1. Introduction
Sericea lespedeza (SL;
Lespedeza cuneata) is a warm-season perennial legume that has gained attention in small ruminant production for its nutritive value and anthelmintic properties. This plant, native to eastern Asia, was introduced to the U.S. in the early 20th century for erosion control and has since established itself as a beneficial forage resource [
1], particulary with small ruminants (sheep and goats). The agronomic benefits of SL of drought tolerance and ability to grow on acidic, infertile soils where other legumes cannot thrive have been known for over a century [
2] , but recent research has revealed its value as a nutraceutical forage, particularly for its bioactivity against internal parasite infection in sheep and goats [
3] . This bioactivity, which has been attributed to the high level of prodelphinidin-type condensed tannins in SL [
4,
5],also includes anti-bacterial properties [
6]. reduction in ruminal methane production [
7,
8] and stress reduction [
9,
10,
11]. However, the value of SL as a natural (non-chemical) dewormer has been the primary driver for the recent renewed interest in the plant by producers and scientists.
For proprietors keen on amplifying biodiversity, incorporating SL is an informed step towards encouraging a dynamic and diverse biotic milieu. While the merits of SL in agricultural and ecological contexts are clear, innovative tools are needed to identify and manage it more effectively. This is particularly true during SL establishment, which can be challenging due to its small seed size and relatively slow initial growth [
2]. Competing weeds can be an issue during SL establishment and may compete later with SL during growth stage although SL is a drought-resistant crop, in general. Inability to differentiate SL plants from weeds can lead producers to assume they have a planting failure when this may not be the case [
11].
According to Buchanan and Burns [
12], as having small seeds, producing weak seedlings, and getting usually established during early spring, SL finds a strong competition from natural weeds in the field when conditions favor its rapid growth. Serecia Lespedeza’s (SL’s) poor competitive ability with weed, weed control becomes a major problem during establishment (first year) and therefore, identifying weed in SL field and eradicating early is a major necessity. So far, only a few studies have been conducted that uses satellite remote sensing [
13], aerial imagery [
14], and microsatellite imaging including this Research Group that used Landsat satellite imagery combined with Unmanned Aerial Imageries [
16] to detect SL but not weed from SL. Therefore, an increase in necessity is there presently to study image classification based approach to detect weed in a SL field during establishment so that precautionary measures can be taken efficiently and economically to eradicate weeds on a site-specific-crop-management (SSCM) approach.
With the advent of machine learning (ML) and the broader field of artificial intelligence (AI), innovative solutions are emerging for detecting and managing invasive species (
weeds). Early studies, such as that by Turner et al. [
17], highlighted the potential of remote sensing data in combination with ML to identify specific plant species. These methods use spectral data to provide high accuracy rates in diverse landscapes [
17]. In recent years, Convolution Neural Networks (CNNs), a class of deep learning algorithms, have frequently been applied in plant species identification. Zhang et al. [
18] used CNNs to detect invasive plant species from aerial imagery, demonstrating their potential applicability to remote sensing-based image classification techniques. Several domain-specific studies have been conducted for identifying plants and plant-related diseases using AI, including CNN models. In the process, researchers have used a variety of AI-assisted ML techniques for the identification of different diseases and plant conditions [
19,
20,
21,
22]. Concerning SL, Arc-GIS-based specific models have been developed for identifying production sites to cultivate the crop with low to minimum resource input methodologies [
16,
23]. However, based on a thorough literature search, there has been no previous research conducted on developing an AI-based ML model for identifying weed from SL in field-based studies.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Field Image Acquisition, Preparation and Mobile App Development
The first step for the mobile application development process was obtaining smartphone images for different weeds and SL plants. A total of 5000 images (1000 images of SL, 4000 images for different weeds and plants) were selected to develop the smartphone application for SL identification. The images were taken using a Samsung Galaxy A54. For executing all the detection steps, starting from image acquisition through result dissemination, the smartphone application (SL-app) was developed using android studio software (Version: Flamingo) using the saved trained model. By training the detection algorithm with a large data set of SL images, a functional relationship was established, which was subsequently classified for the screening of the SL plants from weeds and other plants under field conditions. And, although the SL-app was developed using images taken by a Samsung Galaxy A54 phone, it is expected that performing this imaging task using other smartphones will show similar results due to the procedure of normalizing the image data.
2.2. Image Classification Model Selection
The present study used Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), a regularized type of feed-forward neural networks (similar to widely used backpropagation neural network (BPNN)) specifically is used for image classification-based studies. Randomized weights are provided to input and output neurons in BPNN making network learning may take much longer to achieve the best-fit correlation and vanishing gradients and exploding gradients situation may occur [
24] (Balas et al. 2020). , Therefore, in CNNS, these occurrences are prevented by using regularized weights over fewer connections [
24]. Therefore, CNNs are known as Shift Invariant or Space Invariant Artificial Neural Networks (SIANN) [
25] as in the network a designated group of neurons shares a fixed or regularized weights provided by users and it works better in image classification with close similarity to Self-Organizing Map (SOM) ANN image classification approach of a fixing window of pixels 3x3, 5x5, or nxn sizes but through a feed forward learning process. Given the complex nature of image data (
Figure 1), the choice of methodology greatly influences the effectiveness of such a model in our study. The CNN (SIANN) is based on a stepwise process of delineation of the model intricacies, emphasizing those involved at each stage of model development and showing the pipelines for classification.
2.3. Dataset Stratification
For any image classification-based study, data segmentation is the most fundamental principle. Recognizing that improperly segmented data can lead to overfitting or generalization issues, a two-way split was adopted, comprising training and validation datasets, with an 80:20 ratio [
21,
26] . While the training dataset serves as the primary source from which the model learns, the validation set is a tool for fine-tuning of the model to ensure it is neither over- nor under-fitting. The test set, kept separate, evaluates the model's performance in an 'unseen' scenario. To further systemize the training process, images within these sets were grouped by their respective classes, ensuring balanced representation and easy accessibility during model training.
2.4. Preprocessing Dynamics
Preprocessing digital images, consisting of a grid of pixel values at their core, is essential to ensure uniformity and to enhance training efficacy. To this end, Keras' ImageDataGenerator was used, which allowed augmentation of the data by introducing minor variations in our images, such as rotations, zooms, and shifts. Such augmentation prevents overfitting and exposes the model to a broader set of data scenarios. Along with augmentation, we undertook two standard preprocessing steps through, firstly, resizing all images to 150x150 pixels, eliminated variability in image dimensions, and second, normalizing pixel values, traditionally ranging from [0, 255] to [0, 1], for ensuring a more tractable data range to facilitate gradient descent optimization during model training.
2.5. CNN Architecture
Unlike traditional neural networks, CNNs excel in detecting image patterns, ranging from simple edges to complex features. Our model's inception layer was designed to process 150x150x3-sized tensors, indicative of the image's height, width, and RGB channels. The initial convolutional layer, equipped with 32 3x3 filters and the ReLU activation function, focused on elementary feature detection. Pooling layers, interspersed after convolutional layers, reduced spatial dimensions, condensing information, and aiding computational efficiency. As the network was delved into more deeply, the convolutional layers increased in complexity, with 64 and 128 filters, which honed in on intricate patterns within images. The architecture then transitioned from convolutional to dense layers via a flattening layer, which reshaped the 3D output tensor from the last pooling layer into an 1D vector. This vectorized output fed into a dense layer with 512 neurons, culminating in an output layer that used SoftMax activation to categorize the images.
2.6. Model Compilation and Training Dynamics
Once the CNN's architecture was solidified, the model's compilation phase commenced. The Adam optimizer was the optimizer of choice, since it dynamically adjusts the learning rate, a feature especially useful for deep learning tasks. Given the categorical nature of the present classification, the loss function employed was categorical cross-entropy. Also, accuracy, indicating the proportion of correctly classified images, was the primary metric throughout the training phase.
Iterative refinement was used for the training of the present model, which adjusted its internal parameters with each epoch, using a complete forward and backward pass of training examples, honing its prediction capabilities. This iterative process can be likened to repeatedly studying of a topic, through refining understanding with each pass (iteration). However, since, as with any study regimen, there is a risk of over-studying or 'memorizing', a validation set was used as a safeguard against the model 'memorizing' training data, i.e. overfitting. This separate dataset, providing a check, was included for ensuring that the model generalized well.
2.7. Model Variants
Beyond the baseline CNN model, the research ventured into several model variants. The first variant (CNN Model Variant 1) was accentuated with Batch Normalization with adjusted dropout. This technique, applied post-convolution, standardizes the outputs, stabilizing and accelerating training, and coupled with a 0.4 dropout rate, also introduced a regularizing effect. The second variant (CNN Model Variant 2) delved deeper, introducing an extra step, while, similar to the first, it deviated architecturally in its optimization technique. Here, the RMSprop optimizer, known for its adaptive nature, was implemented with a learning rate of 0.0001. Beyond these custom variants, the exploration also incorporated renowned architectures, like pre-trained models VGG16 and ResNet50, which were equipped with weights trained on the extensive ImageNet dataset and were appended with custom dense layers to fit the classification task.
Each model variant, including the pre-trained architectures, underwent rigorous training, governed by predefined parameters. Crucial to this process were early stopping callback functions, which halted training if the model ceased to improve, as well as learning rate adjustment, which dynamically tweaked the learning rate based on the model's performance.
2.8. Batch Normalization and Adjusted Dropout Method
Batch Normalization (Batch Norm) is a transformative technique in deep learning, designed to accelerate the training of deep networks and optimize their performance [
27] . It addresses the issue of internal covariate shift, where the distribution of network activations changes during training due to parameter adjustments. In practice, Batch Normalization computes the mean and variance for each feature in a mini batch, then normalizes the feature to have a mean of zero and unit variance. This normalized output is further scaled and shifted, using learnable parameters. When integrated into custom CNN models, Batch Normalization often results in faster convergence, allows for the use of higher learning rates, and makes the model less sensitive to initialization strategies [
28,
29,
30]. It also imparts a minor regularization effect, adding slight noise that can counteract overfitting. The Batch Normalization first computes the mini-batch's means (µ) and variance (σ2) scale and shifts the feature using two new parameters per feature, often called γ (scale) and β (shift) [
28,
30,
31]. These parameters are learned during training alongside the original model parameters, and the mathematical expression is provided in equation 1 for an input of m:
On the other hand, dropout, another regularization technique designed to combat overfitting, randomly deactivate a fraction of input units during training in each update cycle. For instance, with a dropout rate of 0.5, roughly half of the input units are "turned off" at each step. However, by adjusting this behavior during the inference phase, dropout is disabled, and all units are active, with weights scaled down proportionally to account for the more extensive unit activity. In CNNs, the concept of dropout is often adjusted for spatial structures. For instance, spatial dropout drops entire channels of feature maps, in this way to ensure consistent absences in the feature map.
In addition to the above, dropout after Batch Normalization is commonly advised in order to avoid unstable training dynamics. When used in image classification using CNNs, Batch Normalization and adjusted dropout techniques, like spatial dropout, often empower the network. This combination facilitates training deeper, more robust models that exhibit superior generalization on unseen data.
2.9. RMSprop and Adjusted Learning Rate method
The RMSprop, standing for Root Mean Square Propagation, is a sophisticated optimization technique tailored to facilitate and expedite the training process of neural networks, notably CNNs, which dominate the realm of image classification [
32,
33]. At its core, RMSprop aims to dynamically adjust each parameter's learning rate based on its gradients' historical magnitudes [
34](Yu et al., 2020). This method of RMSprop solves the common drawback of a static learning rate, which, if set too high, can cause unstable training with erratic oscillations, and, if too low, results in an agonizingly slow convergence [
35,
36].
In RMSprop, the moving average of the squared gradient, which is computed, subsequently informs the adjusted learning rate. A decay factor, β, plays a pivotal role in this latter calculation, in this way determining the balance between the influence of the past average and the present gradient. This emphasis on the recent history of gradients aids in navigating complex optimization landscapes, often characterized by deep CNNs with high dimensionality stemming from copious weights and biases and intricate non-linearities, is ushered in by activation functions [
37,
38,
39].
In addition to the above, RMSprop proved to be more resilient against the drawback of vanishing and exploding gradient issues that plague deep networks [
40] . However, RMSprop's standard formulation can be further augmented by introducing additional strategies to adjust the global learning rate (η). Methods like step, exponential, and plateau-based decay offer nuanced control, in this way to allow the model to adapt to plateaus or steep regions in the loss landscape. Despite modern deep learning, libraries like TensorFlow and PyTorch have simplified their application using RMSprops as a staple optimizer [
41,
42]. However, it is paramount to recognize the existence of other equally competent optimizers, such as Adam, which combines the strengths of RMSprop with the momentum principle [
30]. Ultimately, selecting an optimizer is not a one-size-fits-all decision, but rather a careful choice, often necessitating multiple iterations and experiments tailored to the unique nuances of the specific dataset and problem.
3. Results and Discussion
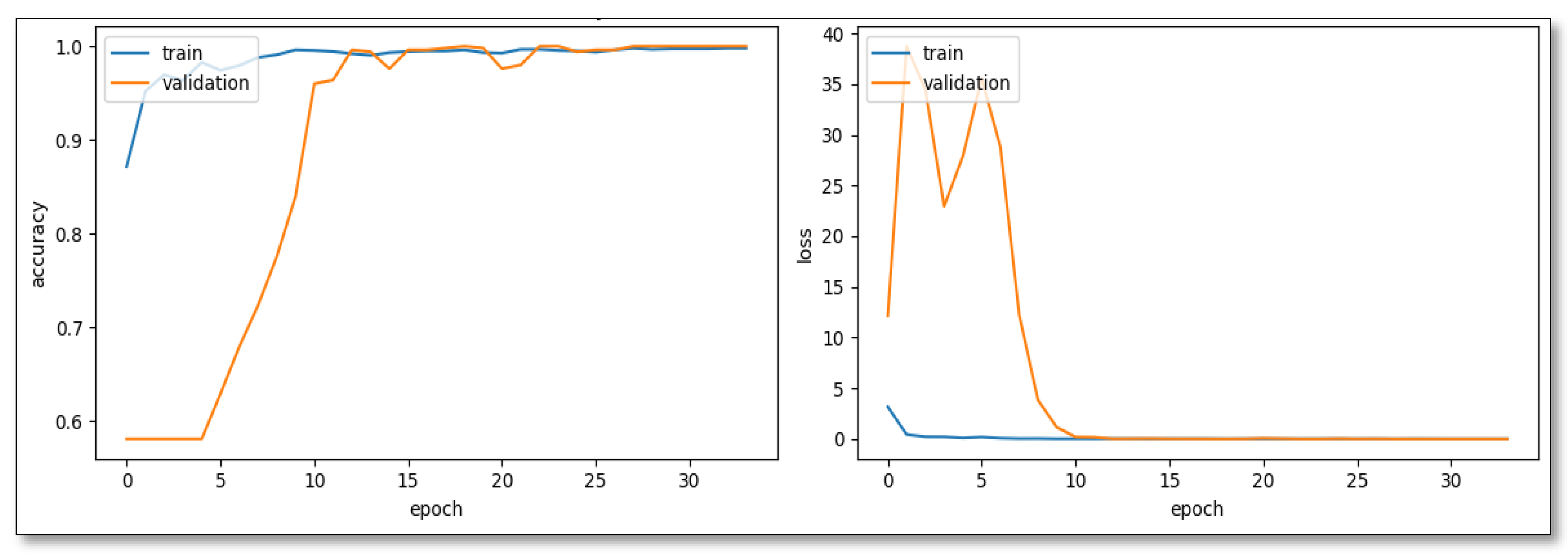
In developing the CNN model for distinguishing SL images from weed images, a quartet of architectures, namely CNN-Model Variant 1, CNN-Model Variant 2, VGG16, and ResNet50, presented a spectrum of capabilities and nuances. The CNN-Model Variant 1, with the combination of Batch Normalization and Adjusted Dropout, showcased an exemplary trajectory, scaling from an initial 87.15% training accuracy to a 99.6% validation accuracy by the 13th epoch (
Figure 2). Its resilience was evident in select epochs where validation accuracy peaked at 100%, indicating robustness and potential for superior generalization.
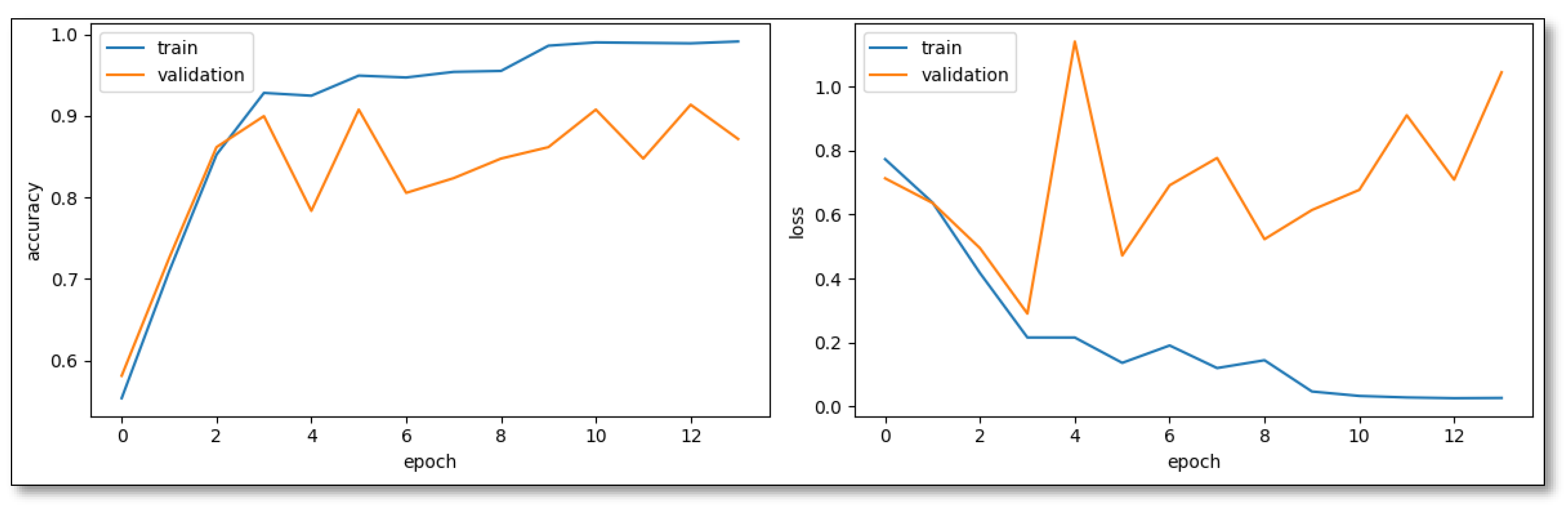
Contrastingly, CNN-Model Variant 2, driven by the RMSprop Optimizer and an adaptive learning rate, embarked on its learning pattern more steadily, but exhibited commendable growth dynamics. Notably, by the 11th epoch, this model logged a 90.78% validation accuracy, showing its rapid maturation towards development. However, the heightened validation loss hints at potential overfitting nuances particularly intrinsic to RMSprop's behavior in the classification context (
Figure 3).
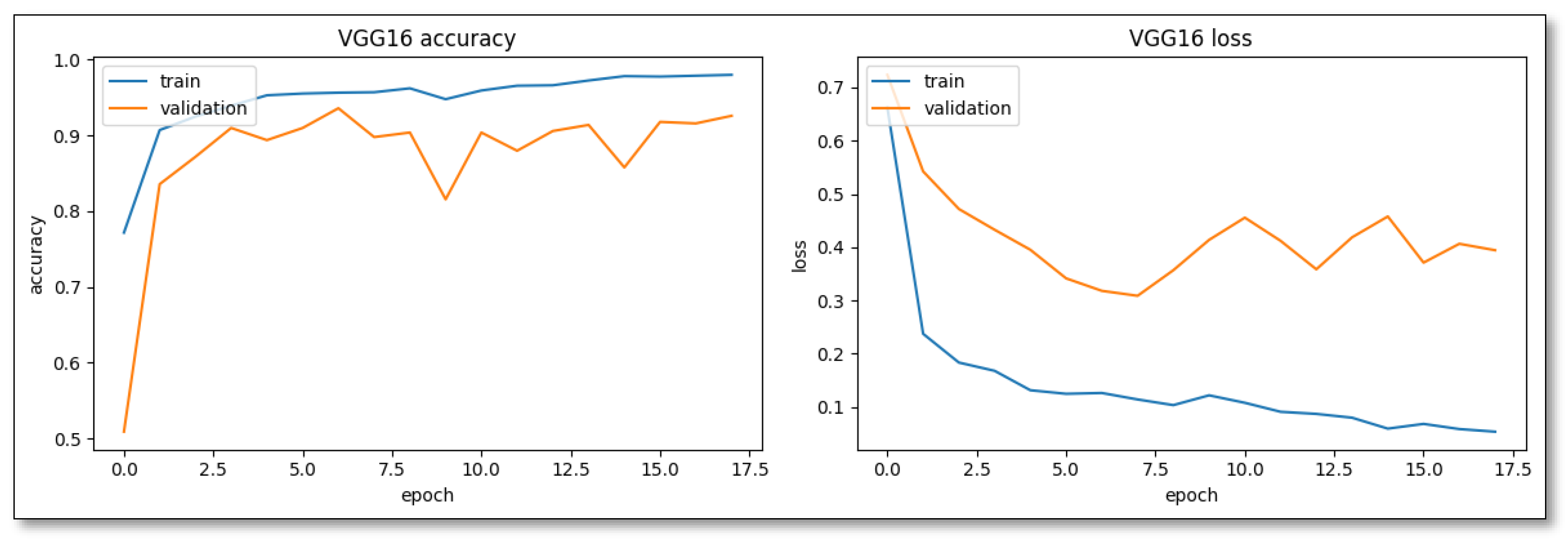
Compared with pre-trained established architectures, such as ResNet50 and VGG16 using transfer learning, VGG16 stood out for its easy convergence, indicating a training accuracy of 77.17% in its initial epochs (
Figure 4). However, its rapid assimilation is double-edged, particularly evident by the 11th epoch, suggesting potential overfitting issues.
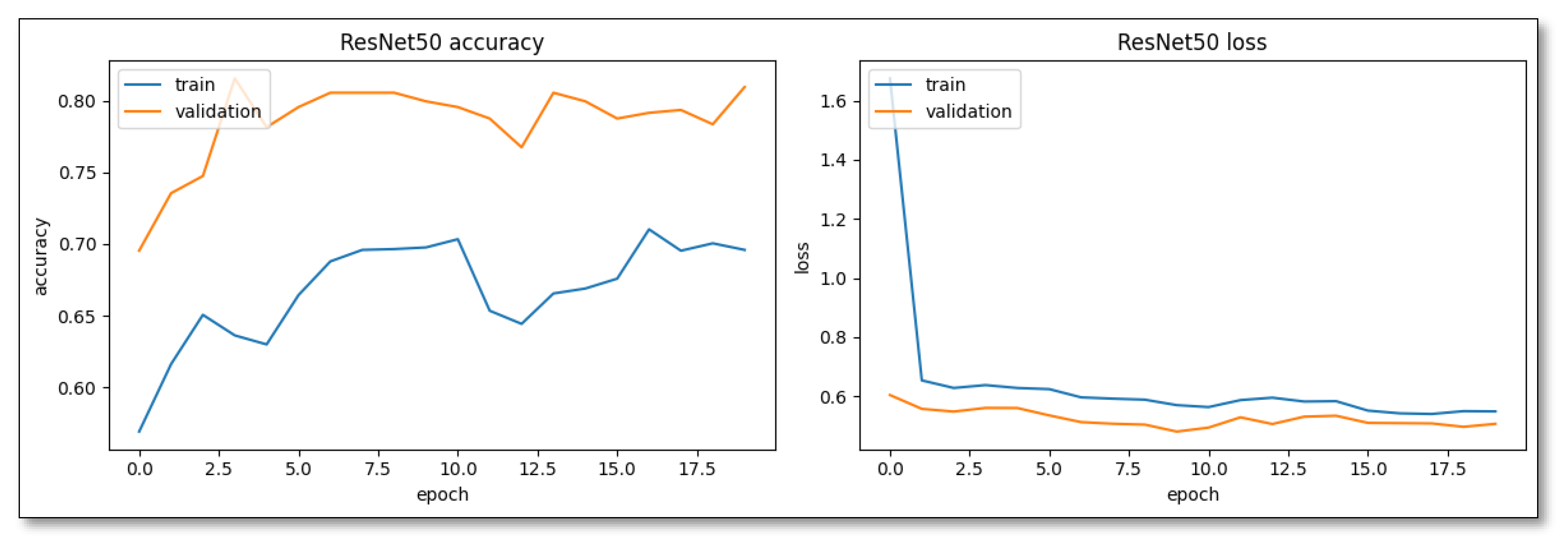
ResNet50, on the other hand, emphasizes steadiness. Despite a more deliberate initial pace, its learning pattern was marked by consistency, potentially leading to better generalization, as evidenced by the narrower disparity between its training and validation accuracies (
Figure 5).
The presented comparative classification reports in
Table 1 provide a detailed performance evaluation of four distinct neural network configurations: Custom CNN Variant 1, Custom CNN Variant 2, VGG16, and ResNet50.
Table 1 elaborates on the precision, recall, and F1-score information, offering a multifaceted perspective on each model's capabilities and limitations.
Starting with CNN Model Variant 1 (
Table 1), results from precision to recall and F1-score showed an impeccable 100% for both classes (SL and weeds), underlining its unparalleled ability to discern and accurately predict both categories in the dataset. Such a performance is rarely achieved and signifies a highly optimized model for this specific dataset, possibly implying meticulous tuning and a beneficial interaction of features like Batch Normalization and Adjusted Dropout methods. Conversely, the performance was notably balanced in the case of Custom Model Variant 2 (
Table 1). Achieving an overall 90% accuracy demonstrated a near-equal proficiency in recognizing and categorizing both classes, with metrics oscillating between 86% and 93%. Model variants developed using RMSprop with adjusted learning rates achieved a harmonious equilibrium between precision and recall, ensuring neither was sacrificed at the expense of the other.
The
VGG16 pre-trained model (
Table 1) mirrored the performance behavior of Custom Model Variant 2. Both precision and recall were clustered closely around the 90% mark for both the SL and weed classes. This ability of VGG16's to maintain this balance suggests its inherent strength in rapidly assimilating intrinsic patterns within datasets. However, given its reputation, it is intriguing to see that it equalizes it behavior, but does not outperform a custom variant CNN image-based classification model. Lastly,
the ResNet50 pre-trained model (
Table 1) showed some idiosyncrasies in its performance. With an overall accuracy of 80%, it is evident that there was a significant discrepancy in precision and recall metrics. For class 0 (SL), a lower recall of 61% juxtaposed against a precision of 87% implied that it was conservative in predicting SL, often missing out. However, for class 1 (Weed), its high recall of 93% suggested an aggressive prediction strategy. Nevertheless, a precision of 77% indicated occasional over-prediction, potentially because some of the images in the dataset might have had SL and weeds in the same image.
In conclusion, from the above insights, Custom CNN Variant 1 emerged as the zenith of performance, epitomizing the perfect blend of precision and recall. To an extent, custom CNN Variant 2 and VGG16 showed commendable, balanced performances, indicating that they stand as close contenders. However, ResNet50, with its inherent biases, and Custom CNN Variant 2, with its specific challenges, underscored the complexities and intricacies associated with deep learning model optimization and the ever-present need for iterative refinement.
4. Future studies
Utilizing technology, especially cutting-edge neural network models like the ones examined in our study, will become more essential as the agricultural sector deals with rising global food demand, shrinking arable land, and the unpredictable effects of climate change. For instance, Custom CNN Variant 1's unprecedented accuracy highlights the potential of such models to revolutionize precision agriculture. In consequence, the use of these models in conjunction with drones or satellite photography in real-time applications should be explored further in future studies to provide immediate, field-level insights regarding weed infestation, damage from pests, or nutrient insufficiency. This would support farmers in making prompt adjustments and maximizing resource use, reducing water, fertilizer, and pesticide wasting. The model would, for instance, be more broadly applicable if the dataset were expanded to cover a wider range of crops, different growth phases, and various biotic and abiotic stress variables. The discriminative capacity of the model may be further improved by multi-spectral and hyperspectral imaging, allowing it to recognize early-stage pest infestations or sub-surface anomalies that are not visible to the naked eye. In this way, a future can be foreseen where farms are more productive, as well as sustainably so, to support a helpful relationship between farmers, technology, and the environment.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Aftab Siddique; Data curation, Kyla Cook and Yasmin Holt; Formal analysis, Aftab Siddique; Funding acquisition, Thomas Terrill; Investigation, Aftab Siddique; Methodology, Aftab Siddique and Sudhanshu Panda; Validation, Thomas Terrill; Writing – original draft, Aftab Siddique; Writing – review & editing, Sudhanshu Panda, ERIC MORGAN, Jan Van Wyk and Thomas Terrill..
Funding
This research was funded by USDA-National Institute of Food and Agriculture (Capacity Building Grant) award number 2022-38821-37299. The University of North Georgia—Gainesville Campus Institute for Environmental Spatial Analysis’ undergraduate cohort—contributed to acquiring and evaluating satellite and aerial imagery using unmanned aerial vehicles.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Terrill, T.; Mosjidis, J.; Moore, D.; Shaik, S.; Miller, J.; Burke, J.; Muir, J.; Wolfe, R. Effect of pelleting on efficacy of sericea lespedeza hay as a natural dewormer in goats. Veter- Parasitol. 2007, 146, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoveland, C.S.; Windham, W.R.; Boggs, D.L.; Durham, R.G.; Calvert, G.V.; Newsome, J.F. Sericea lespedeza production in Georgia. Res Bull-Georgia Agric Exp Stations 1990, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrill, T.H.; Miller, J.E.; Burke, J.M.; Mosjidis, J.A.; Kaplan, R.M. Experiences with integrated concepts for the control of Haemonchus contortus in sheep and goats in the United States. Veter- Parasitol. 2012, 186, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kommuru, D.; Barker, T.; Desai, S.; Burke, J.; Ramsay, A.; Mueller-Harvey, I.; Miller, J.; Mosjidis, J.; Kamisetti, N.; Terrill, T. Use of pelleted sericea lespedeza (Lespedeza cuneata) for natural control of coccidia and gastrointestinal nematodes in weaned goats. Veter- Parasitol. 2014, 204, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mechineni, A.; Kommuru, D.; Gujja, S.; Mosjidis, J.; Miller, J.; Burke, J.; Ramsay, A.; Mueller-Harvey, I.; Kannan, G.; Lee, J.; et al. Effect of fall-grazed sericea lespedeza (Lespedeza cuneata) on gastrointestinal nematode infections of growing goats. Veter- Parasitol. 2014, 204, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, B.R.; Pinchak, W.E.; Merkel, R.; Walker, S.; Tomita, G.; Anderson, R.C. Comparative antimicrobial activity of tannin extracts from perennial plants on mastitis pathogens. Sci Res Essays. 2008, 3, 066–073. [Google Scholar]
- Naumann, H.D.; Muir, J.P.; Lambert, B.D.; Tedeschi, L.O.; Kothmann, M.M. Condensed tannins in the ruminant environment: a perspective on biological activity. J Agric Sci. 2013, 1, 8–20. [Google Scholar]
- Puchala, R.; Animut, G.; Patra, A.; Detweiler, G.; Wells, J.; Varel, V.; Sahlu, T.; Goetsch, A. Methane emissions by goats consuming Sericea lespedeza at different feeding frequencies. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2012, 175, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchu, P.; Hazard, T.; Lee, J.H.; Terrill, T.H.; Kouakou, B.; Kannan, G. High-condensed tannin diet and transportation stress in goats: Effects on physiological responses, gut microbial counts and meat quality. Animals 2021, 11, 2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batchu, P.; Terrill, T.H.; Kouakou, B.; Estrada-Reyes, Z.M.; Kannan, G. Plasma metabolomic profiles as affected by diet and stress in Spanish goats. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botha, H. The use of sericea lespedeza (Smart Man's Lucerne) in South Africa. In: Proceedings of the What Works With Worms 2015 International Congress on Sustainable Parasite Management; 2015 May 25-26; Pretoria, South Africa.
- Buchanan, G.A.; Burns, E.R. Weed control in sericea lespedeza. Circular # 165. Auburn (AL): Agricultural Experiment Station, Auburn University; 1969.
- Wang, C.; Zhou, B.; Palm, H.L. Detecting invasive sericea lespedeza (Lespedeza cuneata) in Mid-Missouri pastureland using hyperspectral imagery. Environ. Manag. 2008, 41, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gholizadeh, H.; Friedman, M.S.; McMillan, N.A.; Hammond, W.M.; Hassani, K.; Sams, A.V.; Charles, M.D.; Garrett, D.R.; Joshi, O.; Hamilton, R.G.; et al. Mapping invasive alien species in grassland ecosystems using airborne imaging spectroscopy and remotely observable vegetation functional traits. Remote. Sens. Environ. 2022, 271, 112887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakotoarivony, M.N.A.; Gholizadeh, H.; Hammond, W.M.; Hassani, K.; Joshi, O.; Hamilton, R.G.; Fuhlendorf, S.D.; Trowbridge, A.M.; Adams, H.D. Detecting the invasive Lespedeza cuneata in grasslands using commercial small satellite imagery. Int. J. Remote. Sens. 2023, 44, 6802–6824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, S.; Terrill, T.; Mahapatra, A.; Morgan, E.; Siddique, A.; A Pech-Cervantes, A.; Van Wyk, J. Geospatial engineering and technology supported climate-sensitive Sericea lespedeza fodder production suitability analysis modeling in the southeastern United States. In: 2023 IST-Africa Conference (IST-Africa); IEEE; 2023. p. 1-12.
- Turner, W.; Rondinini, C.; Pettorelli, N.; Mora, B.; Leidner, A.; Szantoi, Z.; Buchanan, G.; Dech, S.; Dwyer, J.; Herold, M.; et al. Free and open-access satellite data are key to biodiversity conservation. Biol. Conserv. 2015, 182, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, L.; Yan, C.; Ji, X.; Dai, Q. Adaptive Residual Networks for High-Quality Image Restoration. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2018, 27, 3150–3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohanty, S.P.; Hughes, D.P.; Salathé, M. Using deep learning for image-based plant disease detection. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wang, X. Early recognition of tomato gray leaf spot disease based on MobileNetv2-YOLOv3 model. Plant Methods 2020, 16, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, H.; Li, X.; Liang, J.; Peng, Y.; Zhang, C. DeepFish: Accurate underwater live fish recognition with a deep architecture. Neurocomputing 2016, 187, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.H.; Nguyen, T.N.; Ngo, B.V. A VGG-19 model with transfer learning and image segmentation for classification of tomato leaf disease. AgriEngineering. 2022, 4, 871–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, S.S.; Terrill, T.H.; Mahapatra, A.K.; Morgan, E.R.; Siddique, A.; Pech-Cervantes, A.A.; van Wyk, J.A. Optimizing Sericea Lespedeza fodder production in the southeastern US: A climate-informed geospatial engineering approach. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balas, V.E.; Kumar, R.; Srivastava, R. (Eds.) Recent trends and advances in artificial intelligence and internet of things; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Itoh, K.; Tanida, J.; Ichioka, Y. Parallel distributed processing model with local space-invariant interconnections and its optical architecture. Appl. Opt. 1990, 29, 4790–4797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piechaud, N.; Hunt, C.; Culverhouse, P.F.; Foster, N.L.; Howell, K.L. Automated identification of benthic epifauna with computer vision. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2019, 615, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioffe, S.; Szegedy, C. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In: International conference on machine learning; pmlr; 2015. p. 448-456.
- Obla, S.; Gong, X.; Aloufi, A.; Hu, P.; Takabi, D. Effective activation functions for homomorphic evaluation of deep neural networks. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 153098–153112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Qu, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, H.; Luo, B.; Xu, W.; Guo, S.; Li, R. A comprehensive survey on training acceleration for large machine learning models in IoT. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 9, 939–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Chang, C.C.; Jamshidi, M. Bridge damage detection using a single-stage detector and field inspection images. arXiv arXiv:1812.10590. 2018.
- Wu, Y.; He, K. Group normalization. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV); 2018. p. 3-19.
- Agarwal, S.; Terrail, J.O.D.; Jurie, F. Recent advances in object detection in the age of deep convolutional neural networks. arXiv arXiv:1809.03193. 2018.
- Goundar, N.N. Improved deep learning model based on integrated convolutional neural networks and transfer learning for shoeprint image classification. Master’s Thesis, Auckland University of Technology, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, C.; Qi, X.; Ma, H.; He, X.; Wang, C.; Zhao, Y. LLR: Learning learning rates by LSTM for training neural networks. Neurocomputing 2020, 394, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Velazquez, M.; Chen, W.-J.; Li, X.; McMillan, A.B. and construction of deep learning networks in medical imaging. IEEE Trans. Radiat. Plasma Med Sci. 2020, 5, 137–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Sun, G.; Mao, J. Aerodynamic surrogate model based on deep long short-term memory network: An application on high-lift device control. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part G: J. Aerosp. Eng. 2021, 236, 1081–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waheed, A.; Goyal, M.; Gupta, D.; Khanna, A.; Hassanien, A.E.; Pandey, H.M. An optimized dense convolutional neural network model for disease recognition and classification in corn leaf. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 175, 105456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaqub, M.; Feng, J.; Zia, M.S.; Arshid, K.; Jia, K.; Rehman, Z.U.; Mehmood, A. State-of-the-art CNN optimizer for brain tumor segmentation in magnetic resonance images. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, V.; Joshi, R.C.; Dutta, M.K. Deep neural network for multi-class classification of medicinal plant leaves. Expert Syst. 2022, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krohn J, Beyleveld G, Bassens A. Deep Learning Illustrated. Addison-Wesley Professional; 2019.
- Ott, J.; Pritchard, M.; Best, N.; Linstead, E.; Curcic, M.; Baldi, P. A Fortran-Keras deep learning bridge for scientific computing. Sci. Program. 2020, 2020, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, D. AdaXod: a new adaptive and momental bound algorithm for training deep neural networks. J. Supercomput. 2023, 79, 17691–17715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).