Submitted:
16 April 2024
Posted:
16 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Study Subjects
Feeding Practices and Nutritional Calculations
Body Composition Assessment and Anthropometric Measurements
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Nutritional Characteristics
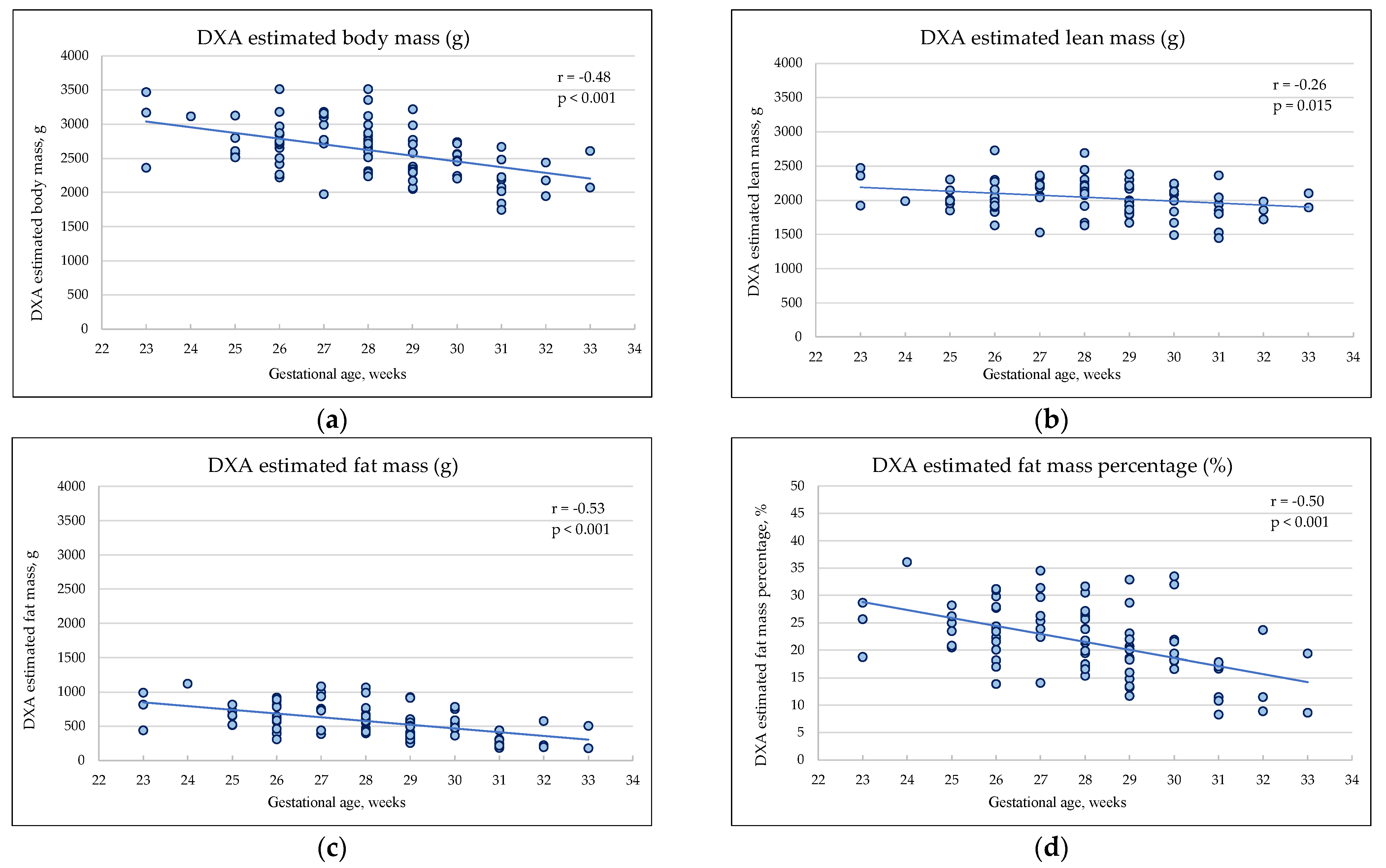
3.2. Body Composition Estimated by DXA at the Hospital Discharge
3.3. The Association Between Early Nutrient Intake And Body Composition
4. Discussion
Body Composition of Preterm Infants at Discharge and at 12 Months of CA
The Association Between Early Nutrient Intake and Body Composition
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johnson, M.J.; Wootton, S.A.; Leaf, A.A.; Jackson, A.A. Preterm Birth and Body Composition at Term Equivalent Age: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Pediatrics 2012, 130, e640–e649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.-T.; Lin, H.-Y.; Wang, C.-H.; Su, B.-H.; Lin, C.-C. Association of preterm birth and small for gestational age with metabolic outcomes in children and adolescents: A population-based cohort study from Taiwan. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2018, 59, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luu TM, Rehman Mian MO, Nuyt AM. Long-Term Impact of Preterm Birth: Neurodevelopmental and Physical Health Outcomes. Clin Perinatol. 2017, 44, 305–14.
- Lapillonne, A.; Griffin, I.J. Feeding Preterm Infants Today for Later Metabolic and Cardiovascular Outcomes. J. Pediatr. 2013, 162, S7–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demerath, E.W.; Johnson, W.; A Davern, B.; Anderson, C.G.; Shenberger, J.S.; Misra, S.; E Ramel, S. New body composition reference charts for preterm infants. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 105, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikenoue, S.; Kasuga, Y.; Endo, T.; Tanaka, M.; Ochiai, D. Newer Insights Into Fetal Growth and Body Composition. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, B.; Löf, M.; Forsum, E. Body composition in full-term healthy infants measured with air displacement plethysmography at 1 and 12 weeks of age. Acta Paediatr. 2010, 99, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- E Carberry, A.; Colditz, P.B.; E Lingwood, B. Body Composition From Birth to 4.5 Months in Infants Born to Non-Obese Women. Pediatr. Res. 2010, 68, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stutte, S.; Gohlke, B.; Peiler, A.; Schreiner, F.; Born, M.; Bartmann, P.; Woelfle, J. Impact of Early Nutrition on Body Composition in Children Aged 9.5 Years Born with Extremely Low Birth Weight. Nutrients 2017, 9, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matinolli, H.-M.; Hovi, P.; Männistö, S.; Sipola-Leppänen, M.; Eriksson, J.G.; Mäkitie, O.; Järvenpää, A.-L.; Andersson, S.; Kajantie, E. Early Protein Intake Is Associated with Body Composition and Resting Energy Expenditure in Young Adults Born with Very Low Birth Weight. J. Nutr. 2015, 145, 2084–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bua, J.; Risso, F.M.; Bin, M.; Vallon, F.; Travan, L.; Paviotti, G. Association between body composition at term equivalent age and Bayley scores at 2 years in preterm infants. J. Perinatol. 2021, 41, 1852–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfister, K.M.; Zhang, L.; Miller, N.C.; Ingolfsland, E.C.; Demerath, E.W.; Ramel, S.E. Early body composition changes are associated with neurodevelopmental and metabolic outcomes at 4 years of age in very preterm infants. Pediatr. Res. 2018, 84, 713–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Fluiter, K.S.; Kerkhof, G.F.; van Beijsterveldt, I.A.; Breij, L.M.; van de Heijning, B.J.; Abrahamse-Berkeveld, M.; Hokken-Koelega, A.C. Longitudinal human milk macronutrients, body composition and infant appetite during early life. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 40, 3401–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Amissah, E.; Brown, J.; E Harding, J. Protein supplementation of human milk for promoting growth in preterm infants. Emergencias 2020, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Amissah, E.; Brown, J.; E Harding, J. Carbohydrate supplementation of human milk to promote growth in preterm infants. Emergencias 2020, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amissah EA, Brown J, Harding JE. Fat supplementation of human milk for promoting growth in preterm infants. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Aug 25;2020(10).
- Fenton TR, Cormack B, Goldberg D, Nasser R, Alshaikh B, Eliasziw M; et al. “Extrauterine growth restriction” and “postnatal growth failure” are misnomers for preterm infants. J Perinatol. 2020, 40, 704–14.
- Villar, J.; Giuliani, F.; Barros, F.; Roggero, P.; Coronado Zarco, I.A.; Rego, M.A.S.; Ochieng, R.; Gianni, M.L.; Rao, S.; Lambert, A.; et al. Monitoring the Postnatal Growth of Preterm Infants: A Paradigm Change. Pediatrics 2018, 141, e20172467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villar, J.; Giuliani, F.; Figueras-Aloy, J.; Barros, F.; Bertino, E.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Kennedy, S.H. Growth of preterm infants at the time of global obesity. Arch. Dis. Child. 2019, 104, 725–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinkis R, Albertsson-Wikland K, Tamelienė R, Vinskaitė A, Šmigelskas K, Verkauskienė R. Nutrient Intake with Early Progressive Enteral Feeding and Growth of Very Low-Birth-Weight Newborns. Nutrients. 2022 Mar 11;14, 1181.
- Koo, W.W.K.; Walters, J.C.; Hockman, E.M. Body Composition in Neonates: Relationship Between Measured and Derived Anthropometry with Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry Measurements. Pediatr. Res. 2004, 56, 694–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakley JR, Parsons RJ, Whitelaw AG. Standards for skinfold thickness in British newborn infants. Arch Dis Child. 1977 Apr 1;52, 287–90.
- The International Fetal and Newborn Growth Consortium International Fetal and Newborn Growth Standards for the 21 st Century Anthropometry Handbook. [Internet]. 2012.
- Morkuniene, R.; Cole, T.J.; Jakimaviciene, E.M.; Bankauskiene, A.; Isakova, J.; Drazdiene, N.; Basys, V.; Tutkuviene, J. Regional references vs. international standards for assessing weight and length by gestational age in Lithuanian neonates. Front. Pediatr. 2023, 11, 1173685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamatschek, C.; Yousuf, E.I.; Möllers, L.S.; So, H.Y.; Morrison, K.M.; Fusch, C.; Rochow, N. Fat and Fat-Free Mass of Preterm and Term Infants from Birth to Six Months: A Review of Current Evidence. Nutrients 2020, 12, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yumani DFJ, de Jongh D, Lafeber HN, van Weissenbruch MM. A comparative study using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry, air displacement plethysmography, and skinfolds to assess fat mass in preterms at term equivalent age. Eur J Pediatr. 2021, 180, 919–27.
- de Knegt VE, Carlsen EM, Bech Jensen JE, Lade Rasmussen AM, Pryds O. DXA performance in a pediatric population: Precision of body composition measurements in healthy term-born infants using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry. J Clin Densitom. 2015, 18, 117–23.
- Tremblay, G.; Boudreau, C.; Bélanger, S.; St-Onge, O.; Pronovost, E.; Simonyan, D.; Marc, I. Body Composition in Very Preterm Infants: Role of Neonatal Characteristics and Nutrition in Achieving Growth Similar to Term Infants. Neonatology 2016, 111, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godang, K.; Qvigstad, E.; Voldner, N.; Isaksen, G.A.; Frøslie, K.F.; Nøtthellen, J.; Henriksen, T.; Bollerslev, J. Assessing Body Composition in Healthy Newborn Infants: Reliability of Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry. J. Clin. Densitom. 2010, 13, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmelzle, H.R.; Fusch, C. Body fat in neonates and young infants: validation of skinfold thickness versus dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry,, Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 76, 1096–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruckner, M.; Khan, Z.; Binder, C.; Morris, N.; Windisch, B.; Holasek, S.; Urlesberger, B. Extremely Preterm Infants Have a Higher Fat Mass Percentage in Comparison to Very Preterm Infants at Term-Equivalent Age. Front. Pediatr. 2020, 8, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiechers, C.; Avellina, V.; Luger, B.; Böckmann, K.; Minarski, M.; Maas, C.; Bernhard, W.; Poets, C.F.; Franz, A.R. Body Composition of Preterm Infants following Rapid Transition to Enteral Feeding. Neonatology 2022, 119, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrottesley, S.V.; Pisa, P.T.; Micklesfield, L.K.; Pettifor, J.M.; A Norris, S. A comparison of body composition estimates using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry and air-displacement plethysmography in South African neonates. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 70, 1254–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas, A.A.; Jerome, M.; Finck, A.; Razzaghy, J.; Chandler-Laney, P.; Carlo, W.A. Body composition of extremely preterm infants fed protein-enriched, fortified milk: a randomized trial. Pediatr. Res. 2021, 91, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, L.; Frondas-Chauty, A.; Senterre, T.; Flamant, C.; Darmaun, D.; Rozé, J.-C. Determinants of body composition in preterm infants at the time of hospital discharge. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 100, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, L.; Borrego, P.; Darmaun, D.; Legrand, A.; Rozé, J.-C.; Chauty-Frondas, A. Effect of sex and gestational age on neonatal body composition. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 109, 1105–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Embleton, N.D.M.; Moltu, S.J.; Lapillonne, A.; Akker, C.H.v.D.; Carnielli, V.; Fusch, C.; Gerasimidis, K.; van Goudoever, J.B.; Haiden, N.M.; Iacobelli, S.; et al. Enteral Nutrition in Preterm Infants (2022): A Position Paper From the ESPGHAN Committee on Nutrition and Invited Experts. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2022, 76, 248–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moltu SJ, Bronsky J, Embleton N, Gerasimidis K, Indrio F, Köglmeier J; et al. Nutritional Management of the Critically Ill Neonate: A Position Paper of the ESPGHAN Committee on Nutrition. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2021, 73, 274–89.
- Brinkis, R.; Albertsson-Wikland, K.; Tamelienė, R.; Aldakauskienė, I.; Rimdeikienė, I.; Marmienė, V.; Šmigelskas, K.; Verkauskienė, R. Impact of Early Nutrient Intake and First Year Growth on Neurodevelopment of Very Low Birth Weight Newborns. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agostoni, C.; Buonocore, G.; Carnielli, V.P.; De Curtis, M.; Darmaun, D.; Decsi, T.; Domellöf, M.; Embleton, N.D.; Fusch, C.; Genzel-Boroviczeny, O.; et al. Enteral Nutrient Supply for Preterm Infants: Commentary From the European Society of Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Committee on Nutrition. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2010, 50, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashyap, S.; Ohira-Kist, K.; Abildskov, K.; Towers, H.M.; Sahni, R.; Ramakrishnan, R.; Schulze, K. Effects of Quality of Energy Intake on Growth and Metabolic Response of Enterally Fed Low-Birth-Weight Infants. Pediatr. Res. 2001, 50, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLeod, G.; Simmer, K.; Sherriff, J.; Nathan, E.; Geddes, D.; Hartmann, P. Feasibility study: Assessing the influence of macronutrient intakes on preterm body composition, using air displacement plethysmography. J. Paediatr. Child Heal. 2015, 51, 862–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Dou, Y.; Dong, P.; Lv, Y.; et al. Associations of early nutrition with growth and body composition in very preterm infants: a prospective cohort study. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 76, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingwood BE, Al-Theyab N, Eiby YA, Colditz PB, Donovan TJ. discharge is associated with macronutrient intakeBody composition in very preterm infants before. Br J Nutr. 2020, 123, 800–6.
- Belfort, M.; Cherkerzian, S.; Bell, K.; Soldateli, B.; Ramos, E.C.; Palmer, C.; Steele, T.; Pepin, H.; Ellard, D.; Drouin, K.; et al. Macronutrient Intake from Human Milk, Infant Growth, and Body Composition at Term Equivalent Age: A Longitudinal Study of Hospitalized Very Preterm Infants. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochow, N.; Fusch, G.; Ali, A.; Bhatia, A.; So, H.Y.; Iskander, R.; Chessell, L.; el Helou, S.; Fusch, C. Individualized target fortification of breast milk with protein, carbohydrates, and fat for preterm infants: A double-blind randomized controlled trial. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 40, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singhal, A.; Kennedy, K.; Lanigan, J.; Fewtrell, M.; Cole, T.J.; Stephenson, T.; Elias-Jones, A.; Weaver, L.T.; Ibhanesebhor, S.; MacDonald, P.D.; et al. Nutrition in infancy and long-term risk of obesity: evidence from 2 randomized controlled trials. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 92, 1133–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerkhof, G.F.; Willemsen, R.H.; Leunissen, R.W.; Breukhoven, P.E.; Hokken-Koelega, A.C. Health Profile of Young Adults Born Preterm: Negative Effects of Rapid Weight Gain in Early Life. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, 4498–4506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
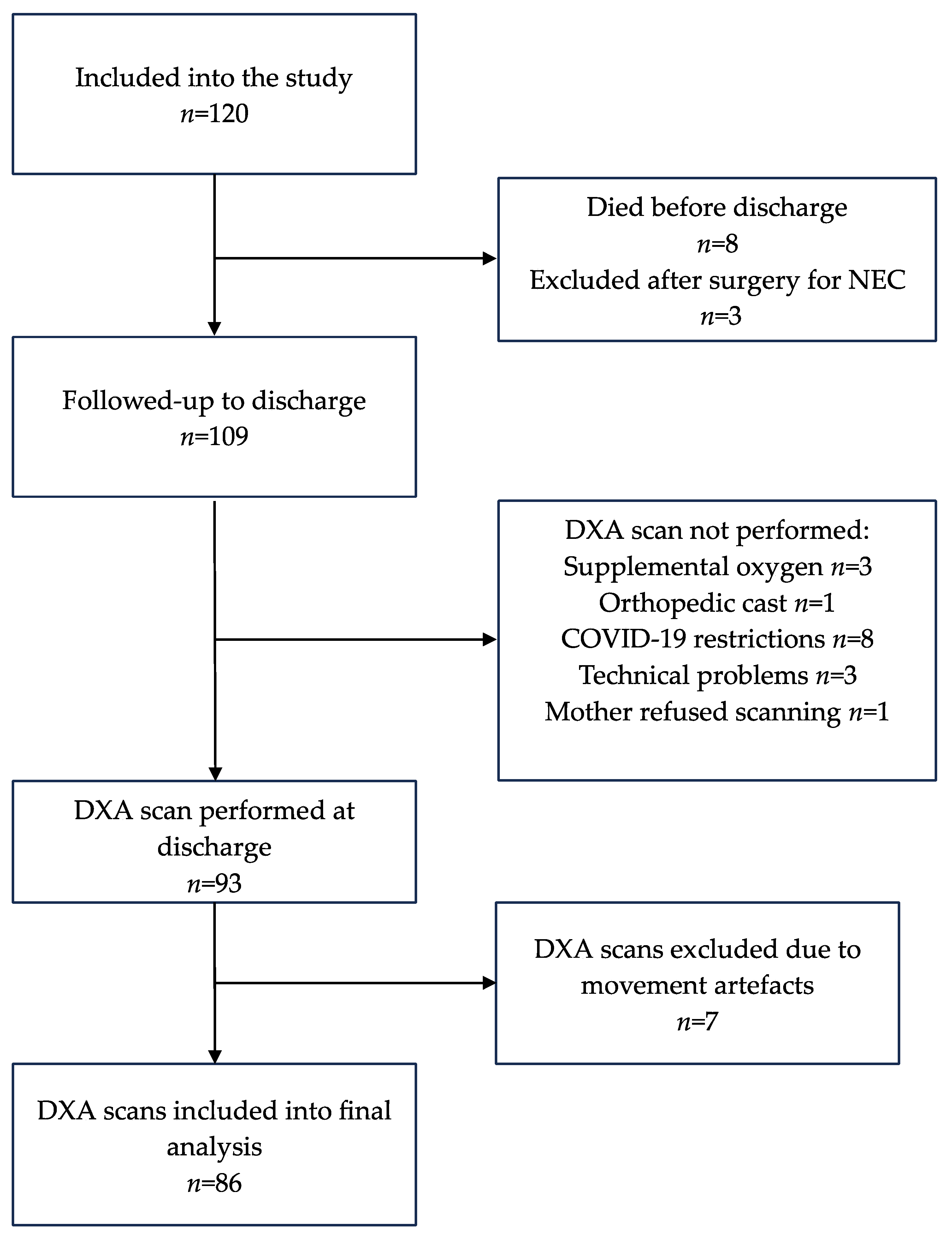
| Characteristics | Extremely Preterm n=32 |
Very Preterm n=54 |
p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male sex, n (%) | 16 (50.0) | 21 (38.9) | 0.314 |
| Gestational age, weeks | 26 (25–27) | 29 (28–30) | <0.001 |
| Birthweight g, mean (SD) | 878 (±197) | 1267 (±140) | <0.001 |
| Apgar score 1 min | 6 (3–8) | 8 (7–8) | <0.001 |
| Apgar score 5 min | 8 (6–8) | 8 (8–9) | <0.001 |
| Caesarean section, n (%) | 14 (43.8) | 32 (59.3) | 0.163 |
| Multiple pregnancy, n (%) | 5 (15.6) | 18 (33.3) | 0.073 |
| SGA, n (%) | 6 (18.8) | 12 (22.2) | 0.702 |
| Mechanical ventilation, n (%) | 16 (50.0) | 2 (3.8) | <0.001 |
| Sepsis*, n (%) | 18 (56.3) | 7 (13.0) | <0.001 |
| PDA (HS), n (%) | 18 (56.3) | 8 (14.8) | <0.001 |
| BPD, n (%) | 3 (9.4) | 1 (1.9) | 0.143 |
| NEC, n (%) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (1.9) | N/A |
| Characteristics | Extremely Preterm n=32 |
Very Preterm n=54 |
p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enteral feeding started, hours | 5 (3–6) | 3 (3–5) | 0.005 |
| Parenteral nutrition, days | 7 (6–9) | 5 (4–6) | <0.001 |
| Fortification started, days | 9 (7–11) | 7 (6–8) | <0.001 |
| Parenteral | |||
| Protein, g/kg/day | 2.3 (2.1–2.7) | 2.0 (1.8–2.3) | <0.001 |
| Carbohydrates, g/kg/day | 7.4 (6.1–8.4) | 6.2 (5.3–6.8) | <0.001 |
| Fat, g/kg/day | 1.5 (1.3–1.8) | 1.5 (1.2–1.8) | 0.712 |
| Energy, kcal/kg/day | 48 (44–56) | 43 (38–47) | 0.003 |
| Enteral* | |||
| Protein, g/kg/day | 3.3 (2.9–3.7) | 3.6 (3.1–3.9) | 0.148 |
| Carbohydrates, g/kg/day | 14.6 (11.5–15.7) | 15.1 (13.8–15.8) | 0.376 |
| Fat, g/kg/day | 5.8 (5.1–7.0) | 5.9 (4.9–6.8) | 0.469 |
| Energy, kcal/kg/day | 129 (112–142) | 131 (122–142) | 0.714 |
| Total | |||
| Protein, g/kg/day | 3.1 (3.0–3.4) | 3.2 (3.0–3.4) | 0.908 |
| Carbohydrates, g/kg/day | 13.4 (11.4–14.1) | 12.9 (12.1–13.8) | 0.655 |
| Fat, g/kg/day | 5.0 (4.6–5.8) | 5.0 (4.4–5.7) | 0.503 |
| Energy, kcal/kg/day | 114 (105–125) | 114 (107–120) | 0.886 |
| Protein/NPE ratio, g/100kcal | 3.1 (3.0–3.4) | 3.1 (2.9–3.4) | 0.872 |
| Characteristics | Extremely Preterm n=32 |
Very Preterm n=54 |
p |
|---|---|---|---|
| CGA at the DXA scan, weeks |
36 (35–36) | 35 (34–36) | 0.007 |
| Chronological age on DXA scan, weeks | 10 (9–11) | 6 (4–7) | <0.001 |
| Weight on the DXA day, g |
2558 (± 354) | 2284 (± 358) | <0.001 |
| Length on the DXA day, cm | 46.0 (± 1.9) | 45.3 (± 2.0) | 0.074 |
| DXA estimated total mass, g | 2786 (± 374) | 2512 (± 371) | 0.001 |
| DXA estimated lean mass, g |
2086 (± 246) | 2012 (± 249) | 0.188 |
| DXA estimated fat mass, g | 700 (± 212) | 500 (± 209) | <0.001 |
| DXA estimated fat mass percentage, % | 24.8 (± 5.4) | 19.4 (± 6.4) | <0.001 |
| Skinfold thickness sum at DXA scan day, mm | 17.8 (±2.6) | 15.9 (±2.9) | 0.004 |
| Skinfold thickness sum at 12 months of CA, mm | 26.9(±5.5) | 26.3(±4.6) | 0.661 |
| Extremely Preterm, n=32 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DXA mass, g | DXA LM, g | DXA FM, g | DXA FM, % | ∑ SFT, mm | ||||||
| R2=0.207 | R2=0.250 | R2=0.096 | R2=0.066 | R2=0.192 | ||||||
| βs | p | βs | p | βs | p | βs | p | βs | p | |
| Protein, g/kg/day | 0.027 | 0.923 | -0.049 | 0.858 | 0.106 | 0.726 | 0.125 | 0.685 | -0.274 | 0.373 |
| Carbohydrates, g/kg/day | -0.148 | 0.627 | 0.021 | 0.942 | -0.287 | 0.381 | -0.297 | 0.373 | 0.361 | 0.287 |
| Fat, g/kg/day | 0.411 | 0.080 | 0.331 | 0.143 | 0.340 | 0.170 | 0.226 | 0.364 | 0.145 | 0.559 |
| Sex | -0.327 | 0.114 | -0.475 | 0.022 | -0.026 | 0.906 | 0.150 | 0.496 | -0.103 | 0.629 |
| Gestational age, weeks | -0.272 | 0.239 | -0.305 | 0.177 | -0.126 | 0.604 | -0.006 | 0.981 | 0.221 | 0.379 |
| Very preterm, n=54 | ||||||||||
| DXA mass, g | DXA LM, g | DXA FM, g | DXA FM, % | ∑ SFT, mm | ||||||
| R2=0.411 | R2=0.298 | R2=0.410 | R2=0.375 | R2=0.163 | ||||||
| βs | p | βs | p | βs | p | βs | p | βs | p | |
| Protein, g/kg/day | 0.099 | 0.558 | 0.207 | 0.262 | -0.072 | 0.670 | -0.196 | 0.261 | -0.248 | 0.344 |
| Carbohydrates, g/kg/day | -0.186 | 0.280 | -0.094 | 0.617 | -0.218 | 0.207 | -0.169 | 0.341 | -0.087 | 0.736 |
| Fat, g/kg/day | 0.198 | 0.126 | -0.062 | 0.657 | 0.424 | 0.002 | 0.455 | 0.001 | 0.406 | 0.021 |
| Sex | -0.370 | 0.002 | -0.400 | 0.003 | -0.179 | 0.127 | -0.057 | 0.632 | 0.089 | 0.565 |
| Gestational age, weeks | -0.460 | <0.001 | -0.268 | 0.035 | -0.495 | <0.001 | -0.461 | <0.001 | -0.037 | 0.807 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





