Submitted:
27 April 2024
Posted:
29 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction:
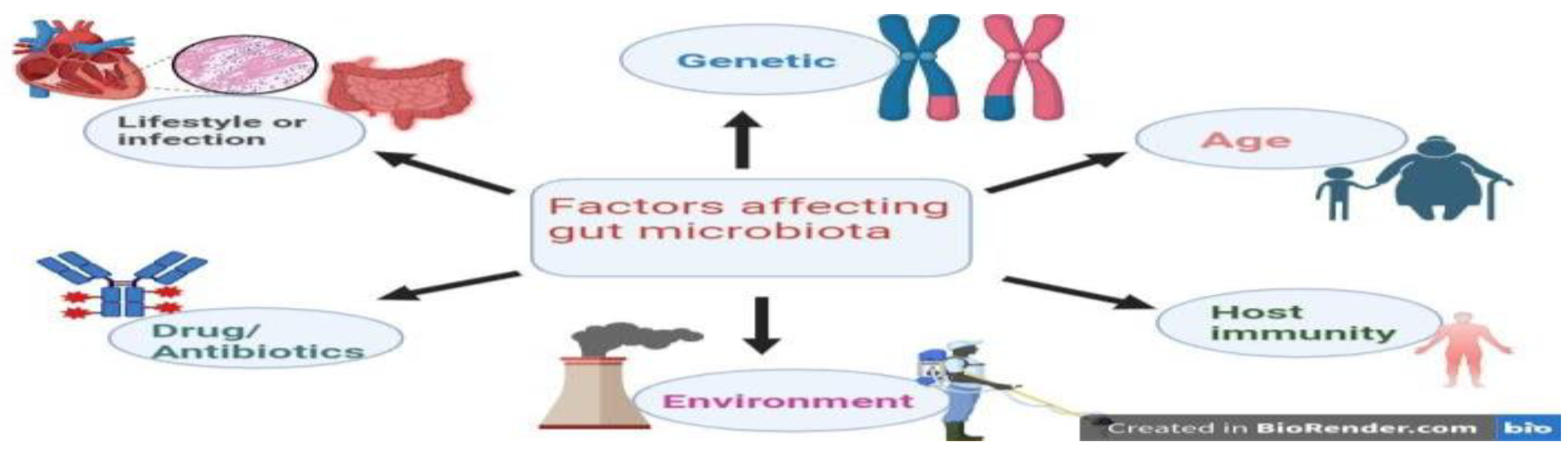
The Probiotics: A Dynamic Relationship with Gut Microbiota
| GUT | MICROBIOTA | pH | BACTERIAL LOAD | DIVERSITY | REFERENCE |
| Stomach |
Helecobacter Streptococcus Prevotella |
Stomach (2-4) | ~107 CFU ml-1, | limited diversity of gut microbiota | [6,7] |
| Small intestine |
Streptococcaceae Veillonellaceae Enterobacteriaceae |
Duodenum (6) | ~101 - 103 CFU ml−1 | Unique and less diverse | [7,8] |
| Illium (7.5) | ~104–107 CFU ml−1 | ||||
| Jejunum (7.5) | ~104–107 CFU ml−1 | ||||
| large intestine |
Bacteroidaceae Lachnospiraceae Ruminococcaceae |
Caecum (7.4 to 6.3) |
~1011–1012 CFU ml−1 | Abundant and diverse microbiota | [7,9] |
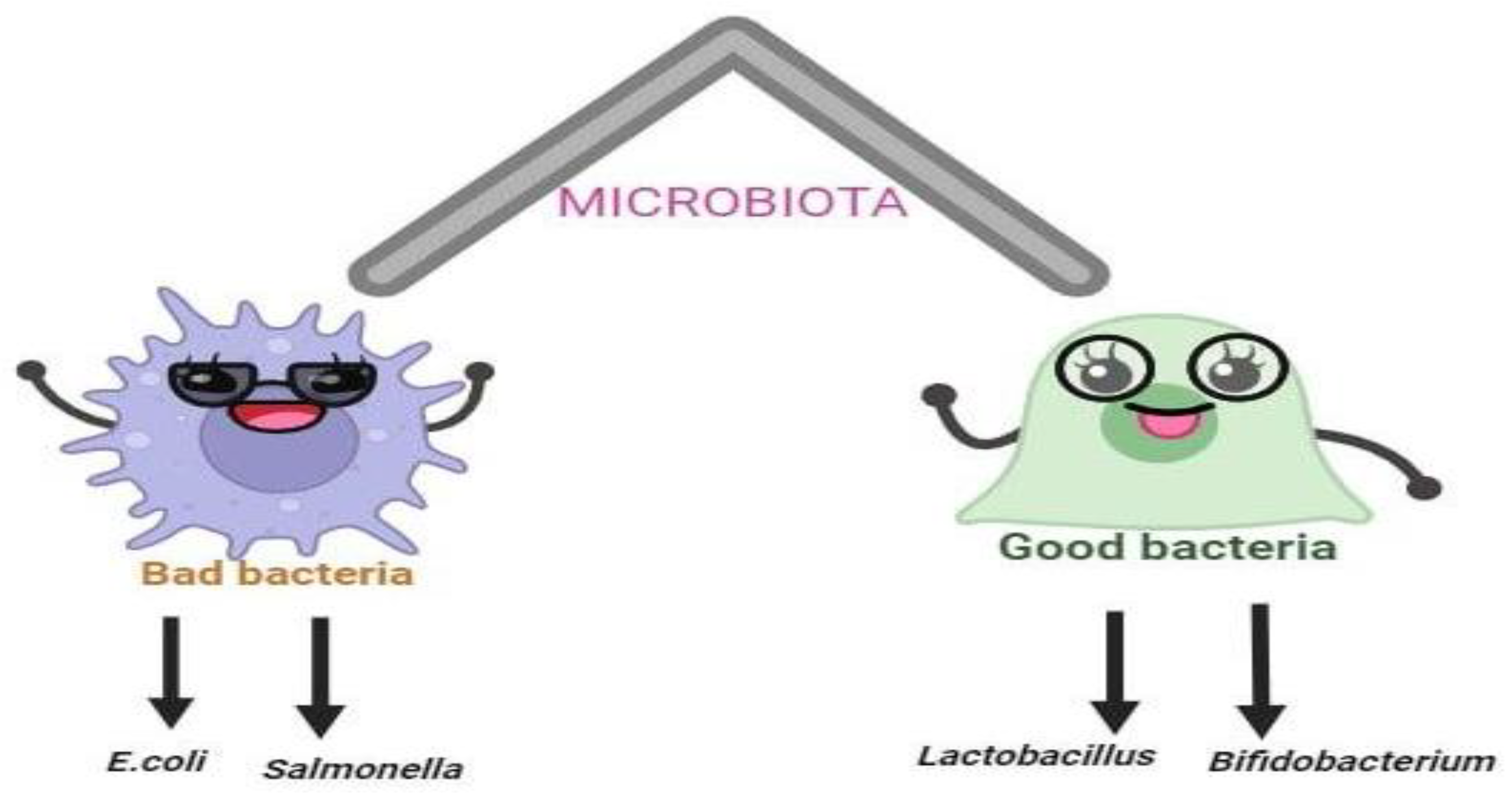
| Probiotics | Effect on health | Mechanism of action | Reference |
|
L. acidophilus, S. thermophilus, B. longum, L. rhamnosus GG and B.bifidum |
Inhibits Escherichia coli, Salmonella, Clostridium difficile and rotavirus that may cause diahrea |
Production of organic acids, bacteriocins, hydrogen peroxide, carbon dioxide and diacetyl |
[15] |
|
Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium infantis |
Inhibits Staphylococcus aureus, Salmonella typhimurium, Yersinia enterocolitica, Clostridium perfringens that may cause intestinal infection |
Production of organic acids, bacteriocins and other primary metabolites, such as hydrogen peroxide, carbon dioxide and diacetyl |
[14] |
|
B. longum, L. casei Shirota, L. acidophilus, Bifidobaterium spp. and L. rhamnosus GG |
Inhibits formation and proliferation of tumor | Inhibition of carcinogens and/or procarcinogens, inhibition of bacteria that convert procarcinogens to carcinogens, activation of the host’s immune system, reduce the levels of faecal enzymes responsible for catalysing the conversion of carcinogenic amines |
[16] |
|
L. acidophilus and Bifidobacterium spp. |
Inhibits Helicobacter pylori that Reduction of peptic ulcer, gastro-oesophageal reflux, nonulcer dyspepsia and gastric cancer |
Production of acetic and lactic acids, bacteriocins etc |
[17] |
| L. rhamnosus GG | Help to relieve intestinal inflammation and hypersensitivity reactions in infants with food allergies |
Hydrolyse the complex casein to smaller peptides and amino acids and hence decrease the proliferation of mitogen-induced human lymphocytes |
[18] |
| L. acidophilus | Reduces cholesterol level | Assimilation of cholesterol and deconjugation of bile s |
[19] |
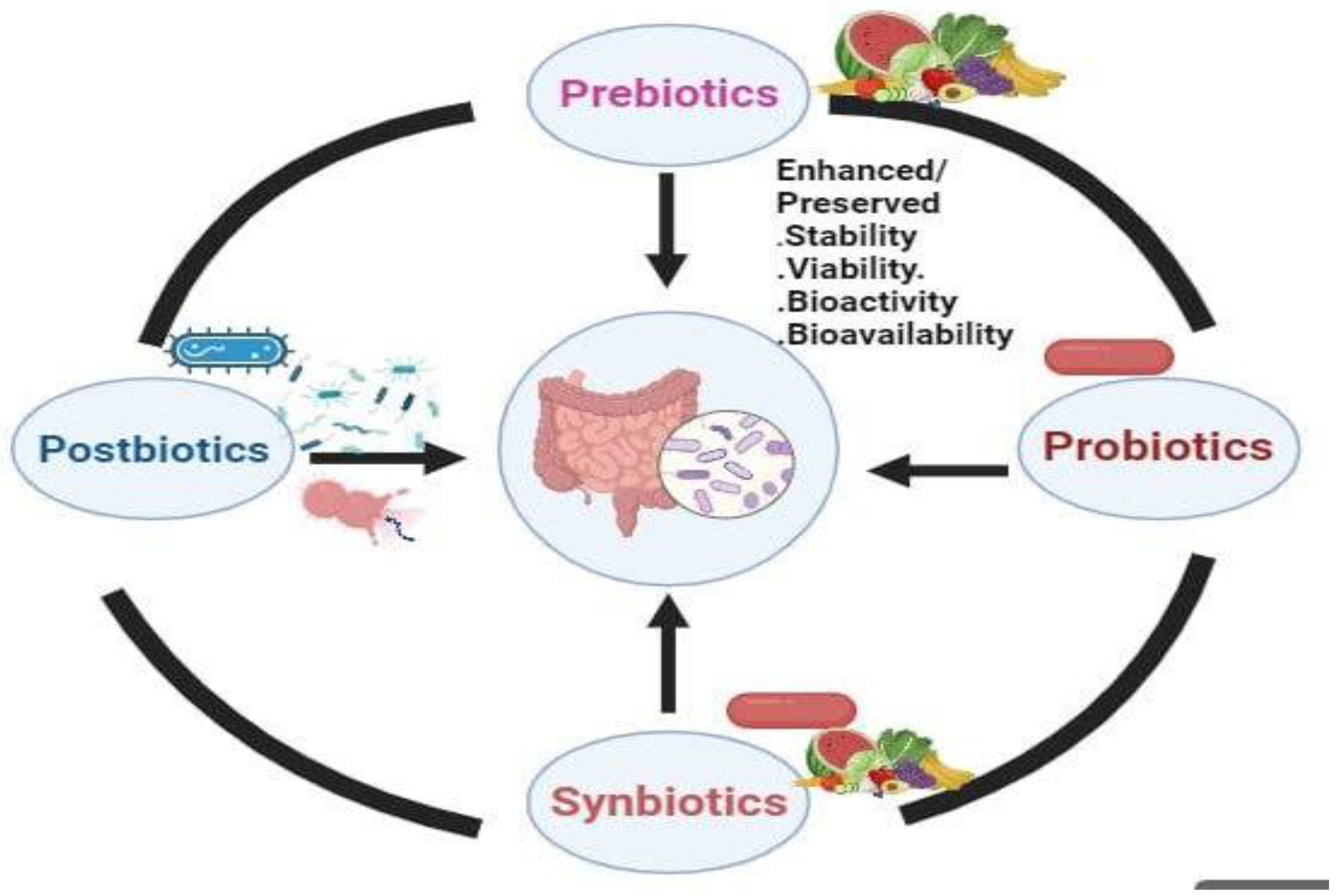
Prebiotics: Nourishing the Gut Microbiota for Health
| Prebiotics | Impact on health | Mechanism of action | Reference |
| Isomalto-oligosaccharides (IMO) from miso, soy sauce and honey |
Local and systemic Th-1-like immune response and regulation of immune function, balancing the dysbiosis of gut microbiota |
Bifidobacterium and the Bacteroides groups are able to utilize IMO |
[21] |
| Inulin from chicory roots | promotes healthy gut | Stimulate the growth of Bifidobacterium |
[22] |
| Xylooligosaccharides (XOS) from fruits, bamboo shoots, vegetables, honey, |
promotes healthy gut | B. adolescentis utilizes xylobiose and xylotriose, whereas L. lactis, L. rhamnosus and L. plantarum utilize oat β-galactooligosaccharides |
[23] |
Synbiotics: Synergistic Effects For Enhanced Health Benefits
| Symbiotics | Impact on health | Mechanism of action | Reference |
|
L. acidophilus, L. rhamnosus, B. bifidum, B. longum, E. faecium and FOS |
Changes in anthropometric measurements that may cure obesity |
Decrease in TC, LDL-C and total oxidative stress serum levels |
[24] |
| Oral synbiotic preparation containing L. plantarum and FOS |
Significant reduction in sepsis and lower respiratory tract infections that may lower sepsis in early infancy |
Promotes growth of L. plantarum ATCC202195 |
[25] |
|
L. rhamnosus GG, B. lactis Bb12 and inulin |
Increase in probiotics in stools and decrease in Clostridium perfringens led to increase in the IL2 in polypectomies patients that may reduce cancer |
Increases production of interferon-ϒ |
[26] |
|
L. rhamnosus CGMCC1.3724 and inulin |
Weight loss that may decrease obesity | Reduction in leptin increase in Lachnospiraceae |
[27] |
| Curd containing B. longum and fructooligosaccharide (FOS) |
Reduces cardiovascular risk factors, metabolic syndrome prevalence and markers of insulin resistance in elderly patients |
Increase in good bacteria | [29] |
|
L. plantarum La-5, B. animalis subsp. lactisBB-12 and dietary fibres |
Improvement in the IBS score and satisfaction in bowel movement reported |
Increase in good bacteria | [28] |
| Food products containing B. animalis and amylose corn starch |
promotes gut health | Promote the growth of bifidobacteria |
[30] |
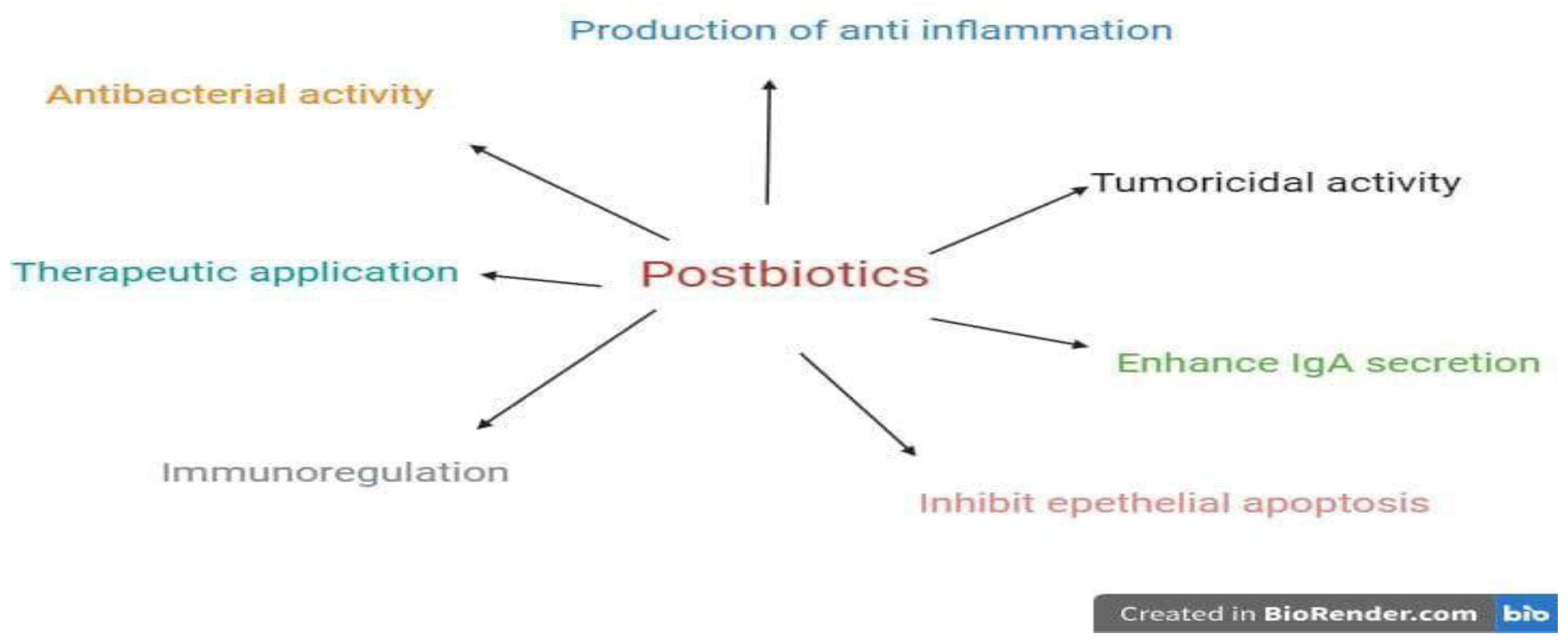
Postbiotics: Unveiling the Potential of Microbiome Metabolites
| Postbiotics (microorganism) | Impact on health | Disease | Reference |
| Lysates of Methylococcus capsulatus Bath (McB) | Improve glucose regulation, reduce body and liver fat, and diminish hepatic immune infiltration | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) | [88] |
| Extracellular vesicles (Lactobacillus animalis) | Increase angiogenesis, augment osteogenesis, and reduce cell apoptosis | Osteonecrosis of the femoral head (ONFH) | [89] |
| Outer membrane vesicles (OMVs) of Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron | Direct a balanced immune response to constituents of the microbiota locally and systemically | Inflammation bowel disease (IBD) | [89] |
| Short-chain fatty acid (SCFA) butyrate | Repress HK2 expression via histone deacetylase 8 (HDAC8) and reduce mitochondrial respiration | Colitis | [90] |
Therapeutic Applications: Harnessing The Power of Probiotics, Prebiotics, Synbiotics, And Postbiotics (Ppsp) in Microbiome Modulation

| Disease | ppsp | Functions | Reference | |
| Diarrhea | oral rehydration and probiotics | S.boulardii, L.acidophilus, L.rhamnosus GG, L.fermentum | Stimulation of immune system,constipation,changes in bile salt conjugation enhancement of antibacterial activity,antiinflammatory | [31,55,56,57,58,59] |
| Irritable bowel syndrome | probiotics and prebiotics |
probiotics: L.rhamnosus GG ,B.infantis,B.breveBb99 prebiotics: Soluble, non-viscous fibers, such as partially hydrolyzed guar gum |
Modulate the gut microbiota, improve stool frequency, improve gut transit time and improve stool consistency | [32,60,61,62,63] |
| Inflammatory bowel disorder(Ulcerative Colitis (UC), Crohn’s Disease (CD)) | probiotics |
S.boulardii,L.casei,Bifidobacterium bifidum pouchitis. Probiotics: S. boulardii, Lactobacillus casei, Bifidobacterium bifidum for UC; general benefits for CD; probiotic mixes for pouchitis |
Balance the intestinal homeostasis, induce remission in IBD,inhibit epithelium attachment | [33,64,65,66,67,68] |
| Lactose intolerance | probiotics | probiotics: L.acidophilus, L.casei shirota, Bifidobacterium breve Yakult,L.helveticus | Modulation of mucin production, enhance Ig A secretion by a GALT, production of SCFA | [69] |
| Cardiovascular disease | probiotics, prebiotics and synbiotics |
L.bulgaricus, L.reuteri,, B.coagulans, L.acidophilus prebiotics: Inulin can enhance hypocholesterolemic activity. synbiotics1; combine both |
Potential therapeutic, enhance the hypercholesterolemic activity | [70,71,72,73] |
| Cancer | probiotics and synbiotics |
probiotics: L.acidophilus, B.longum and Comprehensive approach preventing pro-carcinogen transformation and inducing cell death |
Preventing the onset of cancer, treatment of existing tumors | [34,74,75,76] |
| Urinary tract infection | probiotics and synbiotics | Lactobacillus GG, L.rhamnosus | Stimulate the growth of different indigenous gut bacteria, immunomodulation, adjuvant therapy | [35,77,78,79] |
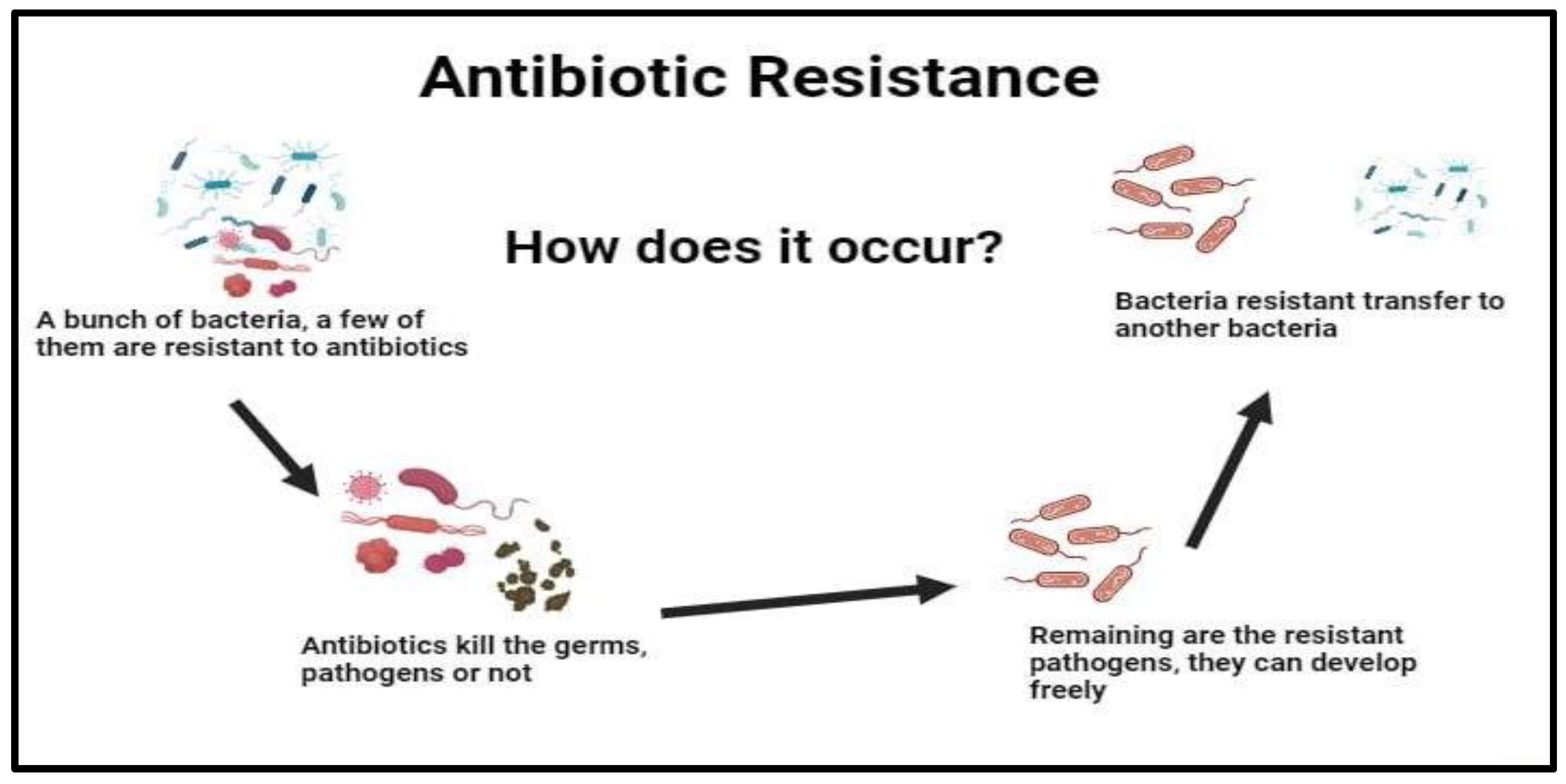
Exploring the Role of Probiotics, Prebiotics, Synbiotics, and postbiotics (ppsp) as Antibiotic Alternatives
Discussion:
References
- Vergin, F. Anti-und Probiotica. Hipokrates 1954, 25, 116–119. [Google Scholar]
- Silva DR, OrlandiSardi JC, Pitangui NS, MagriRoque S, Barbosa da Silva AC, Rosalen PL (2020) Probiotics as an alternative antimicrobial therapy: current reality and future directions. J Funct Foods 73:104080. [CrossRef]
- Cummings JH, Macfarlane GT, Englyst HN. Prebiotic digestion and fermentation. Am J Clin Nutr. 2001;73:415s–420s. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/73.2.415s. [CrossRef]
- Markowiak P, Slizewska K. Effects of probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics on human health. Nutrients. 2017;9:1021. [CrossRef]
- Oren, A. & Garrity, G.M. Valid publication of the names of forty-two phyla of prokaryotes. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 71, 005056 (2021).
- Konradt, M. et al. The spatial orientation of Helicobacter pylori in the gastric mucus. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 101, 5024–5029 (2004).
- Hara, A. M. O. & Shanahan, F. The gut flora as a forgotten organ. EMBO Rep. 7, 688–693 (2006).
- Evans, D. F. et al. Measurement of gastrointestinal pH profiles in normal ambulant human subjects. Gut 29, 1035–1041 (1988).
- (2006). 33. Sender, R., Fuchs, S. & Milo, R. Revised estimates for the number of human and bacteria cells in the body. PLoS Biol. 14, e1002533 (2016).
- Odamaki et al. (2016) Odamaki T, Kato K, Sugahara H, Hashikura N, Takahashi S, Xiao J-Z, Abe F, Osawa R. Age-related changes in gut microbiota composition from newborn to centenarian: a cross-sectional study. BMC Microbiology. 2016;16(1):90. [CrossRef]
- Jandhyala et al. (2015) Jandhyala SM, Talukdar R, Subramanyam C, Vuyyuru H, Sasikala M, Reddy DN. Role of the normal gut microbiota. World Journal of Gastroenterology. 2015;21(29):8787. [CrossRef]
- DiGiulio et al. (2008) DiGiulio DB, Romero R, Amogan HP, Kusanovic JP, Bik EM, Gotsch F, Kim CJ, Erez O, Edwin S, Relman DA, Fisk NM. Microbial prevalence, diversity and abundance in amniotic fluid during preterm labor: a molecular and culture-based investigation. PLOS ONE. 2008;3(8):e3056. [CrossRef]
- Albenberg L, Wu G. Diet and the intestinal microbiome: associations, functions, and implications for health and disease. Gastroenterology. 2014;146(6):1564–72.
- Laroia S, Martin J. Bifidobacteria as possible dietary adjuncts in cultured dairy products-a review. Cult Dairy Prod J. 1990;25:18–22.
- Barefoot SF, Klaenhammer TR. Detection and activity of lactacin B, a bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus acidophilus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983;45:1808–1815. [CrossRef]
- Goldin BR, Gualtieri LJ, Moore RP. The effect of Lactobacillus GG on the initiation and promotion of DMH-induced intestinal tumors in the rat. Nutr Cancer. 1996;25:197–204. [CrossRef]
- McIntosh GH. Probiotics and colon cancer prevention. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 1996;5:48–52.
- Hughes DB, Hoover DG. Viability and enzymatic activity of bifidobacteria in milk. J Dairy Sci. 1995;78:268–276. [CrossRef]
- Guarino MPL, Altomare A, Emerenziani S, Di Rosa C, Ribolsi M, Balestrieri P, Iovino P, Rocchi G, Cicala M. Mechanisms of action of prebiotics and their effects on gastro-intestinal disorders in adults. Nutrients. 2020;12:1037. [CrossRef]
- Gibson, R.G.; Roberfroid, M.B. Dietary modulation of the human colonic microbiota: Introducing the concept of prebiotics. J. Nutr. 1995, 125, 1401–1412.
- Kohmoto T, Fukui F, Takaku H, Machida Y, Arai M, Mitsuoka T. Effect of isomalto-oligosaccharides on human fecal flora. Bifidobacteria Microflora. 1988;7:61–69. [CrossRef]
- Desai AR (2008) Strain identification, viability and probiotics properties of Lactobacillus casei. Ph.D. Thesis, School of Biomedical and Health Sciences. Victoria University, Werribee Campus Victoria, Australia.
- Okazaki M, Fujikawa S, Mastumoto N. Effects of xylooligosaccharides on growth of Bifidobacteria. Bifidobactetria Microflora. 1990;9:77–86. [CrossRef]
- par N, Aydogdu SD, Yildirim GK, Inal M, Gies I, Vandenplas Y, Dinleyici EC. Effects of synbiotic on anthropometry, lipid profile and oxidative stress in obese children. Benef Microbes. 2015;6:775–782. [CrossRef]
- Panigrahi P, Parida S, Nanda NC, Satpathy R, Pradhan L, Chandel DS, Baccaglini L, Mohapatra A, Mohapatra SS, Misra PR, Chaudhry R, Chen HH, Johnson JA, Morris JG, Paneth N, Gewolb IH. A randomized synbiotic trial to prevent sepsis among infants in rural India. Nature. 2017;548:407–412. [CrossRef]
- Safavi M, Farajian S, Kelishadi R, Mirlohi M, Hashemipour M. The effects of synbiotic supplementation on some cardio-metabolic risk factors in overweight and obese children: a randomized triple-masked controlled trial. Int J Food Sci Nutr. 2013;64:687–693. [CrossRef]
- Sanchez M, Darimont C, Drapeau V, Emady-Azar S, Lepage M, Rezzonico E, Ngom-Bru C, Berger B, Philippe L, Ammon-Zuffrey C, Leone P, Chevrier G, St-Amand E, Marette A, Doré J, Tremblay A. Effect of Lactobacillus rhamnosus CGMCC1.3724 supplementation on weight loss and maintenance in obese men and women. Br J Nutr. 2014;111:1507–1519. [CrossRef]
- Šmid A, Strniša L, Bajc K, Vujić-Podlipec D, Matijašić BB, Rogelj I. Randomized clinical trial: the effect of fermented milk with the probiotic cultures Lactobacillus acidophilus La-5® and Bifidobacterium BB-12® and Beneo dietary fibres on health-related quality of life and the symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome in adults. J Funct Foods. 2016;24:549–557. [CrossRef]
- Eslamparast T, Zamani F, Hekmatdoost A, Sharafkhah M, Eghtesad S, Malekzadeh R, Poustchi H. Effects of synbiotic supplementation on insulin resistance in subjects with the metabolic syndrome: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study. Br J Nutr. 2014;112:438–445. [CrossRef]
- Bruno FA, Lankaputhra WEV, Shah NP. Growth, viability and activity of Bifidobacterium spp. in skim milk containing prebiotics. J Food Sci. 2002;67:2740–2744. [CrossRef]
- Thursby E, Juge N. Introduction to the human gut microbiota. Biochem J. 2017;474(11):1823-1836. [CrossRef]
- Smits WK, Lyras D, Lacy DB, et al. Clostridium difficile infection. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16020. [CrossRef]
- https://isappscience.
- Glenn G., Roberfroid M. Dietary modulation of the human colonic microbiota: Introducing the concept of prebiotics. J. Nutr. 1995;125:1401–1412.
- Louis P., Flint H.J., Michel C. Microbiota of the Human Body. Springer; Basel, Switzerland: 2016. How to manipulate the microbiota: Prebiotics; pp. 119–142.
- Dutt, Y., Pandey, R.P., Dutt, M. et al. Therapeutic applications of nanobiotechnology. J Nanobiotechnol 21, 148 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Clinical Profile and Sensitivity Pattern of Salmonella Serotypes in Children: A Hospital Based Study.
- BG Joshi, K Keyal, R Pandey, BM Shrestha – 2011.
- Sharma M, Maheswari M, Pandey R. Development of air quality index for data interpretation and public information. Department of civil Engineering, IIT Kanpur, Report submitted to CPCB, Delhi. 2001.
- Tyagi, R., Srivastava, M., Jain, P., Pandey, R. P., Asthana, S., Kumar, D., & Raj, V. S. (2022). Development of potential proteasome inhibitors against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics, 40(5), 2189–2203. [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee S, Mishra AK, Peer GDG, Bagabir SA, Haque S, Pandey RP, Raj VS, Jain N, Pandey A, Kar SK. The Interplay of the Unfolded Protein Response in Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Therapeutic Role of Curcumin. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021 Nov 19;13:767493. [CrossRef]
- Pandey, R.P.; Mukherjee, R.; Chang, C.-M. Emerging Concern with Imminent Therapeutic Strategies for Treating Resistance in Biofilm. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 476. [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S., Dahiya, V., Vibhuti, A., Pandey, R.P., Tripathi, M.K., Yadav, M.K. (2023). Therapeutic Protein-Based Vaccines. In: Singh, D.B., Tripathi, T. (eds) Protein-based Therapeutics. Springer, Singapore. [CrossRef]
- Himanshu, R. Prudencio C, da Costa AC, Leal E, Chang C-M, Pandey RP. Systematic Surveillance and Meta-Analysis of Antimicrobial Resistance and Food Sources from China and the USA. Antibiotics. 2022; 11(11):1471. [CrossRef]
- Gunjan, Vidic J, Manzano M, Raj VS, Pandey RP, Chang CM. Comparative meta-analysis of antimicrobial resistance from different food sources along with one health approach in Italy and Thailand. One Health. 2022 Dec 22;16:100477. [CrossRef]
- Gibson G.R., Scott K.P., Rastall R.A., Tuohy K.M., Hotchkiss A., Dubert-Ferrandon A., Gareau M., Murphy E.F., Saulnier D., Loh G., et al. Dietary prebiotics: Current status and new definition. Food Sci. Technol. Bull. Funct. Foods. 2010;7:1–19. [CrossRef]
- Fuentes-Zaragoza E., Sánchez-Zapata E., Sendra E., Sayas E., Navarro C., Fernández-López J., Pérez-Alvarez J.A. Resistant starch as prebiotic: A review. Starch-Stärke. 2011;63:406–415. [CrossRef]
- Tzounis X., Rodriguez-Mateos A., Vulevic J., Gibson G.R., Kwik-Uribe C., Spencer J.P. Prebiotic evaluation of cocoa-derived flavanols in healthy humans by using a randomized, controlled, double-blind, crossover intervention study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011;93:62–72. [CrossRef]
- Louis P., Flint H.J., Michel C. Microbiota of the Human Body. Springer; Basel, Switzerland: 2016. How to manipulate the microbiota: Prebiotics; pp. 119–142.
- Cencic A, Chingwaru W. The role of functional foods, nutraceuticals, and food supplements in intestinal health. Nutrients. 2010;2(6):611–625. [CrossRef]
- DeVrese M, Schrezenmeir J (2008) Probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics. in food biotechnology (pp. 1–66).
- Romeo J, Nova E, Wärnberg J, Gómez-Martínez S, DíazLigia LE, Marcos A. Immunomodulatory effect of fibres, probiotics and synbiotics in different life-stages. Nutr Hosp. 2010;25(3):341–9.
- Peña AS. Intestinal flora, probiotics, prebiotics, synbiotics and novel foods. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2007;99(11):653. [CrossRef]
- Zhang MM, Cheng JQ, Lu YR, Yi ZH, Yang P, Wu XT. Use of pre-, pro-and synbiotics in patients with acute pancreatitis: a meta-analysis. World J Gastroenterol: WJG. 2010;16(31):3970. [CrossRef]
- Harish K, Varghese T. Probiotics in humans–evidence based review. Calicut Med J. 2006;4(4):e3.
- Tsilingiri K., Rescigno M. Postbiotics: What else? Benef. Microbes. 2013;4:101–107. [CrossRef]
- Furusawa Y., Obata Y., Fukuda S., Endo T.A., Nakato G., Takahashi D., Nakanishi Y., Uetake C., Kato K., Kato T., et al. Commensal microbe-derived butyrate induces the differentiation of colonic regulatory T cells. Nature. 2013;504:446–450. [CrossRef]
- Khodaii Z., Ghaderian S.M.H., Natanzi M.M. Probiotic Bacteria and their Supernatants Protect Enterocyte Cell Lines from Enteroinvasive Escherichia coli (EIEC) Invasion. Int. J. Mol. Cell. Med. 2017;6:183–189. [CrossRef]
- Harish K, Varghese T. Probiotics in humans–evidence based review. Calicut Med J. 2006;4(4):e3.
- Narayan SS, Jalgaonkar S, Shahani S, Kulkarni VN. Probiotics: current trends in the treatment of diarrhoea. Hong Kong Med J. 2010;16(3):213–218.
- Szymański H, Pejcz J, Jawień M, Chmielarczyk A, Strus M, Heczko PB. Treatment of acute infectious diarrhoea in infants and children with a mixture of three Lactobacillus rhamnosus strains– a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2006;23(2):247–253. [CrossRef]
- Bartlett JG. Antibiotic-associated diarrhea. N Engl J Med. 2002;346(5):334–339. [CrossRef]
- Hill DR, Ryan ET (2008) Management of travellers’ diarrhoea.
- McFarland LV. Meta-analysis of probiotics for the prevention of traveler’sdiarrhea. Travel Med Infect Dis. 2007;5(2):97–105. [CrossRef]
- Chapman CMC, Gibson GR, Rowland I. Health benefits of probiotics: are mixtures more effective than single strains? Eur J Nutr. 2011;50(1):1–17. [CrossRef]
- Guglielmetti S, Mora D, Gschwender M, Popp K. Randomised clinical trial: Bifidobacterium bifidum MIMBb75 significantly alleviates irritable bowel syndrome and improves quality of life––a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2011;33(10):1123–1132. [CrossRef]
- Kim HJ, Vazquez Roque MI, Camilleri M, Stephens D, Burton DD, Baxter K, Zinsmeister AR. A randomized controlled trial of a probiotic combination VSL# 3 and placebo in irritable bowel syndrome with bloating. Neuro-gastroenterology and Motility. 2005;17(5):687–696. [CrossRef]
- Hardy H, Harris J, Lyon E, Beal J, Foey AD. Probiotics, prebiotics and immunomodulation of gut mucosal defenses: homeostasis and immunopathology. Nutrients. 2013;5(6):1869–1912. [CrossRef]
- Moeinian M, FarnazGhasemi-Niri S, Mozaffari S, Abdollahi M. Synergistic effect of probiotics, butyrate and l-Carnitine in treatment of IBD. J Med Hypotheses Ideas. 2013;7(2):50–53. [CrossRef]
- Kelesidis T, Pothoulakis C. Efficacy and safety of the probiotic Saccharomyces boulardii for the prevention and therapy of gastrointestinal disorders. Ther Adv Gastroenterol. 2012;5(2):111–125. [CrossRef]
- Sheil B, Shanahan F, O’Mahony L. Probiotic effects on inflammatory bowel disease. J Nutr. 2007;137(3):819S–824S.
- Jonkers D, Penders J, Masclee A, Pierik M. Probiotics in the management of inflammatory bowel disease. Drugs. 2012;72(6):803–823. [CrossRef]
- Scaldaferri F, Gerardi V, Lopetuso LR, Del Zompo F, Mangiola F, Boškoski I, Gasbarrini, A (2013) Gut microbial flora, prebiotics, and probiotics in IBD: their current usage and utility. BioMed Res Intern 2013. [CrossRef]
- Vonk RJ, Reckman GA, Harmsen HJ, Priebe MG (2012) Probiotics and lactose intolerance. [CrossRef]
- Homayouni A, Payahoo L, Azizi A (2012) Effects of probiotics on lipid profile: a review.
- Teitelbaum JE, Walker WA. Nutritional impact of pre-and probiotics as protective gastrointestinal organisms. Annu Rev Nutr. 2002;22(1):107–138. [CrossRef]
- Parnell JA, Reimer RA. Effect of prebiotic fibre supplementation on hepatic gene expression and serum lipids: a dose–response study in JCR: LA-cp rats. Br J Nutr. 2010;103(11):1577–1584. [CrossRef]
- Liong MT, Dunshea FR, Shah NP. Effects of a synbiotic containing Lactobacillus acidophilus ATCC 4962 on plasma lipid profiles and morphology of erythrocytes in hypercholesterolaemic pigs on high-and low-fat diets. Br J Nutr. 2007;98(4):736–744. [CrossRef]
- Andrews JM, Tan M. Probiotics in luminal gastroenterology: the current state of play. Intern Med J. 2012;42(12):1287–1291. [CrossRef]
- Macfarlane S, Macfarlane GT, Cummings JT. Review article: prebiotics in the gastrointestinal tract. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2006;24(5):701–714. [CrossRef]
- Kaur N, Gupta AK. Applications of inulin and oligofructose in health and nutrition. J Biosci. 2002;27(7):703–714. [CrossRef]
- Intravesical Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG is safe and well tolerated in adults and children with neurogenic lower urinary tract dysfunction: first-in-human trial Ther. Adv. Urol., 11 (2019), pp. 1-13. [CrossRef]
- T. Antunes-Lopes, L. Vale, A.M. Coelho, C. Silva, M. Rieken, B. Geavlete, T. Rashid, S.M. Rahnama’i, J.N. Cornu, T. Marcelissen The role of urinary microbiota in lower urinary tract dysfunction: a systematic reviewm Eur. Urol. Focus, 6 (2) (2020), pp. 361-369. [CrossRef]
- G. Orive, E. Santos, J.L. Pedraz, R.M. Hernández Application of cell encapsulation for controlled delivery of biological therapeutics Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 67–68 (2013), pp. 3-14 Google Scholar.
- Nathan C, Cars O. Antibiotic resistance-problems, progress, and prospects. N Engl J Med. 2014;371(19):1761–1763.
- Goma Epidemiology Group. Public health impact of Rwandan refugee crisis: what happened in Goma, Zaire, in July, 1994. The Lancet. 1995;345:339–344.
- Sengupta PG, Niyogi SK, Bhattacharya SK. An outbreak of Eltor cholera in Aizwal town of Mizoram, India. Journal of Communicable Diseases. 2000;32:207–211.
- Okeke IN, Abudu AB, Lamikanra A. Microbiological investigation of an outbreak of acute gastroenteritis in Niger State, Nigeria. Clinical Microbiology and Infection. 2001;7:514–516.
- Singer AC, Shaw H, Rhodes V, Hart A. Review of antimicrobial resistance in the environment and its relevance to environmental regulators. Front Microbiol. 2016;7:1728.
- Davies J, Davies D. Origins and evolution of antibiotic resistance. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2010;74(3):417–433. [CrossRef]
- Jensen BAH, Holm JB, Larsen IS, von Burg N, Derer S, Sonne SB, et al. Lysates of Methylococcus capsulatus Bath induce a lean-like microbiota, intestinal FoxP3(+)RORγt(+)IL-17(+) Tregs and improve metabolism. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):1093. [CrossRef]
- Chen CY, Rao SS, Yue T, Tan YJ, Yin H, Chen LJ, et al. Glucocorticoid-induced loss of beneficial gut bacterial extracellular vesicles is associated with the pathogenesis of osteonecrosis. Sci Adv. 2022;8(15):eabg8335. [CrossRef]
- Durant L, Stentz R, Noble A, Brooks J, Gicheva N, Reddi D, et al. Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron-derived outer membrane vesicles promote regulatory dendritic cell responses in health but not in inflammatory bowel disease. Microbiome. 2020;8(1):88. [CrossRef]
- Hinrichsen F, Hamm J, Westermann M, Schröder L, Shima K, Mishra N, et al. Microbial regulation of hexokinase 2 links mitochondrial metabolism and cell death in colitis. Cell Metab. 2021;33(12):2355–66.e8. [CrossRef]
- Li HY, Zhou DD, Gan RY, Huang SY, Zhao CN, Shang A, Xu XY, Li HB. Effects and Mechanisms of Probiotics, Prebiotics, Synbiotics, and Postbiotics on Metabolic Diseases Targeting Gut Microbiota: A Narrative Review. Nutrients. 2021 Sep 15;13(9):3211. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohail MU, Yassine HM, Sohail A, Thani AAA. Impact of Physical Exercise on Gut Microbiome, Inflammation, and the Pathobiology of Metabolic Disorders. Rev Diabet Stud. 2019;15:35-48. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blount K, Jones C, Walsh D, Gonzalez C, Shannon WD. Development and Validation of a Novel Microbiome-Based Biomarker of Post-antibiotic Dysbiosis and Subsequent Restoration. Front MicroBiol. 2021;12:781275. [CrossRef]
- Elbere I, Kalnina I, Silamikelis I, Konrade I, Zaharenko L, Sekace K, Radovica-Spalvina I, Fridmanis D, Gudra D, Pirags V, Klovins J. Association of metformin administration with gut microbiome dysbiosis in healthy volunteers. PLoS One. 2018 Sep 27;13(9):e0204317. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camelo-Castillo A, Rivera-Caravaca JM, Orenes-Piñero E, et al. Gut microbiota and the quality of oral anticoagulation in vitamin K antagonists users: A review of potential implications. J Clin Med. 2021;10(4):1-15. [CrossRef]
- Rani V, Singhal S, Sharma K, et al. Human gut microbiome: A new frontier in cancer diagnostics & therapeutics. Curr Pharm Des. 2021;27(45):4578-4592. [CrossRef]
- Foley SE, Tuohy C, Dunford M, et al. Gut microbiota regulation of P-glycoprotein in the intestinal epithelium in maintenance of homeostasis. Microbiome. 2021;9(1):183. [CrossRef]
- Stolfi C, Maresca C, Monteleone G, Laudisi F. Implication of intestinal barrier dysfunction in gut dysbiosis and diseases. Biomedicines. 2022;10(2):1-27. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





