Submitted:
11 April 2024
Posted:
15 April 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
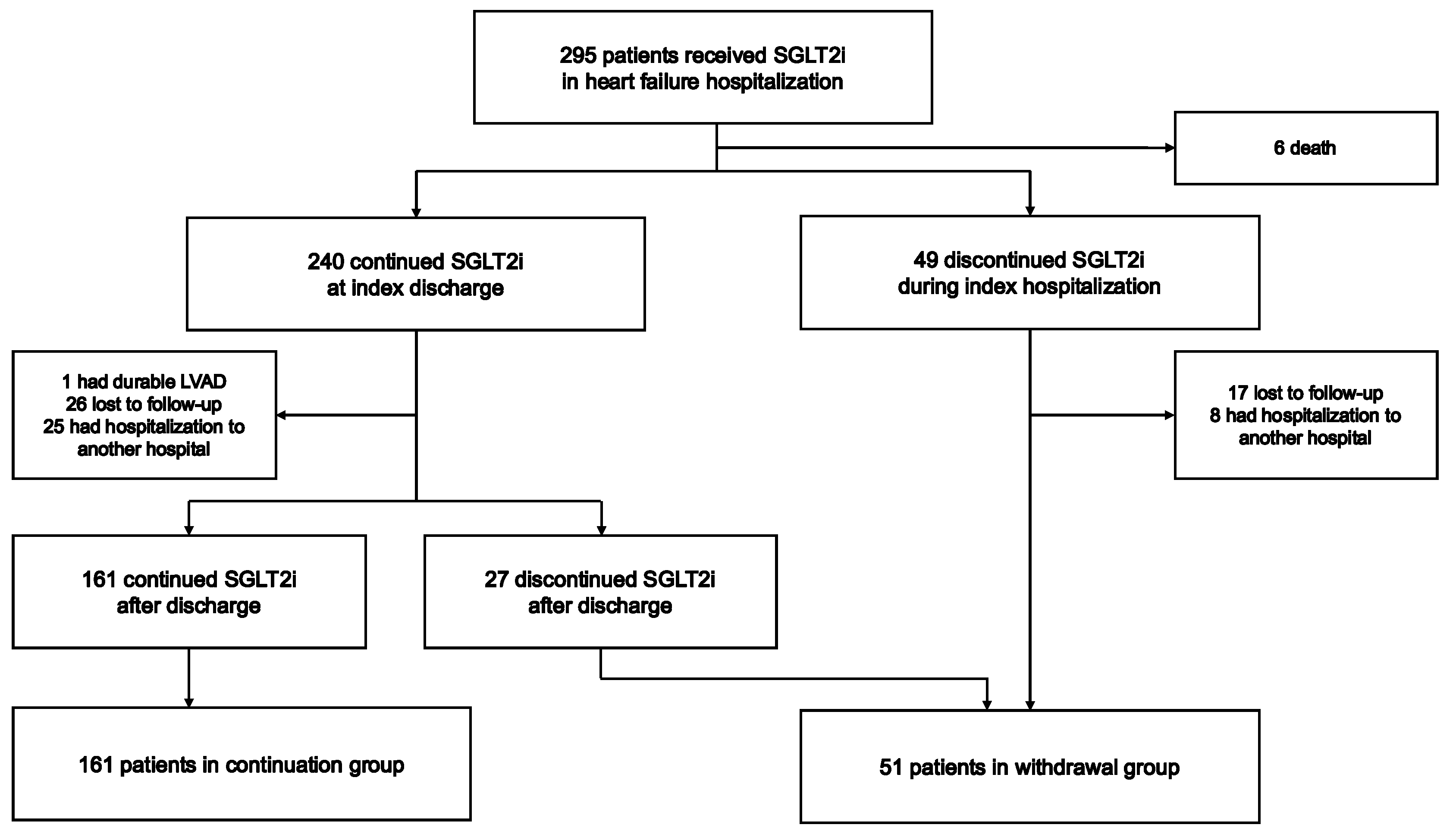
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Follow-Up and Patient Characteristics
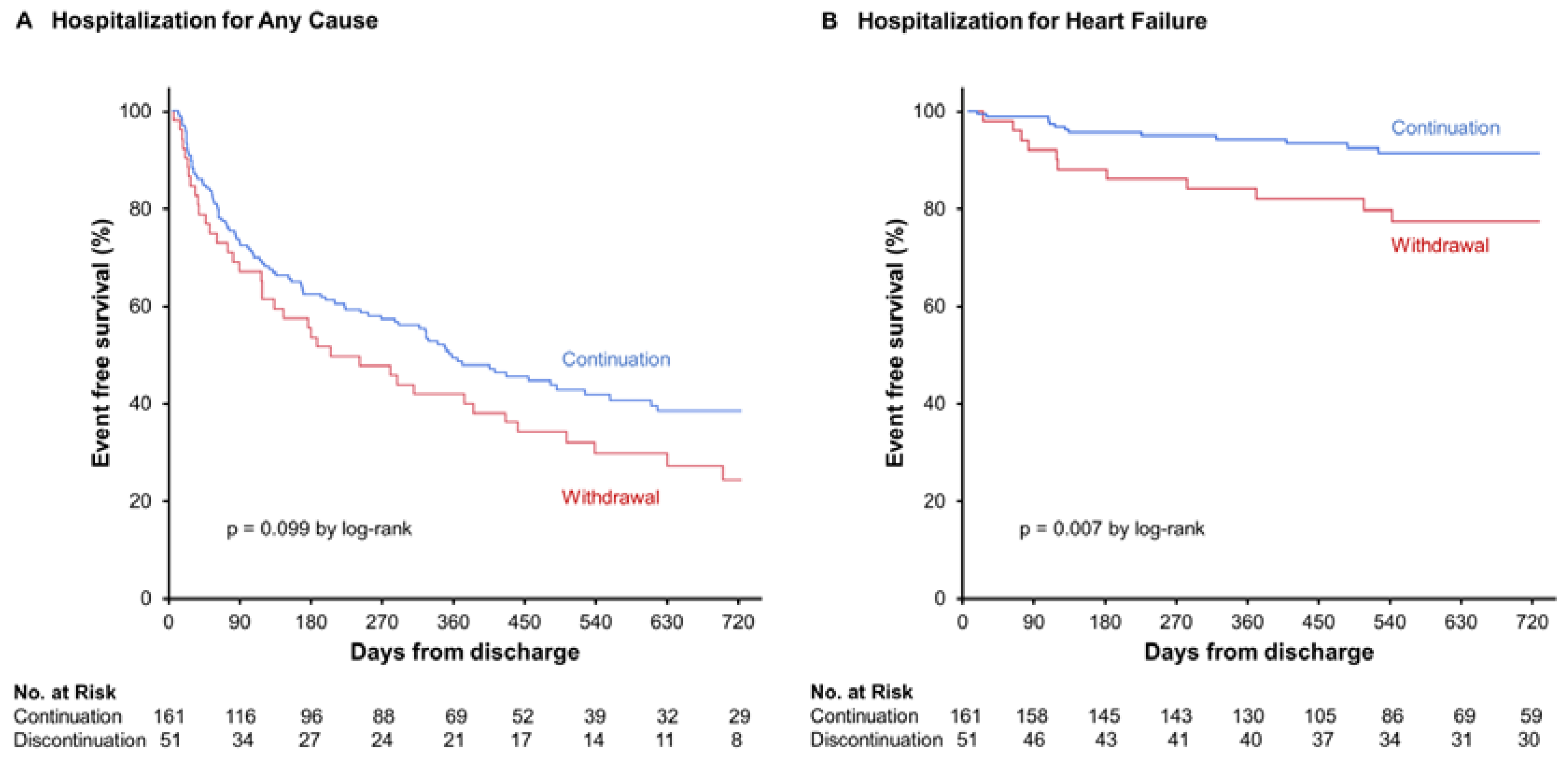
3.2. Primary Clinical Assessments
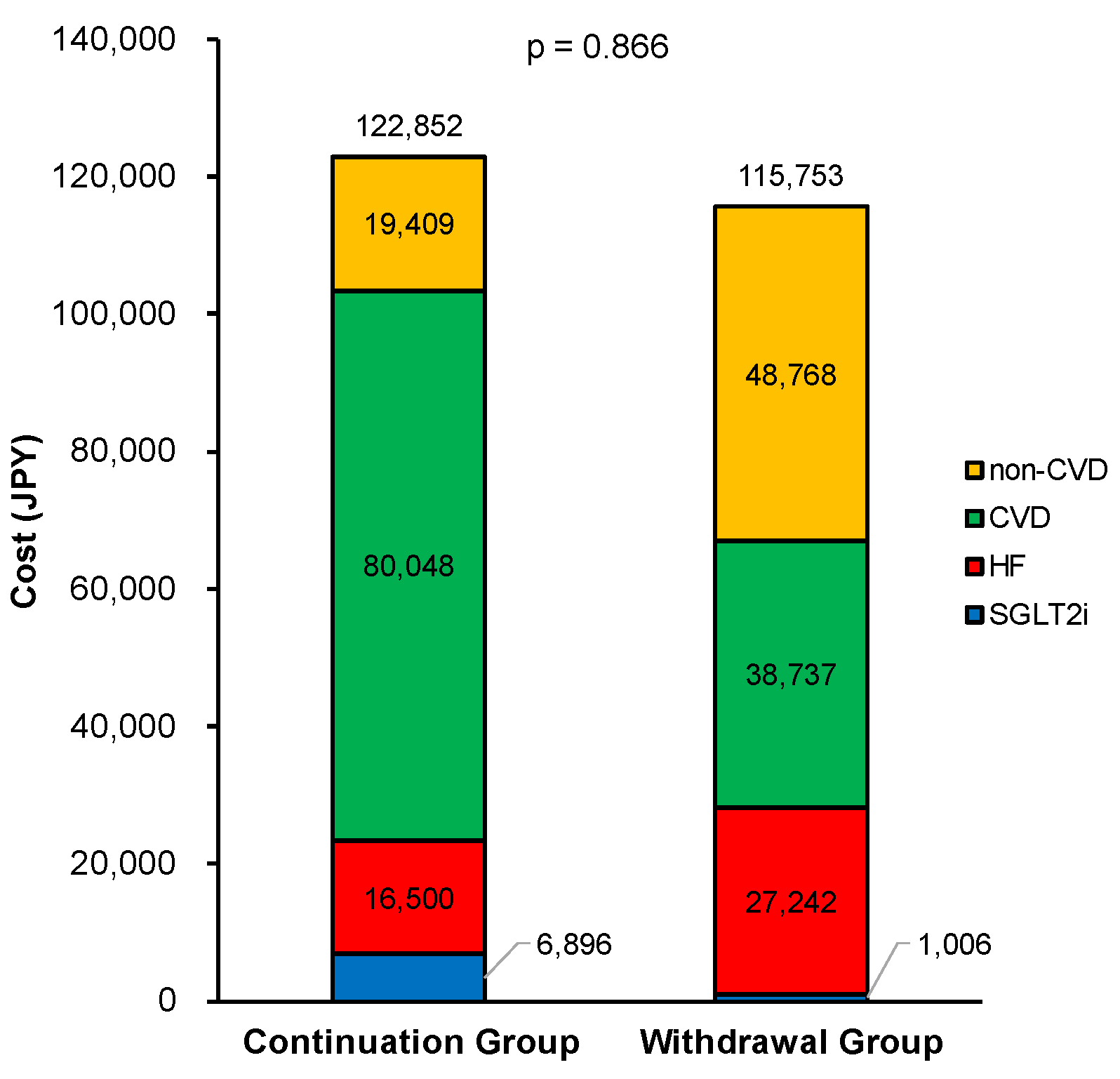
3.3. Secondary Clinical Assessments
4. Discussion
4.1. Clinical Outcomes
4.2. Medical Costs
4.3. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tsao, C. W.; Aday, A. W.; Almarzooq, Z. I.; Anderson, C. A. M.; Arora, P.; Avery, C. L.; Baker-Smith, C. M.; Beaton, A. Z.; Boehme, A. K.; Buxton, A. E.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2023 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2023, 147, e93–e621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMurray, J. J. V.; Solomon, S. D.; Inzucchi, S. E.; Køber, L.; Kosiborod, M. N.; Martinez, F. A.; Ponikowski, P.; Sabatine, M. S.; Anand, I. S.; Bělohlávek, J.; et al. Dapagliflozin in Patients with Heart Failure and Reduced Ejection Fraction. N Engl J Med 2019, 381, 1995–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Packer, M.; Anker, S. D.; Butler, J.; Filippatos, G.; Pocock, S. J.; Carson, P.; Januzzi, J.; Verma, S.; Tsutsui, H.; Brueckmann, M.; et al. Cardiovascular and Renal Outcomes with Empagliflozin in Heart Failure. N Engl J Med 2020, 383, 1413–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anker, S. D.; Butler, J.; Filippatos, G.; Ferreira, J. P.; Bocchi, E.; Böhm, M.; Brunner-La Rocca, H. P.; Choi, D. J.; Chopra, V.; Chuquiure-Valenzuela, E.; et al. Empagliflozin in Heart Failure with a Preserved Ejection Fraction. N Engl J Med 2021. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, S. D.; McMurray, J. J. V.; Claggett, B.; de Boer, R. A.; DeMets, D.; Hernandez, A. F.; Inzucchi, S. E.; Kosiborod, M. N.; Lam, C. S. P.; Martinez, F.; et al. Dapagliflozin in Heart Failure with Mildly Reduced or Preserved Ejection Fraction. N Engl J Med 2022, 387, 1089–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Packer, M.; Butler, J.; Zeller, C.; Pocock, S. J.; Brueckmann, M.; Ferreira, J. P.; Filippatos, G.; Usman, M. S.; Zannad, F.; Anker, S. D. Blinded Withdrawal of Long-Term Randomized Treatment With Empagliflozin or Placebo in Patients With Heart Failure. Circulation 2023, 148, 1011–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heerspink, H. J. L.; Stefánsson, B. V.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Chertow, G. M.; Greene, T.; Hou, F. F.; Mann, J. F. E.; McMurray, J. J. V.; Lindberg, M.; Rossing, P.; et al. Dapagliflozin in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. N Engl J Med 2020, 383, 1436–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrington, W. G.; Staplin, N.; Wanner, C.; Green, J. B.; Hauske, S. J.; Emberson, J. R.; Preiss, D.; Judge, P.; Mayne, K. J.; Ng, S. Y. A.; et al. Empagliflozin in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. N Engl J Med 2023, 388, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McEwan, P.; Darlington, O.; McMurray, J. J. V.; Jhund, P. S.; Docherty, K. F.; Böhm, M.; Petrie, M. C.; Bergenheim, K.; Qin, L. Cost-effectiveness of dapagliflozin as a treatment for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: a multinational health-economic analysis of DAPA-HF. Eur J Heart Fail 2020, 22, 2147–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallinen, T.; Kivelä, S.; Soini, E.; Harjola, V. P.; Pesonen, M. Cost-Effectiveness of Empagliflozin in Combination with Standard Care versus Standard Care Only in the Treatment of Heart Failure Patients in Finland. Clinicoecon Outcomes Res 2023, 15, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, L. P.; Isaza, N.; Hernandez, I.; Lewis, G. D.; Ho, J. E.; Fonarow, G. C.; Kazi, D. S.; Bellows, B. K. Cost-effectiveness of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction. JAMA Cardiol 2023, 8, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, C. T.; Yang, C. T.; Toh, H. S.; Chang, W. T.; Chang, H. Y.; Kuo, F. H.; Lee, M. C.; Hua, Y. M.; Tang, H. J.; Strong, C.; et al. Cost-effectiveness evaluation of add-on dapagliflozin for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction from perspective of healthcare systems in Asia-Pacific region. Cardiovasc Diabetol 2021, 20, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, C. T.; Yang, C. T.; Kuo, F. H.; Lee, M. C.; Chang, W. T.; Tang, H. J.; Hua, Y. M.; Chang, H. Y.; Chen, Z. C.; Strong, C.; et al. Cost-Effectiveness Evaluation of Add-on Empagliflozin in Patients With Heart Failure and a Reduced Ejection Fraction From the Healthcare System’s Perspective in the Asia-Pacific Region. Front Cardiovasc Med 2021, 8, 750381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagaito, M.; Imamura, T.; Ushijima, R.; Nakamura, M.; Kinugawa, K. Predictors and Outcomes of SGLT2 Inhibitor Discontinuation in a Real-World Population after Hospitalization for Heart Failure. Biomedicines 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, K.; Cho, D. S.; Kim, H.; Kwon, B.; Yoon, Y.; Park, C.; Kim, E. S.; Youn, J. C.; Park, S. K. Systematic Review of the Economic Evaluation of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors Used as Treatment in Patients with Heart Failure. In Clin Drug Investig, Vol. 43; © 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Switzerland AG., 2023; pp 463-474.
- Liu, J.; Liu, D.; Gong, X.; Wei, A.; You, R. Cost-effectiveness of empagliflozin for the treatment of heart failure: a systematic review. In Front Pharmacol, Vol. 14; Copyright © 2023 Liu, Liu, Gong, Wei and You., 2023; p 1186579.
- Wu, M.; Qin, S.; Wang, L.; Tan, C.; Peng, Y.; Zeng, X.; Luo, X.; Yi, L.; Wan, X. Economic Evaluation of Dapagliflozin in the Treatment of Patients With Heart Failure: A Systematic Review. In Front Pharmacol, Vol. 13; Copyright © 2022 Wu, Qin, Wang, Tan, Peng, Zeng, Luo, Yi and Wan., 2022; p 860109.
- Suzuki, Y.; Kaneko, H.; Okada, A.; Itoh, H.; Matsuoka, S.; Fujiu, K.; Michihata, N.; Jo, T.; Takeda, N.; Morita, H.; et al. Comparison of cardiovascular outcomes between SGLT2 inhibitors in diabetes mellitus. Cardiovasc Diabetol 2022, 21, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reifsnider, O. S.; Kansal, A. R.; Gandhi, P. K.; Cragin, L.; Brand, S. B.; Pfarr, E.; Fahrbach, K.; Ustyugova, A. Cost-effectiveness of empagliflozin versus canagliflozin, dapagliflozin, or standard of care in patients with type 2 diabetes and established cardiovascular disease. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Total (n = 212) |
Continuation (n = 161) |
Withdrawal (n = 51) |
P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 72 (66-81) | 72 (63-79) | 76 (71-84) | 0.004* |
| Male, n (%) | 141 (67) | 114 (71) | 27 (53) | 0.019* |
| Body weight, kg | 56.6 (49.9-67.5) | 57.3 (50.9-69.3) | 54.0 (44.1-64.1) | 0.021* |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 22.2 (19.8-24.8) | 22.6 (20.2-25.3) | 21.7 (18.8-23.6) | 0.026* |
| Systolic blood pressure, mmHg | 107 (96-118) | 107 (95-119) | 106 (97-116) | 0.990 |
| Heart rate, beats per minutes | 71 (63-78) | 70 (62-78) | 71 (64-83) | 0.772 |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 147 (69) | 106 (66) | 41 (80) | 0.050* |
| Ischemic etiology, n (%) | 86 (41) | 62 (39) | 24 (47) | 0.279 |
| Atrial fibrillation, n (%) | 61 (29) | 43 (26) | 18 (35) | 0.238 |
| Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator, n (%) | 22 (10) | 20 (12) | 2 (4) | 0.083 |
| Cardio resynchronization therapy, n (%) | 15 (7) | 12 (8) | 3 (6) | 0.703 |
| New York Heart Association class Ⅲ-Ⅳ, n (%) | 57 (27) | 40 (25) | 17 (33) | 0.234 |
| Left ventricular ejection fraction, % | 43 (33-55) | 44 (34-56) | 42 (31-52) | 0.294 |
| Value of <40% (HFrEF), n (%) | 84 (39) | 59 (37) | 25 (49) | 0.115 |
| HbA1c, % | 6.6 (6.1-7.4) | 6.6 (6.1-7.3) | 6.7 (6.4-7.9) | 0.115 |
| Hemoglobin, g/dL | 12.7 (11.2-14.2) | 12.8 (11.5-14.3) | 12.0 (10.8-13.8) | 0.078 |
| Serum albumin, g/dL | 3.6 (3.3-3.9) | 3.6 (3.4-3.9) | 3.5 (3.1-3.7) | 0.006* |
| Serum sodium, mEq/L | 138 (136-140) | 138 (137-140) | 137 (134-139) | <0.001* |
| Serum potassium, mEq/L | 4.4 (4.1-4.6) | 4.4 (4.1-4.6) | 4.4 (3.9-4.8) | 0.612 |
| eGFR, mL/minute/1.73m2 | 51.1 (38.2-64.2) | 52.8 (40.3-64.6) | 49.2 (32.6-60.3) | 0.109 |
| Uric acid, mg/dL | 5.7 (4.7-6.9) | 5.5 (4.6-6.9) | 5.9 (5.1-7.2) | 0.060 |
| Plasma BNP, pg/mL | 142 (69-302) | 132 (64-266) | 182 (95-353) | 0.022* |
| Heart failure therapies | ||||
| Beta-blockers, n (%) | 184 (87) | 137 (85) | 47 (92) | 0.194 |
| ACEI/ARB/ARNI, n (%) | 200 (94) | 153 (95) | 47 (92) | 0.439 |
| Loop diuretics, n (%) | 139 (66) | 99 (62) | 40 (78) | <0.001* |
| Dose of loop diuretics, mg/day | 10 (0-20) | 10 (0-20) | 20 (10-20) | 0.223 |
| MRA, n (%) | 145 (68) | 112 (70) | 33 (65) | 0.515 |
| Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors | ||||
| Canagliflozin, n (%) | 40 (19) | 24 (15) | 16 (31) | 0.009* |
| Dapagliflozin, n (%) | 116 (55) | 95 (59) | 21 (41) | 0.026* |
| Empagliflozin, n (%) | 56 (26) | 42 (26) | 14 (28) | 0.847 |
| eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; HFrEF, heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (ejection fraction <40%); HbA1c, glycated hemoglobin; BNP, b-type natriuretic peptide; ARB, angiotensin receptor blockers; ARNI, angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitors; MRA, mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists. *p <0.050. | ||||
| All patients (n = 212) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Univariable analysis | Multivariable analysis | |||||
| Variables | Hazard ratio | 95% CI | p value | Hazard ratio | 95% CI | p value |
| Age, years | 1.01 | 0.99, 1.02 | 0.394 | |||
| Male, yes | 0.75 | 0.53, 1.07 | 0.112 | |||
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 0.99 | 0.94, 1.03 | 0.510 | |||
| Systolic blood pressure, mmHg | 1.00 | 0.99, 1.01 | 0.744 | |||
| Heart rate, bpm | 1.01 | 0.99, 1.02 | 0.551 | |||
| Ischemic etiology, yes | 0.99 | 0.70, 1.41 | 0.973 | |||
| Atrial fibrillation, yes | 1.54 | 1.07, 2.21 | 0.022* | 1.44 | 1.07, 2.23 | 0.020* |
| NYHA class Ⅲ-Ⅳ, n (%) | 1.29 | 0.88, 1.88 | 0.188 | |||
| HFrEF, yes | 0.69 | 0.48, 0.99 | 0.041* | 0.66 | 0.46, 0.95 | 0.023* |
| Diabetes mellitus, yes | 1.36 | 0.92, 2.01 | 0.123 | |||
| Hemoglobin, g/dL | 0.95 | 0.88, 1.03 | 0.239 | |||
| Serum albumin, g/dL | 1.08 | 0.73, 1.58 | 0.713 | |||
| Serum sodium, mEq/L | 1.00 | 0.95, 1.06 | 0.981 | |||
| Serum potassium, mEq/L | 0.82 | 0.59, 1.15 | 0.238 | |||
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73m2 | 0.99 | 0.98, 1.00 | 0.047* | 0.99 | 0.98, 1.00 | 0.044* |
| Uric acid, mg/dL | 0.98 | 0.88, 1.08 | 0.635 | |||
| ln BNP | 1.08 | 0.91, 1.28 | 0.379 | |||
| Beta-blockers, yes | 1.03 | 0.62, 1.72 | 0.905 | |||
| ACEI/ARB/ARNI, yes | 0.70 | 0.37, 1.34 | 0.280 | |||
| Loop diuretics, yes | 1.12 | 0.78, 1.62 | 0.531 | |||
| MRA, yes | 0.81 | 0.56, 1.16 | 0.241 | |||
| Termination of SGLT2i, yes | 1.37 | 0.94, 2.00 | 0.100 | |||
| NYHA, New York Heart Association; HFrEF, heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (ejection fraction <40%); eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; BNP, b-type natriuretic peptide; ACEI, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors; ARB, angiotensin receptor blockers; ARNI, angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitors; MRA, mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists. *p <0.050. | ||||||
| All patients (n = 212) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Univariable analysis | Multivariable analysis | |||||
| Variables | β | 95% CI | p value | β | 95% CI | p value |
| Age, years | -0.03 | -0.06, 0.04 | 0.681 | |||
| Male, yes | -0.10 | -1.07, 0.15 | 0.137 | |||
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | -0.08 | -0.23, 0.06 | 0.251 | |||
| Systolic blood pressure, mmHg | -0.08 | -0.05, 0.02 | 0.280 | |||
| Heart rate, bpm | -0.05 | -0.07, 0.03 | 0.530 | |||
| Ischemic etiology, yes | 0.10 | -0.14, 1.03 | 0.136 | |||
| Atrial fibrillation, yes | -0.03 | 0.79, 0.49 | 0.640 | |||
| NYHA class Ⅲ-Ⅳ, n (%) | 0.16 | 0.11, 1.40 | 0.022* | 0.15 | 0.06, 1.34 | 0.032* |
| HFrEF, yes | 0.06 | -0.32, 0.86 | 0.369 | |||
| Diabetes mellitus, yes | -0.08 | -0.99, 0.25 | 0.244 | |||
| Hemoglobin, g/dL | -0.04 | -0.36, 0.20 | 0.568 | |||
| Serum albumin, g/dL | 0.02 | -1.08, 1.51 | 0.743 | |||
| Serum sodium, mEq/L | -0.04 | -0.23, 0.12 | 0.559 | |||
| Serum potassium, mEq/L | 0.08 | -0.46, 1.89 | 0.230 | |||
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73m2 | -0.10 | -0.05, 0.01 | 0.158 | |||
| Uric acid, mg/dL | 0.01 | -0.31, 0.34 | 0.923 | |||
| ln BNP | 0.08 | -0.22, 0.90 | 0.235 | |||
| Beta-blockers, yes | 0.04 | -0.63, 1.07 | 0.606 | |||
| ACEI/ARB/ARNI, yes | 0.01 | -1.18, 1.31 | 0.920 | |||
| Loop diuretics, yes | 0.04 | -0.41, 0.80 | 0.524 | |||
| MRA, yes | 0.03 | -0.51, 0.73 | 0.722 | |||
| Termination of SGLT2i, yes | 0.15 | 1.40, 0.06 | 0.032* | 0.14 | 0.01, 1.34 | 0.048* |
| NYHA, New York Heart Association; HFrEF, heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (ejection fraction <40%); eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; BNP, b-type natriuretic peptide; ACEI, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors; ARB, angiotensin receptor blockers; ARNI, angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitors; MRA, mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists. *p <0.050. | ||||||
| All patients (n = 212) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Univariable analysis | Multivariable analysis | |||||
| Variables | Hazard ratio | 95% CI | p value | Hazard ratio | 95% CI | p value |
| Age, years | 1.01 | 0.97, 1.05 | 0.704 | |||
| Male, yes | 0.93 | 0.40, 2.20 | 0.873 | |||
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 0.98 | 0.87, 1.08 | 0.646 | |||
| Systolic blood pressure, mmHg | 0.98 | 0.96, 1.01 | 0.230 | |||
| Heart rate, bpm | 0.97 | 0.93, 1.01 | 0.115 | |||
| Ischemic etiology, yes | 1.15 | 0.51, 2.63 | 0.733 | |||
| Atrial fibrillation, yes | 2.34 | 1.03, 5.31 | 0.041* | 1.75 | 0.76, 4.03 | 0.193 |
| NYHA class Ⅲ-Ⅳ, n (%) | 1.33 | 0.55, 3.25 | 0.526 | |||
| HFrEF, yes | 1.11 | 0.49, 2.53 | 0.809 | |||
| Diabetes mellitus, yes | 2.12 | 0.72, 6.24 | 0.171 | |||
| Hemoglobin, g/dL | 0.88 | 0.71, 1.08 | 0.239 | |||
| Serum albumin, g/dL | 0.87 | 0.35, 2.17 | 0.767 | |||
| Serum sodium, mEq/L | 0.97 | 0.87, 1.10 | 0.641 | |||
| Serum potassium, mEq/L | 0.75 | 0.36, 1.70 | 0.477 | |||
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73m2 | 0.96 | 0.93, 0.99 | 0.003* | 0.97 | 0.94, 0.99 | 0.019* |
| Uric acid, mg/dL | 1.04 | 0.81, 1.30 | 0.751 | |||
| ln BNP | 1.31 | 0.87, 2.08 | 0.222 | |||
| Beta-blockers, yes | 1.02 | 0.30, 3.45 | 0.970 | |||
| ACEI/ARB/ARNI, yes | 0.61 | 0.14, 2.60 | 0.502 | |||
| Loop diuretics, yes | 3.61 | 1.07, 12.16 | 0.038* | 1.95 | 0.54, 7.04 | 0.308 |
| MRA, yes | 1.06 | 0.43, 2.56 | 0.907 | |||
| Termination of SGLT2i, yes | 2.93 | 1.29, 6.65 | 0.010* | 2.38 | 1.04, 5.45 | 0.041* |
| NYHA, New York Heart Association; HFrEF, heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (ejection fraction <40%); eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; BNP, b-type natriuretic peptide; ACEI, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors; ARB, angiotensin receptor blockers; ARNI, angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitors; MRA, mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists. *p <0.050. | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





