Submitted:
27 June 2024
Posted:
27 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- Presentation of the most used MLMs for ED.
- Division of MLMs for ED into two main categories: Single Base Model (SBM) and Stacking Ensemble Model (SEM).
- Identification of SBM or SEM in ED for fraud.
- Discussion on how ML-based ED can improve processes in fraud.
2. Article Selection Process
- RQ1: Which MLMs are currently used in the literature for early detection in multiple areas?
- RQ2: How have these MLMs for ED been implemented in the context of fraud?
3. MLM Data Balancing and Performance Metrics
3.1. Data Balancing
3.2. Performance Metrics
4. Machine Learning Models for ED and Applications
4.1. Machine Learning Models for ED in Fraud Detection
5. Discussion
- Improved prediction performance by maximizing fraud detection through effective identification of patterns and anomalies in the data, leading to better prediction performance. Using features based on SBM responses allows the analysis of behaviors that may not have been explored in traditional methods, thereby enhancing a more comprehensive analysis of fraud indicators. Additionally, the adaptability and robustness of SEM enable it to adjust to the strengths and weaknesses of multiple baseline models, improving overall detection performance and robustness in identifying fraudulent activities [16].
- Combining the predictive power of various models enables the identification of fraudulent behaviors at an early stage with greater accuracy, which allows for timely intervention and prevention of fraudulent activities [20].
- SEM provides a more reliable balance between precision and interpretability, making them operationally viable for fraud detection tasks, due to the adoption of features and operating dynamics of SBMs.
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saheed, Y.K.; Baba, U.A.; Raji, M.A. Big Data Analytics for Credit Card Fraud Detection Using Supervised Machine Learning Models. In Big Data Analytics in the Insurance Market; 2022; pp. 31–56 ISBN 978-1-80262-637-7.
- Prakash, S.; Mahapatra, S.; Nayak, M. Data Analysis in Clinical Decision Making—Prediction of Heart Attack. Smart Innov. Syst. Technol. 2023, 317, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darville, J.; Yavuz, A.; Runsewe, T.; Celik, N. Effective Sampling for Drift Mitigation in Machine Learning Using Scenario Selection: A Microgrid Case Study. Appl. Energy 2023, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghbanpourasl, A.; Kirchberger, D.; Eitzinger, C. Failure Prediction through a Model-Driven Machine Learning Method.; 2021; pp. 527–531.
- Mollaoglu, A.; Baltaoglu, G.; Cakrr, E.; Aktas, M.S. Fraud Detection on Streaming Customer Behavior Data with Unsupervised Learning Methods.; 2021.
- Ollagnier, C.; Kasper, C.; Wallenbeck, A.; Keeling, L.; Bee, G.; Bigdeli, S.A. Machine Learning Algorithms Can Predict Tail Biting Outbreaks in Pigs Using Feeding Behaviour Records. PLoS ONE 2023, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojajuni, O.; Ayeni, F.; Akodu, O.; Ekanoye, F.; Adewole, S.; Ayo, T.; Misra, S.; Mbarika, V. Predicting Student Academic Performance Using Machine Learning. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. Subser. Lect. Notes Artif. Intell. Lect. Notes Bioinforma. 2021, 12957 LNCS, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, B.; Xiang, W.; Deng, A.; Fu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Ouyang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Z.; et al. Incorporating SULF1 Polymorphisms in a Pretreatment CT-Based Radiomic Model for Predicting Platinum Resistance in Ovarian Cancer Treatment. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heistracher, C.; Casas, P.; Stricker, S.; Weissenfeld, A.; Schall, D.; Kemnitz, J. Should I Sample It or Not? Improving Quality Assurance Efficiency Through Smart Active Sampling.; 2023.
- Li, M.; Nanda, G.; Chhajedss, S.S.; Sundararajan, R. Machine Learning-Based Decision Support System for Early Detection of Breast Cancer. Indian J. Pharm. Educ. Res. 2020, 54, S705–S715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, M.A. Conceptual Modeling Interacts with Machine Learning – A Systematic Literature Review. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. Subser. Lect. Notes Artif. Intell. Lect. Notes Bioinforma. 2021, 12957 LNCS, 522–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, S.; van Rees, C.B.; Hand, B.K.; Muhlfeld, C.C.; Luikart, G.; Kimball, J.S. Testing a Generalizable Machine Learning Workflow for Aquatic Invasive Species on Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus Mykiss) in Northwest Montana. Front. Big Data 2021, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santamaria-Bonfil, G.; Arroyo-Figueroa, G.; Zuniga-Garcia, M.A.; Azcarraga Ramos, C.G.; Bassam, A. Power Transformer Fault Detection: A Comparison of Standard Machine Learning and autoML Approaches. Energies 2024, 17, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghomrawi, H.M.K.; O’Brien, M.K.; Carter, M.; Macaluso, R.; Khazanchi, R.; Fanton, M.; DeBoer, C.; Linton, S.C.; Zeineddin, S.; Pitt, J.B.; et al. Applying Machine Learning to Consumer Wearable Data for the Early Detection of Complications after Pediatric Appendectomy. Npj Digit. Med. 2023, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damre, S.S.; Shendkar, B.D.; Kulkarni, N.; Chandre, P.R.; Deshmukh, S. Smart Healthcare Wearable Device for Early Disease Detection Using Machine Learning. Int. J. Intell. Syst. Appl. Eng. 2024, 12, 158–166. [Google Scholar]
- Ghasemieh, A.; Lloyed, A.; Bahrami, P.; Vajar, P.; Kashef, R. A Novel Machine Learning Model with Stacking Ensemble Learner for Predicting Emergency Readmission of Heart-Disease Patients. Decis. Anal. J. 2023, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iparraguirre-Villanueva, O.; Espinola-Linares, K.; Flores Castañeda, R.O.; Cabanillas-Carbonell, M. Application of Machine Learning Models for Early Detection and Accurate Classification of Type 2 Diabetes. Diagnostics 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, A.; Samanta, S.; Mishra, S.; Alkhayyat, A.; Gupta, D.; Sharma, V. Medi-Assist: A Decision Tree Based Chronic Diseases Detection Model.; 2023.
- Anbananthen, K.S.M.; Busst, M.B.M.A.; Kannan, R.; Kannan, S. A Comparative Performance Analysis of Hybrid and Classical Machine Learning Method in Predicting Diabetes. Emerg. Sci. J. 2023, 7, 102–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Fan, L.; Jia, Q.; Wen, L.; Shi, C. Early Diabetes Prediction Based on Stacking Ensemble Learning Model.; 2021; pp. 2687–2692.
- Tripathi, P.; Vishwakarma, K.; Sahu, S.; Vishwakarma, A.; Kori, D. Enhancing Cardiovascular Health: A Machine Learning Approach to Predicting Heart Disease.; 2023; pp. 238–242.
- Dhivya, P.; Bazilabanu, A.; Ponniah, T. Machine Learning Model for Breast Cancer Data Analysis Using Triplet Feature Selection Algorithm. IETE J. Res. 2023, 69, 1789–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, H.; Park, J.; Lee, Y. Stacking Ensemble Technique for Classifying Breast Cancer. Healthc. Inform. Res. 2019, 25, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.; Bhargava, R.; Jayabalan, M. Diagnosis of Breast Cancer on Imbalanced Dataset Using Various Sampling Techniques and Machine Learning Models.; 2021; Vol. 2021-December, pp. 162–167.
- Broman, S.; O’Hara, E.; Ali, M.L. A Machine Learning Approach for the Early Detection of Dementia.; 2022.
- Laganaro, F.; Mazza, M.; Marano, G.; Piuzzi, E.; Pallotti, A. Classification-Based Screening of Depressive Disorder Patients Through Graph, Handwriting and Voice Signals.; 2023; pp. 6–10.
- Chauhan, R.; Goel, A.; Alankar, B.; Kaur, H. Predictive Modeling and Web-Based Tool for Cervical Cancer Risk Assessment: A Comparative Study of Machine Learning Models. MethodsX 2024, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pachón Rodríguez, W.A.; Melo Martínez, C.E. Fraud Detection in Utilities Using Data Analytics and Geospatial Analysis. Int. J. Saf. Secur. Eng. 2023, 13, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Roux, D.; Pérez, B.; Moreno, A.; Del Pilar Villamil, M.; Figueroa, C. Tax Fraud Detection for Under-Reporting Declarations Using an Unsupervised Machine Learning Approach.; 2018; pp. 215–222.
- Rahul, K.; Seth, N.; Dinesh Kumar, U. Spotting Earnings Manipulation: Using Machine Learning for Financial Fraud Detection. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. Subser. Lect. Notes Artif. Intell. Lect. Notes Bioinforma. 2018, 11311 LNAI, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepa, N.; Pham, Q.-V.; Nguyen, D.C.; Bhattacharya, S.; Prabadevi, B.; Gadekallu, T.R.; Maddikunta, P.K.R.; Fang, F.; Pathirana, P.N. A Survey on Blockchain for Big Data: Approaches, Opportunities, and Future Directions. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2022, 131, 209–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saggi, M.K.; Jain, S. A Survey towards an Integration of Big Data Analytics to Big Insights for Value-Creation. Inf. Process. Manag. 2018, 54, 758–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghib, A.; Jafari Navimipour, N.; Hosseinzadeh, M.; Sharifi, A. A Comprehensive and Systematic Literature Review on the Big Data Management Techniques in the Internet of Things. Wirel. Netw. 2023, 29, 1085–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santana-Mancilla, P.C.; Castrejón-Mejía, O.E.; Fajardo-Flores, S.B.; Anido-Rifón, L.E. Predicting Abnormal Respiratory Patterns in Older Adults Using Supervised Machine Learning on Internet of Medical Things Respiratory Frequency Data. Information 2023, 14, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, A.; Wiil, U.K.; Baskaran, R.; Peimankar, A.; Andersen, K.; Nielsen, A.S. AUD-DSS: A Decision Support System for Early Detection of Patients with Alcohol Use Disorder. BMC Bioinformatics 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayakumar, J.; Kumar, H.S.; Kalyanasundaram, P.; Markkandeyan, S.; Sengottaiyan, N. An Intelligent Stacking Ensemble-Based Machine Learning Model for Heart Abnormality.; 2022.
- Appiahene, P.; Dogbe, S.S.D.; Kobina, E.E.Y.; Dartey, P.S.; Afrifa, S.; Donkoh, E.T.; Asare, J.W. Application of Ensemble Models Approach in Anemia Detection Using Images of the Palpable Palm. Med. Nov. Technol. Devices 2023, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolles, J.; Meurer, W.J. Logistic Regression: Relating Patient Characteristics to Outcomes. JAMA - J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2016, 316, 533–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, A.; Boostani, R.; Odeh, M.; AL-Mousa, M.R. Two-Layer SVM, Towards Deep Statistical Learning. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Engineering Conference on Electrical, Energy, and Artificial Intelligence (EICEEAI); November 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Rahmatillah, I.; Astuty, E.; Sudirman, I.D. An Improved Decision Tree Model for Forecasting Consumer Decision in a Medium Groceries Store. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 17th International Conference on Industrial and Information Systems (ICIIS); IEEE: Peradeniya, Sri Lanka, August 25, 2023; pp. 245–250. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, T.; Mishra, C.S.; Sampson, J.; Kandemir, M.T.; Narayanan, V. An Efficient Edge–Cloud Partitioning of Random Forests for Distributed Sensor Networks. IEEE Embed. Syst. Lett. 2024, 16, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijay, V.; Verma, P. Variants of Naïve Bayes Algorithm for Hate Speech Detection in Text Documents. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Smart Communication (AISC); IEEE: Greater Noida, India, January 27, 2023; pp. 18–21. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, M.; Thacker, C.; Goswami, L.; Tr, T.; Abdulrahman, I.S.; Raj, A.S. Alzheimer’s Disease Detection Using Weighted KNN Classifier in Comparison with Medium KNN Classifier with Improved Accuracy. In Proceedings of the 2023 3rd International Conference on Advance Computing and Innovative Technologies in Engineering (ICACITE); IEEE: Greater Noida, India, May 12, 2023; pp. 715–718. [Google Scholar]
- Shivaji Rao, S.S.; Gangadhara Rao, K. Diagnosis of Liver Disease Using ANN and ML Algorithms with Hyperparameter Tuning. In Proceedings of the 2024 2nd International Conference on Intelligent Data Communication Technologies and Internet of Things (IDCIoT); IEEE: Bengaluru, India, January 4, 2024; pp. 629–634. [Google Scholar]
- Cengiz, K.; Lipsa, S.; Dash, R.K.; Ivković, N.; Konecki, M. A Novel Intrusion Detection System Based on Artificial Neural Network and Genetic Algorithm With a New Dimensionality Reduction Technique for UAV Communication. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 4925–4937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, S.P.; Sudha, I. A Novel Logistic Regression in Coronary Artery Disease Prediction and Comparison of XGBoost Classifier for Improved Accuracy. In Proceedings of the 2023 Intelligent Computing and Control for Engineering and Business Systems (ICCEBS); IEEE: Chennai, India, December 14, 2023; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Garg, K.; Gill, K.S.; Malhotra, S.; Devliyal, S.; Sunil, G. Implementing the XGBOOST Classifier for Bankruptcy Detection and Smote Analysis for Balancing Its Data. In Proceedings of the 2024 2nd International Conference on Computer, Communication and Control (IC4); IEEE: Indore, India, February 8 2024; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Varma, B.S.S.; Kalyani, G.; Asish, K.; Bai, M.I. Early Detection of Alzheimer’s Disease Using SVM, Random Forest & FNN Algorithms.; 2023.
- Selvi, S.S.; Barkur, P.; Agarwal, N.; Kumar, A.; Mishra, Y. Time Series Based Models for Corona Data Analytics.; 2022.
- Kim, M.; Kim, J.; Qu, J.; Huang, H.; Long, Q.; Sohn, K.-A.; Kim, D.; Shen, L. Interpretable Temporal Graph Neural Network for Prognostic Prediction of Alzheimer’s Disease Using Longitudinal Neuroimaging Data.; 2021; pp. 1381–1384.
- Chen, R.; Stewart, W.F.; Sun, J.; Ng, K.; Yan, X. Recurrent Neural Networks for Early Detection of Heart Failure from Longitudinal Electronic Health Record Data: Implications for Temporal Modeling with Respect to Time before Diagnosis, Data Density, Data Quantity, and Data Type. Circ. Cardiovasc. Qual. Outcomes 2019, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaliappan, J.; Bagepalli, A.R.; Almal, S.; Mishra, R.; Hu, Y.-C.; Srinivasan, K. Impact of Cross-Validation on Machine Learning Models for Early Detection of Intrauterine Fetal Demise. Diagnostics 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, L.K. ; Pooja; Garg, H. ; Khanna, M. An IoT Based Predictive Modeling for Glaucoma Detection in Optical Coherence Tomography Images Using Hybrid Genetic Algorithm. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 37203–37242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Martino, F.; Delmastro, F.; Dolciotti, C. Malnutrition Risk Assessment in Frail Older Adults Using M-Health and Machine Learning.; 2021.
- Nasim, S.; Almutairi, M.S.; Munir, K.; Raza, A.; Younas, F. A Novel Approach for Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Prediction Using Machine Learning in Bioinformatics. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 97610–97624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ain Nazir, N.U.; Shaukat, M.H.; Luo, R.; Abbas, S.R. Novel Breath Biomarkers Identification for Early Detection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Cirrhosis Using ML Tools and GCMS. PLoS ONE 2023, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oladimeji, O.O.; Oladimeji, A.; Olayanju, O. Machine Learning Models for Diagnostic Classification of Hepatitis C Tests. Front. Health Inform. 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambay, M.A.; Mohideen, S.P. Applying Data Science Approach to Predicting Diseases and Recommending Drugs in Healthcare Using Machine Learning Models – A Cardio Disease Case Study. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-M.; Chen, P.-C.; Lin, W.-C.; Hung, K.-C.; Chen, Y.-C.B.; Hung, C.-F.; Wang, L.-J.; Wu, C.-N.; Hsu, C.-W.; Kao, H.-Y. Predicting New-Onset Post-Stroke Depression from Real-World Data Using Machine Learning Algorithm. Front. Psychiatry 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathis, M.R.; Engoren, M.C.; Joo, H.; Maile, M.D.; Aaronson, K.D.; Burns, M.L.; Sjoding, M.W.; Douville, N.J.; Janda, A.M.; Hu, Y.; et al. Early Detection of Heart Failure With Reduced Ejection Fraction Using Perioperative Data Among Noncardiac Surgical Patients: A Machine-Learning Approach. Anesth. Analg. 2020, 130, 1188–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Maheshwari, S.; Sharma, A.; Linda, S.; Kumar, S.; Chatterjee, I. Ensemble Learning-Based Early Detection of Influenza Disease. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 5723–5743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, J.; Zhang, Y. Brain MRI Analysis for Alzheimer’s Disease Diagnosis Using an Ensemble System of Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Brain Inform. 2018, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Krishna, T.A.; Adeeb, M. Cough Sound Based COVID-19 Detection with Stacked Ensemble Model.; 2022; pp. 1391–1395.
- Nesvijevskaia, A.; Ouillade, S.; Guilmin, P.; Zucker, J.-D. The Accuracy versus Interpretability Trade-off in Fraud Detection Model. Data Policy 2021, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadesse, T. Combining Control Rules, Machine Learning Models, and Community Detection Algorithms for Effective Fraud Detection.; 2022; pp. 42–46.
- Hao, Y.; Qiu, F. Research on the Application of DM Technology with RF in Enterprise Financial Audit. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2022, 2022, e4051469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, N.; Panigrahi, S. A Comparative Analysis of Fraud Detection in Healthcare Using Data Balancing & Machine Learning Techniques.; 2023.
- Aggarwal, R.; Sarangi, P.K.; Sahoo, A.K. Credit Card Fraud Detection: Analyzing the Performance of Four Machine Learning Models.; 2023; pp. 650–654.
- El Barakaz, F.; Boutkhoum, O.; Hanine, M.; El Moutaouakkil, A.; Rustam, F.; Din, S.; Ashraf, I. Optimization of Imbalanced and Multidimensional Learning Under Bayes Minimum Risk and Savings Measure. Big Data 2022, 10, 425–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soleh, M.; Djuwitaningrum, E.R.; Ramli, M.; Indriasari, M. Feature Engineering Strategies Based on a One-Point Crossover for Fraud Detection on Big Data Analytics.; 2020; Vol. 1566.
- Kumari, P.; Mittal, S. Fraud Detection System for Financial System Using Machine Learning Techniques: A Review.; 2024.
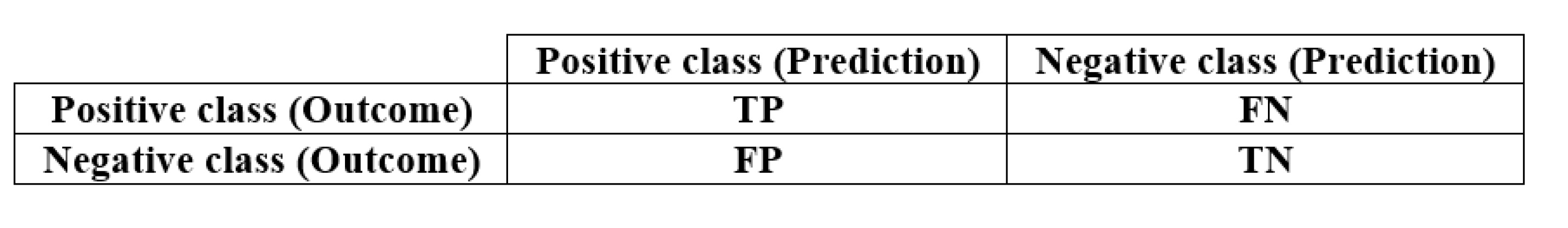
| Metric | Description | Formulation |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | Proportion of correct predictions out of the total predictions made by the model. | |
| Precision | Proportion of true positives (TP) over the sum of true positives and false positives (FP). | |
| Recall (Sensitivity) | Proportion of true positives to the sum of true positives and false negatives (FN). | |
| Specificity | Proportion of true negatives (TN) over the sum of true negatives and false positives (FP). | |
| F1-Score | It is the harmonic mean of precision and recall. | |
| AU-ROC | ROC chart represents the true positive rate (TPR) versus the false positive rate (FPR) at various thresholds. A higher AU-ROC indicates better model performance. | (TPR) Vs (FPR) |
| AU-PRC | PRC chart shows the relationship between precision (P) and recall (R) for different classification thresholds of the model. A higher AU-PRC indicates better model performance. | (P) Vs (R) |
| MCC | Correlation between true classes and predicted labels. |
| Model | Description |
|---|---|
| LR[38] | A statistical model used to analyze the relationship between a dependent variable (binary outcome) and one or more independent variables. It is commonly used for binary classification tasks where the outcome variable is categorical with two possible outcomes. Logistic regression estimates the probability that a given input belongs to a specific category by fitting the data to a logistic function, which transforms the outcome into an interval between 0 and 1. |
| SVM[39] | A supervised machine learning algorithm used for classification and regression tasks. SVM works by finding the optimal hyperplane that best separates data points into different classes in a high-dimensional space. Its goal is to maximize the margin between the classes, making it effective for both linear and non-linear classification problems. SVM can handle high-dimensional data and is known for its ability to generalize well to unseen new data. |
| DT[40] | A machine learning algorithm used for classification and regression tasks. It is a tree-shaped model where internal nodes represent features, branches represent decisions based on those features, and leaf nodes represent the outcome or decision. The algorithm recursively splits the data based on the most significant feature at each node, aiming to create homogeneous subsets. Decision trees are easy to interpret and visualize, making them valuable for understanding the decision-making process in a model. It can handle both numerical and categorical data, making them versatile for various types of datasets. |
| RF[41] | A machine learning algorithm composed of multiple decision trees. Each tree is built using bootstrapping and random feature selection to create an ensemble of uncorrelated trees, resulting in more accurate predictions than individual trees. The algorithm leverages the concept of collective knowledge, where the forest of decision trees works together to make predictions, and the final prediction is based on the majority vote of the trees. |
| NB[42] | A probabilistic classifier based on the application of Bayes' theorem. It assumes that the presence of a particular feature in a class is not related to the presence of any other feature. Despite their simplicity, Naive Bayes classifiers are known for their efficiency and effectiveness in various classification tasks, especially in text classification and spam filtering. |
| KNN[43] | A machine learning algorithm used for classification and regression tasks. In KNN, the class or value of a data point is determined by the majority class or the mean value of its nearest neighbors in the feature space. The algorithm calculates the distance between data points and classifies them based on the majority class of the nearest k data points. |
| ANN[44,45] | A computational model inspired by the structure and functioning of the neural networks in the human brain. ANNs consist of interconnected nodes, known as artificial neurons, that process information and learn patterns from data. These networks are used in machine learning and deep learning to solve complex problems such as pattern recognition, classification, and regression, among others. |
| XGBoost[46,47] | A model that uses gradient boosting to optimize the loss function and handle complex patterns in data. XGBoost is widely used for classification, regression, and ranking tasks due to its speed, accuracy, and ability to handle large datasets efficiently. It uses decision trees as base models and trains them sequentially. XGBoost in some cases is considered a base model grounded in DT. |
| Ref. | Application | *: Best Model - +: Other Models | Evaluation Metric | Area | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LR | SVM | DT | RF | NB | KNN | ANN | XGB | + | ||||
| [48] | Alzheimer’s disease Detection | x | x | *x | ACC:88% | Medicine | ||||||
| [49] | Forecasting coronavirus | x | x | *x | 1PR | RMSE:78 | ||||||
| [50] | Prognostic prediction of Alzheimer's disease | x | x | *x | ACC:53.5% | |||||||
| [51] | Predict the early onset of heart failure | x | x | *x | AUC:77% | |||||||
| [18] | breast cancer, heart disease, and diabetes detection | x | x | *x | x | ACC > 90% | ||||||
| [52] | Intrauterine Fetal Demise detection | x | x | x | x | x | x | *2GB | ACC:99% | |||
| [34] | Predicting Abnormal Respiratory Patterns in Older Adults | x | x | *2GB | ACC:100% | |||||||
| [17] | Detection and Accurate Classification of Type 2 Diabetes | x | x | x | x | *x | ACC:79.6% | |||||
| [26] | Classification-based screening of Depressive Disorder patients through graph, handwriting and voice signals | x | *x | ACC:78.13% | ||||||||
| [53] | Glaucoma recognition | x | x | *x | x | ACC:99% | ||||||
| [22] | Early detection of breast cancer | *x | x | x | x | x | x | ACC:95.4% | ||||
| [54] | Malnutrition Risk Assessment in Frail Older Adults | *x | x | x | x | 3AB | ACC > 90% | |||||
| [55] | Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Prediction | x | x | x | x | x | *4GNB,2,5 | ACC:100% | ||||
| [25] | Early Detection of Dementia | x | *x | x | x | ACC:100% | ||||||
| [14] | early detection of complications after pediatric appendectomy | x | x | *x | x | x | x | 2,3,5 | AUCROC:80% | |||
| [56] | Early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma and cirrhosis | *x | ACC:80% | |||||||||
| [21] | Predicting Heart Disease | x | x | *x | x | ACC:94.15% | ||||||
| [57] | diagnostic classification of hepatitis C tests | x | x | *x | x | x | ACC:98.9% | |||||
| [58] | Prediction of diseases and recommending drugs in healthcare | x | x | *x | x | 5,2 | ACC:96.26% | |||||
| [2] | Prediction of Heart Attack | *x | x | x | ACC:85% | |||||||
| [8] | Prediction of platinum resistance in ovarian cancer treatment | *x | x | AUC>96% | ||||||||
| [59] | Prediction of post-stroke depression | *x | ACC>81% | |||||||||
| [60] | Early Detection of Heart Failure | x | x | *x | ACC:80.82% | |||||||
| [27] | Early detection of cervical cancer | x | x | x | x | *x | 3 | AUCROC:91.2% | ||||
| [3] | Prediction of stochastic Climate factors | *x | RMSE:7.029 | Energy | ||||||||
| [13] | Power Transformer Fault Detection | x | x | x | x | x | x | *6GP | ACC>80% | |||
| [6] | Tail biting outbreaks predictions in pigs using feeding behaviors records | x | x | *x | x | ACC:96% | Agronomy | |||||
| [12] | Prediction of biological species invasion | x | x | *x | x | x | 2 | ACC:89% | ||||
| [9] | Production line sampling prediction | *x | ACC:84% | Industry | ||||||||
| [4] | Predict failures in the production line. | *7IF | TPR:66.7% | |||||||||
| [5] | Fraud Detection on Streaming Customer Behavior Data | *8DS | ACC:99% | Telecom | ||||||||
| [7] | Predict student academic performance | x | x | x | x | *x | 3,5 | ACC:97.12% | academy | |||
| FREQUENCY MODEL | 13 | 18 | 14 | 19 | 8 | 18 | 11 | 9 | ||||
| FREQUENCY AS BEST MODEL | 2 | 2 | 1 | 8 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 4 | ||||
| Ref. | Application | Base Learners | Best Meta Learner | Evaluation Metric | Area | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LR | SVM | DT | RF | NB | KNN | ANN | XGB | + | |||||
| [61] | Detection of infuenza disease | x | x | x | x | x | 9 | SVM | ACC:84.7% | Medicine | |||
| [10] | Early Detection of Breast Cancer | x | x | x | x | 10 | 11DSS | ACC:96.2% | |||||
| [23] | Classification of Breast Cancer | x | x | 2,12GLM | GLM | ACC:97.34% | |||||||
| [62] | Brain MRI analysis for Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis | x | ANN | ACC:93% | |||||||||
| [37] | Detection using images of the palpable palm | x | x | x | x | x | NB | ACC:99.73% | |||||
| [16] | predicting emergency readmission of heart-disease patients | x | x | x | x | x | x | XGB | ACC:88% | ||||
| [35] | early detection of patients with alcohol use disorder | x | x | x | x | x | 13LIR | ACC:98% | |||||
| [19] | Diabetes prediction | x | 3,13GBT | GBT | ACC:83.9% | ||||||||
| [36] | Heart abnormality detection | x | x | x | x | 15CB | LR | AUCROC:92% | |||||
| [63] | Cough Sound based COVID-19 Detection | x | x | x | LR | ACC:79.86% | |||||||
| [20] | Early Diabetes Prediction | x | 3,14 | LR | ACC:96% | ||||||||
| [24] | Diagnosis of Breast Cancer | x | x | x | LR | AUC>72% | |||||||
| FREQUENCY MODEL | 5 | 5 | 6 | 9 | 2 | 5 | 4 | 4 | |||||
| Ref. | Application | *: Best Model - +: Other Models | Evaluation Metric | Area | ||||||||
| LR | SVM | DT | RF | NB | KNN | ANN | XGB | + | ||||
| [28] | Fraud detection in utility companies | x | *x | x | x | x | x | x | 16CART | ACC:62.3% | Fraud | |
| [66] | Enterprise Financial Audit | x | *x | x | ACC:84.35% | |||||||
| [67] | Analysis of Fraud Detection in Healthcare | x | x | x | *x | ACC:74.8% | ||||||
| [68] | Credit Card Fraud Detection | x | x | *x | x | ACC:100% | ||||||
| [69] | Fraud detection problem in credit cards | x | x | x | *15 | ACC>90% | ||||||
| [1] | Big Data Analytics for Credit Card Fraud Detection | x | *x | 2,3 | ACC:96.29% | |||||||
| [65] | Fraud in financial institutions | x | *x | x | 5 | ACC:98% | ||||||
| [64] | Fraud detection in financial and banking systems | x | x | x | x | x | x | *x | 13 | ACC:6.7% | ||
| [70] | Fraud Detection in Credit card and Transactions | x | x | x | *16 | ACC:96% | ||||||
| [29] | Detection of under-declarations in tax payments | *17SC | ACC:58% | |||||||||
| [30] | Detection in earnings manipulation in financial firms | x | x | *3 | AUCROC: 74.4% | |||||||
| FREQUENCY MODEL | 5 | 5 | 3 | 8 | 3 | 6 | 3 | 5 | ||||
| FREQUENCY AS BEST MODEL | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





