1. Introduction
The Ebola virus disease (EVD), also called Ebola haemorrhagic fever, is a highly contagious and deadly disease that is caused by four viruses within the genus Ebolavirus (EBOV) [
1]. The four viruses are
Sudan virus (SUDV),
Taï Forest virus (TAFV),
Bundibugyo virus (BDBV), and
Ebola virus (EBOV) [
1]. The EBOV was first discovered in humans during the South Sudan and Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) outbreaks of 1976 [
7,
8], and since then, several outbreaks have been registered in different parts of the world, especially in Africa as follows: DRC in 1995, 2002, and between 2018 and 2019; Uganda in 2000, 2007 and 2022; and West Africa between 2014 and 2016. EVD outbreaks usually start from a single case of probable zoonotic transmission, followed by human-to-human transmission through contact with infected body fluids or corpses [
2]. The virus causes severe and acute systemic disease with a high mortality rate. The 1995 outbreak in the DRC killed 245 out of the 317 people who were infected (a case fatality rate of 77.3%) [
3] whilst the West Africa outbreak of 2014 had a fatality rate of 52% in Sierra Leone [
4], and a fatality rate of over 50% in each of Guinea, Liberia, and Nigeria [
5]. Overall, a total of 35 EVD outbreaks have been registered in Sub-Saharan Africa in the past four decades, causing over 34 356 infections and 14 823 deaths [
6].
On 20
th - September 2022, the Uganda’s Ministry of Health, together with the World Health Organization, declared yet again another Ebola outbreak of the SUDV strain in Mubende district, Central Uganda. The declaration was followed by extensive media coverage of the event. Social media sites such as Facebook and Twitter were inundated with millions of people airing and discussing their views on the outbreak. The aim of this study is to extract, analyze, and classify Ebola-related tweets published between 20
th - September 2022 and 30
th - November 2022 using deep learning sentiment analysis techniques. It is hoped that the findings of this study will provide valuable insights to the government, healthcare organizations, the general public, and other stakeholders about public sentiments towards the EVD outbreak. By understanding the public sentiment about the EVD outbreak, responsible health organizations will be able to effectively tailor communication and health policy implementation strategies to reach out to the general public [
9,
10,
11].
Sentiment analysis, also known as opinion mining, uses natural language processing and machine learning techniques to extract, analyse and classify opinions expressed in a body of text [
12]. It has a wide range of applications, including identifying customer sentiment towards products and services, analyzing political opinions, and detecting public sentiment towards events such as natural disasters or epidemics. A total 50 000 tweets related to the September Ebola outbreak in Uganda were collected between 20
th - September 2022 and 30
th - November 2022. After preprocessing the tweets, in a manner described in a later section of the study, three deep-learning algorithms, namely Convolutional neural networks (CNNs), Long Short-Term Memory(LSTM), and Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT) are trained, validated, and tested on the resulting data to perform sentiment analysis and classify the tweets as positive, negative, or neutral. The performance of the algorithms is compared based on the most popular evaluation metrics of accuracy, precision, recall, and F-measure.
The rest of the paper is organised as follows. In Section II a brief review of the relevant literature is given. Section III discusses the data collection procedure and preprocessing done to make it suitable as input to deep learning algorithms. In addition, the section presents the models used in this study. In Section IV, the study results are given. Section V discusses the results while Section IV presents the conclusions and recommendations.
2. Related Work
Sentiment analysis has proved to be one of the most effective techniques for extracting expressed opinions from unstructured texts [
13,
14,
15]. Several studies have used the method to conduct epidemic/pandemic sentiment analysis too using lexicon-based methods, machine learning and deep learning classifiers. [
13,
22,
23,
24,
25]. Chintalapudi et al. For example, [
22] compared the performance of a deep learning Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT) model with three other machine learning models; namely logistic regression (LR), support vector machines (SVM), and long-short term memory (LSTM) in analyzing sentiments in tweets posted by India Twitter users during the COVID-19 outbreak. They reported that the BERT model outperformed the other three models at predicting sentiments, achieving an accuracy rate of 89%, compared to the accuracy rate of 75%, 74.75%, and 65% achieved by LR, SVM, and LSTM, respectively.
Furqan et al. [
17] employed five supervised learning techniques; namely random forest (RF), XGBoost classifier, support vector classifier (SVC), extra trees classifier (ETC), and decision tree (DT) in addition to the deep LSTM to identify sentiments in tweets related to COVID-19 that could be used to improve the management of the pandemic. Their results showed that Extra Trees Classifiers outperformed all other trained models with an accuracy of 93%.
Leelawat et al. [
27] examined the effectiveness of three machine learning models: decision tree, random forest, and SVM in determining the sentiments and intentions of the tweets about tourism in Thailand during the COVID-19 pandemic. The support vector machine algorithm provided the best results for sentiment analysis, with a maximum accuracy of 77.4%. In the intention analysis, the random forest algorithm achieved an accuracy of 95.4%.
Imran et al. [
15] used a deep learning LSTM architecture utilising pre-trained embedding models to find the correlation between the sentiments and emotions of people from different cultures towards during the coronavirus outbreak. Tweets from six neighboring countries, namely the USA and Canada; Pakistan and India: and Sweden and Norway were analyzed. The study found a high correlation between the polarity of tweets posted from the USA and Canada, and Pakistan and India. However, despite the many cultural similarities between Sweden and Norway, the correlation between the polarity of the tweets from these two countries was surprisingly low. This study differed from similar studies investigating sentiment analysis in that it used emotion emoticons to validate and test the models.
Yin et al. [
26] presented a framework for detecting topics and sentiment dynamics due to COVID-19 from a collection of 13 million tweets related to COVID-19 over a period of two weeks. They found that the positive sentiment showed a higher ratio than the negative sentiment during the study period and that different aspects of COVID-19 were been constantly discussed and showed comparable sentiment polarities. A topic such as “stay safe home” was dominated by positive sentiment. Others such as “people death” were consistently showing negative sentiment. Overall, the proposed framework provided insightful findings based on the analysis of the topic-level sentiment dynamics.
Martinez et al. [
32] used lexicon-based techniques on 187,349 tweets gathered from May 2020 to March 2021 to examine how COVID-19 vaccine sentiment corresponded with USA vaccine deployment. The study found that most tweets expressing positive sentiments coincided with the announcements signalling the imminent deployment of COVID-19 vaccines and that the level of positive tweets remained high at above 63% for many months thereafter.
Qin and Ronchieri [
28] utilized sentiment analysis and topic modelling techniques to investigate and analyze comments related to various pandemics such as cholera, Ebola, HIV/AIDS, influenza, malaria, Spanish influenza, swine flu, tuberculosis, typhus, yellow fever, and Zika. They found that people’s discussions were primarily focused on malaria, influenza, and tuberculosis. Kaushik and Bhatia [
29] proposed a framework for extracting tweets related to coronavirus all over the world and employed unsupervised learning techniques (K-means and hierarchical clustering algorithms) to gain insight into the situation in different countries. The study found that there were mixed emotions among people with a high degree of pessimism.
Odlum and Yoon [
30] examined and evaluated the public sentiment on HIV/AIDS from Twitter data on World AIDS Day 2013. Song et al. [
31] proposed a novel text representation model for a short-text sentiment analysis framework based on probabilistic linguistic terms and relevant theory. Their proposed framework combined both supervised learning and unsupervised learning.
3. Materials and Methods
This section describes in detail the dataset, methods, and evaluation metrics that were used during the training and testing of the sentiment classification algorithms. We utilized the Python natural language toolkit (NLTK) package for most of the preprocessing tasks[
16] as well as the in-built Python package “re” for performing regular expression operations. The classification algorithms were implemented following a series of preprocessing phases as detailed in
Figure 1.
3.1. Dataset
The dataset used in this study comprised over 13,629 tweets related to the Ugandan Ebola outbreak posted between 20th - September 2022 and 30th - November 2022. The tweets were extracted using the Twitter Search API with the Python Tweepy library. The extraction was performed using keywords such as “Ebola", “Ebola virus", “Ebola outbreak", “EVD", and “Ebola crisis". Only English-language tweets were included in the dataset.
3.2. Data Preprocessing
Preprocessing of data is a very vital step in machine learning modelling, as it affects the accuracy of the models. In this study, tweets were cleaned to remove redundant text and symbols which are generally associated with tweets, such as: stop words (e.g. a, an, as, etc.), usernames, and symbols (e.g. @, RT, #, URLs), punctuation marks, and numeric values (alpha-numeric words were not removed). The removal of these symbols and text also helps in reducing the noise in the dataset. Furthermore, duplicate tweets and tweets containing non-English words were eliminated, resulting in a reduction of the dataset from the original 13,629 tweets to 8,395 tweets. Finally, to make the data uniform and reduce noise, all the tweets were converted to lowercase [
17]. The other preprocessing tasks performed on the data are explained in the subsections below.
3.2.1. Word Tokenization
In sentiment analysis of tweets, word tokenization is the process of breaking down the text of a tweet into individual words, also known as tokens. This is a very important step in the sentiment analysis process, as it allows a language model to understand the context and meaning of each word in the tweet.
3.2.2. Token Labelling
After tokenization, the resulting tokens along with their labels are used as input to a sentiment analysis model. Token labelling assigns a label or tag to each token based on its context and meaning within the tweet [
21]. For this study, tokens were either assigned positive, negative or neutral tags using the Python NTLK package [
16]. A Negative sentiment tag typically refers to tweets expressing concerns, fear, or distress related to the Ebola outbreak. A neutral tag refers to a tweet that conveys factual information, updates, or statistics about the outbreak without expressing any emotional tone whereas a positive tag represents a tweet expressing optimism, relief, or praise for efforts towards the Ebola outbreak such as applauding healthcare worker’s successful containment measures, or supportive international aid. The overall dataset sentiment distribution consisted of 1,888 negative tokens, 2,820 positive tokens, and 3,693 neutral tokens, as illustrated in
Figure 2.
3.2.3. Stemming
Stemming is a pre-processing technique used in text processing to reduce inflected words to their root form [
18] so that words with the same stem are recognized as the same word, even if they have different endings. For example, the words “bringing" and “brought" would be reduced to the root word or stem “bring”. This technique is very useful in natural language processing tasks such as text classification and information retrieval [
19,
20].
3.2.4. Lemmatization
Lemmatization is a text-processing technique similar to
stemming, but it takes into account the context and grammatical function of a word in order to produce a valid base form, known as the
lemma [
33]. Lemmatisation aims to simplify inflected words to their base form, making them more meaningful and conveying the same meaning as the original words. It helps to match synonyms using a thesaurus. For example, when one searches for “hot" the word “warm" is matched as well.
Figure 2.
Count of the number of occurrences of each sentiment category
Figure 2.
Count of the number of occurrences of each sentiment category
After completing all the preprocessing steps, the Python library, TextBlob, for processing textual data was applied to the data to find and assign sentiment scores.
3.3. Deep Learning
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that uses neural networks with multiple layers to learn from data [
37]. In recent years, deep learning-based techniques have become popular for sentiment analysis. The most widely used deep learning techniques are CNNs [
40], LSTM [
38,
39] and Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT) [
43,
44,
45]. The following subsections provide a brief general description of the CNN, LSTM and BERT models as applied to sentiment analysis.
3.3.1. Convolutional Neural Network
Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) are one of the deep learning models used for sentiment analysis in this study. CNNs are a type of deep learning model that has been proven to be effective for text classification tasks [
34,
35,
36]. They are composed of multiple layers of neurons, with each layer performing a different operation on the input data.
The first layer of a sentiment analysis CNN model is the embedding layer, which maps each word in the input text to a dense vector representation. This allows the model to capture the semantic meaning of the words and their relationships to each other [
40]. The output of the embedding layer is passed through a series of convolutional and pooling layers, which extract features from the input text. Finally, the output of the convolutional and pooling layers is passed through a fully connected layer, which performs the actual classification. We based our implementation on the architecture proposed by [
51] but with slight modifications and adjusted hyperparameters.
3.3.2. Long Short-Term Memory
Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) is a type of Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) that is commonly used for sentiment analysis. LSTMs are designed to handle sequential data, such as text, by learning to remember information for longer periods of time [
41]. This allows them to understand the context of a sentence or a whole paragraph, which is important for determining the sentiment of the text. LSTMs are trained on large datasets of labelled text, where the sentiment of each text is labelled as positive, negative, or neutral. The model learns to identify patterns and features that are indicative of a particular sentiment by adjusting the weights of the network through backpropagation.
Compared to CNN, LSTM models are a bit more complicated to interpret due to their complex structure [
42]. In addition, LSTM models require large amounts of labelled data and computational resources to train.
3.3.3. Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers
Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT) is a deep learning model that has been used in several natural language processing tasks, including sentiment analysis [
43,
44,
45]. BERT is a transformer-based model that uses an attention mechanism to learn the context of a sentence by attending to different parts of the input text [
46]. In a sentiment analysis task similar to LSTM, BERT is trained on large datasets of labelled text. The model learns to identify patterns and features that are indicative of a particular sentiment by adjusting the weights of the network through backpropagation.
One of the key advantages of BERT is that it can be fine-tuned on a smaller labelled dataset, which is helpful when working with limited data [
47]. However, BERT requires a considerable amount of computational resources to train, and it may not be suitable for small-scale or low-resource devices.
3.4. Evaluation Parameters
We evaluated the classification performance of different algorithms using the most common evaluation metrics of accuracy, precision, recall, and F-measure.
3.4.1. Accuracy
Accuracy is a performance evaluation indicator that measures the percentage of correct predictions made by the model. It is mathematically defined as:
where;
True Positives (TP) - The number of correct positive predictions.
True Negatives (TN) - The number of correct negative predictions.
False Positives (FP) - The number of incorrect positive predictions.
False Negatives (FN) - The number of incorrect negative predictions.
3.4.2. Precision
Precision is the measure of the proportion of true positive predictions among all the positive predictions made by the model. It is calculated as:
3.4.3. Recall
Recall indicates the proportion of true positive predictions among all the actual positive examples in the dataset, and it is calculated as:
3.4.4. F1 Score
F1 Score is a harmonic mean of precision and recall, which gives equal weight to both precision and recall. It is calculated as:
3.5. Modelling
This study investigates and compares the performance of three deep learning algorithms: CNN, LSTM, and BERT on the task of deriving sentiments from tweets. The dataset utilized in this study consisted of over 8,395 distinctive tweets. To prevent the algorithms from overfitting, the dataset was divided into three sets: the training set and the testing set in a 4:1 ratio. The training set was subsequently partitioned into a validation set, which constituted 20% of the training data, and was used first, to fine-tune the hyperparameters of the algorithms and second, to evaluate the performance of the algorithms throughout the training process. A range of parameters was used to train and refine the three models - iterating through multiple rounds of training and fine-tuning until satisfactory results were achieved. The implementation details of each algorithm are discussed in the next three subsections.
3.5.1. CNN Model
The CNN model was built using six convolutional layers. Two of these layers had 32 filters, two with 64 filters, and the last two with 128 and 256 filters, respectively. Additionally, the model included a GlobalMaxPooling1D layer and a flattened layer. Dropout layers with a rate of 0.5 were incorporated into the model to ensure regularisation. These layers were subsequently connected through two dense layers to perform sentiment classification. For a comprehensive view of the parameters used during the training of the CNN model, please refer to
Table 1.
3.5.2. LSTM Model
The LSTM model architecture used in this study consisted of four main layers - an Embedding layer, two LSTM layers, one fully connected layer, and a final output layer. The Embedding layer took input data of size 20, with 100 unique words in the vocabulary, and outputted a lower-dimensional representation of size 16 for each word. The two LSTM layers had 32 and 64 neurons, respectively, with a dropout rate of 0.2 to prevent overfitting during training. The fully connected layer had 16 units, which acted as an intermediary layer between the LSTM layers and the final output layer. The final output layer consisted of three neurons responsible for classifying the sentiment of the input text using a softmax activation function.
The selection of the parameters for the LSTM model was an iterative process that involved training and evaluating the model’s performance under various conditions. After several rounds of experimentation and fine-tuning, the final set of parameters was selected. The model was trained for 10 epochs, indicating the number of times the entire training set was processed. To balance the computational efficiency and model accuracy, a batch size of 64 was used. The Adam optimizer was chosen to manage the update of the model weights, as it has been shown to be effective in optimizing deep-learning models [
48,
49]. Additionally, a learning rate of 0.0001 was set to control the step size when performing the update, as it affects the convergence speed of the model during training.
3.5.3. BERT Model
We developed a BERT-based sentiment analysis model using the “bert-base-uncased" pre-trained BERT model [
46], which comprises 12 transformer layers and 110 million parameters. Additionally, we used the corresponding tokenizer from the Python Hugging Face Transformers library.
The architecture of our BERT model involved an embedding layer followed by two BERT LSTM layers, each with 32 units and “return_sequences=True" to capture sequential information effectively. To obtain a fixed-length representation of the BERT embeddings, we applied a GlobalMaxPooling1D layer. For regularization, we incorporated a series of Dropout layers with a rate of 0.5.
Next, we employed Dense layers with varying units and ReLU activation functions to perform non-linear transformations on the extracted features. During the training process, the model underwent 30 epochs using the Adam optimizer, and the sparse categorical cross-entropy loss function was employed for multi-class classification. We kept the BERT layers frozen throughout the training to retain the pre-trained weights and limit trainable parameters, as discussed in [
50].
We utilized a batch size of 64 to optimise the training procedure and implemented early stopping based on validation performance.
3.5.4. Word Cloud
According to
Figure 3, the most frequently used words in the tweets were
ebola, lockdown, Mubende, outbreak, hospital, people, and erroneous.
4. Results
In this study, we tested and evaluated the performance of three trained deep learning models at predicting sentiment from tweeter data related to the Ebola outbreak in Uganda in 2022. The results in
Table 2 indicate that the BERT model exhibited superior performance in classifying sentiments as neutral, positive, or negative to the CNN and LSTM models. Thus, the BERT model accurately classified 480 tweets as negative, 606 tweets as neutral, and 509 as positive out of 500, 620 and 559 tweets, respectively. Meanwhile, the CNN model obtained accurate predictions for 376 out of 500 negative sentiments, 461 out of 620 positive sentiments and 455 out of 620 neutral sentiments, whilst the LSTM model achieved correct classification for 501 neutral sentiments, 479 positive sentiments and 480 negative sentiments out of 620, 559 and 500, respectively.
The results of the evaluation are presented in
Table 2.
5. Discussion
The results emphasize the effectiveness of employing transformer-based architectures, such as the BERT model, in tasks related to natural language processing, such as sentiment analysis. This indicates a transition towards more advanced deep learning techniques that have the capability to capture semantic relationships within text data comprehensively. Consequently, it opens up new possibilities for sentiment analysis, sentiment-aware content curation, and opinion mining on social media platforms.
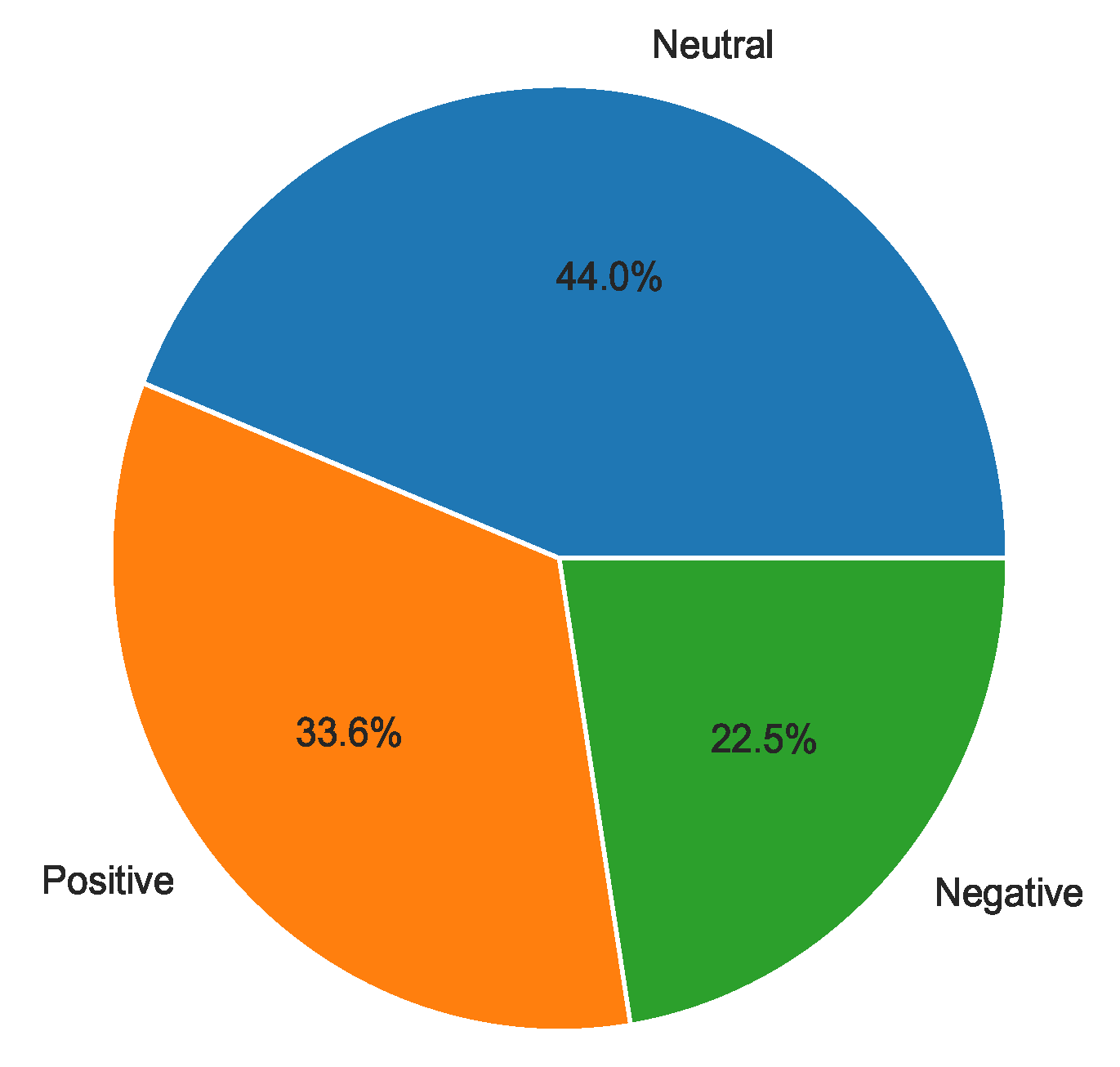
Furthermore, the study reveals that a significant proportion (44.0%) of the tweets carried a neutral tone, signifying that most Twitter users shared factual information, updates, or statistics about the Ebola outbreak without conveying any emotional bias. Meanwhile, 33.6% of the tweets conveyed positive sentiments: reflecting the optimism, relief, or praise directed towards the country’s efforts in responding to the Ebola outbreak, and 22.5% of tweets conveyed negative sentiments in which individuals expressed fear or distress.
6. Conclusions
In this study, the comparative performance of three deep learning models, CNN, LSTM and BERT, at carrying out sentiment analysis on tweeter data related to the 2022 Ebola outbreak in Uganda was investigated. The study found that the BERT model is superior to the other two models at performing sentiment analysis on several metrics, including accuracy, precision and recall.
The success achieved by the BERT model in comparison to conventional deep learning models emphasizes the importance of continuing to explore and integrate these cutting-edge deep learning methodologies. Such efforts are crucial to fully harness the potential of sentiment analysis in comprehending human emotions and opinions as expressed in online conversations, such as those on Twitter. These advancements will undoubtedly prove invaluable to health experts and other stakeholders, empowering them to make well-informed decisions during outbreaks like Ebola and COVID-19.
Considering of these findings, it is also evident that communication strategies should incorporate sentiment analysis of social media data for future outbreaks. This approach promises to enhance the effectiveness of communication efforts by tailoring them more precisely to the prevailing sentiments within the online discourse.
Author Contributions
Alex Mirugwe: Conceptualization, Data Extraction, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft. Clare Ashaba, Alice Namale, Evelyn Akello, Edward Bichetero, Edgar Kansiime: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. Juwa Nyirenda: Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
This study was not funded.
Informed Consent Statement
Regarding ethics approval and consent to participate, since this study did not involve any human or animal subjects, no ethical approval or consent was required from participants.
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
The author takes full responsibility for the content of this review paper, and it does not necessarily reflect the official views of the Makerere University School of Public Health. We also extend our sincere gratitude to Twitter for granting us access to the Twitter API, which allowed us to extract tweets beyond the free trial period typically offered. This invaluable support played a crucial role in the success of our project. Without it, our endeavor would not have been possible.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests related to this study.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| EVD |
Ebola Virus Disease |
| CNN |
Convolutional Neural Network |
| LSTM |
Long-Short-Term Memory Model ( |
| BERT |
Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers |
References
- Jacob, Shevin T., Ian Crozier, William A. Fischer, Angela Hewlett, Colleen S. Kraft, Marc-Antoine de La Vega, Moses J. Soka, Victoria Wahl, Anthony Griffiths, Laura Bollinger, and others. "Ebola virus disease." Nature reviews Disease primers 6.1 (2020): 1-31.
- Denis Malvy, Anita K. McElroy, Hilde de Clerck, Stephan Günther, Johan van Griensven Ebola virus disease, The Lancet, vol. 393, no. 10174, pp. 936–948, 2019, Elsevier.
- JJ Muyembe-Tamfum, M Kipasa, C Kiyungu, R Colebunders, Ebola outbreak in Kikwit, Democratic Republic of the Congo: discovery and control measures,The Journal of infectious diseases, vol. 179, no. Supplement, pp. S259–S262, 1999, The University of Chicago Press.
- Silvia Dallatomasina, Rosa Crestani, James Sylvester Squire, Hilde Declerk, Grazia Marta Caleo, Anja Wolz, Kathryn Stinson, Gabriela Patten, Raphael Brechard, Osman Bamba-Moi Gbabai, and others, Ebola outbreak in rural West Africa: epidemiology, clinical features and outcomes, Tropical Medicine & International Health, vol. 20, no. 4, pp. 448–454, 2015, Wiley Online Library.
- Chih-Peng Tseng, Yu-Jiun Chan, Overview of Ebola virus disease in 2014, Journal of the Chinese Medical Association, vol. 78, no. 1, pp. 51–55, 2015, Elsevier.
- Sima Rugarabamu, Leonard Mboera, Mark Rweyemamu, Gaspary Mwanyika, Julius Lutwama, Janusz Paweska, Gerald Misinzo, Forty-two years of responding to Ebola virus outbreaks in Sub-Saharan Africa: a review, BMJ Global Health, vol. 5, no. 3, pp. e00 1955, 2020, BMJ Specialist Journals.
- P Bres, The epidemic of Ebola haemorrhagic fever in Sudan and Zaire, 1976: introductory note., Bulletin of the World Health Organization, vol. 56, no. 2, pp. 245, 1978, World Health Organization.
- Alicia Rosello, Mathias Mossoko, Stefan Flasche, Albert Jan Van Hoek, Placide Mbala, Anton Camacho, Sebastian Funk, Adam Kucharski, Benoit Kebela Ilunga, W John Edmunds, and others, Ebola virus disease in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, 1976-2014, Elife, vol. 4, pp. e0 9015, 2015, eLife Sciences Publications Limited.
- Marcel Salathé, Shashank Khandelwal, Assessing vaccination sentiments with online social media: implications for infectious disease dynamics and control, PLoS computational biology, vol. 7, no. 10, pp. e100 2199, 2011, Public Library of Science San Francisco, USA.
- Tanushree Mitra, Scott Counts, James W Pennebaker, Understanding anti-vaccination attitudes in social media, Tenth International AAAI Conference on Web and Social Media, 2016.
- Viju Raghupathi, Jie Ren, Wullianallur Raghupathi, Studying public perception about vaccination: A sentiment analysis of tweets, International journal of environmental research and public health, vol. 17, no. 10, pp. 3464, 2020, Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute.
- Walaa Medhat, Ahmed Hassan, Hoda Korashy, Sentiment analysis algorithms and applications: A survey, Ain Shams engineering journal, vol. 5, no. 4, pp. 1093– 1113, 2014, Elsevier.
- Koyel Chakraborty, Surbhi Bhatia, Siddhartha Bhattacharyya, Jan Platos, Rajib Bag, Aboul Ella Hassanien, Sentiment Analysis of COVID-19 tweets by Deep Learning Classifiers—A study to show how popularity is affecting accuracy in social media, Applied Soft Computing, vol. 97, pp. 10 6754, 2020, Elsevier.
- Rohitash Chandra, Aswin Krishna, COVID-19 sentiment analysis via deep learning during the rise of novel cases, PLoS One, vol. 16, no. 8, pp. e025 5615, 2021, Public Library of Science San Francisco, CA USA.
- Ali Shariq Imran, Sher Muhammad Daudpota, Zenun Kastrati, Rakhi Batra, Cross-cultural polarity and emotion detection using sentiment analysis and deep learning on COVID-19 related tweets, Ieee Access, vol. 8, pp. 181074–18 1090, 2020, IEEE.
- CR Rao, Venkat N Gudivada, Computational analysis and understanding of natural languages: principles, methods and applications,2018, Elsevier.
- Furqan Rustam, Madiha Khalid, Waqar Aslam, Vaibhav Rupapara, Arif Mehmood, Gyu Sang Choi, A performance comparison of supervised machine learning models for Covid-19 tweets sentiment analysis, Plos one, vol. 16, no. 2, pp. e024 5909, 2021, Public Library of Science San Francisco, CA USA.
- Anjali Ganesh Jivani, and others, A comparative study of stemming algorithms, Int. J. Comp. Tech. Appl, vol. 2, no. 6, pp. 1930–1938, 2011.
- BP Pande, HS Dhami, Application of natural language processing tools in stemming, International Journal of Computer Applications, vol. 27, no. 6, pp. 14–19, 2011, Citeseer.
- Divya Khyani, BS Siddhartha, NM Niveditha, BM Divya, An Interpretation of Lemmatization and Stemming in Natural Language Processing, Journal of University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, vol. 22, no. 10, pp. 350–357, 2021.
- Mohammed Jabreel, Antonio Moreno, A deep learning-based approach for multi-label emotion classification in tweets, Applied Sciences, vol. 9, no. 6, p. 1123, 2019, MDPI.
- Nalini Chintalapudi, Gopi Battineni, Francesco Amenta, Sentimental analysis of COVID-19 tweets using deep learning models, Infectious Disease Reports, vol. 13, no. 2, pp. 329–339, 2021, MDPI.
- Harleen Kaur, Shafqat Ul Ahsaan, Bhavya Alankar, Victor Chang, A proposed sentiment analysis deep learning algorithm for analyzing COVID-19 tweets, Information Systems Frontiers, vol. 23, no. 6, pp. 1417– 1429, 2021, Springer.
- Mohammad Ehsan Basiri, Shahla Nemati, Moloud Abdar, Somayeh Asadi, U Rajendra Acharrya, A novel fusion-based deep learning model for sentiment analysis of COVID-19 tweets, Knowledge-Based Systems, vol. 228, p. 10 7242, 2021, Elsevier.
- Md Mahbubar Rahman, Muhammad Nazrul Islam, Exploring the performance of ensemble machine learning classifiers for sentiment analysis of COVID-19 tweets, in Sentimental Analysis and Deep Learning: Proceedings of ICSADL 2021, pp. 383–396, 2021, Springer.
- Hui Yin, Shuiqiao Yang, Jianxin Li, Detecting topic and sentiment dynamics due to COVID-19 pandemic using social media, in International conference on advanced data mining and applications, pp. 610–623, 2020, Springer.
- Natt Leelawat, Sirawit Jariyapongpaiboon, Arnon Promjun, Samit Boonyarak, Kumpol Saengtabtim, Ampan Laosunthara, Alfan Kurnia Yudha, Jing Tang, Twitter data sentiment analysis of tourism in Thailand during the COVID-19 pandemic using machine learning, Heliyon, vol. 8, no. 10, p. e1 0894, 2022, Elsevier.
- Zhikang Qin, Elisabetta Ronchieri, Exploring Pandemics Events on Twitter by Using Sentiment Analysis and Topic Modelling, Applied Sciences, vol. 12, no. 23, p. 1 1924, 2022, MDPI.
- Nainika Kaushik, Manjot Kaur Bhatia, Twitter Sentiment Analysis Using K-means and Hierarchical Clustering on COVID Pandemic, in International Conference on Innovative Computing and Communications, pp. 757–769, 2022, Springer.
- M. Odlum and S. Yoon, HIV/AIDS and the millennium development goals: a public sentiment analysis of World AIDS Day Twitter chat, Int J AIDS Res, vol. 3, no. 9, pp. 129–132, 2016.
- C. Song, X.-K. Wang, P.-F. Cheng, J.-q. Wang, and L. Li, SACPC: A framework based on probabilistic linguistic terms for short text sentiment analysis,bKnowledge-Based Systems, vol. 194, p. 105572, 2020, Elsevier.
- L. S. Martinez, M. W. Savage, E. Jones, E. Mikita, V. Yadav, and M.-H. Tsou, Examining Vaccine Sentiment on Twitter and Local Vaccine Deployment during the COVID-19 Pandemic, International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, vol. 20, no. 1, p. 354, 2022, MDPI.
- V. Balakrishnan and E. Lloyd-Yemoh, Stemming and lemmatization: A comparison of retrieval performances, UM Research Repository, vol. 170, no. 2, pp. 174–179, 2014.
- A. Jacovi, O. S. Shalom, and Y. Goldberg, Understanding convolutional neural networks for text classification, arXiv preprint arXiv:1809.08037, vol. 3, no. 1, p. 10, 2018.
- J. Wang, Z. Wang, D. Zhang, and J. Yan, Combining Knowledge with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for Short Text Classification, in IJCAI, vol. 350, pp. 3172077–3172295, 2017.
- P. Song, C. Geng, and Z. Li, Research on text classification based on convolutional neural network, in 2019 International Conference on Computer Network, Electronic and Automation (ICCNEA), pp. 229–232, 2019, IEEE.
- Y. LeCun, Y. Bengio, and G. Hinton, Deep learning, nature, vol. 521, no. 7553, pp. 436–444, 2015, Nature Publishing Group.
- J. Wang, L.-C. Yu, K. R. Lai, and X. Zhang, Dimensional sentiment analysis using a regional CNN-LSTM model, in Proceedings of the 54th annual meeting of the association for computational linguistics (volume 2: Short papers), pp. 225–230, 2016.
- F. Huang, X. Li, C. Yuan, S. Zhang, J. Zhang, and S. Qiao, Attention-emotion-enhanced convolutional LSTM for sentiment analysis, IEEE transactions on neural networks and learning systems, vol. 33, no. 9, pp. 4332–4345, 2021, IEEE.
- S. Liao, J. S. Liao, J. Wang, R. Yu, K. Sato, and Z. Cheng, CNN for situations understanding based on sentiment analysis of twitter data, Procedia computer science, vol. 111, pp. 376–381, 2017, Elsevier.
- Sepp Hochreiter and Jürgen Schmidhuber, Long short-term memory, Neural computation, vol. 9, no. 8, pp. 1735– 1780, 1997, MIT Press.
- Yuandong Luan and Shaofu Lin, Research on text classification based on CNN and LSTM, 2019 IEEE international conference on artificial intelligence and computer applications (ICAICA), pp. 352–355, 2019, IEEE.
- Hu Xu, Bing Liu, Lei Shu, and Philip S. Yu, BERT post-training for review reading comprehension and aspect-based sentiment analysis, arXiv preprint arXiv:1904.02232, vol. 2, no. 1, p. 12, 2019.
- Xin Li, Lidong Bing, Wenxuan Zhang, and Wai Lam, Exploiting BERT for end-to-end aspect-based sentiment analysis, arXiv preprint arXiv:1910.00883, vol. 2, no. 1910, p. 8, 2019.
- Shivaji Alaparthi and Manit Mishra, BERT: A sentiment analysis odyssey, Journal of Marketing Analytics, vol. 9, no. 2, pp. 118–126, 2021,Springer.
- Jacob Devlin, Ming-Wei Chang, Kenton Lee, and Kristina Toutanova, Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding, arXiv preprint arXiv:1810.04805, vol. 2, no. 1, p. 16, 2018.
- Moritz Laurer, W v Atteveldt, Andreu Casas, and Kasper Welbers, Less annotating, more classifying–addressing the data scarcity issue of supervised machine learning with deep transfer learning and bert-nli, May 2022.
- José Alberto Benítez-Andrades, Álvaro González-Jiménez, Álvaro López-Brea, Jose Aveleira-Mata, José-Manuel Alija-Pérez, and María Teresa García-Ordás, Detecting racism and xenophobia using deep learning models on Twitter data: CNN, LSTM and BERT, PeerJ Computer Science, vol. 8, p. e906, 2022,PeerJ Inc.
- Irwan Bello, Barret Zoph, Vijay Vasudevan, and Quoc V Le, Neural optimizer search with reinforcement learning, International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 459–468, 2017, PMLR.
- M. P., Renuka, D. K, Improving the performance of aspect-based sentiment analysis using fine-tuned Bert Base Uncased model, International Journal of Intelligent Networks, 2, 64-69,2021.
- Ouyang, Xi and Zhou, Pan and Li, Cheng Hua and Liu, Lijun, Sentiment analysis using convolutional neural network, 2015 IEEE international conference on computer and information technology; ubiquitous computing and communications; dependable, autonomic and secure computing; pervasive intelligence and computing,pp. 2359–2364,2015.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).