Submitted:
12 April 2024
Posted:
15 April 2024
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Background
- Heuristic set: The heuristic set originally contained 9 heuristics, extracted from the work by Molich and Nielsen [14]. It serves as a way to categorize usability problems, however they not provide information about how to solve them.
- Number of evaluators: They noticed that the number of evaluators was a critic factor determining that an optimus number of them might be around 3 and 5 and that more than 10 evaluators might be unnecessary.
- Evaluators biases: The answers from the evaluators are subjected to their expertise, previous experience and own judgement; providing a potential limitations and biases of the results.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Heuristic Instrument
- Visibility and system state (five questions): Focuses on ensuring that users are always aware of what the system is doing and their position within it.
- Connection with the real world (four questions): Prioritizes using familiar language, metaphors, and concepts, aligning the system with real-world analogs.
- User control and freedom (three questions): Emphasizes the importance of allowing users to navigate freely and undo actions easily.
- Consistency and standards (six questions): Ensures uniformity in the interface, with consistent actions and standards across different elements.
- Recognition rather than memory (five questions): Aims to design systems that minimize the need for remembering information, enhancing user learning and anticipation.
- Flexibility and efficiency (six questions): Focuses on providing shortcuts and efficient paths for experienced users while remaining accessible to novices.
- Help users recognize, diagnose and recover from errors (four questions): Focuses on designing systems that provide clear, understandable error messages, aiding users in recognizing and rectifying issues efficiently.
- Error prevention (three questions): Involves designing systems to prevent errors before they occur.
- Aesthetic and minimalist design (four questions): Encourages visually appealing designs and minimal in unnecessary elements.
- Help and documentation (five questions): Stresses the importance of accessible, clear help and documentation for users.
- Save the state and protect the work (three questions): Addresses the need to save user progress and protect against data loss.
- Colour and readability (four questions): Ensures that text is readable with appropriate color contrast and size.
- Autonomy (three questions): Allows users to make personal choices and customizations in the system.
- Defaults (three questions): Focuses on providing sensible default settings while allowing users to revert to these defaults when needed.
- Latency reduction (two questions): Aim to minimize delays and provide feedback during processes that require time.
3.2. Analytical Hierarchical Process
- Input: Pairwise comparison matrices for criteria and alternatives.
- Output: Priority vector (weights) for criteria and alternatives.
-
For each pairwise comparison matrix:
- -
- Normalize the matrix by column.
- -
- Compute the principal eigenvector to determine weights.
- -
- Calculate the consistency ratio.
- -
-
If CR is less than 0.1:
- ∗
- Accept the weights.
- -
-
Else:
- ∗
- Re-evaluate comparisons.
- Aggregate the weights for final decision-making.
3.3. Simulation
3.4. Data Acquisition
4. Results
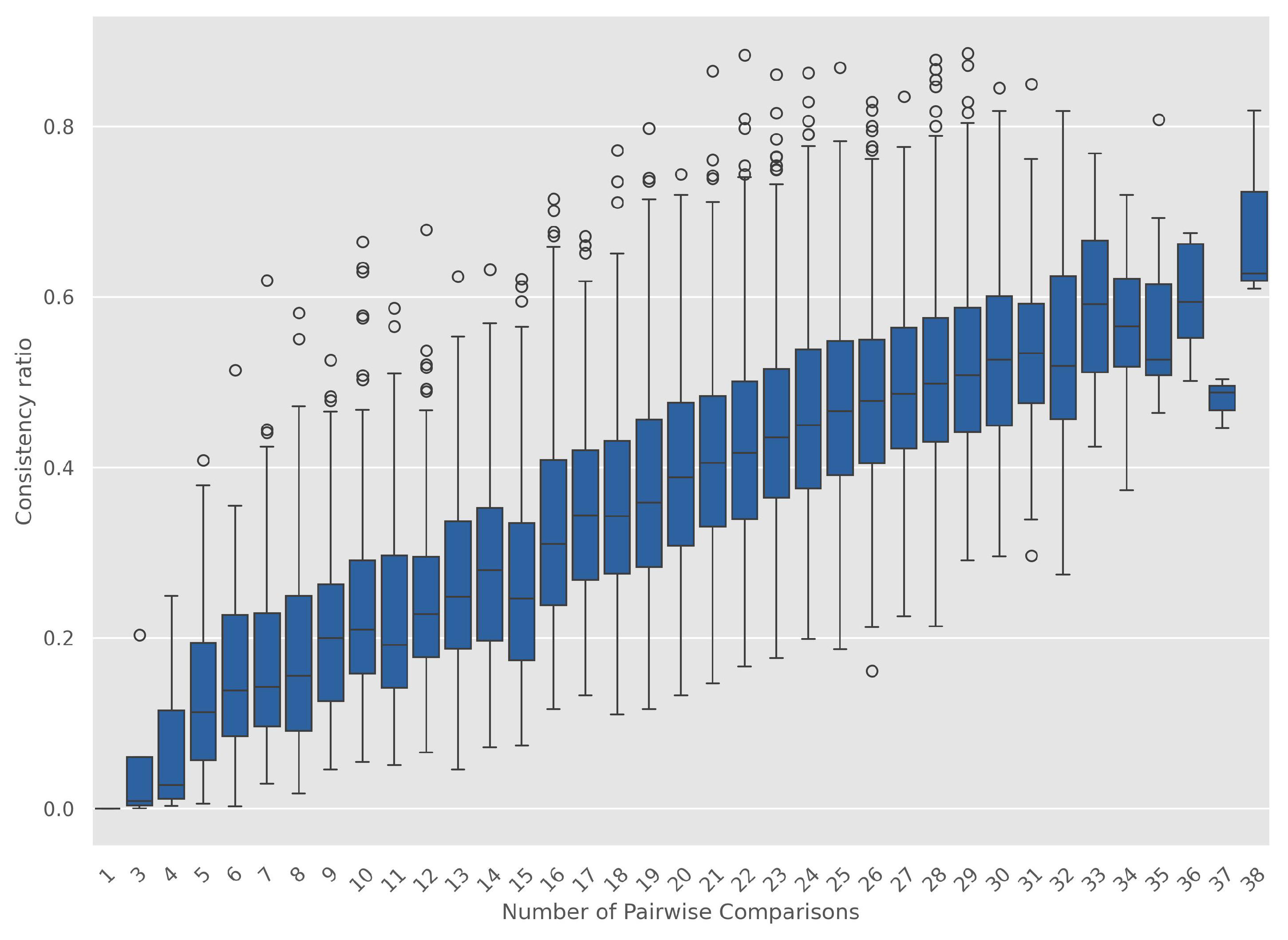
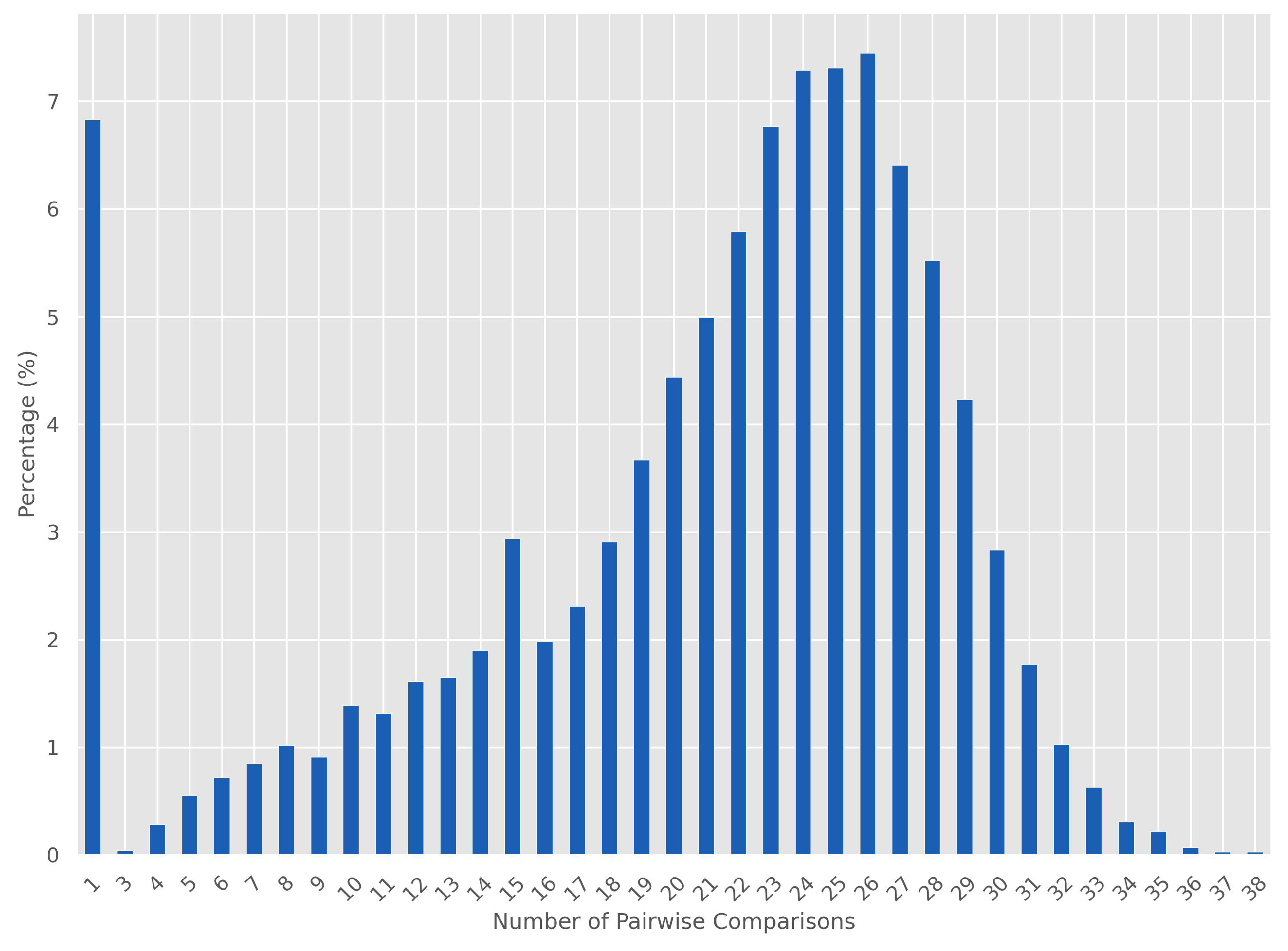
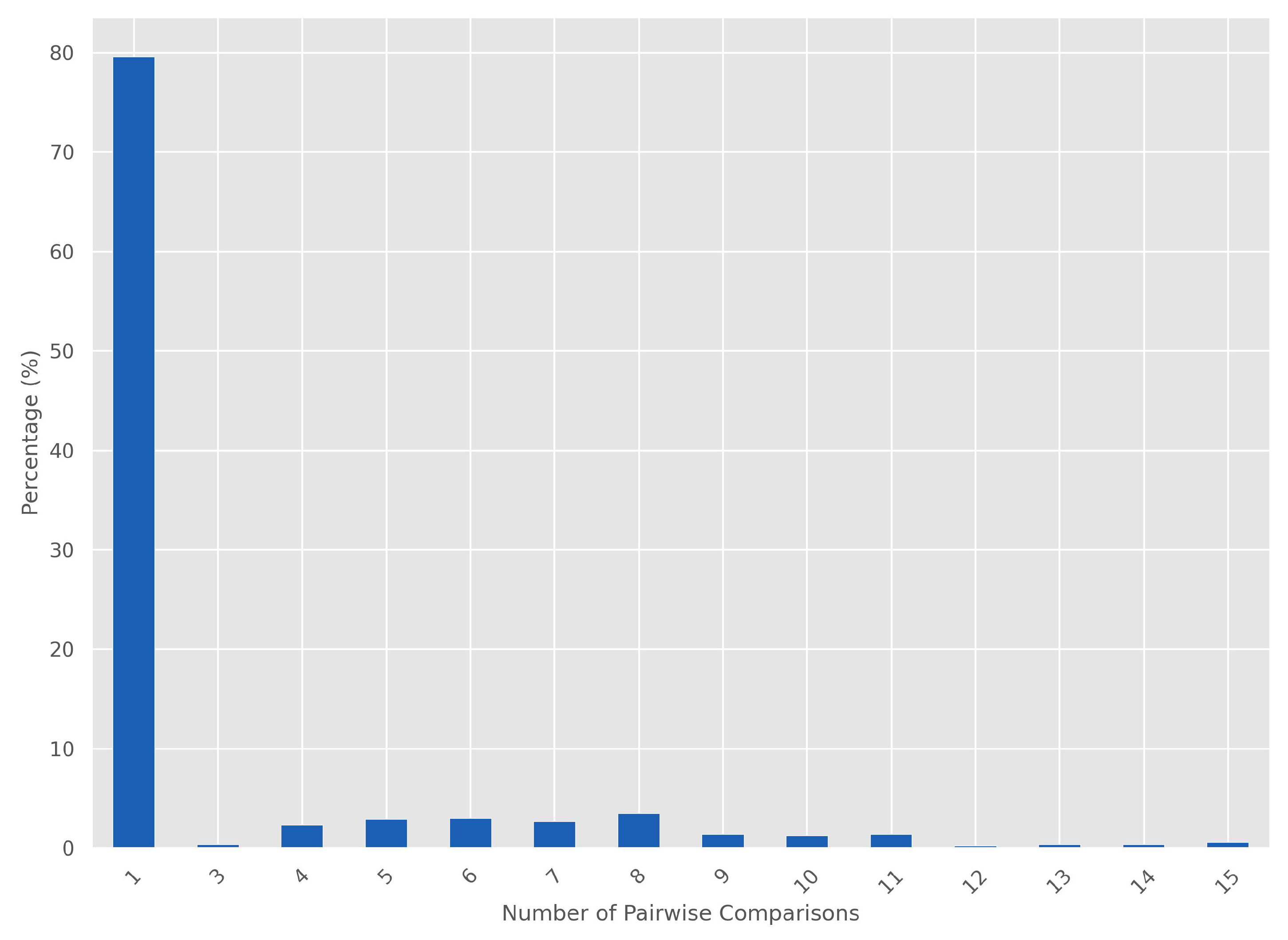
4.1. Algorithm for Pairwise Comparison
4.1.1. Algorithm Performance
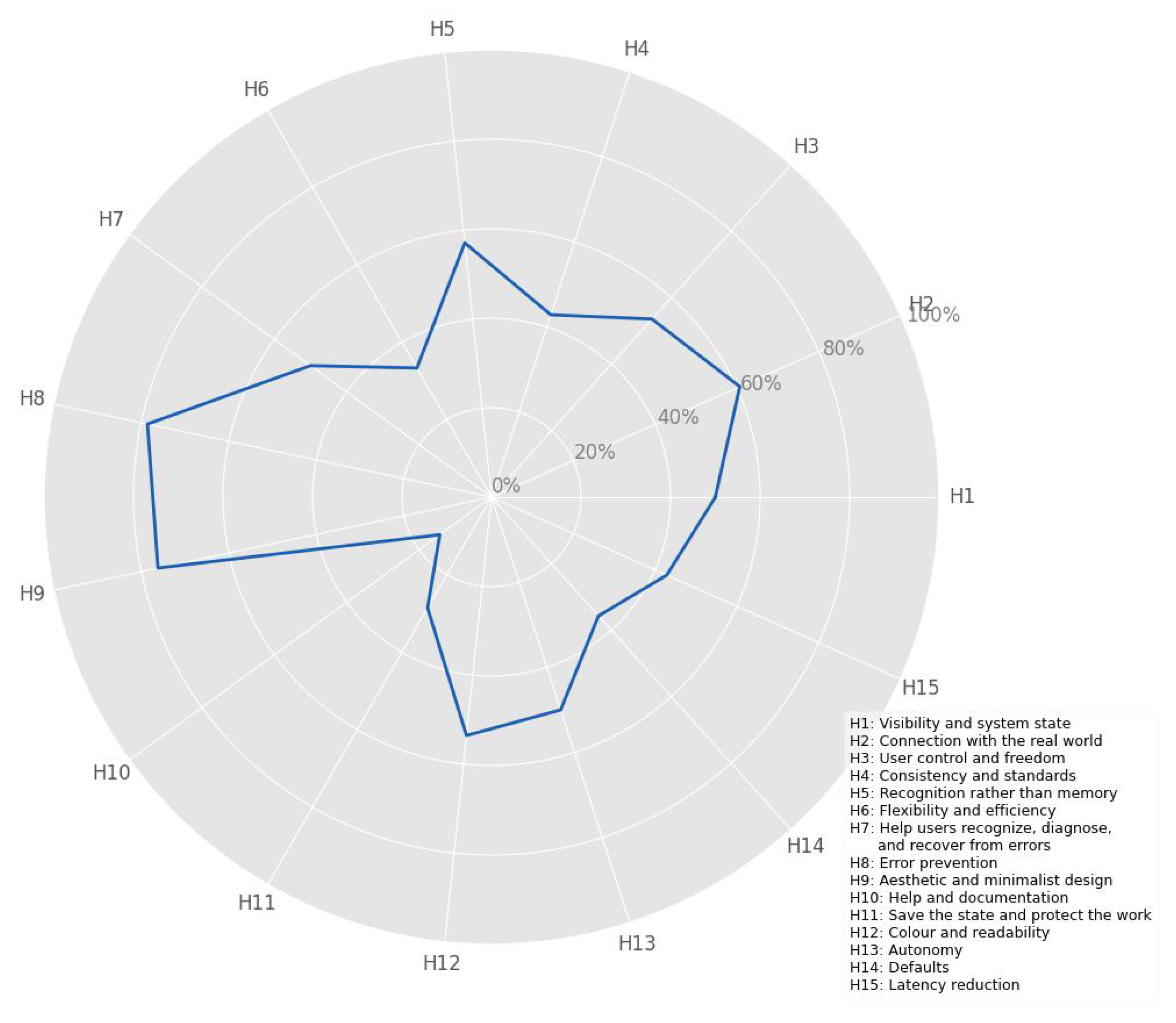
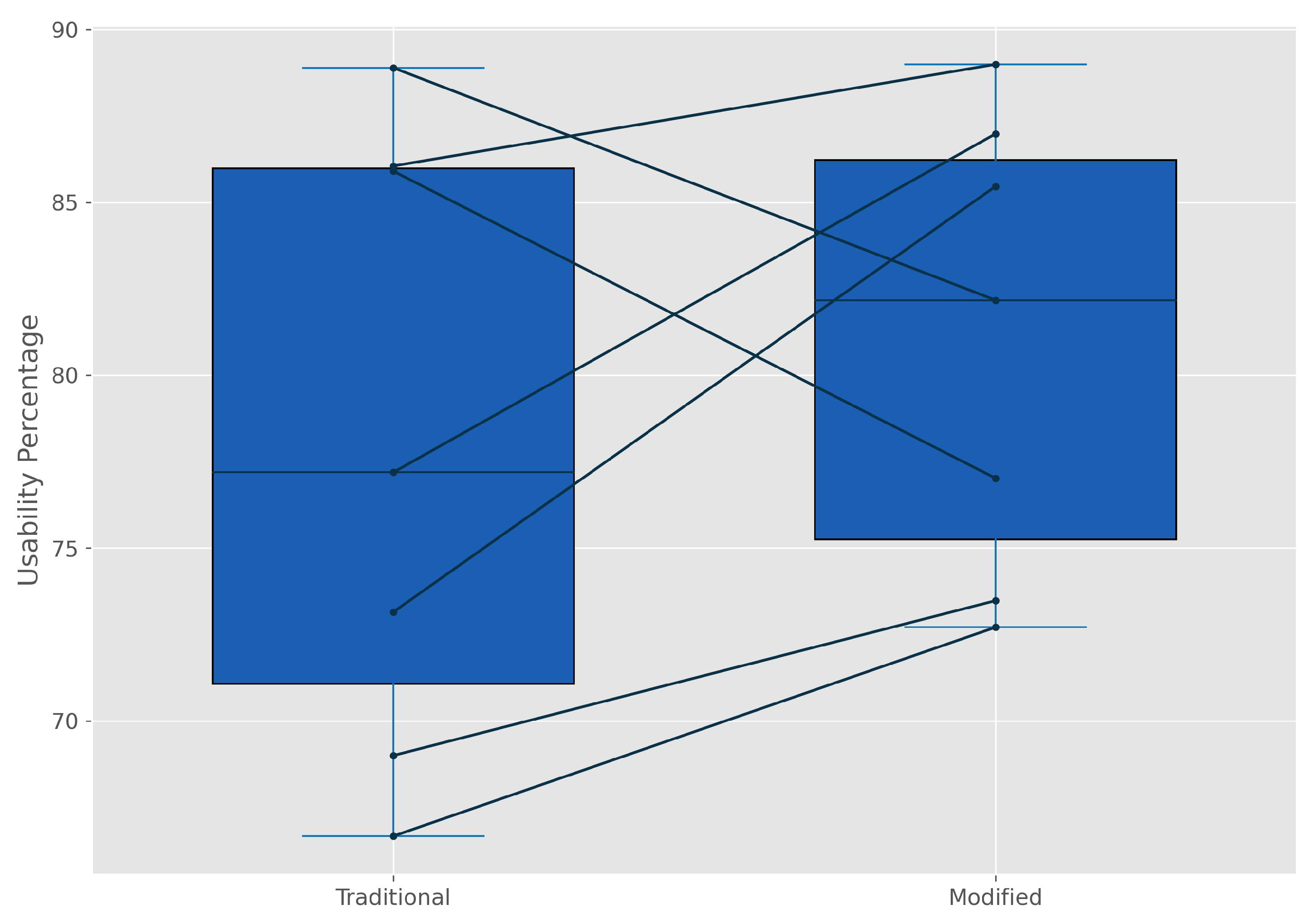
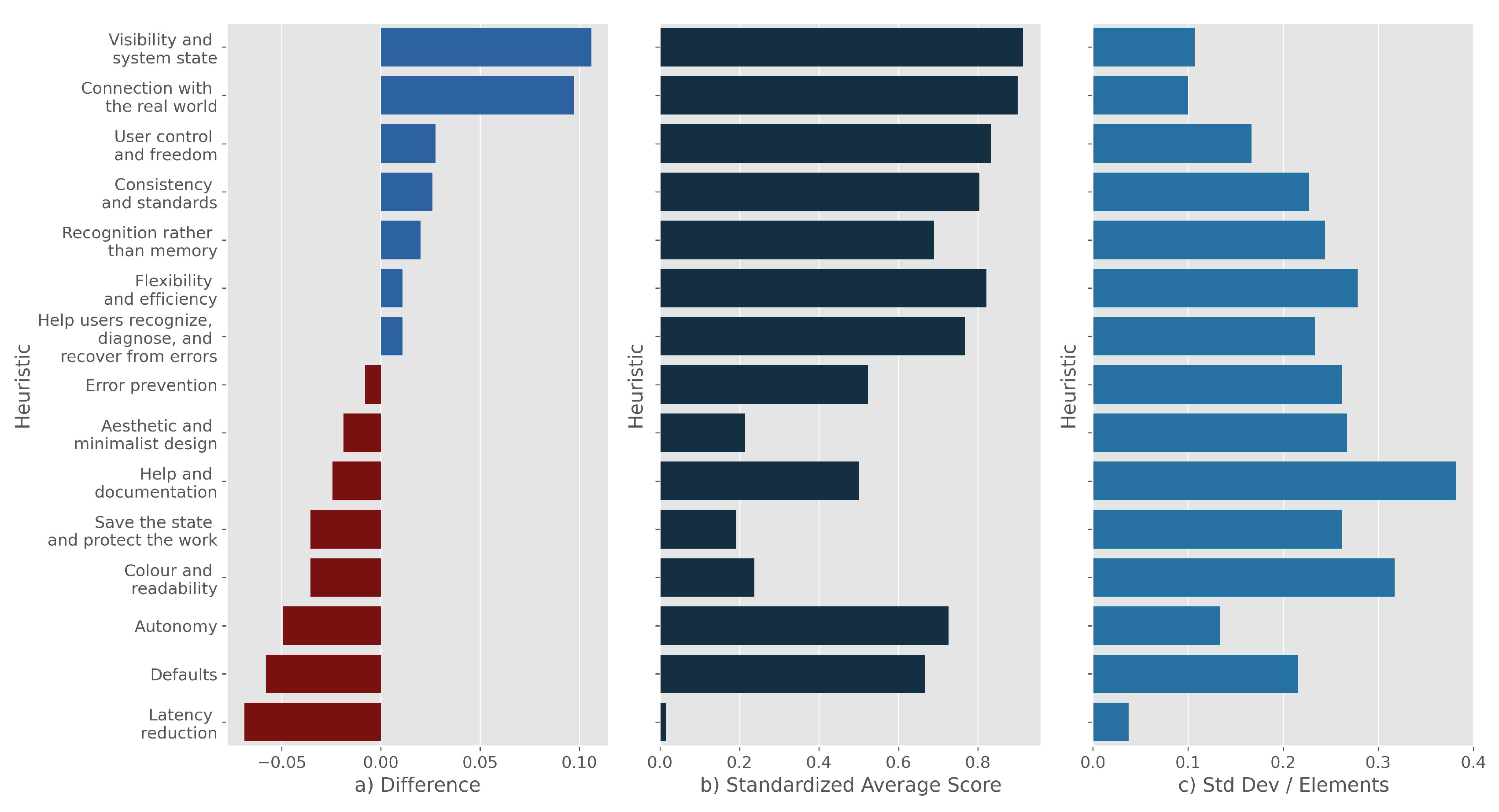
4.2. Weightened Heuristic Application
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AHP | Analytic Hierarchy Process |
| CI | Consistency Index |
| CR | Consistency Ratio |
| DOC | Document (Microsoft Word Format) |
| HCI | Human-Computer Interaction |
| ISO | International Organization for Standardization |
| Portable Document Format | |
| PSSUQS | Post-Study System Usability Questionnaire Software |
| QUIS | User Interaction Satisfaction |
| SUS | System Usability Scale |
| SUMI | Usability Measurement Inventory |
| UI | User Interface |
| UP | Usability Percentage |
| UTL | Usability Testing Leader |
| XLS | Excel Spreadsheet (Microsoft Excel Format) |
Appendix A Tailored algorithm for AHP
References
- Vlachogianni, P.; Tselios, N. Perceived usability evaluation of educational technology using the System Usability Scale (SUS): A systematic review. Journal of Research on Technology in Education 2022, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacomin, J. What is human centred design? Design Journal 2014, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holeman, I.; Kane, D. Human-centered design for global health equity. Information Technology for Development 2020, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peruzzini, M.; Carassai, S.; Pellicciari, M. The Benefits of Human-centred Design in Industrial Practices: Re-design of Workstations in Pipe Industry. Procedia Manufacturing 2017, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, J.; Arness, D.; Gronowski, A.; Qu, Z.; Lau, C.W.; Catchpoole, D.; Nguyen, Q.V. Exocentric and Egocentric Views for Biomedical Data Analytics in Virtual Environments—A Usability Study. Journal of Imaging 2024, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, R.; Flood, D.; Duce, D. Usability of mobile applications: literature review and rationale for a new usability model. Journal of Interaction Science 2013, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, I.; Tj, H.W.; ., F.; Wahyoedi, S.; Widjaja, B.T. The Effect of Usability, Information Quality, and Service Interaction on E-Loyalty Mediated by E-Satisfaction on Hallobumil Application Users. KnE Social Sciences 2023. [CrossRef]
- Bevan, N. Measuring usability as quality of use. Software Quality Journal 1995, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tullis, T.; Albert, W. Measuring the User Experience, Second Edition: Collecting, Analyzing, and Presenting Usability Metrics, 2nd ed.; Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc.: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Brooke, J., SUS: A ’Quick and Dirty’ Usability Scale; CRC Press, 1996. [CrossRef]
- Chin, J.P.; Diehl, V.A.; Norman, K.L. Development of an instrument measuring user satisfaction of the human-computer interface. 1988, Vol. Part F130202. [CrossRef]
- Kirakowski, J.; Cierlik, B. Measuring the Usability of Web Sites. Proceedings of the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society Annual Meeting 1998, 42, 424–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, J.R. Psychometric evaluation of the post-study system usability questionnaire: the PSSUQ. 1992, Vol. 2. [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, J.; Molich, R. Heuristic evaluation of user interfaces. ACM Press, 1990, pp. 249–256. [CrossRef]
- Bangor, A.; Kortum, P.T.; Miller, J.T. An empirical evaluation of the system usability scale. International Journal of Human-Computer Interaction 2008, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Păsărelu, C.R.; Kertesz, R.; Dobrean, A. The Development and Usability of a Mobile App for Parents of Children with ADHD. Children 2023, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weichbroth, P. Usability Testing of Mobile Applications: A Methodological Framework. Applied Sciences 2024, 14, 1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenzweig, E., Usability Inspection Methods; Elsevier, 2015; pp. 115–130. [CrossRef]
- Maqbool, B.; Herold, S. Potential effectiveness and efficiency issues in usability evaluation within digital health: A systematic literature review. Journal of Systems and Software 2024, 208, 111881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Generosi, A.; Villafan, J.Y.; Giraldi, L.; Ceccacci, S.; Mengoni, M. A Test Management System to Support Remote Usability Assessment of Web Applications. Information 2022, 13, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veral, R.; Macías, J.A. Supporting user-perceived usability benchmarking through a developed quantitative metric. International Journal of Human Computer Studies 2019, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz, F.; Pow-Sang, J.A. A systematic mapping review of usability evaluation methods for software development process. International Journal of Software Engineering and its Applications 2016, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shneiderman, B. Designing the user interface strategies for effective human-computer interaction. ACM SIGBIO Newsletter 1987, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, D. The Design of Everyday Things; Vahlen, 2016. [CrossRef]
- Tognazzini, B. First Principles, HCI Design, Human Computer Interaction (HCI), Principles of HCI Design, Usability Testing. http://www.asktog.com/basics/firstPrinciples.html, 2014. Online; accessed 2024-01-01.
- Shyr, W.J.; Wei, B.L.; Liang, Y.C. Evaluating Students’ Acceptance Intention of Augmented Reality in Automation Systems Using the Technology Acceptance Model. Sustainability 2024, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, J.; Molich, R. Heuristic evaluation of user interfaces. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the SIGCHI conference on Human factors in computing systems, 1990, pp. 249–256.
- Scholtz, J. Beyond Usability: Evaluation Aspects of Visual Analytic Environments. IEEE, 10 2006, pp. 145–150. [CrossRef]
- Lewis, C.; Poison, P.; Wharton, C.; Rieman, J. Testing a walkthrough methodology for theory-based design of walk-up-and-use interfaces. 1990. [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.; Bevan, N. Usability Context Analysis: A Practical Guide. Serco Usability Services 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Jaspers, M.W. A comparison of usability methods for testing interactive health technologies: Methodological aspects and empirical evidence. International Journal of Medical Informatics 2009, 78, 340–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, J.; Chisnell, D.; Spool, J. Handbook of Usability Testing: How to Plan, Design, and Conduct Effective Tests, 2 ed.; Wiley, 2008; p. 384. Foreword by Jared Spool.
- Law, E.L.C.; Hvannberg, E.T. Analysis of combinatorial user effect in international usability tests. ACM, 4 2004, pp. 9–16. [CrossRef]
- Molich, R.; Nielsen, J. Improving a Human-Computer Dialogue. Communications of the ACM 1990, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartson, R.; Pyla, P.S., Rapid Evaluation Methods; Elsevier, 2012; pp. 467–501. [CrossRef]
- Delice, E.K.; Güngör, Z. The usability analysis with heuristic evaluation and analytic hierarchy process. International Journal of Industrial Ergonomics 2009, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virzi, R.A.; Sorce, J.F.; Herbert, L.B. Comparison of three usability evaluation methods: Heuristic, think-aloud, and performance testing. 1993, Vol. 1. [CrossRef]
- Lazar, J.; Feng, J.H.; Hochheiser, H., Usability testing; Elsevier, 2017; pp. 263–298. [CrossRef]
- Quiñones, D.; Rusu, C. How to develop usability heuristics: A systematic literature review. Computer Standards and Interfaces 2017, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaferian, P.; Hawkey, K.; Sotirakopoulos, A.; Velez-Rojas, M.; Beznosov, K. Heuristics for evaluating IT security management tools. 2014, Vol. 29. [CrossRef]
- Lechner, B.; Fruhling, A.L.; Petter, S.; Siy, H.P. The Chicken and the Pig: User Involvement in Developing Usability Heuristics. In Proceedings of the AMCIS, 2013.
- Sim, G.; Read, J.C.; Cockton, G. Evidence based design of heuristics for computer assisted assessment. 2009, Vol. 5726 LNCS. [CrossRef]
- Ling, C.; Salvendy, G. Extension of heuristic evaluation method: a review and reappraisal. Ergonomia IJE & HF 2005, 27, 179–197. [Google Scholar]
- Paddison, C.; Englefield, P. Applying heuristics to accessibility inspections. Interacting with Computers 2004, 16, 507–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inostroza, R.; Rusu, C.; Roncagliolo, S.; Rusu, V.; Collazos, C.A. Developing SMASH: A set of SMArtphone’s uSability Heuristics. Computer Standards and Interfaces 2016, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermawati, S.; Lawson, G. Establishing usability heuristics for heuristics evaluation in a specific domain: Is there a consensus?, 2016. [CrossRef]
- Bailey, R.W.; Wolfson, C.A.; Nall, J.; Koyani, S. Performance-Based Usability Testing: Metrics That Have the Greatest Impact for Improving a System’s Usability. In Proceedings of the Human Centered Design. Springer, 2009, pp. 3–12. [CrossRef]
- Mitta, D.A. A Methodology for Quantifying Expert System Usability. Human Factors: The Journal of the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society 1991, 33, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benaida, M. Developing and extending usability heuristics evaluation for user interface design via AHP. Soft Computing 2023, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaty, R.W. The analytic hierarchy process-what it is and how it is used. Mathematical Modelling 1987, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granollers, T. Usability Evaluation with Heuristics , Beyond Nielsen ’ s List. ThinkMind Digital Library, 3 2018, pp. 60–65.
- Sharp, H.; Preece, J.; Rogers, Y. Interaction Design: Beyond Human-Computer Interaction, 5 ed.; John Wilei & Sons Inc., 2019; p. 656.
- Bonastre, L.; Granollers, T. A set of heuristics for user experience evaluation in E-commerce websites. 2014.
- Paz, F.; Paz, F.A.; Sánchez, M.; Moquillaza, A.; Collantes, L. Quantifying the usability through a variant of the traditional heuristic evaluation process. 2018, Vol. 10918 LNCS. [CrossRef]
- Kemp, E.A.; Thompson, A.J.; Johnson, R.S. Interface evaluation for invisibility and ubiquity - An example from E-learning. 2008. [CrossRef]
- Pierotti, D. Heuristic evaluation-a system checklist. Xerox Corporation 1995, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Khowaja, K.; Al-Thani, D. New Checklist for the Heuristic Evaluation of mHealth Apps (HE4EH): Development and Usability Study. JMIR mHealth and uHealth 2020, 8, e20353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holey, R.H. Handbook of Structural Equation Modeling, 1 ed.; The Guilford Press, 2012; pp. 3–16.
- Brodsky, S.L.; Lichtenstein, B. The Gold Standard and the Pyrite Principle: Toward a Supplemental Frame of Reference. Frontiers in Psychology 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, K., Questionnaires, individual interviews and focus group interviews; Elsevier, 2018; pp. 379–403. [CrossRef]
- Thiem, A.; Duşa, A. Qualitative Comparative Analysis with R; Vol. 5, Springer New York, 2013; p. 99. [CrossRef]
- Contreras-Pacheco, O.E.; Talero-Sarmiento, L.H.; Camacho-Pinto, J.C. Effects of Corporate Social Responsibility on Employee Organizational Identification: Authenticity or Fallacy. Contaduría y Administración 2019, 64, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leventhal, B.C.; Ames, A.J.; Thompson, K.N., Simulation Studies for Psychometrics. In International Encyclopedia of Education: Fourth Edition; Elsevier, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Tanner, K., Survey Designs. In Research Methods: Information, Systems, and Contexts: Second Edition; Elsevier, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Bubaš, G.; Čižmešija, A.; Kovačić, A. Development of an Assessment Scale for Measurement of Usability and User Experience Characteristics of Bing Chat Conversational AI. Future Internet 2024, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Linden, W.J. Item Response Theory. In Encyclopedia of Social Measurement; Elsevier, 2004. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, K.; Roy, S.; Poonia, R.C.; Nayak, S.R.; Kumar, R.; Alzahrani, K.J.; Alnfiai, M.M.; Al-Wesabi, F.N. Evaluating the Usability of mHealth Applications on Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Using Various MCDM Methods. Healthcare 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, A.; Siddique, A.; Naveed, Q.N.; Khaliq, U.; Aseere, A.M.; Hasan, M.A.; Qureshi, M.R.N.; Shahzad, B. Evaluating Usability of Academic Websites through a Fuzzy Analytical Hierarchical Process. Sustainability 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iryanti, E.; Santosa, P.I.; Kusumawardani, S.S.; Hidayah, I. Inverse Trigonometric Fuzzy Preference Programming to Generate Weights with Optimal Solutions Implemented on Evaluation Criteria in E-Learning. Computers 2024, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulzar, K.; Tariq, O.; Mustafa, S.; Mohsin, S.M.; Kazmi, S.N.; Akber, S.M.A.; Abazeed, M.; Ali, M. A Fuzzy Analytic Hierarchy Process for Usability Requirements of Online Education Systems. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 146076–146089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakulin, S.; Alfimtsev, A. Multicriteria Decision Making in Tourism Industry Based on Visualization of Aggregation Operators. Applied System Innovation 2023, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Tu, J. Managing transitivity and consistency of preferences in AHP group decision making based on minimum modifications. Information Fusion 2021, 67, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, K.; Rapp, B.; Gómez, J.M. Heuristic evaluation checklist for mobile ERP user interfaces. In Proceedings of the 2016 7th International Conference on Information and Communication Systems (ICICS). IEEE, 2016, pp. 180–185.
- Aballay, L.; Lund, M.I.; Gonzalez Capdevila, M.; Granollers, T. Heurísticas de Usabilidad utilizando una Plataforma Abierta y Colaborativa Práctica Áulica Aplicada a Sitios e-commerce. In Proceedings of the V Congreso Internacional de Ciencias de la Computación y Sistemas de Información 2021 – CICCSI 2021, CICCSI, Mendoza - San Juan, Argentina, November 2021.
- Yáñez Gómez, R.; Cascado Caballero, D.; Sevillano, J.L.; et al. Heuristic evaluation on mobile interfaces: A new checklist. The scientific world journal 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, M.I. Heurísticas de Usabilidad utilizando una Plataforma Abierta y Colaborativa: Práctica Aulica Aplicada a Sitios e-commerce. In Proceedings of the CICCSI 2021, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Komarkova, J.; Visek, O.; Novak, M. Heuristic evaluation of usability of GeoWeb sites. In Proceedings of the Web and Wireless Geographical Information Systems: 7th International Symposium, W2GIS 2007, Cardiff, UK, November 28-29, 2007. Proceedings 7. Springer, 2007, pp. 264–278.
- Almenara, A.P.; Humanes, J.; Granollers, T. MPIu+aX, User-Centered Design methodology that empathizes with the user and generates a better accessible experience. (From theory to practice). ACM, 9 2023, pp. 1–3. [CrossRef]
| 1 | ISO/CD 9241-11: Ergonomics of human-system interaction - Part 11: Guidance on usability (1998). Available at: https://www.iso.org/standard/63500.html. Accessed date: April 12, 2024. |
| 2 | Remote User eXperience Artificial Intelligence LAB. https://github.com/ruxailab. Last access: April 12, 2024 |
| Heuristic | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | |
| 8.33 | 6.67 | 5.00 | 10.00 | 8.33 | 10.00 | 6.67 | 5.00 | 6.67 | 8.33 | 5.00 | 6.67 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 3.33 | |
| Heuristic | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | |
| 1 | 1.00 | 3.00 | 5.00 | 3.00 | 1.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 3.00 | 7.00 | 7.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 7.00 | 7.00 |
| 2 | 0.33 | 1.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 0.33 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 1.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 |
| 3 | 0.2 | 0.33 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.14 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 1.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 |
| 4 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.33 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 |
| 5 | 1.00 | 3.00 | 7.00 | 3.00 | 1.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 3.00 | 7.00 | 7.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 7.00 | 7.00 |
| 6 | 0.2 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 1.00 | 0.20 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.33 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 5.00 | 5.00 |
| 7 | 0.2 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 1.00 | 0.20 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.33 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 5.00 | 5.00 |
| 8 | 0.2 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 1.00 | 0.20 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.33 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 0.33 | 0.33 | 5.00 | 5.00 |
| 9 | 0.33 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.33 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 1.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 |
| 10 | 0.14 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.33 | 0.14 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| 11 | 0.14 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.33 | 0.14 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| 12 | 0.33 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.33 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 1.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 |
| 13 | 0.33 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.33 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 3.00 | 1.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 5.00 | 5.00 |
| 14 | 0.14 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.33 | 0.14 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| 15 | 0.14 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.33 | 0.14 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Heuristici | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | |
| 18.06 | 9.26 | 6.99 | 5.06 | 18.96 | 4.21 | 4.21 | 4.21 | 7.74 | 1.45 | 1.45 | 7.75 | 7.75 | 1.45 | 1.45 | |
| Evaluator | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heuristic | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
| H1 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 4.0 | 4.5 | 4.0 | 5.0 | 4.0 |
| H2 | 3.0 | 2.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 3.5 | 4.0 | 2.0 |
| H3 | 3.0 | 2.0 | 3.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 1.0 | 1.5 |
| H4 | 5.0 | 4.0 | 5.0 | 5.5 | 3.5 | 4.0 | 3.5 |
| H5 | 5.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 4.0 |
| H6 | 5.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 6.0 | 3.0 | 5.0 | 3.0 |
| H7 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 4.0 |
| H8 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 0.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 1.0 |
| H9 | 4.0 | 3.0 | 4.0 | 3.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 1.0 |
| H10 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| H11 | 2.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| H12 | 4.0 | 3.0 | 2.5 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 |
| H13 | 2.0 | 2.5 | 2.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 2.0 |
| H14 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.0 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 2.0 |
| H15 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





