Submitted:
17 April 2024
Posted:
18 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Study Samples, Patient Data and Phenotypic Drug Susceptibility Testing
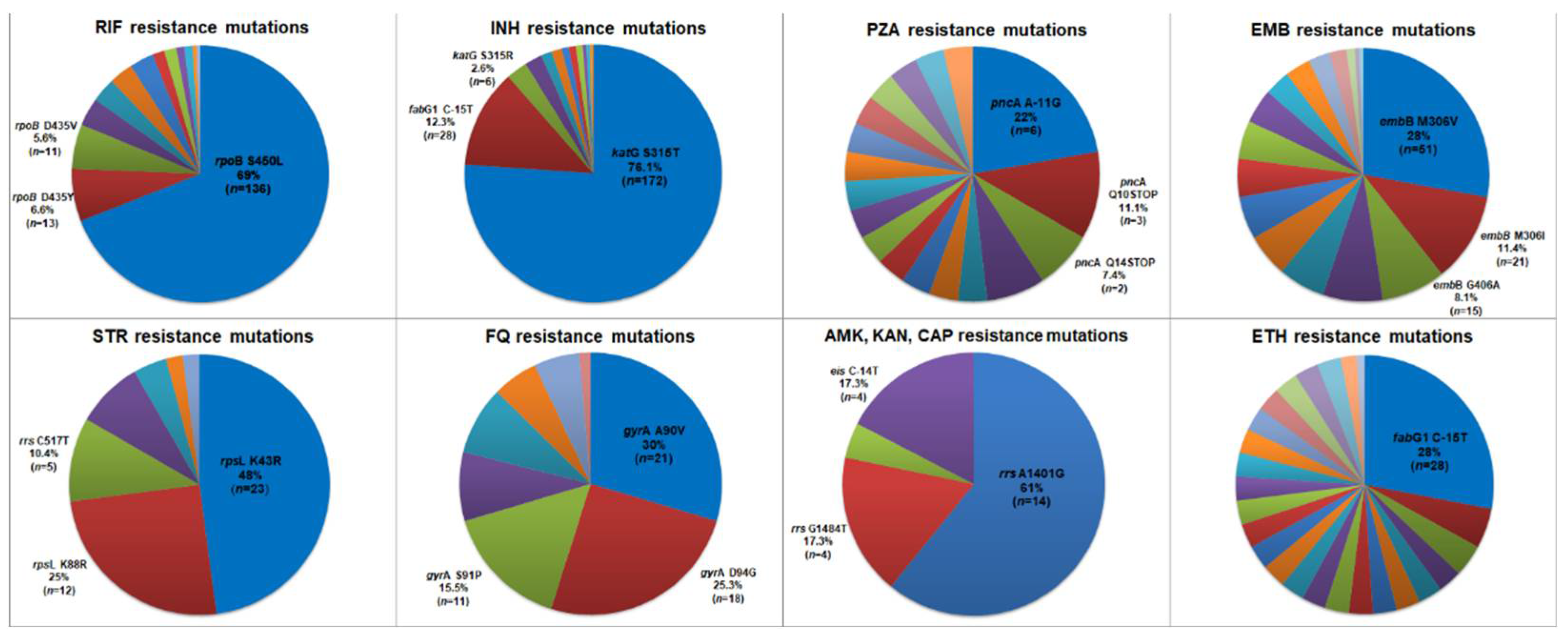
2.2. Novel Mutations, In Silico Drug Susceptibility and Resistance Prediction Using Different Pipelines
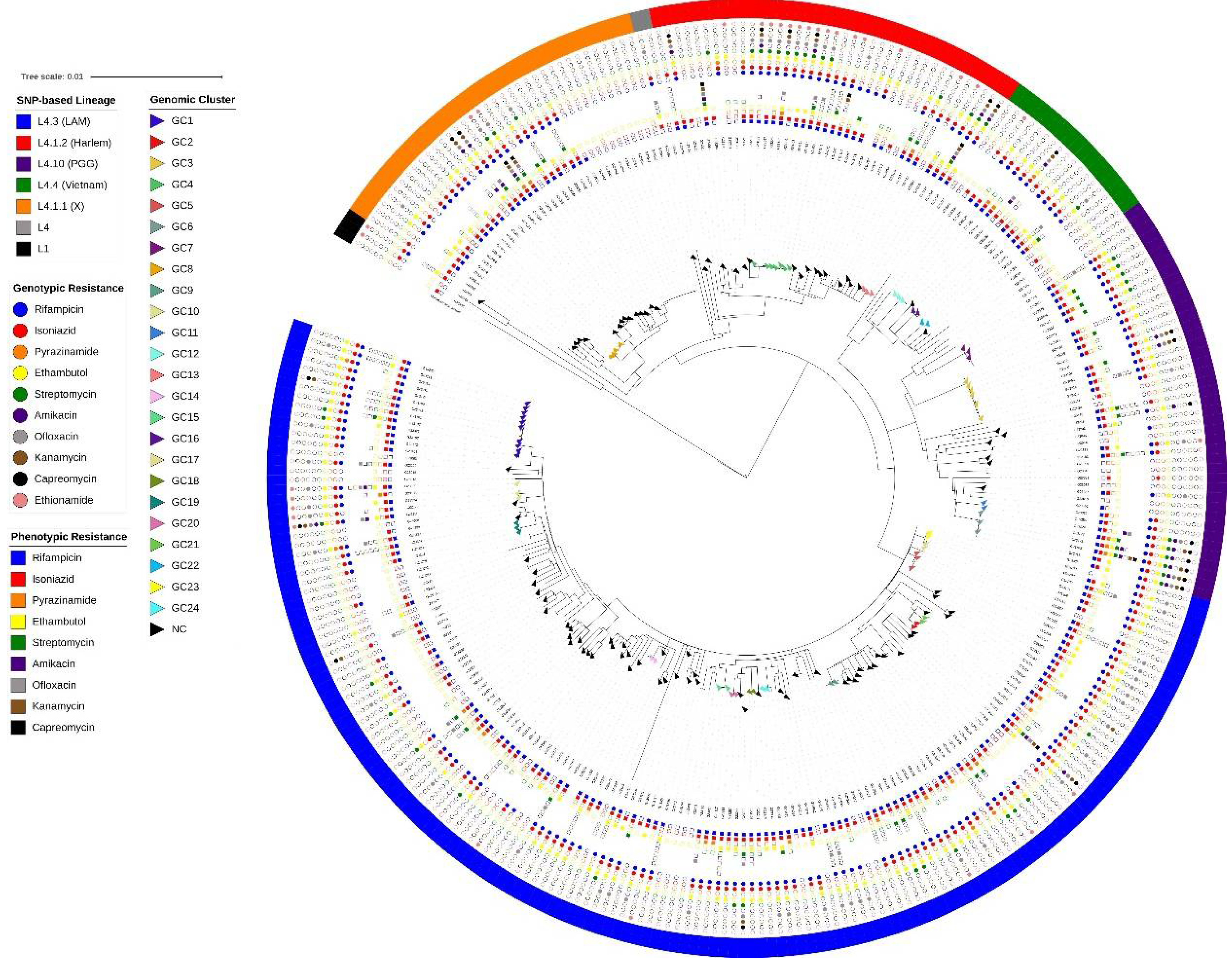
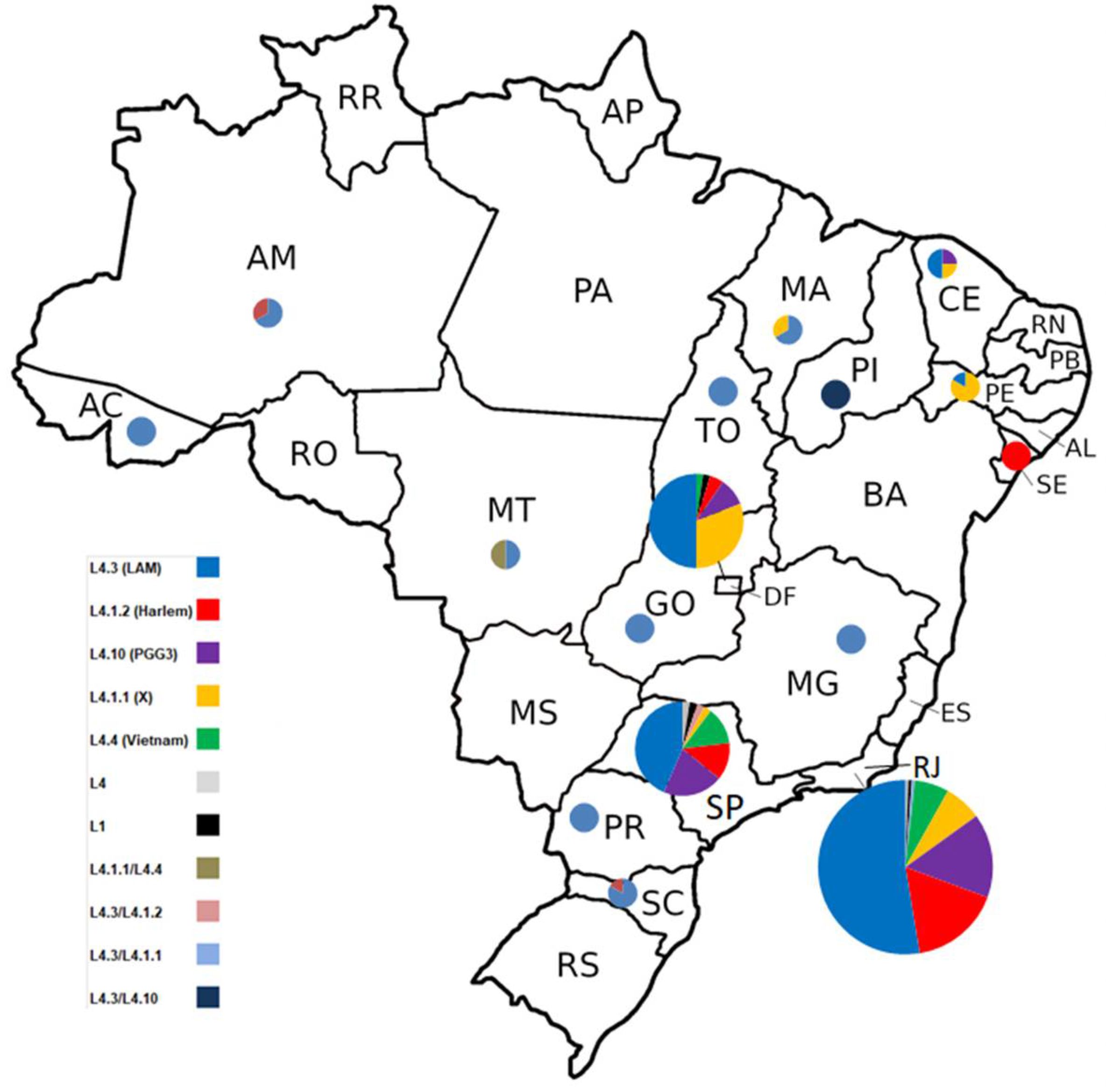
2.3. Genomic Diversity, Phylogenetic Analysis and Lineage Classification Using Different Pipelines
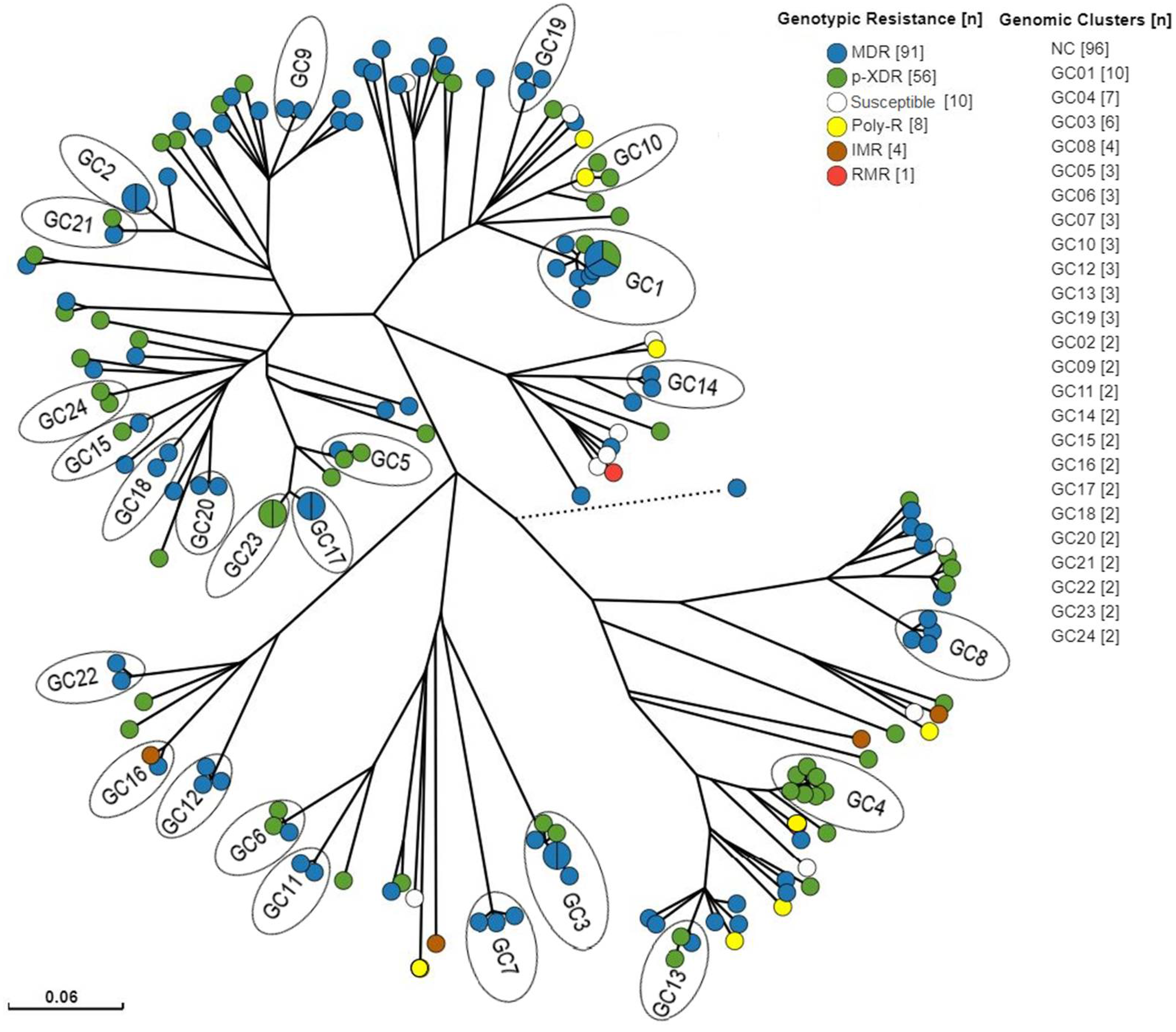
2.4. Genomic Clusters Analysis
2.5. Evolution of Drug Susceptibility Patterns in Patients with Multiple Isolates of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis
2.6. Treatment Outcome, Risk Factors and Lineage Associations with Genotypic and Phenotypic Resistance
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Collections and Phenotypic Drug Resistance
4.2. Whole Genome Sequencing and in-House Pipeline
4.3. Phylogenetic Analysis
4.4. Lineage Classification Pipelines Comparisons
4.5. Genotypic Resistance Detection and Pipelines Evaluation
4.6. Cluster Analysis and Recent Transmission
4.7. Patient data
4.8. Statistical Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO Global Tuberculosis Report 2023; Geneve, 2023; ISBN 9789240083851.
- Brazil Epidemiological Report - Tuberculosis 2021; 2021.
- WHO Global Tuberculosis Report 2021; Geneva, 2021.
- WHO Global Tuberculosis Report 2019; Geneva, 2019.
- Bhering, M.; Kritski, A. Short Communication Trends in Primary Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis in the State of Rio de Janeiro : A Retrospective Study Conducted during 2000-2019. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2021, 54, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tagliani, E.; Anthony, R.; Kohl, T.A.; De Neeling, A.; Nikolayevskyy, V.; Ködmön, C.; Maurer, F.P.; Niemann, S.; Van Soolingen, D.; Van Der Werf, M.J.; et al. Use of a Whole Genome Sequencingbased Approach for Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Surveillance in Europe in 2017-2019: An ECDC Pilot Study. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, T.M.; Choisy, M.; Dedicoat, M.; Drennan, P.G.; Wyllie, D.; Yang-Turner, F.; Crook, D.W.; Robinson, E.R.; Walker, A.S.; Smith, E.G.; et al. Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Transmission in Birmingham, UK, 2009–19: An Observational Study. Lancet Reg. Heal. - Eur. 2022, 17, 100361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meehan, C.J.; Goig, G.A.; Kohl, T.A.; Verboven, L.; Dippenaar, A.; Ezewudo, M.; Farhat, M.R.; Guthrie, J.L.; Laukens, K.; Miotto, P.; et al. Whole Genome Sequencing of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis: Current Standards and Open Issues. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaventsis, D.; Casali, N.; Kontsevaya, I.; Drobniewski, F.; Cirillo, D.M.; Nikolayevskyy, V. Whole Genome Sequencing of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis for Detection of Drug Resistance: A Systematic Review. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2017, 23, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiner, A.; Stucki, D.; Coscolla, M.; Borrell, S.; Gagneux, S. KvarQ: Targeted and Direct Variant Calling from Fastq Reads of Bacterial Genomes. BMC Genomics 2014, 15, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coll, F.; McNerney, R.; Guerra-Assunção, J.A.; Glynn, J.R.; Perdigão, J.; Viveiros, M.; Portugal, I.; Pain, A.; Martin, N.; Clark, T.G. A Robust SNP Barcode for Typing Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Complex Strains. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, P.; Gordon, N.C.; Walker, T.M.; Dunn, L.; Heys, S.; Huang, B.; Earle, S.; Pankhurst, L.J.; Anson, L.; De Cesare, M.; et al. Rapid Antibiotic-Resistance Predictions from Genome Sequence Data for Staphylococcus Aureus and Mycobacterium Tuberculosis. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verboven, L.; Phelan, J.; Heupink, T.H.; Van Rie, A. TBProfiler for Automated Calling of the Association with Drug Resistance of Variants in Mycobacterium Tuberculosis. PLoS One 2022, 17, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J.; et al. Freedom in Bioinformatics. Front. Genet. 2014, 5, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.R. Buying in to Bioinformatics: An Introduction to Commercial Sequence Analysis Software. Brief. Bioinform. 2014, 16, 700–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coscolla, M.; Gagneux, S. Consequences of Genomic Diversity in Mycobacterium Tuberculosis. Semin. Immunol. 2014, 26, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oppong, Y.E.A.; Phelan, J.; Perdigão, J.; Machado, D.; Miranda, A.; Viveiros, M.; Clark, T.G.; Hibberd, M.L. Genome-Wide Analysis of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Polymorphisms Reveals Lineage- Specific Associations with Drug Resistance. 2019, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvato, R.S.; Schiefelbein, S.; Barcellos, R.B.; Praetzel, B.M.; Anusca, I.S.; Esteves, L.S.; Halon, M.L.; Unis, G.; Dias, C.F.; Miranda, S.S.; et al. Molecular Characterisation of Multidrug-Resistant Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Isolates from a High-Burden Tuberculosis State in Brazil. Epidemiol. Infect. 2019, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verza, M.; Scheffer, M.C.; Salvato, R.S.; Schorner, M.A.; Barazzetti, F.H.; Machado, H.D.M.; Medeiros, T.F.; Rovaris, D.B.; Viveiros, M. Genomic Epidemiology of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis in Santa Catarina, Southern Brazil. Sci. Rep. 2020, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteves, L.S.; Dalla Costa, E.R.; Vasconcellos, S.E.G.; Vargas, A.; Ferreira Junior, S.L.M.; Halon, M.L.; Ribeiro, M.O.; Rodenbusch, R.; Gomes, H.M.; Suffys, P.N.; et al. Genetic Diversity of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Isoniazid Monoresistant and Multidrug-Resistant in Rio Grande Do Sul, a Tuberculosis High-Burden State in Brazil. Tuberculosis 2018, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, H.M.; Elias, A.R.; Oelemann, M.A.C.; Pereira, M.A. da S.; Montes, F.F.O.; Marsico, A.G.; Kritski, A.L.; Filho, L. dos A.; Caldas, P.C.; Possuelo, L.G.; et al. Spoligotypes of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Complex Isolates from Patients Residents of 11 States of Brazil. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2012, 12, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasconcellos, S.E.G.; Acosta, C.C.; Gomes, L.L.; Conceição, E.C.; Lima, K.V.; De Araujo, M.I.; De Lourdes Leite, M.; Tannure, F.; De Souza Caldas, P.C.; Gomes, H.M.; et al. Strain Classification of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Isolates in Brazil Based on Genotypes Obtained by Spoligotyping, Mycobacterial Interspersed Repetitive Unit Typing and the Presence of Large Sequence and Single Nucleotide Polymorphism. PLoS One 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dantas, N.G.T.; Suffys, P.N.; Carvalho, W. da S.; Gomes, H.M.; de Almeida, I.N.; de Assis, L.J.; Augusto, C.J.; Gomgnimbou, M.K.; Refregier, G.; Sola, C.; et al. Genetic Diversity and Molecular Epidemiology of Multidrug-Resistant Mycobacterium Tuberculosis in Minas Gerais State, Brazil. BMC Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conceição, E.C.; Rastogi, N.; Couvin, D.; Lopes, M.L.; Furlaneto, I.P.; Gomes, H.M.; Vasconcellos, S.E.G.; Suffys, P.N.; Schneider, M.P.C.; de Sousa, M.S.; et al. Genetic Diversity of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis from Pará, Brazil, Reveals a Higher Frequency of Ancestral Strains than Previously Reported in South America. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2017, 56, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, A.E.D.S.; Sharma, A.; Furlaneto, I.P.; Rutaihwa, L.; Cardoso, J.F.; da Conceição, M.L.; Spinassé, L.B.; Machado, E.; Lopes, M.L.; Duarte, R.S.; et al. Evaluation of Drug Susceptibility Profile of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Lineage 1 from Brazil Based on Whole Genome Sequencing and Phenotypic Methods. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 2020, 115, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conceição, E.C.; Refregier, G.; Gomes, H.M.; Olessa-Daragon, X.; Coll, F.; Ratovonirina, N.H.; Rasolofo-Razanamparany, V.; Lopes, M.L.; van Soolingen, D.; Rutaihwa, L.; et al. Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Lineage 1 Genetic Diversity in Pará, Brazil, Suggests Common Ancestry with East-African Isolates Potentially Linked to Historical Slave Trade. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2019, 73, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menardo, F.; Gagneux, S.; Rutaihwa, L.K.; Zwyer, M.; Borrell, S.; Comas, I.; Conceição, E.C.; Coscolla, M.; Cox, H.; Joloba, M.; et al. Local Adaptation in Populations of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Endemic to the Indian Ocean Rim. F1000Research 2021, 10, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobkowiak, B.; Glynn, J.R.; Houben, R.M.G.J.; Mallard, K.; Phelan, J.E.; Guerra-assunção, J.A.; Banda, L.; Mzembe, T.; Viveiros, M.; Mcnerney, R.; et al. Identifying Mixed Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Infections from Whole Genome Sequence Data. 2018, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eyre, D.W.; Cule, M.L.; Griffiths, D.; Crook, D.W.; Peto, T.E.A.; Walker, A.S.; Wilson, D.J. Detection of Mixed Infection from Bacterial Whole Genome Sequence Data Allows Assessment of Its Role in Clostridium Difficile Transmission. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2013, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallard, K.; McNerney, R.; Crampin, A.C.; Houben, R.; Ndlovu, R.; Munthali, L.; Warren, R.M.; French, N.; Glynn, J.R. Molecular Detection of Mixed Infections of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Strains in Sputum Samples from Patients in Karonga District, Malawi. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 4512–4518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdigão, J.; Gomes, P.; Miranda, A.; Maltez, F.; Machado, D.; Silva, C.; Phelan, J.E.; Brum, L.; Campino, S.; Couto, I.; et al. Using Genomics to Understand the Origin and Dispersion of Multidrug and Extensively Drug Resistant Tuberculosis in Portugal. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyllie, D.H.; Davidson, J.A.; Grace Smith, E.; Rathod, P.; Crook, D.W.; Peto, T.E.A.; Robinson, E.; Walker, T.; Campbell, C. A Quantitative Evaluation of MIRU-VNTR Typing Against Whole-Genome Sequencing for Identifying Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Transmission: A Prospective Observational Cohort Study. EBioMedicine 2018, 34, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrazoli, L.; Palaci, M.; Marques, L.R.M.; Jamal, L.F.; Afiune, J.B.; Chimara, E.; Martins, M.C.; Da Silva Telles, M.A.; Oliveira, C.A.F.; Palhares, M.C.; et al. Transmission of Tuberculosis in an Endemic Urban Setting in Brazil. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2000, 4, 18–25. [Google Scholar]
- Telles, M.A.S.; Ferrazoli, L.; Waldman, E.A.; Giampaglia, C.M.S.; Martins, M.C.; Ueki, S.Y.M.; Chimara, E.; Silva, C.A.; Cruz, V.; Waldman, C.C.S.; et al. A Population-Based Study of Drug Resistance and Transmission of Tuberculosis in an Urban Community. Int. J. Tuberc. Lung Dis. 2005, 9, 970–976. [Google Scholar]
- Nogueira, C.L.; Prim, R.I.; Senna, S.G.; Rovaris, D.B.; Maurici, R.; Rossetti, M.L.; Couvin, D.; Rastogi, N.; Bazzo, M.L. First Insight into the Molecular Epidemiology of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis in Santa Catarina, Southern Brazil. Tuberculosis 2016, 97, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvato, R.; Regina, E.; Costa, D.; Júlia, A.; Hee, S.; Laura, M.; Bones, R.; Unis, G.; Fontoura, C.; Viveiros, M.; et al. Infection, Genetics and Evolution First Insights into Circulating XDR and Pre-XDR Mycobacterium Tuberculosis in Southern Brazil. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2020, 78, 104127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zong, Z.; Huo, F.; Shi, J.; Jing, W.; Ma, Y.; Liang, Q.; Jiang, G.; Dai, G.; Huang, H.; Pang, Y. Relapse versus Reinfection of Recurrent Tuberculosis Patients in a National Tuberculosis Specialized Hospital in Beijing, China. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerra-Assunção, J.A.; Houben, R.M.G.J.; Crampin, A.C.; Mzembe, T.; Mallard, K.; Coll, F.; Khan, P.; Banda, L.; Chiwaya, A.; Pereira, R.P.A.; et al. Recurrence Due to Relapse or Reinfection with Mycobacterium Tuberculosis: A Whole-Genome Sequencing Approach in a Large, Population-Based Cohort with a High HIV Infection Prevalence and Active Follow-Up. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 211, 1154–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, D.; Andersson, D.I. Evolutionary Trajectories to Antibiotic Resistance. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 71, 579–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anley, D.T.; Akalu, T.Y.; Dessie, A.M.; Anteneh, R.M.; Zemene, M.A.; Bayih, W.A.; Solomon, Y.; Gebeyehu, N.A.; Kassie, G.A.; Mengstie, M.A.; et al. Prognostication of Treatment Non-Compliance among Patients with Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis in the Course of Their Follow-up: A Logistic Regression–based Machine Learning Algorithm. Front. Digit. Heal. 2023, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanji, A.; Hasan, R.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, W.; Imtiaz, K.; Iqbal, K.; Shafiq, S.; Hasan, Z. Increased Expression of Efflux Pump Genes in Extensively Drug-Resistant Isolates of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis. Int. J. Mycobacteriology 2016, 5, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigouts, L.; Miotto, P.; Schats, M.; Lempens, P.; Cabibbe, A.M.; Galbiati, S.; Lampasona, V.; de Rijk, P.; Cirillo, D.M.; de Jong, B.C. Fluoroquinolone Heteroresistance in Mycobacterium Tuberculosis: Detection by Genotypic and Phenotypic Assays in Experimentally Mixed Populations. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalla Costa, E.R.; Ribeiro, M.O.; Silva, M.S.; Arnold, L.S.; Rostirolla, D.C.; Cafrune, P.I.; Espinoza, R.C.; Palaci, M.; Telles, M.A.; Ritacco, V.; et al. Correlations of Mutations in KatG, OxyR-AhpC and InhA Genes and in Vitro Susceptibility in Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Clinical Strains Segregated by Spoligotype Families from Tuberculosis Prevalent Countries in South America. BMC Microbiol. 2009, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford, C.B.; Shah, R.R.; Maeda, M.K.; Gagneux, S.; Murray, M.B.; Cohen, T.; Johnston, J.C.; Gardy, J.; Lipsitch, M.; Fortune, S.M. Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Mutation Rate Estimates from Different Lineages Predict Substantial Differences in the Emergence of Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 784–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayoso, R.; Dalcolmo, M.; Ueleres, J.; Barreira, D. Predictors of Mortality in Multidrug-Resistant Centers, 2005 to 2012. Brazilian J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 22, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zürcher, K.; Reichmuth, M.L.; Ballif, M.; Loiseau, C.; Borrell, S.; Reinhard, M.; Skrivankova, V.; Hömke, R.; Sander, P.; Avihingsanon, A.; et al. Articles Mortality from Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis in High-Burden Countries Comparing Routine Drug Susceptibility Testing with Whole-Genome Sequencing : A Multicentre Cohort Study. 2021, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, L.G.; Garcia, M.T.; Zaccarioto, T.R.; MOretti, M.L.; Levy, C.E.; Resende, M.R. Clinical Outcomes and Molecular Characterization of Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis in Pre- and Extensively Drug-Resistant Disease Based on Line Probe Assays. 2021, 5, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitnick, C.D.; Franke, M.F.; Rich, M.L.; Viru, F.A.A.; Appleton, S.C.; Atwood, S.S.; Bayona, J.N.; Bonilla, C.A.; Chalco, K.; Fraser, H.S.F.; et al. Aggressive Regimens for Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis Decrease All-Cause Mortality. 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, L.; Olson, L.; Khu, D.T.K.; Linnros, S.; Le, N.K.; Hanberger, H.; Hoang, N.T.B.; Tran, D.M.; Larsson, M. Multiple Antibiotic Resistance as a Risk Factor for Mortality and Prolonged Hospital Stay: A Cohort Study among Neonatal Intensive Care Patients with Hospital-Acquired Infections Caused by Gram-Negative Bacteria in Vietnam. PLoS One 2019, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, K.S. Mutations Found in Mycobacterium Tuberculosis. 2018, 103, 1034–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, T.; Maíra, J.; Pinhata, W.; Christiane, M.; Brandão, A.P.; Ferrazoli, L.; Leão, S.C.; Viana-niero, C. Frequency of First and Second-Line Drug Resistance-Associated Mutations among Resistant Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Clinical Isolates from São Paulo, Brazil. 2020, 115, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daoqun, L.; Yuzhu, S.; Cheng-lin, Z.; Xiaofei, L.; Xueshan, X. Journal of Infection and Public Health Screening Mutations in Drug-Resistant Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Strains in Yunnan, China. J. Infect. Public Health 2017, 10, 630–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dokht, A.; Etemad, N.; Hashemzadeh, M. Journal of Global Antimicrobial Resistance Frequency of Rrs and RpsL Mutations in Streptomycin-Resistant Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Isolates from Iranian Patients. Integr. Med. Res. 2017, 9, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Li, L.; Zhao, Y.; Jia, Q.; Li, H.; Coulter, C.; Jin, Q.; Zhu, G. Characteristics of EmbB Mutations in Multidrug-Resistant Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Isolates in Henan, China. 2011, 2240–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Takiff, H.E.; Gao, Q. Phenotypic Instability of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Strains Harbouring Clinically Prevalent Drug-Resistant Mutations. The Lancet Microbe 2023, 4, e292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Feng, S.; Chen, Y.; Yu, M.; Wei, W.; Tian, G.B. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing in Clinical Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Isolates. The Lancet Microbe 2023, 4, e68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, C.; Lei, B.; Musser, J.M.; Tu, S. Isoniazid Activation Defects in Recombinant Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Catalase-Peroxidase (KatG) Mutants Evident in InhA Inhibitor Production. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, S.J.; Thibert, L.; Sanchez, T.; Heifets, L.; Zhang, Y. PncA Mutations as a Major Mechanism of Pyrazinamide Resistance in Mycobacterium Tuberculosis: Spread of a Monoresistant Strain in Quebec, Canada. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44, 528–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.W.; Lee, J.-M.; Jung, K.-S. Characterization of PncA Mutations of Pyrazinamide-Resistant Mycobacterium Tuberculosis in Korea. J Korean Med Sci 2001, 16, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Yang, Z.; Gu, J.; Luo, M.; Deng, J.; Chen, Y. Characterization of PncA Mutations and Prediction of PZA Resistance in Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Clinical Isolates From Chongqing, China. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scorpio, A.; Lindholm-Levy, P.; Heifets, L.; Gilman, R.; Siddiqi, S.; Cynamon, M.; Zhang, Y. Characterization of PncA Mutations in Pyrazinamide-Resistant Mycobacterium Tuberculosis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1997, 41, 540–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marttila, H.J.; Marjamäki, M.; Vyshnevskaya, E.; Vyshnevskiy, B.I.; Otten, T.F.; Vasilyef, A. V.; Viljanen, M.K. PncA Mutations in Pyrazinamide-Resistant Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Isolates from Northwestern Russia. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1999, 43, 1764–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morlock, G.P.; Metchock, B.; Sikes, D.; Crawford, J.T.; Cooksey, R.C. EthA, InhA, and KatG Loci of Ethionamide-Resistant Clinical Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Isolates. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 3799–3805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghafli, H.; Kohl, T.A.; Merker, M.; Varghese, B.; Halees, A.; Niemann, S.; Al-Hajoj, S. Drug-Resistance Profiling and Transmission Dynamics of Multidrug-Resistant Mycobacterium Tuberculosis in Saudi Arabia Revealed by Whole Genome Sequencing. Infect. Drug Resist. 2018, 11, 2219–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valim, A.R.M.; Rossetti, M.L.R.; Ribeiro, M.O.; Zaha, A. Mutations in the RpoB Gene of Multidrug-Resistant Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Isolates from Brazil. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 3119–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanches-Padilha, E.; Merker, M.; Beckert, P.; Jochims, F.; Dlamini, T.; Kahn, P.; Bonnet, M.; Niemann, S. Detection of Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis by Xpert MTB/RIF in Swaziland. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1179–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makhado, N.A.; Matabane, E.; Faccin, M.; Pinçon, C.; Jouet, A.; Boutachkourt, F.; Goeminne, L.; Gaudin, C.; Maphalala, G.; Beckert, P.; et al. Outbreak of Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis in South Africa Undetected by WHO-Endorsed Commercial Tests: An Observational Study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 1350–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beckert, P.; Sanchez-Padilla, E.; Merker, M.; Dreyer, V.; Kohl, T.A.; Utpatel, C.; Köser, C.U.; Barilar, I.; Ismail, N.; Omar, S.V.; et al. MDR M. Tuberculosis Outbreak Clone in Eswatini Missed by Xpert Has Elevated Bedaquiline Resistance Dated to the Pre-Treatment Era. Genome Med. 2020, 12, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization Technical Report on Critical Concentrations for Drug Susceptibility Testing of Isoniazid and the Rifamycins (Rifampicin, Rifabutin and Rifapentine); 2021; ISBN 9789240017283.
- Denkinger, C.M.; Kik, S. V; Cirillo, M.; Casenghi, M.; Shinnick, T.; Weyer, K.; Gilpin, C.; Boehme, C.C.; Schito, M.; Kimerling, M.; et al. Defining the Needs for Next Generation Assays for Tuberculosis. 2015, 211, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macedo, R.; Nunes, A.; Portugal, I.; Duarte, S.; Vieira, L.; Gomes, J.P. Dissecting Whole-Genome Sequencing-Based Online Tools for Predicting Resistance in Mycobacterium Tuberculosis: Can We Use Them for Clinical Decision Guidance? Tuberculosis 2018, 110, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Beek, J.; Haanperä, M.; Smit, P.W.; Mentula, S.; Soini, H. Evaluation of Whole Genome Sequencing and Software Tools for Drug Susceptibility Testing of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 25, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coll, F.; McNerney, R.; Preston, M.D.; Guerra-Assunção, J.A.; Warry, A.; Hill-Cawthorne, G.; Mallard, K.; Nair, M.; Miranda, A.; Alves, A.; et al. Rapid Determination of Anti-Tuberculosis Drug Resistance from Whole-Genome Sequences. Genome Med. 2015, 7, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coll, F.; Phelan, J.; Hill-Cawthorne, G.A.; Nair, M.B.; Mallard, K.; Ali, S.; Abdallah, A.M.; Alghamdi, S.; Alsomali, M.; Ahmed, A.O.; et al. Genome-Wide Analysis of Multi- and Extensively Drug-Resistant Mycobacterium Tuberculosis. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamoto, T.; Murase, Y.; Yoshida, S.; Aono, A.; Kuroda, M.; Sekizuka, T.; Yamashita, A.; Kato, K.; Takii, T.; Arikawa, K.; et al. Overcoming the Pitfalls of Automatic Interpretation of Whole Genome Sequencing Data by Online Tools for the Prediction of Pyrazinamide Resistance in Mycobacterium Tuberculosis. PLoS One 2019, 14, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Embden, J.D.A. van.; Cave, M.D.; Crawford, J.T.; Dale, J.W.; Eisenach, K.D.; Gicquel, B.; Hermans, P.; Martin, C.; Mcadam, R.; Shinnick, T.M.; et al. Strain Identification of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis by DNA Fingerprinting : Recommendations for a Standardized Methodology. 1993, 31, 406–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eldholm, V.; Pettersson, J.H.O.; Brynildsrud, O.B.; Kitchen, A.; Rasmussen, E.M.; Lillebaek, T.; Rønning, J.O.; Crudu, V.; Mengshoel, A.T.; Debech, N.; et al. Armed Conflict and Population Displacement as Drivers of the Evolution and Dispersal of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2016, 113, 13881–13886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menardo, F.; Loiseau, C.; Brites, D.; Coscolla, M.; Gygli, S.M.; Rutaihwa, L.K.; Trauner, A.; Beisel, C.; Borrell, S.; Gagneux, S. Treemmer: A Tool to Reduce Large Phylogenetic Datasets with Minimal Loss of Diversity. BMC Bioinformatics 2018, 19, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A Flexible Trimmer for Illumina Sequence Data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comas, I.; Chakravartti, J.; Small, P.M.; Galagan, J.; Niemann, S.; Kremer, K.; Ernst, J.D.; Gagneux, S. Human T Cell Epitopes of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Are Evolutionarily Hyperconserved. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stucki, D.; Brites, D.; Jeljeli, L.; Coscolla, M.; Qingyun; Liu, Andrej Trauner, Lukas Fenner, Liliana Rutaihwa, Sonia Borrell, T.; Luo, Qian Gao, Midori Kato-Maeda, Marie Ballif, Matthias Egger, R.; Macedo, Helmi Mardassi, Milagros Moreno, Griselda Tudo Vilanova11, J.; Fyfe, Maria Globan, Jackson Thomas, Frances Jamieson, J.L.; Guthrie, Adwoa Asante-Poku, Dorothy Yeboah-Manu, E.W.; et al. Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Lineage 4 Comprises Globally Distributed and Geographically Restricted Sublineages. 2016, 48, 1535–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree of Life (ITOL) v4: Recent Updates and New Developments. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 256–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phelan, J.E.; O’Sullivan, D.M.; Machado, D.; Ramos, J.; Oppong, Y.E.A.; Campino, S.; O’Grady, J.; McNerney, R.; Hibberd, M.L.; Viveiros, M.; et al. Integrating Informatics Tools and Portable Sequencing Technology for Rapid Detection of Resistance to Anti-Tuberculous Drugs. Genome Med. 2019, 11, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faksri, K.; Xia, E.; Tan, J.H.; Teo, Y.Y.; Ong, R.T.H. In Silico Region of Difference (RD) Analysis of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Complex from Sequence Reads Using RD-Analyzer. BMC Genomics 2016, 17, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, T.M.; Ip, C.L.C.; Harrell, R.H.; Evans, J.T.; Kapatai, G.; Dedicoat, M.J.; Eyre, D.W.; Wilson, D.J.; Hawkey, P.M.; Crook, D.W.; et al. Whole-Genome Sequencing to Delineate Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Outbreaks : A Retrospective Observational Study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comas, I. Genomic Epidemiology of Tuberculosis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 1019, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merker, M.; Kohl, T.A.; Niemann, S.; Supply, P. The Evolution of Strain Typing in the Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Complex; 2017; Vol. 1019; ISBN 9783319643717.
- Zhou, Z.; Alikhan, N.F.; Sergeant, M.J.; Luhmann, N.; Vaz, C.; Francisco, A.P.; Carriço, J.A.; Achtman, M. Grapetree: Visualization of Core Genomic Relationships among 100,000 Bacterial Pathogens. Genome Res. 2018, 28, 1395–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warrens, M.J. Inequalities between Multi-Rater Kappas. 2010, 271–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
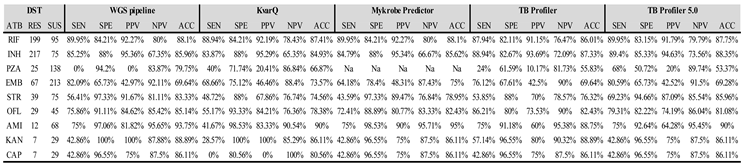
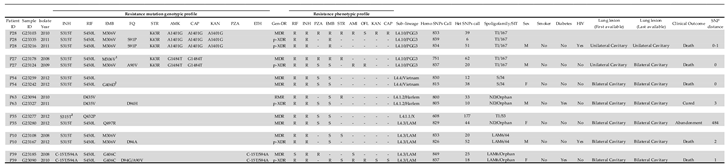
| n Isolates | Drug | DST | Novel Mutation | Phenotypic Profile | Genotypic Profile╪ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | INH | R | katG_c.2070delC¹ | MDR | p-XDR |
| 1 | INH | S | katG_c.1141dupG² | RMR | IMR |
| 1 | ETH | NA | ethA_c.306_307delCA | MDR | p-XDR |
| 1 | ETH | NA | ethA_c.-382_*857del | p-XDR | p-XDR |
| 1 | ETH | NA | ethA_c.40dupA | MDR | MDR |
| 4 | ETH | NA | ethA_c.851dupC | MDR | 2 MDR/2 p-XDR |
| 4 | PZA | 2R/2NA | pncA_c.193_200dupTCCTCGTC | MDR | MDR |
| 1 | PZA | NA | pncA_c.289_293dupGGTGC | MDR | MDR |
| 1 | PZA | NA | pncA_c.502delA | Poly-R | Poly-R |
| 1 | PZA | R | pncA_c.452dupT | MDR | p-XDR |
| 2 | PZA | R | pncA_c.75_79delCGCGC | p-XDR | p-XDR |
| 4 | PZA | R/2S/NA | pncA_c.443_444dupGC³ | MDR | 2 MDR/2 p-XDR |
| 1 | PZA | S | pncA_c.117_124delGGACTACC | MDR | p-XDR |
| 1 | PZA | S | pncA_c.300delC | MDR | Poly-R |
| 2 | PZA | R/NA | pncA_c.305dupC | p-XDR/Poly-R | p-XDR |
| 1 | PZA | S | pncA_c.329_338delACGAGAACGG | p-XDR | Poly-R |
| 1 | PZA | S | pncA_c.-3449_*7353del | p-XDR | p-XDR |
| 1 | PZA | S | pncA_c.423_424delGA | p-XDR | p-XDR |
| 2 | PZA | S | pncA_c.454_455insT | MDR | MDR |
| 1 | PZA | S | pncA_c.527dupG | MDR | MDR |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





