1. Introduction
To the best of the available knowledge, no studies have explored the potential benefits of a plant-based diet (PBD) for patients with COVID-19, particularly for high-risk elderly individuals with comorbidities. Recent studies suggest that a PBD may help reduce the occurrence and severity of COVID-19 in the general population. This may potentially lead to lower mortality rates [
1,
2,
3]. However, these studies have utilized mainly retrospective questionnaires to survey a diverse population, and their ability to establish causal relationships between PBD and COVID-19 outcomes has been questioned [
4]. Additionally, concerns have been raised regarding the potential lack of vitamins and essential minerals in PBD, which may not be suitable for COVID-19 patients [
5].
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), older individuals aged 65 or above are most likely to require hospitalization. This correlation between age and health conditions suggests that the severity of COVID-19 is directly linked to the affected individuals' age and pre-existing health issues [
6,
7]. Elderly patients have a higher case fatality rate, estimated at 10-20%, due to their aging bodies and increased likelihood of having pre-existing health conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, autoimmune disease, and respiratory disorders [
8]. These underlying conditions can exacerbate COVID-19 symptoms, leading to a higher mortality risk. Intensive care unit (ICU) admission is a critical factor in the prognosis of coronavirus patients, particularly when mechanical ventilation is employed, as this significantly elevates the mortality rate [
9]. At the outset of the pandemic, a shortage of ICU facilities and human resources led to the inability to admit numerous critical coronavirus patients, ultimately resulting in numerous fatalities.
In the Asian region, Indonesia ranks second in COVID-19 deaths [
10] and has the highest mortality rate [
11]. It's alarming that most Indonesians consume an unhealthy diet (omnivorous) like the American standard diet. 25% of the Indonesian population is categorized as obese, and more than 90% of the patients residing in big cities lack vitamin D. It is important to note that an unhealthy lifestyle and poor dietary habits can lead to chronic inflammation [
12,
13], leaving one's body vulnerable to severe inflammation caused by COVID-19. Therefore, lifestyle change by adopting healthy habits is crucial to reduce the risk of developing a severe form of the disease or succumbing to it.
Table 1.
COVID-19 Cases and Death: comparison of Indonesia with other countries [
10,
11].
Table 1.
COVID-19 Cases and Death: comparison of Indonesia with other countries [
10,
11].
| COUNTRY |
TOTAL COVID CASES |
TOTAL COVID DEATHS |
MORTALITY RATE |
POPULATION |
| USA |
110.486.719 |
1.191.840 |
1% |
334.805.269 |
| India |
45.021.383 |
533.412 (1st in Asia) |
1.2% |
1.406.631.776 |
| Japan |
33.803.572 |
74.694 (5th in Asia) |
0.2% |
125.584.838 |
| Australia |
11.768.389 |
23.910 |
0.2% |
26.068.792 |
| Indonesia |
6.823.536 |
161.954 (2nd in Asia) |
2.4% |
279.134.505 |
| Malaysia |
5.244.578 |
37.315 (8th in Asia) |
0.7% |
33.181.072 |
| Singapore |
2.945.715 |
1.933 |
0.07% |
5.943.546 |
| China |
503.302 |
5.272 |
1% |
1.448.471.400 |
| Bhutan |
62.697 |
21 |
0.03% |
787.941 |
Three years before our COVID-19 treatment program, we introduced lifestyle modifications to our cardiology patients at Bethsaida Hospital in Indonesia, including a whole food PBD, regular physical activity, stress management, restorative sleep, smoking cessation, and supplement consumption. The outcomes of these interventions were astonishingly satisfactory. Patients suffering from hypertension achieved remission without resorting to medication. Those with hyperlipidemia were able to reach their optimal lipid levels. Many patients have their kidney function improved, and many patients with type 2 diabetes or glucose intolerance were able to manage their sugar levels without the need for insulin or extensive medication. Moreover, coronary obstructions in numerous cardiac patients regressed, and there was a low occurrence of in-stent restenosis (ISR). These results align with previous research that has demonstrated the effectiveness of PBD interventions in treating patients with chronic inflammatory diseases [
14,
15,
16]. We believe our previous PBD's experience in managing chronic inflammatory conditions will also be beneficial in managing COVID-19.
Our therapeutic approach commenced by exploring the potential benefits of PBDs in treating coronavirus patients. We identified several mechanisms by which PBDs could be advantageous for COVID-19 patients, including increasing nitric oxide availability, altering the microbiota, rectifying endothelial dysfunction, suppressing inflammation, safeguarding against oxidative stress, bolstering mitochondria, extending telomeres, and limiting caloric intake [
17]. The severe symptoms, multi-organ damage, and fatal consequences of SARS-CoV-2 are attributed to the acute, severe inflammation triggered by the virus [
18,
19,
20,
21,
22,
23]. Consequently, we selected PBD foods that possess properties to suppress inflammation, combat oxidative stress, modulate the immune system, are anti-thrombotic, and can eliminate viruses. The quantity of patients' foods should be determined precisely, and the food processing method should be carefully considered: raw vegetables instead of cooked ones. We also included supplements that can enhance the immune system, reduce inflammation, increase antioxidants, have antithrombotic properties, and support the antiviral properties of PBDs to overcome coronavirus. These various supplements, including vitamins, minerals, and natural substances, were selected from previous viral epidemics studies [
17]. By integrating PBD intervention with strategic supplementation, we were confident that the severity and fatality rates of COVID-19 could be reduced to the lowest possible levels.
Undertaking an intervention study on the disease with uncertain treatment and vaccination at the outset of the COVID-19 pandemic, given its high mortality rate among the elderly, would have been impossible unless the practitioners were confident that their interventions would protect them from severe illness and death upon contracting the virus.
2. Case Description
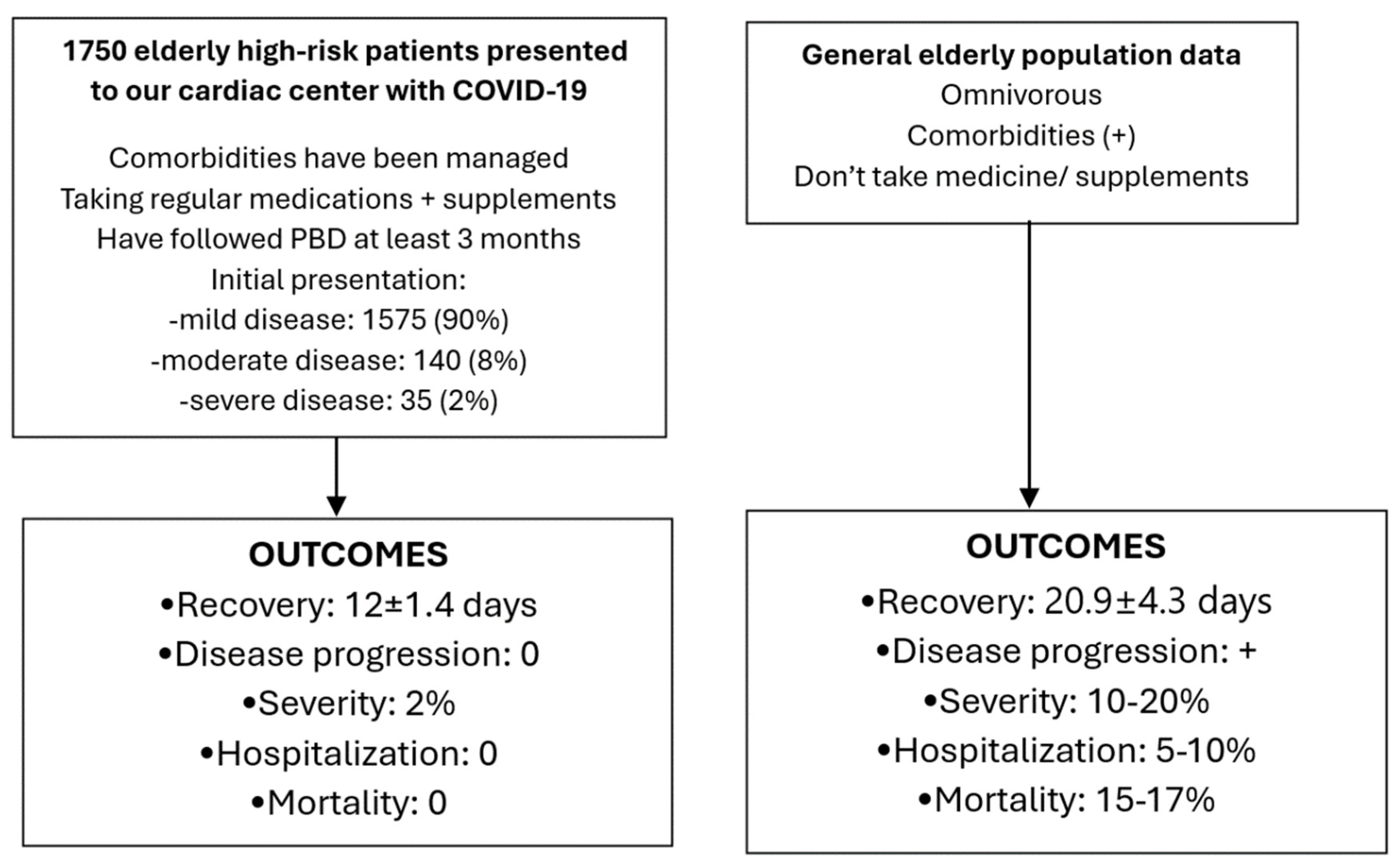
1,750 elderly individuals who adhered to our lifestyle program were diagnosed with COVID-19. These patients were assessed using clinical symptoms and signs, blood tests, X-ray/CT scans, and PCR tests, which yielded positive results [
24,
25]. They were classified into three groups: 1. Patients with mild illness exhibiting COVID-19 symptoms, such as fever, cough, sore throat, malaise, headache, muscle pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, anosmia, or dysgeusia, but without shortness of breath or abnormal chest imaging. 2. Patients with moderate illness presenting with clinical symptoms and radiologic evidence of lower respiratory tract disease and oxygen saturation or SpO
2 ≥ 94% on room air. 3. Patients with severe illness displaying SpO
2 ≤ 94% but still able to increase to ≥ 90% with oxygen 2-6 liters per minute. Patients who were unable to consume PBDs and supplementation orally due to severe shortness of breath or had lung infiltrates exceeding 50% of the total lung volume were referred to hospitals for further care.
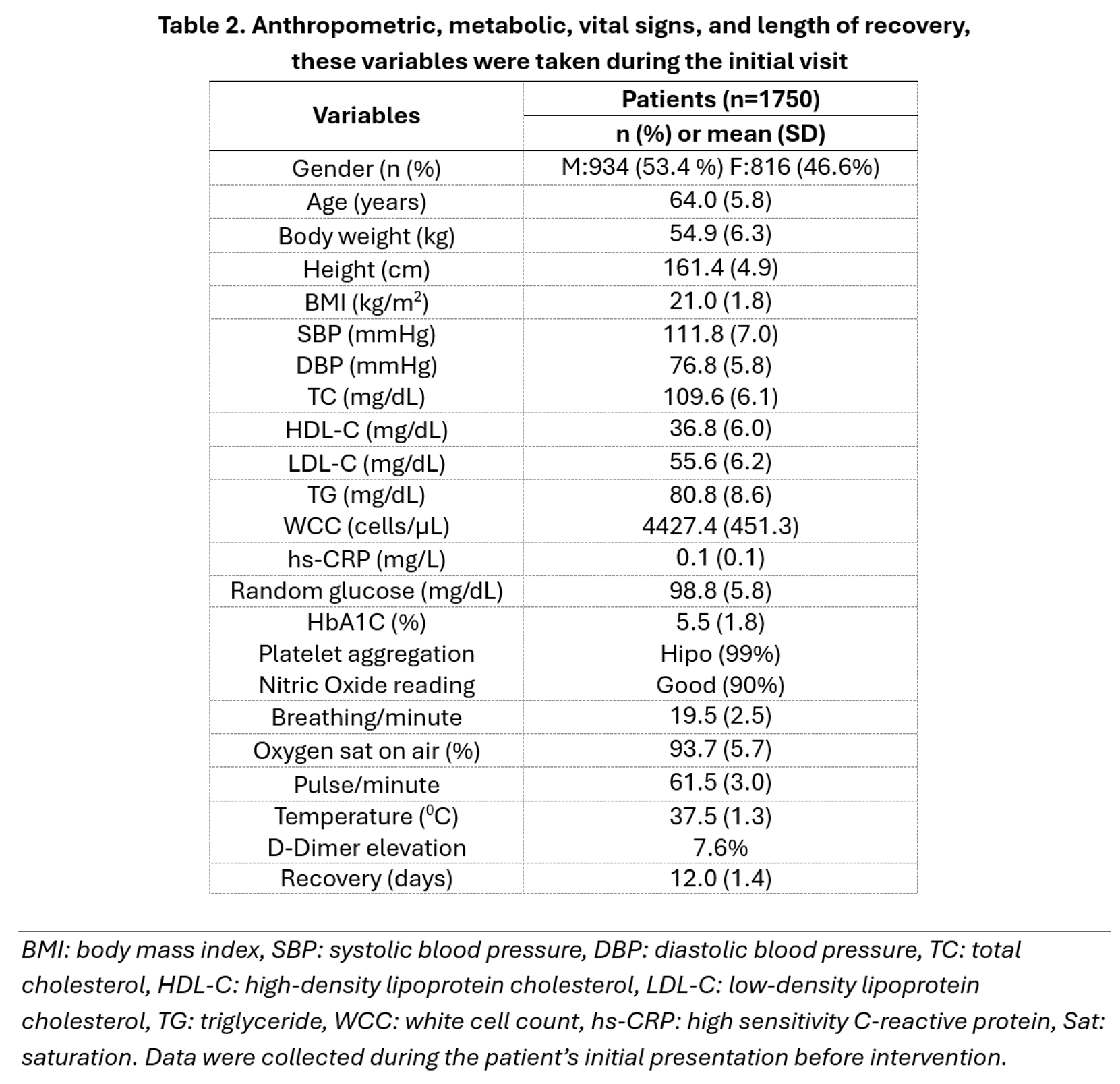
The treatment program was undertaken between April 2020 and June 2023. The majority of our patients were over the age of 60 and had comorbidities, including coronary artery disease, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and glucose intolerance or type 2 diabetes mellitus. However, these patients had their health conditions optimized through coronary interventions and medications administered by us in the cardiology clinic at Bethsaida Hospital, as evidenced by the results obtained during their initial presentation to our clinic with COVID-19, as shown in Table 2.
1575 (90%) of the patients were classified as having mild disease, while 140 (8%) were classified as having moderate disease, and 35 (2%) were considered to have severe disease. Patients with severe disease required only two to four liters of oxygen per minute to maintain their oxygen saturation above 90%, which allowed them to be managed at home.
2.1. Dietary Intervention
All patients will be mandated to adhere to a stringently structured PBD as part of our therapy plan. For their morning meal, they will be served a one-liter blender containing 400 grams of raw vegetables such as spinach, arugula, celery, parsley, or any vegetables that are high in fiber, nitrates, carotenoids, and phytochemicals. This will be mixed with 400 grams of fresh fruits like pomegranates, berries, grapes, or fruits that are rich in antioxidants and phytonutrients. Additionally, two tablespoons of flaxseeds or chia seeds will be mixed into the blender. For lunch, patients will consume 500-750 ml of porridge made from legumes, including 50g of soybeans, 100g of green beans, and 50g of barley, mixed with two dates for flavor. For dinner, they will enjoy a vibrant fruit salad consisting of apples, kiwis, oranges, mangos, and berries paired with 100-200 grams of whole grains mixed with 200-300 ml of soy or almond milk. Patients can reasonably modify their food if the vegetables and fruits are raw and contain the recommended nutrients. We will provide all patients with educational reading and visual materials and closely monitor them via video or phone calls. Patients are advised to incorporate Indonesian spices like ginger, turmeric, clove, cinnamon, lemongrass, and fermented foods into their diet, which are rich in antioxidants and act as anti-inflammatories. Fruits and vegetables should be purchased from supermarkets that offer high-quality products. Drinking coffee and green tea are also encouraged. As most COVID-19 patients experience a loss of appetite, food restriction is no longer necessary.
2.2. Supplementation Intervention
Patients must adhere to their prescribed medications and supplements as instructed during regular clinic visits. However, they are prohibited from taking medications prescribed by other doctors for the treatment of COVID-19, such as antibiotics, antivirals, and antiparasitics (e.g., Azithromycin, Doxycycline, Cephalosporin, Lopinavir/Ritonavir, Oseltamivir, Favipiravir, Chloroquine, and Ivermectin). All patients receive only symptomatic treatments, such as oxygen, antipyretics for high temperature, anti-cough, anti-nausea, anti-diarrheal medications, painkillers, anxiolytics, and sleeping tablets. Patients who experience complications from COVID-19 will be treated in accordance with either the international guidelines or the consensus of experts in the relevant field. For instance, patients with high D-dimer levels will receive anticoagulation therapy with non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants or NOACs.
Our patients were administered a comprehensive range of supplements, including Vitamin C, Vitamin D, B3/Nicotinamide Riboside Chloride (Truniagen), Zinc, Copper, Selenium, CoQ10, Astaxanthin, Quercetin, Curcumin, and Taurine. The daily dosage of Vitamin C was set at 1 gram, while the dosage of Vitamin D was adjusted between 5000 IU and 20000 IU based on each patient's laboratory level of Vitamin D, targeted at a range of 60-80 ng/mL. The patients were also administered two doses of 300 mg of Truniagen. Moreover, they received daily supplements of 60 mg of Zinc, 3 mg of Copper, 150 mcg of Selenium, 300 mg of CoQ10, 12 mg of Astaxanthin, 2.4 grams of Quercetin, 100 mg of Curcumin, and 1 gram of Taurine [
17]. All supplements our clinic provides were standardized to ensure consistency in quantity and quality.
2.3. Comparison with General Population Length of Recovery, Severity, and Mortality
Recovery from COVID-19 has been defined in multiple ways. In this study, we have defined recovery based on clinical symptoms, regardless of the PCR test result. The literature suggests that the recovery time for the elderly population typically ranges between 20.9±4.3 days. To assess the severity and mortality of our patients, we will use a general Indonesian population with a comparable age demographic, prevalent comorbidities, and unhealthy dietary habits (omnivorous) as a comparison. The comparison group data was derived from the literature on the general Indonesian population who contracted the virus between March 2020 and June 30, 2023. The severity rate for elderly individuals with comorbidities, estimated in the literature, is approximately 10-20%, with a rate of hospitalization of 5-10%. It is essential to note that these figures are based on available data and may vary depending on the population being studied. The mortality rate for this group was as follows: for those aged 40-49, it was 2-3%; for those aged 50-59, it was 5-8%; for those aged 60-69, it was 15-17%; and for those above 70 years of age, it was 18-20% [
26,
27,
28,
29,
30,
31].
3. Discussions
The majority of our elderly patients exhibited exceptional metabolic parameters and mild disease because they consistently attended our cardiology center and adhered to a healthy lifestyle, which included consuming whole-food PBDs and taking their prescribed medications and supplements. These patients' metabolic parameters (BMI, blood pressure, cholesterol, triglyceride, glucose, WCC, hs-CRP, platelet function, and NO reading [
32]) were excellent, which indicates that advanced age was the sole determining factor for their susceptibility to severe illness and death from COVID-19.
Almost all of the study participants demonstrated a reduction in platelet aggregation, attributed to their use of antiplatelet drugs, such as acetylsalicylic acid, clopidogrel, and ticagrelor, routinely given after coronary interventions. They had taken their antiplatelet medications before contracting COVID-19. As individuals age, their respiratory rate increases. This is particularly relevant when dealing with geriatric patients suffering from respiratory illness. Moreover, the oxygen saturation of the geriatric population tends to decrease with age [
33,
34]. So, as healthcare providers, we should consider these factors. The heart rate of our patients was significantly lower than the general population, which can be attributed to the fact that most patients are cardiac patients who typically received medication such as beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, or Ivabradine. Temperature in the elderly is generally lower than in younger individuals, which is also an important consideration when assessing the severity of respiratory infections in the geriatric population [
35]. Additionally, it is essential to recognize that elderly individuals may exhibit low temperatures even during sepsis [
36]. Therefore, when evaluating clinical symptoms and signs in the geriatric population, it is crucial to consider other relevant clinical parameters. It has been observed that D-dimer levels ≥ 1 µg/ml are associated with worse outcomes in COVID-19 infection [
37]. However, all of our participants had much lower levels of D-dimer, possibly because we measured it early in the development of their disease. Our approach was to administer oral anticoagulation to all patients with elevated D-dimer levels, provided there were no contraindications. The anticoagulation dosage was varied based on the patient's laboratory results and the level of their D-Dimer.
On average, our patients recovered in 12±1.4 days, significantly shorter than the 20.9±4.3 days observed in the general population. As illustrated in
Figure 1, ninety percent of the participants had mild diseases, eight percent had moderate diseases, and only two percent had severe diseases. Patients with severe diseases had stable respiratory status, requiring only two to four liters of oxygen per minute to maintain their oxygen saturation levels above ninety percent. The severity of our participants who had followed healthy lifestyles and had their metabolic parameters optimized was only 2%, which is significantly lower than the general population's rate, particularly among individuals aged 60-65, where the incidence ranges from 10% to 20% [
26,
27,
28,
29,
30,
31]. It is important to note that none of our participants progressed to the sores stage of the disease. No hospitalization was observed throughout the entire study period, in contrast to the general population's 5-10% hospitalization rate. In stark contrast to the general population of Indonesia, which has a fatality rate of 15-17%, our study demonstrated a zero-fatality rate [
26,
27,
28,
29,
30,
31]. Thus, our research findings confirm that PBDs and supplementation interventions are effective for high-risk elderly individuals with multiple comorbidities.
Our report has shown that the positive outcomes, such as quicker recovery times, lower severity, lack of hospitalization, and zero fatalities, may be attributed to the quality, selection, and amount of food provided, as well as the method of preparation (raw vegetables instead of cooked vegetables), compared to previous studies [
1,
2,
3]. Additionally, we have addressed concerns about providing a PBD to COVID-19 patients regarding the scarcity of vitamins and minerals [
4,
5]. Recent research has supported our approach to provide supplements to COVID-19 patients. Supplements, including Vitamin C, Vitamin D, Vitamin B3/NAD+, zinc, copper, selenium, and anti-inflammatory natural products such as astaxanthin, curcumin, quercetin, CoQ10, and taurine, have been shown to be beneficial for COVID-19 patients [
17]. To the best of our knowledge, our case report was unique because it involved the administration of supplements, which has not been included in any previous PBD studies on COVID-19. Our initial hypothesis that the supplements would enhance the anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, immune regulatory, antithrombotic, and anti-viral properties of the PBD also explains the exceptional results of the study. The administration of antiplatelet medication to participants in our study group was another important aspect of our report, which could enhance the antithrombotic effect of PBD [
38,
39] and possibly help prevent the development of thrombosis in COVID-19 patients. Additionally, we were among the innovators in employing non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants (NOACs) for COVID-19 treatment, providing these medications even during the initial stages of the disease, when D-Dimer levels were only slightly elevated (with adjusted dose). Postmortem examinations have revealed that a substantial proportion of COVID-19 fatalities displayed thromboembolism, further underscoring the crucial role that these medications play in managing the disease [
40,
41].
Acknowledging the significant bond between physicians and patients demonstrated in our study is essential. This relationship is characterized by medical professionals who are accessible to patients by phone to address their concerns and alleviate their anxiety, particularly during the peak of the COVID-19 pandemic when many doctors have taken leave. This connection involves providing quality care and support to patients all the time during their illness. The provision of quality care and support is crucial because negative emotions such as bad mood, resentment, anxiety, and lack of sleep can lead to severe inflammation and cytokine storms, which can worsen a patient's prognosis [
42,
43].
During times of crisis, panic can hinder a practitioner’s effectiveness. Unfortunately, the COVID-19 pandemic led to widespread panic, causing physicians to prescribe medications such as antivirals, antibiotics, and antiparasitics without evidence-based support [
24,
25], which can harm patients by damaging their microbiota [
17] and exacerbating their condition. Therefore, our program discontinued all unproven treatments provided to our participants by other doctors. Panic among healthcare professionals can negatively impact the emotional state of patients and worsen their illness. Studies have shown that patients' conditions can deteriorate during hospitalization due to inadequate management, a lack of emotional support, and the provision of an unhealthy omnivorous diet in hospitals.
The principle of "first, do no harm" was upheld in this study. Unfortunately, many COVID-19 patients from the upper class spent a considerable amount of money on unproven treatments, and despite their efforts, many still succumbed to death. In contrast, our methods, consisting of diets and supplements, have prevented unnecessary hospitalizations, saved numerous lives, and resulted in substantial cost savings for many patients. Therefore, safe and affordable interventions, such as dietary changes and supplementation, should be considered before resorting to vaccinations or new antiviral medications. We implemented the intervention long before the availability of the COVID-19 vaccine, and over half of our patients were treated before vaccinations were available. We know the limitations of vaccine efficacy in specific populations, including elderly individuals with comorbidities [
44,
45]. Our findings indicate that the exceptional results of our studies are unlikely to be attributable to vaccinations, as half of our patients received treatment before vaccination, and many elderly individuals in the general population still experienced severe COVID-19 symptoms and mortality despite being vaccinated.
Achieving optimal health goals, including a BMI of 20-21, normal blood pressure, an LDL level of less than 55 mg/dL, optimal Hb A1C, optimal reading salivary NO strip, and low hs-CRP, can be challenging without implementing dietary modifications to control risk factors. Both patients and doctors share the responsibility for ensuring optimal health. Therefore, it is better to manage and optimize the patient's metabolic parameters as soon as possible rather than waiting until a disaster like COVID-19 strikes and then rushing to fix the patient's metabolic disorder. The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the limitations of relying solely on medications to combat pandemics. The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the limitations of relying solely on medications to combat pandemics. Many doctors worldwide have struggled to manage COVID-19 and to optimize patient metabolic disorders. The more we learn about the advantages of consuming a PBD and a healthy diet, the more reasons are discovered to support it. On the other hand, as the negative consequences of an omnivorous diet become increasingly apparent, it becomes more difficult to justify this choice. While these diets may provide temporary satisfaction, the long-term health risks they entail are challenging to overlook. Therefore, it is crucial to carefully consider the potential costs and benefits of one's dietary choices.
Due to the significant mortality rate associated with COVID-19, patients are often inclined to adhere to PBD interventions. Moreover, numerous individuals have observed an elevated number of fatalities among patients who were treated at top hospitals in Indonesia. Maintaining such healthy eating habits is of utmost importance. Unfortunately, it is with a heavy heart that we must report the unfortunate occurrence of more than five of our previous patients. All of these individuals had received complete vaccinations; however, they subsequently contracted COVID-19 and passed away without implementing dietary changes or supplementation. Despite our previous outstanding results, these individuals appeared to disregard our method for their subsequent COVID-19 infection. It seems that they continued to follow an omnivorous diet and relied on various COVID-19 medications, which ultimately proved to be detrimental to their lives.
Acknowledging the noteworthy outcome of PBD intervention, it is essential to recognize the substantial dedication required from patients and healthcare professionals. Despite evidence of its effectiveness, there has been reluctance among the medical community to embrace this approach fully. As a result, we can only hope for more favorable circumstances to encourage the broader acceptance and application of PBDs in the future.