1. Introduction
The increased electrical energy demand from utilities resulted in the rapid development of new power networks. The reliability of the insulation of the high voltage transmission networks is vital to ensure the continuity of the electrical supply. Solid dielectrics, particularly polymers, are the backbone of high voltage insulation [
1,
2,
3]. Continuous high voltage stress can initiate localised discharges at specific sites where the electric stress is higher than the breakdown strength, leading to the deterioration of dielectric insulating materials [
4,
5,
6,
7]. The presence of a void or cavity within the insulation during the manufacturing of cable insulation, the surface roughness, or the presence of any protrusion at the interface of different layers of the power cable either because of a manufacturing fault or due to mechanical stress, alter the homogeneity of the material which affect the dielectric characteristics (specifically dielectric constant) of the material [
8,
9,
10]. Due to the non-homogeneity, highly divergent electric stress occurs around the cavity or defect, which ionizes the gas inside the cavity, and PDs are developed inside the insulation, which can lead to insulation breakdown [
11,
12,
13].
To ensure reliability and continuous electric supply, in parallel with the engineering of novel insulation materials with better dielectric strength, it is necessary to develop suitable monitoring techniques to observe the reliability and life of the power cables. Many online and offline PD detection techniques, such as chemical, electrical, and optical, are widely used to detect and locate PD events in various insulating mediums [
14]. Chemical detection techniques can only be applied offline, while electrical and optical techniques can be used online to detect PD [
14,
15,
16]. The disadvantage of the latter two techniques is that the electrical and optical signals are prone to external interference, and the interpretation of the resultant electrical or optical signal becomes very complex [
9].
The PD events also produce short duration acoustic pulses, which ultrasonic transducers can detect, and the information can be used to locate the source of these PD events [
14,
17,
18,
19]. This technique is well established in gas-insulated systems (GIS) and in systems insulated with liquids to detect the PD and locate its source but is still not fully explored in solid insulation systems. Further, the effect of scattering and reflections on a propagating acoustic pulse is a fundamental challenge in AE detection techniques, as they can attenuate the propagating signal and make the signal interpretation more complex. So far, many models have been suggested in the recent past to detect the AE from a PD event [
20,
21] in different mediums. Still, the effects of acoustic scattering and reflections on the propagating acoustic pulse are not addressed yet. This is particularly the case when employing this technique to locate PD sources in liquid insulation which is characterised by substantial reflections and scattering of acoustic pulses, as well as in underground power cables with solid polymeric insulation that can cause reflections and scattering of the acoustic signals due to the morphology of the polymers. Neglecting the effects of acoustic scattering and reflections and interpreting the attenuated acoustic signal can lead to inaccurate information about the PD event.
Hence, this article analyses the effects of reflections and scattering on the propagating acoustic pulse in the solid insulating medium. The approach can also help address the impact of reflections and scattering on the propagating acoustic pulse in other media. The findings of this study have the potential to contribute to future research involving the use of acoustic emission as a detection technique in various types of insulating mediums.
2. Acoustic Emission (AE) from Discharge
The PD event releases energy, and because of the short duration of the PD event, it creates an acoustic pressure pulse that can propagate through the material. The propagation of this acoustic pulse depends upon the energy supplied at the time of initiation and the material's response towards this propagating pulse. A simulation model was developed in electrostatic module of COMSOL Multiphysics to predict the electric field inside the spherical cavity for a 33kV high voltage cable topology. The geometric parameters considered are shown in
Table 1.
The electric field across the cavity is not uniform. It is higher around the surface facing the conductor and lower at the cavity's surface opposite the conductor. As the diameter of the cavity is much smaller than the diameter of the insulation, the percentage change in the electric field across the cavity is very small. Hence, it was assumed that the electric field across the cavity is uniform. The electric field inside the cavity estimated from the COMSOL Multiphysics model was 5.5*10
6 V/m. Further, the electrostatic energy stored in the cavity can be calculated by using the equation;
For a spherical cavity, the expression
can be represented as;
The electrostatic energy stored in the cavity was calculated using the above equations and found to be 5.6×10
-7J. It is assumed that the energy stored in the cavity is converted into a shock wave propagating through the insulation material. Further, the amount of pressure developed by this energy can be calculated using the equation below [
22];
Where V is the volume of the cavity. The pressure calculated from the above equations was . This was used to define the peak value of acoustic pulse at source to analyse the propagation characteristics of AE in COMSOL Multiphysics.
3. Finite Element Analysis model
A three-dimensional (3D) COMSOL Multiphysics model was developed using partial differential equations to analyse the propagation characteristics of the acoustic pulse. Moreover, the mathematical module was chosen from the application mode of COMSOL Multiphysics as this module provides the flexibility to specify customised mathematical equations, allowing for the precise definition of conditions governing the propagation of the acoustic pulse. From the mathematical mode of COMSOL Multiphysics, the coefficient form of the partial differential equation was selected to analyse the propagation of the acoustic pulse.
Further, the wave equation governing the propagation characteristics of an acoustic wave can be represented as;
here,
is the density of the material in kg/m
3, P(x,t) is the pressure in Pa, and S(x, t) is the acoustic source. Equation 4 was modified by changing the parameters and variables to get the PDE of acoustic wave propagation. The partial discharge was assumed to act as a point source emitting acoustic waves. This point source in the FEA model can be described as:
Here,
) is the Gaussian pulse, which can be described as:
This above equation is obtained from the acoustic model of the Gaussian pulse point source [
23]. Here,
represents the pulse width, and
f0 represents the pulse bandwidth, which is inversely proportional to the pulse width
f0 =1/
. The duration of a discharge event varies between tens and hundreds of nanoseconds. Therefore, in the simulation, the values for
can be adjusted to reduce the computing complexity. In the above model
was used and preliminary studies revealed that the pressure signal was not significantly sensitive to the pressure pulse width. The notation A represents the flow of energy away from the acoustic source in m
3/s. The value of the flow of energy defines the peak value of the acoustic pressure. The pressure value calculated analytically from equation 3 was used to determine the peak of the pressure pulse emitted from the source.
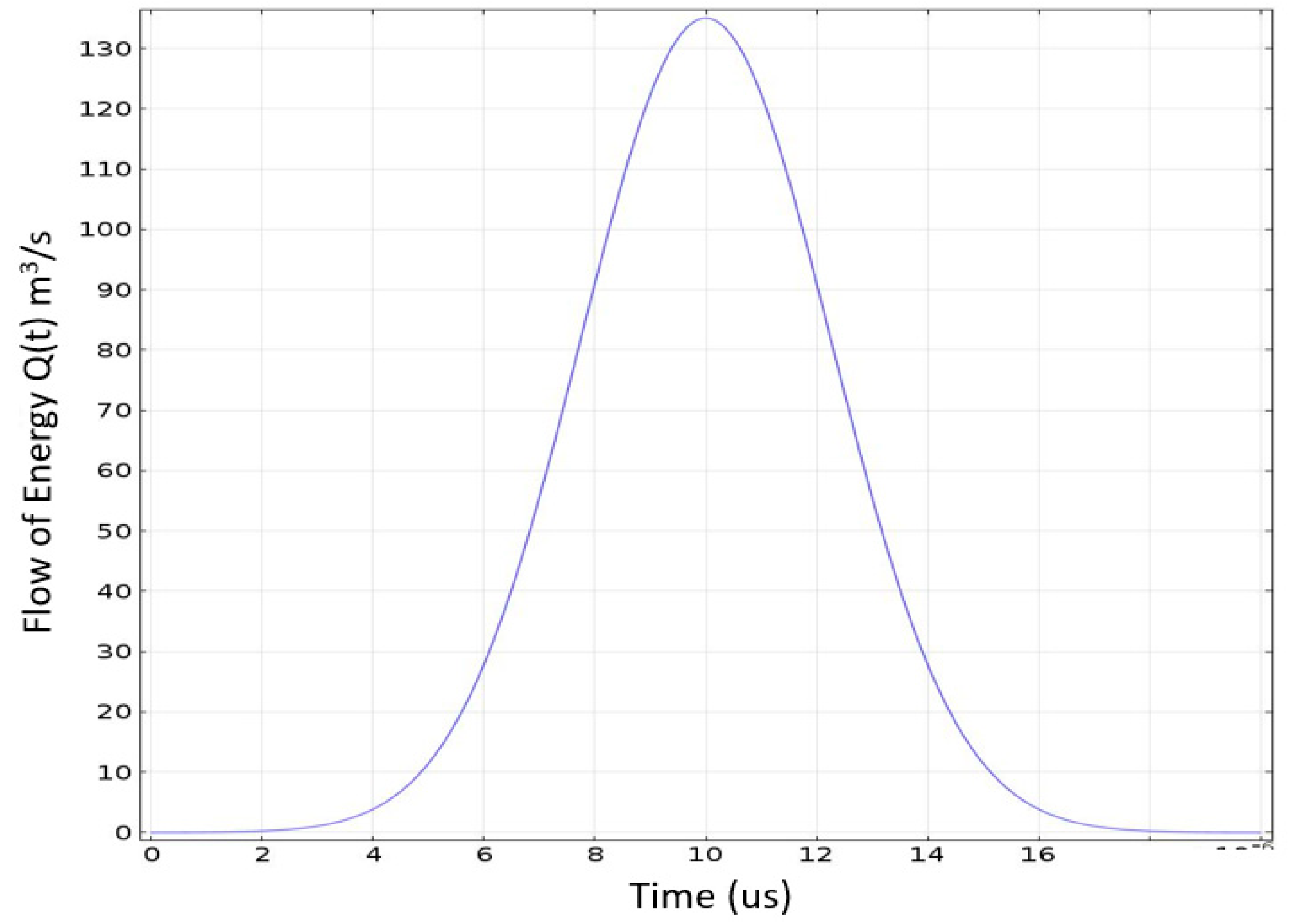
Figure 1.
The Gaussian point source excitation function at S(0, t).
Figure 1.
The Gaussian point source excitation function at S(0, t).
Meshing: The polymer domain was meshed using tetrahedral-shaped elements of quadratic Lagrange order, divided into three sets. To accurately resolve the propagation of acoustic pulses, a minimum of 5 to 6 mesh elements per wavelength is required when using quadratic Lagrange elements. The maximum mesh size was calculated analytically using the below equation [
20]:
Where
is the maximum size of the element in mesh,
is the minimum wavelength calculated at maximum frequency related to the bandwidth of the Gaussian pulse and speed of sound
in the polymer as defined in
Table 2, and N is the number of elements per wavelength. For the model,
, N=6 was considered. The maximum element size
= 0.0017m was taken for the meshing of the polymer domain.
Study and Solver: The model is computed for a time-dependent study of 1000µs using the MUMPS (Multifrontal massively parallel sparse) direct solver. To adequately resolve the propagation of acoustic pulse in the time, a minimum value of time step △t is calculated by:
CFL is a dimensionless number; it can be interpreted as the fraction of an element the wave travels in a single time step. To minimise the error, the value of the CFL number should be less than 0.2 for quadratic mesh elements [
20]. For the model, CFL=0.1 and a time step of
was considered to solve the model.
4. Simulations and Results
4.1. Cylinderical Boundary
4.1.1 Description of Model
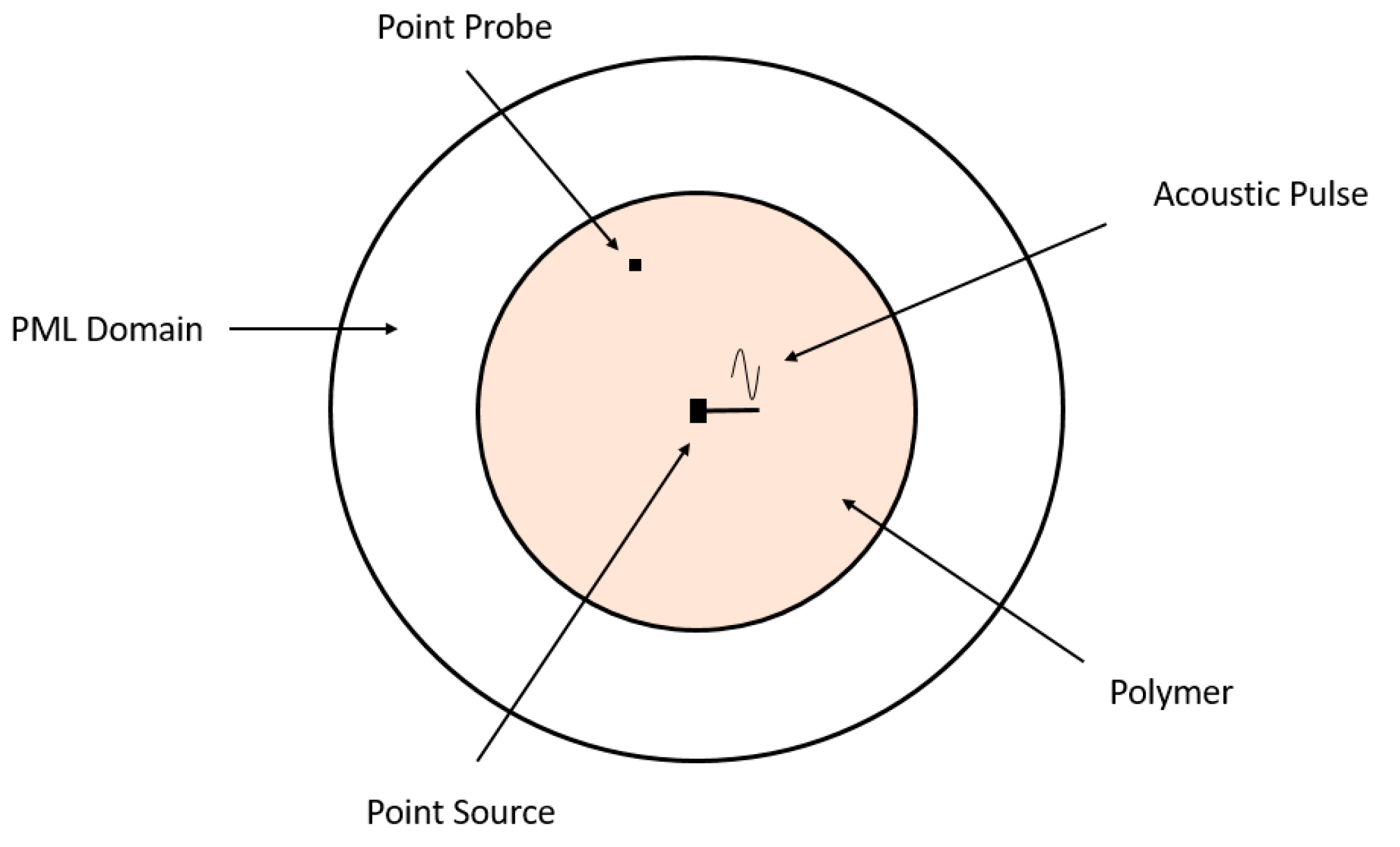
To analyse the propagation of an acoustic pulse, a cylinder with a length of 100 cm and a radius of 10 cm was modelled in COMSOL surrounded by air. A point source located at a distance of 50 cm along the axial axis was considered. The point probe was used to observe the acoustic pulse at different points inside the geometry. The materials considered during the analysis and the characteristics, are shown in
Table 2.
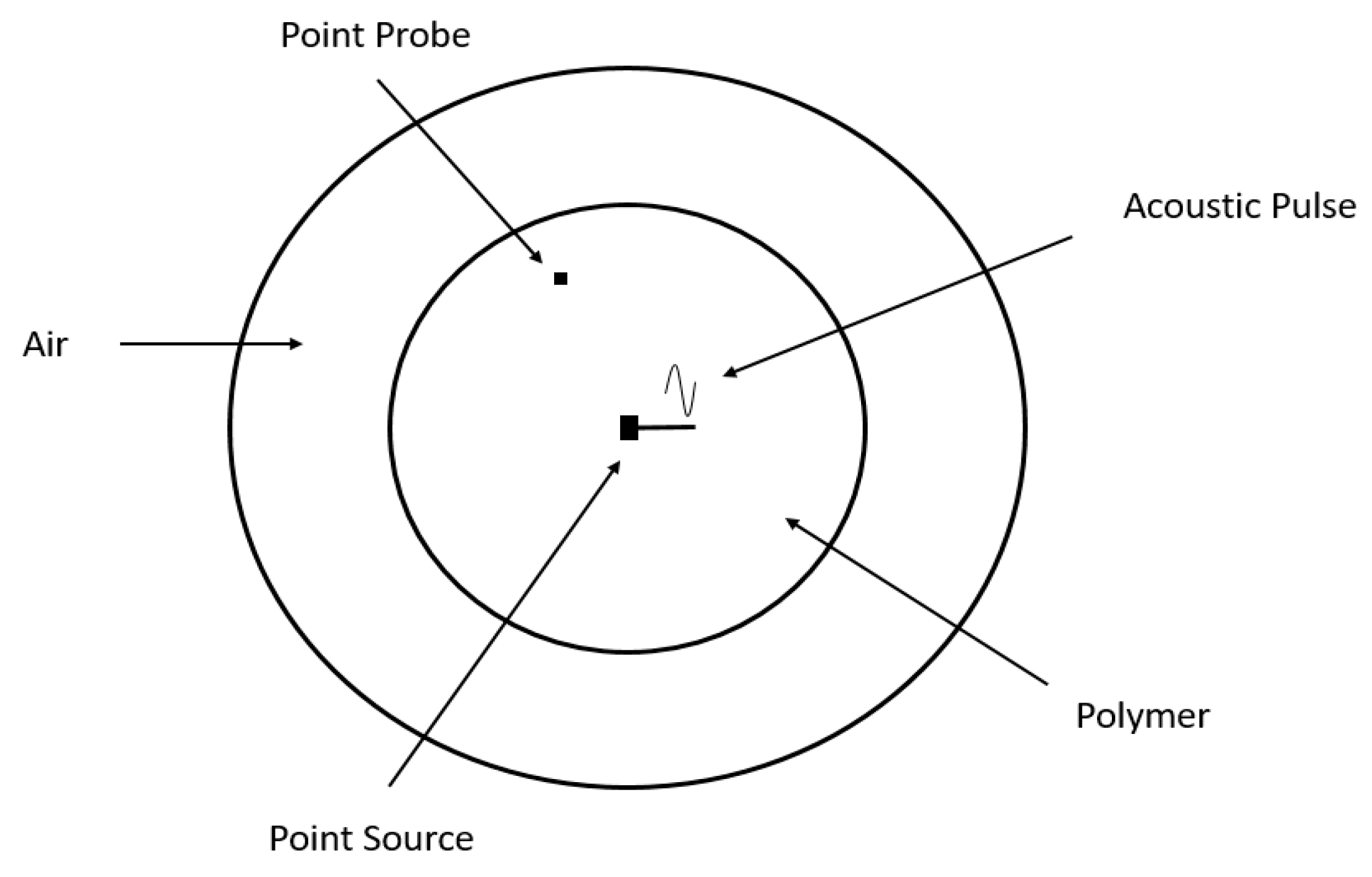
Figure 2.
XY cylindrical model geometry implemented in COMSOL.
Figure 2.
XY cylindrical model geometry implemented in COMSOL.
4.1.2 Results Obtained
The study analysed the propagation of acoustic pressure pulses generated by a point source in a cylindrical geometry at different points along the axial axis of the cylinder. The study observed that the reflections from the radial boundaries of the cylinder caused a shift in the shape and peak magnitude of the acoustic pulse. The extent of the shift in pulse shape and peak magnitude depended on the number of reflections.
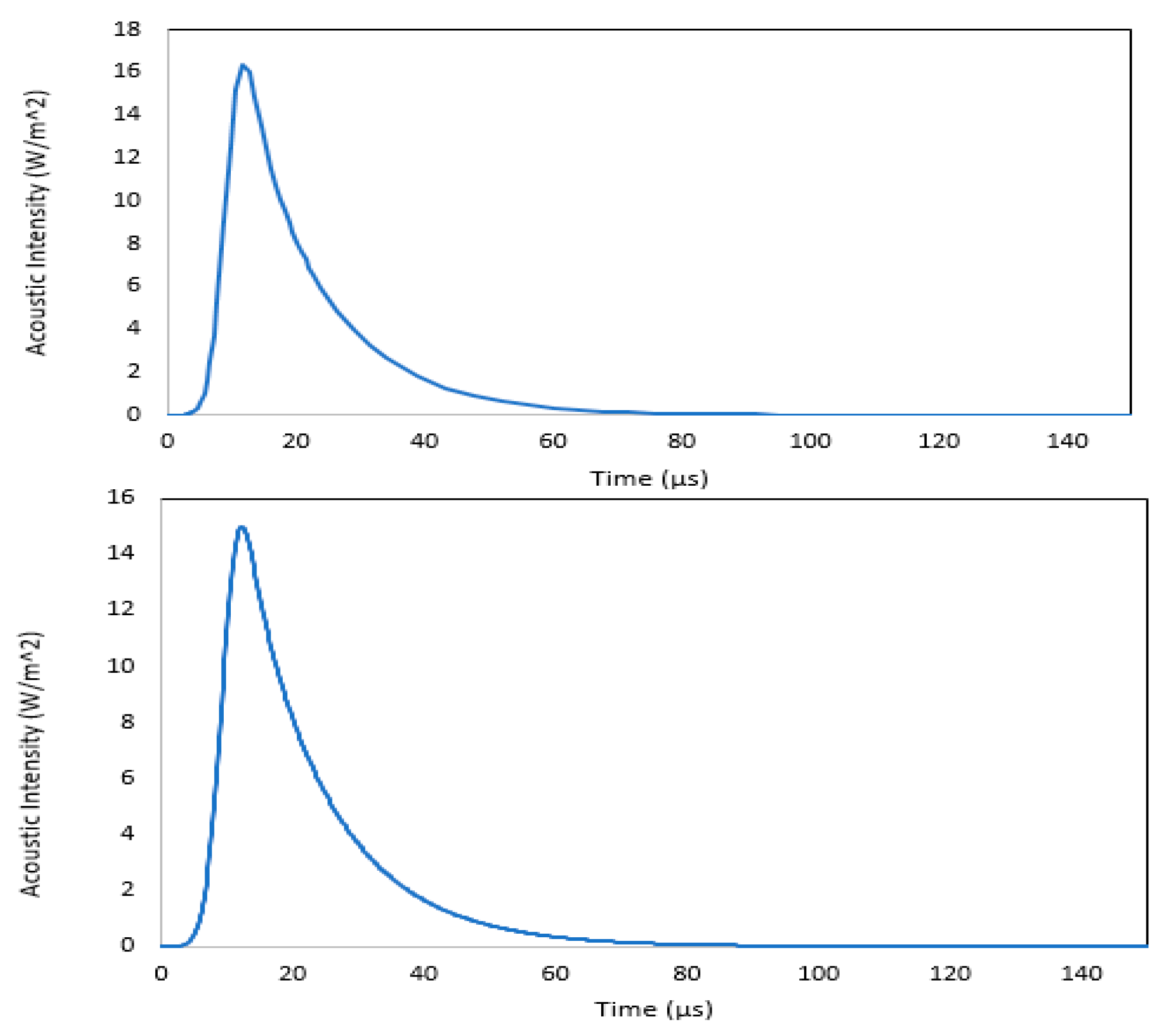
Figure 3 depicts the propagation of an acoustic pulse within a cylindrical model, specifically in polyethylene and XLPE materials. Notably, both polymeric materials exhibited noticeable distortion in the pulse shape. Furthermore, it was observed that the degree of distortion increased with distance from the source, indicating a cumulative effect of multiple reflected pulses shaping the final pulse.
4.1.3 Modelling Role of Reflections
To gain deeper insights into the impacts of reflections on the propagating acoustic pulse, additional analysis was conducted using the MATLAB pulse propagation model. This computational approach allowed for a comprehensive exploration of the effects and behaviour of the pulse in the presence of reflections.
In this model, it was assumed that i) the rod is infinite in length with no reflections occurring at the end of the rod, ii) the point of observation is assumed to lie on the axis of the rod, iii) the material is linear and lossless, iv) the pulses represent pressure, v) the base unit for time is the microsecond, and vi) the propagation velocity is constant.
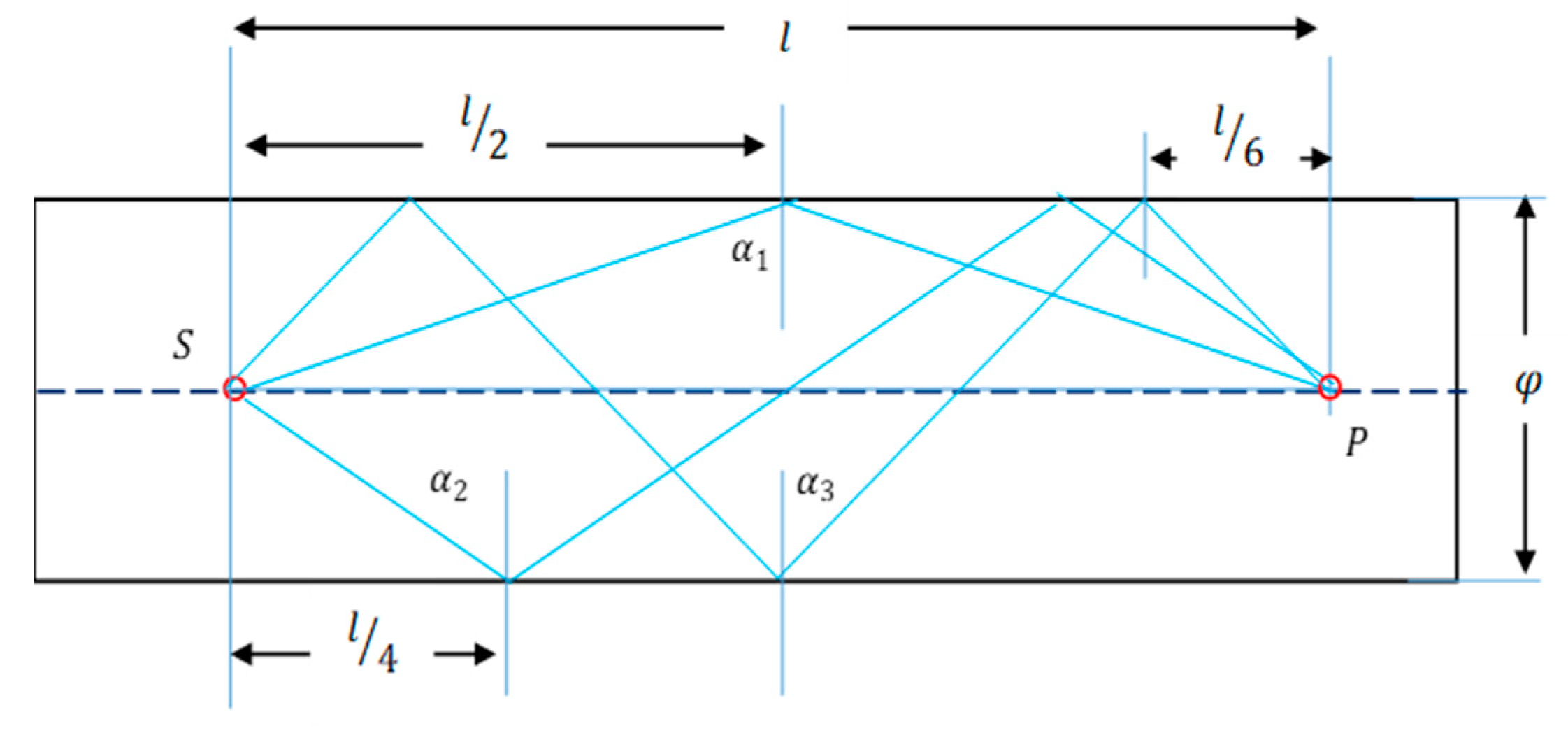
Figure 3 shows a set of 4 possible paths for pressure pulse to travel between the source ‘S’ and point of observation ‘P’.
Figure 4.
Possible paths of a pressure pulse propagation in the cylinder.
Figure 4.
Possible paths of a pressure pulse propagation in the cylinder.
The length of a path with n reflections can be expressed as;
The path length ‘
’ was defined for no reflection and the remaining path lengths were calculated using Equation 10. Further, the sin of the angle
associated with the path with n reflections can be represented as:
To estimate the pressure after ‘n’ reflections at point P, it was assumed that a pressure wave defined by the function
, propagates along each path following:
where
is the propagation velocity of the pressure wave. The pressure wave normal to the cross-section of the rod associated with a path with n reflections is given by:
If a reflection coefficient
is considered the expression can be expressed as:
4.1.4 Pulse Set Up
A trapezoidal pulse was considered and two parameters defined it: i) the pulse is non-zero and pulse width indicates the time in microseconds, and ii) the maximum amplitude of the pulse is defined as pulse ramp, and it is the time taken for the pulse to transition between zero and one. The observation point ‘P’ away from the source was used to measure the pressure, and the distance was measured in metres. Further, the propagation speed was defined in m/µs and the diameter of the rod was defined in meters. Moreover, the period of the simulation was defined in microseconds and the path index was defined to observe the reflections. Further, an array was initiated to store the temporal behaviour of the pulse on each path. The temporal behaviour for all pulses was calculated at the point of observation. The sum of individual temporal behaviour was analysed, and the output was plotted in MATLAB.
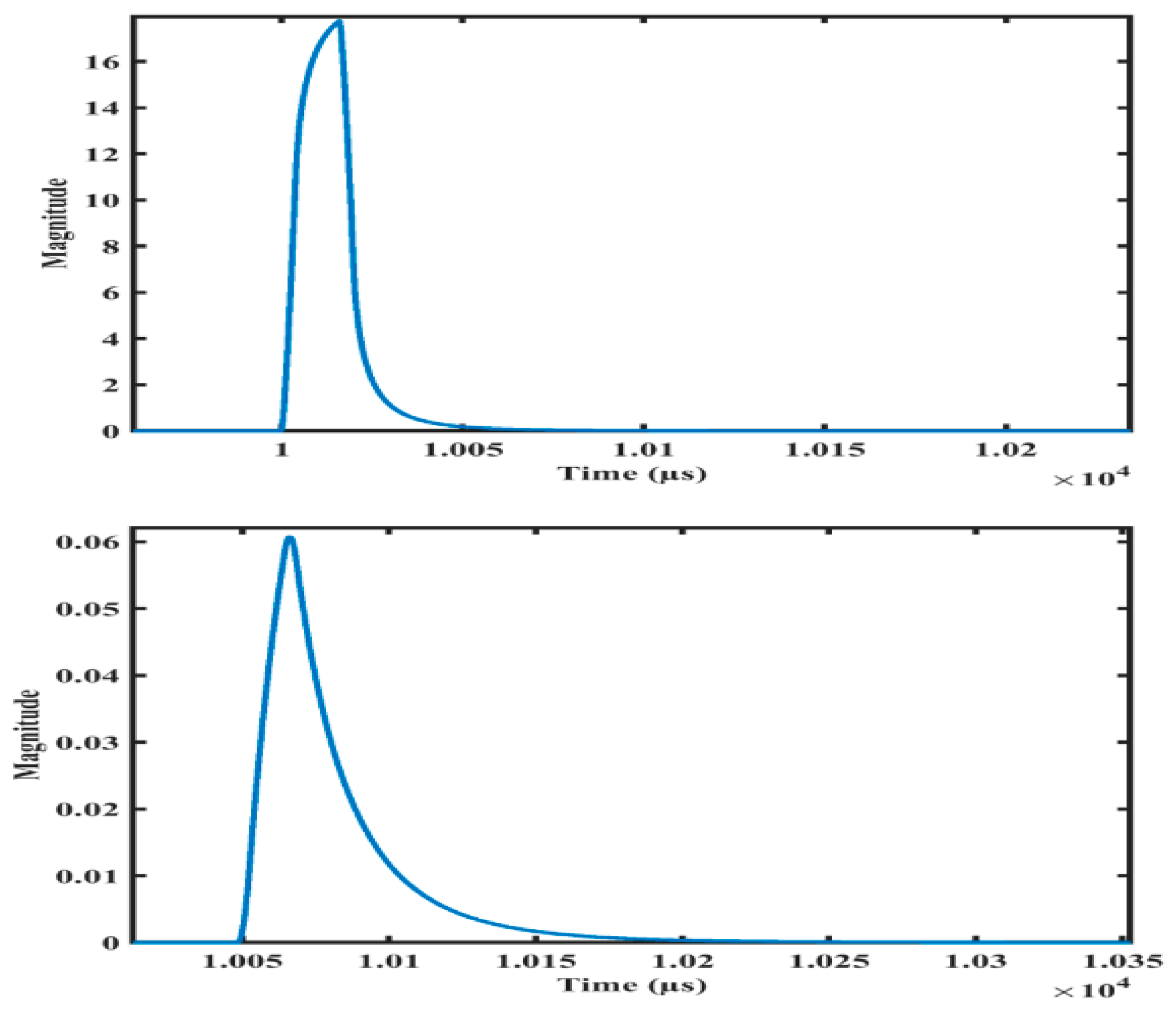
The initial simulation of pulse propagation involved configuring the model to account for a single propagation path. Upon plotting the resulting pulse, it was observed that there were no effects on the shape of the pulse. Subsequently, the model was modified to simulate the pulse propagation through multiple paths, and the output was plotted again. The results are illustrated in
Figure 5. The MATLAB model showed that the shape, peak magnitude and the arrival time of an acoustic pulse are significantly affected by the number of propagation paths considered. Therefore, detecting and locating PD in high voltage insulation materials using acoustic detection techniques, regardless of material`s state (solid, liquid, or gas), is challenging without considering the effects of multiple propagation paths or reflections phenomena. Further, the characteristics of acoustic pulse propagation cannot be accurately analysed solely based on the results obtained from the COMSOL modelling. This is because the effects of the multiple path lengths and reflections need to be eliminated to obtain a clear understanding of the true nature of acoustic pulse propagation.
Figure 5.
Acoustic pulse from MATLAB model. (Top) Number of paths =10, (Bottom) number of paths =100.
Figure 5.
Acoustic pulse from MATLAB model. (Top) Number of paths =10, (Bottom) number of paths =100.
5. Perfect Matched Layer (PML):
The perfect Matched Layer (PML) is a common technique used to absorb outgoing waves in numerical simulations of wave propagation. In COMSOL, the PML can be built for a spherical or cylindrical geometry by defining an absorbing layer that surrounds the geometric region of interest. The layer absorbs the propagating waves before reaching the numerical boundaries of the simulation, reducing the reflections. The absorption properties can be adjusted by specifying the width of the PML. Therefore, to mitigate the effects of reflections on the propagating acoustic pulse in the above model, a perfect matched layer (PML) was used in COMSOL Multiphysics. Unlike frequency domain, The PML doesn`t include any real stretching in time domain and needs an adequate setting of the layers or geometric thickness to work as an absorbing boundary for the propagating acoustic pulse.
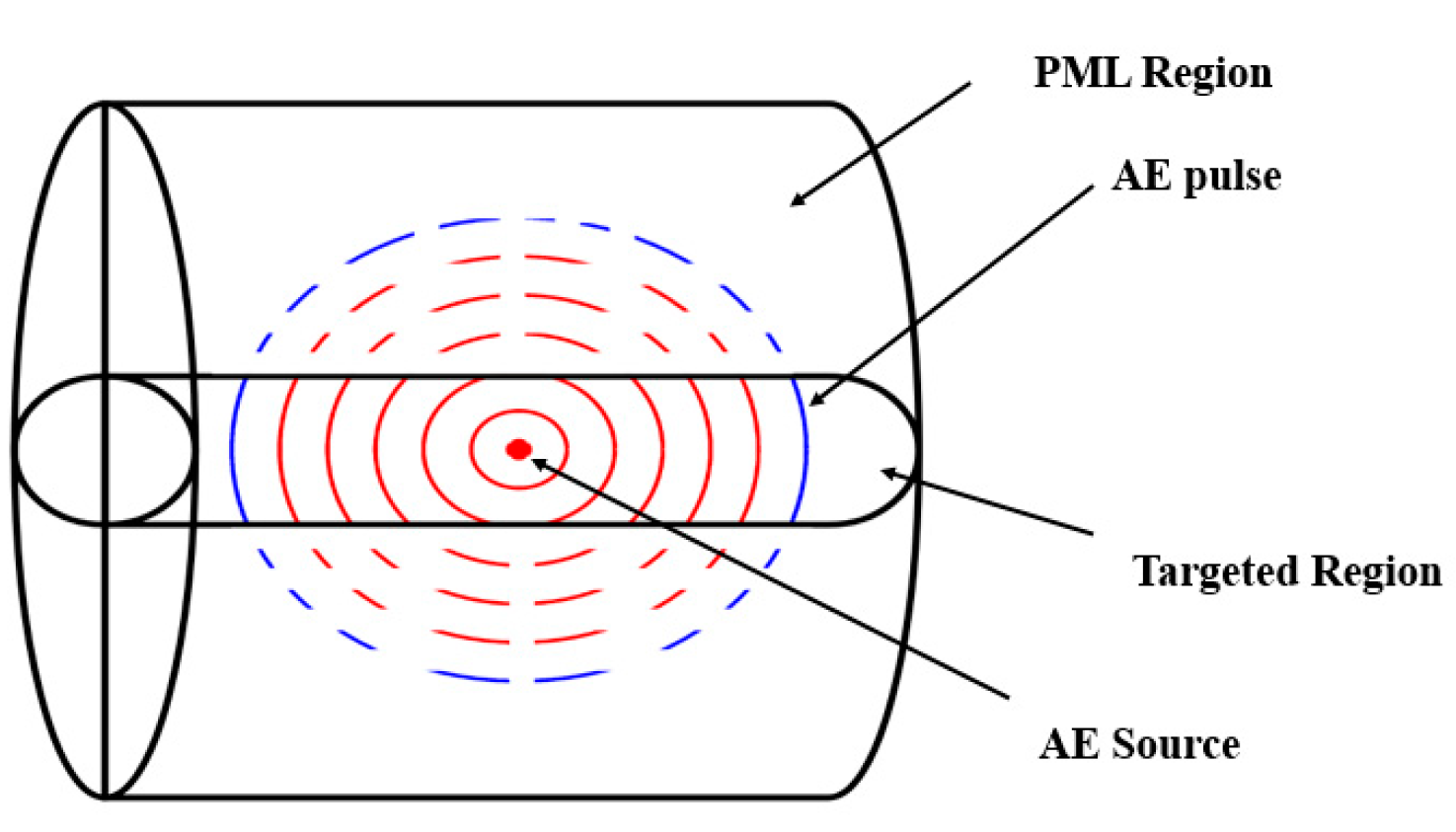
5.1 Model geometry:
In time domain analysis, adding a PML for smaller geometries is challenging due to the absence of a real stretching component. In case of a cylinder geometry with radial thickness much smaller than the length of the cylinder, implementing geometric thickness is critical. Therefore, to simplify the model, initially spherical geometry was used to analyse the performance of the PML and same approach was then used to implement the PML on cylindrical geometry.
The COMSOL model was run to observe the propagation of acoustic pulse after the implementation of PML. With the implementation of PML in the COMSOL simulation model, the distortion caused by reflections during the propagation of acoustic pulse was mitigated. This resulted in an undistorted shape of the propagating pulse, as compared with the model without PML.
Figure 7 shows the acoustic pulse detected at 40cm away from the source in cylindrical model geometry using polyethylene and XLPE. It is to be noted that in addition to the shift in the shape of acoustic pulse, there was also a noticeable damping in pulse peak magnitude when observed without the presence of PML.
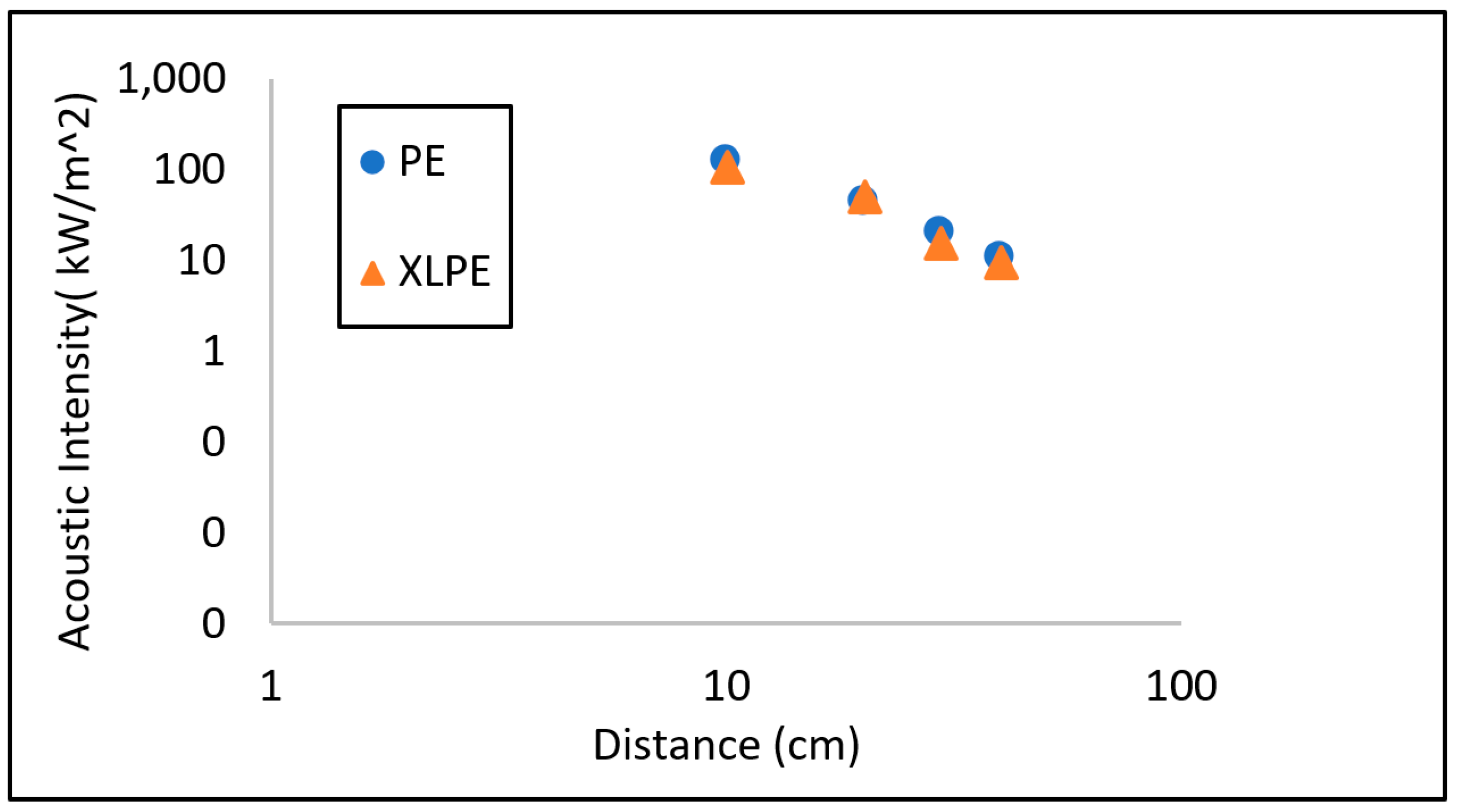
Further, the propagating acoustic pulse was analysed at different locations away from the source after the implementation of the PML to observe the drop-in magnitude of the propagating acoustic pulse. It was observed that the magnitude of the propagating acoustic pulse decreases rapidly with distance as shown in
Figure 8. This drop-in magnitude can be described by the inverse square law, where the decay is proportional to the square of the distance from the source.
6. Discussion
The MATLAB and COMSOL simulation models provide valuable insights into the propagation of acoustic pulse in polymeric insulating materials. The MATLAB model demonstrate that multiple paths of a propagating acoustic pulse can alter not only its shape and magnitude but also the arrival time of the pulse. The same behaviour was observed during the COMSOL simulation prior to applying the PML. From
Figure 5, the distortion in the shape and magnitude of the propagating acoustic pulse analysed from the COMSOL Multiphysics model without implementing the PML can be correlated to the results from the MTALAB model in terms of a shift in the shape and magnitude of the propagating acoustic pulse. However, the distortion in pulse magnitude and shape in COMSOL model is greater than in the MATLAB model. This could be due to the fact that the MATLAB model is limited to simple geometry and idealized conditions, while the COMSOL simulation allows for more realistic modelling of geometry and physical conditions.
The MATLAB simulation model revealed that multiple paths can also impact the arrival time of the acoustic pulse, a higher number of paths can cause a delay in the arrival time of the pulse. as shown in
Figure 6. This finding is significant in practical applications, particularly in locating the source of PD in transformer oil where the reflections and scattering can be high. In such scenarios, reflections or multiple paths can affect the arrival time of the pulse, which is used to estimate the location of PD source. The quantified relationship between the number of paths and delayed arrival time of the pulse can help improve the accuracy of locating the source of PD.
To further improve the accuracy of the pulse detection, the implementation of PML in acoustic pulse propagation model in COMSOL, revealed that the PML is effective in reducing reflections and preserving the amplitude of the propagating pulse. This is particularly crucial in scenarios with complex boundaries and geometries, which can cause significant interference and distortion without PML. The results revealed that the drop-in magnitude of the propagating pulse was high for both PE and XLPE as shown in
Figure 8. The significant decay in magnitude is attributed to the interaction between the emitted spherical wave front from the source and the geometry of the system. As the wave front originates from the source along the axial direction, the radial boundary of the thin cylinder serves as an absorbing boundary, causing a rapid decrease in observed intensity with distance. The increasing radius of the spherical wave front leads to a reduction in the effective portion of the wave front observed within the cylinder, while a substantial portion is absorbed by the radial boundary as shown in
Figure 9.
However, it is to be noted that the assumptions of constant acoustic properties of the materials and perfect uniform structures may not always hold in practical scenarios. Thus, future work can explore improving the pulse detection accuracy and develop more realistic and complex models that account for the variability of the materials and the impact of physical dimensions on the acoustic pulse characteristics.
Overall, the study`s findings have important implications for the practical detection of the acoustic pulses in various materials, particularly for non-destructive testing and condition monitoring applications. By accounting for the effects of reflections and multiple paths, more accurate detection techniques can be developed, leading to a better maintenance and safety practice in various industries. The study`s approach of using a spherical model and later designing a cylindrical model can also be applied to more complex geometries in practical settings.
7. Conclusions
The study used COMSOL and MATLAB simulations to analyse the propagation of acoustic pulses from a PD and their detection in polymeric insulating materials. The simulations revealed the significant impact of reflections and multiple paths on the shape, magnitude, and arrival time of the acoustic pulse. The PML technique was implemented to mitigate the reflections and improve the pulse detection accuracy. The study highlights the importance of accounting for these phenomena in practical applications, particularly non-destructive testing. Further research can explore the potential of these techniques in detecting and locating defects in various materials and developing more advanced models that incorporate additional factors such as material properties and environmental conditions, ultimately improving the accuracy and efficiency of acoustic pulse detection in real world settings.
References
- Ullah, I., et al., Impact of accelerated ultraviolet weathering on polymeric composite insulators under high voltage DC stress. CSEE Journal of Power and Energy Systems, 2020. 8(3): p. 922-932. [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.Z. and M. Akbar, Review of the performance of high-voltage composite insulators. Polymers, 2022. 14(3): p. 431. [CrossRef]
- Haque, S.M., et al., Application and suitability of polymeric materials as insulators in electrical equipment. Energies, 2021. 14(10): p. 2758. [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Z., et al. Analysis of partial discharge signals in medium voltage XLPE cables. in 2016 17th International Scientific Conference on Electric Power Engineering (EPE). 2016. IEEE. [CrossRef]
- Fasil, V. and S. Karmakar. Modeling and simulation based study for on-line detection of partial discharge of solid dielectric. in 2012 IEEE 10th International Conference on the Properties and Applications of Dielectric Materials. 2012. IEEE. [CrossRef]
- Kreuger, F.H., Partial discharge detection in high-voltage equipment. (No Title), 1989.
- Kemp, I., Partial discharge plant-monitoring technology: Present and future developments. IEE Proceedings-Science, Measurement and Technology, 1995. 142(1): p. 4-10. [CrossRef]
- Boggs, S.A., Partial discharge. III. Cavity-induced PD in solid dielectrics. IEEE Electrical Insulation Magazine, 1990. 6(6): p. 11-16. [CrossRef]
- Yaacob, M., et al., Review on partial discharge detection techniques related to high voltage power equipment using different sensors. Photonic sensors, 2014. 4: p. 325-337. [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, A.P., M. Danikas, and R. Sarathi. Understanding of partial discharge activity in transformer oil under transient voltages adopting acoustic emission technique. in 2011 6th International Conference on Industrial and Information Systems. 2011. IEEE. [CrossRef]
- AlShaikh Saleh, M., et al., The effect of protrusions on the initiation of partial discharges in XLPE high voltage cables. Bulletin of the Polish Academy of Sciences. Technical Sciences, 2021. 69(1). [CrossRef]
- Li, C., et al., Grafted UV absorber as voltage stabilizer against electrical degradation and breakdown in cross-linked polyethylene for high voltage cable insulation. Polymer Degradation and Stability, 2021. 185: p. 109498. [CrossRef]
- Mansour, D.-E.A., et al., Recent advances in polymer nanocomposites based on polyethylene and polyvinylchloride for power cables. Materials, 2020. 14(1): p. 66. [CrossRef]
- Refaat, S.S. and M.A. Shams. A review of partial discharge detection, diagnosis techniques in high voltage power cables. in 2018 IEEE 12th International Conference on Compatibility, Power Electronics and Power Engineering (CPE-POWERENG 2018). 2018. IEEE. [CrossRef]
- Refaat, S.S., et al. A review of partial discharge detection techniques in power transformers. in 2018 Twentieth International Middle East Power Systems Conference (MEPCON). 2018. IEEE. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.S., et al. Online partial discharge detection and location techniques for condition monitoring of power transformers: A review. in 2008 International Conference on Condition Monitoring and Diagnosis. 2008. IEEE. [CrossRef]
- Casals-Torrens, P., A. González-Parada, and R. Bosch-Tous, Online PD detection on high voltage underground power cables by acoustic emission. Procedia Engineering, 2012. 35: p. 22-30. [CrossRef]
- Phung, B., T. Blackburn, and Z. Liu, Acoustic measurements of partial discharge signals. Journal of Electrical & Electronics Engineering, Australia, 2001. 21(1): p. 41-47.
- Samad, A., et al. Propagation of Acoustic Pulse Due to PD in Polymeric Insulating Material. in 2023 INSUCON-14th International Electrical Insulation Conference (INSUCON). 2023. IEEE.
- Rathod, V.B., G.B. Kumbhar, and B.R. Bhalja. Simulation of Partial Discharge Acoustic Wave Propagation Using COMSOL Multiphysics and Its Localization in a Model Transformer Tank. in 2020 21st National Power Systems Conference (NPSC). 2020. IEEE. [CrossRef]
- Howells, E. and E. Norton, Detection of partial discharges in transformers using acoustic emission techniques. IEEE Transactions on Power Apparatus and Systems, 1978(5): p. 1538-1549. [CrossRef]
- Czaszejko, T. and J. Sookun. Acoustic emission from partial discharges in solid dielectrics. in 2014 IEEE Electrical Insulation Conference (EIC). 2014. IEEE. [CrossRef]
- COMSOL Acoustics Module Model Library Manual: Transient Gaussian Explosion", COMSOL, 2013.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).