Submitted:
29 April 2024
Posted:
30 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
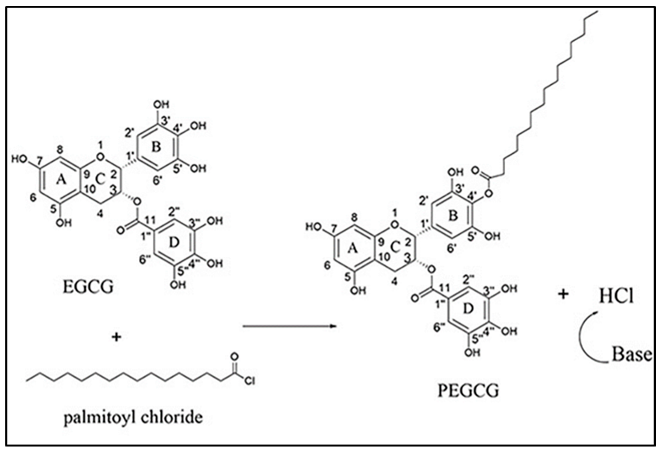
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Virus and Cell Lines
2.2. EC16m and Other Supplies
2.3. EC16 Mucoadhesive Nanoformulations
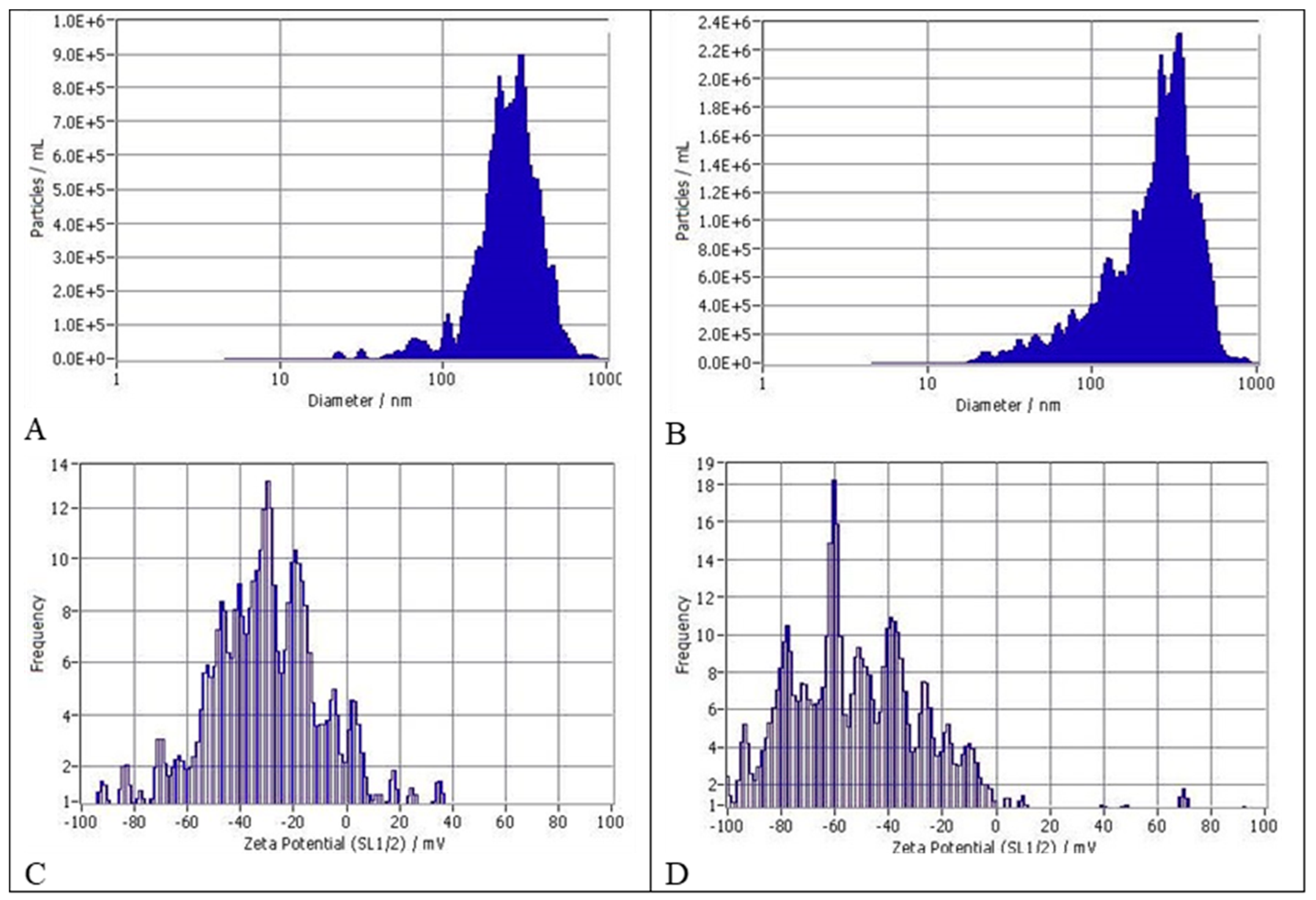
2.4. Evaluation of Particle Size Distribution (Detailed Data Sheets Are in Appendix A)
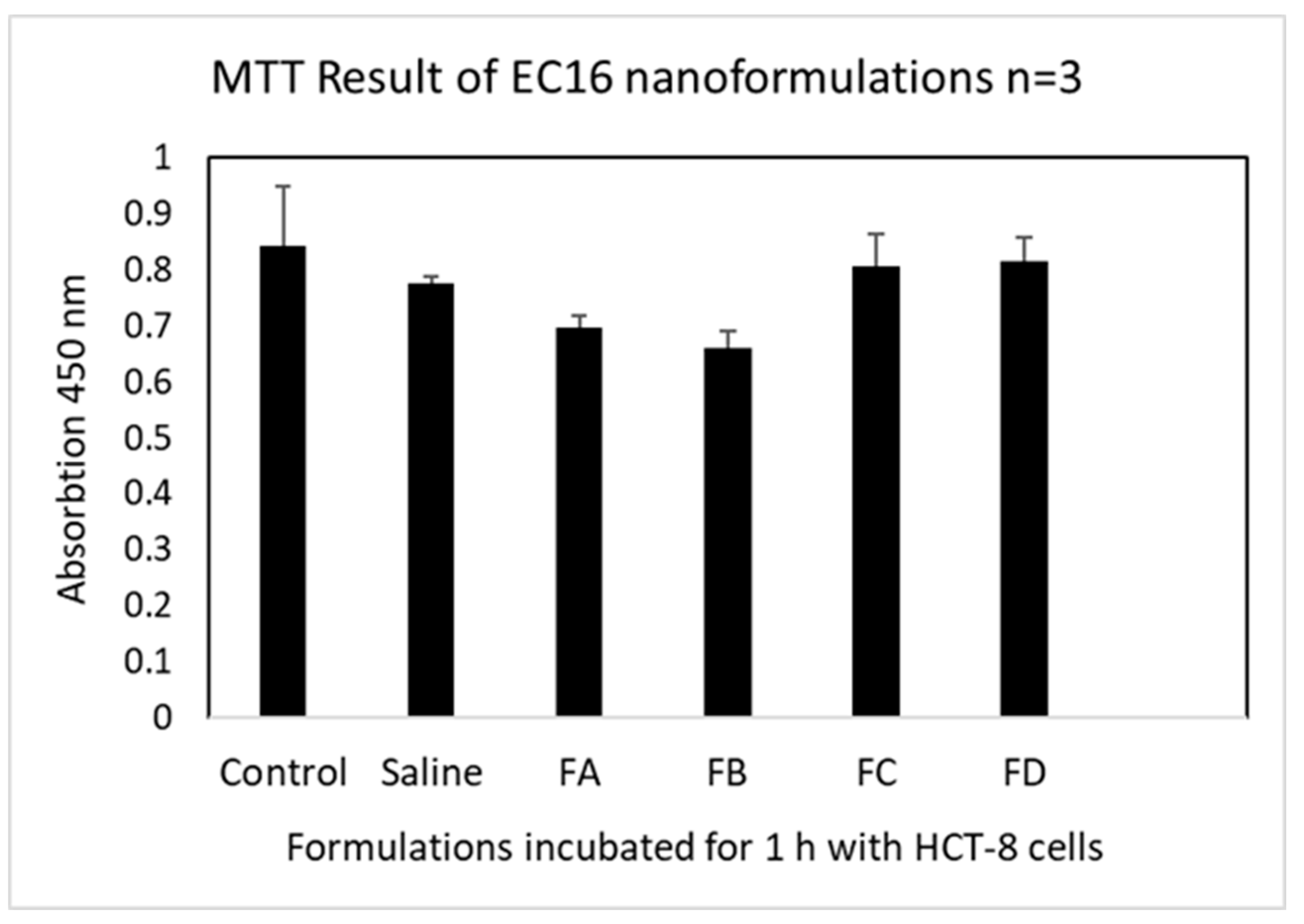
2.5. Evaluation of Cytotoxicity by Cell Viability (MTT) Assay
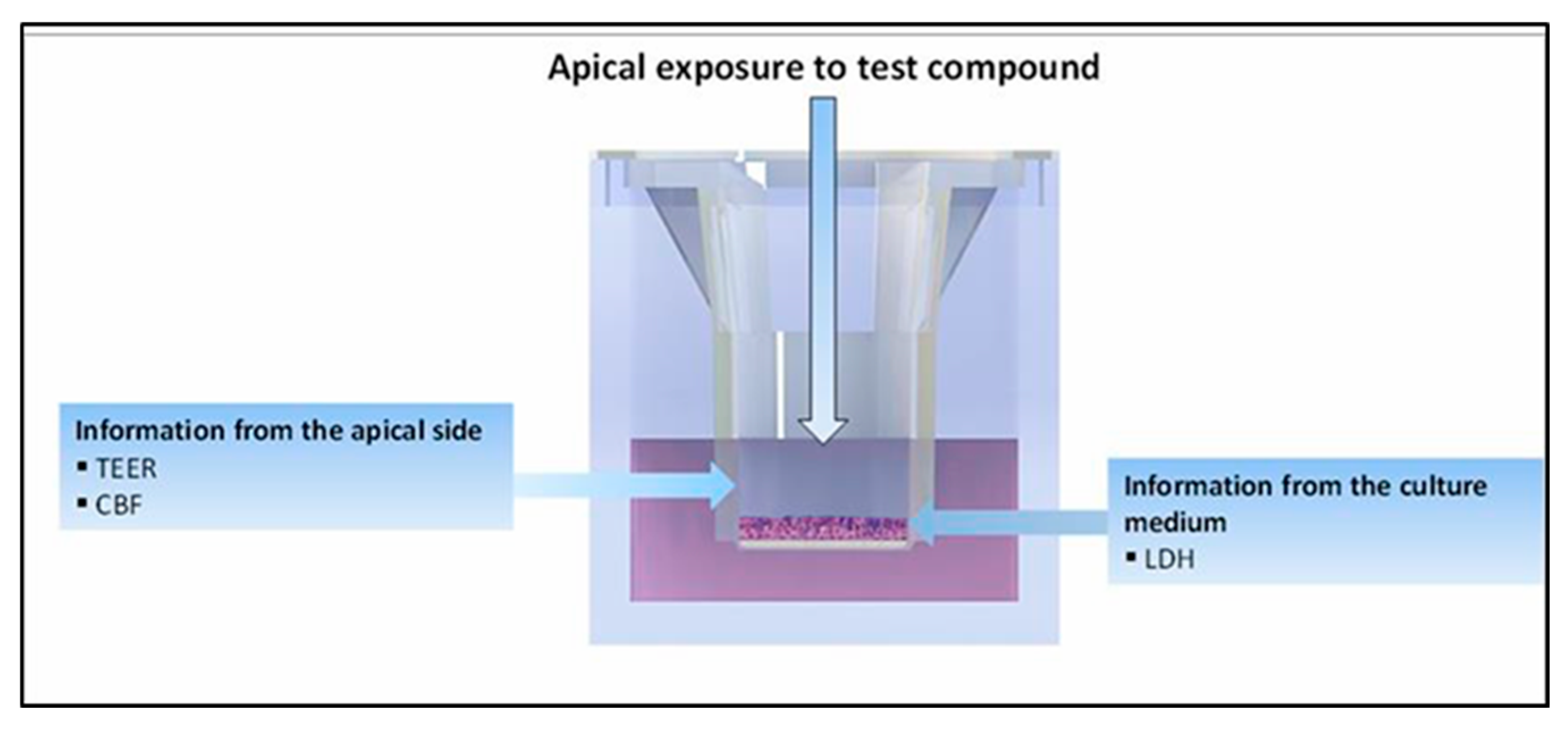
2.6. Evaluation of Mucociliary Toxicities of EC16m Nanoformulations by 3D MucilAir Human Nasal Epithelium Model (Performed by Epithelix Sàrl, Plan-les-Ouates Switzerland. Detailed Protocols Are in Appendix B)
2.7. Direct Contact Antiviral Activity Tests
2.8. Post-Infection Test
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Size Distribution and Zeta Potentials of Particles
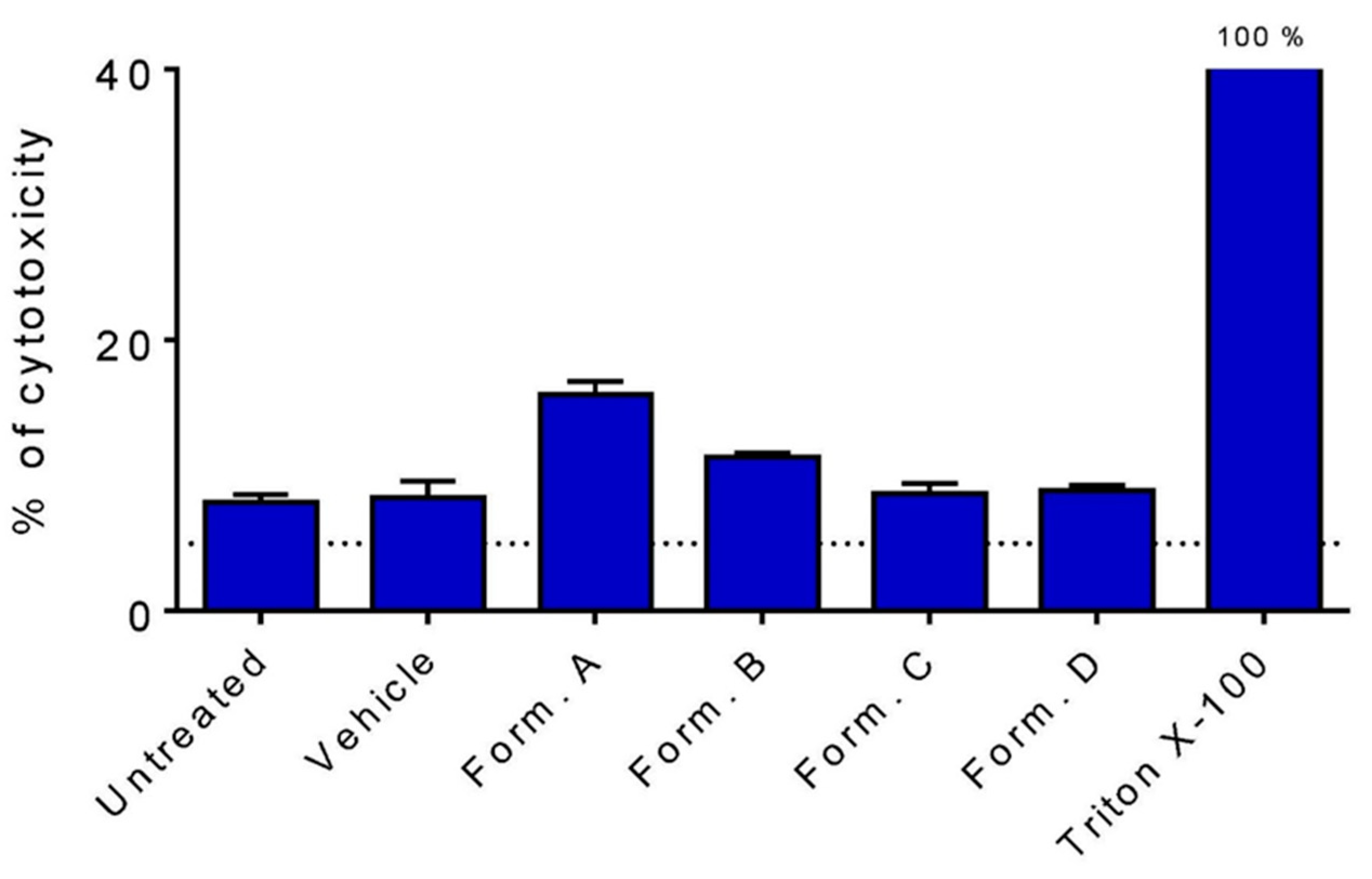
3.2. Cell Viability after 1 h Incubation with HCT-8 Cells
3.3. Mucociliary Toxicity
3.3.1. Tissue Integrity
3.3.2. Cytotoxicity Measured by LDH Release
3.3.3. Cilia Beating Frequency (CBF)
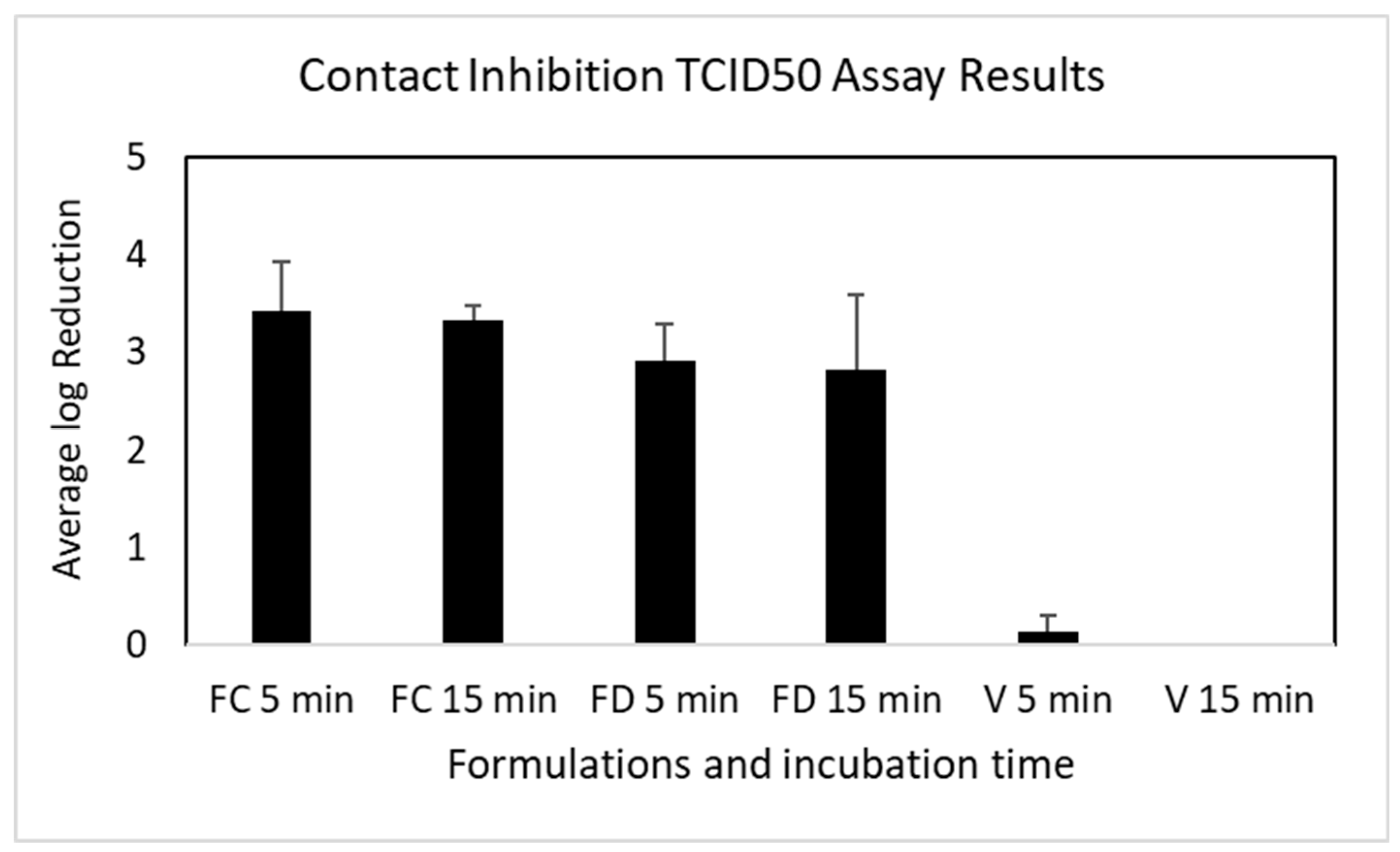
3.4. Contact Inhibition of OC43 Viral Infectability
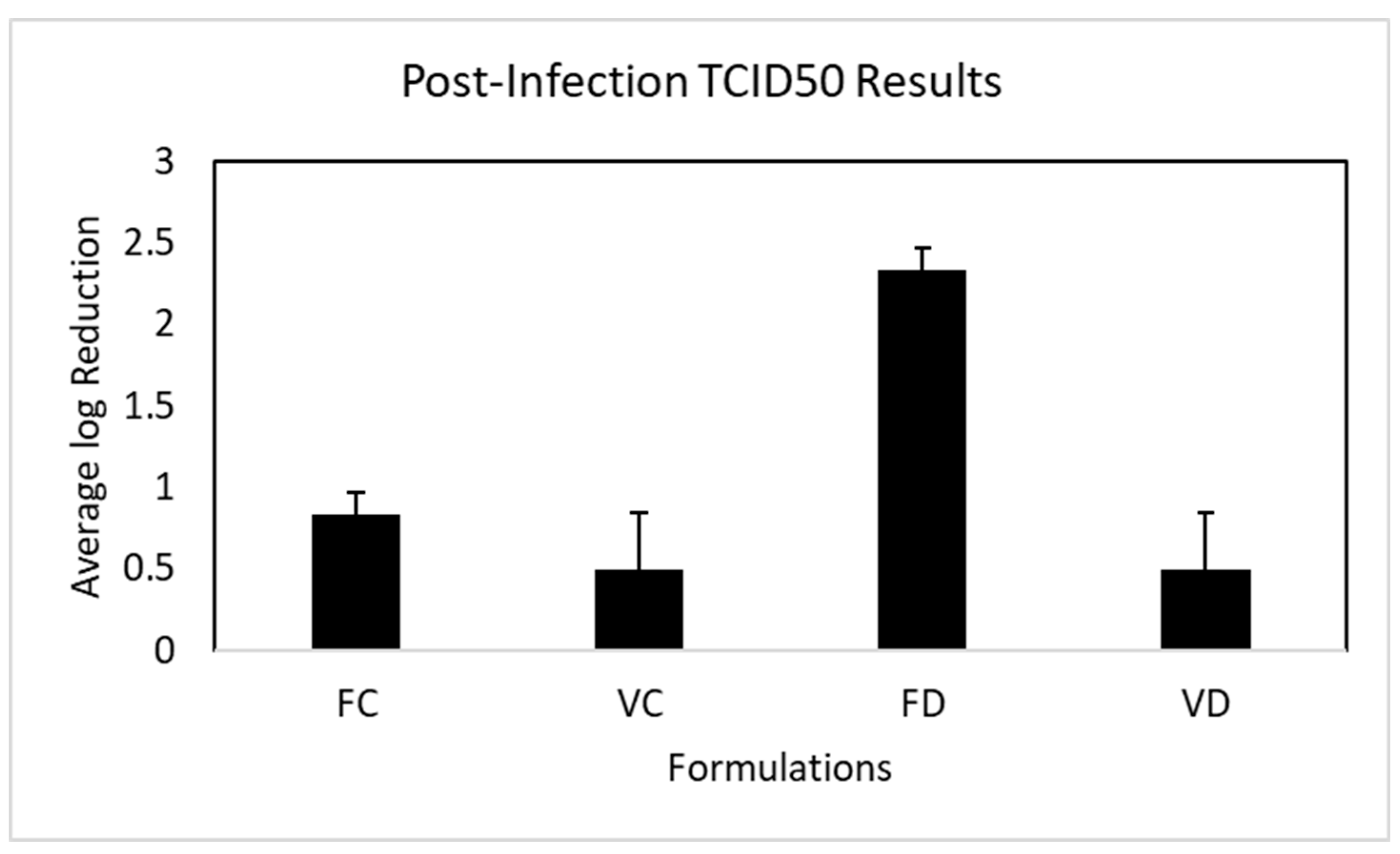
3.5. Post-Infection Inhibition of OC43 Viral Replication
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Appendix A
Appendix B
References
- Leonel, J.W.; Ciurleo, G.C.V.; Formiga, A.M.; et al. Long COVID: neurological manifestations - an updated narrative review. Dement. Neuropsychol. 2024, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanou, M.I. , Palaiodimou L., Bakola E., et al. Neurological manifestations of long-COVID syndrome: a narrative review. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groff, D.; Sun, A.; Ssentongo, A.E; et al. Short-term and Long-term Rates of Postacute Sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Systematic Review. JAMA Netw Open. 2021, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, A.; Shah, M.; Ahmad, S.A.; et al. Pathogenesis Underlying Neurological Manifestations of Long COVID Syndrome and Potential Therapeutics. Cells. 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelalim, A.A.; Mohamady, A.A.; Elsayed, R.A.; Elawady, M.A.; Ghallab, A.F. Corticosteroid nasal spray for recovery of smell sensation in COVID-19 patients: A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2021, 42. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, S.; Lee, J.J.; Perrin, A.; Khan, A.; Smith, H.J.; Farrell, N.; Kallogjeri, D.; Piccirillo, J.F. Efficacy and Safety of Saline Nasal Irrigation Plus Theophylline for Treatment of COVID-19-Related Olfactory Dysfunction: The SCENT2 Phase 2 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2022, 148, 830–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafloo, R.; Majidi, J.; Asghari, A.; Aleemardani, M.; Kamrava, S.K.; Simorgh, S.; Seifalian, A.; Bagher, Z.; Seifalian. A.M. Mechanism of Anosmia Caused by Symptoms of COVID-19 and Emerging Treatments. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2021, 12, 3795–3805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, N.; Dickinson, D.; Garcia, W.; Xiao, L.; Xayaraj, A.; Lee, L.H.; Chu, T.; Kumar, M.; Stone, S.; Liu, Y.; Yu, H.; Cai, J.; Yao, B.; Jiang, X.; Hsu, S. Evaluation of Aqueous Nanoformulations of Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate-Palmitate (EC16) Against Human Coronavirus as a Potential Intervention Drug. Biomed J Sci & Tech Res. 2023, 50. [Google Scholar]
- Frank, N.; Dickinson, D.; Garcia, W.; Liu, Y.; Yu, H.; Cai, J.; Patel, S.; Yao, B.; Jiang, X.; Hsu, S. Feasibility Study of Developing a Saline-Based Antiviral Nanoformulation Containing Lipid-Soluble EGCG: A Potential Nasal Drug to Treat Long COVID. Viruses. 2024, 16, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinda, B.; Dinda, S.; Dinda, M. Therapeutic potential of green tea catechin, (-)-epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate (EGCG) in SARS-CoV-2 infection: Major interactions with host/virus proteases. Phytomed Plus. 2023, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, S. Compounds Derived from Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate (EGCG) as a Novel Approach to the Prevention of Viral Infections. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 2015, 14, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, B.L.; Dickinson, D.; Hsu, S. Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate (EGCG) Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Primate Epithelial Cells: (A Short Communication). Microbiol Infect Dis. 2021, 5, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Dickinson, D.; Hsu, S. Lipid-soluble Green Tea Polyphenols: Stabilized for Effective Formulation. In Handbook of Green Tea and Health Research. McKinley, H., Jamieson, M., Eds.; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: New York, 2009; pp. 45–61. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, S.; Dickinson, D. Green tea and skin protection: Mechanism of action and practical applications. Household and Personal Care. TODAY 2009, 2, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Kang, Z.; Yan, W. Synthesis, Stability, and Antidiabetic Activity Evaluation of (−)-Epigallo-catechin Gallate (EGCG) Palmitate Derived from Natural Tea Polyphenols. Molecules. 2021, 26, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, S.; Dickinson, D.; Borke, J.; Walsh, D.S.; Wood, J.; Qin, H.; Winger, J.; Pearl, H.; Schuster, G.; Bollag, W.B. Green tea polyphenol induces caspase 14 in epidermal keratinocytes via MAPK pathways and reduces psoriasiform lesions in the flaky skin mouse model. Experimental Dermatology. 2007, 16, 678–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, K.; Kodani, I.; Dickinson, D.P.; Ogbureke, K.U.E.; Camba, A.M.; Wu, M.; Looney, S.; Chu, T.C.; Qin, H.; Bisch, F.; Sharawy, M.; Schuster, G.S.; Hsu. S.D. Effects of oral consumption of the green tea polyphenol EGCG in a murine model for human Sjogren's syndrome, an autoimmune disease. Life Sciences. 2008, 83, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, S.D.; Dickinson, D.P.; Qin, H.; Borke, J.; Ogbureke, K.U.E.; Winger, J.N.; Camba, A.M.; Bollag, W.B.; Stöppler, H.J.; Sharawy, M.M.; Schuster, G.S. Green tea polyphenols reduce autoimmune symptoms in a murine model for human Sjogren's syndrome and protect human salivary acinar cells from TNF-alpha-induced cytotoxicity. Autoimmunity. 2007, 40, 138–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, D.; DeRossi, S.; Yu, H.; Thomas, C.; Kragor, C.; Paquin, B.; Hahn, E.; Ohno, S.; Yamamoto, T.; Hsu, S. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate modulates antioxidant defense enzyme expression in murine submandibular and pancreatic exocrine gland cells and human HSG cells. Autoimmunity. 2014, 47, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, D.; Yu, H.; Ohno, S.; Thomas, C.; Derossi, S.; Ma, Y.H.; Yates, N.; Hahn, E.; Bisch, F.; Yamamoto, T.; Hsu, S. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate prevents autoimmune-associated down- regulation of p21 in salivary gland cells through a p53-independent pathway. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets. 2014, 13, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Torre, R.; de Sola, S.; Farre, M.; Xicota, L.; Cuenca-Royo, A.; Rodriguez, J.; Leon, A.; Langohr, K.; Gomis-Gonzalez, M.; Hernandez, G.; et al. A phase 1, randomized double-blind, placebo controlled trial to evaluate safety and efficacy of epigallocatechin-3-gallate and cognitive training in adults with Fragile X syndrome. Clin Nutr. 2020, 39, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.A.; Mandal, A.K.; Khan, Z.A. Potential neuroprotective properties of epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG). Nutr J. 2016, 15, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano, A.; Ettcheto, M.; Espina, M.; Auladell, C.; Calpena, A.C.; Folch, J.; Barenys, M.; Sánchez-López, E.; Camins, A.; García, M.L. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate loaded PEGylated-PLGA nanoparticles: A new anti-seizure strategy for temporal lobe epilepsy. Nanomedicine: Nanotechnology, Biology and Medicine. 2018, 14, 1073–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.Y.; Li, X.M.; Liang, J.P.; Xiang, L.P.; Wang, K.R.; Shi, Y.L.; Yang, R.; Shi, M.; Ye, J.H.; Lu, J.L.; et al. Bioavailability of Tea Catechins and Its Improvement. Molecules. 2018, 23, 2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.S.; Chen, L.; Lee, M.J.; Balentine, D.; Kuo, M.C.; Schantz, S.P. Blood and urine levels of tea catechins after ingestion of different amounts of green tea by human volunteers. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 1998, 7, 351–354. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhong, J.; Dickinson, D.; Sampath, L.; Hsu, S. Effects of Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate-Palmitate (EC16) on In Vitro Norovirus Infection. Microbiol Infect Dis. 2021, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y. , Chen, P., Ling, T., Wang, Y., Dong, R., Zhang, C., Zhang, L., Han, M., Wang, D., Wan, X., & Zhang, J. Certain (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG) auto-oxidation products (EAOPs) retain the cytotoxic activities of EGCG. Food Chem. 2016, 204, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, A.; Adams, S.D.; Lee, L.H.; Murray, S.R.; Hsu, S.D.; Hammond, J.R.; Dickinson, D.; Chen, P.; Chu, T.C. Inhibition of herpes simplex virus type 1 with the modified green tea polyphenol palmitoyl-epigallocatechin gallate. Food Chem Toxicol. 2013, 52, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, S.; Miyake, S.; Kobe, T.; Nakaya, T.; Fuller, S.D.; Kato, N.; Kaihatsu, K. Enhanced anti-influenza A virus activity of (-)-epigallocatechin-3-O-gallate fatty acid monoester derivatives: effect of alkyl chain length. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2008, 18, 4249–4252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barhoum, A.; García-Betancourt, M.L.; Jeevanandam, J.; Hussien, E.A.; Mekkawy, S.A.; Mostafa, M.; Omran, M.M.; Abdalla, M.S.; Bechelany, M. Review on Natural, Incidental, Bioinspired, and Engineered Nanomaterials: History, Definitions, Classifications, Synthesis, Properties, Market, Toxicities, Risks, and Regulations. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022, 12, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farabegoli, F.; Granja, A.; Magalhães, J.; Purgato, S.; Voltattorni, M.; Pinheiro, M. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate Delivered in Nanoparticles Increases Cytotoxicity in Three Breast Carcinoma Cell Lines. ACS Omega. 2022, 7, 41872–41881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farabegoli, F.; Pinheiro, M. Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Delivery in Lipid-Based Nanoparticles: Potentiality and Perspectives for Future Applications in Cancer Chemoprevention and Therapy. Front Pharmacol. 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.H.; Hsieh, C.H.; Tsai, S.Y.; Wang, C.Y.; Wang, C.C. Anticancer effects of epigallocatechin-3-gallate nanoemulsion on lung cancer cells through the activation of AMP-activated protein kinase signaling pathway. Sci Rep. 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, A.; Guan, X.; Song, H.; Li, S.; Huang, K. Encapsulation of (−)-epigallocatechin-gallate (EGCG) in hordein nanoparticles. Food Bioscience. 2020, 37. [Google Scholar]
- Song, H.; He, A.; Guan, X.; Chen, Z.; Bao, Y.; Huang, K. Fabrication of chitosan-coated epigallocatechin-3-gallate (EGCG)-hordein nanoparticles and their transcellular permeability in Caco-2/HT29 cocultures. Int J Biol Macromol. 2022, 196, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Ma, L.; Huang, Q. Advances in Nanodelivery of Green Tea Catechins to Enhance the Anticancer Activity. Molecules. 2021, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzyzowska, M.; Janicka, M.; Chodkowski, M.; Patrycy, M.; Obuch-Woszczatyńska, O.; Tomaszewska, E.; Ranoszek-Soliwoda, K.; Celichowski, G.; Grobelny, J. Epigallocatechin Gallate-Modified Silver Nanoparticles Show Antiviral Activity against Herpes Simplex Type 1 and 2. Viruses. 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meesaragandla, B.; Hayet, S.; Fine, T.; Janke, U.; Chai, L.; Delcea, M. Inhibitory Effect of Epigallocatechin Gallate-Silver Nanoparticles and Their Lysozyme Bioconjugates on Biofilm Formation and Cytotoxicity. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2022, 5, 4213–4221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakakura, Y. , Ukai, K., Majima, Y., Murai, S., Harada, T., & Miyoshi, Y. Nasal mucociliary clearance under various conditions. Acta Otolaryngol. 1983, 96, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helwa, I.; Cai, J.; Drewry, M.D.; et al. A Comparative Study of Serum Exosome Isolation Using Differential Ultracentrifugation and Three Commercial Reagents. PLoS One. 2017, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, L.J.; Muench, H. ; A simple method of estimating 50 percent end points. Am. J. Hyg. 1938, 27, 493–497. [Google Scholar]
- US FDA GRAS NOTICE 772, U.G.N. GRAS Notice for Oil-Soluble Green Tea Extract (Green Tea Catechin Palmitate). 2018. (Chrome-extension://efaidnbmnnnibpcajpcglclefindmkaj/https://www.fda.gov/media/126906/download).
- Rabago, D.; Zgierska, A. Saline nasal irrigation for upper respiratory conditions. Am Fam Physician. 2009, 80, 1117–1119. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- de Melo, G.D.; Lazarini, F.; Levallois, S.; Hautefort, C.; Michel, V.; Larrous, F.; Verillaud, B.; Aparicio, C.; Wagner, S.; Gheusi, G.; et al. COVID-19-related anosmia is associated with viral persistence and inflammation in human olfactory epithelium and brain infection in hamsters. Sci Transl Med. 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.I.; Lee, C. Human Coronavirus OC43 as a Low-Risk Model to Study COVID-19. Viruses. 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




