1. Background
In 2022, many countries adopted the aim of living with the virus, whereas the Hong Kong government maintained stringent contact tracing and social distancing practice to keep COVID-19 cases at low level. This strategy conferred the community a seven-month nearly zero local cases in 2021 [
1]. However, in January 2022, the fifth wave of local outbreak was kick started by Omicron variant BA.2.2, with more than one million self-testing or laboratory confirmed infections from February to March 2022 recorded [
2]. During the fifth wave, the Government adjusted the social distancing policy and quarantine arrangements for inbound travelers several times. The number of confirmed local cases fluctuated and new lineages were found in the community. In this study, we aimed to elucidate the relationship between the social distancing policy, quarantine arrangement and the dynamics of Omicron sub-lineages in the community in 2022.
2. Methods
Samples
A total of 4,684 COVID-19-positive cases were collected from three public hospitals, namely Pamela Youde Nethersole Eastern Hospital (PYNEH), Tuen Mun Hospital (TMH) and Prince of Wales Hospital (PWH), during the whole 2022. All these cases were defined as local cases as these patients did not have any travel history during the incubation period. All samples were de-identified before being sent to the laboratory for genomic surveillance. This study was approved by the Institutional Review Boards of The Hong Kong Polytechnic University (RSA20021) and these three hospitals (HKECREC-20200014; KWC-20200040; NTWC-20200038).
Whole-Genome Sequencing of SARS-CoV-2
The extraction of total nucleic acid from these respiratory specimens was done using NucliSENS® easyMAG® (bioMérieux, The Netherlands) following the standard protocol from the manufacturers. The SAR-CoV-2 RNA were reverse-transcribed into cDNA using LunaScript™ RT SuperMix Kit (New England Biolabs, UK) following the manufacturer’s instruction. The viral cDNA was then amplified using the SARS-CoV-2-Midnight-1200 Amplicon Panel and Q5® High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase (New England Biolabs). The amplicons were quantified using the Qubit 2 fluorometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, US) prior to library preparation. The library preparation was performed following the protocol ‘PCR tiling of SARS-CoV-2 virus - rapid barcoding (SQK-RBK110.96)’ (version: PCTR_9125_v110_revH_24Mar2021-minion). The library was loaded and whole-genome seqeuenced on MinION or GridION (Oxford Nanopore Technologies, UK) with R9.4.1 flow cells.
Analysis of Phylogeny and the Dynamics of Co-Circulation of Omicron Sub-Variants
The SARS-Cov-2 consensus genomes were constructed using wf-artic v0.3.21 [
3] and multiple sequence alignment (MSA) was performed using MAFFT [
4]. Genomes with coverage >90% were then subject to lineage identification by pangolin v4.2. The maximum likelihood phylogeny of the cases were determined using IQ-TREE with GTR+G+I as the substitution model [
5], while the dynamics of co-circulation of Omicron sub-variants in the community over the study period were illustrated by a time tree constructed using Nextstrain [
6]. The number of confirmed cases and death cases were retrieved from DATA.GOV.HK [
7]. The implementation dates and details of the quarantine arrangement in phases for the inbound travelers and social distancing policies were reviewed to investigate the change in the lineage distribution after each time of amendment.
Statistical Analysis
One-way analysis of variance (one-way ANOVA) test was used to compare the number of new lineages between different quarantine arrangement models. A P value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Overview of The Epidemic in 2022
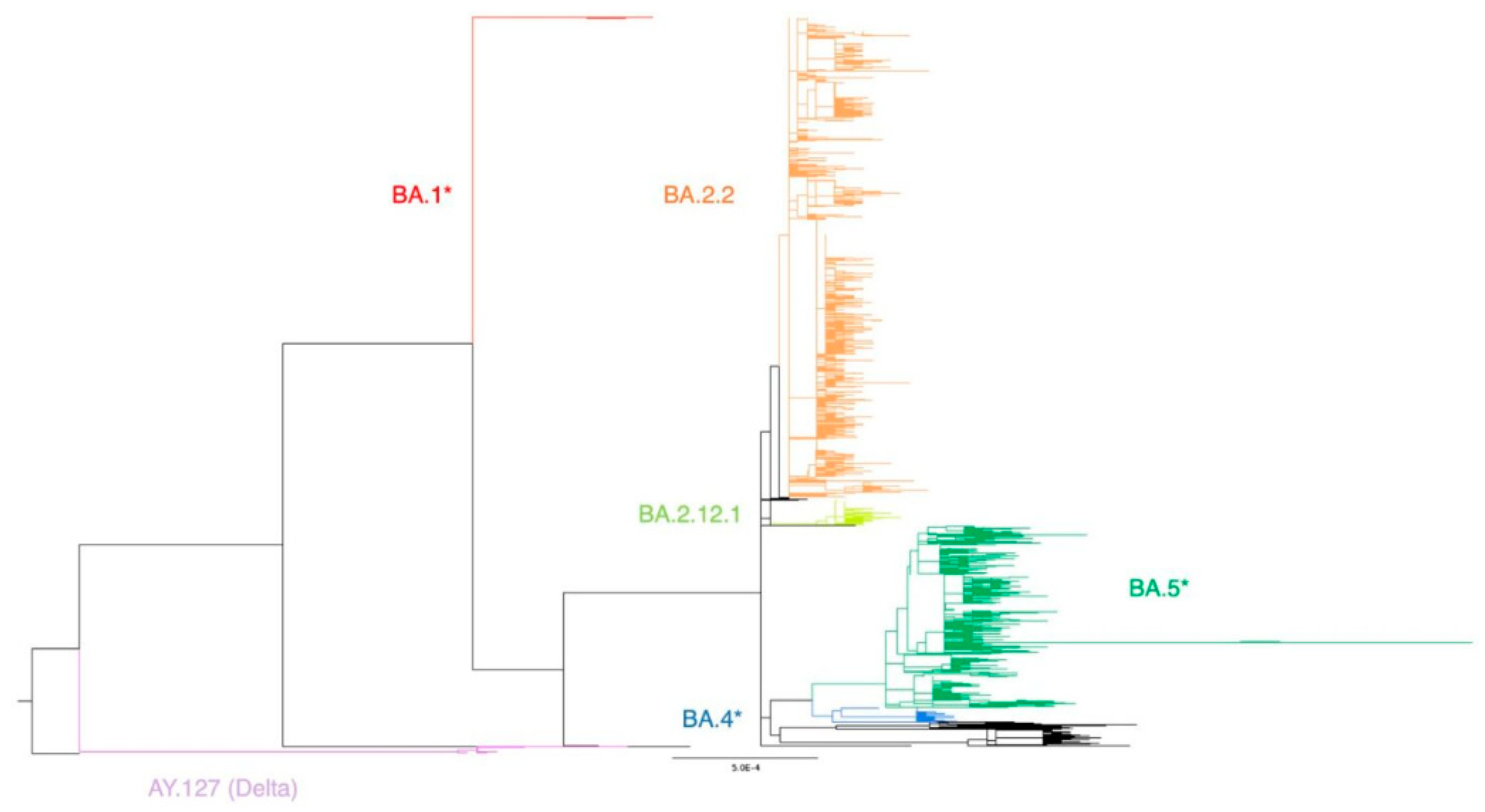
Our genomic surveillance using 4,684 local COVID-19 genomes revealed the emergence of 83 lineages in Hong Kong throughout 2022. Phylogenetic analysis of all sequences demonstrated that BA.2.2, which caused the flare-up of the epidemic, occupied the heaviest proportion. The remaining cases were categorized into the Delta variant AY.127 and four Omicron-related clusters (BA.1 sub-lineages, BA.2.12.1, BA.4 sub-lineages and BA.5 sub-lineages) (
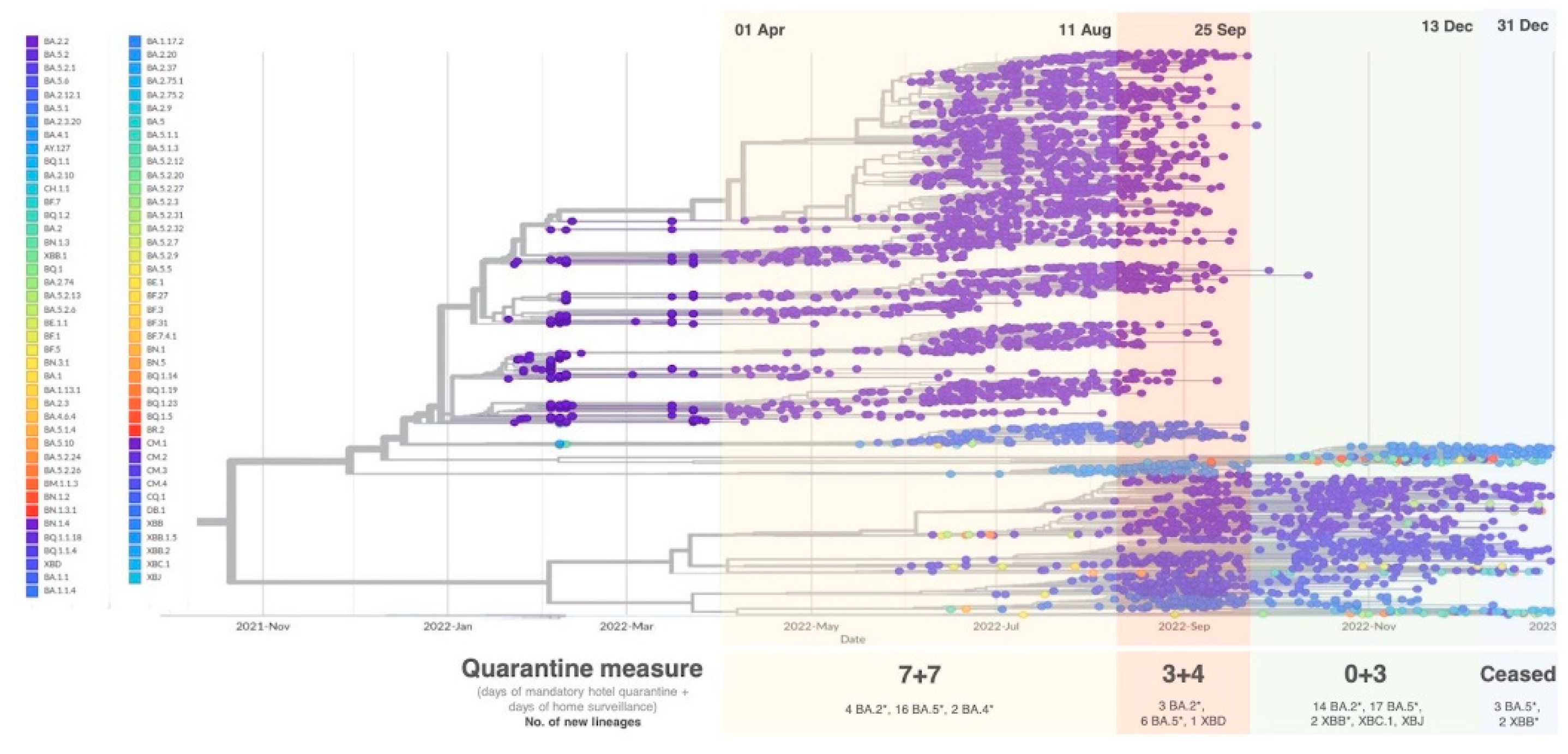
Figure 1). Nextstrain was used to illustrate the timing of occurrence of the lineages (
Figure 2). At the beginning of the fifth wave, sporadic variants were detected in the community, but BA.2.2-related cases still constituted the majority until the middle of May, when the detected lineages became more diverse. In June, another wave of the epidemic was accompanied by the expansion of BA.5 sub-lineage population. Ultimately, BA.5 sub-lineages outshone BA.2.2 and other co-circulating lineages to be the predominant strains. Our analysis of the association between various social distancing measures (
Table S1) and the dynamics of Omicron variants in the community revealed a significant association between the relaxation of quarantine arrangements for inbound travelers and an increase in the number of new lineages (One-way ANOVA, (F(5,47) = 18.233, p < 0.001)) (
Figure S1).
3.2. Change in The Dynamics of Circulating Lineages with the Adjustment of Quarantine Arrangement
The Hong Kong government implemented an up to 21-day mandatory hotel quarantine measurement for inbound travelers since the end of 2020. The monthly number of local confirmed cases from May to December 2021 was controlled at a near-zero level. In January 2022, a Pakistani woman who was infected by another inbound traveler during mandatory hotel quarantine sparked the Yat Kwai House-related cluster and triggered the local spread of Omicron variant BA.2.2 [
8]. In that month, a total of 1,554 tested-positive cases were reported, which was more than two-third of the total number of cases recorded in 2021 [
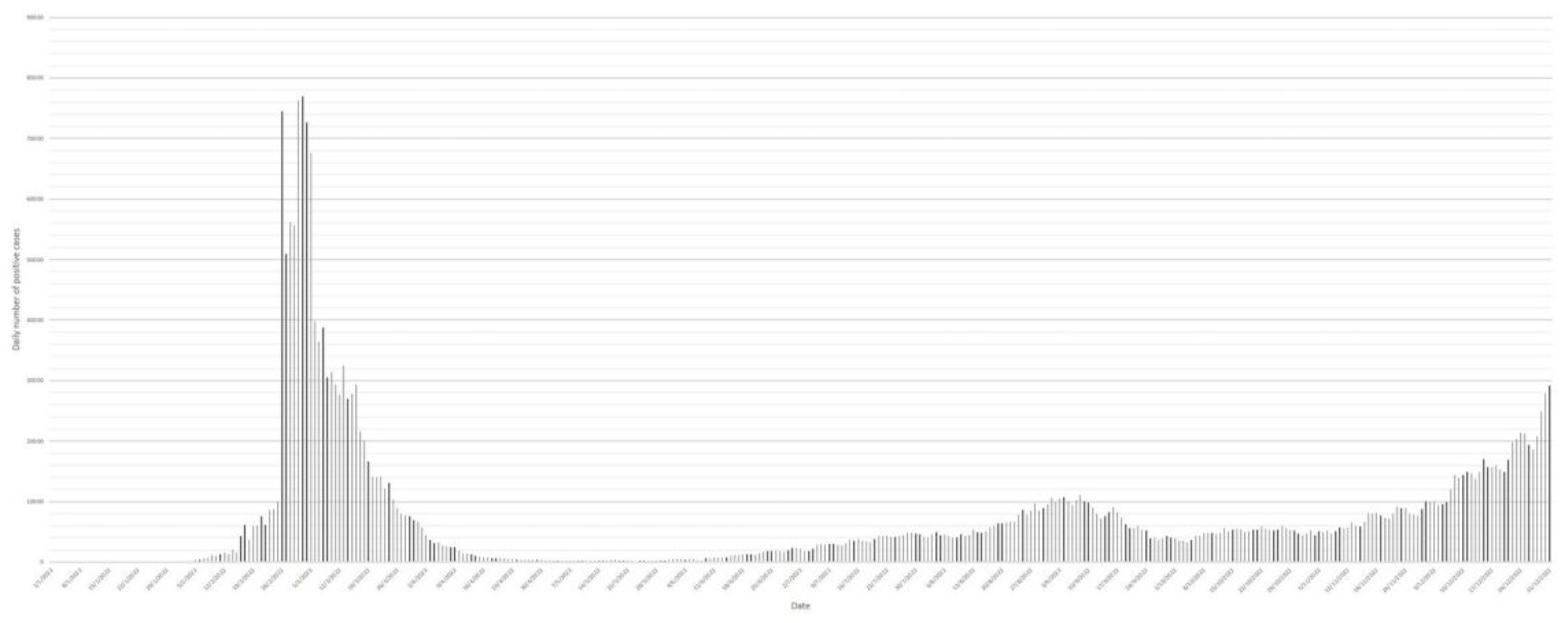
9]. The Government tightened social distancing measures and imposed ambush lockdowns, but the spread of the virus in the community was unmanageable. While the confirmed case number was surging, the Government cut the mandatory hotel quarantine period by seven days (14 days of mandatory hotel quarantine and seven days of medical surveillance at home, also known as ‘14+7’ model) on 5th February, considering the short incubation period of Omicron variants. Finally, the number of confirmed cases peaked in the early March 2022, with Omicron variant BA.2.2 as the only circulating strain (
Figure 3 and
Figure 4). On 1st April, the Government adjusted the quarantine arrangement for inbound persons, reducing the duration of mandatory hotel quarantine from 14 days to seven days, followed by seven-day self-monitoring (‘7+7’ model). The case number declined and plateaued at a low level in April and May (
Figure 3). However, about seven weeks after the arrangement, new lineages started to emerge; four BA.2 sub-lineages, two BA.4 sub-lineages and 16 BA.5 sub-lineages were found in the community (
Figure 2).
The number of local cases dropped from the peak and stayed at a relatively stable level at the end of September. The Government then announced the cancellation of mandatory hotel quarantine and shortened the period of medical surveillance at home from four days to three days (‘0+3’ model). Prior to the cessation of this arrangement on 14th December, 35 new lineages, including 14 BA.2 sub-variants, 17 BA.5 sub-variants, two XBB sub-variants, XBC.1 and XBJ, were first detected in local cases (
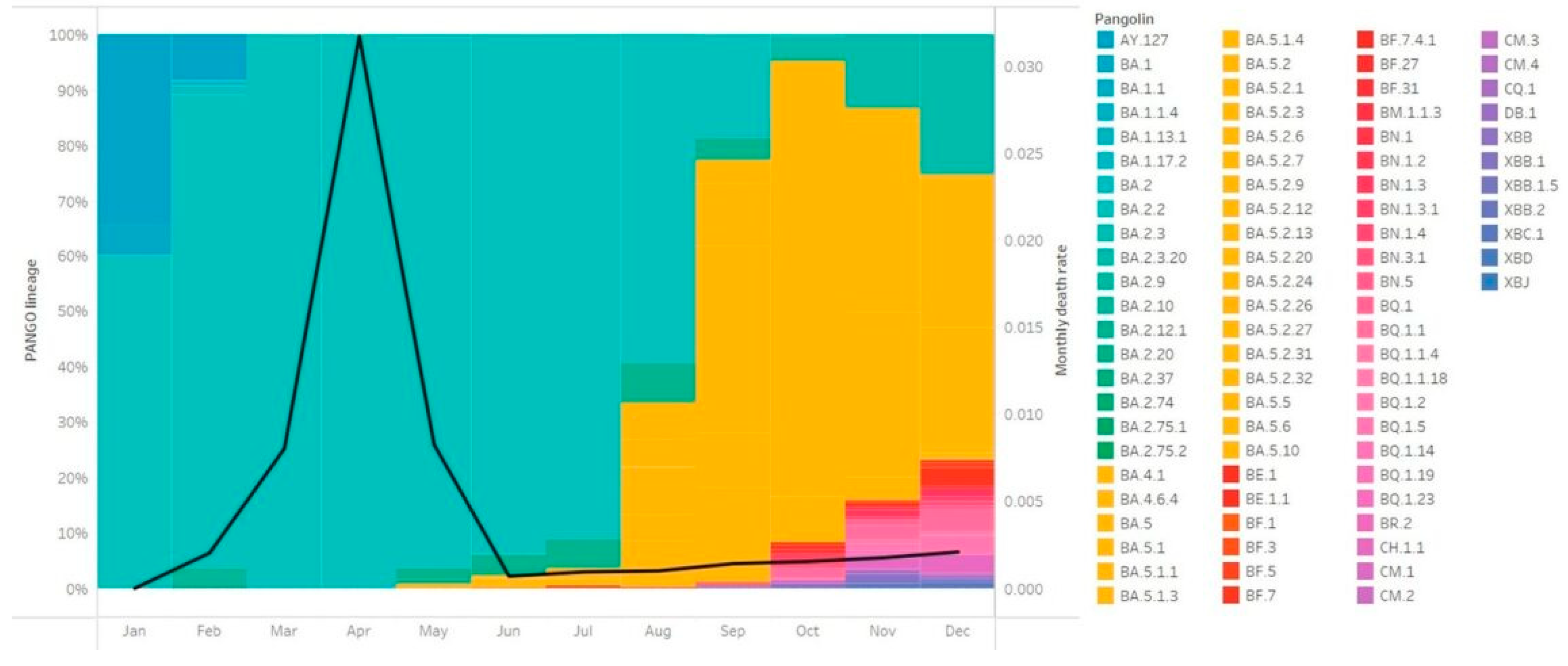
Figure 2). BA.2 sub-lineages were co-circulating with BA.5 sub-lineages, but the proportion of BA.2 sub-lineages continued to shrink, and that of BA.5 kept expanding (
Figure 4). Of note, the level of case number during this period did not fluctuated significantly. Also, no remarkable change in the death rate was observed when the number of cases climbed up (one-way ANOVA, F(5,47) = 2.037, p =0.091) (
Figure 4).
4. Discussion
To control the import of COVID-19 cases from other countries and prevent the spread of viruses in the local community, quarantine arrangements in phases for the inbound travelers and social distancing measurements were imposed since the emergence of the first case in Hong Kong. Since the latter half of 2021, Hong Kong experienced a seven-month period with nearly zero local cases due to the stringent quarantine policy (up to 21-day mandatory hotel quarantine) for inbound travelers implemented at the end of 2020. Unfortunately, such stringent measurements failed to prevent the fifth wave of pandemic, which was triggered by a Pakistani woman, who got infected by another inbound travelers during mandatory hotel quarantine and brought the Omicron sub-variant BA.2 into the community in January 2022 [
8]. Since then, the quarantine measurements were adjusted several times regarding the pandemic situation. A total of four times of quarantine arrangements for inbound travelers and social distancing measures were implemented sequentially during the whole 2022 (
Table S1). Fluctuations of the local case number and emergence of new lineages were observed after each time of adjustment. The first adjustment was the replacement of 21-day mandatory hotel quarantine by the ‘14+7’ model, which was implemented on 5th February. This amendment was followed by the peak of confirmed case number in early March. In the end of February, the Government implemented a vaccine pass arrangement to encourage the community to get vaccinated. Boosted vaccination coverage, together with previous natural infections, might have been the major cause of the subsided number of confirmed cases (
Figure 3).
During the effective period of ‘7+7’ model (1st April to 11th August 2022), the number of cases were successfully suppressed at a low level. However, the emergence of new lineages indicated that the seven-day-shortened mandatory quarantine period led to the penetration of new lineages brought by the imported cases into the community (
Figure 2). Simultaneously, the Government relaxed the social distancing measures, including resumption of face-to-face classes and dinnertime dine-in service, as well as re-opening of most previously closed premises (
Table S1). These factors may have contributed to the rebound in local cases in late May (
Figure 3).
The sixth wave appeared in the early September, when the ‘3+4’ model was implemented to replace the ‘7+7’ model. Significant increase in case number was accompanied by the expansion of BA.5-infected population. This could be explained by several reasons. First, the shortened mandatory quarantine period may have allowed travelers to bring BA.5 sub-lineages into the community. The compulsory hotel quarantine period was shortened from seven days to three days. After three-day mandatory hotel quarantine, they were given an ‘amber code’ under the vaccine pass during the period of medical surveillance at home. Although the inbound travelers were not allowed to enter the premises subject to ‘active checking’ of the vaccine pass such as catering premises and fitness premises, they could take public transport and go to work or study. This provided a window to introduce the imported cases and new lineages into the community. Second, BA.5 was shown to have higher transmissibility and was better able to evade immunity from vaccines and previous infections with other variants [
10]. The relaxed control measures, together with the natural advantages of BA.5, allowed the BA.5-infected population to expand rapidly compared to other Omicron variants.
From the end of September, when ‘0+3’ model was launched, to the cessation of all quarantine measurement on 14th December, a pool of new lineages was detected in the community (
Figure 2), resulting in a subversion of the dynamics of circulating lineages. In the end of 2022, BA.5 sub-lineages became the major circulating lineages in the local community. Interestingly, the overall case number did not significantly change. This might be attributed to the broad immunity driven by natural infection in the past few months. On the other hand, the relatively steady death rate could be explained by the weaker virulence of Omicron variants, which have been shown to cause less severe symptoms and be less fatal, comparing to other variants [
11].
Our study suggested that the emergence of new lineage was inevitable unless the mandatory quarantine period was seven days or longer, as the highly infectious nature of Omicron variants made transmission difficult to contain. Additionally, such a rigorous quarantine policy resulted in a drastic decline in the number of passenger arrivals [
12,
13]. In the era of Omicron, the reduced virulence of the variants has provided an impetus for the resumption of the tourism industry and other economic activities. At the end of 2022, the Government canceled all the social distancing measures, restrictions and vaccination requirement for inbound travelers were lifted. However, molecular surveillance of COVID-19 remains essential to monitor the emergence of new recombinant variants that may bear significant genetic variations and to correlate their predominance in the community with the hospitalization rate and death rate in order to assess their virulence.
5. Conclusions
To conclude, this study utilized thousands of COVID-19 whole genomes to illustrate the dynamic changes of circulating lineages in the local community throughout 2022. This study also acted as a good model of combined analysis of epidemiological data and well-organised public health policy information, which could be adapted to study a variety of contagious diseases in the future.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on
Preprints.org, Table S1: Quarantine arrangements in phases for the inbound travelers and social distancing measures implemented in 2022. Figure S1: Comparison of the mean number of new lineages emerged among different quarantine models in 2022. The quarantine model was expressed as ‘days of mandatory hotel quarantine+ days of home surveillance’. Red blocks are associated to the most significant difference and green blocks to the non-significant difference. Table S2: List of local COVID-19 positive clinical samples during the study period.
Authors’ Contributions
TL, NC, LKL, BWYM and HC contributed to conceptualization. TL, NC, LKL, ITFW, AWTL, WYT, HFTW contributed to methodology. TL, NC, LKL and ITFW performed investigation. TL, NC, LKL, ITFW, AWTL, WYT, HFTW, JSLL, FWNC, KSL, JYWL, BWYM and HC performed validation. TL, NC and BWYM wrote the original draft of the manuscript. TL, NC, LKL, ITFW, AWTL, WYT, HFTW, JSLL, FWNC, BWYM and HC reviewed and edited the draft. Data curation performed by LKL, AWTL, AYMH, MCYY, TLQ, KTY, VCYC and RCWW. KSL, JYWL, TLQ, VCYC and HC provided supervision. KSL, JYWL, TLQ, VCYC, AYMH, MCYY, KTY and RCWW provided resources for this study. Formal analysis was carried out by AYMH, MCYY, KTY, RCWW and HC.
Funding
This work was support by the Health and Medical Research Fund (HMRF) Commissioned Research on COVID-19 (COVID190204).
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Availability of data and materials
The data that support the findings of this study are openly available in GISAID at
https://gisaid.org/. Accession numbers were listed in
Table S2.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the laboratory staff from PMH, PYNEH, TMH and PWH, and their Infection Control Team for their contributions and valuable support on this study.
Competing interests
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Wong, S.C.; Au, A.K.; Lo, J.Y.; Ho, P.L.; Hung, I.F.; To, K.K.; et al. Evolution and Control of COVID-19 Epidemic in Hong Kong. Viruses. 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mefsin, Y.M.; Chen, D.; Bond, H.S.; Lin, Y.; Cheung, J.K.; Wong, J.Y.; et al. Epidemiology of Infections with SARS-CoV-2 Omicron BA.2 Variant, Hong Kong, January-March 2022. Emerg Infect Dis. 2022, 28, 1856–1858. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Loman, N.; Rowe, W.; Rambaut, A. nCoV-2019 novel coronavirus bioinformatics protocol 2020. https://artic.network/ncov-2019/ncov2019-bioinformatics-sop.html Accessed 30 May 2023.
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: improvements in performance and usability. Molecular biology and evolution. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L.-T.; Schmidt, H.A.; Von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: a fast and effective stochastic algorithm for estimating maximum-likelihood phylogenies. Molecular biology and evolution. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadfield, J.; Megill, C.; Bell, S.M.; Huddleston, J.; Potter, B.; Callender, C.; et al. Nextstrain: real-time tracking of pathogen evolution. Bioinformatics. 2018, 34, 4121–4123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Data in Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19). https://data.gov.hk/en-data/dataset/hk-dh-chpsebcddr-novel-infectious-agent Accessed 20 May 2023.
- Cheung, P.H.; Chan, C.P.; Jin, D.Y. Lessons learned from the fifth wave of COVID-19 in Hong Kong in early 2022. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2022, 11, 1072–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Center for Health Protection. Archives of Latest situation of cases of COVID-19. https://www.chp.gov.hk/en/features/102997.html Accessed 20 May 2023.
- Abas, A.H.; Marfuah, S.; Idroes, R.; Kusumawaty, D.; Fatimawali Park, M.N.; et al. Can the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Variant Confer Natural Immunity against COVID-19? Molecules. 2022, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christie, B. Covid-19: Early studies give hope omicron is milder than other variants. BMJ. 2021, 375, n3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsui, K.W.H.; Fu, X.; Chen, T.; Lei, Z.; Wu, H. Analyzing Hong Kong's inbound tourism: The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic. IATSS Research. 2021, 45, 440–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Song, H.; Wen, L.; Liu, C. Forecasting tourism recovery amid COVID-19. Annals of Tourism Research. 2021, 87, 103149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).