Submitted:
12 April 2024
Posted:
17 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Methods
Data
Prevalence of Macrolide Resistance
Macrolide use in Food-Producing Animals
Macrolide Consumption in Humans
Statistical Analyses
Results
Discussion
Funding
Acknowledgements
Consent for Publication
Data Availability Statements
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peuchant, O.; Menard, A.; Renaudin, H.; Morozumi, M.; Ubukata, K.; Bebear, C.M.; Pereyre, S. Increased macrolide resistance of Mycoplasma pneumoniae in France directly detected in clinical specimens by real-time PCR and melting curve analysis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2009, 64, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S. Malhotra-Kumar, C. S. Malhotra-Kumar, C. Lammens, S. Coenen, K. Van Herck, and H. Goossens, "Effect of azithromycin and clarithromycin therapy on pharyngeal carriage of macrolide-resistant streptococci in healthy volunteers: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study," The Lancet, vol. 369, no. 9560, pp. 482-490, 2007. [CrossRef]
- Kenyon, C.; De Baetselier, I.; Vanbaelen, T.; Buyze, J.; Florence, E. The Population-Level Effect of Screening for Mycoplasma genitalium on Antimicrobial Resistance: A Quasi-Experimental Study. Sex. Transm. Dis. 2021, 48, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenyon, C.; Manoharan-Basil, S.S. Macrolide consumption and resistance in Mycoplasma genitalium. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 1235–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenyon, C.; Manoharan-Basil, S.S.; Van Dijck, C. Is There a Resistance Threshold for Macrolide Consumption? Positive Evidence from an Ecological Analysis of Resistance Data from Streptococcus pneumoniae, Treponema pallidum, and Mycoplasma genitalium. Microb. Drug Resist. 2021, 27, 1079–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGee L and Klugman P, "Resistance in Streptococcus pneumoniae," in Antimicrobial drug resistance: Clinical and epidemiological aspects, vol. 2, D. L. Mayers, J. D. Sobel, M. Ouellette, K. S. Kaye, and D. Marchaim Eds.: Springer, 2017.
- Baquero, F.; Baquero-Artigao, G.; Cantón, R.; García-Rey, C. Antibiotic consumption and resistance selection in Streptococcus pneumoniae. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2002, 50, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Li, X.; Chen, X.; Luo, F.; Pan, C.; Zheng, X.; Tan, F. Macrolide-Resistant Mycoplasma pneumoniae in Adults in Zhejiang, China. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 1048–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenyon, C. Prevalence of macrolide resistance in Treponema pallidum is associated with macrolide consumption. J. Med Microbiol. 2019, 68, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Li, S.; Li, L.; Wang, X.; Yao, Z.; Ye, X. Alarming regional differences in prevalence and antimicrobial susceptibility of group B streptococci in pregnant women: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2016, 7, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenyon, C.; Buyze, J.; Wi, T. Antimicrobial Consumption and Susceptibility of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: A Global Ecological Analysis. Front. Med. 2018, 5, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, E.Y.; Van Boeckel, T.P.; Martinez, E.M.; Pant, S.; Gandra, S.; Levin, S.A.; Goossens, H.; Laxminarayan, R. Global increase and geographic convergence in antibiotic consumption between 2000 and 2015. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E3463–E3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gullberg, E.; Cao, S.; Berg, O.G.; Ilbäck, C.; Sandegren, L.; Hughes, D.; Andersson, D.I. Selection of Resistant Bacteria at Very Low Antibiotic Concentrations. PLOS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- C. Kenyon, "Positive Association between the Use of Quinolones in Food Animals and the Prevalence of Fluoroquinolone Resistance in E. coli and K. pneumoniae, A. baumannii and P. aeruginosa: A Global Ecological Analysis," Antibiotics, vol. 10, no. 10, p. 1193, 2021.
- Gullberg, E.; Albrecht, L.M.; Karlsson, C.; Sandegren, L.; Andersson, D.I. Selection of a Multidrug Resistance Plasmid by Sublethal Levels of Antibiotics and Heavy Metals. mBio 2014, 5, e01918–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC); European Food Safety Authority (EFSA); European Medicines Agency (EMA). ECDC/EFSA/EMA second joint report on the integrated analysis of the consumption of antimicrobial agents and occurrence of antimicrobial resistance in bacteria from humans and food-producing animals: Joint Interagency Antimicrobial Consumption and Resistance Analysis (JIACRA) Report (In English). EFSA J. 2017, 15, 4872–5007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.L.; Caffrey, N.P.; Nóbrega, D.B.; Cork, S.C.; E Ronksley, P.; Barkema, H.W.; Polachek, A.J.; Ganshorn, H.; Sharma, N.; Kellner, J.D.; et al. Restricting the use of antibiotics in food-producing animals and its associations with antibiotic resistance in food-producing animals and human beings: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Planet. Heal. 2017, 1, e316–e327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenyon, C. Positive association between the use of macrolides in food-producing animals and pneumococcal macrolide resistance: a global ecological analysis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2022, 116, 344–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- T. P. Van Boeckel et al., "Reducing antimicrobial use in food animals," Science, vol. 357, no. 6358, pp. 1350-1352, 2017.
- Collignon, P.; Beggs, J.J.; Walsh, T.R.; Gandra, S.; Laxminarayan, R. Anthropological and socioeconomic factors contributing to global antimicrobial resistance: a univariate and multivariable analysis. Lancet Planet. Heal. 2018, 2, e398–e405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
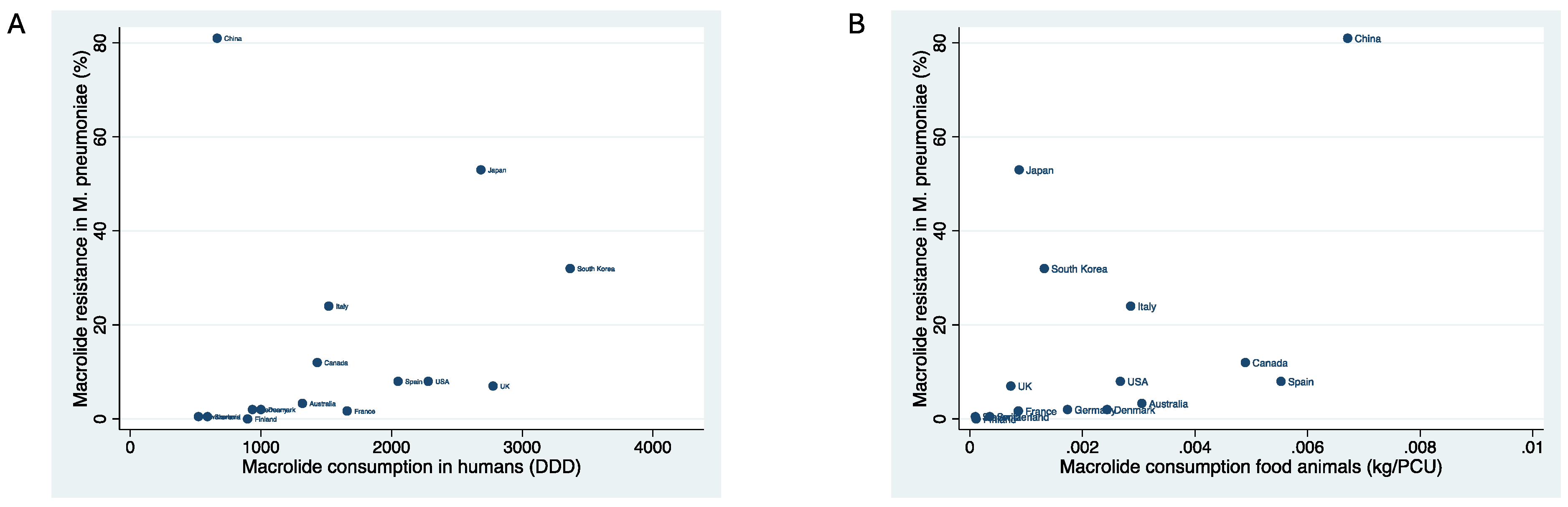
| Country | Year of macrolide resistance estimate | Macrolide resistance in M. pneumoniae | Macrolide consumption in food animals (kg/PCU) | Macrolide consumption in humans (DID) |
| Australia | 2014 | 3.3 | .0030558 | 1318 |
| Canada | 2013 | 12 | .0048947 | 1431 |
| China | 2014 | 81 | .0067121 | 665 |
| Colombia | 2018 | 0 | . | . |
| Cuba | 2017 | 19 | . | . |
| Denmark | 2012 | 2 | .0024353 | 1000 |
| Finland | 2019 | 0 | .0001106 | 898 |
| France | 2007 | 1.7 | .0008601 | 1660 |
| Germany | 2015 | 2 | .0017334 | 935 |
| Iran | 2017 | 25 | . | . |
| Israel | 2011 | 30 | . | . |
| Italy | 2015 | 24 | .0028562 | 1519 |
| Japan | 2013 | 53 | .0008748 | 2684 |
| Russia | 2020 | 1 | . | . |
| Singapore | 2017 | 13 | . | . |
| Slovenia | 2015 | .5 | .0000965 | 591 |
| South Korea | 2017 | 32 | .0013214 | 3367 |
| Spain | 2020 | 8 | .0055277 | 2050 |
| Switzerland | 2014 | .5 | .0003538 | 522 |
| Thailand | 2017 | 80 | . | . |
| UK | 2013 | 7 | .000727 | 2777 |
| USA | 2015 | 8 | .0026729 | 2281 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





