1. Introduction
Interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR) is a promising geodetic tool which enables geophysical and hazard studies with a very large spatial coverage unprecedented by any other geodetic technique. Since its first utilization of achieving ground motion measurement by Gabriel et al. (1989), applications of InSAR for deformation monitoring have been developed (Dong et al., 2019; Shamshiri et al., 2020; Yang et al., 2021a). Nowadays, InSAR technique can measure surface deformation on the mm/yr scale, which has been proved to be particularly valuable for studies of slow tectonic movement over strike-slip fault zone within interseismic period, such as the San Andreas (Ryder and Bürgmann, 2008; Chaussard et al., 2016; Jin et al., 2017), North Anatolian (Cakir et al., 2005; Rousset et al., 2016; Aslan et al., 2019), Altyn Tagh (Zhu et al., 2016; Xu and Zhu, 2019), Xianshuihe (Ji et al., 2020; Li and Bürgmann, 2021; Qiao and Zhou, 2021), Haiyuan (Cavalie et al., 2008; Jolivet et al., 2012; Song et al., 2019), and Shahroud (Mousavi et al., 2015; Tong et al., 2018) faults.
Orbital errors commonly exist in the produced interferograms from classical InSAR processing, which is traditionally considered as the principal limitation of InSAR technique for measuring slow tectonic displacements (Fattahi and Amelung, 2014). The most-used method of mitigating the effect of orbital errors is the linear or quadratic approximation that best fits the observed interferometric phases (Massonnet and Feigl, 1998). This approach is effective in measurements of glacier, volcano, and coseismic motions, however, it is inadequate for studies of interseismic tectonic movements. Because both orbital errors and interseismic tectonic deformation are characterized as the long-wavelength phase patterns, that is, there is no true “far-field” which is not affected by tectonic deformation and can be used to estimate the linear or quadratic orbital surface.
More accurate methods are developed to reduce the orbital errors. Biggs et al. (2007) develop a network orbital correction approach based on multiple interferograms. And correcting long-wavelength phase contributions in time-domain has been conducted (Gourmelen et al., 2010; Fattahi and Amelung 2014). However, these methods have the general drawback that all long-wavelength phase patterns are treated as orbital errors, thus such attempt of removing orbital ramps will also mitigate the interseismic tectonic deformation signals. Then, it is verified that long-wavelength deformation can be efficaciously separated from the mixed phase signals based on GPS measurements (Lundgren et al., 2009; Wei et al., 2010; Wang and Wright, 2012), but this means makes the InSAR results dependent on GPS. With a model assumption about the deformation, Biggs et al. (2007) use a three-stage iterative algorithm to separate deformation from orbital errors. This approach has been widely used in subsequent studies (Lin et al., 2010; Zhu et al., 2016; Barnhart, 2017), while, it is also worth pointing out that the derived deformation relies on the assumption about the fault geometry heavily.
Although orbital error reduction has been explored for more than two decades and several methods for reducing orbital contribution are already in existence, the errors cannot always be efficiently removed. Abnormal long-wavelength signals are remained around the northeastern corner of the SAR coverage in the shown descending velocity field by Qiao and Zhou (2021), which could be attributed to the inaccuracy of their estimated orbital ramp by using only the data from the western side of the Xianshuihe fault. Although Zhao et al. (2022) correct the orbital errors by temporal filtering, significant irregular signals are still remained. Similar phenomenon can be found in the InSAR observations given in the study by Jian et al. (2022), the observed deformation rates change along the diagonal from southwest to northeast, characterizing as long-wavelength signal pattern. This suggests that the orbital errors are not efficiently removed.
The primary goal of this study is to develop a novel approach for jointly estimating orbital errors and tectonic rigid block motions from multiple SAR interferograms without ancillary data. Utilizing this improved temporal network orbital correction method, the long-wavelength orbital errors can be effectively mitigated from the preliminary InSAR observations, after which the subtle interseismic ground velocities could be precisely extracted from multiple interferometric pairs. Both simulated data and real SAR images acquired by the Sentinel-1 satellite that cover the Tuosuo Lake segment of the Kunlun fault are used to assess the performance of the proposed method.
2. Methodology
The orbital errors in individual interferogram can be assumed to be random (Biggs et al., 2007), whereas, the tectonic signal is highly related to the temporal baseline of the interferogram. Their different features inspire us to come up with the proposed method. With the consensus that far-fault tectonic velocities are mainly contributed by the rigid block movements and scarcely influenced by the velocity perturbations caused by the bounding faults, our proposed method is based on the assumption that far-fault tectonic velocities can be treated as constants within limited areas (a sub-patch of the SAR coverage).
First, a critical distance is needed to separate the far-/near- fault zones. The critical distance can be determined using the simple screw dislocation model that has been extensively exploited to represent the tectonic motion along the fault (Savage and Burford, 1973; Prescott and Nur, 1981; Biggs et al., 2007; Wang et al., 2019). In this model, the rate of ground displacement in fault-parallel direction, V, at a perpendicular distance x from the fault with locking depth D and slip rate s can be expressed as. And 90% of the relative motions occur between to( Savage and Burford, 1973).
Based on the screw model, together with priori information of the specific study area including locking depth and slip rate, the fault-parallel velocityat the point that is 6.3D far from the fault can be derived, which could further be projected into the line-of-sight (LOS) direction using satellite geometry parameters (). Considering the accuracy of millimeter to centimeter level of the InSAR measurements, we here deem that the velocities with differences less than 1 mm/yr can be considered as constant, thus the distance with LOS velocity of can be treated as the critical distance to separate the far-/near- fault zones. In case the SAR measurements extend sufficiently far from the boundary fault, we recommend to enlarge the critical distance. The critical distance of 30 km is commonly accepted. However, sometimes it may be difficult to get perfect cover, but above criteria should always be implemented. The samples in the near-fault zone will not be used in further temporal network orbital correction.
Then, we remove the near-fault measurements, and divide the far-fault region into
N sub-patches. The choice of
N is variable for different research areas, which should be a comprehensive consideration of the variations in locking depths and slip rates along the bounding fault and the fluctuation of fault strikes. The only protocol is that the tectonic velocity differences of samples within each sub-patch are less than 1 mm/yr, that is, the tectonic velocities of the points within a far-fault sub-patch can be treated as constants.
Figure S1 shows the diagram of a Sentinel SAR image with its far-fault zone divided into 6 sub-patches.
The phases in the preliminary differential SAR interferograms are dominated by the orbital errors and tectonic deformation. Both orbital errors and tectonic deformation are characterized as long-wavelength phase patterns, thus, for a pixel,
P, at location [
,
], within the sub-patch
n, of the interferogram
i, a quadratic approximation is performed to fit the observed phases, as expressed as:
For individual interferogram
i with
N sub-patches, we can derive
N constants [
,
]. Each constant is consisted of two parts. One is the shift for the orbital errors, and the other is the tectonic displacement.
where,
is the far-field tectonic velocity constant for sub-patch
n,
means the temporal baseline of the interferogram
i. The former term is the orbital offset, and the latter indicates the tectonic displacement. For a system of
I interferograms, with one interferogram consisted of
N patches, there are
derived constants and
unknowns (including
I orbital offsets and
N velocity constants). The least square method can be utilized to solve the problem. Finally, [
,
] can be treated as the coefficient of the orbital quadratic approximation for interferogram
i, which can be removed from the preliminary interferogram to reduce the effects of orbital errors. Our proposed approach is able to jointly estimate the interseismic tectonic deformation and orbital errors.
3. Algorithm Testing with Synthetic Data Set
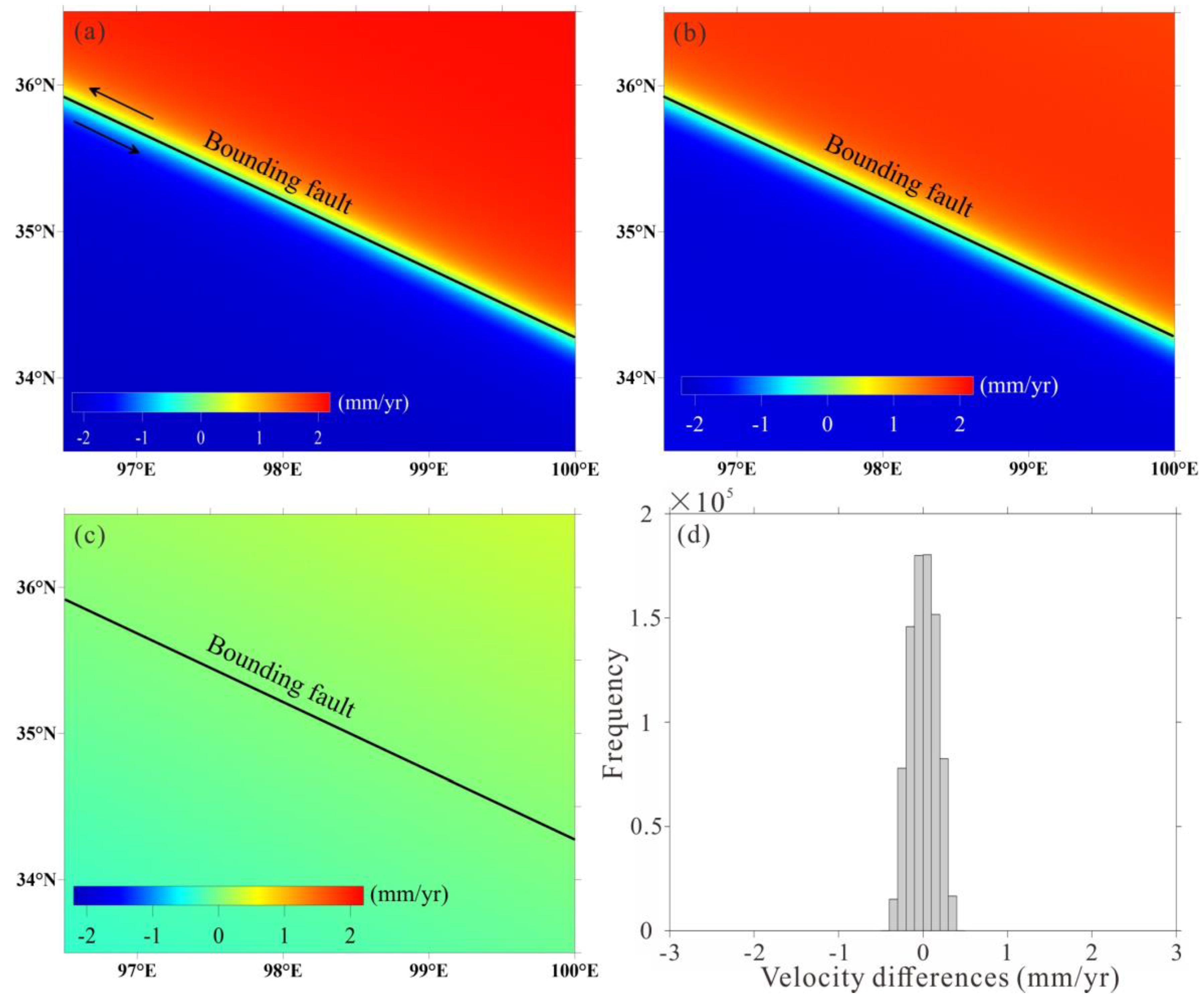
We simulate a surface velocity map along a sinistral bounding fault with a locking depth of 10.5 km and a slip rate of 9.5 mm/yr using the simple screw dislocation model. The fault-parallel deformation rate is then projected into the LOS direction based on the geometry parameters of the used ascending SAR images, and the predicted LOS velocity field is shown in
Figure 1a. The simulated LOS deformation rates vary between ±2.14 mm/yr (positive/negative means the velocity towards/away from the sensor in slant direction).
To carry out the proposed temporal network orbital correction experiment, we predict 200 interferograms using above LOS velocity over a random period within the range of [200, 2000] days, together with the orbital errors and random noises. The orbital errors are simulated by using a set of second-order polynomials, varying from 30~200 mm for different interferograms. The random noises obey the normal distribution with a mean of 1 mm and a standard deviation of 2 mm.
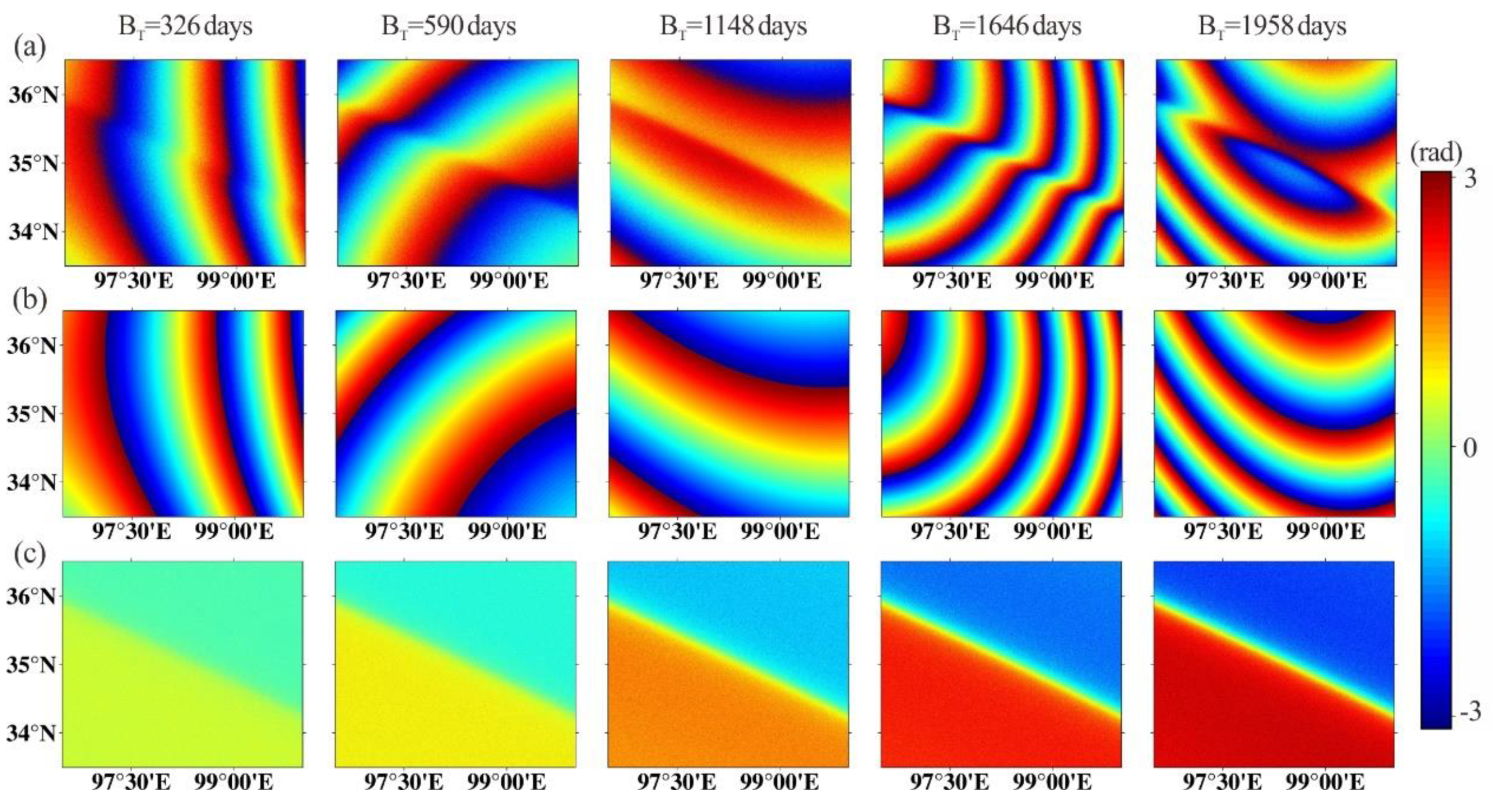
Figure 2a shows the examples of the predicted interferograms, noting the corresponding temporal baselines.
The proposed orbital correction method is applied to the simulated data sets. The simulated SAR deformation field extends pretty far from the boundary fault, hence we choose the typical critical distance of 30 km. Considering that the whole simulated fault segment shares the same locking depth and slip rate, thus there is no need to differentiate the far-field region along strike, the selection of
N= 2 is appropriate.
Figure 2b shows the corresponding estimated orbital ramps to the example interferograms mapped in
Figure 2a, and the related corrected interferograms are presented in
Figure 2c. It can be seen that after removing the estimated orbital surfaces, the distribution patterns of the remained phases in the corrected interferograms are familiar with each other, and the phase magnitudes increase with the temporal baseline.
We can derive the average velocity map by easily summing the total range changes and dividing by the total time duration of all simulated interferograms (Equation 3, Wright et al., 2001), as mapped in
Figure 1b. The calculated average LOS velocity field generally coincides with the simulated velocity map (
Figure 1a) in aspects of both distribution pattern and magnitude. The derived biggest velocity away from the satellite is 2.01 mm/yr, and the maximum deformation rate towards the satellite is 1.98 mm/yr.
To quantitatively evaluate the accuracy of the derived LOS velocity, we calculate the differences between the true values (
Figure 1a) and estimated ones (
Figure 1b), and the result is shown in
Figure 1c and
Figure 1d. It can be found that the velocity differences are quite small, with a maximum difference (absolute value) of 0.4 mm/yr and a standard deviation of 0.16 mm/yr. The histogram shown in
Figure 1d indicates that 77.4% of the velocity differences (absolute value) are less than 0.2 mm/yr.
Furthermore, we tested the performance of the proposed method in correcting orbital errors with different image partition strategies (namely different choice of
N), and the results are presented in
Figure S2. As depicted in
Figure S2a, the peak deformation rates towards and away from the satellite sensor are 1.95 mm/yr and 1.98 mm/yr, respectively, and 68.4% of the velocity differences in
Figure S2b are less than 0.2 mm/yr.
Figure S2c and S2d illustrate the solution obtained with
N=6, which exhibit the highest velocity of 1.98 mm/yr towards the satellite and a maximum of 2.00 mm/yr away from the satellite. Additionally, 73.4% of the velocity differences in the solution are smaller than 0.2 mm/yr. The three velocity maps (
Figure 1b,
Figure S2a, and
Figure S2c) generated using different values of
N (
N=2, 4, 6) exhibit a high degree of agreement, indicating that the solution is independent of the selection of
N when the locking depth and slip rate are unique along the bounding fault. It is clear from the result that our proposed temporal network orbital correction approach is able to effectively isolate the interseismic tectonic deformation signals from the orbital errors, indicating the reliability of the proposed method.
4. Interseismic Surface Deformation Monitoring along the Tuosuo Lake Segment
4.1. SAR Data and InSAR Processing
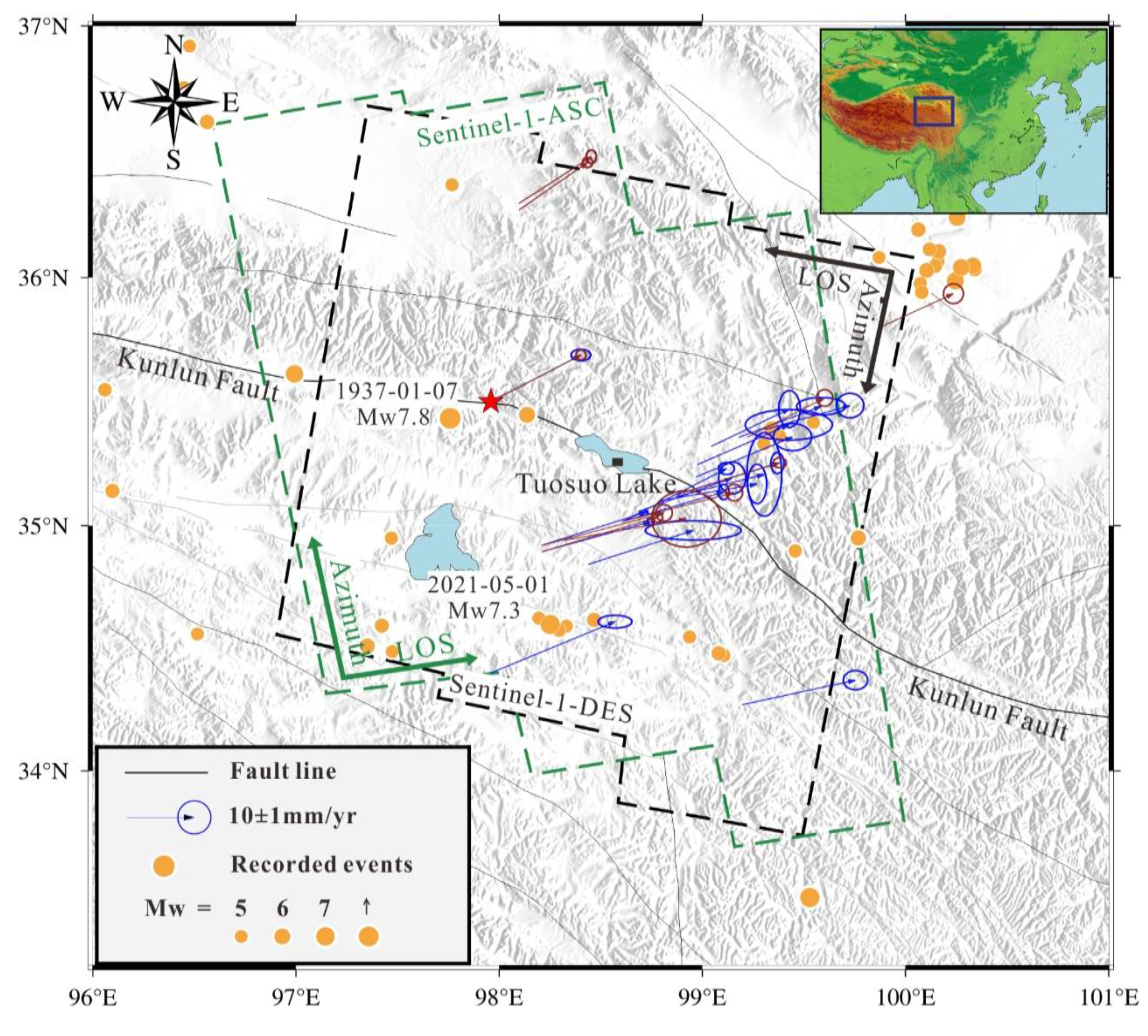
The active Kunlun Fault is one of the most important bounding faults across the Tibetan Plateau that is characterized by the left-lateral strike-slip movement (Van Der Woerd et al., 2000; Liao et al., 2003; Zhu et al., 2021; Zhao et al., 2022). In this study, we use SAR images from both Sentinel-1 ascending (T99) and descending (T106) tracks to investigate the surface deformation rates around the Tuosuo Lake segment of the Kunlun fault. The spatial coverage of the utilized radar data is shown in
Figure 3. The acquisition times of the used data are from October 2014 to May 2021. Detailed information about the derived interferograms is listed in
Table S1.
The InSAR data are processed using GAMMA software based on the two-pass differential interferometry method (Wegmüller and Werner, 1997). The simulation and removal of the topography phase are performed using the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) DEM with 30 m resolution. The multilook factors are set as 100 (in range direction) ×25 (in azimuth direction) to make the ground range and azimuth pixel spacing change into approximately 300 m×300 m. Considering that the study area characterizes the ragged topography and short baseline helps to extract accurate deformation with residual removal of topographic phase caused by the uncertainty of the used DEM (Chen et al., 2014; Xu et al., 2020; Yang et al., 2021b), thus we constrain the time interval and perpendicular baseline, as shown in
Table S2. The minimum-cost-flow (MCF) method provided by the GAMMA package is utilized to unwrap the interferograms. The Generic Atmosphere Correction Online Service for InSAR (GACOS) data are introduced to correct for atmospheric delay within the interferograms. It should be noted that we choose the interferograms that are further used in the estimation of the average velocity fields by visual inspection. Finally, there are 210 and 274 interferograms from the ascending and descending tracks preserved for forming the velocity maps.
4.2. Interseismic Velocity Field along the Tuosuo Lake Segment
The presented approach of mitigating orbital errors is also applied to the analyzing of multiple real SAR interferometric pairs along the Tuosuo Lake segment. In the orbital correction, the critical distance is also set as 30 km due to the prefect cover of the used Sentinel SAR images. Comprehensively considering the priori information including the variations of locking depths and slip rates along the Tuosuo Lake segment from previous study by Zhao et al. (2022) and the differences of fault strikes in different fault parts (Styron and Pagani, 2020) within the SAR coverage, we divide the far-fault region of the used SAR images into 6 sub-patches. The examples of ascending/descending interferograms before/after the orbital correction are shown in
Figure 4. It is shown that the tectonic signals can be well isolated from the orbital errors even though the orbital errors are much more significant than the tectonic deformation, verifying the effectiveness and applicability of our developed method.
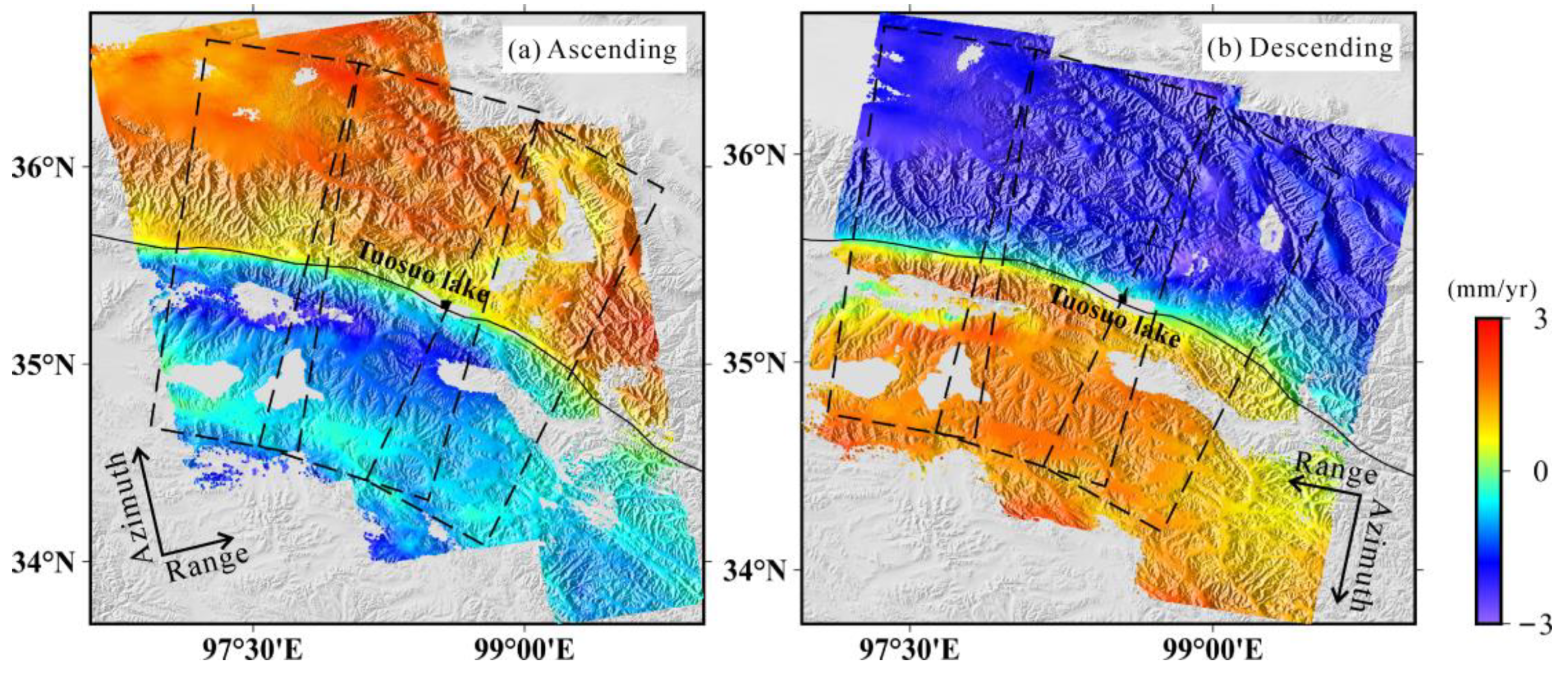
The average velocity maps along the Tuosuo Lake segment are formed by stacking the phase changes of multiple interferometric pairs. The derived average velocity fields from both ascending and descending tracks are shown in
Figure 5. The LOS velocities measured in two different satellite-viewing geometries have opposite signs across the Kunlun fault, which suggests that the crustal deformation within SAR coverage is mainly dominated by the horizontal motion. This is qualitatively in accordance with the predominant left-lateral strike-slip motion along the Kunlun fault. Significant offsets between the far fields on both sides of the Tuosuo Lake segment can be seen, with velocity differences of 2–4 mm/yr.
5. Discussion
For the strike-slip Kunlun fault (fault-normal motion can be neglected), the LOS observations from ascending and descending tracks can be decomposed into the fault-parallel and vertical components:
where,
and
are the LOS measurements from the ascending and descending InSAR tracks, respectively,
S is the strike angle,
and
indicate the heading angles,
and
mean the incidence angles,
and
are the fault-parallel and vertical motion components.
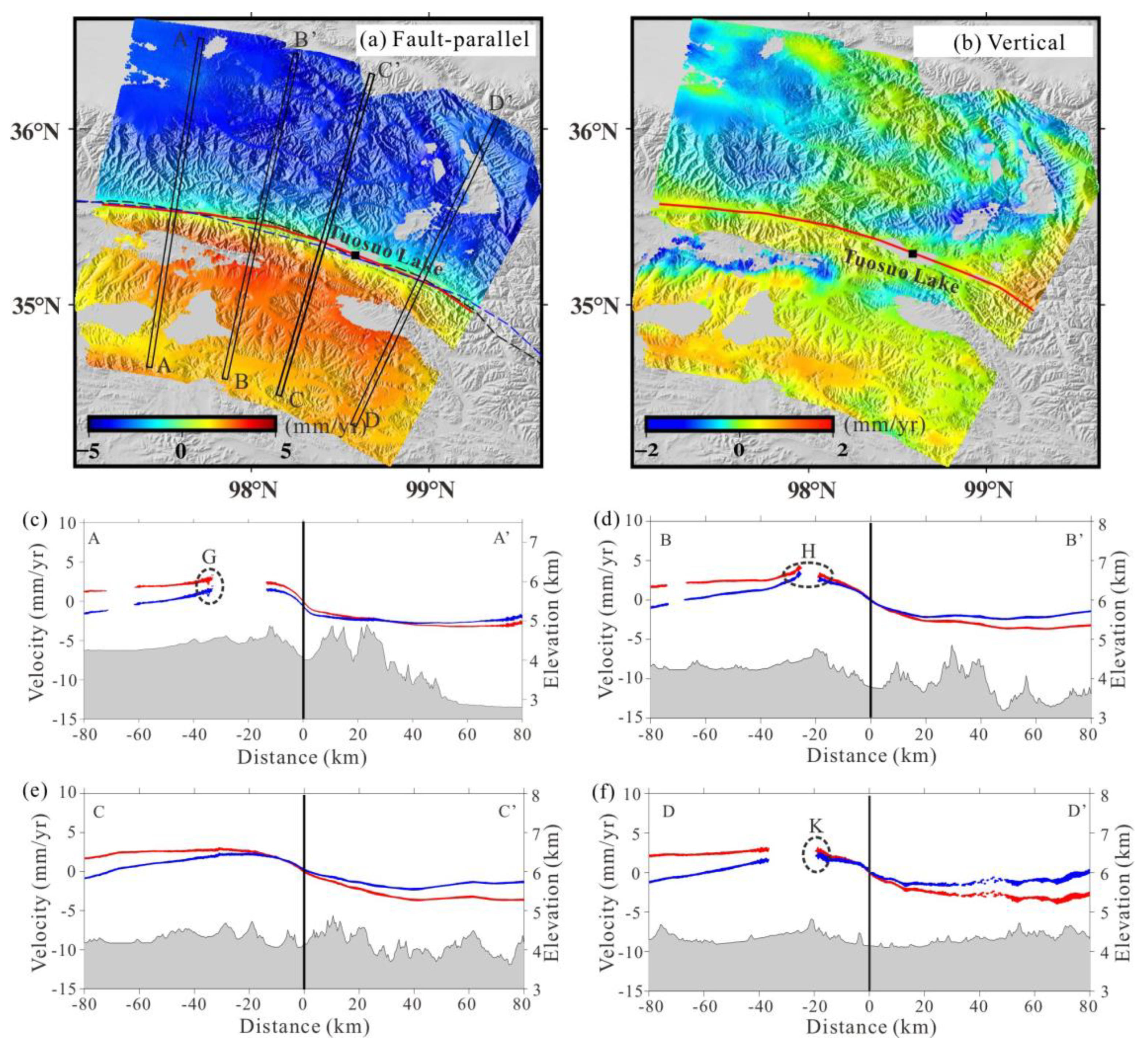
However, the variation of strikes along the Tuosuo Lake segment is significant. Thus, we divide the LOS velocity field into three patches (marked by dashed rectangles in
Figure 5 and
Figure S3), and the average strike angle of each patch is 99°, 110° and 120° from west to east. All patches share the width of 170 km, extending for 85 km on either side of the Kunlun fault. Based on Equation 4, we can obtain the velocity fields of the fault-parallel and vertical components, as shown in
Figure 6. As shown in
Figure 6a, the velocity differences of the far-field fault-parallel velocities (~50 km away from the fault) across the fault are found to be 5–6 mm/yr, which are in accordance with the velocities estimated by Jian et al. (2022), but slightly smaller than those reported in the study by Zhao et al. (2022) at the same region.
The vertical component shown in
Figure 6b suggests that the vertical movements around Tuosuo Lake fault segment are insignificant compared with the horizontal motions. For the northeast side, both tiny subsidence and uplift are shown in our result, which is consistent with the solution by Zhao et al. (2022). We found slight uplift on the southwestern flank of the fault, with an average magnitude of ~1 mm/yr. However, the study by Zhao et al. (2022) shows subsidence with an average magnitude of ~2 mm/yr in the same region. This may be attributed to probable errors in data processing using different sets of SAR acquisitions and different analyzing methods (Stacking in our study and Persistent Scatterer (PS) method in Zhao’s study) of multiple interferograms in these two studies. It should be noted that the precision of the LOS velocity solved by Zhao et al. (2022) is poor, with an uncertainty of up to 5 mm/yr. Hao et al. (2014) presents the vertical motion rates obtained from precise leveling measurements across the eastern margin of the Tibeten Plateau. Despite having a significantly smaller number of leveling points compared to InSAR observations, their results show an uplift signal of 1–2 mm/yr (with an uncertainty of 1–2 mm/yr) on the southwestern flank of the Tuosuo Lake segment, which is consistent with the findings of this study. However, there are no leveling observation points available in the same region on the northeastern side, making comparison impossible.
We quantify the uncertainties of the estimated LOS velocity maps by using bootstrapping. A detailed description of this process can be found in Text S1. The pixel-by-pixel standard deviation of the velocity maps from the ascending and descending tracks are shown in
Figures S3a and S3b, which suggest that the uncertainties of the two tracks are tiny, with a peak value of 0.16 mm/yr and 0.12 mm/yr, respectively. And the derived uncertainties of fault-parallel and vertical velocity fields are mapped in
Figures S3c and S3d. The maximum uncertainty of the fault-parallel and vertical deformation components is less than 0.3 mm/yr, suggesting the high precision of our derived velocity fields.
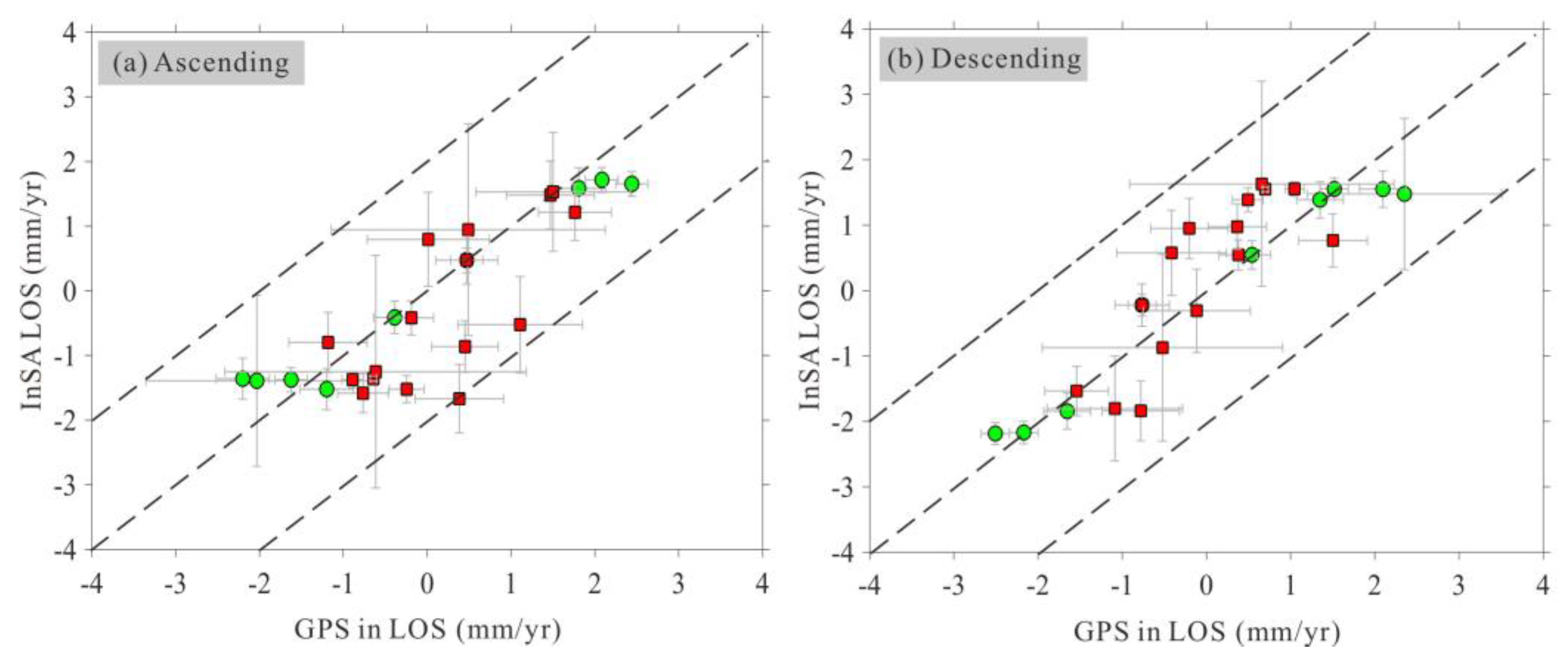
Meanwhile, the comparison of the InSAR-derived and GPS-derived velocities is addressed. The GPS data utilized in this study were obtained from two sources: the first group was collected by Wang and Shen (2020), while the second group was collected by Diao et al. (2019). The red arrow vectors shown in
Figure 3 represent the first group of GPS velocities, which are widely dispersed, while the blue arrow vectors represent the second group of GPS velocities, which are mainly concentrated along a single profile. Wang and Shen (2020) generated a comprehensive GPS velocity field for the entire Chinese mainland, incorporating both continuous and campaign stations, resulting in a rich dataset. Diao et al. (2019) mainly utilized campaign stations in their analysis. Hence, a reference point was chosen (marked by a red star in
Figure 3) to align the second group of GPS data with the reference frame of the first group. The spatial relationship between the GPS data and the coverage of the ascending and descending InSAR tracks is also illustrated in
Figure 3. To facilitate comparison, we should convert the GPS horizontal velocity to the LOS direction (LOS
GPS) based on the satellite geometry parameters, and the result is shown in Figure7.
It can be easily observed that the dots in
Figure 7(b) are more concentrated along the diagonal line of the map compared to those in
Figure 7(a). The majority of differences in LOS
GPS and descending InSAR LOS are less than 1.0 mm/yr, with a maximum difference of 1.2 mm/yr (
Figure 7b). In
Figure 7(a), we can see that velocity differences at four stations are larger than 1.0 mm/yr, and the peak value is approximately 2 mm/yr. The RMSE value between the ascending InSAR and LOS
GPS is 0.8 mm/yr, slightly bigger than that of 0.6 mm/yr between the descending InSAR and LOS
GPS. The low RMS values confirm the high consistency between the LOS
GPS and InSAR LOS, and the agreement between the LOS
GPS and descending InSAR is stronger than that with ascending InSAR. Meanwhile, the green dots are more concentrated along the diagonal line of the map than the red dots and all the stations with velocity difference larger than 1.0 mm/yr are colored in red, confirming a higher consistency between the InSAR and LOS
GPS from Wang and Shen (2020) than those from Diao et al. (2019).
In the study by Jian et al. (2022), the comparison between LOSGPS (the same GPS groups as we used) and their derived descending InSAR LOS measurements result in an RMSE value of 1.9 mm/yr, more than triple our results. It should be noted that Jian et al. (2022) only show the descending InSAR velocity map, both of us use GACOS data to correct the atmospheric delay, however Jian et al. (2022) do not introduce the way they used for mitigating orbital errors. The more robust agreement between LOSGPS and our derived InSAR velocities further verify the precision of our InSAR measurements and the efficiency of our proposed method of reducing orbital errors.
To further illustrate the different performances of our proposed method and traditional quadratic approximate in extracting interseismic ground velocities, we generated another set of average rate maps (named as LOS
T) based on interferograms with orbital correction by the traditional quadratic approximate, using the same interferometric pairs and same stacking method, and the result is shown in
Figure S4. The sharp deformation rate gradients can still be recognized in the vicinity of the fault. In the ascending (
Figure S4a) and descending (
Figure S4b) LOS rate fields, movements away from and toward the satellite are simultaneously observed on one flank of the fault. Additionally, movements along and in the opposite direction to the fault strike are simultaneously seen on the same flank of the fault in the fault-parallel velocity map (
Figure S4c). This indicates that the tectonic movement and orbital error contributions cannot be effectively separated in the far-field region, using the traditional quadratic approximation.
For a more direct comparison between the two results, we draw the velocity profiles from InSAR measurements derived by two different orbital correction strategies, and the result can be seen in
Figure 6(c-f) with red velocity profiles from
Figure 6(a) and blue ones from
Figure S4(c). Four sub-figures depict a consistent pattern wherein the red and blue profiles converge when approaching the fault line and diverge when moving away from it. This suggests the two orbital correction methods show comparable performance in the near-fault region but significant differences in the far-field. For the blue profiles, ground velocity approximates zero in the vicinity of the fault, then gradually increases within 20 km from the fault line. After reaching maximum velocity, it gradually decreases in the far-field, followed by the occurrence of opposite movements. The surface velocity variation trend depicted in the blue profiles diverges from the typical inverse tangent deformation distribution observed in interseismic period. For the red profiles, the deformation rate also approaches zero around the fault line and gradually increases within 30 km from it, finally stabilizing in the far-field, exhibiting the inverse tangent deformation distribution.
With the precise fault-parallel velocity map (Figure 8a), we can first manually extract the fault trace within the SAR coverage by finding the maximum InSAR deformation rate gradient. It is shown that the extracted fault trace is in good agreement with previously published fault traces (Deng et al., 2003; Styron and Pagani, 2020), which further indicates the accuracy of our derived velocity fields to some extent.
6. Conclusions
A novel temporal network orbital correction method has been proposed, focusing on isolating the interseismic tectonic deformation from the orbital ramps. The distinctive advantage of our developed algorithm is that the joint estimation of orbital errors and tectonic deformation is performed in spatial domain, without ancillary data. The quantitative assessment using the synthetic data verifies the reliability of the proposed method, and the experiment with real ascending/descending SAR images confirms its effectiveness and applicability. Even though the probable orbital errors are much more significant than the tectonic deformation signals, our proposed method of reducing orbital errors works well. The presented simple but efficacious approach enhances the availability of InSAR technology for precisely measuring slow interseismic crustal deformation.
The precise InSAR-derived deformation rate maps clearly indicate that the deformation field around the Tuosuo Lake segment of the Kunlun fault is predominantly contributed by the left-lateral strike-slip motions. The fault-parallel velocity differences of 5-6 mm/yr across the fault between areas ~50 km away from the fault trace are addressed. The clear comparison between the traditional quadratic approximate and our algorithm indicates that two different methods show comparable performance in the near-fault region but significant differences in the far-field. Our derived InSAR deformation rate and the published GPS velocity are in a good agreement, and the RMSE between the LOSGPS and our derived descending InSAR LOS is reduced to less than one-third of the previous study, further verifying the precision of our measurements and efficiency of the proposed orbital correction method.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on
Preprints.org.
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the Applied Basic Research Program of Science and Technology Department of Sichuan Province (2020YJ0116), the Open Funding Project of State Key Laboratory of Geohazard Prevention and Geoenvironment Protection (SKLGP2020K019), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, Grant no. 24CAFUC04033. The Sentinel-1 images were provided by the ESA (European Space Agency), and were processed by the GAMMA software [Wegmüller and Werner, 1997]. Most of the figures were plotted with Generic Mapping Tool (GMT) software provided by Wessel and Smith (1998).
References
- Aslan, G.; Lasserre, C.; Cakir, Z.; Ergintav, S.; Özarpaci, S.; Dogan, U.; Renard, F. Shallow creep along the 1999 Izmit Earthquake rupture (Turkey) from GPS and high temporal resolution interferometric synthetic aperture radar data (2011–2017). Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth 2019, 124, 2218–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnhart, W.D. Fault creep rates of the Chaman fault (Afghanistan and Pakistan) inferred from InSAR. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth 2017, 122, 372–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggs, J.; Wright, T.; Lu, Z.; Parsons, B. Multi-interferogram method for measuring interseismic deformation: Denali fault, Alaska. Geophysical Journal International 2007, 170, 1165–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakir, Z.; Akoglu, A.M.; Belabbes, S.; Ergintav, S.; Meghraoui, M. Creeping along the Ismetpasa section of the North Anatolian fault (Western Turkey): Rate and extent from InSAR. Earth and Planetary Science Letters 2005, 238, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalie, O.; Lasserre, C.; Doin, M.P.; Peltzer, G.; Sun, J.; Xu, X.; Shen, Z. Measurement of interseismic strain across the Haiyuan fault (Gansu, China), by InSAR. Earth and Planetary Science Letters 2008, 275, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaussard, E.; Johnson, C.W.; Fattahi, H.; Burgmann, R. Potential and limits of InSAR to characterize interseismic deformation independently of GPS data: Application to the southern San Andreas Fault system. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystem 2016, 17, 1214–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Cheng, H.Q.; Yang, Y.H.; Liu, G.X.; Liu, L.Y. Quantification of mass wasting volume associated with the giant landslide Daguangbao induced by the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake from persistent scatterer InSAR. Remote Sensing of Environment 2014, 152, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.D.; Zhang, P.Z.; Ran, Y.K.; Yang, X.P.; Min, W.; Chen, L.C. (2003). Active tectonics and earthquake activities in China. Earth Science Frontiers, 10(z1): 66-73, (in Chinses). -73. [CrossRef]
- Diao, F.; Xiong, X.; Wang, R.; Walter, T.R.; Wang, Y.; Wang, K. Slip rate variation along the Kunlun fault (Tibet): Results from new GPS observations and a viscoelastic earthquake-cycle deformation model. Geophysical Research Letters 2019, 46, 2524–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Zhang, L.; Liao, M.S.; Gong, J. Improved correction of seasonal tropospheric delay in InSAR observations for landslide deformation monitoring. Remote Sensing of Environment 2019, 233, 111370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattahi, H.; Amelung, F. InSAR uncertainty due to orbital errors. Geophysical Journal International 2014, 199, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourmelen, N.; Amelung, F.; Lanari, R. Interferometric synthetic aperture radar–GPS integration: interseismic strain accumulation across the Hunter Mountain fault in the eastern California shear zone. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, A.K.; Goldstein, R.M.; Zebker, H.A. Mapping small elevation changes over large areas: Differential radar interferometry. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth 1989, 94, 9183–9191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.Y.; Zhang, W.T.; Liu, C.J.; Zhu, L.Y.; Xu, J.; Xu, X.X. Characterizing interseismic deformation of the Xianshuihe fault, eastern Tibetan Plateau, using Sentinel-1 SAR images. Advances in Space Research 2020, 66, 378–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Funning, G.J. Testing the inference of creep on the northern Rodgers Creek fault, California, using ascending and descending persistent scatterer InSAR data. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth 2017, 122, 2373–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolivet, R.; Lasserre, C.; Doin, M.P.; Guillaso, S.; Peltzer, G.; Dailu, R.; Xu, X. Shallow creep on the Haiyuan fault (Gansu, China) revealed by SAR interferometry. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth 2012, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.X.; Bürgmann, R. Partial coupling and earthquake potential along the Xianshuihe Fault, China. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth 2021, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.T.; Zhang, C.S.; Wu, M.L.; Ma, Y.S.; Ou, M.Y. Stress change near the Kunlun fault before and after the Ms 8.1 Kunlun earthquake. Geophysical Research Letters 2003, 30, 2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.N.; Simons, M.; Hetland, E.A.; Muse, P.; DiCaprio, C. A multiscale approach to estimating topographically correlated propagation delays in radar interferograms. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystem 2010, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundgren, P.E.; Hetland, A.; Liu, Z.; Fielding, E.J. Southern San Andreas–San Jacinto fault system slip rates estimated from earthquake cycle models constrained by GPS and interferometric synthetic aperture radar observations. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massonnet, D.; Feigl, K. Radar interferometry and its applications to changes in the Earth’s surface. Reviews of Geophysics 1998, 36, 441–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, Z.; Pathier, E.; Walker, R.T.; Walpersdorf, A.; Tavakoli, F.; Nankali, H.; Sedighi, M.; Doin, M.P. Interseismic deformation of the Shahroud fault system (NE Iran) from space-borne radar interferometry measurements. Geophysical Research Letters 2015, 42, 5753–5761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescott, W.; Nur, A. The accommodation of relative motion at depth on the San Andreas Fault System in California. Journal of Geophysical Research 1981, 88, 999–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.; Zhou, Y. Geodetic imaging of shallow creep along the Xianshuihe fault and its frictional properties. Earth and Planetary Science Letters 2021, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousset, B.; Jolivet, R.; Simons, M.; Lasserre, C.; Riel, B.; Milillo, P.; Renard, F. An aseismic slip transient on the North Anatolian Fault. Geophysical Research Letters 2016, 43, 3254–3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryder, I.; Bürgmann, R. Spatial variations in slip deficit on the central San Andreas Fault from InSAR. Geophysical Journal International 2008, 175, 837–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, J.; Burford, R. Geodetic determination of relative plate motion in California. Journal of Geophysical Research 1973, 78, 832–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamshiri, R.; Motagh, M.; Nahavandchi, H.; Haghshenas Haghighi, M.; Hoseini, M. Improving tropospheric corrections on large-scale Sentinel-1 interferograms using a machine learning approach for integration with GNSS-derived zenith total delay (ZTD). Remote Sensing of Environment 2020, 239, 111608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Jiang, Y.; Shan, X.; Gong, W.; Qu, C. A fine velocity and strain rate field of present-day crustal motion of the northeastern tibetan plateau inverted jointly by InSAR and GPS. Remote Sensing 2019, 11, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Styron, R.; Pagani, M. The GEM Global Active Faults Database. Earthquake Spectra 2020, 36, 160–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Sandwell, D.T.; Schmidt, D.A. Surface creep rate and moment accumulation rate along the aceh segment of the sumatran fault from L-band ALOS-1/PALSAR-1 observations. Geophysical Research Letters 2018, 45, 3404–3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Woerd, J.; Ryerson, F.J.; Tapponnier, P.; Meriaux, A.S.; Gaudemer, Y.; Meyer, B.; Finkel, R.C.; Caffee, M.W.; Zhao, G.G.; Xu, Z.Q. Uniform slip-rate along the Kunlun Fault: Implications for seismic behaviour and large-scale tectonics. Geophysical Research Letters 2000, 27, 2353–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wright, T.J. Satellite geodetic imaging reveals internal deformation of western Tibet. Geophysical Research Letters 2012, 39, L07303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wright, T.J.; Jing, L.Z.; Peng, L. Strain rate distribution in south-central Tibet from two decades of InSAR and GPS. Geophysical Research Letters 2019, 46, 5170–5179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Shen, Z.K. Present-day crustal deformation of continental China derived from GPS and its tectonic implications. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth 2020, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegmüller, U.; Werner, C. (1997). Gamma SAR processor and ineterferometry software. In Proceedings of 3rd ERS Symposium, Florence, Italy, 14-21March 1997; pp. 1687–1692. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, M.; Sandwell, D.; Smith-Konter, B. Optimal combination of InSAR and GPS for measuring interseismic crustal deformation. Advanced in Space Research 2010, 46, 236–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessel, P.; Smith WH, F. New, improved version of Generic Mapping Tools released. EOS Transactions American Geophysical Union 1998, 79, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, T.J.; Parsons, B.; Fielding, E.J. Measurement of interseismic strain accumulation across the North Anatolian Fault by satellite radar interferometry. Geophysical Research Letters 2001, 28, 2117–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.J.; Zhu, S. Temporal and spatial movement characteristics of the Altyn Tagh fault inferred from 21 years of InSAR observations. Journal of Geodesy 2019, 93, 1147–1160. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Q.; Chen, Q.; Zhao, J.J.; Liu, X.W.; Yang, Y.H.; Zhang, Y.J.; Liu, G.X. Sequential modelling of the 2016 central italy earthquake cluster using multisource satellite observations and quantitative assessment of coulomb stress change. Geophysical Journal International 2020, 221, 451–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.H.; Hu, J.C.; Chen, Q.; Lei, X.L.; Zhao, J.J.; Li, W.L.; Xu, R.; Chiu, C.Y. Shallow slip of blind fault associated with the 2019 Ms 6.0 Changning earthquake in fold-and-thrust belt in salt mines of Southeast Sichuan, China. Geophysical Journal International 2021, 224, 909–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.H.; Tsai, M.C.; Hu, J.C.; Chen, Q.; Aurelio, M.; Xu, Q.; Jiang, Z.Q.; Xu, L.; Yang, C.; Li, L. Assessment of the Seismic Hazards of the Marikina Valley Fault from 2019 Mw 6.1 Castillejos Earthquake and Historical Events. Seismological Research Letters 2021, 92, 3360–3374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Qu, C.Y.; Bürgmann, R.; Gong, W.; Shan, X.; Qiao, X.; Zhao LChen, H.; Liu, L. Large-scale Crustal Deformation, Slip-Rate Variation and Strain Distribution along the Kunlun Fault (Tibet) from Sentinel-1 InSAR Observations (2015-2020). Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth 2022, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Ji, L.; Liu, C. Interseismic slip rate and locking along the Maqin–Maqu Segment of the East Kunlun Fault, Northern Tibetan Plateau, based on Sentinel-1 images. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences 2021, 211, 104703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Xu, C.; Wen, Y.; Liu, Y. Interseismic deformation of the altyn tagh fault determined by interferometric synthetic aperture radar (INSAR) measurements. Remote Sensing 2016, 8, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).