1. Introduction
The integration of Precision Agriculture (PA) stands to significantly enhance agricultural efficiency, especially considering the expected global population rise and increasing demands for food security. Focusing on economically crucial crops like corn, PA employs advanced tools such as remote sensing, GIS, and GPS to optimize field management. This approach aims at maximizing resource efficiency and minimizing waste, thereby increasing crop yields, and promoting environmental sustainability. Despite its potential, the adoption of PA is hindered by financial constraints and technical complexities, which deter stakeholder engagement [
1,
2,
3].
Remote sensing has emerged as a dependable method for monitoring fields, utilizing UAVs, piloted aircraft, and satellites for data collection [
4,
5]. UAVs are becoming increasingly vital in agriculture, thanks to their ability to carry diverse sensors and provide high-resolution, cost-effective imaging [
6]. Even with their limited flight time, UAVs are found to be more efficient than other technologies [
7]. They play a critical role in crop monitoring, offering detailed insights into individual crop characteristics, tree height, biomass, and overall field uniformity, and have been employed in the identification of tree species [
8,
9].
However, a significant gap exists in the application of these technologies for the precise and scalable monitoring and management of individual crop characteristics, particularly in understanding and optimizing the complex canopy structures of crops like corn. This gap highlights the need for more refined, efficient, and broadly applicable methodologies for crop management. Although traditional methods for measuring crop height are common, they face challenges such as errors and time consumption. UAVs offer a superior alternative, significantly improving the accuracy of crop height measurements. Their high-resolution imagery has proven invaluable [
10,
11]. This technology's potential was highlighted by Dorbu et al. [
5], who demonstrated its use in assessing field heterogeneity and health status for yield prediction.
The diversity of algorithms for crop detection and canopy size delineation underscores the scholarly discourse in this area. The Canopy Height Model (CHM) has been a key tool, facilitating various plant detection algorithms and methodologies for tree canopy delineation, such as region-growing, watershed-segmentation, and valley-following [
12,
13,
14,
15,
16].CHMs derived from the difference between the Digital Terrain Model (DTM) and the Digital Surface Model (DSM), offering a nuanced understanding of field topography [
17,
18].Its versatility is further evidenced in the assessment of individual tree crown parameters and canopy sizes [
7,
19,
20,
21,
22,
23].
Alternative algorithms have also been explored, revealing ongoing challenges and advancements in agricultural image processing and plant detection [
24,
25,
26,
27,
28,
29]. The presence of noise elements like soil, background, and shadows presents additional challenges in canopy size delineation, prompting the exploration of machine learning algorithms for plant identification tasks [
18,
30,
31,
32].
This research introduces an innovative method that leverages a Canopy Height Model (CHM) and a modified Voronoi diagram for efficient corn canopy detection and delineation, incorporating domain-specific knowledge to enhance accuracy and efficiency in agricultural monitoring and management [
22,
24]. This approach aims to build upon previous work by filtering out noise and precisely estimating individual corn crop peaks, using corn spectral data to discriminate individual crops from soil and shadows for effective canopy size estimation.
2. Materials and Methods
The execution of the proposed research methodology utilized a synergistic approach combining Python scripting, Agisoft Photoscan for detailed photogrammetric processing, and ArcGIS Pro 3.0 for extensive spatial analyses and the effective visualization of crop models. This combination was instrumental in navigating the complex data processing and analysis phases required for precise crop modeling.
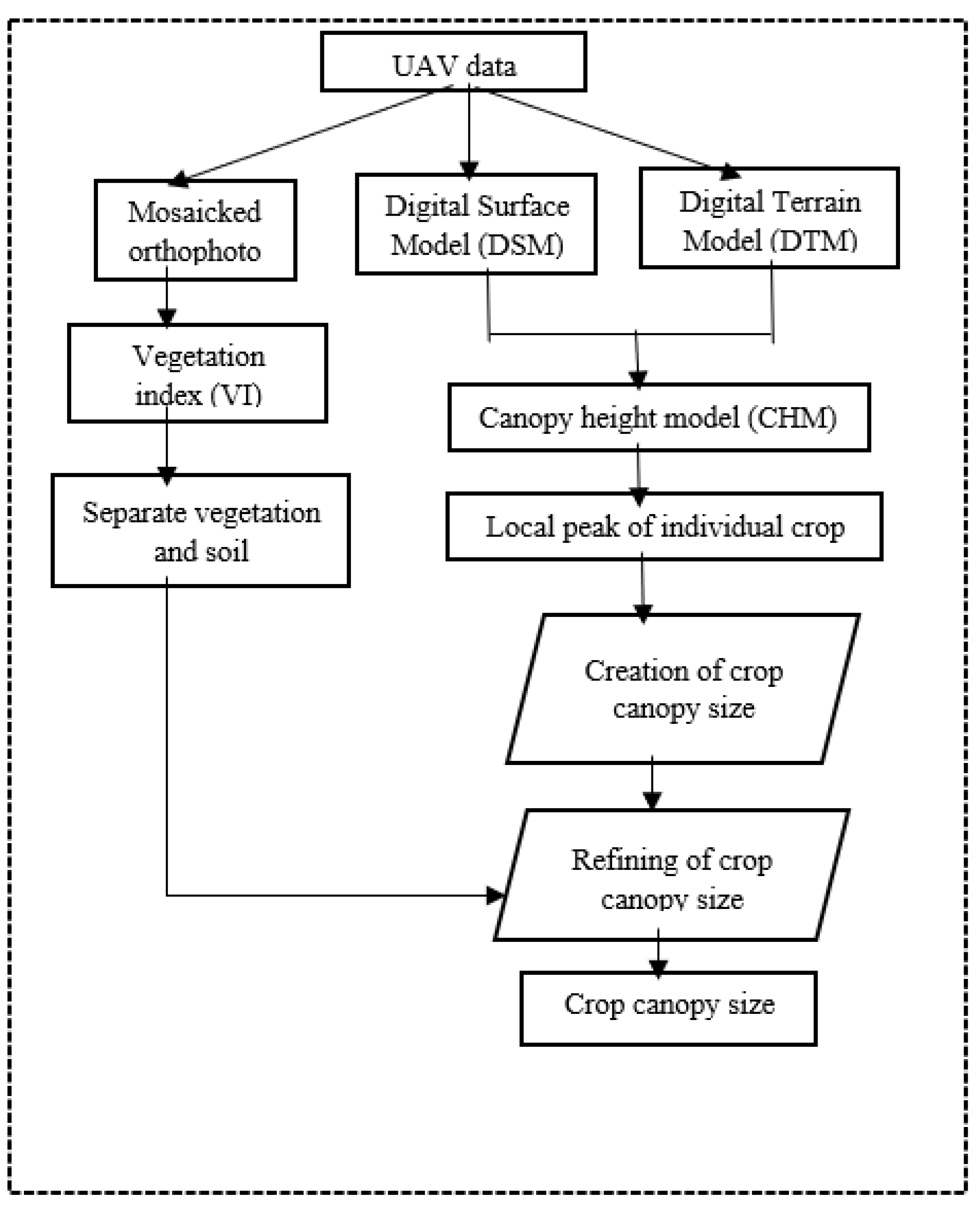
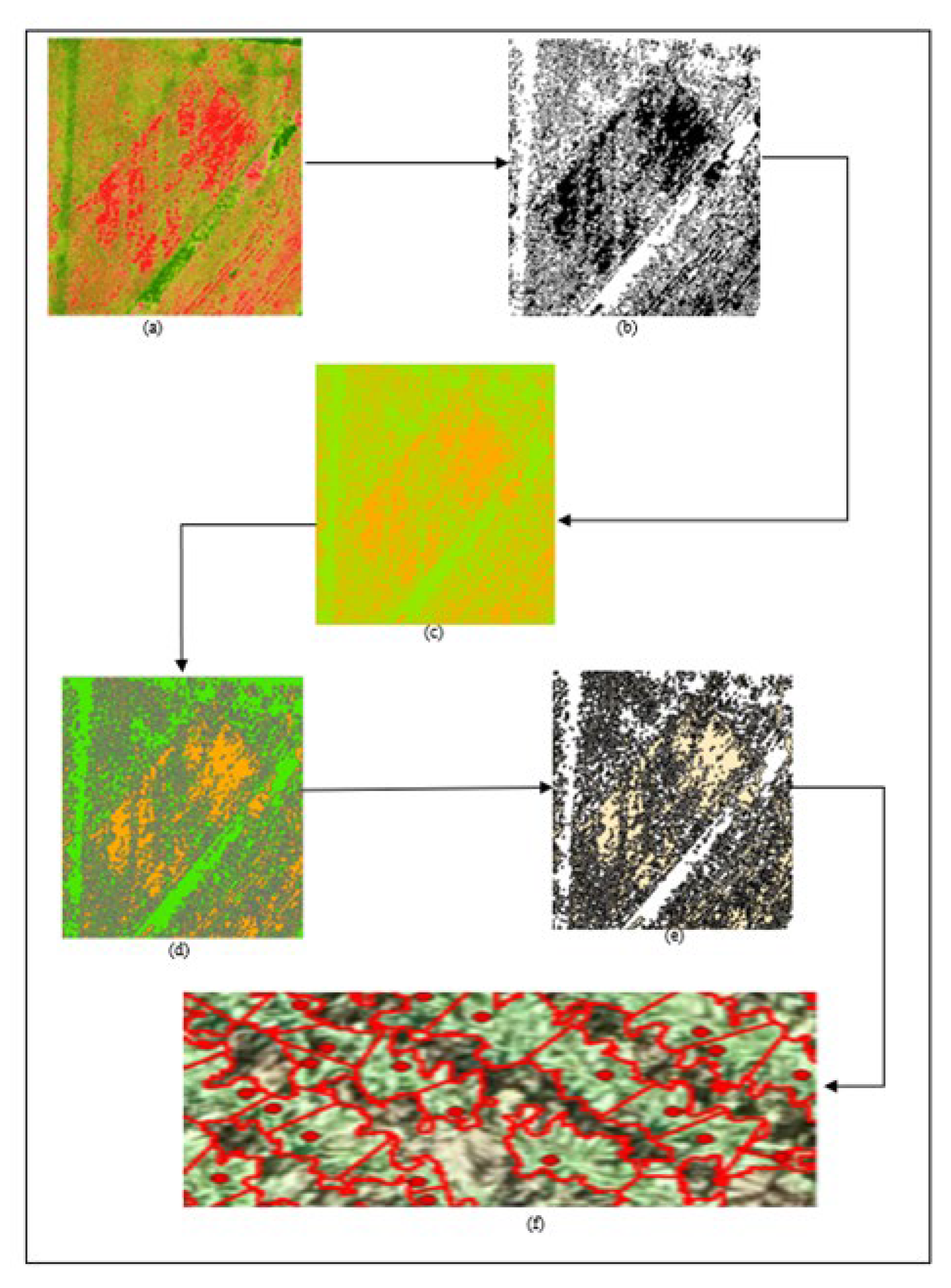
The project commences with the acquisition of high-resolution RGB time-series imagery, captured throughout the cultivation phase until the crops reach maturity. Employing Structure from Motion (SFM) photogrammetry techniques, Digital Elevation Models and orthophotos are generated and subsequently fed into the proposed algorithms. These inputs undergo geospatial data processing, facilitating the estimation of the Canopy Height Model and the automated identification of individual crop peak heights. Thereafter, computational geometry techniques are utilized to determine individual canopy sizes based on the identified peak heights. To refine the canopy size calculations and exclude non-vegetative elements, a vegetation index is introduced. The entire process, from crop identification to canopy size delineation, adheres to a meticulously designed framework, ensuring high-precision results, as outlined in
Figure 1 of the project documentation.
2.1. Preprocessing
The imagery captured at varying flight altitudes underwent processing via Structure from Motion (SFM), a technique that constructs an orthophoto and three-dimensional crop model from overlapping two-dimensional images. This process incorporates feature matching and camera alignment algorithms[
33]. Generating a Digital Surface Model (DSM) and a Digital Terrain Model (DTM) was pivotal in this endeavor. The DSM, depicting crop elevation, and the DTM, representing bare ground elevation, were derived from unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) images acquired before planting, when the field was bare, and from subsequent time-series imagery. The accuracy of crop height estimation and crop detection heavily relied on the quality of the DSM, which accurately represents the crop surface and ensures precise characterization of the study field.
2.2. Canopy Height Model Processing
In our study, we developed a Canopy Height Model (CHM) to aid in the identification of individual crops by calculating the difference between the Digital Surface Model (DSM), which captures the crop elevation, and the Digital Terrain Model (DTM), representing the elevation of the bare earth. This calculation effectively highlights the height of the crops, discounting the elevation of the terrain [
32,
34]. A user-specified threshold, based on the characteristic height of mature corn (typically at least 3 meters), was employed to improve the model's accuracy by filtering out unrelated noise and retaining essential vegetation and soil features. Further binary thresholding refined the CHM, differentiating between vegetation and remaining soil components. This preprocessing step not only enhanced the analytical accuracy but also optimized computational efficiency. Overlaying the CHM onto orthophotos allowed for a visual evaluation of crop heights via their spectral characteristics, facilitating a detailed and effective analysis of the crop data.
2.3. Individual Crop Identification
A unique methodology was utilized for the detection of individual crops within the study by pinpointing each crop's local peak height through the CHM. This was accomplished by deploying a local maxima function on the CHM, designating a pixel as a local maximum when its value is greater than or equals the values of its surrounding pixels, marking the apex of crops. Various sizes of moving windows were tested on the CHM to determine the most suitable window size for this analysis, with a 10x10 window size proving most effective in accurately identifying local peak heights and discerning corn crops. The validity of this approach was confirmed through a comparison of the produced local maxima map with the original CHM, ensuring accurate crop identification. This local maximum map was then transformed into point data to detail the specific heights of individual crops.
where the
is the maximum value assigned to the cell at position
in the output raster map.
represents the value of the cell in the input CHM and the ranges
to
and
to
define the 10x10 window around cell
, considering a zero-based index. If the CHM is 1-based, the indices would adjust accordingly.
2.4. Delineation of Individual Canopy Sizes
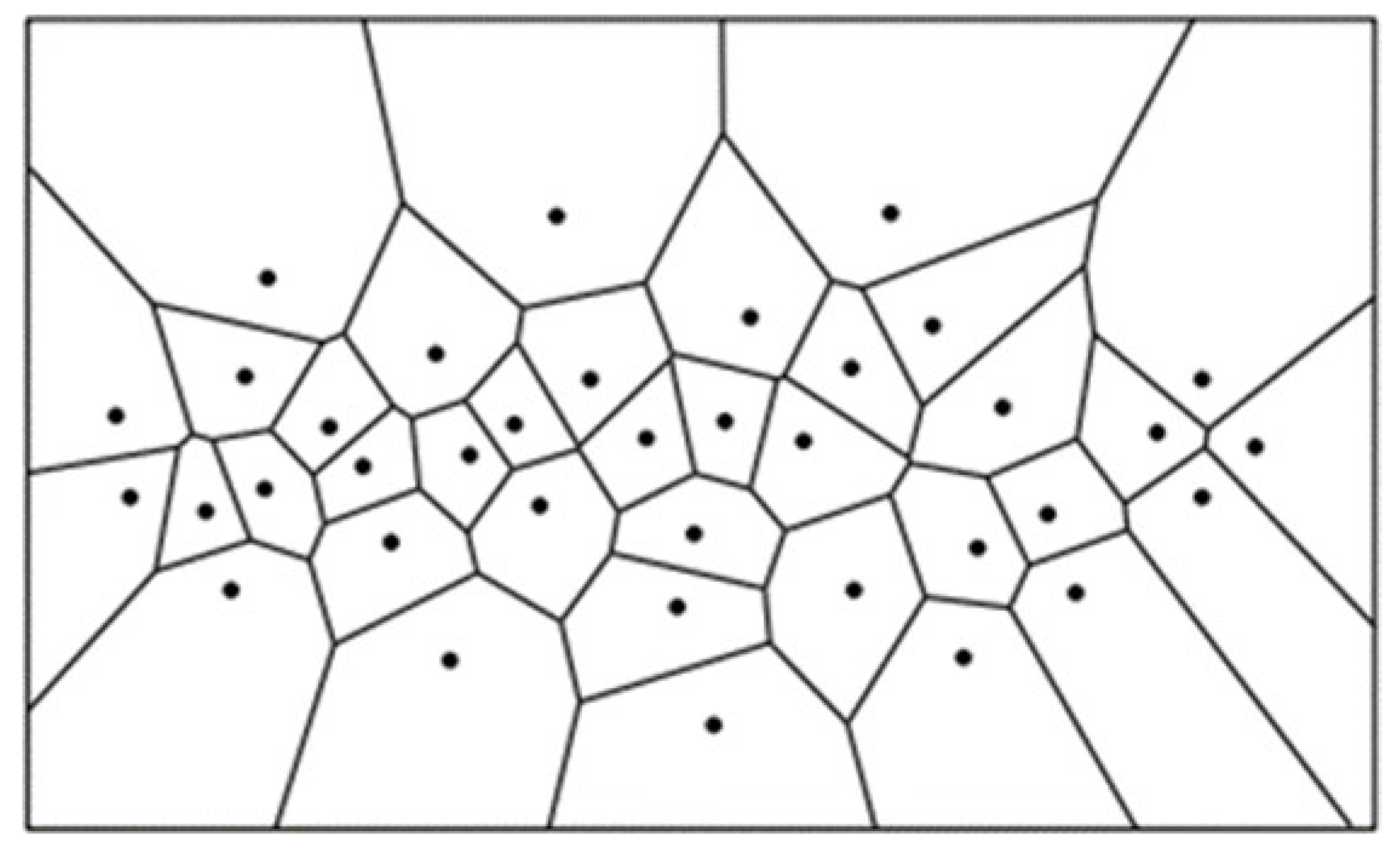
For estimating the sizes of individual crop canopies, the produced map of local peak heights was used as input for a computational geometry function. This function delineates a boundary around each identified crop, depicting the extent of its canopy. Utilizing a Voronoi Diagram for the geometrical calculation of canopy sizes, this method divides a region into zones nearest to each local maximum point, based on calculations of the Euclidean Distance between neighboring local maxima, thus offering a precise geometrical delineation of individual crop canopies. In mathematical terms, if the set of local maxima on the field is denoted as P, and any two points as p and q, the Euclidean distance between these points forms the basis for the Voronoi diagram calculation.
The Voronoi diagram, when illustrating canopy sizes, is calculated as follows:
Figure 2.
A Voronoi diagram delineating points [
35,
36].
Figure 2.
A Voronoi diagram delineating points [
35,
36].
The Voronoi diagram used for delineating individual crop canopies may include both vegetation and soil, particularly at different crop growth stages. To address this, a refinement method was developed to remove soil features from the tessellation polygons within the diagram, ensuring the final delineation more accurately represents the vegetation-only areas, enhancing the precision of crop canopy size estimation.
2.5. Refinement of Canopy Size Estimates
To differentiate soil from vegetation in the estimated canopy sizes, vegetation indices (VIs) were employed. These indices utilize specific features to effectively separate vegetation from non-vegetative elements. The orthophotos, generated during the preprocessing phase, played a crucial role in creating these VIs, facilitating the accurate separation of soil from vegetation in the canopy size estimates. This approach ensures that the final canopy size calculations are more representative of the actual vegetative area.
2.6. Vegetation Indices Calculation
Various vegetation indices were extensively evaluated to determine the most effective one for refining the process of delineating crop canopies. The indices examined included the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI), Green Chromatic Coordinate (GCC), Excess Green (ExG), and Green Leaf Index (GLI). NDVI, particularly noted for its effectiveness in estimating vegetation greenness, is a scale that ranges from -1 to +1, with values closer to +1 indicating healthier vegetation. This approach is based on research by Alface et al. (2019), who highlighted NDVI's capability in distinguishing between soil, healthy, and non-healthy crops. To validate our results, we utilized multispectral orthophotos derived from the images captured at the study site, analyzing them for NDVI to assess field greenness. NDVI is mathematically estimated as [
37]:
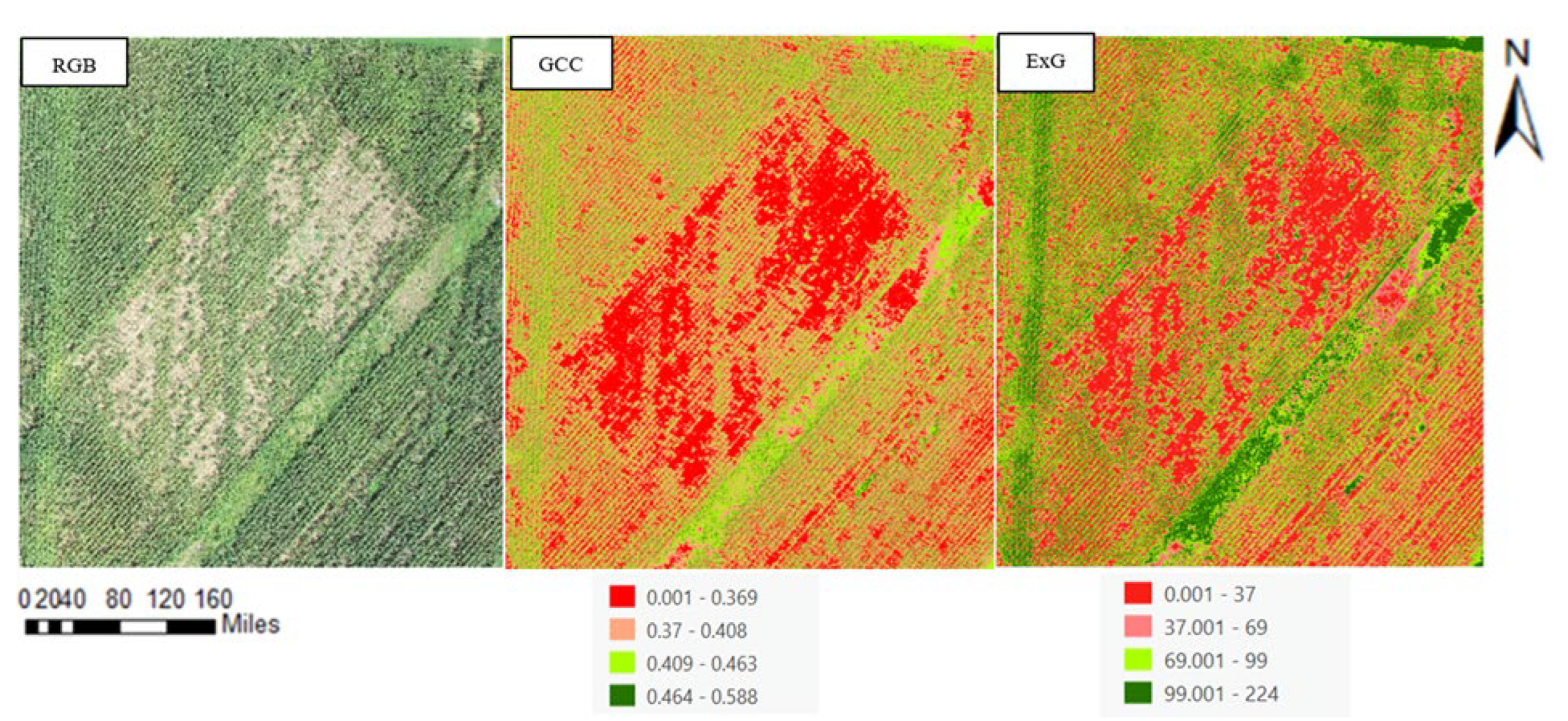
Further, we investigated the application of GCC and ExG indices, which as per [
38], have been known to sometimes surpass NDVI in accuracy (
Figure 3). The mathematical expressions for these indices involve the measurement of the green band relative to the red and blue bands. The effectiveness of these indices, as stated by [
39],depends on the specific plant species and canopy structure under study. In our project, ExG was particularly used for crown delineation due to its effectiveness in segmenting vegetation from other features, as demonstrated in [
40]. The ExG and GCC indices are mathematically expressed as per the formulations provided by [
41]:
The Green Leaf Index (GLI), a crucial vegetative index, measures the one-sided green area of leaves per ground surface area and is a key factor in enhancing grain yield. It plays a significant role in crop monitoring and yield forecasting by affecting photosynthetic radiation interception [
42,
43].
For our project, the ExG index was selected for further refining the delineation of crop canopies due to its effectiveness in vegetation segmentation. Additionally, the study explored the impact of crop inclination on canopy size estimations, introducing a slope index to represent the angular deviation of crop stems from the vertical, crucial for identifying different vegetative conditions and contributing to our comprehensive analysis of crop health through the growth cycle [
44,
45].
2.7. Validation
To validate the proposed method, a comparative analysis was conducted between the locations of points indicating the individually detected crops and the planting schema based on domain knowledge. Additionally, the top crop point and the canopy size delineation output were overlaid on the original RGB image. This comparison served as a verification of the location accuracy of vegetation and soil, ensuring that the results accurately represented the crops in the study area. Observing changes in tabulated canopy sizes after refinement provided further insights into the effectiveness of the canopy size refinement approach. A Mann-Whitney test with a 0.05 significance level was also run to validate the refinement process.
3. Results
3.1. Study Area and Data Collection
The research was conducted on a corn crop field at North Carolina Agricultural and Technical State University's research farm in Greensboro during the summer season (April to August 2020). The 415x210 ft field is located at 36.07260°N, 79.79200°W. Greensboro's humid subtropical climate, with an average July temperature of 78.5°F and annual rainfall of 45 inches, provides favorable conditions for corn growth. The soil type is Cecil, and the region sits at an average elevation of 243m above sea level. Standard agronomy practices were followed for corn planting, with winter crops retained before planting to assess their impact on corn growth. Eight ground control points (GCPs) were established for georeferencing UAV imagery. Two UAVs carrying RGB and near-infrared sensors were flown at 40 and 70 meters to capture aerial imagery at 1 and 1.9 cm spatial resolutions, respectively. The dual flight heights facilitated result validation through comparative analysis. UAV operations adhered to North Carolina flight planning regulations, with flights predominantly conducted late in the morning to minimize issues like sun reflection and wind interference. Images were captured with 80% overlap for 3D crop model construction (
Figure 4). Spectral profiling of selected field areas was conducted to understand variability (
Figure 5).
3.2. CHM Development and Crop Detection
A Canopy Height Model (CHM) was generated and meticulously refined using a height threshold reflective of mature corn's growth characteristics. This refinement phase was crucial for enhancing the analytical precision, allowing for the exclusion of extraneous noise and the focus on data representing the mature corn growth cycle. Spatial focal statistical analysis applied to the refined CHM revealed local peak heights of crops, providing an in-depth understanding of crop density and distribution across the field (
Figure 6 and
Figure 7).
3.3. Validation of Crop Detection Techniques
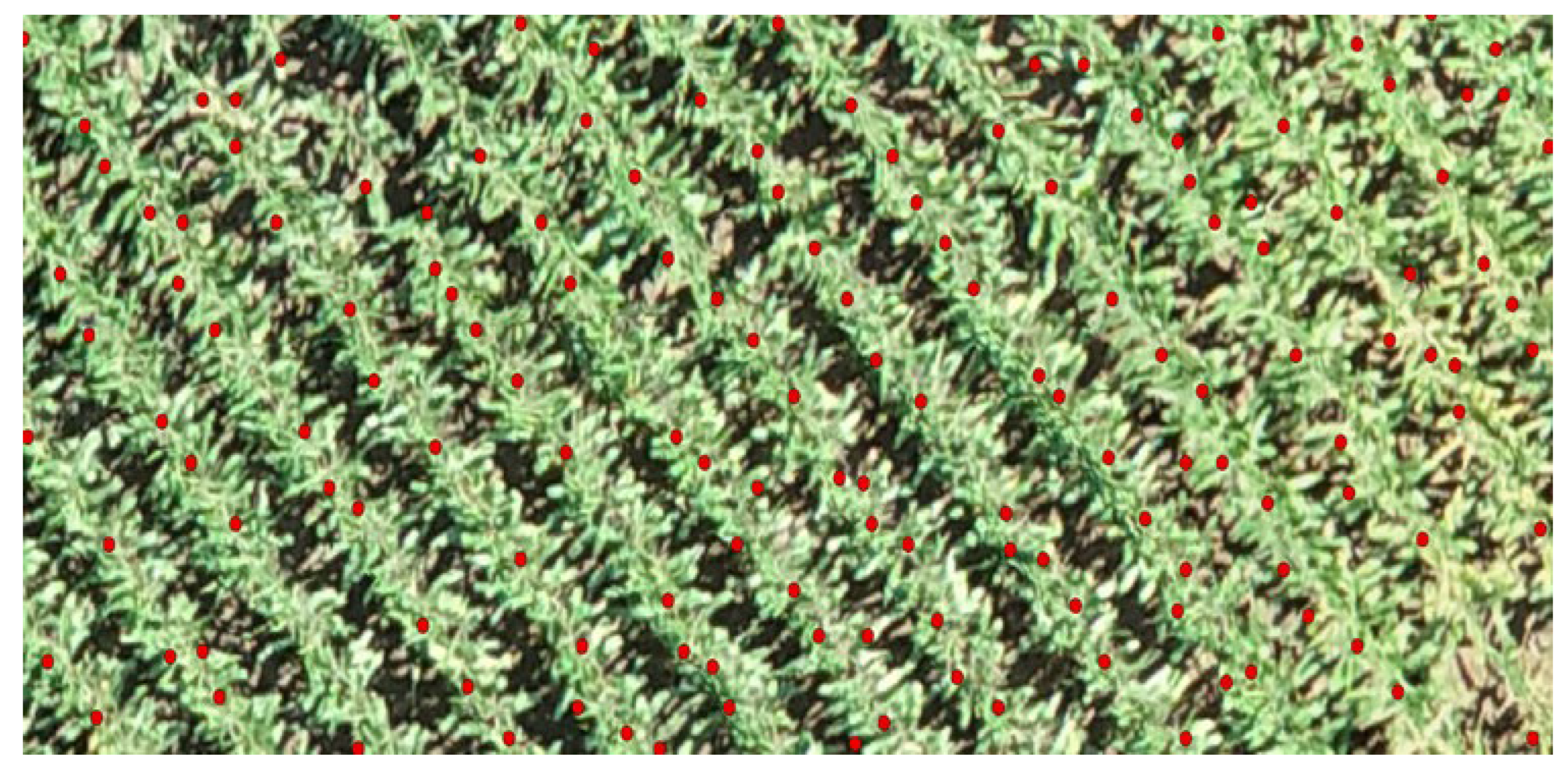
The validation of crop detection methodologies was significantly bolstered by the analysis of local peak height data, meticulously converted into point form and then cross-referenced with the established planting schema. This analytical step was visually corroborated by overlaying the resulting data points onto orthophotos of the study area. The comparative analysis revealed a high degree of accuracy in the representation of crop peaks within the study area, as evidenced in
Figure 8. Despite this high level of accuracy, the analysis also highlighted instances where non-vegetative elements were erroneously classified as crop heights, indicating areas where further refinement was necessary to enhance the precision of our crop detection technique. This crucial step in our study not only confirmed the effectiveness of our CHM filtering and local maxima identification strategy but also underscored the importance of additional analytical rigor to eliminate extraneous noise. Such refinement ensures a more accurate depiction of the crops, ultimately contributing to the robustness of our methodological approach in agricultural monitoring and analysis.
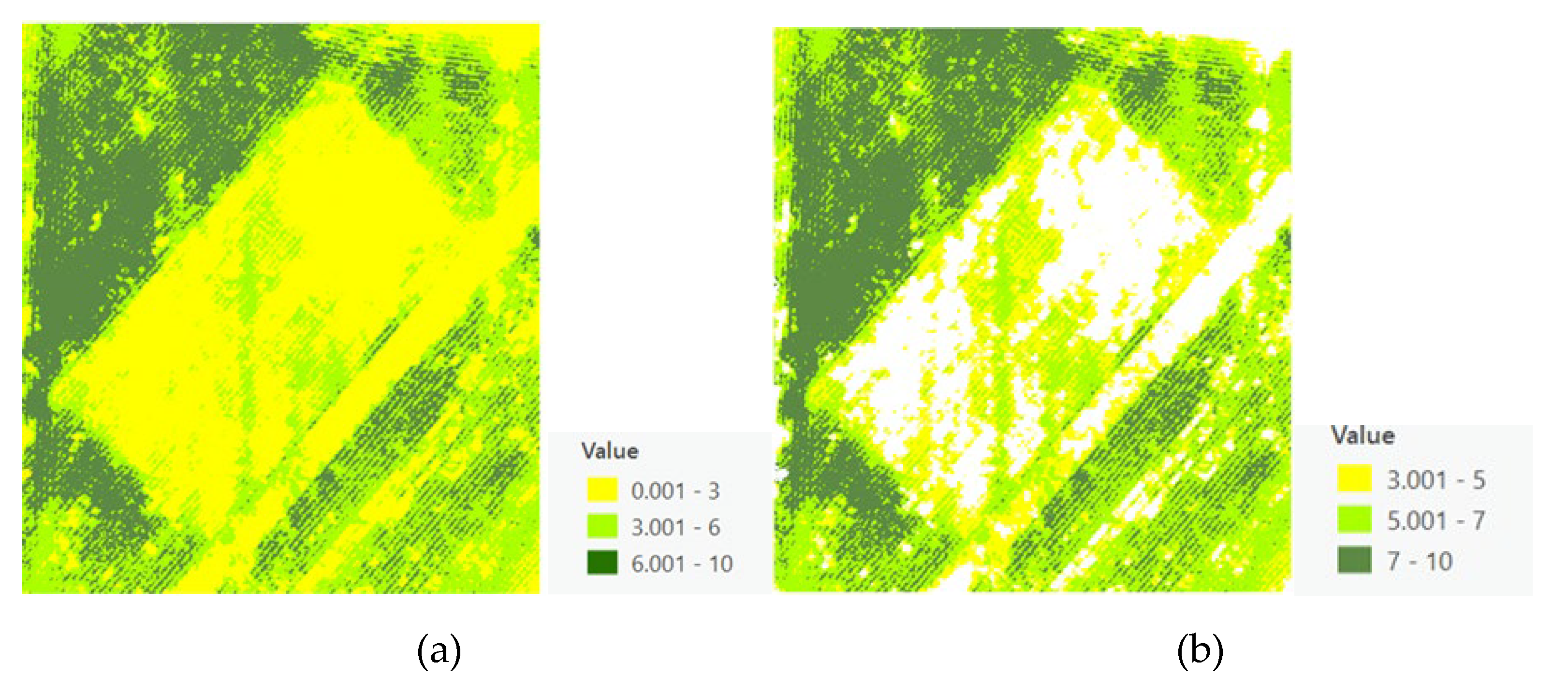
3.4. Canopy Size Estimation and Refinement
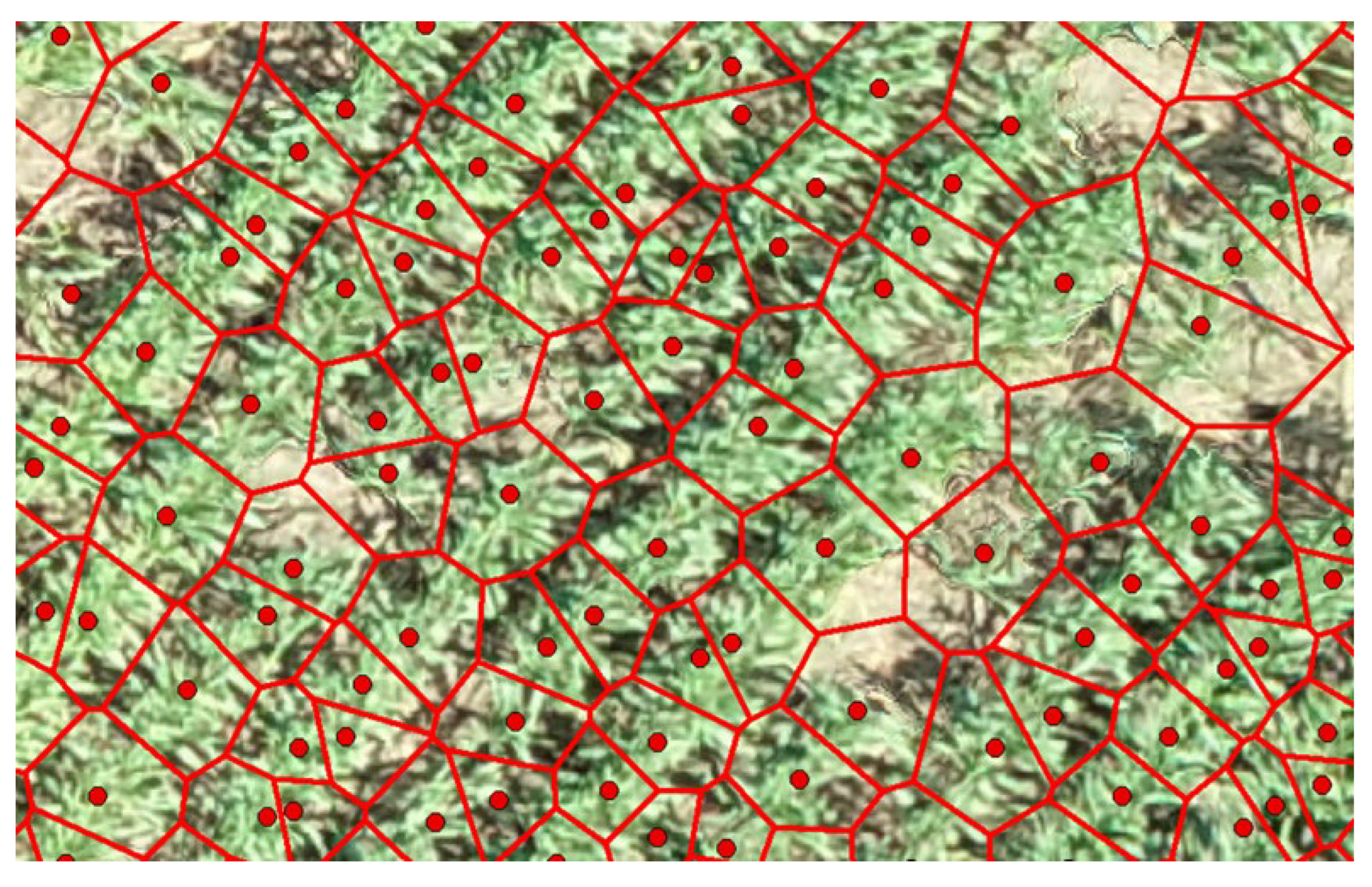
The innovative application of a Voronoi Diagram based on local peak heights facilitated the spatial partitioning of the field, delineating clear boundaries around each identified crop. However, initial estimates of canopy sizes included inaccuracies due to the inclusion of soil and shadows, necessitating further refinement processes to achieve precise canopy size estimations (
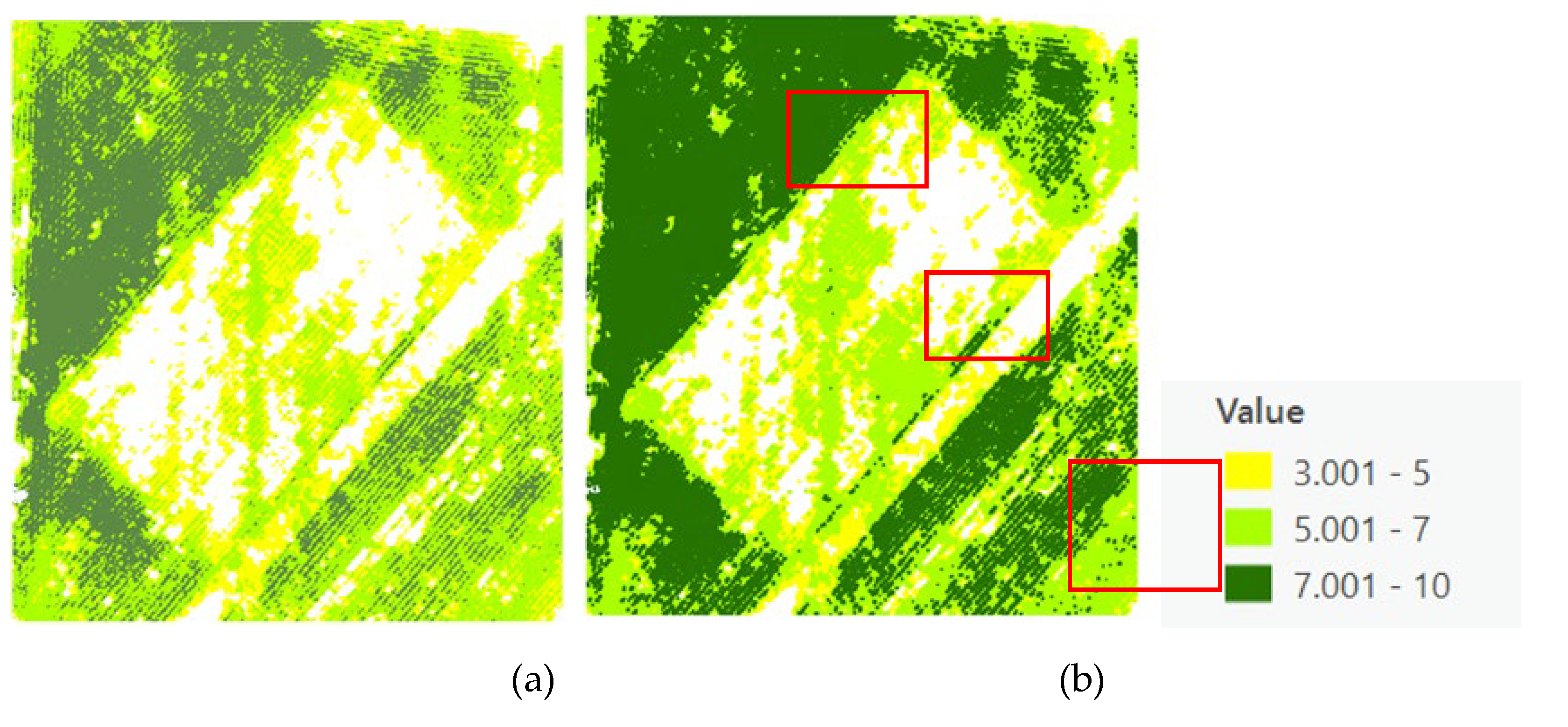
Figure 9). The refined canopy size estimations employed the Excess Green vegetation index, significantly enhancing the accuracy by differentiating between vegetative and non-vegetative elements (
Figure 10).
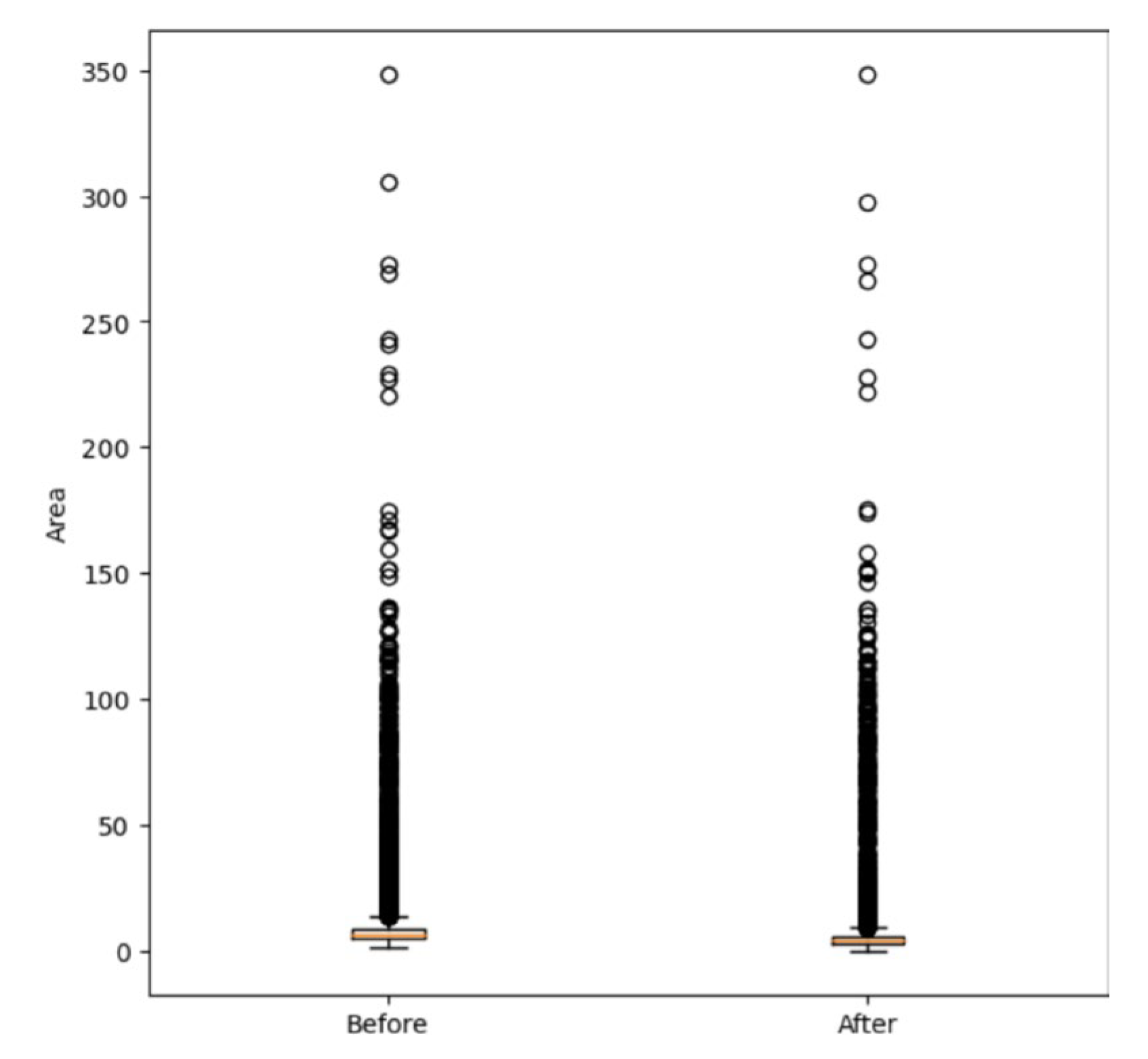
Additionally, a p-value of 0 obtained from the Mann-Whitney test indicates a significant difference in the data distribution of canopy sizes before and after the refinement process (Figure11).
The methodologies employed in this study successfully leveraged advanced technological tools to achieve a nuanced understanding of crop growth patterns within the designated study area. The results demonstrate high accuracy in crop detection and canopy size delineation, highlighting the critical role of continuous refinement in the data processing and analysis phases to mitigate inaccuracies and enhance precision in agricultural research.
3.5. Statistical Analysis
In exploring the influence of NDVI and crop height on canopy size, we employed several machine learning models to analyze their impact on crop yield, leveraging NDVI's established correlation with yield[
46]. The analysis used canopy size as the dependent variable, with crop height and NDVI serving as independent variables.
The performance metrics of the models, detailed in
Table 1, include R-squared values indicating the proportion of variance in canopy size explained by the models, and Mean Absolute Error (MAE) reflecting the models' prediction accuracy.
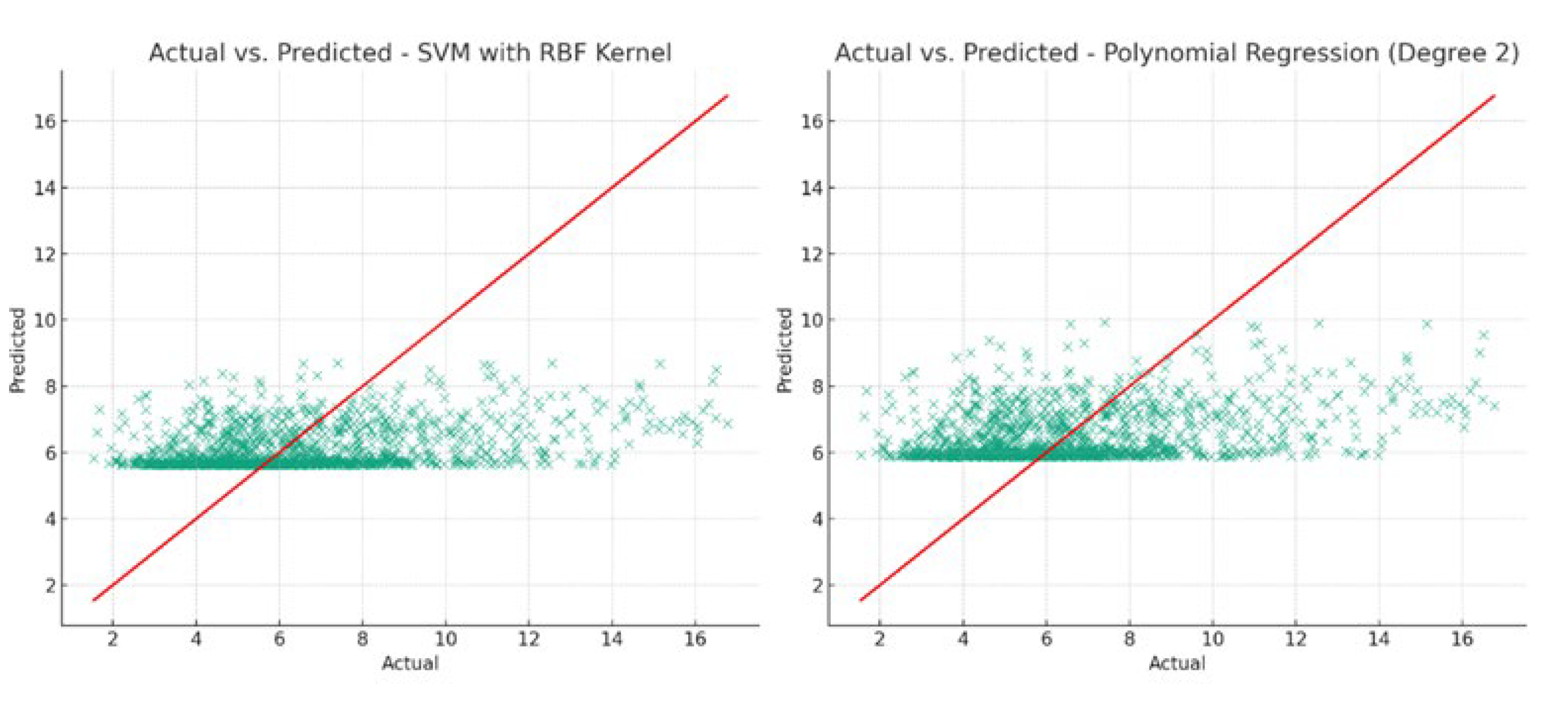
The relatively low R-squared values across models suggest that, under their current configurations, they do not explain a substantial portion of the variance in canopy size. The Polynomial Regression model, despite having the highest R-squared, still indicates a limited explanatory power. However, the lower MAE values for the Support Vector Machine and Polynomial Regression suggest these models are marginally more accurate in predicting canopy size from NDVI and crop height. This outcome implies that the relationship between NDVI, crop height, and canopy size may be weak, or that improving model performance might require more data, further feature engineering, or alternative modeling approaches. The polynomial regression model provided an equation that encapsulates the relationship between the predicted canopy sizes and NDVI and crop height as follows:
This equation reveals not only the direct (linear) impacts of crop height (
X1) and NDVI (
X2) on canopy size but also their combined (interaction) and non-linear (squared terms) effects, offering a comprehensive view of their relationships.
Figure 12 illustrates the predictive capabilities of the SVM with RBF kernel and Polynomial Regression models. The proximity of data points to the perfect prediction line (red line) indicates the accuracy of the model predictions.
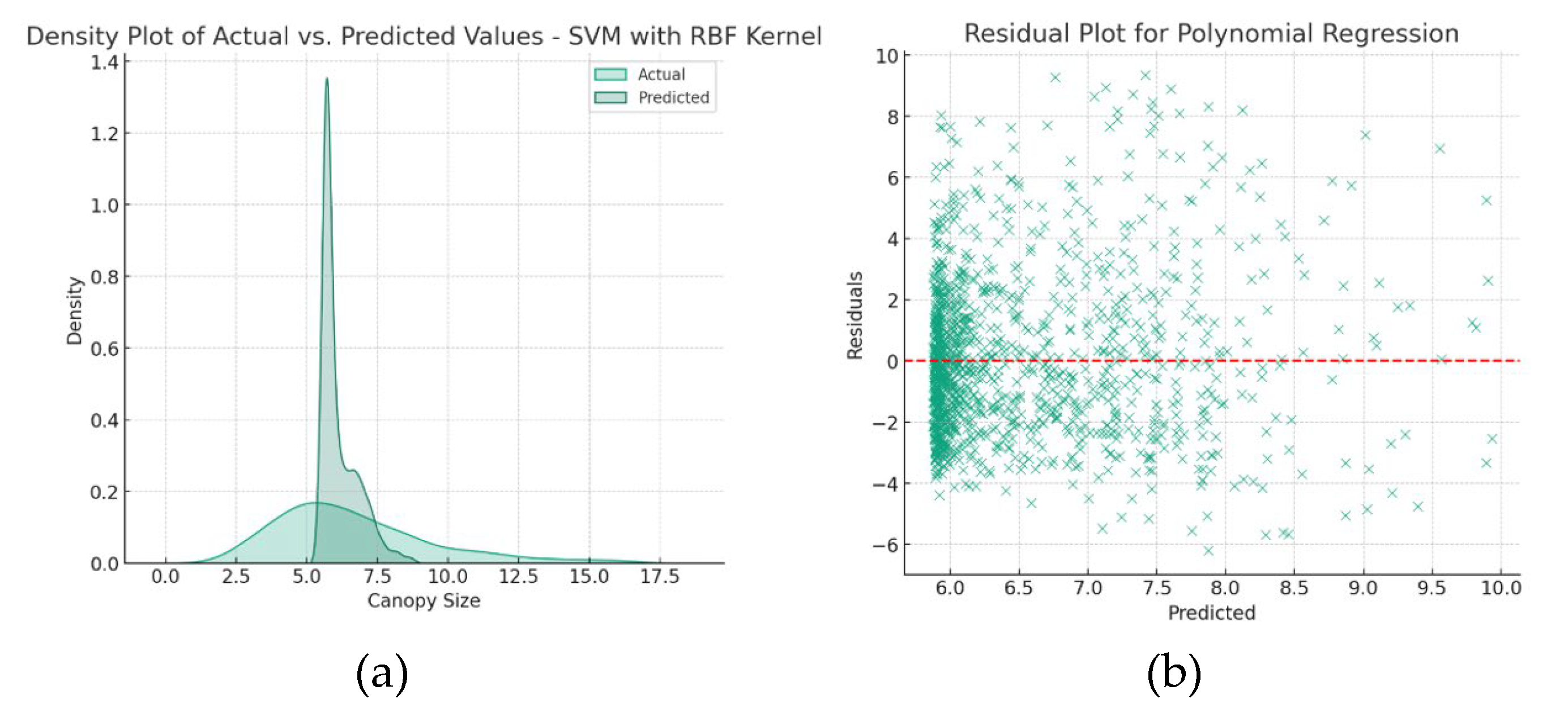
Figure 13 presents the density plot for the SVM model and the residual plot for the Polynomial Regression model, helping to identify residual patterns and overall prediction alignment.
3.5.1. Ordinary Least Squares (OLS) Analysis
An OLS analysis performed further investigated the relationship between canopy size and its predictors. The OLS estimator equation is as follows:
This analysis resulted in a regression equation for canopy size:
Canopy size=10.3126−0.5111×Crop height−0.3698×NDVI
This model suggests that increases in crop height and NDVI are associated with decreases in canopy size, under the assumption that other variables remain constant. The R-squared value of 7.5% and an MAE of 2.058 provide insights into the model's explanatory power and prediction accuracy, respectively.
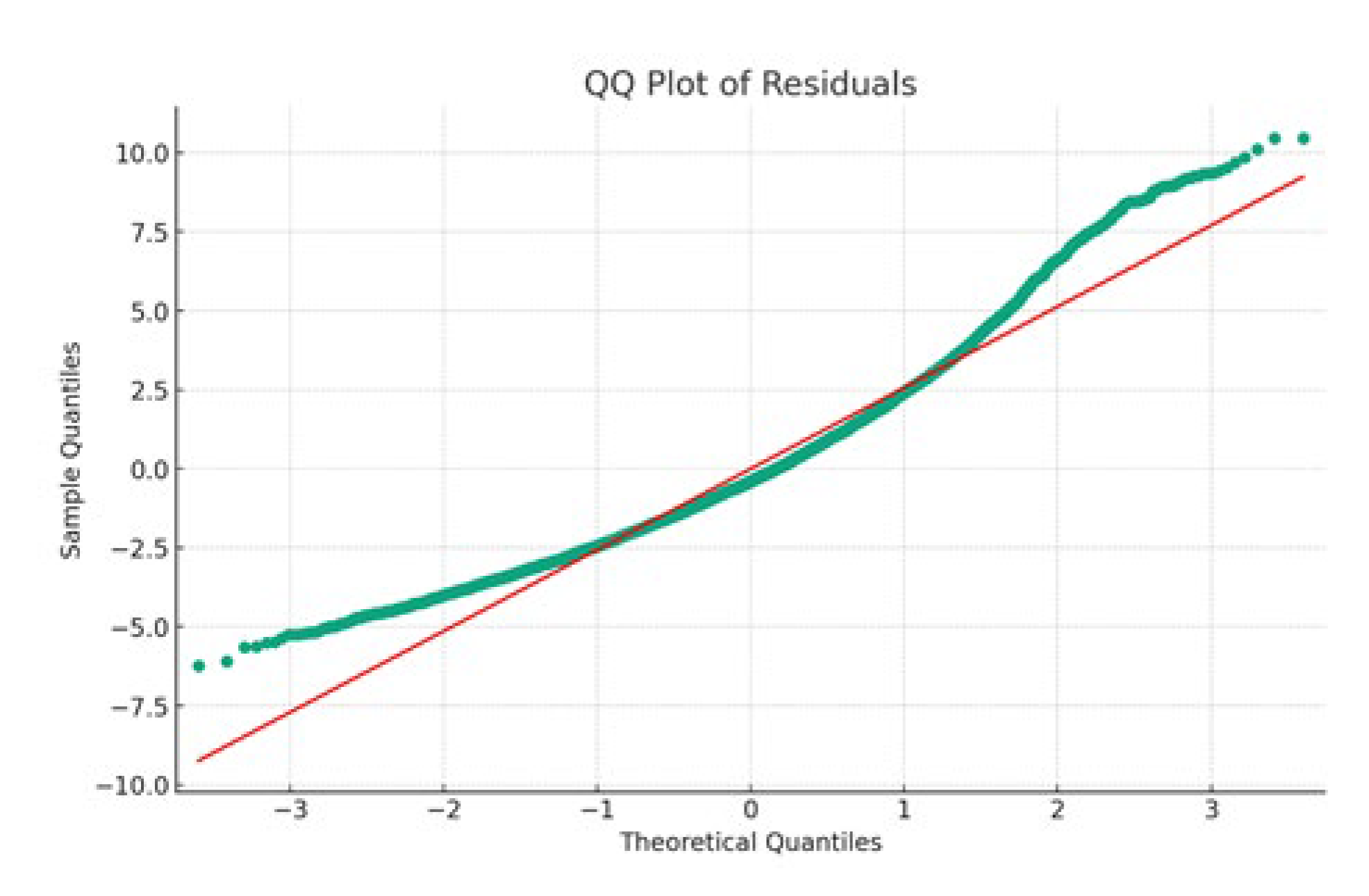
Figure 14 showcases the quantile-quantile plot of the OLS model, comparing the distribution of the model's residuals against a normal distribution. This visual analysis is critical for assessing the normality of residuals, a key assumption in OLS regression.
4. Discussion
Our investigation into individual crop identification and canopy delineation, leveraging computational geometry via high-resolution UAV imagery, proved highly effective for precise crop boundary delineation and canopy structure characterization. By adopting two distinct flight altitudes for data collection, we secured high-resolution, continuous RGB imagery critical for generating accurate 3D orthoimages essential for individual crop detection. While RGB sensors delivered quality data, integrating a hyperspectral sensor, as recommended by [
34], might furnish a richer geometrical representation vital for enhanced crop detection. The CHM filtering process, pivotal in noise elimination during preprocessing, bolstered the accuracy of our canopy size delineation, aligning with improvements highlighted by [
22] and [
24]. The selection of a plant height threshold was crucial, requiring precision to avoid omitting vital features while achieving optimal results. Our geospatial analytical approach proved successful in pinpointing individual crop peak heights, akin to CNNs' feature extraction in tree detection and classification as utilized by [
32]. However, CNNs faced challenges in precise crop delineation, underscoring the need for domain knowledge integration for heightened accuracy. Our methodology allowed for necessary adjustments to address any misrepresentations effectively.
Employing the maximum functionality enabled the discernment of individual crop tops through a detailed pixel-to-pixel comparison. The determination of an optimal kernel size for the moving window, based on domain knowledge regarding crop row spacing, further refined our analysis. The local peak heights derived were instrumental in creating Voronoi polygons for canopy delineation, accurately demarcating crop boundaries and showcasing advancements in remote sensing and precision agriculture. This study not only enhances crop monitoring and management practices but also underscores the potential of the Voronoi diagram method in crop canopy structure characterization, albeit with a need for further research to evaluate its efficacy across diverse regions and cropping systems.
Our results affirm the UAV approach as superior for plant information acquisition, highlighting its accuracy in plant height estimation and eliminating human error and accessibility issues associated with traditional methods. The proposed method's flexibility and efficacy are evident in its ability to generate accurate CHMs, discriminate between vegetation and soil automatically, and select an optimal moving window size that accurately reflects the real-world state of the study site. This approach, coupled with mean shift segmentation for precise vegetation index segmentation, represents a significant stride in remote sensing-based crop analysis and precision agriculture.
Author Contributions
F.D. contributed to the conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, methodology, visualization, original draft writing, software development, and investigation aspects of the study. L.H. was involved in conceptualization, methodology development, acquiring funding, project administration, resource management, supervision, validation, and the review and editing of the manuscript.
Funding
This work received partial support from the National Science Foundation under the grants "Developing a Robust, Distributed, and Automated Sensing and Control System for Smart Agriculture" [grant number 1832110] and "Remote Sensing for Flood Modeling and Management" [grant number 1800768].
Data Availability Statement
The data supporting this study's findings are available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
We extend our gratitude to the team responsible for piloting the UAVs during the data collection phase of our study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have influenced the work reported in this paper.
References
- M. D. McConnell, "Bridging the gap between conservation delivery and economics with precision agriculture," Wildl. Soc. Bull., vol. 43, (3), pp. 391-397, 2019. [CrossRef]
- V. Higgins et al, "Ordering adoption: Materiality, knowledge and farmer engagement with precision agriculture technologies," J. Rural Stud., vol. 55, pp. 193-202, 2017. [CrossRef]
- I. Cisternas et al, "Systematic literature review of implementations of precision agriculture," Comput. Electron. Agric., vol. 176, pp. 105626, 2020. Available: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0168169920312357. [CrossRef]
- M. Beland et al, "On promoting the use of lidar systems in forest ecosystem research," For. Ecol. Manage., vol. 450, pp. 117484, 2019. Available: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0378112719306218. [CrossRef]
- F. E. Dorbu et al, "UAV Remote Sensing Assessment of Crop Growth," Photogrammetric Engineering & Remote Sensing, vol. 87, (12), pp. 891-899, 2021.
- Q. Sun et al, "Monitoring maize lodging grades via unmanned aerial vehicle multispectral image," Plant Phenomics, vol. 2019, 2019. [CrossRef]
- H. Yurtseven et al, "Determination and accuracy analysis of individual tree crown parameters using UAV based imagery and OBIA techniques," Measurement, vol. 145, pp. 651-664, 2019. Available: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0263224119305421. [CrossRef]
- W. S. Wan Mohd Jaafar et al, "Improving individual tree crown delineation and attributes estimation of tropical forests using airborne LiDAR data," Forests, vol. 9, (12), pp. 759, 2018. [CrossRef]
- M. Mohan et al, "Optimizing individual tree detection accuracy and measuring forest uniformity in coconut (Cocos nucifera L.) plantations using airborne laser scanning," Ecol. Model., vol. 409, pp. 108736, 2019.
- K. Stereńczak et al, "Factors influencing the accuracy of ground-based tree-height measurements for major European tree species," J. Environ. Manage., vol. 231, pp. 1284-1292, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Y. Pang et al, "Improved crop row detection with deep neural network for early-season maize stand count in UAV imagery," Comput. Electron. Agric., vol. 178, pp. 105766, 2020. [CrossRef]
- S. C. Popescu, "Estimating biomass of individual pine trees using airborne lidar," Biomass Bioenergy, vol. 31, (9), pp. 646-655, 2007. [CrossRef]
- T. Ota et al, "Aboveground biomass estimation using structure from motion approach with aerial photographs in a seasonal tropical forest," Forests, vol. 6, (11), pp. 3882-3898, 2015. [CrossRef]
- B. Hu et al, "Improving the efficiency and accuracy of individual tree crown delineation from high-density LiDAR data," International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, vol. 26, pp. 145-155, 2014. [CrossRef]
- Y. S. Lim et al, "Calculation of tree height and canopy crown from drone images using segmentation," 한국측량학회지, vol. 33, (6), pp. 605-613, 2015. [CrossRef]
- L. Duarte, P. L. Duarte, P. Silva and A. C. Teodoro, "Development of a QGIS plugin to obtain parameters and elements of plantation trees and vineyards with aerial photographs," ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, vol. 7, (3), pp. 109, 2018. [CrossRef]
- J. M. Peña et al, Estimating tree height and biomass of a poplar plantation with image-based UAV technology. AIMS Agric.Food 2018, 3, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. Miraki et al, Detection of mistletoe infected trees using UAV high spatial resolution images. Journal of Plant Diseases and Protection. 2021, 128, 1679–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- F. Rodríguez-Puerta et al, "UAV-based LiDAR scanning for individual tree detection and height measurement in young forest permanent trials," Remote Sensing, vol. 14, (1), pp. 170, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Q. Ma, Y. Su and Q. Guo, Comparison of canopy cover estimations from airborne LiDAR, aerial imagery, and satellite imagery. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing 2017, 10, 4225–4236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M. Miraki et al, "Individual tree crown delineation from high-resolution UAV images in broadleaf forest," Ecological Informatics, vol. 61, pp. 101207, 2021. Available: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1574954120301576. [CrossRef]
- A. Abd-Elrahman et al, "Automated canopy delineation and size metrics extraction for strawberry dry weight modeling using raster analysis of high-resolution imagery," Remote Sensing, vol. 12, (21), pp. 3632, 2020. [CrossRef]
- M. Ghasemi, H. M. Ghasemi, H. Latifi and M. Pourhashemi, "A Novel Method for Detecting and Delineating Coppice Trees in UAV Images to Monitor Tree Decline," Remote Sensing, vol. 14, (23), pp. 5910, 2022. [CrossRef]
- A.B. Valluvan et al, "Canopy height estimation using drone-based RGB images," Smart Agricultural Technology, vol. 4, pp. 100145, 2023. [CrossRef]
- L. Jing et al, "An individual tree crown delineation method based on multi-scale segmentation of imagery," ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, vol. 70, pp. 88-98, 2012. [CrossRef]
- R. Marasigan, E. R. Marasigan, E. Festijo and D. E. Juanico, "Mangrove crown diameter measurement from airborne lidar data using marker-controlled watershed algorithm: Exploring performance," in 2019 IEEE 6th International Conference on Engineering Technologies and Applied Sciences (ICETAS), 2019,.
- H. Huang, X. H. Huang, X. Li and C. Chen, "Individual tree crown detection and delineation from very-high-resolution UAV images based on bias field and marker-controlled watershed segmentation algorithms," IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, vol. 11, (7), pp. 2253-2262, 2018. [CrossRef]
- J. L. Jensen and A. J. Mathews, "Assessment of image-based point cloud products to generate a bare earth surface and estimate canopy heights in a woodland ecosystem," Remote Sensing, vol. 8, (1), pp. 50, 2016. [CrossRef]
- M. Gao et al, "Individual maize location and height estimation in field from UAV-borne LiDAR and RGB images," Remote Sensing, vol. 14, (10), pp. 2292, 2022. [CrossRef]
- B. T. Kitano et al, "Corn plant counting using deep learning and UAV images," IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019. [CrossRef]
- S. Varela et al, "Early-season stand count determination in corn via integration of imagery from unmanned aerial systems (UAS) and supervised learning techniques," Remote Sensing, vol. 10, (2), pp. 343, 2018. [CrossRef]
- A. Fujimoto et al, "An end to end process development for UAV-SfM based forest monitoring: Individual tree detection, species classification and carbon dynamics simulation," Forests, vol. 10, (8), pp. 680, 2019.
- C. Torresan et al, "Forestry applications of UAVs in Europe: A review," Int. J. Remote Sens., vol. 38, (8-10), pp. 2427-2447, 2017. [CrossRef]
- A. Aeberli et al, "Characterisation of Banana Plant Growth Using High-Spatiotemporal-Resolution Multispectral UAV Imagery," Remote Sensing, vol. 15, (3), pp. 679, 2023. [CrossRef]
- M. A. Mostafavi, L. H. Beni and K. H. Mallet, "Geosimulation of geographic dynamics based on voronoi diagram," in Transactions on Computational Science IXAnonymous 2010,.
- L. H. Beni, "Development of a 3D kinetic data structure adapted for a 3D spatial dynamic field simulation," 2009.
- H. Hashim, Z. Abd Latif and N. A. Adnan, "Urban vegetation classification with NDVI threshold value method with very high resolution (VHR) Pleiades imagery," vol. 42, pp. 237-240, 2019. [CrossRef]
- W. Nijland et al, "Monitoring plant condition and phenology using infrared sensitive consumer grade digital cameras," Agric.For.Meteorol., vol. 184, pp. 98-106, 2014.
- S. Y. Dillen et al, "Seasonal patterns of foliar reflectance in relation to photosynthetic capacity and color index in two co-occurring tree species, Quercus rubra and Betula papyrifera," Agric.For.Meteorol., vol. 160, pp. 60-68, 2012.
- A.M. Reid et al, "Response of lodgepole pine health to soil disturbance treatments in British Columbia, Canada," vol. 45, (8), pp. 1045-1055, 2015. [CrossRef]
- J. St. Peter et al, "Linking phenological indices from digital cameras in Idaho and Montana to MODIS NDVI," vol. 10, (10), pp. 1612, 2018. [CrossRef]
- F. Tardieu, "Any trait or trait-related allele can confer drought tolerance: just design the right drought scenario," J.Exp.Bot., vol. 63, (1), pp. 25-31, 2012. [CrossRef]
- Y. Song, J. Y. Song, J. Wang and J. Shang, "Estimating effective leaf area index of winter wheat using simulated observation on unmanned aerial vehicle-based point cloud data," vol. 13, pp. 2874-2887, 2020. [CrossRef]
- S. Chauhan et al, "Estimation of crop angle of inclination for lodged wheat using multi-sensor SAR data," Remote Sens.Environ., vol. 236, pp. 111488, 2020. Available: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0034425719305073. [CrossRef]
- S. Chauhan et al, "Remote sensing-based crop lodging assessment: Current status and perspectives," vol. 151, pp. 124-140, 2019. Available: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0924271619300747. [CrossRef]
- A.B. Alface et al, "Sugarcane spatial-temporal monitoring and crop coefficient estimation through NDVI," vol. 23, pp. 330-335, 2019. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).