1. Introduction
Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion (ALIF) and Posterior Spinal Fusion (PSF) represent cornerstone surgical techniques in the comprehensive management of degenerative disc disease, lumbar lordosis restoration, and spinal fusion [
1]. Despite sharing the common objective of achieving spinal stability, these procedures are distinguished by their unique approaches and positional considerations.
ALIF is typically performed through an anterior retroperitoneal approach, commonly in the supine or lateral decubitus position. This approach involves the insertion of interbody cages and placement of bone graft material to reconstruct and stabilize the anterior column of the spine. ALIF is often favored for its direct access to the intervertebral disc space, facilitating optimal restoration of disc height and alignment. In contrast, PSF is executed through a posterior approach, predominantly with the patient positioned prone on the operating table. During PSF, pedicle screws and rods are inserted to stabilize the posterior elements of the spine, providing additional support and stability. This approach allows for comprehensive decompression of neural elements and fusion of multiple spinal levels, making it particularly suitable for addressing complex spinal pathologies. Both ALIF and PSF have demonstrated favorable outcomes in terms of achieving spinal fusion, alleviating pain, and improving functional outcomes in appropriately selected patients. However, the choice between these procedures depends on various factors, including the location and extent of spinal pathology, patient comorbidities, and surgeon expertise.
Existing literature consistently demonstrates the effectiveness of ALIF and PSF in mitigating pain, improving functional outcomes, and reducing disability in patients with spinal degenerative conditions[
1,
2,
3,
4,
5]. The amalgamation of ALIF and PSF, often performed sequentially with ALIF in the supine position followed by PSF in the prone position, has gained prominence as a favored approach [
6]. This dual-position strategy is recognized for its ability to enhance circumferential fusion, which is a crucial objective in managing complex spinal interventions [
7].
However, the integration of ALIF and PSF techniques presents unique challenges that require careful consideration. The dual-position strategy demands meticulous orchestration to strike a balance between achieving optimal surgical outcomes and managing the complexities associated with patient repositioning [
8].
Furthermore, there is ongoing debate within the neurosurgical community regarding the optimal patient positioning for spinal fusion surgeries. While some surgeons advocate for lateral decubitus positioning as a pragmatic alternative to mitigate the challenges associated with dual-position surgery, others argue that prone PSF may optimize segmental lumbar lordosis compared to single-position surgery [
10]. These considerations underscore the importance of conducting nuanced investigations and adopting evidence-based decision-making in spinal interventions.
In this study, we aim to investigate the impact of prone positioning on segmental lumbar lordosis subsequent to anterior column reconstruction via supine ALIF. Our investigation involves detailed analysis of segmental lumbar lordosis, measured using the Cobb angle, to determine the extent of its increase when patients shift from the supine position in ALIF to the prone position during PSF. By comparing preoperative, intraoperative, and postoperative radiographic data, we seek to inform evidence-based clinical approaches, optimize patient outcomes, and drive innovative advancements within the realm of spine neurosurgery.
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design and Patient Selection
This retrospective study aimed to evaluate changes in lumbar lordosis among patients undergoing combined ALIF and PSF for degenerative lumbar diseases. The study period spanned from January 2020 to July 2023, during which time lumbar interbody fusion procedures were performed at our institution by a single surgeon. Adult patients aged 18 years and above who underwent ALIF in the supine position followed by PSF in the prone position during the same admission were included in the analysis. Exclusion criteria encompassed patients with incomplete or missing relevant imaging records and those who had undergone PSF prior to ALIF. This exclusion criterion aimed to ensure the homogeneity of the study population and minimize confounding factors related to prior surgical interventions. The retrospective design was chosen due to its ability to efficiently assess a large cohort of patients undergoing specific surgical procedures within a defined timeframe. Additionally, the single-surgeon approach ensured consistency in surgical techniques and minimized variability in surgical practices.
2.2. Data Collection
Demographic information, surgical characteristics, and radiographic data were systematically extracted from electronic health records (EHRs) for all eligible patients. The data collection process adhered to established guidelines and protocols to ensure accuracy and consistency.
Preoperative radiographs consisted of standing lateral views, providing baseline measurements of lumbar lordosis prior to surgery. The post-ALIF radiograph was obtained in the supine position, typically while the patient was under anesthesia before repositioning for prone PSF. This imaging modality allowed for the assessment of lumbar lordosis immediately following ALIF, capturing the immediate postoperative status of the anterior column reconstruction. Subsequently, the final radiograph was acquired post-PSF, with the patient in the prone position. This radiographic view enabled the evaluation of lumbar lordosis following the completion of both ALIF and PSF procedures, providing insights into the overall postoperative spinal alignment. The timing and selection of radiographic views were carefully considered to facilitate a comprehensive analysis of lumbar lordosis changes throughout the surgical process. By capturing preoperative, intraoperative, and postoperative radiographic data, the study aimed to elucidate the dynamic changes in lumbar lordosis resulting from combined ALIF and PSF.
2.3. Lordosis Measurements
Cobb angles were measured using standardized techniques between the superior endplate of the uppermost instrumented vertebral body and the inferior endplate of the lowermost instrumented vertebral body. This measurement encompassed both global lumbar lordosis (from L1 to S1) and segmental lordosis at the operated level.
Measurements were conducted at three key time points: before ALIF in the standing position, post-ALIF in the supine position, and post-PSF in the prone position. These specific time points were chosen to capture the dynamic changes in lumbar lordosis throughout the surgical process, from preoperative baseline to immediate postoperative status. Two experienced neurosurgeons independently performed the lordosis angle measurements to ensure accuracy and reliability. Inter-rater reliability was assessed using appropriate statistical methods, and any discrepancies were resolved through consensus or consultation with a third reviewer if necessary. The mean of the measurements obtained by the two neurosurgeons was used for subsequent analysis to minimize potential bias. The choice of measurement technique was based on its widespread use in clinical practice and its established reliability in assessing spinal alignment. Additionally, the selected measurement points were consistent with standard protocols for evaluating lumbar lordosis in spinal surgery research.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
The statistical analysis was conducted using the R statistical software package. To compare within-subjects means across the different time points (pre-ALIF, post-ALIF, and post-PSF), a one-way repeated measures analysis of variance (ANOVA) was employed. This statistical test was chosen to assess whether there were significant differences in lumbar lordosis measurements over the course of the surgical intervention. Post-hoc analyses were performed using Bonferroni adjustments to determine pairwise differences between the time points while controlling for multiple comparisons. This approach was used to minimize the risk of type I errors by adjusting the significance level accordingly.
Assumptions underlying the ANOVA, such as the normal distribution of residuals and homogeneity of variances, were checked to ensure the validity of the results. Additionally, potential confounding factors, such as age, gender, and diagnosis, were considered and accounted for in the analysis where appropriate. Significance was set at p < 0.05, indicating that differences between means were considered statistically significant if the probability of observing such differences by chance alone was less than 5%.
2.5. Ethical Considerations
This study involved the analysis of de-identified patient data, approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) at our institution (eProtocol #64120) prior to the commencement of the study. The IRB review process ensured that the study protocol adhered to ethical principles and regulatory requirements governing research involving human participants.
To protect patient confidentiality and privacy, all data were de-identified before analysis, with unique patient identifiers removed or encrypted to prevent identification of individual participants. Additionally, strict data security measures were implemented to safeguard the confidentiality of patient information throughout the study duration. Informed consent was waived by the IRB given the retrospective nature of the study and the use of de-identified patient data. Patients were provided with information regarding the research objectives and their rights regarding the use of their medical records for research purposes in accordance with institutional policies and regulatory guidelines. The study was conducted in accordance with the principles outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki and other applicable ethical guidelines for research involving human participants.
3. Results
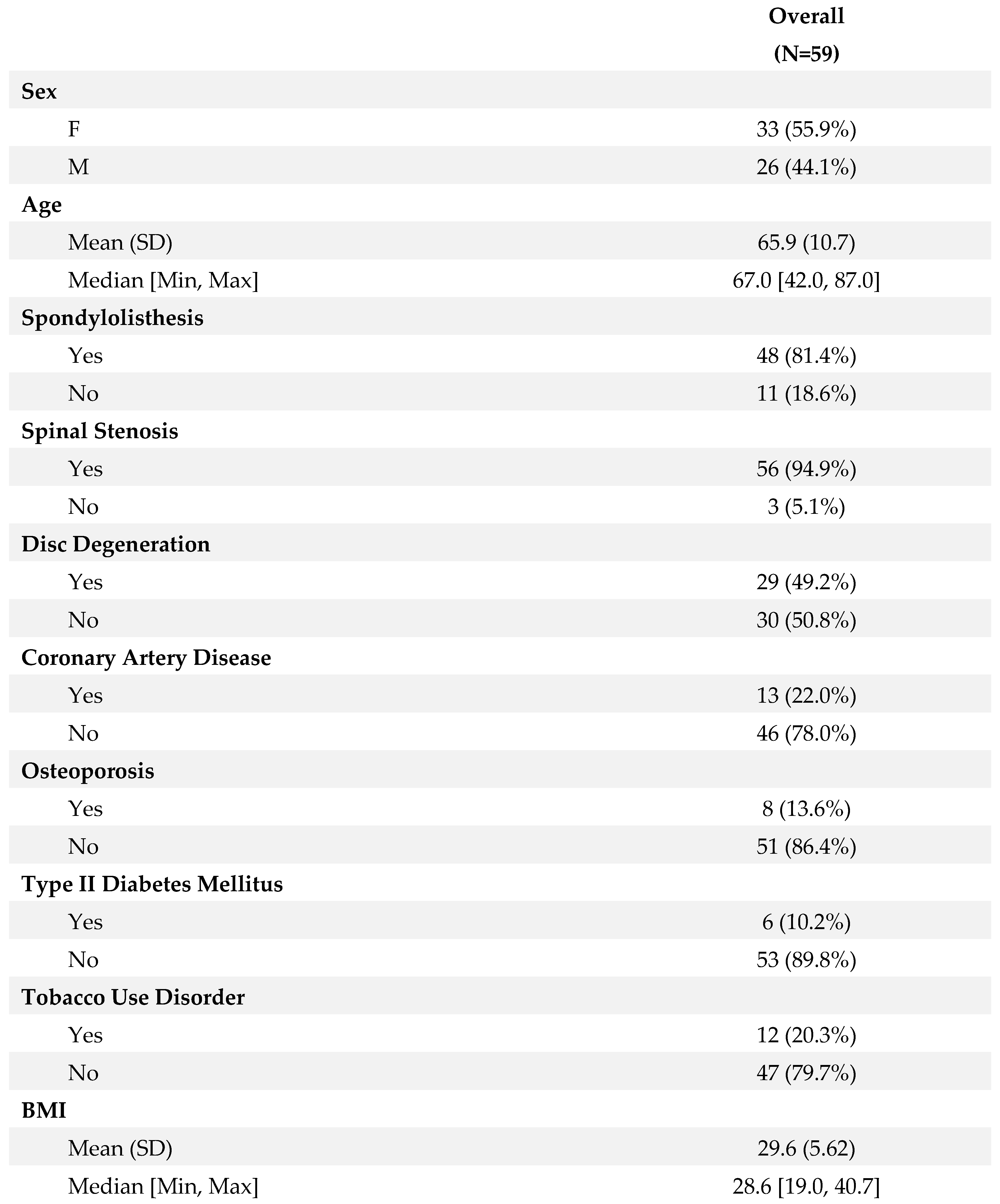
A total of 59 patients meeting the inclusion and exclusion criteria were enrolled in the study. The cohort had a mean age of 65 ± 10.72 years, with a male-to-female ratio of 0.78. The age range within the cohort varied from 45 to 85 years, reflecting a diverse patient population. Predominant diagnoses included spondylolisthesis (n=48, 81.4%), spinal stenosis (n=56, 94.9%), and disc degeneration (n=29, 49.2%). These diagnoses were established based on clinical evaluations, imaging studies, and diagnostic criteria established by relevant professional societies.
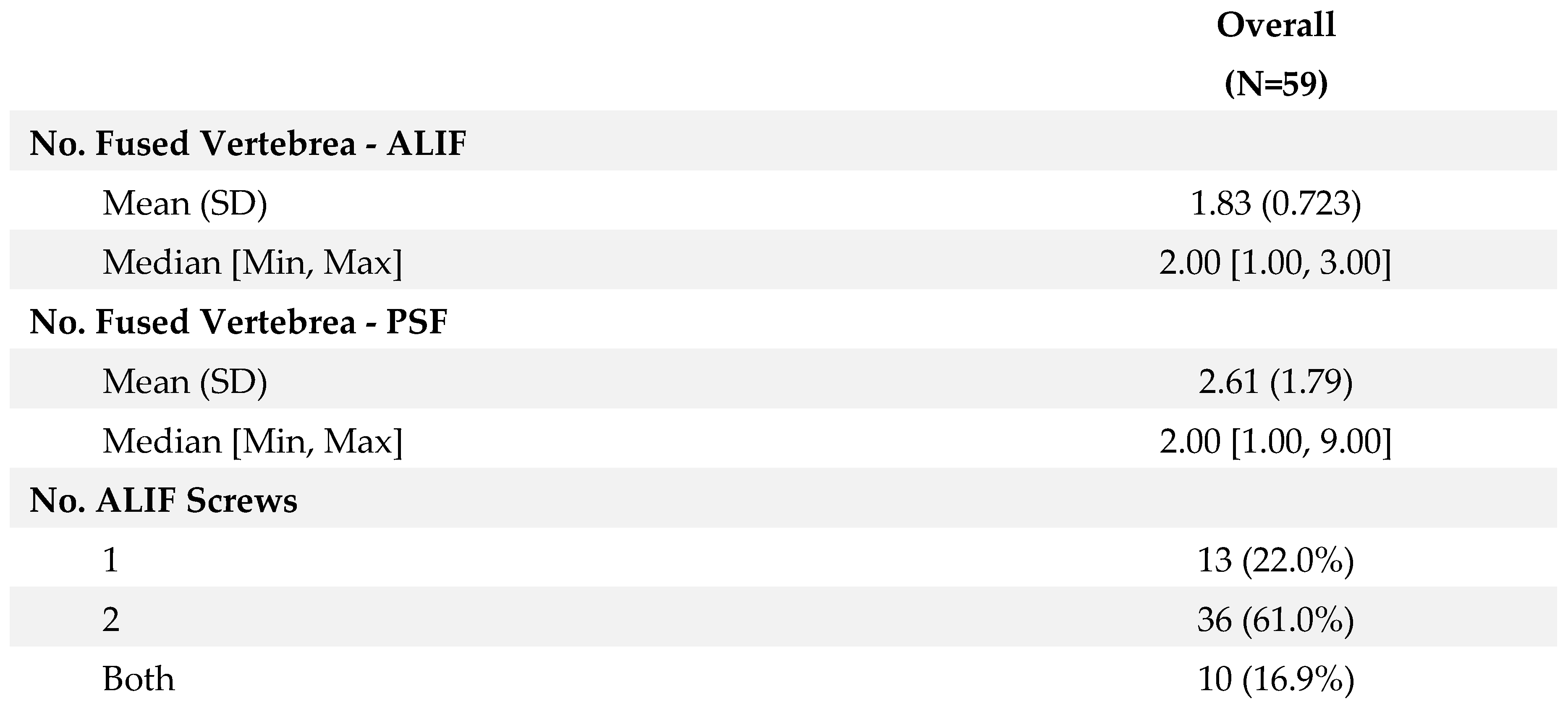
Surgical intervention typically involved fusion of an average of 1.83 ± 0.72 levels by ALIF and 2.61 ± 1.79 levels by PSF. The choice of fusion levels was determined based on preoperative imaging findings, symptomatology, and intraoperative assessment of spinal stability. ALIF constructs varied among the cohort, with 22% (n=13) receiving single screw constructs, 61% (n=36) receiving two screw constructs, and 16.9% (n=10) receiving a combination of constructs. The decision on the type of ALIF construct was individualized for each patient, taking into account factors such as vertebral anatomy, pathology, and anticipated biomechanical demands postoperatively. Detailed demographic characteristics of the patient cohort are summarized in
Table 1, while
Table 2 presents surgical details including fusion levels and ALIF constructs.
3.1. Lumbar Lordosis Measurements
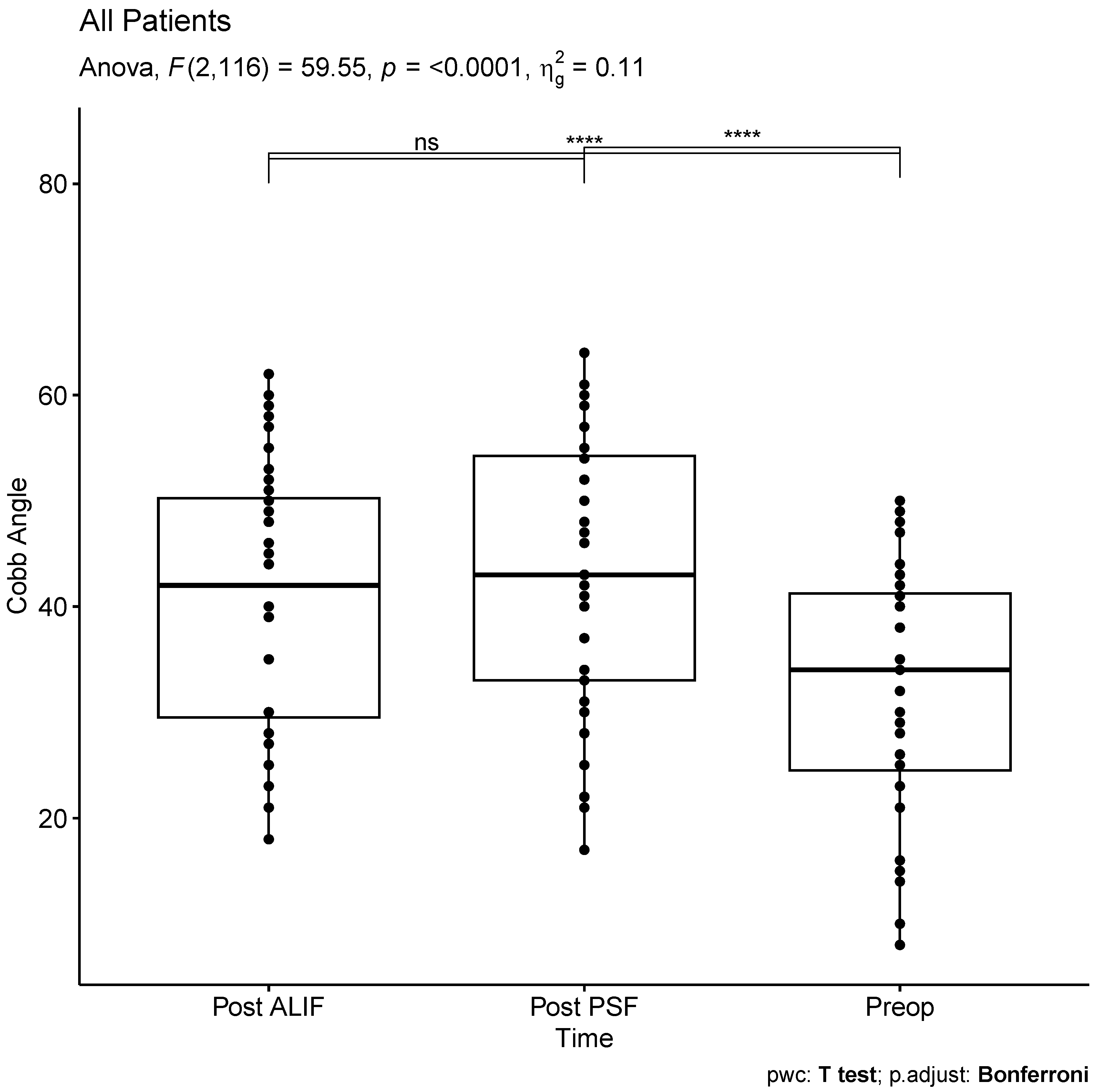
The mean preoperative Cobb angle was 32.2 ± 13.8 degrees, exhibiting a significant increase to 42.2 ± 14.3 degrees post-ALIF and further to 43.6 ± 14.6 degrees post-PSF. Notably, no extreme outliers were identified, and the angles demonstrated a normal distribution across all three time points (Supplemental
Figure 1). Statistical analysis revealed a significant difference in Cobb angles across the observed time points (F (2, 116) = 59.55, p < 0.0001, generalized eta squared = 0.11). Post-hoc analyses with a Bonferroni adjustment indicated no significant difference between Cobb angles after ALIF and after PSF (p = 0.14). Moreover, both post-ALIF and post-PSF segmental lumbar lordosis were significantly higher than the preoperative measurements (p < 0.0001 for both) (
Figure 1).
3.2. Subgroup Analysis
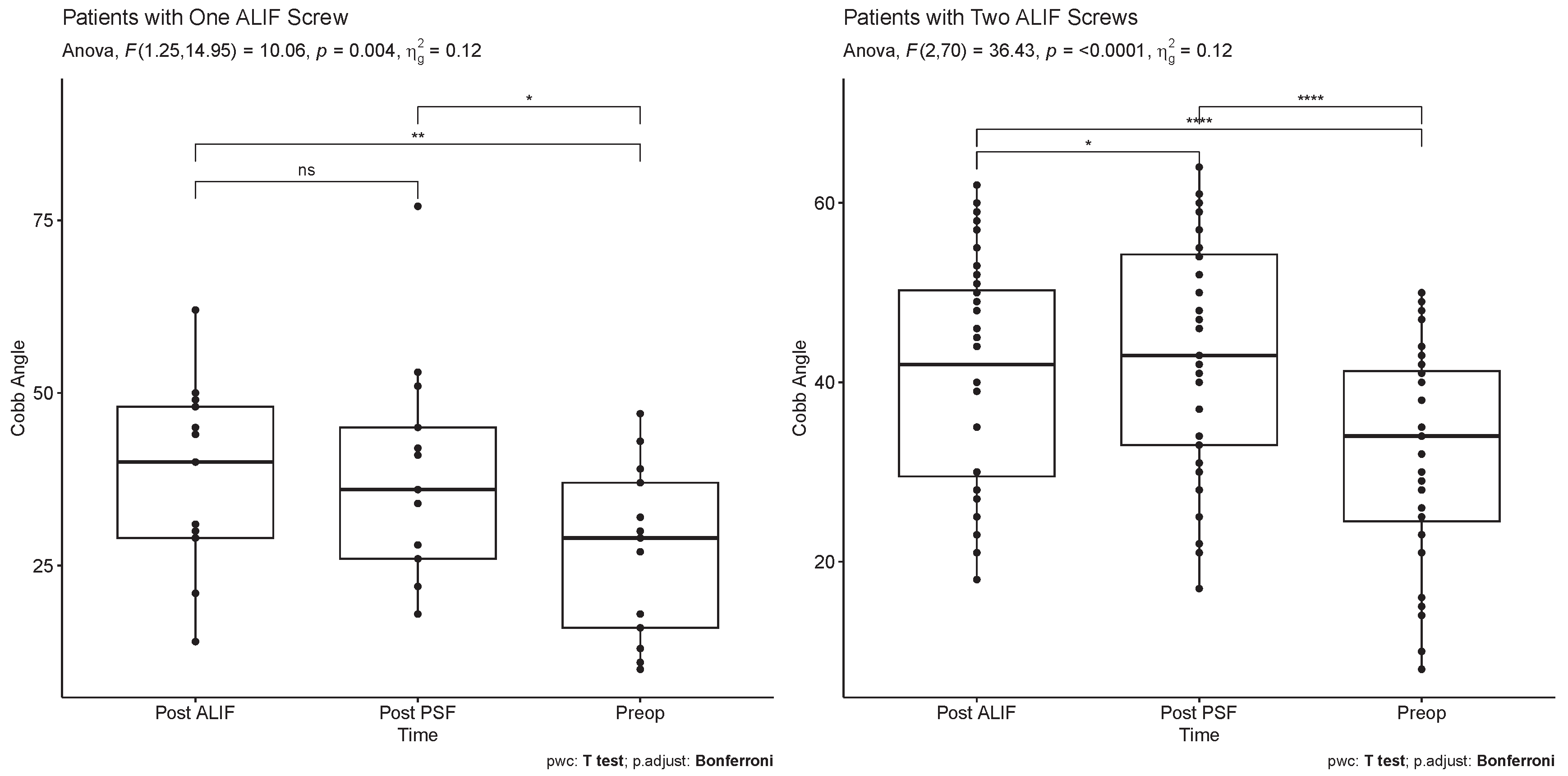
In patients with two-screw ALIF constructs, segmental lumbar lordosis demonstrated a significant increase post-ALIF (40.5 ± 12.7 degrees) and post-PSF (43.5 ± 13.1 degrees) compared to preoperative measurements (32.4 ± 12.3 degrees) (p < 0.0001 for both). Notably, post-PSF segmental lumbar lordosis was significantly higher than post-ALIF segmental lumbar lordosis (p = 0.043). Conversely, in the single-screw ALIF cohort, segmental lumbar lordosis increased significantly post-ALIF (37.2 ± 14.1 degrees) and post-PSF (38.1 ± 16.2 degrees) compared to preoperative values (27.1 ± 12.5 degrees) (p = 0.003 and p = 0.031, respectively). However, no significant difference was observed between post-ALIF and post-PSF segmental lumbar lordosis (p = 1) (
Figure 2).
Importantly, it is worth noting that while statistically significant changes in segmental lumbar lordosis were observed following both ALIF and PSF procedures, the clinical significance of these changes in terms of functional outcomes and patient satisfaction warrants further investigation. Additionally, the absence of significant demographic differences between groups and the normal distribution of angles at all time points (Supplemental
Figure 1) support the robustness of the findings.
4. Discussion
Our study delved into the intricate dynamics of lumbar spine surgery, with a particular focus on exploring positional variations during anterior lumbar interbody fusion (ALIF) followed by posterior spinal fusion (PSF). The objective was to unravel the nuances of segmental lumbar lordosis enhancement through the sequential use of supine ALIF and prone PSF techniques.
Historically, prone positioning has been conventionally favored in spinal surgeries, particularly in the context of PSF, with the belief that it optimally restores segmental lumbar lordosis [
11,
12]. However, emerging evidence and clinical experiences have prompted a reevaluation of this longstanding practice. Our analysis challenges the traditional notion surrounding prone positioning in lumbar spine surgeries and seeks to provide empirical insights into the efficacy of alternative approaches, such as the combination of supine ALIF followed by prone PSF.
4.1. Comparative Analysis: Supine ALIF versus Prone PSF
Contrary to prevailing notions, our study reveals that both supine ALIF and prone PSF result in comparable and significantly higher increases in segmental lumbar lordosis compared to preoperative measurements. This observation challenges the orthodoxy surrounding the necessity of prone positioning for achieving superior lordotic outcomes in lumbar spine surgery [
13,
14]. The comparable outcomes between supine ALIF and prone PSF suggest a potential paradigm shift in surgical approaches, offering avenues for more streamlined procedures that can reduce operative time, anesthesia requirements, and overall resource utilization.
These findings carry significant implications for clinical practice, suggesting that surgeons may have more flexibility in selecting the optimal approach for lumbar spine surgery based on patient-specific factors and surgical preferences. In addition, the potential reduction in resource utilization associated with supine ALIF may have implications for healthcare delivery and cost-effectiveness. Further research and prospective studies are warranted to validate these findings and explore their long-term impact on patient outcomes and healthcare resource allocation.
4.2. Significance of ALIF Constructs
Our investigation has yielded significant insights into the influence of different ALIF constructs on lordosis enhancement. Specifically, employing two-screw ALIF configurations led to statistically significant increases in lordosis measurements, highlighting their efficacy in achieving favorable outcomes compared to one-screw ALIF constructs. The observed consistency in lordosis levels post-ALIF and post-PSF within the one-screw ALIF group aligns with broader trends observed in the literature [
15].
This nuanced understanding underscores the pivotal role of tailored ALIF constructs customized to individual patient anatomy and pathology. By discerning the varying impact of different constructs on lordosis, clinicians can navigate surgical decision-making more effectively to optimize patient outcomes. Moreover, these findings emphasize the importance of adopting a personalized approach in spinal surgery, where treatment strategies are meticulously adjusted to each patient's unique characteristics.
Furthermore, these findings have implications for surgical planning and patient management. Surgeons may consider the use of two-screw ALIF constructs in cases where greater lordosis enhancement is desired, while recognizing that one-screw ALIF constructs may provide satisfactory outcomes in select patients. Additionally, further research exploring the biomechanical mechanisms underlying the observed differences in lordosis enhancement between diverse ALIF constructs could provide valuable insights into optimizing surgical techniques and improving patient outcomes.
4.3. Clinical Implications and Resource Optimization
Our findings carry significant clinical implications, particularly in the realms of resource optimization and patient safety. Single-position surgeries, as demonstrated in our research, offer clear advantages, including reduced operative duration, decreased anesthesia requirements, and minimized risks associated with patient repositioning. Prolonged repositioning periods have been associated with increased susceptibility to infection, blood loss, and other perioperative complications [
16]. Furthermore, prone positioning presents inherent risks, encompassing postoperative vision impairment, cardiovascular events, hypovolemia, compromised pulmonary compliance, and potential cardiac arrest [
17].
While prone positioning has traditionally been favored in spinal surgeries, our study advocates for the adoption of more efficient and streamlined surgical approaches, such as supine ALIF. By highlighting the comparable effectiveness of supine ALIF, our findings support a paradigm shift towards single-position procedures, which not only improve operative efficiency but also enhance patient safety and foster better postoperative outcomes.
However, it is important to acknowledge potential challenges associated with the adoption of supine ALIF, such as access to the surgical site or technical feasibility in certain cases. Surgeons should carefully consider the balance between reduced complications and potential drawbacks when evaluating the suitability of supine ALIF as a standalone strategy, taking into account patient-specific factors and clinical considerations.
4.4. Limitations
While our study provides valuable insights, it is imperative to acknowledge its limitations. The retrospective design inherently introduces selection bias, compounded by the absence of a control group, which may have influenced the observed outcomes. Additionally, the single-center, single-surgeon approach employed in our study may limit the generalizability of our findings to broader patient populations, as variations in surgical techniques and patient demographics across different centers may yield different results.
Furthermore, the lack of postoperative follow-up data impedes the accurate assessment of long-term outcomes, potentially limiting the comprehensive understanding of the efficacy and durability of the surgical interventions studied. It is noteworthy that emerging literature challenges the conventional requirement of prone positioning for achieving optimal lordotic outcomes, advocating alternative techniques such as XLIF, OLIF, or supine ALIF. The absence of postoperative follow-up data may have precluded the opportunity to evaluate the comparative effectiveness of these alternative techniques, which could have implications for the interpretation of our results.
Moreover, the extent of lordosis improvement observed in our study is intricately influenced by various factors, including the surgical level, prior interventions, bone quality, and utilization of osteotomies. While our study aimed to control for these factors to the extent possible, residual confounding may still exist, which should be considered when interpreting the results.
Moving forward, future research efforts must address these limitations by encompassing larger, more diverse patient cohorts, employing standardized methodologies, and incorporating long-term follow-up evaluations. Such endeavors are indispensable for validating our findings and establishing comprehensive guidelines to guide optimal surgical decision-making in spinal procedures.
5. Conclusion
In conclusion, our study challenges the traditional preference for prone positioning in posterior spine surgeries by demonstrating the comparable efficacy of supine ALIF followed by prone PSF in enhancing segmental lumbar lordosis. These findings advocate for the adoption of streamlined, single-position surgical approaches, which have the potential to reduce operative time, anesthesia requirements, and associated risks. Moreover, embracing evidence-based practices and innovative techniques is essential for driving the evolution of lumbar spine surgeries, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes and optimized resource utilization in neurosurgical interventions in spine neurosurgery.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org.
Conflicts of interest/Competing interests
Nothing to report.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
SS: MNS, and AV contributed to the conception and design of the study. SS, ES, TJ, and NJM conducted material preparation, data collection, and analysis. The initial manuscript draft was prepared by SS, with feedback provided by IL, KHY, and AV on earlier versions. All authors have reviewed and approved the final manuscript.
References
- Mobbs, R.J.; Phan, K.; Malham, G.; Seex, K.; Rao, P.J. Lumbar interbody fusion: techniques, indications and comparison of interbody fusion options including PLIF, TLIF, MI-TLIF, OLIF/ATP, LLIF and ALIF. Journal of spine surgery (Hong Kong) 2015, 1, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsarrag, M.; Soldozy, S.; Patel, P.; Norat, P.; Sokolowski, J.D.; Park, M.S.; Tvrdik, P.; Kalani, M.Y.S. Enhanced recovery after spine surgery: a systematic review. Neurosurg. Focus 2019, 46, E3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannion, A.F.; Brox, J.I.; Fairbank, J.C. Comparison of spinal fusion and nonoperative treatment in patients with chronic low back pain: long-term follow-up of three randomized controlled trials. Spine J. 2013, 13, 1438–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duggal, N.; Mendiondo, I.; Pares, H.R.; Jhawar, B.S.; Das, K.; Kenny, K.J.; Dickman, C.A. Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion for Treatment of Failed Back Surgery Syndrome: An Outcome Analysis. Neurosurgery 2004, 54, 636–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapustka, B.; Kiwic, G.; Chodakowski, P.; Miodoński, J.P.; Wysokiński, T.; Łączyński, M.; Paruzel, K.; Kotas, A.; Marcol, W. Anterior lumbar interbody fusion (ALIF): biometrical results and own experiences. Neurosurg. Rev. 2019, 43, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drazin, D.; Kim, T.T.; Johnson, J.P. Simultaneous Lateral Interbody Fusion and Posterior Percutaneous Instrumentation: Early Experience and Technical Considerations. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elgafy, H.; Vaccaro, A.R.; Chapman, J.R.; Dvorak, M.F. Rationale of Revision Lumbar Spine Surgery. Glob. Spine J. 2012, 2, 007–014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phan, K.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, J.H.; Somani, S.; Di’capua, J.; Dowdell, J.E.; Cho, S.K. Anesthesia Duration as an Independent Risk Factor for Early Postoperative Complications in Adults Undergoing Elective ACDF. Glob. Spine J. 2017, 7, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckland, A.J.; Ashayeri, K.; Leon, C.; Manning, J.; Eisen, L.; Medley, M.; Protopsaltis, T.S.; Thomas, J.A. Single position circumferential fusion improves operative efficiency, reduces complications and length of stay compared with traditional circumferential fusion. Spine J. 2020, 21, 810–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziino, C.; Konopka, J.A.; Ajiboye, R.M.; Ledesma, J.B.; Koltsov, J.C.B.; Cheng, I. Single position versus lateral-then-prone positioning for lateral interbody fusion and pedicle screw fixation. J. Spine Surg. 2018, 4, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DePasse, J.M. Complications associated with prone positioning in elective spinal surgery. World J. Orthop. 2015, 6, 351–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.-K.; Lee, S.-H.; Song, K.-S.; Park, B.-M.; Lim, S.-Y.; Jang, G.; Lee, B.-S.; Moon, S.-H.; Lee, H.-M. Lumbar Lordosis of Spinal Stenosis Patients during Intraoperative Prone Positioning. Clin. Orthop. Surg. 2016, 8, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mobbs, R.J.; Phan, K.; Malham, G.; Seex, K.; Rao, P.J. Lumbar interbody fusion: techniques, indications and comparison of interbody fusion options including PLIF, TLIF, MI-TLIF, OLIF/ATP, LLIF and ALIF. 2015, 1, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guanciale, A.F.; Dinsay, J.M.; Watkins, R.G. Lumbar Lordosis in Spinal Fusion. A comparison of intraoperative results of patient positioning on two different operative table frame types. Spine 1996, 21, 964–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sembrano, J.N.; Yson, S.C.; Horazdovsky, R.D.; Santos, E.R.G.; Polly, D.W. Radiographic Comparison of Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion Versus Traditional Fusion Approaches: Analysis of Sagittal Contour Change. Int. J. Spine Surg. 2015, 9, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manara, J.; Sandhu, H.; Wee, M.; Odutola, A.; Wainwright, T.; Knowles, C.; Middleton, R. Prolonged operative time increases risk of blood loss and transfusion requirements in revision hip surgery. Eur. J. Orthop. Surg. Traumatol. 2020, 30, 1181–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwee, M.M.; Ho, Y.-H.; Rozen, W.M. The Prone Position During Surgery and its Complications: A Systematic Review and Evidence-Based Guidelines. Int. Surg. 2015, 100, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).