1. Introduction
The production of amorphous metal granules opens avenues for creating functionally unique materials, including nanostructured variants. Techniques and equipment for generating spherical metal granules of specified sizes, characterized by rapid cooling rates during solidification, are rooted in the developed technology of the film flow granulation. Cooling rates during solidification have reached up to 10
4 degrees Celsius per second, resulting in the formation of amorphous metal structures. The impetus for advancing granulation technology stems from Ya.I. Frenkel's theoretical assessments of iron's strength properties, suggesting potential strength increases by orders of magnitude [
1].
Conventional metallurgical processes often lead to diminished metal properties due to slow cooling rates, promoting the formation of large crystals instead of fine amorphous structures. Granular technology in materials science relies on uniform, amorphous particles of similar sizes and high cooling rates to prevent the formation of large crystals, which can drastically reduce metal quality. Compared to powder metallurgy, which yields particles of varying sizes through slower cooling rates, granular technology offers superior material properties. Consequently, small granule sizes are typically preferred, barring specialized applications outside the realm of material science.
Our research has yielded highly efficient processes and promising technological devices, leveraging the previously developed theory of parametrically controlled film flows and the discovery of three new phenomena governing controlled flow disintegration into droplets, followed by rapid solidification into granules [
2,
3,
4,
5]. The paper elucidates the underlying physical processes driving this effective granulation technology and outlines the scientific novelty in developing principles and optimal regimes for producing amorphous granules, essential for creating super hard and functionally unique composite metals. Various technical and technological applications for the developed methods are presented and discussed.
While the phenomena of jet and film flows and their disintegration into drops have been known for over a century, the work over the past 50 years has advanced a new theory of parametrically controlled jet and film flows [
2,
3,
4,
5]. This has led to the development of novel technological processes and patented methods and devices for materials granulation, with successful implementation in metallurgical and other industries [
6,
7,
8,
9,
10]. For instance, granulation machines operating on the principle of electromagnetic resonance disintegration of jet flows at their first Eigen harmonics of instability produce strictly spherical granules of predetermined sizes starting from 1 mm. The size of granules is dictated by the frequency of the applied electromagnetic force.
Since the early 1980s, we have pioneered a new theory focusing on the controlled disintegration of film flows into drops as an alternative to jet disintegration. This was motivated by addressing the primary drawbacks of jet granulation machines, namely their relatively low productivity and the production of granules larger than 1 mm. In the development of a new granulation machine based on controlled film flow disintegration, several crucial challenges were addressed:
Parametric control of the disintegration of the liquid metal film flow into drops of predetermined size (dispersing node).
Achieving high cooling rates for the drops (up to 104 Celsius degrees per second).
Ensuring protection of the melt against oxidation within the working chamber of granulation.
Key accomplishments include:
Development of theory and methods for parametric excitation of oscillations on film flow surfaces under the influence of electromagnetic fields and vibrations.
Theoretical prediction and experimental validation of three new phenomena related to film flow disintegration into drops using alternating electromagnetic fields and vibration: resonant electromagnetic decay of film flow, vibration soliton-like regime, and shock-wave regime, resulting in drops with a narrow size distribution.
Establishment of experimental facilities for rapid cooling of drops, enabling the production of amorphous nanostructured granules for materials with unique properties.
These findings represent significant advancements in the field of metal granulation, particularly for producing amorphous materials, and hold promise for diverse theoretical and practical applications. They offer valuable insights for scientists involved in developing theories of controlled film flow and in the design and implementation of granulation machinery for industrial purposes.
At the Institute of Electrodynamics of the Ukrainian National Academy of Sciences [
7,
8,
9,
10,
11,
12,
13], engineering applications were furthered, including the development of new methods and devices for granulating liquid metals. The electromagnetic batching installations, designed for metal alloys with melting temperatures up to 10
3 degrees Celsius and slightly higher, operate based on jet disintegration using the first mode of Eigen oscillations. By applying crossed electric and magnetic fields at the nozzle, we achieve a resonance regime with the frequency of the alternating ponderomotive electromagnetic force matching that of the jet's Eigen oscillations. The magnetic field is generated by a permanent magnet, while the melt at the nozzle is subjected to an industrial frequency of 50 Hz.
The installation comprises several essential components, including an induction furnace, a liquid-metal pump for transporting melt through a channel to the electromagnetic batcher, and a droplet crystallizer for producing granules. The electromagnetic batcher facilitates controlled capillary disintegration or fragmentation of a cylindrical jet of liquid metal within the frequency range of 100 to 400 Hz (with an electromagnetic force frequency of 100 Hz, generated by applying a 50 Hz electric current). The diameter of the metal particles (granules) is determined by the resonant frequency of the jet's first harmonics, approximately given by ω=0.23u/d for low-viscosity melts, where u represents flow velocity and d represents nozzle diameter. The diameter of spherical particles produced due to jet decay is roughly estimated as dp=1.88d.
As capillary forces increase inversely with nozzle diameter reduction, controlled jet disintegration is feasible up to a nozzle diameter of about 1 mm. Beyond this threshold, the Coanda effect disrupts the jet's strictly vertical flow, leading to chaotic directional flow from the nozzle. Additionally, even minor accidental clogging of the melt with impurities can disrupt the jet flow regime, halting the granulator's operation. Consequently, jet-type granulators face limitations on resulting particle size, typically around 2 mm in diameter, despite their ability to produce nearly ideal spherical granules of uniform size. This limitation poses challenges for both particle size control and productivity.
Granular technology often necessitates particles smaller than this limit, sometimes significantly below 1 mm. Hence, the theory of parametrically controlled disintegration of liquid metal film flows was developed, and methods and devices for film granulation were invented [
7,
8,
9,
10,
11]. These devices produce granules typically ranging from 0.5 to 1.5 times the average size, with practically no limitations on granule size down to the micrometer scale.
Theoretical developments in the control of liquid metal film flows and their disintegration into particles of predetermined sizes have been ongoing since the early 1980s. Various phenomena related to parametric excitation and damping of oscillations, especially concerning rapidly spreading films on surfaces, have been extensively studied. The results of theoretical and experimental investigations have enabled the design and successful testing of promising new metal granulators and other devices for applications in material science and engineering. These developments are underpinned by three new phenomena discovered by our research team, forming the foundation of our work.
2. Parametrically Controlled Film Flow Granulation of Metals
Below is a description of the principles underlying the innovative film flow granulation machines for zinc, aluminum, magnesium (Zn, Al, Mg), and their alloys, which have been developed and introduced by the author in collaboration with colleagues. These machines represent a groundbreaking advancement with no equivalents in global practice.
2.1. Electromagnetic Resonant Disintegration of Film Flows
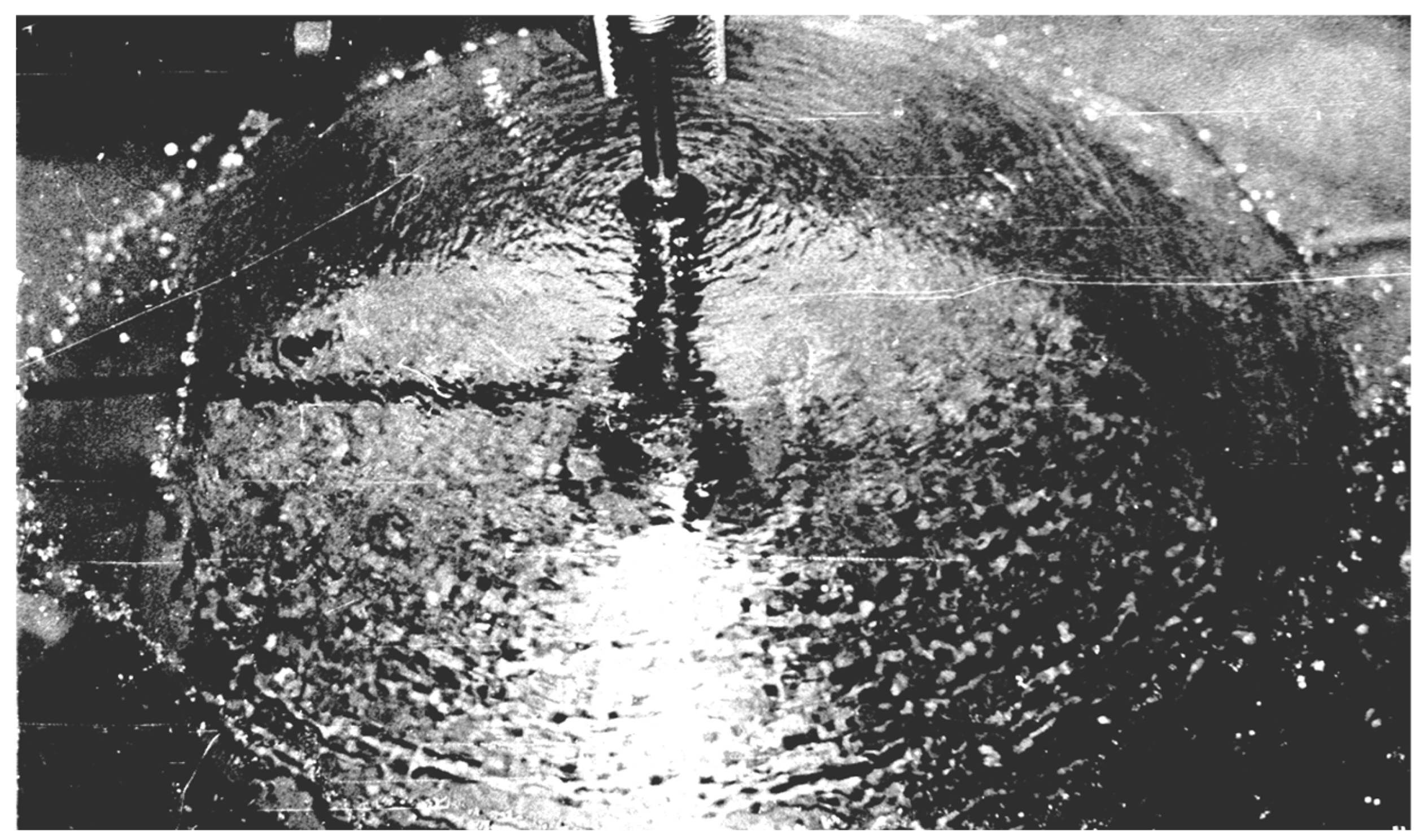
The formation of a thin film flow resulting from the shock of a jet on a horizontal plate represents an intriguing phenomenon [
14], illustrated in
Figure 1.
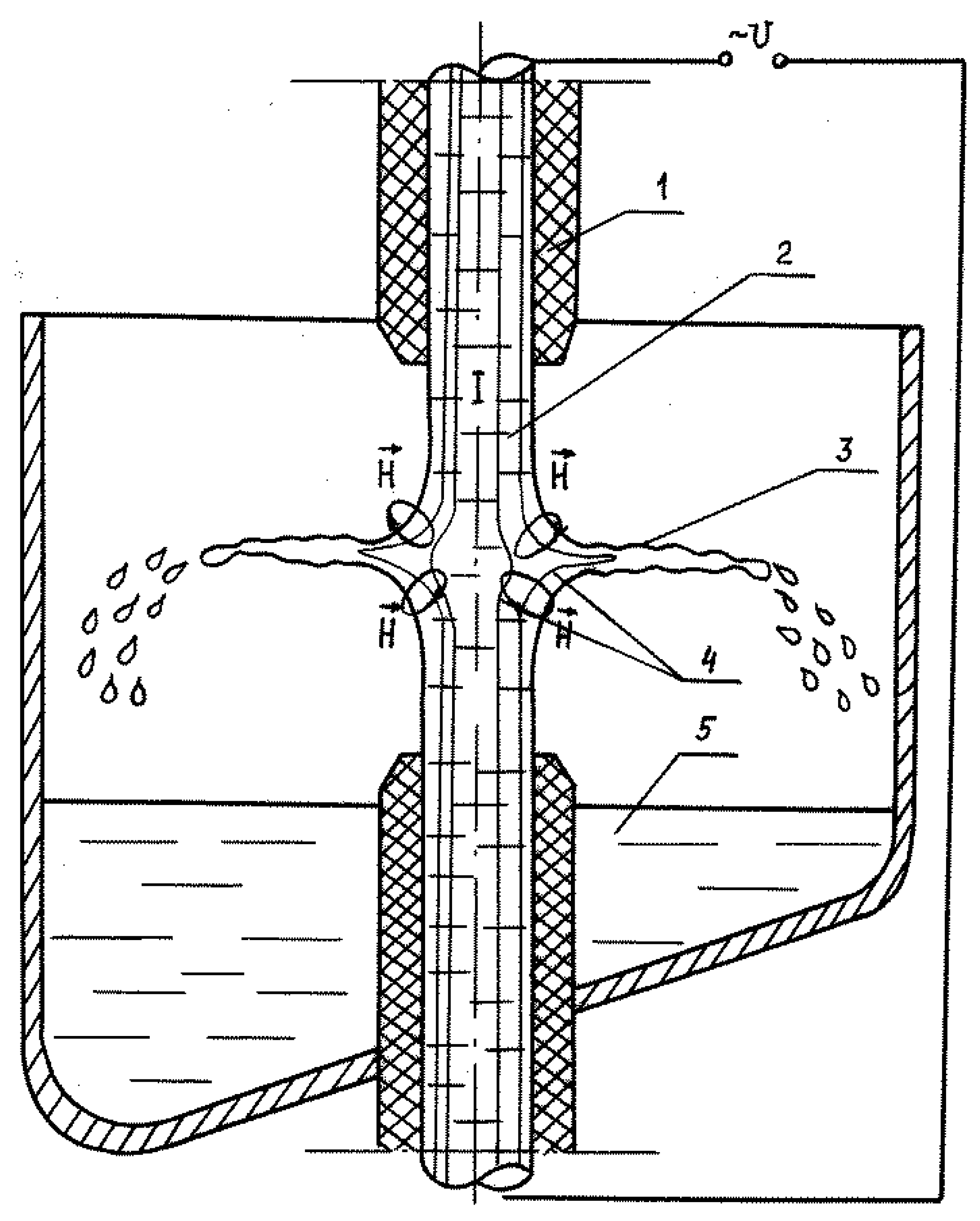
Unlike jet flow, the film flow overcomes a key limitation of jet devices by allowing for droplet size control through the disintegration of the film flow rather than the jet flow from the nozzle. Another configuration of the film flow can be achieved by employing two counter-current high-speed jets (colliding shocks of two jets) from the nozzles 1, as depicted in
Figure 2. The electromagnetic control of the film flow 3 disintegration process is facilitated by applying alternating current I to the jets 2. A coolant 5 is situated at the bottom of the chamber to solidify the drops into granules. The alternating electromagnetic force arises from the interaction of the electric current with the induced magnetic field (H represents the strength of the induced magnetic field).
The first novel phenomenon we theoretically elucidated and experimentally confirmed was the controlled disintegration of film flow into drops of predetermined sizes, followed by their rapid solidification into granules, as illustrated in
Figure 3. Several methods enable the controlled disintegration of film flow into drops. For instance, the film flow on a horizontal disk can be segmented into separate jets, which are subsequently disintegrated in a resonance regime by an applied electromagnetic field from an induction coil positioned above the vertical jet. This method boasts low energy consumption because the frequency of the alternating electromagnetic field corresponds to the first harmonics of the Eigen oscillations in a series of jets on the disk. This regime enables the production of granules within a slightly broader size range and with significantly higher productivity compared to jet machines [
6,
12,
13].
Figure 3 illustrates the generation of a series of drops and granules instead of individual drops emerging one by one from the nozzle. Unlike jet granulation machines that produce spherical granules of uniform size, here, the distribution of sizes around the average size exhibits a deviation of plus or minus no more than 50%, which is entirely acceptable for granulation technology.
2.2. Disintegration of Film Flows Controlled by Vibration
2.2.1. Soliton-like Regime of the Controlled Film Flow Disintegration
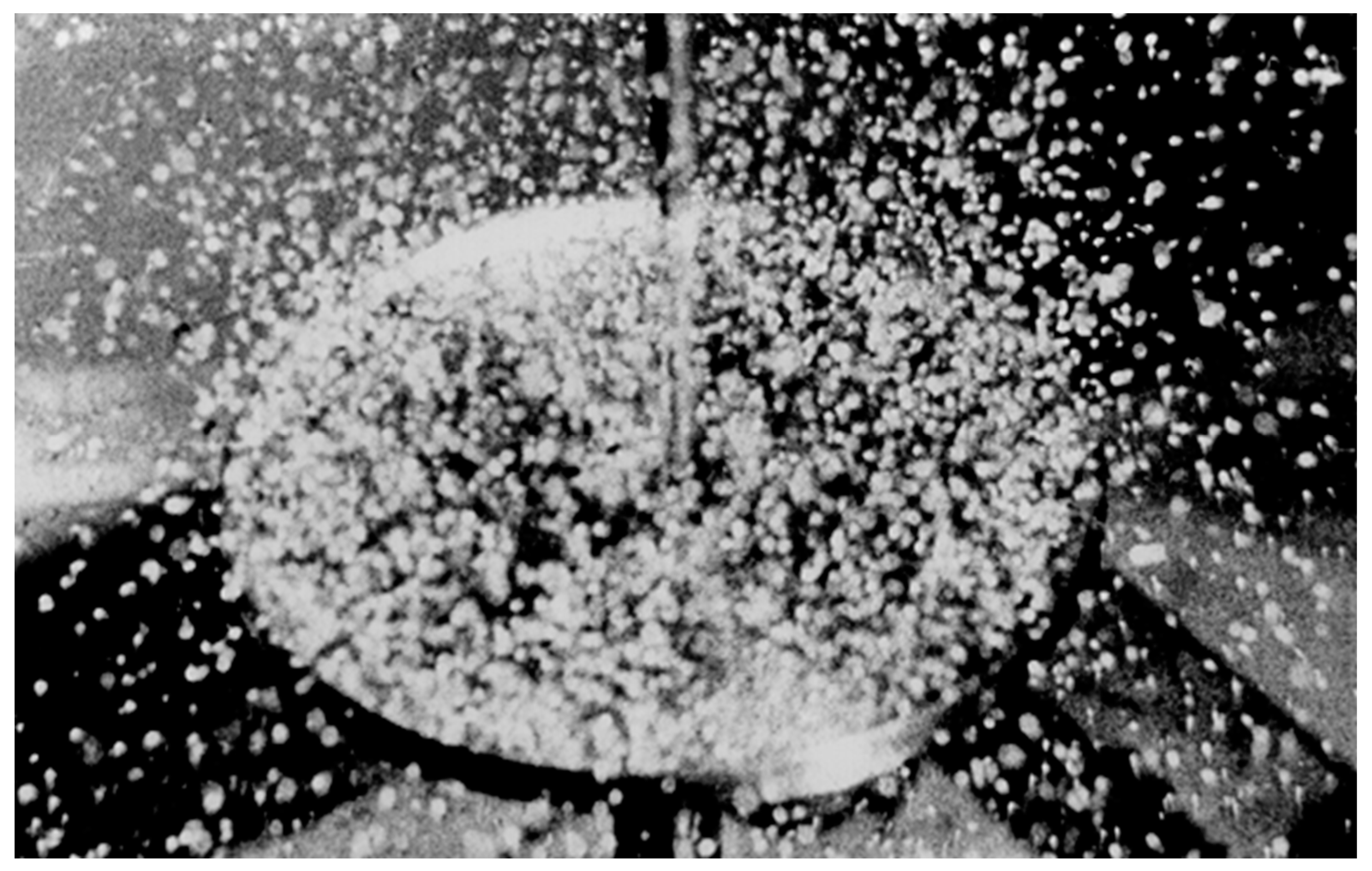
Through theoretical and experimental investigation employing significant vibrational acceleration, we uncovered the phenomenon of film flow disintegration occurring within what we term the soliton-like regime, as depicted in
Figure 4.
This constitutes the second of the novel phenomena we discovered. The soliton-like regime manifests when critical values of the vibrational Euler's number, Eug=gvr0/u2, approach unity. Here, gv, r0, and u respectively represent vibrational acceleration, the radius of the jet generating the film flow (flow rate), and the velocity of the jet prior to its collision with a plate (vertical jet's inertia). Consequently, the vibrational Euler number signifies the ratio of vibrational force to the jet's inertia (pressure force on the vibrational plate).
Surface waves induced on the film flow reach a critical threshold, transforming into solitary waves when the entire surface of the horizontally vibrating plate is enveloped by a series of uniform solitary waves. These waves act as individual uniform jets traversing the plate's surface, generating uniform drops through vibrational force. Therefore, the seemingly chaotic depiction in
Figure 4 is, in fact, not chaotic, as evidenced by the uniform size of the produced granules, stemming exclusively from these solitary waves.
In the soliton regime, several unresolved questions emerged, particularly regarding the observation of cavitation on the surface of the disk due to high vibration accelerations. This cavitation phenomenon was accompanied by a distinctive noise resembling crackling. Such cavitation could significantly contribute to the decay of individual solitons, which resemble separate vertical jets running along the surface of the film flow. The collapse of cavitation bubbles occurring beneath the jets on the vibrating plate could generate impulse forces along their axes, potentially leading to their disintegration into droplets. The parameters necessary to achieve the regime depicted in
Figure 4 were as follows: :
Eug=
gvr0/
u2,
r0=0.8 mm,
u=0.2 m/s,
gv=250
g, with a vibration frequency of 450 Hz, and a horizontal disk diameter of 0.03 m. Consequently, the Vibrational Euler number,
Eug, was approximately 50.
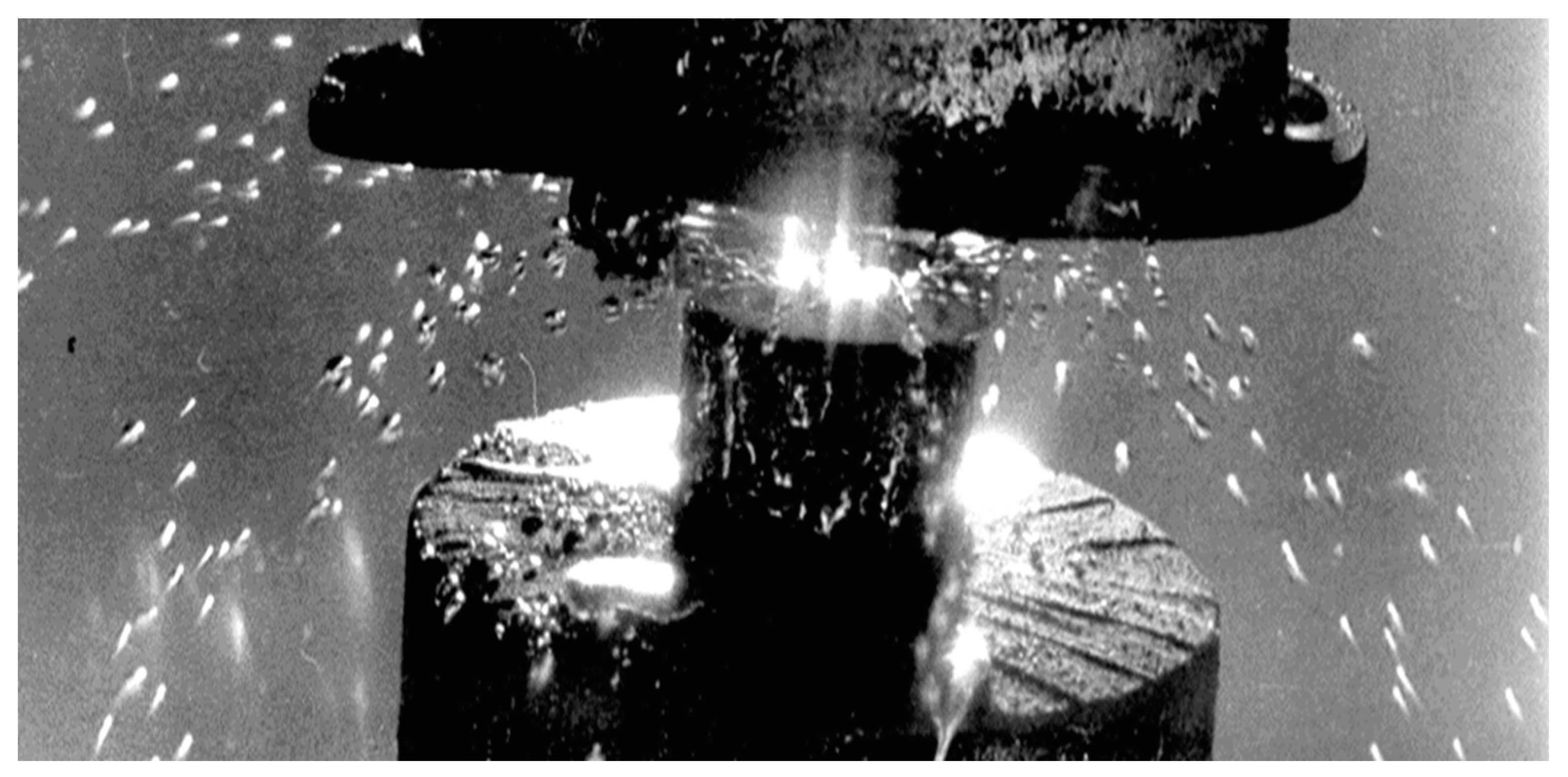
2.2.2. Shock-wave Regime of the Controlled Film Flow Disintegration
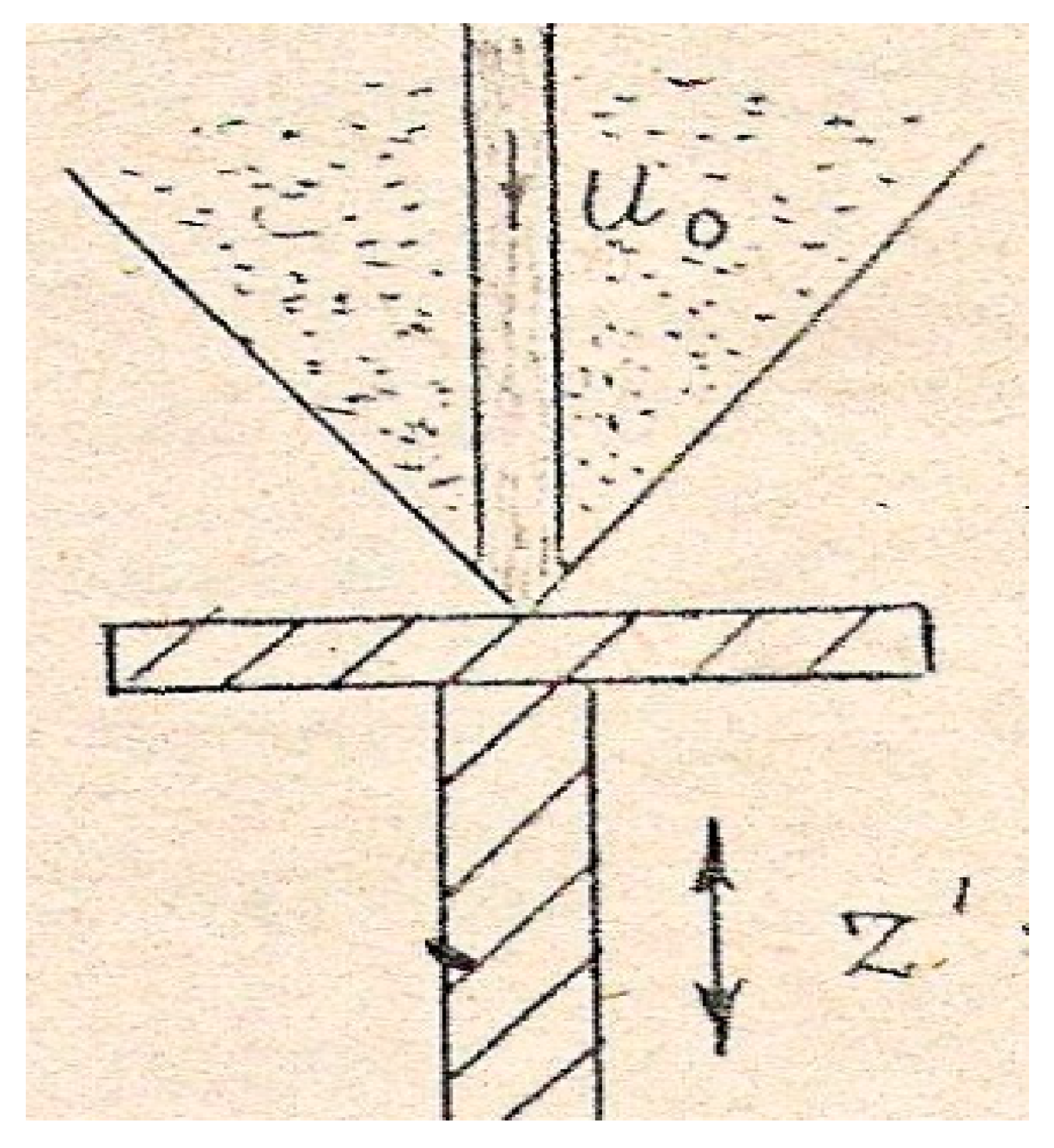
With an increase in vibration acceleration at a constant flow rate, the vibrational Euler number progressively rises, eventually reaching a second critical value. At this juncture, the previously observed soliton-like regime undergoes a distinct transition to what we term the shockwave regime, as depicted in
Figure 5.
As the vibrational acceleration increases, leading to more rapid release of drops from the plate, the region occupied by solitons on the horizontal plate progressively diminishes as less liquid remains in the film flow, as depicted in
Figure 4. Eventually, when the region of the film flow containing the soliton-like waves reaches the vertical jet, there is a sudden and explosive transition in the flow regime to the shockwave regime, as illustrated in
Figure 5.
In the shockwave regime, the resulting droplets are very small, typically around 10 micrometers in diameter. A cloud of such tiny droplets generated from the vertical jet forms within a conical region around the jet, with the sharp end of the conical surface touching the vibrating plate. These droplets are expelled from outside the conical surface, and new portions are continually produced in this manner.
We captured the transition from the soliton-like regime to the subsequent shockwave regime on film, presented in
Figure 5 as a simplified schematic representation. In dynamic observation, this transition unfolds as follows. As the vibration acceleration increases, the decay of solitons (streams) intensifies, causing the area occupied by solitons to diminish. Eventually, when the shrinking area of the film flow over the disk reaches the vertical jet, a sudden and explosive change in the soliton flow regime occurs. The film flow collapses, giving way to a regime characterized by the tearing off drops from the vertical jet, starting from its leading edge, which contacts the disk with its sharp nose. The conical shockwave then strips tiny drops from the nose of the vertical jet, and this process continues uninterrupted.
3. Results and Discussion
Granulation machines have been constructed based on the principle of parametrically controlled disintegration of film flow, leveraging three optimal modes of parametric oscillations that we discovered. Within the working chamber, a nitrogen atmosphere and liquid nitrogen coolant are employed to ensure rapid solidification of drops into granules, maintaining maximum cooling intensity throughout the entire process until complete solidification is achieved.
The uniqueness of these granulation machines lies in their utilization of the three different dispersion units, each tailored to exploit the three newly discovered hydrodynamic phenomena described earlier.
The electromagnetic device is designed for electroconductive melts and is capable of producing granules starting from 1 mm in size and larger. Vibrating units are employed to produce granules across a wide range of sizes with a narrow size distribution, determined by the specified frequency of vibrations. Specifically, the vibrating unit operating in the soliton regime is capable of producing granules ranging from 0.1 to 1 mm in size, accommodating melts beyond metals as well. Conversely, the unit operating in the shockwave regime allows for the production of granules below this range, down to sizes as small as 10 micrometers. It's important to note that smaller granules offer higher cooling rates during solidification, potentially leading to the attainment of the amorphous state in metals.
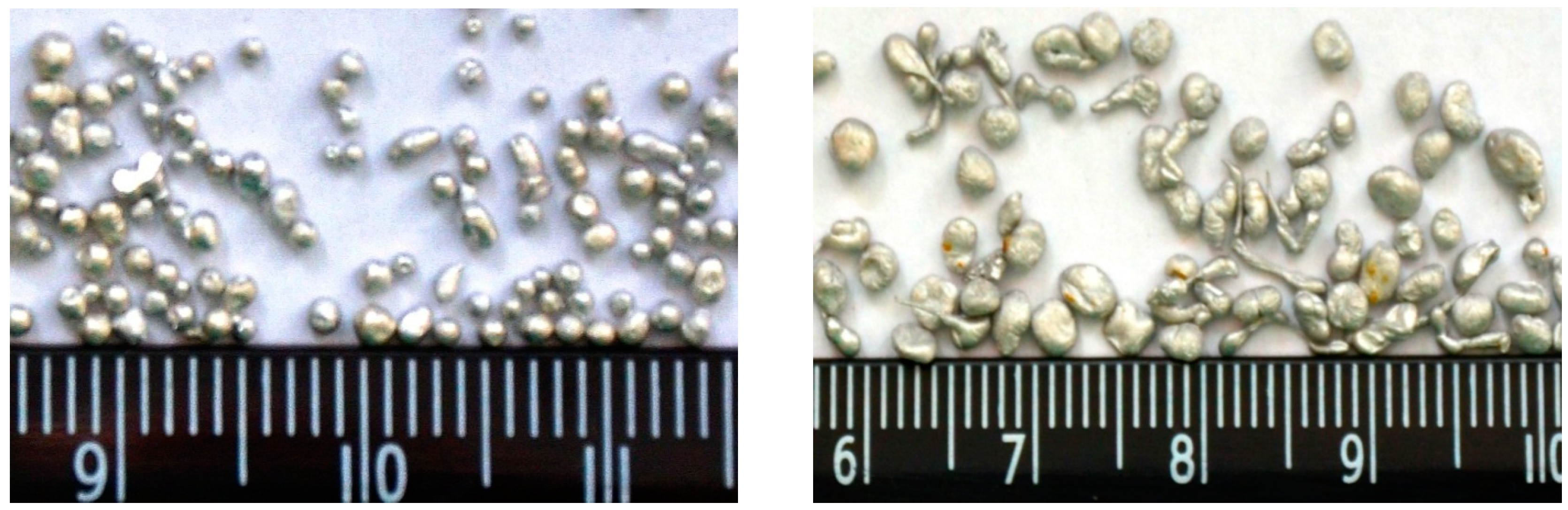
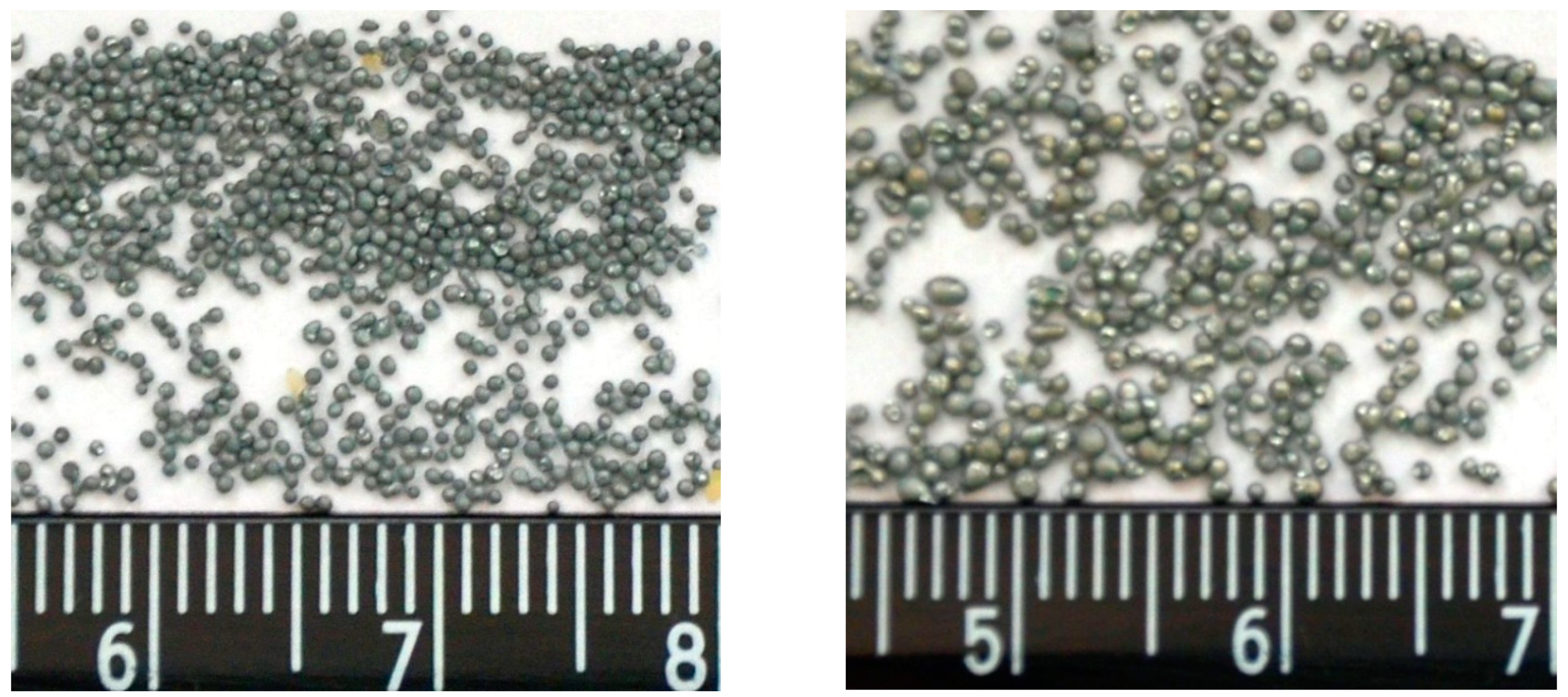
Figure 6 illustrates examples of aluminum granules produced using the different methods:
On the left side, aluminum granules produced in the soliton-like regime are shown without separation by size. On the right side, aluminum particles produced using a centrifugal granulator are displayed, with particles separated into the specified range of sizes. It is evident that there is no comparison between the quality of granules produced using the widely-used centrifugal method and those produced through our film flow granulation process. Our granules are uniform in size and of high quality, capable of reaching the amorphous state, which is particularly exciting for the production of new and unique materials.
The application of a nitrogen or other neutral atmosphere within the working chamber of the granulator addresses the critical issue of melt oxidation, particularly significant for many metal melts. Additionally, the presence of liquid nitrogen at the bottom of the chamber for granule cooling simultaneously resolves the challenge of maintaining a neutral atmosphere. This is achieved as nitrogen vaporization occurs continuously, with the vapor released through upper valves regulating the pressure inside the working chamber.
Figure 7 depicts granules of zinc produced on a film granulator in the soliton-like regime and cooled using nitrogen coolant, achieving an impressive cooling rate of up to 10
4 Celsius degrees per second. However, in cases involving electromagnetic action, rigid modes of instability in film flows were not observed. We attribute this to the electromagnetic field's insufficient strength, typically below 0.6 Tesla, for this specific purpose.
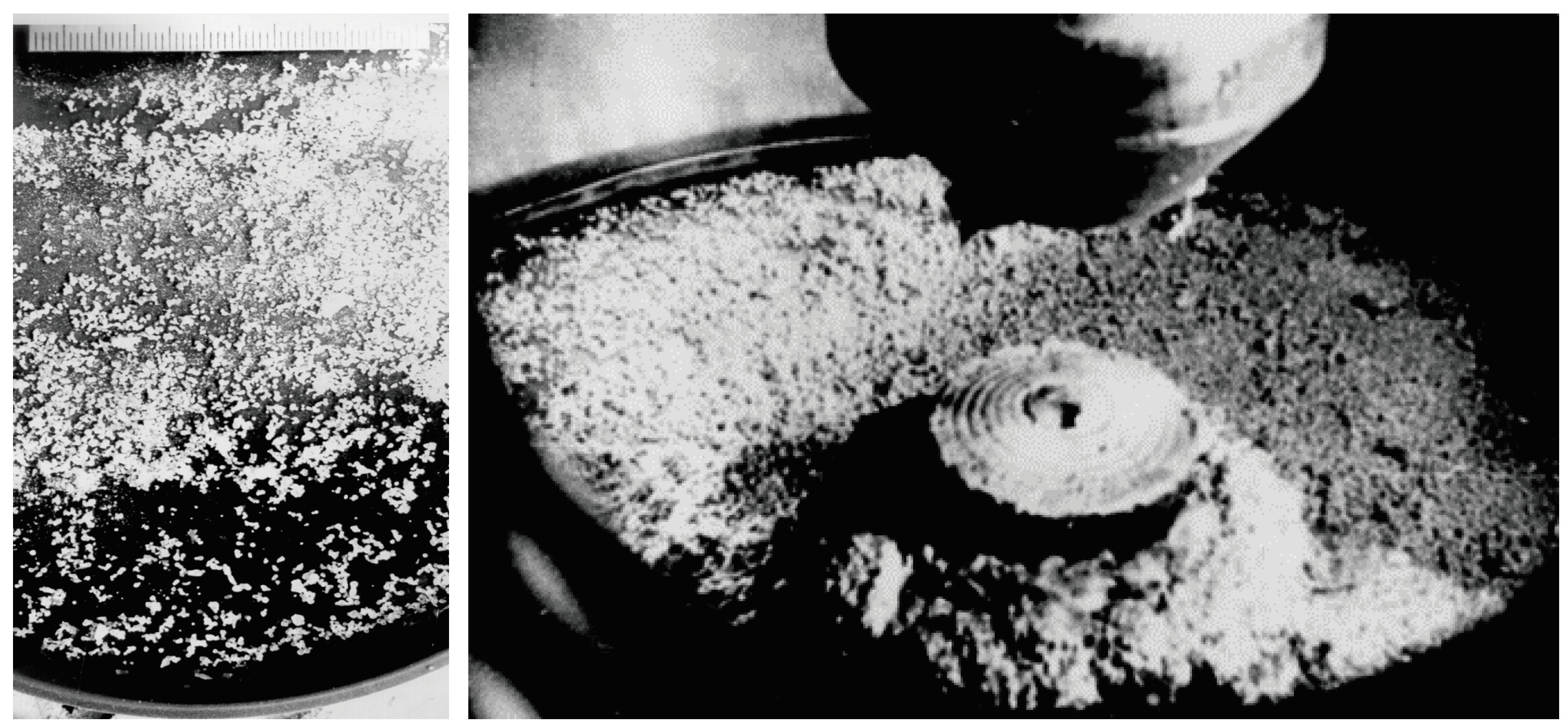
Figure 8 and
Figure 9 provide a visual representation of the granules at the bottom of the granulation machine chamber following the granule production process.
4. Conclusions
Our newly developed granulation technology is founded upon controlled film flow disintegration, leveraging three newly discovered effective phenomena. This technology, along with the corresponding devices, is truly unique. It enables the production of high-quality granules, including amorphous and other specialized varieties, suitable for various applications. For instance, these granules can be utilized in the production of super hard metals and metals/alloys with functionally unique properties.
In contrast, conventional granulation machines such as centrifugal ones produce a broad spectrum of particle sizes and offer significantly lower cooling rates, rendering them unable to compete with our technology. Moreover, these machines generate granules with varying sizes and forms, often of lower quality. Similarly, jet-type granulation machines exhibit lower productivity and are restricted in the size of granules they can produce, typically limited to sizes over 1 mm.
Overall, our granulation technology stands out for its ability to produce high-quality, specialized granules with precise control over size and properties, offering significant advantages over conventional methods. Film flow granulation has demonstrated success in handling metals and alloys with melting temperatures of up to 1200 degrees Celsius. However, there are additional possibilities for further investigation and development. The primary challenges in extending film flow granulation to melts with higher melting temperatures revolve around ensuring the stable operation of the supplying nozzle and disk, where the film flow undergoes disintegration into drops. These technical challenges must be addressed to effectively apply film flow granulation to materials with higher melting temperatures.
Continued research and development efforts are needed to overcome these obstacles and expand the applicability of film flow granulation to a broader range of materials. In addition to addressing the stability of the supplying nozzle and disk for higher melting temperature melts, further considerations may include the optimization of cooling mechanisms to withstand the increased heat. Additionally, exploring advanced materials and coatings that can withstand higher temperatures without degradation could enhance the durability and longevity of the equipment used in film flow granulation processes. Moreover, research into novel techniques for controlling the film flow and drop disintegration at elevated temperatures may be necessary to ensure consistent and reliable performance in processing materials with higher melting points. These efforts will be essential for unlocking the full potential of film flow granulation across a wider range of materials and applications.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the author.
References
- Frenkel, Ya.I. Kinetic theory of liquids; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1946. [Google Scholar]
- Kolesnichenko, A.F.; Kazachkov, I.V.; Vodyanuk, V.O.; Lysak, N.V. and Lysak, N.V. Capillary MHD Flows with Free Surfaces; Naukova Dumka: Kiev, Ukraine, 1988; 176 p. [Google Scholar]
- Kolesnichenko, A.F.; Kazachkov, I.V.; Gorislavets, Yu.M.; et al. Liquid metal MHD; Kluwer Acad. Publ.: Holland, 1989; pp. 293–298. [Google Scholar]
- Kazachkov, I.V. Parametric wave excitation and suppression on the interfaces of continua, D.Sc. Thesis, Riga Institute of Physics of Latvian Acad. Sci., 1991.
- Kazachkov, I.V.; Kolesnichenko, A.F. Pis’ma v Zh. Tekhn. Fiziki (Letters to J. Techn. Phys.); 1991; 17, p. 40.
- Kolesnichenko, A.F. Technological MHD facilities and processes; Naukova Dumka: Kiev, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Kazachkov, I.V.; Kolesnichenko, A.F.; Kuchinsky, V.P. USSR Patent 1814254, 1992.
- Kazachkov, I.V.; Kolesnichenko, A.F.; Kuchinsky, V.P. USSR Patent 1570154, 1991.
- Vodyanuk, V.O.; Kazachkov, I.V.; Kolesnichenko, A.F. USSR Patent 1476736, 1990.
- Kazachkov, I.V.; Kolesnichenko, A.F.; Kuchinsky, V.P. USSR Patent, 1412135, 1989.
- Kazachkov, I.V.; Kolesnichenko, A.F.; Kuchinsky, V.P. USSR Patent 1184153, 1988.
- Gorislavets, Yu.M.; Malakhov, V.V.; Glukhenkii, A.I. Magnetohydrodynamic installation for production of leadshot. J. Tekhnichna elektrodynamika 1997, 6, 68–69. [Google Scholar]
- Gorislavets, Yu.M.; Glukhenkii, A.I.; Mykhalskyi, V.M.; Tokarevskyi, A.V. Magnetohydrodynamic installation for production of leadshot. J. Tekhnichna elektrodynamika 2012, 5, 74–80. [Google Scholar]
- Kazachkov, I.V. On the Modeling of Non-Classical Problems Involving Liquid Jets and Films and Related Heat Transfer Processes. FDMP-Fluid Dynamics & Materials Processing 2019, 15, 491–507. [Google Scholar]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).