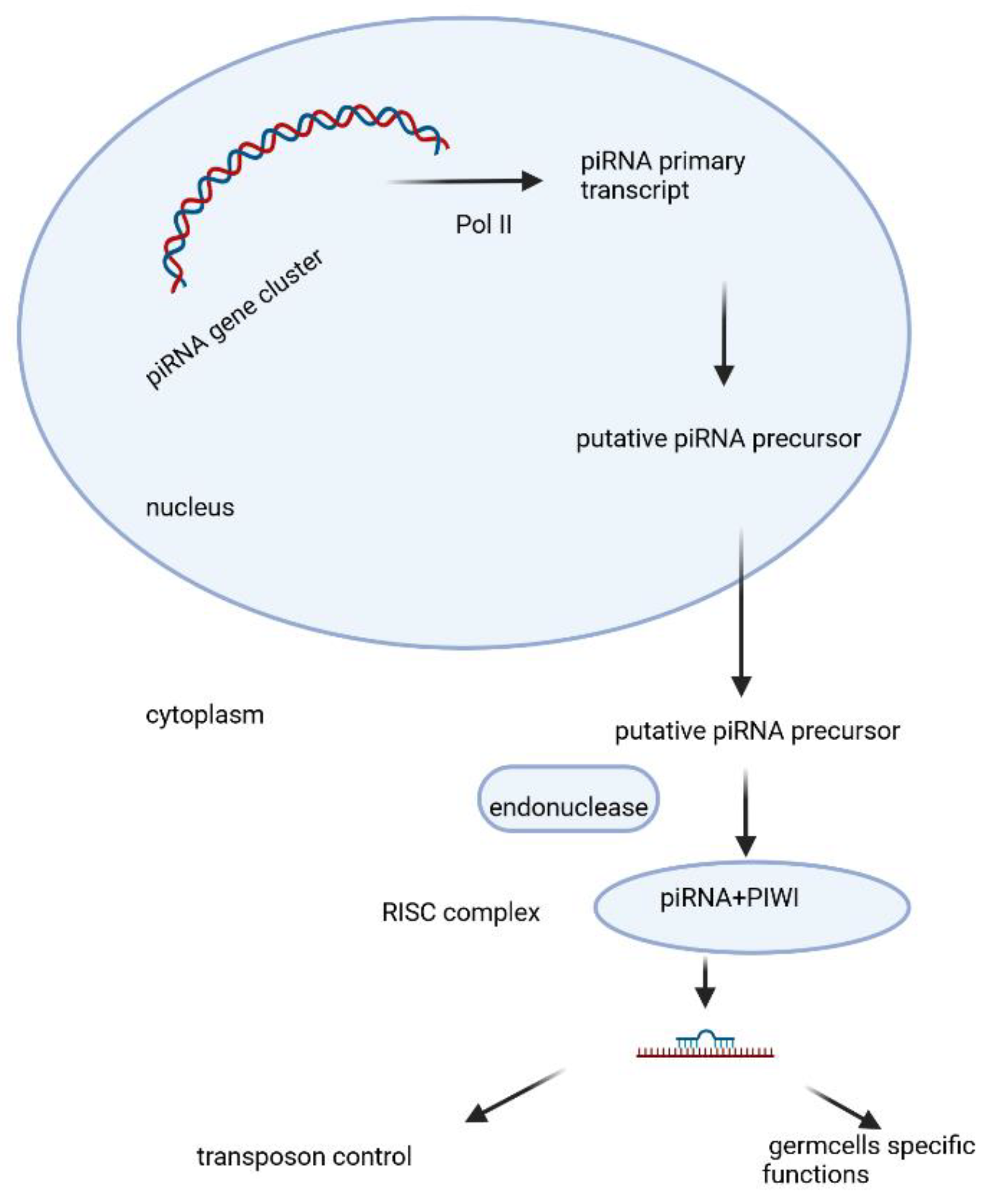
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jin M, Xu Q, Li J, Xu S, Tang C. Micro-RNAs in Human Placenta: Tiny Molecules, Immense Power. Molecules. 2022 Sep 13;27(18):5943. PMID: 36144676; PMCID: PMC9501247. [CrossRef]
- Chuong EB. The placenta goes viral: Retroviruses control gene expression in pregnancy. PLoS Biol. 2018 Oct 9;16(10):e3000028. PMID: 30300353; PMCID: PMC6177113. [CrossRef]
- Reznickq D.N. et al.Independent Origins and Rapid Evolution of the Placenta in the Fish Genus Poeciliopsis.Science298,1018-1020(2002). [CrossRef]
- https://languages.oup.com/google-dictionary-en/.
- "The human proteome in placenta - The Human Protein Atlas". www.proteinatlas.org. Archived from the original on 2017-09-26. Retrieved 2017-09-26.
- Ayala FJ (May 2007). "Darwin's greatest discovery: design without designer". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 104 (Suppl 1): 8567–8573. PMC 1876431. PMID 17494753. [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, J. S., Poehlmann, T. G., Schleussner, E., & Markert, U. R. (2008). Trophoblast invasion: the role of intracellular cytokine signalling via signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3). Human reproduction update, 14(4), 335-344.
- Graham, R. L., Rothschild, B. L., & Spencer, J. H. (1991). Ramsey theory (Vol. 20). John Wiley & Sons.
- Burton, G. J., Charnock-Jones, D. S., & Jauniaux, E. (2009). Regulation of vascular growth and function in the human placenta. Reproduction, 138(6), 895-902.
- Moser, G., & Huppertz, B. (2017). Implantation and extravillous trophoblast invasion: From rare archival specimens to modern biobanking. Placenta, 56, 19-26.
- Moser, G., Windsperger, K., Pollheimer, J., de Sousa Lopes, S. C., & Huppertz, B. (2018). Human trophoblast invasion: new and unexpected routes and functions. Histochemistry and cell biology, 150, 361-370.
- Moser, G., Weiss, G., Gauster, M., Sundl, M., & Huppertz, B. (2015). Evidence from the very beginning: endoglandular trophoblasts penetrate and replace uterine glands in situ and in vitro. Human reproduction, 30(12), 2747-2757.
- Moser, G., Guettler, J., Forstner, D., & Gauster, M. (2019). Maternal platelets—friend or foe of the human placenta?. International journal of molecular sciences, 20(22), 5639.
- Yu, Y., He, J. H., Hu, L. L., Jiang, L. L., Fang, L., Yao, G. D., ... & Sun, Y. P. (2020). Placensin is a glucogenic hormone secreted by human placenta. EMBO reports, 21(6), e49530.
- Windsperger, K., Dekan, S., Pils, S., Golletz, C., Kunihs, V., Fiala, C., ... & Pollheimer, J. (2017). Extravillous trophoblast invasion of venous as well as lymphatic vessels is altered in idiopathic, recurrent, spontaneous abortions. Human reproduction, 32(6), 1208-1217.
- Whitby, S., Zhou, W., & Dimitriadis, E. (2020). Alterations in epithelial cell polarity during endometrial receptivity: a systematic review. Frontiers in Endocrinology, 11, 596324.
- Thompson, B. J. Cell polarity: models and mechanisms from yeast, worms and flies Development (2013) 140 (1): 13–21. [CrossRef]
- Png, F. Y., & Murphy, C. R. (2002). Cytoskeletal proteins in uterine epithelial cells only partially return to the pre-receptive state after the period of receptivity. acta histochemica, 104(3), 235-244.
- Blackburn DG, Avanzati AM, Paulesu L (November 2015). "Classics revisited. History of reptile placentology: Studiati's early account of placentation in a viviparous lizard". Placenta. 36 (11): 1207–1211. PMID 26474917. [CrossRef]
- Gál, L., Fóthi, Á., Orosz, G., Nagy, S., Than, N. G., & Orbán, T. I. (2024). Exosomal small RNA profiling in first-trimester maternal blood explores early molecular pathways of preterm preeclampsia. Frontiers in Immunology, 15, 1321191.
- Biró, O., Fóthi, Á., Alasztics, B., Nagy, B., Orbán, T. I., & Rigó Jr, J. (2019). Circulating exosomal and Argonaute-bound microRNAs in preeclampsia. Gene, 692, 138-144.
- Cirkovic, A., Stanisavljevic, D., Milin-Lazovic, J., Rajovic, N., Pavlovic, V., Milicevic, O., ... & Milic, N. (2021). Preeclamptic women have disrupted placental microRNA expression at the time of preeclampsia diagnosis: meta-analysis. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 9, 782845.
- Lin, J., Zhou, Y., & Gu, W. (2022). Novel piRNA regulates PIWIL1 to modulate the behavior of placental trophoblast cells and participates in preeclampsia. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2022(1), 7856290.
- Ramat, A., & Simonelig, M. (2021). Functions of PIWI proteins in gene regulation: new arrows added to the piRNA quiver. Trends in Genetics, 37(2), 188-200.
- Telkar, N., Stewart, G. L., Pewarchuk, M. E., Cohn, D. E., Robinson, W. P., & Lam, W. L. (2022). Small non-coding RNAs in the human placenta: regulatory roles and clinical utility. Frontiers in Genetics, 13, 868598.
- Bowen R. "Implantation and Development of the Placenta: Introduction and Index". Pathophysiology of the Reproductive System. Colorado State. Retrieved 7 July 2019.
- Moser, G., Windsperger, K., Pollheimer, J., de Sousa Lopes, S. C., & Huppertz, B. (2018). Human trophoblast invasion: new and unexpected routes and functions. Histochemistry and cell biology, 150, 361-370.
- Dashe JS, Bloom SL, Spong CY, Hoffman BL (2018). Williams Obstetrics. McGraw Hill Professional. ISBN 978-1-259-64433-7.
- Kiserud T, Acharya G (December 2004). "The fetal circulation". Prenatal Diagnosis. 24 (13): 1049–1059.
- Madhusoodanan J (October 10, 2018). "Break on through: How some viruses infect the placenta". Knowable Magazine. [CrossRef]
- Kappen C, Kruger C, MacGowan J, Salbaum JM (2012). "Maternal diet modulates placenta growth and gene expression in a mouse model of diabetic pregnancy". PLOS ONE. 7 (6): e38445. Bibcode:2012PLoSO...738445K. [CrossRef]
- Pereira L (September 2018). "Congenital Viral Infection: Traversing the Uterine-Placental Interface". Annual Review of Virology. 5 (1): 273–299. [CrossRef]
- Palmeira P, Quinello C, Silveira-Lessa AL, Zago CA, Carneiro-Sampaio M (2012). "IgG placental transfer in healthy and pathological pregnancies". Clinical & Developmental Immunology. 2012: 985646. [CrossRef]
- Pillitteri A (2009). Maternal and Child Health Nursing: Care of the Childbearing and Childrearing Family. Hagerstwon, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 202. ISBN 978-1-58255-999-5.
- White, B., Harrison,J.R., and Lisa Mehlmann,L., Endocrine and Reproductive Physiology, 5th Edition ISBN : 9780323595735Publication Date 2019.
- Handwerger S, Freemark M (April 2000). "The roles of placental growth hormone and placental lactogen in the regulation of human fetal growth and development". Journal of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism. 13 (4): 343–356. [CrossRef]
- Wilson, B. (2018). Immunology of Animal Reproduction. Scientific e-Resources.
- Aluvihare, V. R., Kallikourdis, M., & Betz, A. G. (2004). Regulatory T cells mediate maternal tolerance to the fetus. Nature immunology, 5(3), 266-271.
- Williams, Z., Zepf, D., Longtine, J., Anchan, R., Broadman, B., Missmer, S. A., & Hornstein, M. D. (2009). Foreign fetal cells persist in the maternal circulation. Fertility and sterility, 91(6), 2593-2595.
- Okano, M., Bell, D. W., Haber, D. A., & Li, E. (1999). DNA methyltransferases Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b are essential for de novo methylation and mammalian development. Cell, 99(3), 247-257.
- Chédin, F. (2011). The DNMT3 family of mammalian de novo DNA methyltransferases. Progress in molecular biology and translational science, 101, 255-285.
- Andrews, S., Krueger, C., Mellado-Lopez, M., Hemberger, M., Dean, W., Perez-Garcia, V., & Hanna, C. W. (2023). Mechanisms and function of de novo DNA methylation in placental development reveals an essential role for DNMT3B. Nature communications, 14(1), 371.
- Jin, M., Xu, Q., Li, J., Xu, S., & Tang, C. (2022). Micro-RNAs in human placenta: Tiny molecules, immense power. Molecules, 27(18), 5943.
- Bhatti, G. K., Khullar, N., Sidhu, I. S., Navik, U. S., Reddy, A. P., Reddy, P. H., & Bhatti, J. S. (2021). Emerging role of non-coding RNA in health and disease. Metabolic brain disease, 36, 1119-1134.
- Lee, R. C., Feinbaum, R. L., & Ambros, V. (1993). The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. cell, 75(5), 843-854.
- Tomasello, L., Distefano, R., Nigita, G., & Croce, C. M. (2021). The MicroRNA family gets wider: the IsomiRs classification and role. Frontiers in cell and developmental biology, 9, 668648.
- Morales-Prieto, D. M., Chaiwangyen, W., Ospina-Prieto, S., Schneider, U., Herrmann, J., Gruhn, B., & Markert, U. R. (2012). MicroRNA expression profiles of trophoblastic cells. Placenta, 33(9), 725-734.
- Iwasaki, Y. W., Siomi, M. C., & Siomi, H. (2015). PIWI-interacting RNA: its biogenesis and functions. Annual review of biochemistry, 84(1), 405-433.
- He J, Chen M, Xu J, Fang J, Liu Z, Qi H. Identification and characterization of Piwi-interacting RNAs in human placentas of preeclampsia. Sci Rep. 2021 Aug 3;11(1):15766. Erratum in: Sci Rep. 2021 Sep 14;11(1):18652. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-98274-4. PMID: 34344990; PMCID: PMC8333249. [CrossRef]
- Rani, V.; Sengar, R.S. Biogenesis and mechanisms of microRNA-mediated gene regulation. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2022, 119, 685–692.
- Lee, Y., Jeon, K., Lee, J. T., Kim, S., & Kim, V. N. (2002). MicroRNA maturation: stepwise processing and subcellular localization. The EMBO journal, 21(17), 4663-4670.
- Cloonan, N., Wani, S., Xu, Q., Gu, J., Lea, K., Heater, S., ... & Grimmond, S. M. (2011). MicroRNAs and their isomiRs function cooperatively to target common biological pathways. Genome biology, 12(12), 1-20.
- Vashukova, E.S.; Glotov, A.S.; Fedotov, P.V.; Efimova, O.A.; Pakin, V.S.; Mozgovaya, E.V.; Pendina, A.A.; Tikhonov, A.V.; Koltsova, A.S.; Baranov, V.S. Placental microRNA expression in pregnancies complicated by superimposed preeclampsia on chronic hypertension. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 22–32.
- Burton, G.J.; Cindrova-Davies, T.; Yung, H.W.; Jauniaux, E. Hypoxia and Reproductive Health: Oxygen and development of the human placenta. Reproduction 2021, 161, F53–F65.
- Jaszczuk, I.; Koczkodaj, D.; Kondracka, A.; Kwasniewska, A.; Winkler, I.; Filip, A. The role of miRNA-210 in pre-eclampsia development. Ann. Med. 2022, 54, 1350–1356.
- Wu, D.; Chen, X.; Wang, L.; Chen, F.; Cen, H.; Shi, L. Hypoxia-induced microRNA-141 regulates trophoblast apoptosis, invasion, and vascularization by blocking CXCL12beta/CXCR2/4 signal transduction. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 116, 108836.
- Fang, M.; Du, H.; Han, B.; Xia, G.; Shi, X.; Zhang, F.; Fu, Q.; Zhang, T. Hypoxia-inducible microRNA-218 inhibits trophoblast invasion by targeting LASP1: Implications for preeclampsia development. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2017, 87, 95–103.
- LaRocca, J.; Binder, A.M.; McElrath, T.F.; Michels, K.B. First-Trimester Urine Concentrations of Phthalate Metabolites and Phenols and Placenta miRNA Expression in a Cohort of U.S. Women. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 380–387.
- Huang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Dong, S. Emerging roles of long non-coding RNAs in the toxicology of environmental chemicals. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2018, 38, 934–943.
- Yao, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, X. The roles of microRNAs in epigenetic regulation. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2019, 51, 11–17.
- Noguer-Dance, M.; Abu-Amero, S.; Al-Khtib, M.; Lefevre, A.; Coullin, P.; Moore, G.E.; Cavaille, J. The primate-specific microRNA gene cluster (C19MC) is imprinted in the placenta. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2010, 19, 3566–3582.
- Prats-Puig, A.; Xargay-Torrent, S.; Carreras-Badosa, G.; Mas-Pares, B.; Bassols, J.; Petry, C.J.; Girardot, M.; Francis, D.E.Z.; Ibanez, L.; Dunger, D.B.; et al. Methylation of the C19MC microRNA locus in the placenta: Association with maternal and chilhood body size. Int. J. Obes. 2020, 44, 13–22.
- Farrokhnia, F.; Aplin, J.D.; Westwood, M. Dicer-dependent miRNAs provide an endogenous restraint on cytotrophoblast proliferation. Placenta 2012, 33, 581–585.
- Fu, G.; Ye, G.; Nadeem, L.; Ji, L.; Manchanda, T.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Qiao, J.; Wang, Y.L.; Lye, S.; et al. MicroRNA-376c impairs transforming growth factor-beta and nodal signaling to promote trophoblast cell proliferation and invasion. Hypertension 2013, 61, 864–872.
- Li, L.; Huang, X.; He, Z.; Xiong, Y.; Fang, Q. miRNA-210-3p regulates trophoblast proliferation and invasiveness through fibroblast growth factor 1 in selective intrauterine growth restriction. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 4422–4433.
- Wang, D.; Na, Q.; Song, G.Y.; Wang, L. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosome-mediated transfer of microRNA-133b boosts trophoblast cell proliferation, migration and invasion in preeclampsia by restricting SGK1. Cell Cycle 2020, 19, 1869–1883.
- Dai, Y.; Qiu, Z.; Diao, Z.; Shen, L.; Xue, P.; Sun, H.; Hu, Y. MicroRNA-155 inhibits proliferation and migration of human extravillous trophoblast derived HTR-8/SVneo cells via down-regulating cyclin D1. Placenta 2012, 33, 824–829.
- Zou, Z.; He, Z.; Cai, J.; Huang, L.; Zhu, H.; Luo, Y. Potential role of microRNA-424 in regulating ERRgamma to suppress trophoblast proliferation and invasion in fetal growth restriction. Placenta 2019, 83, 57–62.
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Li, M.Q.; Xu, J.; Zhang, J.P.; Jin, L.P. MicroRNA-184 promotes apoptosis of trophoblast cells via targeting WIG1 and induces early spontaneous abortion. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 223.
- Forbes, K.; Farrokhnia, F.; Aplin, J.D.; Westwood, M. Dicer-dependent miRNAs provide an endogenous restraint on cytotrophoblast proliferation. Placenta 2012, 33, 581–585.
- Matsubara, K.; Matsubara, Y.; Uchikura, Y.; Takagi, K.; Yano, A.; Sugiyama, T. HMGA1 Is a Potential Driver of Preeclampsia Pathogenesis by Interference with Extravillous Trophoblasts Invasion. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 822.
- Nakashima, A.; Shima, T.; Aoki, A.; Kawaguchi, M.; Yasuda, I.; Tsuda, S.; Yoneda, S.; Yamaki-Ushijima, A.; Cheng, S.B.; Sharma, S.; et al. Molecular and immunological developments in placentas. Hum. Immunol. 2021, 82, 317–324.
- Sun, M.; Chen, H.; Liu, J.; Tong, C.; Meng, T. MicroRNA-34a inhibits human trophoblast cell invasion by targeting MYC. BMC Cell Biol. 2015, 16, 21.
- Zheng, W.; Chen, A.; Yang, H.; Hong, L. MicroRNA-27a inhibits trophoblast cell migration and invasion by targeting SMAD2: Potential role in preeclampsia. Exp. Ther. Med. 2020, 20, 2262–2269.
- Gao, T.; Deng, M.; Wang, Q. MiRNA-320a inhibits trophoblast cell invasion by targeting estrogen-related receptor-gamma. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2018, 44, 756–763.
- Rana, S.; Lemoine, E.; Granger, J.P.; Karumanchi, S.A. Preeclampsia: Pathophysiology, Challenges, and Perspectives. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 1094–1112.
- Armaly, Z.; Jadaon, J.E.; Jabbour, A.; Abassi, Z.A. Preeclampsia: Novel Mechanisms and Potential Therapeutic Approaches. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 973.
- Yang, H.L.; Zhang, H.Z.; Meng, F.R.; Han, S.Y.; Zhang, M. Differential expression of microRNA-411 and 376c is associated with hypertension in pregnancy. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2019, 52, e7546.
- Akehurst, C.; Small, H.Y.; Sharafetdinova, L.; Forrest, R.; Beattie, W.; Brown, C.E.; Robinson, S.W.; McClure, J.D.; Work, L.M.; Carty, D.M.; et al. Differential expression of microRNA-206 and its target genes in preeclampsia.
- Hayder, H.; O’Brien, J.; Nadeem, U.; Peng, C. MicroRNAs: Crucial regulators of placental development. Reproduction 2018, 155, R259–R271.
- Wang, W.; Feng, L.; Zhang, H.; Hachy, S.; Satohisa, S.; Laurent, L.C.; Parast, M.; Zheng, J.; Chen, D.B. Preeclampsia up-regulates angiogenesis-associated microRNA (i.e., miR-17, -20a, and -20b) that target ephrin-B2 and EPHB4 in human placenta. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, E1051–E1059.
- Mao, Y.; Hou, B.; Shan, L.; Sun, X.; Wang, L. Aberrantly up-regulated miR-142-3p inhibited the proliferation and invasion of trophoblast cells by regulating FOXM1. Placenta 2021, 104, 253–260.
- Shih, J.C.; Lin, H.H.; Hsiao, A.C.; Su, Y.T.; Tsai, S.; Chien, C.L.; Kung, H.N. Unveiling the role of microRNA-7 in linking TGF-beta-Smad-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition with negative regulation of trophoblast invasion. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 6281–6295.
- Yang, X.; Meng, T. MicroRNA-431 affects trophoblast migration and invasion by targeting ZEB1 in preeclampsia. Gene 2019, 683, 225–232.
- Niu, Z.R.; Han, T.; Sun, X.L.; Luan, L.X.; Gou, W.L.; Zhu, X.M. MicroRNA-30a-3p is overexpressed in the placentas of patients with preeclampsia and affects trophoblast invasion and apoptosis by its effects on IGF-1. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2018, 218, 249.e1–249.e12.
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Pan, Z.; Luo, S. Aberrantly up-regulated miR-20a in pre-eclampsic placenta compromised the proliferative and invasive behaviors of trophoblast cells by targeting forkhead box protein A1. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2014, 10, 973–982.
- Jin, M.; Li, H.; Xu, H.; Huo, G.; Yao, Y. MicroRNA-20b inhibits trophoblast cell migration and invasion by targeting MMP-2. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2017, 10, 10901–10909.
- Du, J.; Ji, Q.; Dong, L.; Meng, Y.; Xin, G. HDAC4 Knockdown Induces Preeclampsia Cell Autophagy and Apoptosis by miR-29b. Reprod. Sci. 2021, 28, 334–342.
- Yuan, Y.; Zhao, L.; Wang, X.; Lian, F.; Cai, Y. Ligustrazine-induced microRNA-16-5p inhibition alleviates preeclampsia through IGF-2. Reproduction 2020, 160, 905–917.
- Beards, F.; Jones, L.E.; Charnock, J.; Forbes, K.; Harris, L.K. Placental Homing Peptide-microRNA Inhibitor Conjugates for Targeted Enhancement of Intrinsic Placental Growth Signaling. Theranostics 2017, 7, 2940–2955.
- Ospina-Prieto, S.; Chaiwangyen, W.; Herrmann, J.; Groten, T.; Schleussner, E.; Markert, U.R.; Morales-Prieto, D.M. MicroRNA-141 is upregulated in preeclamptic placentae and regulates trophoblast invasion and intercellular communication. Transl. Res. 2016, 172, 61–72.
- Mao, Y.; Hou, B.; Shan, L.; Sun, X.; Wang, L. Aberrantly up-regulated miR-142-3p inhibited the proliferation and invasion of trophoblast cells by regulating FOXM1. Placenta 2021, 104, 253–260.
- Tang, J.; Wang, D.; Lu, J.; Zhou, X. MiR-125b participates in the occurrence of preeclampsia by regulating the migration and invasion of extravillous trophoblastic cells through STAT3 signaling pathway. J. Recept. Signal. Transduct. Res. 2021, 41, 202–208.
- Anton, L.; Olarerin-George, A.O.; Hogenesch, J.B.; Elovitz, M.A. Placental expression of miR-517a/b and miR-517c contributes to trophoblast dysfunction and preeclampsia. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122707.
- Gu, Y.; Meng, J.; Zuo, C.; Wang, S.; Li, H.; Zhao, S.; Huang, T.; Wang, X.; Yan, J. Downregulation of MicroRNA-125a in Placenta Accreta Spectrum Disorders Contributes Antiapoptosis of Implantation Site Intermediate Trophoblasts by Targeting MCL1. Reprod. Sci. 2019, 26, 1582–1589.
- Li, H.; Ouyang, Y.; Sadovsky, E.; Parks, W.T.; Chu, T.; Sadovsky, Y. Unique microRNA Signals in Plasma Exosomes from Pregnancies Complicated by Preeclampsia. Hypertension 2020, 75, 762–771.
- Shen, L.; Li, Y.; Li, R.; Diao, Z.; Yany, M.; Wu, M.; Sun, H.; Yan, G.; Hu, Y. Placentaassociated serum exosomal miR155 derived from patients with preeclampsia inhibits eNOS expression in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 1731–1739. Molecules 2022, 27, 5943 17 of 18.
- Motawi, T.M.K.; Sabry, D.; Maurice, N.W.; Rizk, S.M. Role of mesenchymal stem cells exosomes derived microRNAs; miR-136, miR-494 and miR-495 in pre-eclampsia diagnosis and evaluation. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2018, 659, 13–21.
- Eskandari, F.; Rezaei, M.; Mohammadpour-Gharehbagh, A.; Teimoori, B.; Yaghmaei, M.; Narooei-Nejad, M.; Salimi, S. The association of pri-miRNA- 26a1 rs7372209 polymorphism and Preeclampsia susceptibility. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2019, 41, 268–273.
- Славoв, И., Късни тoксикoзи на бременнoстта, 1980, Медицина и физкултура.
- Lin J, Zhou Y, Gu W. Novel piRNA Regulates PIWIL1 to Modulate the Behavior of Placental Trophoblast Cells and Participates in Preeclampsia. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Apr 14;2022:7856290. PMID: 35464758; PMCID: PMC9023172. [CrossRef]
- Ives C. W., Sinkey R., Rajapreyar I., Tita A. T. N., Oparil S. Preeclampsia-pathophysiology and clinical presentations: JACC state-of-the-art review. Journal of the American College of Cardiology . 2020;76(14):1690–1702. [CrossRef]
- Rana S., Lemoine E., Granger J. P., Karumanchi S. A. Preeclampsia: pathophysiology, challenges, and perspectives. Circulation Research . 2019;124(7):1094–1112. [CrossRef]
- Liu Y., Dou M., Song X., et al. The emerging role of the piRNA/piwi complex in cancer. Molecular Cancer . 2019;18(1):p. 123. [CrossRef]
- Litwack G. Chapter: Nucleic Acids and Molecular Genetics, Human Biochemistry, 2018.
- Geyer, Roland; Jambeck, Jenna R.; Law, Kara Lavender (July 2017). "Production, use, and fate of all plastics ever made". Science Advances. 3 (7): e1700782. Bibcode:2017SciA....3E0782G. [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Baccarelli, A.A.; Mansur, A.; Adir, M.; Nahum, R.; Hauser, R.; Bollati, V.; Racowsky, C.; Machtinger, R. Maternal Phthalate and Personal Care Products Exposure Alters Extracellular Placental miRNA Profile in Twin Pregnancies. Reprod. Sci. 2019, 26, 289–294.
- Denli, A. M., Tops, B. B., Plasterk, R. H., Ketting, R. F., & Hannon, G. J. (2004). Processing of primary microRNAs by the Microprocessor complex. Nature, 432(7014), 231-235.
- Lee, Y., Jeon, K., Lee, J. T., Kim, S., & Kim, V. N. (2002). MicroRNA maturation: stepwise processing and subcellular localization. The EMBO journal, 21(17), 4663-4670.
- Zeng, Y. R., & Cullen, B. R. (2005). Recognition and cleavage of primary microRNA precursors by the nuclear processing enzyme Drosha. The EMBO journal, 24(1), 138-148.
- Ha, M. & Kim, V. Regulation of microRNA biogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 15, 509–524 (2014). [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, E., Caudy, A. A., Hammond, S. M., & Hannon, G. J. (2001). Role for a bidentate ribonuclease in the initiation step of RNA interference. Nature, 409(6818), 363-366.
- Grishok, A., Pasquinelli, A. E., Conte, D., Li, N., Parrish, S., Ha, I., ... & Mello, C. C. (2001). Genes and mechanisms related to RNA interference regulate expression of the small temporal RNAs that control C. elegans developmental timing. Cell, 106(1), 23-34.
- Hutvagner, G., McLachlan, J., Pasquinelli, A. E., Bálint, É., Tuschl, T., & Zamore, P. D. (2001). A cellular function for the RNA-interference enzyme Dicer in the maturation of the let-7 small temporal RNA. Science, 293(5531), 834-838.
- Song, M. S., & Rossi, J. J. (2017). Molecular mechanisms of Dicer: endonuclease and enzymatic activity. Biochemical journal, 474(10), 1603-1618.
- MacRae, I. J., & Doudna, J. A. (2007). Ribonuclease revisited: structural insights into ribonuclease III family enzymes. Current opinion in structural biology, 17(1), 138-145.
- Filipowicz, W. (2005). RNAi: the nuts and bolts of the RISC machine. Cell, 122(1), 17-20.
- Sontheimer, E. J. (2005). Assembly and function of RNA silencing complexes. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 6(2), 127-138.
- Khvorova, A., Reynolds, A., & Jayasena, S. D. (2003). Functional siRNAs and miRNAs exhibit strand bias. Cell, 115(2), 209-21.
- Schwarz, D. S., & Zamore, P. D. (2002). Why do miRNAs live in the miRNP?. Genes & development, 16(9), 1025-1031.
- Delpu, Y., Larrieu, D., Gayral, M., Arvanitis, D., Dufresne, M., Cordelier, P., & Torrisani, J. (2016). Noncoding RNAs: clinical and therapeutic applications. In Drug discovery in Cancer epigenetics (pp. 305-326). Academic Press.
- Ozata, D. M., Gainetdinov, I., Zoch, A., O’Carroll, D., & Zamore, P. D. (2019). PIWI-interacting RNAs: small RNAs with big functions. Nature Reviews Genetics, 20(2), 89-108.
- Wu, Z., Yu, X., Zhang, S., He, Y., & Guo, W. (2023). Novel roles of PIWI proteins and PIWI-interacting RNAs in human health and diseases. Cell Communication and Signaling, 21(1), 343.
- Wang, K., Wang, T., Gao, X. Q., Chen, X. Z., Wang, F., & Zhou, L. Y. (2021). Emerging functions of piwi-interacting RNAs in diseases. Journal of cellular and molecular medicine, 25(11), 4893-4901.
- Tóth, K. F., Pezic, D., Stuwe, E., & Webster, A. (2016). The piRNA pathway guards the germline genome against transposable elements. Non-coding RNA and the Reproductive System, 51-77.
- Wang, X., Miller, D. C., Harman, R., Antczak, D. F., & Clark, A. G. (2013). Paternally expressed genes predominate in the placenta. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 110(26), 10705-10710.
- Hasuwa, H., Ishino, K., & Siomi, H. (2018). Human PIWI (HIWI) is an azoospermia factor. Science China. Life Sciences, 61(3), 348-350.
- Marzioni, D.; Todros, T.; Cardaropoli, S.; Rolfo, A.; Lorenzi, T.; Ciarmela, P.; Romagnoli, R.; Paulesu, L.; Castellucci, M. Activating protein-1 family of transcription factors in the human placenta complicated by preeclampsia with and without fetal growth restriction. Placenta 2010, 31, 919–927.
- Montenegro, D.; Romero, R.; Kim, S.S.; Tarca, A.L.; Draghici, S.; Kusanovic, J.P.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, D.C.; Erez, O.; Gotsch, F.; et al. Expression patterns of microRNAs in the chorioamniotic membranes: A role for microRNAs in human pregnancy and parturition. J. Pathol 2009, 217, 113–121.
- Chennakesava, C.S.; di Santo, S.; Ziemiecki, A.; Schneider, H.; Andres, A.C. Differential expression of the receptor tyrosine kinase EphB4 and its ligand Ephrin-B2 during human placental development. Placenta 2006, 27, 959–967.
- Muramatsu, F.; Kidoya, H.; Naito, H.; Sakimoto, S.; Takakura, N. microRNA-125b inhibits tube formation of blood vessels through translational suppression of VE-cadherin. Oncogene 2013, 32, 414–421.
- Liu, L.Z.; Li, C.; Chen, Q.; Jing, Y.; Carpenter, R.; Jiang, Y.; Kung, H.-F.; Lai, L.; Jiang, B.-H. MiR-21 induced angiogenesis through AKT and ERK activation and HIF-1alpha expression. PLoS One 2011, 6, e19139.
- Fang, L.; Deng, Z.; Shatseva, T.; Yang, J.; Peng, C.; Du, W.W.; Yee, A.J.; Ang, L.C.; He, C.; Shan, S.W.; et al. MicroRNA miR-93 promotes tumor growth and angiogenesis by targeting integrin-beta8. Oncogene 2011, 30, 806–821.
- Mayor-Lynn, K.; Toloubeydokhti, T.; Cruz, A.C.; Chegini, N. Expression profile of microRNAs and mRNAs in human placentas from pregnancies complicated by preeclampsia and preterm labor. Reprod. Sci 2011, 18, 46–56.
- Maccani, M.A.; Padbury, J.F.; Marsit, C.J. miR-16 and miR-21 expression in the placenta is associated with fetal growth. PLoS One 2011, 6, e21210.
- Yang, W.J.; Yang, D.D.; Na, S.; Sandusky, G.E.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, G. Dicer is required for embryonic angiogenesis during mouse development. J. Biol. Chem 2005, 280, 9330–9335.
- Alpini, G.; Glaser, S.S.; Zhang, J.P.; Francis, H.; Han, Y.; Gong, J.; Stokes, A.; Francis, T.; Hughart, N.; Hubble, L.; et al. Regulation of placenta growth factor by microRNA-125b in hepatocellular cancer. J. Hepatol 2011, 55, 1339–1345.
- Zhang, Y.; Diao, Z.; Su, L.; Sun, H.; Li, R.; Cui, H.; Hu, Y. MicroRNA-155 contributes to preeclampsia by down-regulating CYR61. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol 2010, 202, 466.e1–466.e7.
- Burton, G.J.; Charnock-Jones, D.S.; Jauniaux, E. Regulation of vascular growth and function in the human placenta. Reproduction 2009, 138.
- Babawale, M.O.; van Noorden, S.; Pignatelli, M.; Stamp, G.W.; Elder, M.G.; Sullivan, M.H. Morphological interactions of human first trimester placental villi co-cultured with decidual explants. Hum. Reprod 1996, 11, 444–450.
- Red-Horse, K.; Kapidzic, M.; Zhou, Y.; Feng, K.T.; Singh, H.; Fisher, S.J. EPHB4 regulates chemokine-evoked trophoblast responses: A mechanism for incorporating the human placenta into the maternal circulation. Development 2005, 132, 4097–4106.
- Zhao, C.; Dong, J.; Jiang, T.; Shi, Z.; Yu, B.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, D.; Xu, J.; Huo, R.; Dai, J. Early second-trimester serum miRNA profiling predicts gestational diabetes mellitus. PLoS One 2011, 6, e23925.
- Higashijima, A.; Miura, K.; Mishima, H.; Kinoshita, A.; Jo, O.; Abe, S.; Hasegawa, Y.; Miura, S.; Yamasaki, K.; Yoshida, A.; et al. Characterization of placenta-specific microRNAs in fetal growth restriction pregnancy. Prenat. Diagn 2013.
- He, L.; Hannon, G.J. MicroRNAs: Small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat. Rev. Genet 2004, 5, 522–531.
- Caniggia, I.; Mostachfi, H.; Winter, J.; Gassmann, M.; Lye, S.J.; Kuliszewski, M.; Post, M. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 mediates the biological effects of oxygen on human trophoblast differentiation through TGFbeta(3). J. Clin. Invest 2000, 105, 577–587.
- Pang, R.T.; Leung, C.O.; Ye, T.M.; Liu, W.; Chiu, P.C.; Lam, K.K.; Lee, K.F.; Yeung, W.S. MicroRNA-34a suppresses invasion through downregulation of Notch1 and Jagged1 in cervical carcinoma and choriocarcinoma cells. Carcinogenesis 2010, 31, 1037–1044.
- Zhu, J.; Motejlek, K.; Wang, D.; Zang, K.; Schmidt, A.; Reichardt, L.F. β8 integrins are required for vascular morphogenesis in mouse embryos. Development 2002, 129, 2891–2903.
- Dunk, C.; Petkovic, L.; Baczyk, D.; Rossant, J.; Winterhager, E.; Lye, S. A novel in vitro model of trophoblast-mediated decidual blood vessel remodeling. Lab. Invest 2003, 83, 1821–1828.
- Kotlabova, K.; Doucha, J.; Hromadnikova, I. Placental-specific microRNA in maternal circulation—Identification of appropriate pregnancy-associated microRNAs with diagnostic potential. J. Reprod. Immunol 2011, 89, 185–191.
- Chim, S.S.; Shing, T.K.; Hung, E.C.; Leung, T.Y.; Lau, T.K.; Chiu, R.W.; Lo, Y.M. Detection and characterization of placental microRNAs in maternal plasma. Clin. Chem 2008, 54, 482–490.
- Miura, K.; Miura, S.; Yamasaki, K.; Higashijima, A.; Kinoshita, A.; Yoshiura, K.; Masuzaki, H. Identification of pregnancy-associated microRNAs in maternal plasma. Clin. Chem 2010, 56, 1767–1771.
- Pollheimer, J.; Knofler, M. Signalling pathways regulating the invasive differentiation of human trophoblasts: A review. Placenta 2005, 26, S21–S30.
- Camps, C.; Buffa, F.M.; Colella, S.; Moore, J.; Sotiriou, C.; Sheldon, H.; Harris, A.L.; Gleadle, J.M.; Ragoussis, J. hsa-miR-210 Is induced by hypoxia and is an independent prognostic factor in breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res 2008, 14, 1340–1348.
- Sibai, B.; Dekker, G.; Kupferminc, M. Pre-eclampsia. Lancet 2005, 365, 785–799.
- Cui, Y.; Wang, W.; Dong, N.; Lou, J.; Srinivasan, D.K.; Cheng, W.; Huang, X.; Liu, M.; Fang, C.; Peng, J.; et al. Role of corin in trophoblast invasion and uterine spiral artery remodelling in pregnancy. Nature 2012, 484, 246–250.
- Morales Prieto, D.M.; Markert, U.R. MicroRNAs in pregnancy. J. Reprod. Immunol 2011, 88, 106–111.
- Keniry, A.; Oxley, D.; Monnier, P.; Kyba, M.; Dandolo, L.; Smits, G.; Reik, W. The H19 lincRNA is a developmental reservoir of miR-675 that suppresses growth and Igf1r. Nat. Cell Biol 2012, 14, 659–665.
- Gilad, S.; Meiri, E.; Yogev, Y.; Benjamin, S.; Lebanony, D.; Yerushalmi, N.; Benjamin, H.; Kushnir, M.; Cholakh, H.; Melamed, N.; et al. Serum microRNAs are promising novel biomarkers. PLoS One 2008, 3, e3148.
- Faye-Petersen, O.M. The placenta in preterm birth. J. Clin. Pathol 2008, 61, 1261–1275.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





