1. Introduction
Chloride-induced rebar corrosion, often resulting from marine exposure and the widespread use of deicing salts. It is a common cause of degradation in reinforced concrete structures [
1]. The durability of concrete structures in chloride environments seriously affects their long-term performance. The durability of concrete structures refers to the ability to maintain their applicability and safety under normal use and maintenance conditions [
2]. Usually, the durability of concrete structures in chloride environments, especially permeability and diffusion, is influenced by their characteristics, such as concrete quality, environmental exposure conditions, and the presence of stress or cracks [
3,
4,
5,
6,
7]. Many studies have developed corrosion induced models that link corrosion and service life [
2]. In practical environments, the actual durability of concrete is different from the theoretical durability [
8,
9]. In addition, due to the different experimental methods, parameters, and modeling assumptions used by different researchers, the prediction results of different theoretical degradation models vary greatly. In order to minimize the variability of these predictions and improve the confidence of the results, on-site durability inspection information is usually used to calibrate and modify these durability models, which requires consideration and proper handling of uncertainties related to various measurements, and the development of methods that can appropriately use on-site inspection information.
The update of durability models for concrete structures is an important research direction in the field of civil engineering, aiming to optimize and update the durability prediction models of concrete structures continuously through real-time monitoring or detection data and advanced analysis methods, in order to more accurately assess the health status and remaining life of the structures. In Europe and the United States, research on the update of durability models for concrete structures is relatively mature, with many studies focusing on the integration of sensor technology and data-driven methods to achieve real-time monitoring and model updates. For example, Barbara H et al. [
10] proposed a concrete durability model based on the Bayesian updating method, which can adjust model parameters according to real-time monitoring data to improve prediction accuracy. Suo Q, et al. [
11] studied the update method of concrete structure durability models based on reliability theory. By considering the uncertainties of environmental and material properties, they proposed a more flexible and reliable model update framework. Research on the update of durability models for concrete structures in China started late but has made some progress in recent years. Many universities and research institutions have begun to focus on this field, especially in the application of combining Internet of Things technology and big data analysis. Xiong XIAO [
12] proposed a concrete structure durability monitoring and model update system based on reliability method in their research. It can realize real-time data collection and processing of large-scale structures, providing effective technical support for model updates. Hui GU et al. [
13] explored the update method of concrete durability models based on machine learning algorithms. By analyzing historical monitoring data, the model parameters are automatically adjusted, improving the predictive performance and adaptability of the model.
This paper proved a updating methods for durability models with inspection data through Bayesian updating. It is organised as follows: In section 2, the durability models in chlorine environment with Fick’s second law and probabilistic lifetime prediction model are presented.
Section 3 introduces Bayesian updating and the actual numerical method used. Finally, a case study is presented in
Section 4, where the different detection information are applied, evaluated and compared.
2. Existing Durability Model in Chlorine Environment
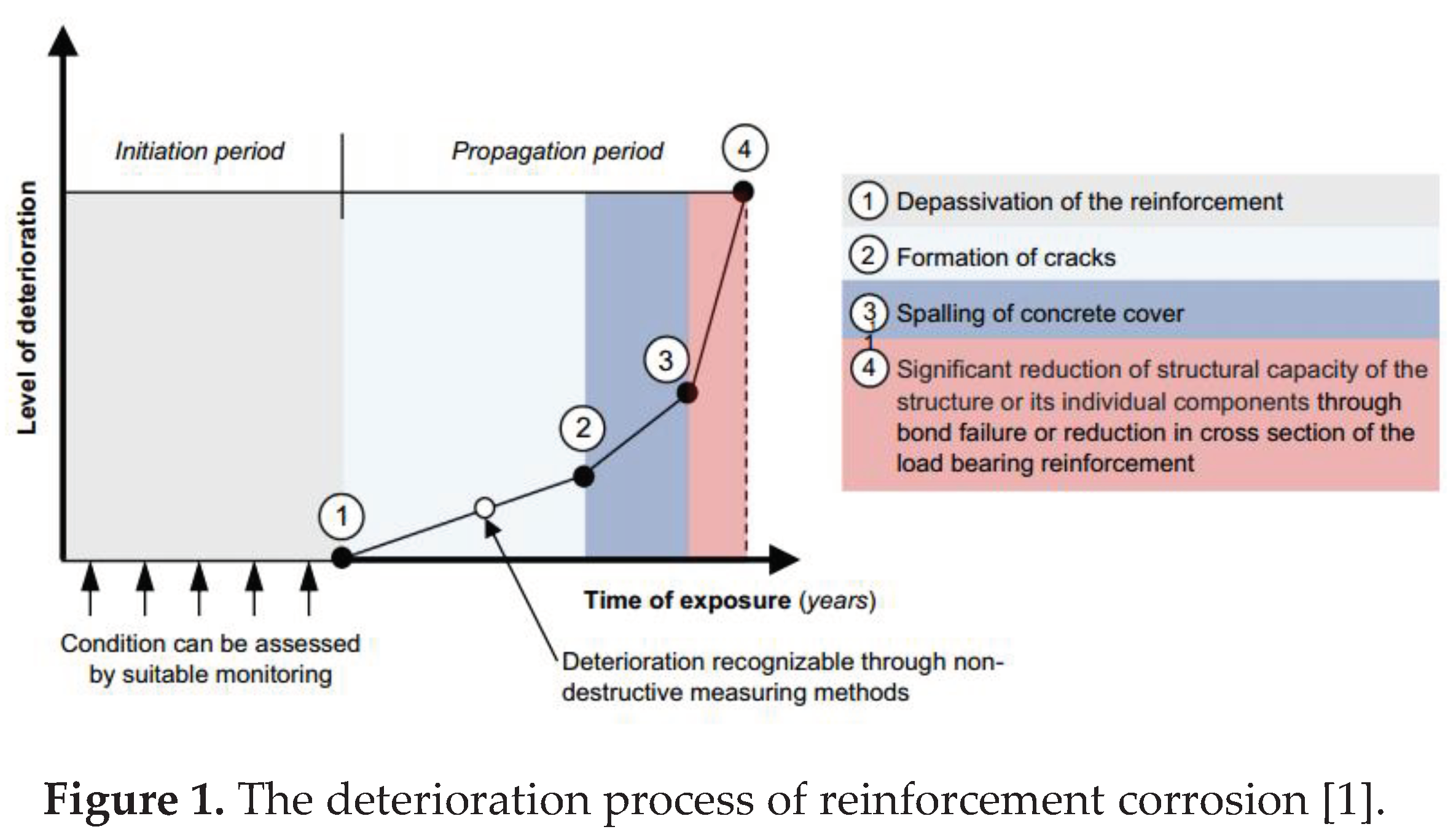
The durability damage of concrete structures under chloride environment is mainly caused by the degradation of structural performance caused by the corrosion of steel bars. Chlorine ions reach the surface of steel through external channels and accumulate to the critical concentration of chloride ions, which can damage the surface passivation film of the steel and form a corrosive battery. The corrosion process in a chlorine environment goes through three stages: the initial corrosion stage of concrete when chloride ions reach a critical concentration; The stage of concrete protective layer cracking caused by corrosion and expansion; The stage of severe degradation of structural performance due to crack propagation. The deterioration process of reinforcement corrosion is shown in
Figure 1 adapted from Tuutti [
14] and from fib bulletin 34 [
15]. Before the concrete protective layer cracks, the corrosion rate caused by chloride salt erosion is slower. After the concrete protective layer cracks, the corrosion rate increases and the remaining life of the structure significantly decreases.
When evaluating durability, different standards should be set according to the functional requirements of the structure to determine the corresponding durability limit state. For example, for components that do not allow corrosion within the target service life, such as prestressed steel bars in prestressed components, the initial corrosion limit state of the steel bars should be evaluated. For components that do not allow concrete cover cracking within the target service life, the limit state of concrete cover rust expansion cracking should be evaluated. This article only discusses the initial corrosion limit state to explain how the model is updated.
2.1. Chloride Ion Diffusion Model
The process of chloride ion from the concrete surface is an unstable diffusion process, which can be characterized using Fick’s second law [
16]. When considering a nonstationary diffusion process, the partial derivative of a concentration (C) to time (t) is equal to the negative value of the diffusion flux (J) to the partial derivative of distance:
Further, in the process of unstable diffusion, the diffusion flux can be written as the negative value of the concentration change rate with distance, and the above equation can be rewritten as:
Where,
the unstable diffusion coefficient of chloride ions. When analyzing the diffusion of chloride ions into concrete, it can be considered that this unstable diffusion of chloride ions is one-dimensional. Thus, it can take the following boundary conditions for Equation (2):
The analytical solution of the PDE can be obtained from the boundary conditions and considering the initial chloride content:
Where,
is the chloride ion concentration on the surface of concrete, expressed in% by mass of the cementitious material;
is the initial chloride ion content inside the concrete, unit for % cementing material mass;
is the initial chloride ion content inside the concrete, measured in% by mass of the bonding material, unit for m
2/s;
is the uncertainty coefficient of the model, which is a random variable that reflects significant uncertainty related to the chloride concentration model. It can be calculated by the ratio of actual measured values to calculated values;
is the chloride concentration of concrete surface depth
over time
, measured in% by mass of cementitious material;
is an error function, expressed as:
This analytical solution provides a method for calculating the chloride concentration within a certain distance from the concrete surface after time t. Currently, Equation (4) is widely used for calculating the diffusion distribution of chloride ions in concrete structures under chloride environments, and its results can serve as a basis for predicting the durability life of concrete structures.
2.2. Initial Corrosion Model of Steel Reinforcement
When the chloride concentration on the surface of the steel bar reaches a certain value
(critical chloride concentration), the steel bar will lose its passivation layer and corrode, which is defined as the initial corrosion durability limit state [
17]. According to the existing specifications. The code specifies ‘Code for design of concrete structures’ [
18] that for marine concrete structures with a design service life of 50 years, the maximum chloride ion content is 0.1% (of the total amount of cementitious materials), and the maximum chloride ion content in prestressed concrete components is 0.06% (of the total amount of cementitious materials). The American Concrete Institute’s ACI 318 standard [
19] has clear regulations on the maximum allowable chloride ion content in concrete to ensure that the reinforcement is not corroded. For prestressed concrete, the chloride ion content must not exceed 0.06% of the weight of the concrete. Therefore, to simplify the calculations, taking the initial chloride ion content inside the concrete equal to 0, as
=0, the durability limit state equation is expressed as:
Here,
is the thickness of the concrete protective layer, unit for mm. The diffusion coefficient of chloride ions
in the model is a function of time [
12], expressed as:
Where,
is the instantaneous chloride diffusion coefficient at
moment,
is the chloride diffusion coefficient at
moment,
is the age attenuation index. Generally, it takes
as 28 days,
as the chloride ion diffusion coefficient of concrete at 28 days(m
2/s). Usually the chloride ion diffusion coefficient in concrete materials does not decay exponentially over time. Life-365[
20] defines that the diffusion coefficient of chloride ions only increases within 25 years, assuming a constant after 25 years. In the durability design of the Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macau offshore passage project, the decay time of the chloride ion diffusion coefficient over time is set to 30 years [
21]. That is to say, after 30 years, the chloride ion diffusion coefficient of concrete is no longer attenuated:
The effect of the fly ash and slag incorporation on the age decay index is
Life-365 [
19] also specifies the relationship between the diffusion coefficient of chloride ions and temperature:
Where, is the diffusion coefficient at time t and temperature T; is the chloride diffusion coefficient over a 28 day period; =293K (200C) temperature; U is the activation energy of the diffusion process (35000J/mol); R is the gas constant, and T is the temperature
When
in equation (6), it can calculate the initial corrosion time
:
According to the limit equation of state of initial corrosion durability of reinforcement, considering the statistical characteristics of each parameter in the equation, the probability of reinforcement initial corrosion at any time
t can be calculated as
3. Bayesian Updating with Detection Information
Using the testing methods specified in ‘Technical standard for building structure detection’ [
22], ‘Technical standard for the field inspection of concrete structure’ [
23], ‘Technical regulations for detecting the compressive strength of concrete by rebound method’ [
24], and ‘Technical regulations for non-damage detection of port engineering concrete’ [
25], it investigates and tests on existing concrete structures in a chlorine environment. The detection information obtained includes the strength of the concrete, the thickness of the concrete cover, the distribution of chloride ions in different thickness layers of the concrete cover in the concrete, the corrosion of the steel bar determined by the semi-battery potential method, and the observed cracking of the concrete surface.
3.1. Updating of the Chloride Diffusion Model
Assuming that the structure is tested after years of use, experiments and analysis have been conducted on the distribution and diffusion of chloride ions in concrete structures. In general, components with different degrees of corrosion are selected to sample drilled powder concrete at different depths. In order to make the data representative and facilitate statistical analysis, no less than 3 sampling points are selected for each sample (with the same component and elevation), with depths of 0-10mm, 10-20mm, 20-40mm, 40-60mm, and 60-80mm, respectively. The chloride ion content in the concrete powder samples was measured by the potential titration method. After calculation, the Cl- concentration of concrete at different depths can be obtained. Perform regression fitting based on Fick’s second law of Cl- concentration at different depths, to calculate surface chloride ion concentration , chloride ion diffusion coefficient , and model uncertainty coefficient .
Scholars from different countries have determined the values of surface chloride ion concentration based on their respective national survey data. Dimitri et al. [
26] based on the inspection data of concrete structures on the coasts of Victoria and Tasmania in Australia, determined that the dispersion of surface chloride ion concentration in the splash zone is described by a log-normal distribution, with a mean of 7.35 kg/m³ and a coefficient of variation of 0.7. Fluge et al. [
27] based on the inspection data of 36 coastal bridges in Norway, considered that the
mean value is 0.51% (of the concrete mass) at 0m to 3m above sea level, with a standard deviation of 0.23% (of the concrete mass). The European DuraCrete method [
28] considers that the average value of
is related to environmental conditions, the water-cement ratio of the concrete, and the type of cementitious materials, which can be represented as
, where
is the water-cement ratio, and for ordinary Portland cement in the splash zone,
is 7.76% (of the cementitious material mass). In the American Life-365[
20]calculation program, the instantaneous value in the tidal splash zone
is set to 0.8% (of the concrete mass).Li Q [
29] measured the statistical values of surface chloride ion concentration in concrete structures of Chinese docks and considered that they follow a log-normal distribution, with a mean of 0.27% (of the concrete mass) and a standard deviation of 0.04% (of the concrete mass). Stewart and Fluge also suggested describing the dispersion of
using a log-normal distribution.
3.2. Updating of the Reinforcement Initial Corrosion Model
With the updated chloride diffusion model, it calculates the limit state of initial corrosion durability at structure detection time
:
According to the limit state equation of initial corrosion durability of steel bars, considering the probability distribution of concrete cover thickness and the prior critical chloride ion concentration model, the prior corrosion probability of reinforcement is calculated as:
The probabilistic model for critical chloride concentration is commonly used to assess the risk of reinforcement corrosion in concrete structures, taking into account the uncertainty and variability of chloride ion concentration. The critical chloride ion concentration values can vary depending on several factors, including the type of cement, the quality of concrete, the type of reinforcement, and the environmental conditions. Stewart [
3,
30] suggested the value of
follows the normal distribution mean of 0.95% cement mass (about 3.35 kg/m
3) and the COV of 0.375. Matsushima [
31] advised
as the mean of 3.07kg/m
3 and the COV of 0.41. The Japanese Civil Society criteria [
32] considered
with 0.3~2.4kg/m
3 when predicting the service life. For the reinforced concrete with high durability requirements, the chloride ion mass does of
does not exceed 0.3kg/m
3. It is higher value of
than in laboratory conditions measured in the actual environment, with 1.2~2.4kg/m
3.
Bayesian updating is a statistical method based on Bayesian theory, used to update existing probability distributions or model parameters based on new evidence or data. Bayesian updating describes how to update the conditional probability of an event based on new evidence. The theorem can be expressed as:
where
is the probability of event A occurring given that event B has occurred,
is the probability of event B occurring given that event A has occurred, P(A) is the prior probability of event A occurring, and P(B) is the total probability of event B occurring. In Bayesian updating, the prior distribution represents the estimation of the probability distribution of model parameters before obtaining new data, while the posterior distribution is the updated probability distribution of model parameters after considering the new data. The goal of Bayesian updating is to obtain a more accurate posterior distribution by combining the prior distribution with new data. The likelihood function is a key concept that represents the probability of observing new data given the model parameters. In Bayesian updating, the likelihood function is used to measure the fit between the new data and the model parameters.
Assumed in
n samples of the actually half-cell potential detected samples, there are
m corrosion samples. It is expressed as event
H here. Then the likelihood function of the rust probability can be expressed as
Where,
refers to the number of combinations of m samples selected from n samples. According to Bayesian update theory, the posterior probability density function of corrosion probability is
Where,
is the prior probability density function of the corrosion probability, which can be assumed to follow a normal distribution(truncation), Weibull distribution, or Beta distribution. The mean value
is calculated using Formula (14), and assuming a coefficient of variation of 0.5. Experiments have shown that the selection of prior distributions has little impact on the updated results. Considering that the Beta distribution has the characteristics of a conjugate prior distribution, it is recommended Beta distribution for convenient calculation. In the case of the test result
H, the mean value of the posterior probability density function of the corrosion probability
is
. Using the posterior mean of density function of corrosion probability, with the updated chloride diffusion model and the measured concrete cover thickness, the calculated updated mean value(assuming constant of standard deviation) of
is calculated as
The above formula adopts the traversal algorithm, selects the mean of
in the effective interval, adopts the Monte Carlo simulation algorithm, calculate the initial corrosion probability
of the steel bar at the time point
。The mean of
consistent with the updated mean of the rust probability was selected, is that determined in the above equation
, to complete the right updating of
. With the updating
, combined with the updated model of chloride ion diffusion, protective layer thickness probability distribution, Formula (19) is used to predict the initial corrosion probability of
(
) years, prediction results of initial corrosion probability of future reinforcement with comprehensive theoretical knowledge and historical information of components. The above update method essentially assumes that the corrosion probability of different components in the same structure is the same in a certain year. Subsequently, the updated initial corrosion time
tini was calculated, providing the basis for the updating of the rust swelling and cracking model:
In the formula, an updated distribution model was used for each parameter, and the calculated initial corrosion time is a variable rather than a specific value.
4. Case Study
Taking a concrete bridge as an example to explain the effectiveness of the method improved in this paper. With test, the thickness of concrete protective layer c follows the normal distribution, with the statistical results shown in
Table 1. Based on the layered detection of chloride ion concentration in the structure, it was determined that
follows a lognormal distribution, and the statistical results are shown in
Table 2.
Due to the material characteristics of concrete, the test environment temperature and humidity, the diversity of test methods and the diversification of expression, the critical chloride ion concentration is highly discrete. The prior distribution of value here is selected Stewart’s recommendations, conversion to follow the normal distribution mean of 0.158% concrete mass, and COV of 0.375.
The mean of the prior probability
of steel corrosion using 12 years is calculated in
Table 3. The corrosion detection samples results are shown in
Table 3. The mean of the posterior probability
and the standard deviation
of the updated reinforcement corrosion are calculated shown in
Table 3. Then the updated mean value of the critical chloride concentration
is calculated. All of these results are shown in
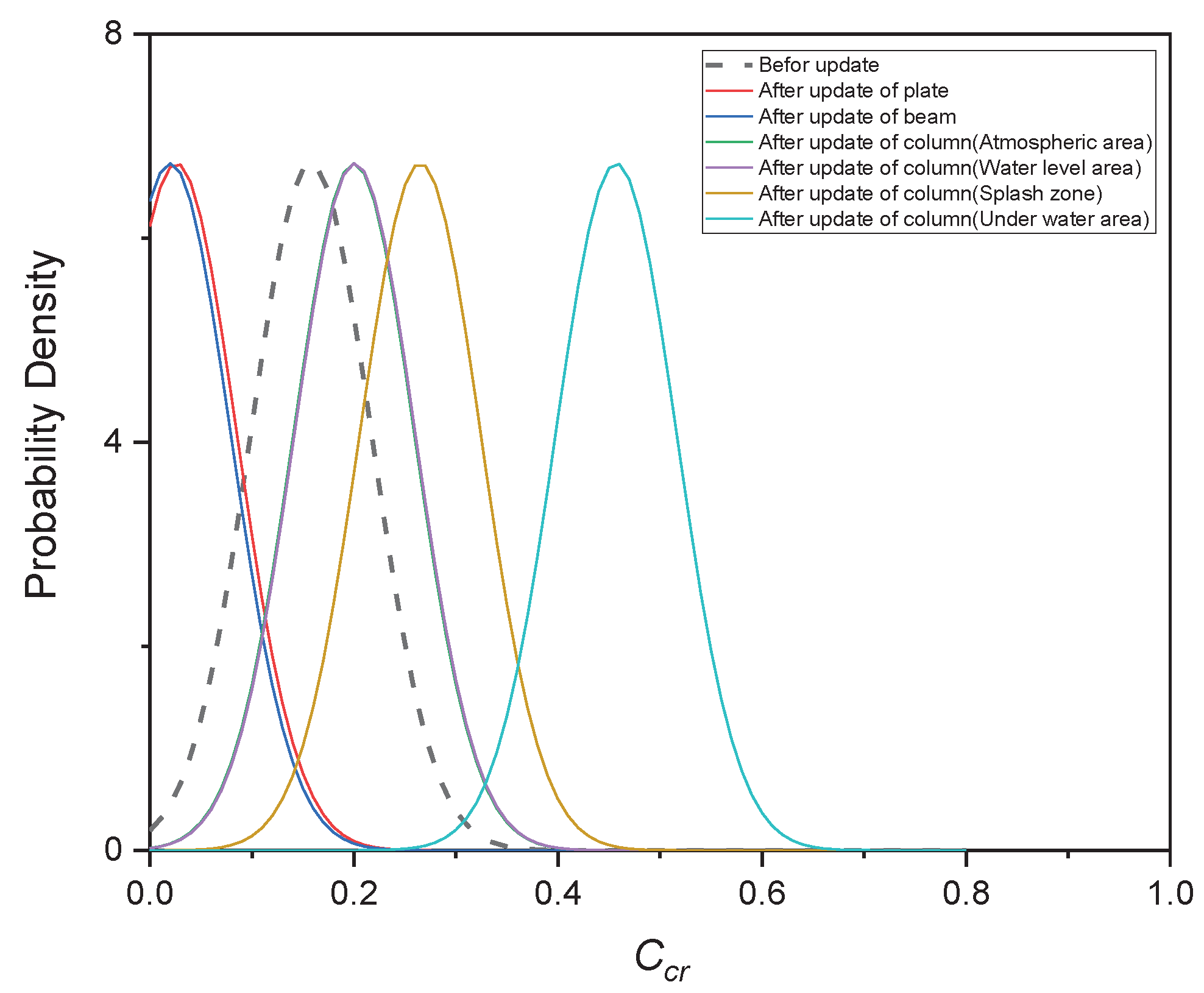
Table 3. For different positions, the mean update result of the critical chloride ion is significantly different from the initial value of 0.158. The critical chloride ion concentrations before and after the update are shown in
Figure 2. As can be seen from the figure, the critical chloride ion concentrations after the update differ significantly from those before the update. For different structural components with different inspection results, the critical chloride ion concentrations after the update vary greatly. The traditional assessment method, which uses a consistent critical chloride ion concentration, can lead to significant assessment errors. The assessment results after the update are relatively accurate.
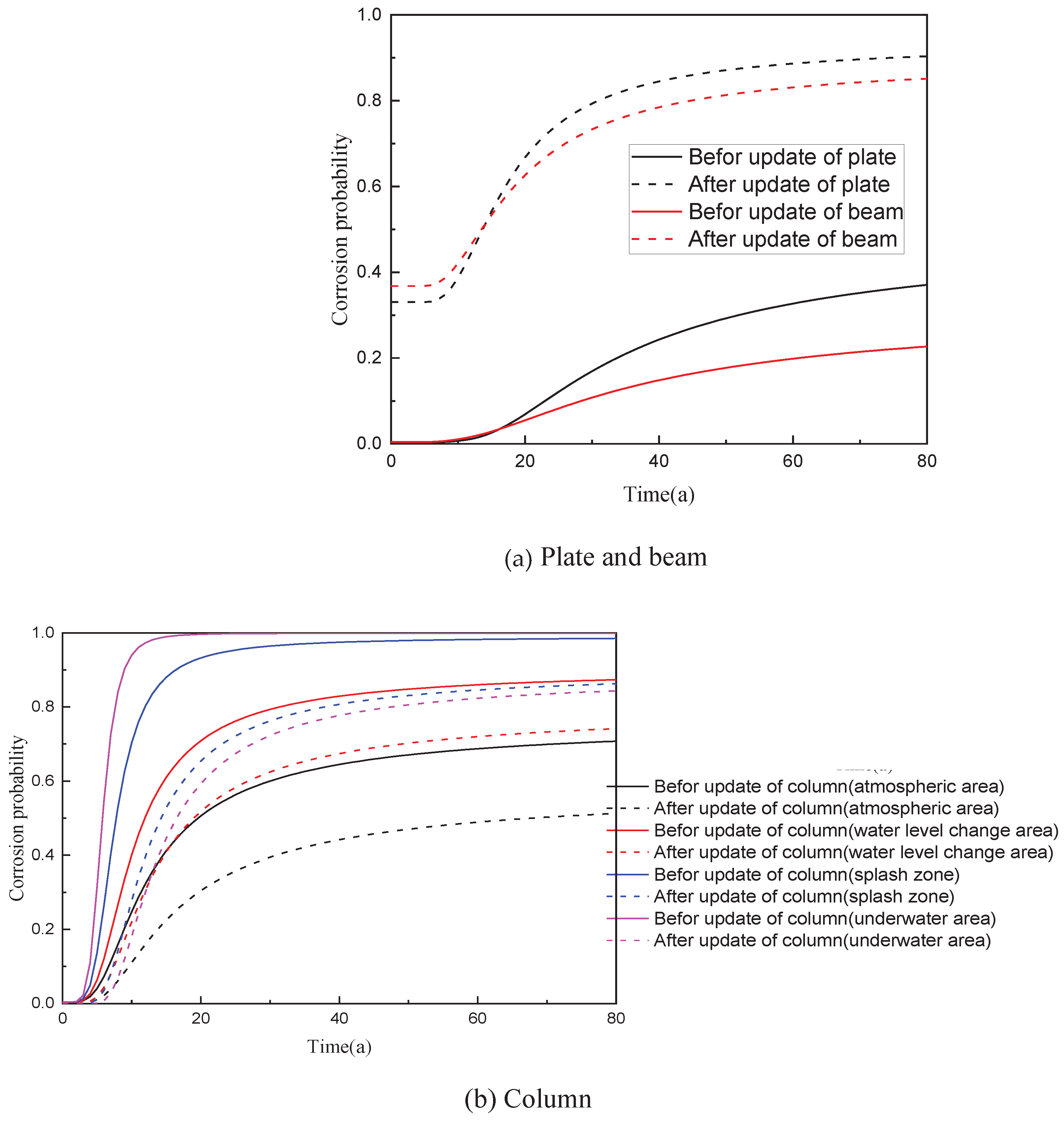
With the updated critical chloride concentration model, the corrosion probabilities is plot in
Figure 3.
Figure 1 also provides estimates of the critical chloride ion concentration before updating (using actual concrete cover thickness, surface chloride ion concentration, and diffusion coefficient obtained through detection) for comparison. According to Figure3, it can be seen that the probability of rust expansion and cracking in concrete structures calculated using the updated model differs significantly from the updated model. For slabs and beams, the updated critical chloride ion concentration is much lower than the theoretical value, which is 0.165 and 0.127 times higher than the theoretical value; For the column, the updated critical chloride ion concentration is about 1.27-2.89 times the theoretical value, indicating a significant updating effect. The updating method of durability models based on actual detection results provided in this article is of great significance.
5. Conclusions
The corrosion of steel bars in concrete structures under chloride environment is the main cause of structural damage. For important marine concrete structures, the durability of the structure is often evaluated based on the durability life criterion of concrete steel corrosion. The traditional evaluation method involves incorporating detection data into the theoretical model without updating the model in accordance with reality, resulting in inaccurate evaluation results. This article proposes a complete method for updating the durability of concrete structures based on the proportion of rust expansion and cracking obtained through detection, in order to reduce the evaluation error of durability and more accurately predict the remaining life of the structure.
This article discusses the updating methods based on the durability model of concrete structures in conventional chloride environments. Currently, there is no unified durability model at home and abroad. Further discussion is needed on whether the selection of models will affect the updating effect. At the same time, the updating efficiency of the methods in the article depends to a certain extent on the number of detection samples. The more samples there are, the more accurate the grasp of the actual situation of the component, and the higher the confidence in the detection information, the more obvious the updating effect. However, the number of samples is influenced by both actual testing conditions and economic factors. How to determine the optimal number of testing samples based on the actual structure is a problem that needs further consideration in engineering.
References
- Alexander M, & Beushausen H. Durability, service life prediction, and modelling for reinforced concrete structures-review and critique. Cement and Concrete Research 2019, 122, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maaddawy TE & Soudki, K. A model for prediction of time from corrosion initiation to corrosion cracking. Cement and Concrete Composites 2007, 29, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim AV, Stewart MG. Structural reliability of concrete bridges including improved chloride-induced corrosion models. Structural Safety 2000, 22, 313–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhri H, Fishman KL, & Ranade R. Rapid determination of critical chloride content in cement-based composites. Construction and Building Materials 2020, 268, 121–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo H, Shi C, Guan X, Zhu J, Ding Y&Ling, TC; et al. Durability of recycled aggregate concrete-a review. Cement and Concrete Composites 2018, 89, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nganga G, Alexander M, & Beushausen H. Practical implementation of the durability index performance-based design approach. Construction and Building Materials 2013, 45, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang Q, Francois R, Zhang DL; et al. Influence of long-term chloride diffusion in concrete and the resulting corrosion of reinforcement on the serviceability of RC beams. Cement and Concrete Composites 2016, 71, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angst U, Ronnquist A, Elsener B, Larsen CK, & Vennesland O. Probabilistic considerations on the effect of specimen size on the critical chloride content in reinforced concrete. Corrosion Science 2011, 53, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke Ler S, Fischer J, Straub D & Gehlen C. Updating of service-life prediction of reinforced concrete structures with potential mapping. Cement and Concrete Composites 2014, 47, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heitner B, OBrien E J, Yalamas T; et al. Updating probabilities of bridge reinforcement corrosion using health monitoring data. Engineering Structures 2019, 190, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo Q, Stewart M G. Corrosion cracking prediction updating of deteriorating RC structures using inspection information. Reliability engineering & system safety 2009, 94, 1340–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao X, Wang Z; et al. Bayesian model updating based on structural reliability method: Case study for chloride-induced durability analysis. Engineering Mechanics 2022, 39, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu H, Li Q. ; et al. Updating method for durability models of concrete structures in carbonation environment. Engineering Mechanics 2021, 38, 113–121. [CrossRef]
- Tuutti K, Corrosion of Steel in Concrete, Report No.CBI Research 4, Swedish Cement and Concrete Research Institute, Stockholm 1982, p. 82.
- Fib, Model code for service life design, Switzerland, fib bulletin 34,2006.
- Angst UM. Predicting the time to corrosion initiation in reinforced concrete structures exposed to chlorides. Cement and Concrete Research 2019, 115, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao Y, Gehlen C, Angst U, Wang L & Yao Y. Critical chloride content in reinforced concrete-an updated review considering chinese experience. Cement and Concrete Research 2019, 117, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T50010-2010 Code for design of concrete structures. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2010.
- American Concrete Institute. ACI 318 standard: Building code requirements for structural concrete, 2020.
- Life-365 Service Life Prediction Model TM Version 2.0. Farmington Hills: American Concrete Institute, 2009.
- Li Q, Li K, Zhou X; et al. Model-based durability design of concrete structures in Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macau sea link project. Structural Safety 2015, 53, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 50344-2004 Technical standards for building structure testing. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2004.
- GB/T 50784-2013 Technical standards for on-site testing of concrete structures. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2013.
- JGJ/T 23-2011 Technical specification for testing compressive strength of concrete using rebound method. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2011.
- JTJ/T272-99 Technical specification for non-destructive testing of concrete in port engineering. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2016.
- Dimitri V Val, Mark G Stewart. Life-cycle cost analysis of reinforced concrete structures in marine environments. Structural Safety 2003, 25, 343–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fluge, F. Marine chlorides: A probabilistic approach to derive provisions for EN 206-1// Proceedings of the 3rd Workshop on Service Life Design of ConcreteStructures: From Theory to Standardisation, DuraNet. Troms¢: 47―68.
- DuraCrete, General guidelines for durability design and redesign: Probabilistic performance based durability design of concrete structures. The European Union-Brite EuRam, 2000.
- Li Q, Ye X. Surface deterioration analysis for probabilistic durability design of RC structures in marine environment. Structural Safety 2018, 75, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang X, Nguyen M, Stewart, MG; et al. Analysis of climate change impacts on the deterioration of concrete infrastructure–part 2: Modelling and simulation of deterioration and adaptation options, 2010. [CrossRef]
- Matsushima, Manabu; et al. Optimum thickness of concrete cover of RC structure based on reliability theory. Concr Library JSCE 1995, 25, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horiguchi K, Yamaguchi T; et al. Study on the Method of Measuring the Chloride Threshold Value of Corrosion and Estimation of the Values in Durability Design of Concrete Structures. Journal of Advanced Concrete Technology 2020, 18, 571–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).