Submitted:
22 May 2024
Posted:
23 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
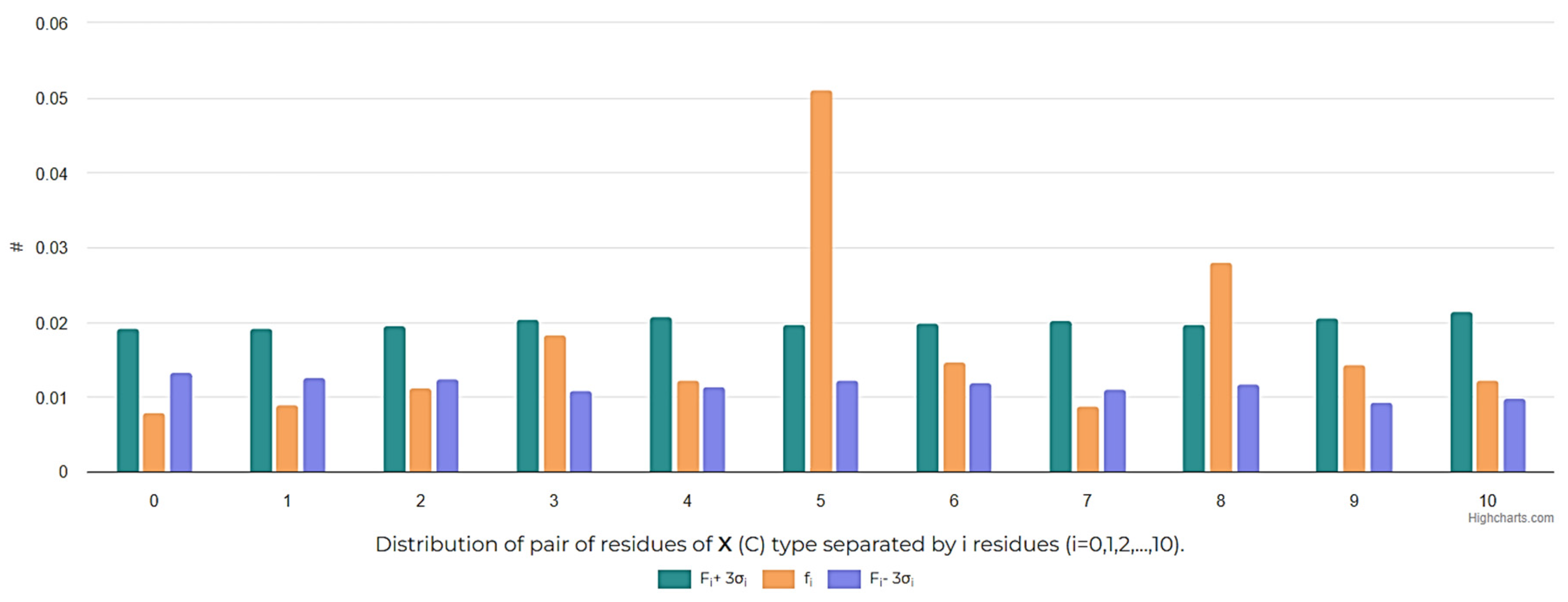
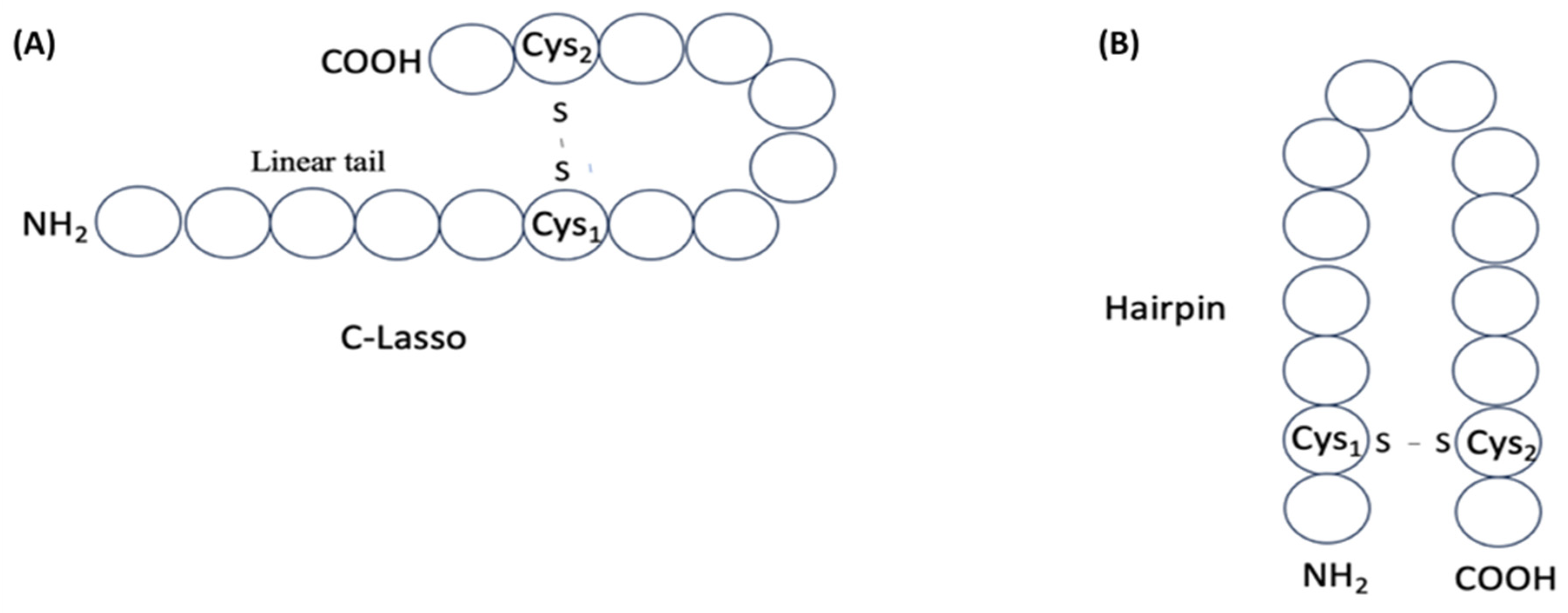
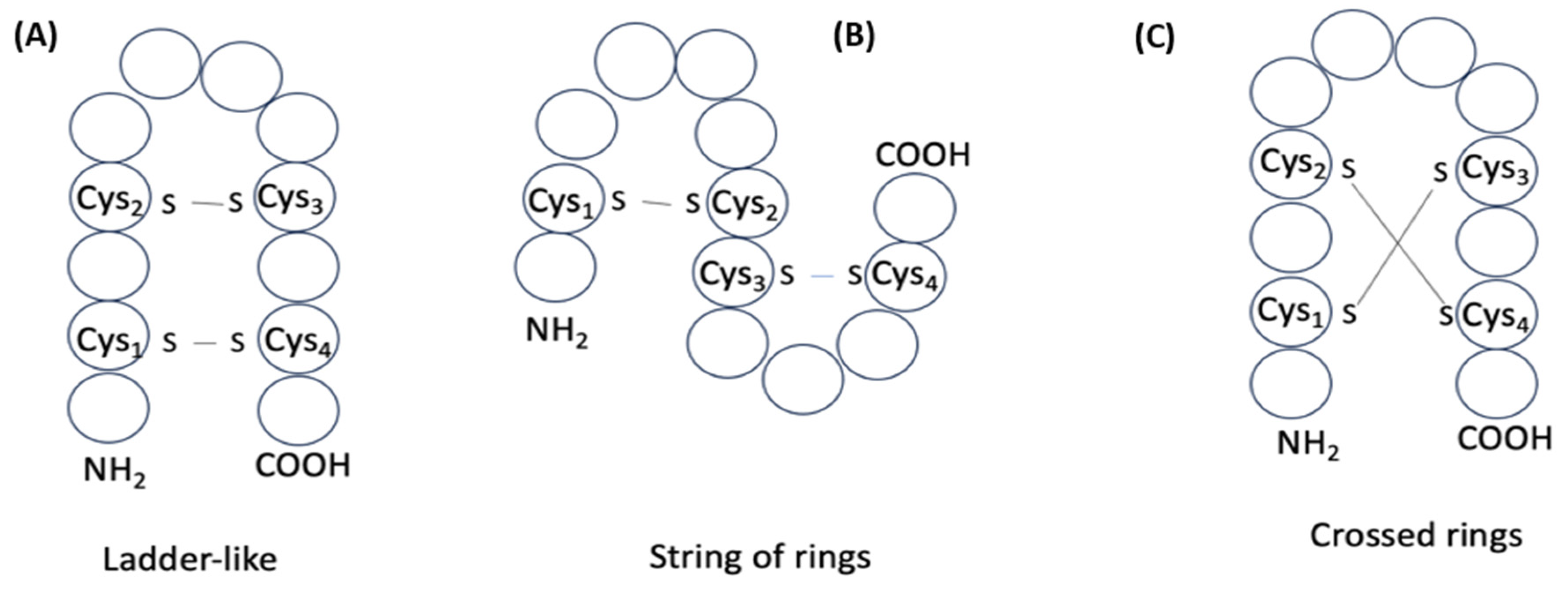
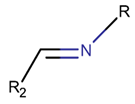
2. Definition of intrachain bonds and rings of natural cyclic peptides
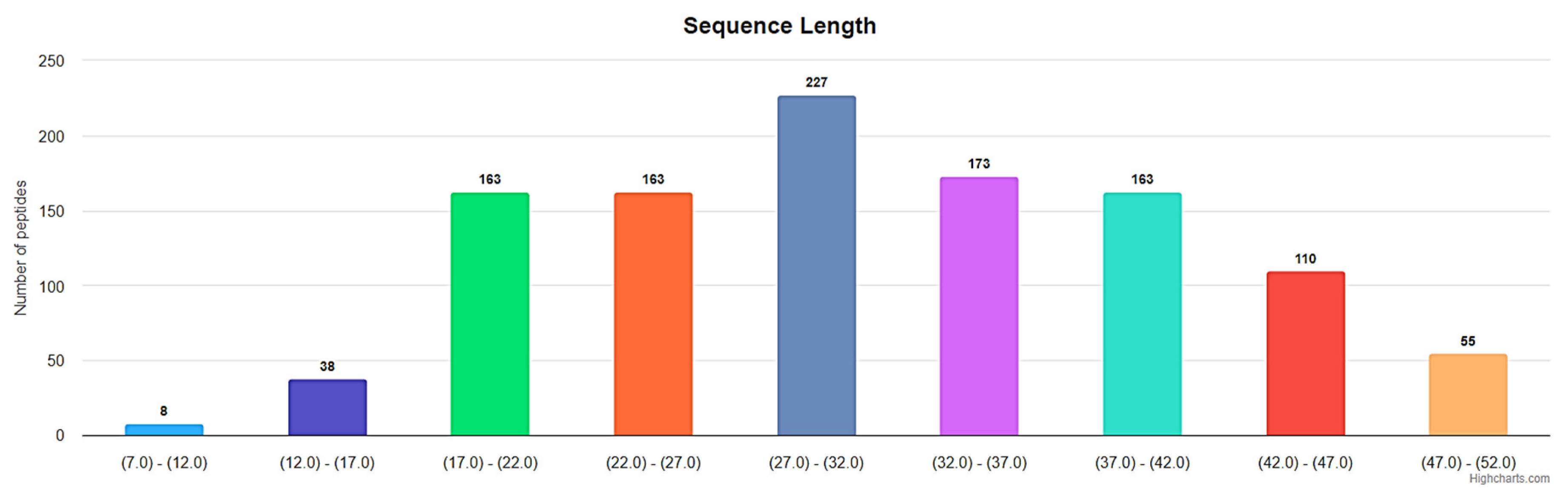
3. Small Cyclic Peptides of DBAASP
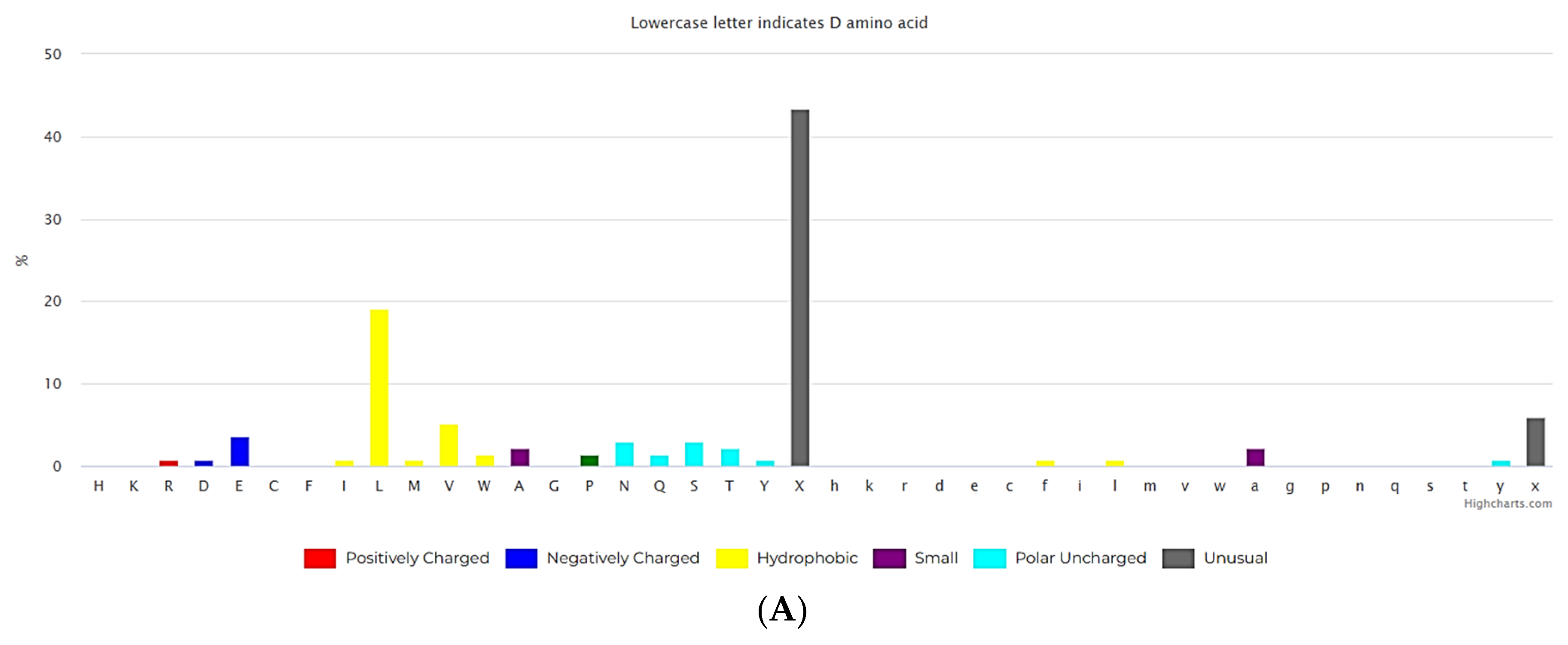
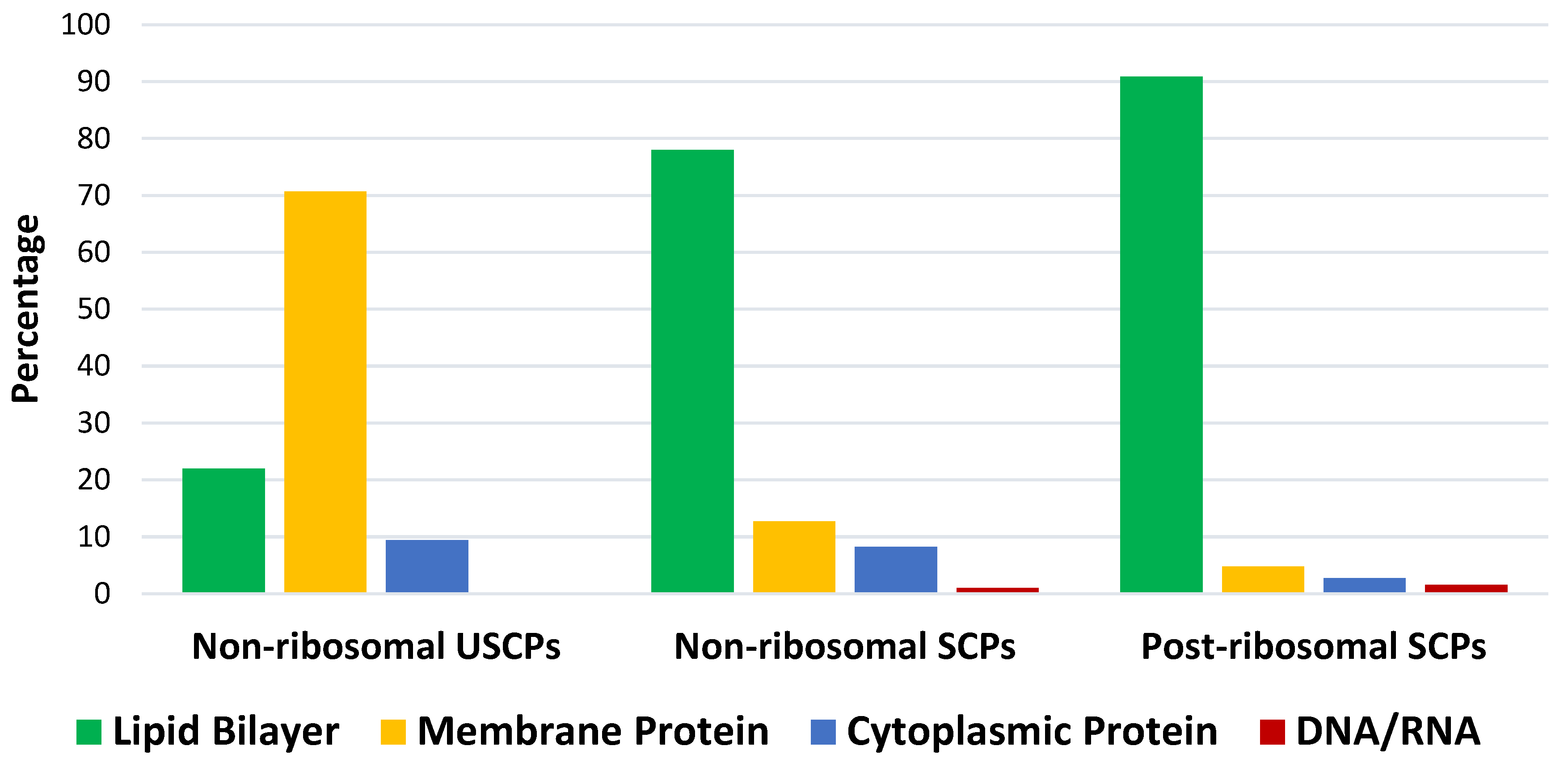
3.1. Ultra Short Cyclic Peptides
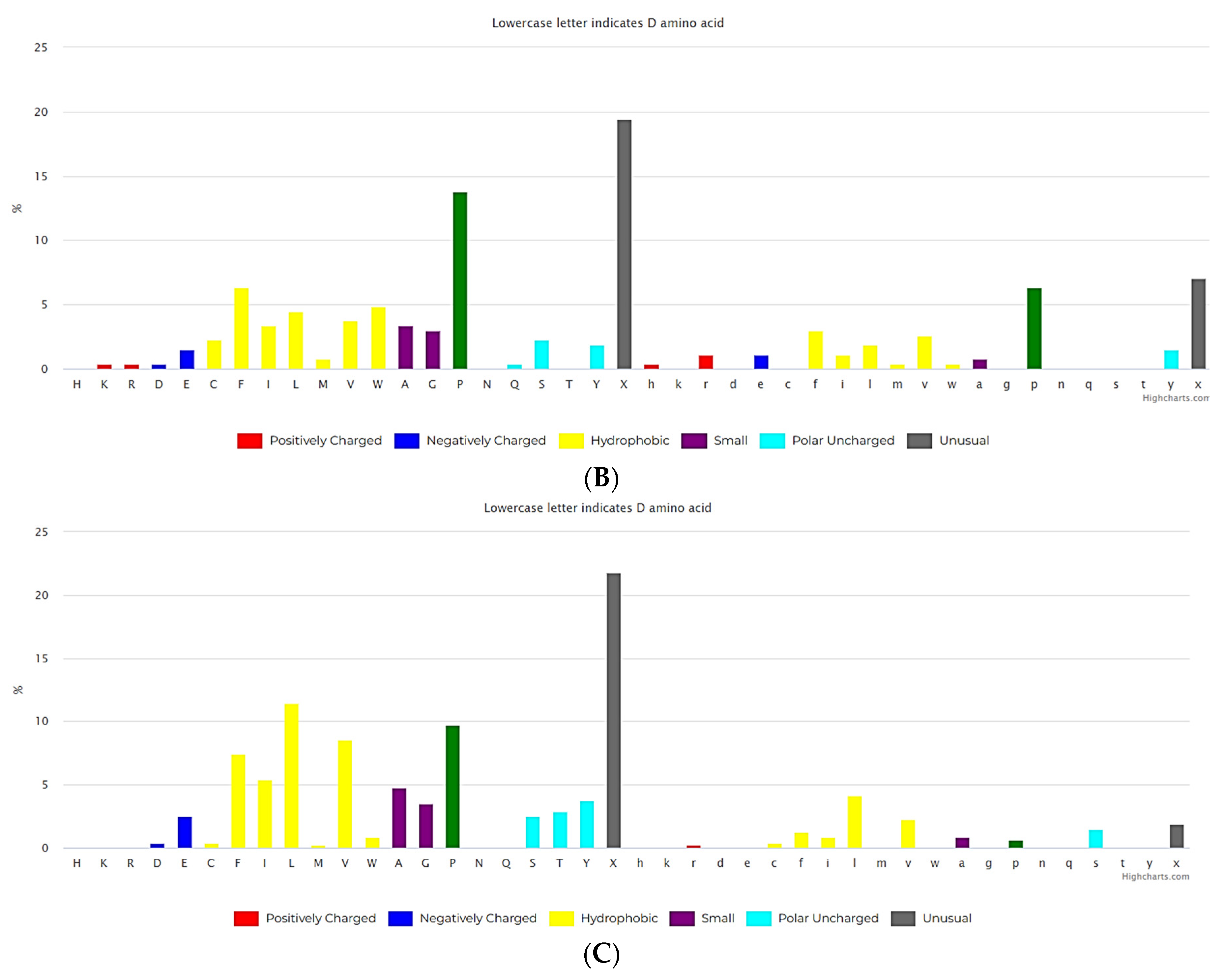
3.2. Short cyclic peptides
3.2.1. Peptides could interact with several ‘undruggable’ binding sites
3.2.2. Non-ribosomal short cyclic peptides
3.2.2.1. Intra-chain bonds and created rings in non-ribosomal peptides
3.2.3. Ribosomal short cyclic peptides
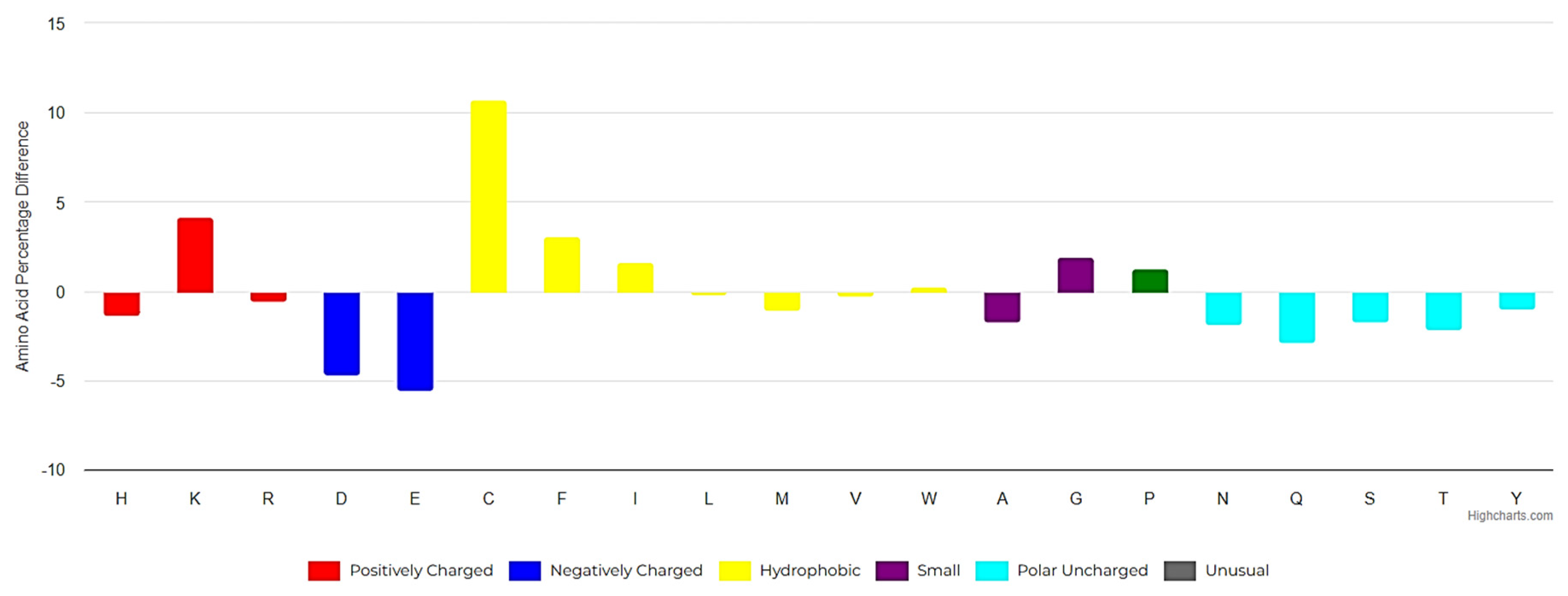
4. An impact of cyclization on peptide potency
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Antimicrobial Resistance Collaborators. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: A systematic analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Yang, Z.; Nie, Y.; Shi, Y.; Fan, D. Multi-drug resistance in cancer chemotherapeutics: Mechanisms and lab approaches. Cancer Lett. 2014, 347, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fath, K.M.; Babakhaniyan, K.; Zokaei, M.; Yaghoubian, A.; Akbari, S.; Khorsandi, M.; Soofi, A.; Nabi-Afjadi, M.; Zalpoor, H.; Jalalifar, F.; et al. Anti-cancer peptide-based therapeutic strategies in solid tumors. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2022, 27, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gori, A.; Lodigiani, G.; Colombarolli, S.G.; Bergamaschi, G.; Vitali, A. Cell penetrating peptides: Classification, mechanisms, methods of study, and applications. ChemMedChem. 2023, 18, e202300236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.H.; Lan, X.P.; Liu, Y.; Jia, A.Q. The effects of diketopiperazines from Callyspongia sp. on release of cytokines and chemokines in cultured J774A.1 macrophages. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2012, 22, 3177–3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mookherjee, N.; Anderson, M.A.; Haagsman, H.P.; Davidson, D.J. Antimicrobial host defence peptides: Functions and clinical potential. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2020, 19, 311–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, L. Strategic approaches to optimizing peptide ADME properties. AAPS J. 2015, 17, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinski, C.A.; Lombardo, F.; Dominy, B.W.; Feeney, P.J. Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 46, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, M.; Griffith, O.L.; Coffman, A.C.; Weible, J.V.; McMichael, J.F.; Spies, N.C.; Koval, J.; Das, I.; Callaway, M.B.; Eldred, J.M.; et al. DGIdb: Mining the druggable genome. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 1209–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doak, B.C.; Over, B.; Giordanetto, F.; Kihlberg, J. Oral druggable space beyond the rule of 5: Insights from drugs and clinical candidates. Chem. Biol. 2014, 21, 1115–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doak, B.C.; Zheng, J.; Dobritzsch, D.; Kihlberg, J. How beyond rule of 5 drugs and clinical candidates bind to their targets. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 2312–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villar, E.A.; Beglov, D.; Chennamadhavuni, S.; Porco Jr, J.A.; Kozakov, D.; Vajda, S.; Whitty, A. How proteins bind macrocycles. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2014, 10, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougherty, P.G.; Sahni, A.; Pei, D. Understanding cell penetration of cyclic peptides. Chem Rev. 2019, 119, 10241–10287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passioura, T.; Katoh, T.; Goto, Y.; Suga, H. Selection-based discovery of druglike macrocyclic peptides. Annu Rev Biochem. 2014, 83, 727–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitty, A.; Zhong, M.; Viarengo, L.; Beglov, D.; Hall, D.R.; Vajda, S. Quantifying the chameleonic properties of macrocycles and other high-molecular-weight drugs. Drug Discov. Today 2016, 21, 21,712–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirtskhalava, M.; Amstrong, A.A.; Grigolava, M.; Chubinidze, M.; Alimbarashvili, E.; Vishnepolsky, B.; Gabrielian, A.; Rosenthal, A.; Hurt, D.E.; Tartakovsky, M. DBAASP v3: Database of antimicrobial/cytotoxic activity and structure of peptides as a resource for development of new therapeutics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D288–D297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, C.; Paul, P.K.C.; Ramanarayan, K. Cyclic peptides––small and big and their conformational aspects. J Biosci. 1985, 8, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, R.B.; Gomez-Castellanos, J.R.; Henry, L.; Ducho, C.; McDonough, M.A.; Schofield, C.J. The enzymes of β-lactam biosynthesis. Nat Prod Rep. 2013, 30, 21–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Li, L.; Sun, S.; Chang, A.; Dai, X.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, H. A cyclic dipeptide from marine fungus penicillium chrysogenum dxy-1 exhibits anti-quorum sensing activity. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 7693–7700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteley, M.; Diggle, S.P.; Greenberg, E.P. Progress in and promise of bacterial quorum sensing research. Nature 2017, 551, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, Y.; Meyer, K.J.; Iinishi, A.; Favre-Godal, Q.; Green, R.; Manuse, S.; Caboni, M.; Mori, M.; Niles, S.; Ghiglieri, M.; et al. A new antibiotic selectively kills Gram-negative pathogens. Nature 2019, 576, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urfer, M.; Bogdanovic, J.; Monte, F.L.; Moehle, K.; Zerbe, K.; Omasits, U.; Ahrens, C.H.; Pessi, G.; Eberl, L.; Robinson, J.A. A peptidomimetic antibiotic targets outer membrane proteins and disrupts selectively the outer membrane in escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 2016, 291, 1921–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UniProt Consortium. UniProt: A worldwide hub of protein knowledge. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D506–D515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirtskhalava, M.K.; Poroikov, V.V.; Tumanyan, V.G. Conformational possibilities of peptide-fragments containing disulfide bridge. Russ J Bioorg Chem. 1980, 6, 1125–1132. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, T.; Chen, X.; Zhou, M.; Ma, C.; Xi, X.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, T.; Shaw, C.; et al. Brevinin-1GHd: A novel Hylarana guentheri skin secretion-derived Brevinin-1 type peptide with antimicrobial and anticancer therapeutic potential. Biosci Rep. 2020, 40, BSR20200019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Kim, E.H.; O’neal, J.T.; Dale, G.E.; Holthausen, D.J.; Bowen, J.R.; Quicke, K.M.; Skountzou, I.; Gopal, S.; George, S.; et al. The amphibian peptide Yodha is virucidal for Zika and dengue viruses. Sci Rep. 2021, 11, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Ren, S.; Guo, C.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, B.; Li, S.; Ren, J.; Hu, Y.; Wang, H. Identification and functional analyses of novel antioxidant peptides and antimicrobial peptides from skin secretions of four East Asian frog species. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) 2017, 49, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randall, J.R.; DuPai, C.D.; Cole, T.J.; Davidson, G.; Groover, K.E.; Slater, S.L.; Mavridou, D.A.I.; Wilke, C.O.; Davies, B.W. Designing and identifying β-hairpin peptide macrocycles with antibiotic potential. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eade0008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willey, J.M.; van der Donk, W.A. Lantibiotics: Peptides of diverse structure and function. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2007, 61, 477–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Hua, Z.C. Lasso peptides: Heterologous production and potential medical application. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 571165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mevaere, J.; Goulard, C.; Schneider, O.; Sekurova, O.N.; Ma, H.; Zirah, S.; Afonso, C.; Rebuffat, S.; Zotchev, S.B.; Li, Y. An orthogonal system for heterologous expression of actinobacterial lasso peptides in Streptomyces hosts. Sci Rep. 2018, 8, 8232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duquesne, S.; Destoumieux-Garzón, D.; Peduzzi, J.; Rebuffat, S. Microcins, gene-encoded antibacterial peptides from enterobacteria. Nat Prod Rep. 2007, 24, 708–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, K.; Yuan, W.; Ma, C.; Yu, X.; Wang, L.; Hong, M.; Xi, X.; Zhou, M.; Chen, T. Modification targeting the ‘Rana Box’ motif of a novel nigrocin peptide from Hylarana latouchii enhances and broadens its potency against multiple bacteria. Front Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, M.; Chen, X.; Ma, C.; Wang, T.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, T.; Shaw, C.; Wang, L. Exploring the active core of a novel antimicrobial peptide, palustrin-2LTb, from the Kuatun frog, Hylarana latouchii, using a bioinformatics-directed approach. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022, 20, 6192–6205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivanesam, K.; Kier, B.L.; Whedon, S.D.; Chatterjee, C.; Andersen, N.H. Hairpin structure stability plays a role in the activity of two antimicrobial peptides. FEBS Lett. 2016, 590, 4480–4488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smirnova, M.P.; Kolodkin, N.I.; Kolobov, A.A.; Afonin, V.G.; Afonina, I.V.; Stefanenko, L.I.; Shpen’, V.M.; Shamova, O.V.; Kolobov, A.A. Indolicidin analogs with broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity and low hemolytic activity. Peptides 2020, 132, 170356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Hancock, R.E. Improved derivatives of bactenecin, a cyclic dodecameric antimicrobial cationic peptide. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1999, 43, 1274–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antcheva, N.; Morgera, F.; Creatti, L.; Vaccari, L.; Pag, U.; Pacor, S.; Shai, Y.; Sahl, H.G.; Tossi, A. Artificial beta-defensin based on a minimal defensin template. Biochem J. 2009, 421, 435–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Lv, X.; Li, F.; Xiang, J. Characterization of a lymphoid organ specific anti-lipopolysaccharide factor from shrimp reveals structure-activity relationship of the lps-binding domain. Front Immunol. 2019, 10, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohan, S.; Mandal, D.; Choi, W.; Konshina, A.G.; Tiwari, R.K.; Efremov, R.G.; Maslennikov, I.; Parang, K. Small amphiphilic peptides: Activity against a broad range of drug-resistant bacteria and structural insight into membranolytic properties. J Med Chem. 2022, 65, 665–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, R.; Waring, A.J.; Lehrer, R.I.; Hong, M. Membrane-disruptive abilities of beta-hairpin antimicrobial peptides correlate with conformation and activity: A 31P and 1H NMR study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2005, 1716, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanojlovic, V.; Müller, A.; Moazzam, A.; Hinterholzer, A.; Ożga, K.; Berlicki, Ł.; Schubert, M.; Cabrele, C. A conformationally stable acyclic β-hairpin scaffold tolerating the incorporation of poorly β-sheet-prone amino acids. Chembiochem. 2022, 23, e202100604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuber, P. Non-ribosomal peptide synthesis. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991, 3, 1046–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIntosh, J.A.; Donia, M.S.; Schmidt, E.W. Ribosomal peptide natural products: Bridging the ribosomal and nonribosomal worlds. Nat Prod Rep. 2009, 26, 537–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
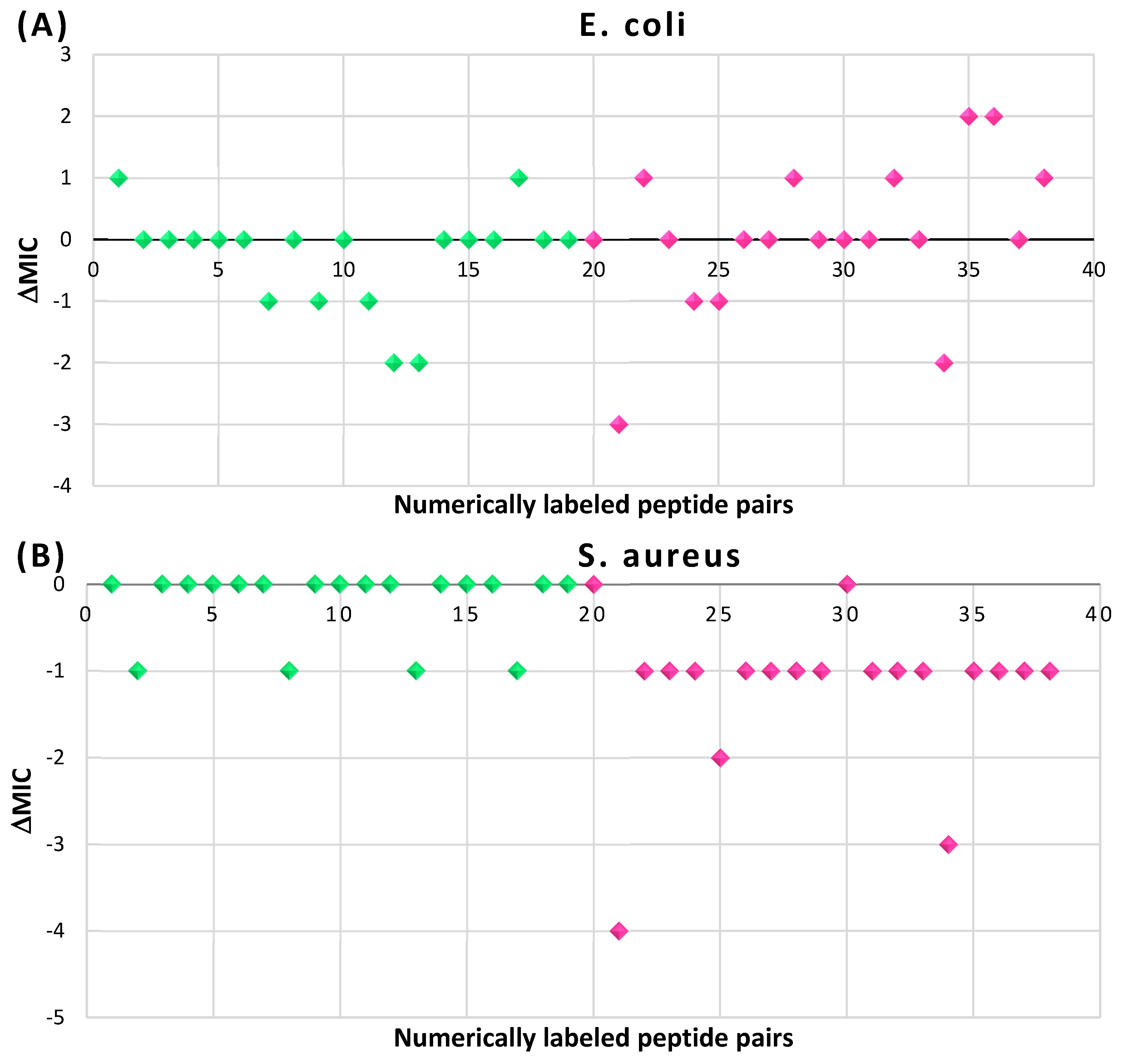
| RCBs | Participating Chains and Types of Rings | In Non-Ribosomal Cyclic AMPs |
In Ribosomal Cyclic AMPs |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SMB** | MMB** | SSB** | |||
TIE**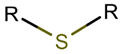
|
THZN***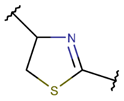
|
– | – | + | – |
THZD***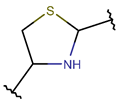
|
– |
THZD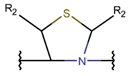
|
+ | – | |
THZ***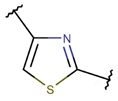
|
– | – | + | + | |
| – | – |
TZ***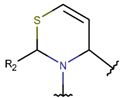
|
+ | – | |
| – | – |
LAN***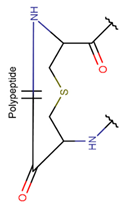
|
– | + | |
| – | – |
MeLAN***
|
– | + | |
| – | – |
AVC***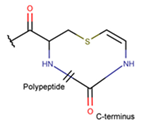
|
– | + | |
| – | – |
MeAVC***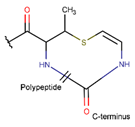
|
– | + | |
ETH*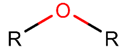
|
OXZN****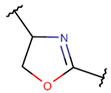
|
– | – | – | + |
OXZ***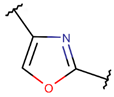
|
– | – | – | + | |
MeOXZ***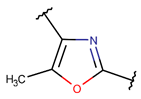
|
– | – | – | + | |
MeOXZN***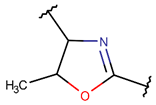
|
– | – | – | + | |
| – | – |
LAC***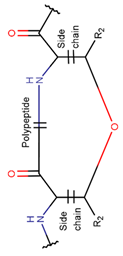
|
+ | + | |
EST*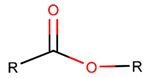
|
LCN***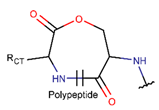
|
– | – | + | – |
| – |
LCN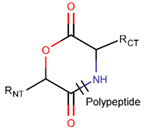
|
– | + | – | |
 DSB* |
– | – |
CST***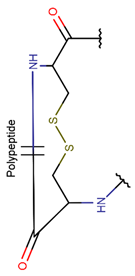
|
+ | + |
| – | – |
DSL***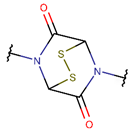
|
+ | – | |
AMD*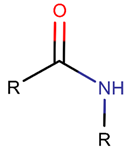
|
– |
NCB***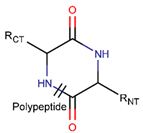
|
– | + | + |
LAC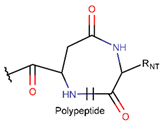
|
– | – | – | + | |
LAC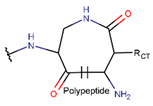
|
– | – | + | – | |
| – |
DKP***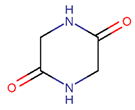
|
– | + | – | |
 IMN* |
– |
LAC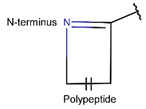
|
– | – | + |
AMN*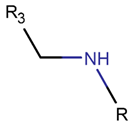
|
βLAC***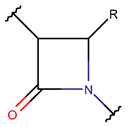
|
– | – | + | – |
δLAC ***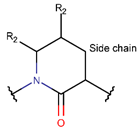
|
– | – | + | – | |
LAC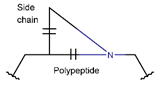
|
– | – | + | – | |
| – | – |
LAC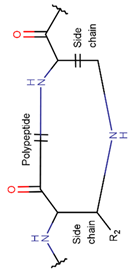
|
– | + | |
PRL***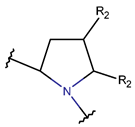
|
– | – | + | – | |
 CAR* |
– | – |
BAR***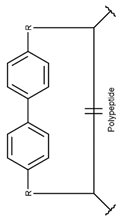
|
+ | – |
| – | – |
LAC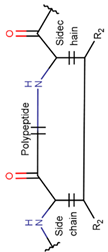
|
– | + | |
LAC
|
– | – | – | + | |
| – |
PYR***
|
PYR
|
– | + | |
| Type of Synthesis | Peptide Length | Number of Peptides | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | Total Cyclic | Certain RCBs, Participating Chains and Types of Rings | |||||||||||
|
AMD* MMB** NCB*** |
AMD MMB DKP* |
AMD SMB** LAC*** |
AMN* SMB βLAC*** |
AMN SMB PRL*** |
DSB SSB CST*** |
DSB* SSB** DSL*** |
EST* SMB LCN*** |
TIE* SSB THZD*** |
TIE SSB TZ*** |
||||
| Non-Ribosomal | 2 | 93 | 89 | 0 | 79 | 0 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 6 | 3 | 1 |
| 3 | 47 | 32 | 13 | 3 | 12 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 | |
| 4 | 55 | 43 | 31 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 0 | 0 | |
| 5 | 68 | 61 | 21 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 39 | 0 | 0 | |
| Post-Ribosomal | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| 5 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| RCBs | Participating Chains | Types of Rings | Non-Ribosomal | Post-Ribosomal |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DSB* | SSB** | CST*** | 0 | 360 |
| TIE* | SSB | LAN*** | 0 | 22 |
| MeLAN*** | 0 | 22 | ||
| AVC*** | 0 | 12 | ||
| MeAVC*** | 0 | 5 | ||
| SMB** | THZ*** | 4 | 8 | |
| THZN*** | 4 | 0 | ||
| THZD*** | 1 | 0 | ||
| AMD* | MMB* | NCB *** | 138 | 66 |
| SMB | LAC*** | 66 | 30 | |
| AMN* | SMB | LAC | 8 | 0 |
| δLAC | 4 | 0 | ||
| SSB | LAC | 0 | 5 | |
| EST* | SMB | LCN*** | 142 | 0 |
| ETH* | SMB | OXZ *** | 0 | 4 |
| MeOXZ*** | 0 | 5 | ||
| OXZN*** | 0 | 2 | ||
| MeOXZN*** | 0 | 1 | ||
| SSB | LAC | 3 | 1 | |
| IMN* | MMB | LAC | 0 | 2 |
| CAR* | SMB | LAC | 0 | 6 |
| SSB | LAC | 0 | 4 | |
| BAR*** | 12 | 0 | ||
| PYR*** | 0 | 1 | ||
| MMB | PYR | 0 | 1 | |
| Total Number | 367 | 482 | ||
| Number of DSBs | Structural Types | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C-LL | N-LL | HP | LD | CR | |
| 1 | 227 | 1 | 60 | NA | NA |
| 2 | NA | NA | 29 | 29 | 8 |
| 3 | NA | NA | 3 | 3 | 10 |
| 4 | NA | NA | 4 | 4 | 16 |
| Type of Synthesis | Non-ribosomal | Post-ribosomal | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RCBs | AMD* | DSB* | EST* | AMD | DSB | EST | |||
| Participating Chains | MMB** | SMB** | SSB** | SMB | MMB | SMB | SSB | SMB | |
| Types of Rings | NCB*** | LAC*** | CST*** | LCN*** | NCB | LAC | CST | LCN | |
| Sources | Animalia | 33 | 0 | 0 | 18 | 18 | 0 | 931 | 0 |
| Plantae | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 139 | 0 | 238 | 0 | |
| Protista | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | |
| Fungi | 74 | 10 | 3 | 61 | 0 | 0 | 24 | 0 | |
| Bacteria | 88 | 66 | 0 | 122 | 19 | 32 | 38 | 0 | |
| Archaea | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




