Submitted:
14 March 2024
Posted:
14 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Regulation of m6A Modification
3. Mechanisms of the Antiviral Innate Immune Response
3.1. Recognition of Viruses by RLP
3.2. Recognition of Viral Nucleic Acids by TLRs
3.3. Recognition of Viruses Using Cytosolic Sensors
3.4. Recognition of Viruses in the Nucleus
4. m6A Methylation of Antiviral Response Factors
4.1. m6A-Dependent Regulation of the RLP Signaling Pathway
4.1.1. m6A and Stimulation of Immunity
4.1.2. Viral Evasion of RLP-Mediated Immune Responses
4.2. m6A-Dependent Regulation of the TLR Signaling Pathway
4.2.1. m6A and Stimulation of Cellular Immunity through the TLR Pathway
4.2.2. m6A-Dependent Regulation of Cytosolic and Nuclear Sensors
4.3. m6A-Dependent Regulation of Type I Interferon Synthesis
5. The Role of the m6A Modifications in the Genetic Material of Viruses
5.1. Retroviruses
5.2. Orthomyxoviruses
5.3. Flaviviruses
5.4. Coronaviruses
5.5. Hepadnaviruses
5.6. Adenoviruses
5.7. Herpesviruses
6. Conclusions and Future Directions
Funding
References
- Desrosiers, R.; Friderici, K.; Rottman, F. Identification of Methylated Nucleosides in Messenger RNA from Novikoff Hepatoma Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1974, 71, 3971–3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccaletto, P.; Machnicka, M.A.; Purta, E.; Piątkowski, P.; Baginski, B.; Wirecki, T.K.; De Crécy-Lagard, V.; Ross, R.; Limbach, P.A.; Kotter, A.; et al. MODOMICS: A database of RNA modification pathways. 2017 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D303–D307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beemon, K.; Keith, J. Localization of N6-methyladenosine in the Rous sarcoma virus genome. J. Mol. Biol. 1977, 113, 165–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaccara, S.; Ries, R.J.; Jaffrey, S.R. Reading, writing and erasing mRNA methylation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 608–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maden, B. Identification of the locations of the methyl groups in 18 S ribosomal RNA from Xenopus laevis and man. J. Mol. Biol. 1986, 189, 681–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berulava, T.; Rahmann, S.; Rademacher, K.; Klein-Hitpass, L.; Horsthemke, B. N6-Adenosine Methylation in MiRNAs. PLOS ONE 2015, 10, e0118438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, S.; Pandya-Jones, A.; Saito, Y.; Fak, J.J.; Vågbø, C.B.; Geula, S.; Hanna, J.H.; Black, D.L.; Darnell, J.E.; Darnell, R.B. m6A mRNA modifications are deposited in nascent pre-mRNA and are not required for splicing but do specify cytoplasmic turnover. Genes Dev. 2017, 31, 990–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominissini, D.; Moshitch-Moshkovitz, S.; Schwartz, S.; Salmon-Divon, M.; Ungar, L.; Osenberg, S.; Cesarkas, K.; Jacob-Hirsch, J.; Amariglio, N.; Kupiec, M.; et al. Topology of the human and mouse m6A RNA methylomes revealed by m6A-seq. Nature 2012, 485, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lu, Z.; Gomez, A.; Hon, G.C.; Yue, Y.; Han, D.; Fu, Y.; Parisien, M.; Dai, Q.; Jia, G.; et al. N6-methyladenosine-dependent regulation of messenger RNA stability. Nature 2013, 505, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Dahl, J.A.; Niu, Y.; Fedorcsak, P.; Huang, C.-M.; Li, C.J.; Vågbø, C.B.; Shi, Y.; Wang, W.-L.; Song, S.-H.; et al. ALKBH5 Is a Mammalian RNA Demethylase that Impacts RNA Metabolism and Mouse Fertility. Mol. Cell 2013, 49, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, R.; Zou, J.; Tian, S.; Yu, L.; Zhou, Y.; Ran, Y.; Jin, M.; Chen, H.; Zhou, H. N6-methyladenosine reader protein YTHDC1 regulates influenza A virus NS segment splicing and replication. PLOS Pathog. 2023, 19, e1011305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, B.S.; Roundtree, I.A.; Lu, Z.; Han, D.; Ma, H.; Weng, X.; Chen, K.; Shi, H.; He, C. N6-methyladenosine Modulates Messenger RNA Translation Efficiency. Cell 2015, 161, 1388–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavi, S.; Shatkin, A.J. Methylated simian virus 40-specific RNA from nuclei and cytoplasm of infected BSC-1 cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1975, 72, 2012–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFadden, M.J.; McIntyre, A.B.; Mourelatos, H.; Abell, N.S.; Gokhale, N.S.; Ipas, H.; Xhemalçe, B.; Mason, C.E.; Horner, S.M. Post-transcriptional regulation of antiviral gene expression by N6-methyladenosine. Cell Rep. 2021, 34, 108798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFadden, M.J.; Horner, S.M. N6-Methyladenosine Regulates Host Responses to Viral Infection. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2020, 46, 366–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.; Zhang, Z.; Xue, M.; Zhao, B.S.; Harder, O.; Li, A.; Liang, X.; Gao, T.Z.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, J.; et al. N6-methyladenosine modification enables viral RNA to escape recognition by RNA sensor RIG-I. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 584–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöller, E.; Weichmann, F.; Treiber, T.; Ringle, S.; Treiber, N.; Flatley, A.; Feederle, R.; Bruckmann, A.; Meister, G. Interactions, localization, and phosphorylation of the m6A generating METTL3–METTL14–WTAP complex. RNA 2018, 24, 499–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, J.; Lin, S.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Q.; Wang, L.; Ramirez-Moya, J.; Du, P.; Kim, W.; Tang, S.; Sliz, P.; et al. mRNA circularization by METTL3–eIF3h enhances translation and promotes oncogenesis. Nature 2018, 561, 556–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Doxtader, K.A.; Nam, Y. Structural Basis for Cooperative Function of Mettl3 and Mettl14 Methyltransferases. Mol. Cell 2016, 63, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yue, Y.; Han, D.; Wang, X.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Jia, G.; Yu, M.; Lu, Z.; Deng, X.; et al. A METTL3–METTL14 complex mediates mammalian nuclear RNA N6-adenosine methylation. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2013, 10, 93–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, X.-L.; Sun, B.-F.; Wang, L.; Xiao, W.; Yang, X.; Wang, W.-J.; Adhikari, S.; Shi, Y.; Lv, Y.; Chen, Y.-S.; et al. Mammalian WTAP is a regulatory subunit of the RNA N6-methyladenosine methyltransferase. Cell Res. 2014, 24, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, D.P.; Chen, C.-K.; Pickering, B.F.; Chow, A.; Jackson, C.; Guttman, M.; Jaffrey, S.R. m6A RNA methylation promotes XIST-mediated transcriptional repression. Nature 2016, 537, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Lv, R.; Ma, H.; Shen, H.; He, C.; Wang, J.; Jiao, F.; Liu, H.; Yang, P.; Tan, L.; et al. Zc3h13 Regulates Nuclear RNA m6A Methylation and Mouse Embryonic Stem Cell Self-Renewal. Mol. Cell 2018, 69, 1028–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, Y.; Liu, J.; Cui, X.; Cao, J.; Luo, G.; Zhang, Z.; Cheng, T.; Gao, M.; Shu, X.; Ma, H.; et al. VIRMA mediates preferential m6A mRNA methylation in 3′UTR and near stop codon and associates with alternative polyadenylation. Cell Discov. 2018, 4, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bawankar, P.; Lence, T.; Paolantoni, C.; Haussmann, I.U.; Kazlauskiene, M.; Jacob, D.; Heidelberger, J.B.; Richter, F.M.; Nallasivan, M.P.; Morin, V.; et al. Hakai is required for stabilization of core components of the m6A mRNA methylation machinery. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turkalj, E.M.; Vissers, C. The emerging importance of METTL5-mediated ribosomal RNA methylation. Exp. Mol. Med. 2022, 54, 1617–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, R.; Vågbø, C.B.; E Jakobsson, M.; Kim, Y.; Baltissen, M.P.; O’donohue, M.-F.; Guzmán, U.H.; Małecki, J.M.; Wu, J.; Kirpekar, F.; et al. The human methyltransferase ZCCHC4 catalyses N6-methyladenosine modification of 28S ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 48, 830–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.A.; Kinzig, C.G.; DeGregorio, S.J.; Steitz, J.A. Methyltransferase-like protein 16 binds the 3′-terminal triple helix of MALAT1 long noncoding RNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2016, 113, 14013–14018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nance, D.J.; Satterwhite, E.R.; Bhaskar, B.; Misra, S.; Carraway, K.R.; Mansfield, K.D. Characterization of METTL16 as a cytoplasmic RNA binding protein. PLOS ONE 2020, 15, e0227647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warda, A.S.; Kretschmer, J.; Hackert, P.; Lenz, C.; Urlaub, H.; Höbartner, C.; E Sloan, K.; Bohnsack, M.T. Human METTL16 is a N 6 -methyladenosine (m 6 A) methyltransferase that targets pre-mRNAs and various non-coding RNAs. Embo Rep. 2017, 18, 2004–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.; Dong, L.; Li, Y.; Gao, M.; He, P.C.; Liu, W.; Wei, J.; Zhao, Z.; Gao, L.; Han, L.; et al. METTL16 exerts an m6A-independent function to facilitate translation and tumorigenesis. Nature 2022, 24, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendleton, K.E.; Chen, B.; Liu, K.; Hunter, O.V.; Xie, Y.; Tu, B.P.; Conrad, N.K. The U6 snRNA m 6 A Methyltransferase METTL16 Regulates SAM Synthetase Intron Retention. Cell 2017, 169, 824–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, G.; Fu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Dai, Q.; Zheng, G.; Yang, Y.; Yi, C.; Lindahl, T.; Pan, T.; Yang, Y.-G.; et al. N6-Methyladenosine in nuclear RNA is a major substrate of the obesity-associated FTO. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2011, 7, 885–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Yang, Y.; Sun, B.-F.; Shi, Y.; Yang, X.; Xiao, W.; Hao, Y.-J.; Ping, X.-L.; Chen, Y.-S.; Wang, W.-J.; et al. FTO-dependent demethylation of N6-methyladenosine regulates mRNA splicing and is required for adipogenesis. Cell Res. 2014, 24, 1403–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathiyalagan, P.; Adamiak, M.; Mayourian, J.; Sassi, Y.; Liang, Y.; Agarwal, N.; Jha, D.; Zhang, S.; Kohlbrenner, E.; Chepurko, E.; et al. FTO-Dependent N 6 -Methyladenosine Regulates Cardiac Function During Remodeling and Repair. Circ. 2019, 139, 518–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Feng, J.; Jiang, D.; Zhou, X.; Jiang, Q.; Cai, M.; Wang, X.; Shan, T.; Wang, Y. AMPK regulates lipid accumulation in skeletal muscle cells through FTO-dependent demethylation of N6-methyladenosine. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, R.; Liu, Y.; Yao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Bi, Z.; Jiang, Q.; Liu, Q.; Cai, M.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y.; et al. FTO regulates adipogenesis by controlling cell cycle progression via m6A-YTHDF2 dependent mechanism. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) - Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2018, 1863, 1323–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Liu, F.; Lu, Z.; Fei, Q.; Ai, Y.; He, P.C.; Shi, H.; Cui, X.; Su, R.; Klungland, A.; et al. Differential m6A, m6Am, and m1A Demethylation Mediated by FTO in the Cell Nucleus and Cytoplasm. Mol. Cell 2018, 71, 973–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, G.; Yang, C.-G.; Yang, S.; Jian, X.; Yi, C.; Zhou, Z.; He, C. Oxidative demethylation of 3-methylthymine and 3-methyluracil in single-stranded DNA and RNA by mouse and human FTO. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 3313–3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoilov, P.; Rafalska, I.; Stamm, S. YTH: a new domain in nuclear proteins. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2002, 27, 495–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Wang, X.; Liu, K.; Roundtree, I.A.; Tempel, W.; Li, Y.; Lu, Z.; He, C.; Min, J. Structural basis for selective binding of m6A RNA by the YTHDC1 YTH domain. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2014, 10, 927–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtas, M.N.; Pandey, R.R.; Mendel, M.; Homolka, D.; Sachidanandam, R.; Pillai, R.S. Regulation of m6A Transcripts by the 3ʹ→5ʹ RNA Helicase YTHDC2 Is Essential for a Successful Meiotic Program in the Mammalian Germline. Mol. Cell 2017, 68, 374–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Zhao, Y.; He, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xi, H.; Liu, M.; Ma, J.; Wu, L. YTHDF2 destabilizes m6A-containing RNA through direct recruitment of the CCR4–NOT deadenylase complex. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Chen, Y.-S.; Ping, X.-L.; Yang, X.; Xiao, W.; Yang, Y.; Sun, H.-Y.; Zhu, Q.; Baidya, P.; Wang, X.; et al. Cytoplasmic m6A reader YTHDF3 promotes mRNA translation. Cell Res. 2017, 27, 444–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Wang, X.; Lu, Z.; Zhao, B.S.; Ma, H.; Hsu, P.J.; Liu, C.; He, C. YTHDF3 facilitates translation and decay of N6-methyladenosine-modified RNA. Cell Res. 2017, 27, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roundtree, I.A.; Luo, G.-Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhou, T.; Cui, Y.; Sha, J.; Huang, X.; Guerrero, L.; Xie, P.; et al. YTHDC1 mediates nuclear export of N6-methyladenosine methylated mRNAs. eLife 2017, 6, e31311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Y.; Dong, L.; Liu, X.-M.; Guo, J.; Ma, H.; Shen, B.; Qian, S.-B. m6A in mRNA coding regions promotes translation via the RNA helicase-containing YTHDC2. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCloskey, A.; Taniguchi, I.; Shinmyozu, K.; Ohno, M. hnRNP C Tetramer Measures RNA Length to Classify RNA Polymerase II Transcripts for Export. Science 2012, 335, 1643–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Zhou, K.I.; Parisien, M.; Dai, Q.; Diatchenko, L.; Pan, T. N 6-methyladenosine alters RNA structure to regulate binding of a low-complexity protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 6051–6063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alarcón, C.R.; Goodarzi, H.; Lee, H.; Liu, X.; Tavazoie, S.; Tavazoie, S.F. HNRNPA2B1 Is a Mediator of m6A-Dependent Nuclear RNA Processing Events. Cell 2015, 162, 1299–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, J.L.; Wächter, K.; Mühleck, B.; Pazaitis, N.; Köhn, M.; Lederer, M.; Hüttelmaier, S. Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding proteins (IGF2BPs): post-transcriptional drivers of cancer progression? Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2012, 70, 2657–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, T.; Hung, L.-H.; Aziz, M.; Wilmen, A.; Thaum, S.; Wagner, J.; Janowski, R.; Müller, S.; Schreiner, S.; Friedhoff, P.; et al. Combinatorial recognition of clustered RNA elements by the multidomain RNA-binding protein IMP3. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Weng, H.; Sun, W.; Qin, X.; Shi, H.; Wu, H.; Zhao, B.S.; Mesquita, A.; Liu, C.; Yuan, C.L.; et al. Recognition of RNA N6-methyladenosine by IGF2BP proteins enhances mRNA stability and translation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2018, 20, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manners, O.; Baquero-Perez, B.; Whitehouse, A. m6A: Widespread regulatory control in virus replication. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) - Gene Regul. Mech. 2018, 1862, 370–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, D.; McCarthy, J.; O’driscoll, C.; Melgar, S. Pattern recognition receptors—Molecular orchestrators of inflammation in inflammatory bowel disease. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2013, 24, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eletto, D.; Mentucci, F.; Voli, A.; Petrella, A.; Porta, A.; Tosco, A. Helicobacter pylori Pathogen-Associated Molecular Patterns: Friends or Foes? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, J.S.; Sohn, D.H. Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns in Inflammatory Diseases. Immune Netw. 2018, 18, e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehwinkel, J.; Gack, M.U. RIG-I-like receptors: their regulation and roles in RNA sensing. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 537–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lind, N.A.; Rael, V.E.; Pestal, K.; Liu, B.; Barton, G.M. Regulation of the nucleic acid-sensing Toll-like receptors. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 22, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decout, A.; Katz, J.D.; Venkatraman, S.; Ablasser, A. The cGAS–STING pathway as a therapeutic target in inflammatory diseases. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 548–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFadden, M.J.; Gokhale, N.S.; Horner, S.M. Protect this house: cytosolic sensing of viruses. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2017, 22, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempsey, A.; Bowie, A.G. Innate immune recognition of DNA: A recent history. Virology 2015, 479-480, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, O.; Akira, S. Pattern Recognition Receptors and Inflammation. Cell 2010, 140, 805–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoneyama, M.; Kikuchi, M.; Yonehara, S.; Kato, A.; Fujita, T.; Matsumoto, K.; Imaizumi, T.; Miyagishi, M.; Taira, K.; Foy, E.; et al. Shared and Unique Functions of the DExD/H-Box Helicases RIG-I, MDA5, and LGP2 in Antiviral Innate Immunity. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 2851–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, D.; Kohlway, A.; Pyle, A.M. Duplex RNA activated ATPases (DRAs): platforms for RNA sensing, signaling and processing. RNA Biol. 2013, 10, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goubau, D.; Schlee, M.; Deddouche, S.; Pruijssers, A.J.; Zillinger, T.; Goldeck, M.; Schuberth, C.; Van der Veen, A.G.; Fujimura, T.; Rehwinkel, J.; et al. Antiviral immunity via RIG-I-mediated recognition of RNA bearing 5′-diphosphates. Nature 2014, 514, 372–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Hato, S.V.; Langereis, M.A.; Zoll, J.; Virgen-Slane, R.; Peisley, A.; Hur, S.; Semler, B.L.; van Rij, R.P.; van Kuppeveld, F.J. MDA5 Detects the Double-Stranded RNA Replicative Form in Picornavirus-Infected Cells. Cell Rep. 2012, 2, 1187–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Yuan, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Lian, Z.; Liu, P.; Li, X. LGP2 Promotes Type I Interferon Production To Inhibit PRRSV Infection via Enhancing MDA5-Mediated Signaling. J. Virol. 2023, 97, e0184322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisien, J.; Lenoir, J.J.; Mandhana, R.; Rodriguez, K.R.; Qian, K.; Bruns, A.M.; Horvath, C.M. RNA sensor LGP 2 inhibits TRAF ubiquitin ligase to negatively regulate innate immune signaling. Embo Rep. 2018, 19, e45176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Kohlway, A.; Vela, A.; Pyle, A.M. Visualizing the Determinants of Viral RNA Recognition by Innate Immune Sensor RIG-I. Structure 2012, 20, 1983–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Civril, F.; Bennett, M.; Moldt, M.; Deimling, T.; Witte, G.; Schiesser, S.; Carell, T.; Hopfner, K. The RIG-I ATPase domain structure reveals insights into ATP-dependent antiviral signalling. Embo Rep. 2011, 12, 1127–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, F.; Sun, L.; Zheng, H.; Skaug, B.; Jiang, Q.-X.; Chen, Z.J. MAVS Forms Functional Prion-like Aggregates to Activate and Propagate Antiviral Innate Immune Response. Cell 2011, 146, 448–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seth, R.B.; Sun, L.; Ea, C.-K.; Chen, Z.J. Identification and Characterization of MAVS, a Mitochondrial Antiviral Signaling Protein that Activates NF-κB and IRF3. Cell 2005, 122, 669–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, E.; Boulant, S.; Zhang, Y.; Lee, A.S.; Odendall, C.; Shum, B.; Hacohen, N.; Chen, Z.J.; Whelan, S.P.; Fransen, M.; et al. Peroxisomes Are Signaling Platforms for Antiviral Innate Immunity. Cell 2010, 141, 668–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabeta, K.; Hoebe, K.; Janssen, E.M.; Du, X.; Georgel, P.; Crozat, K.; Mudd, S.; Mann, N.; Sovath, S.; Goode, J.; et al. The Unc93b1 mutation 3d disrupts exogenous antigen presentation and signaling via Toll-like receptors 3, 7 and 9. Nat. Immunol. 2006, 7, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botos, I.; Segal, D.M.; Davies, D.R. The Structural Biology of Toll-like Receptors. Structure 2011, 19, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: update on Toll-like receptors. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-C.; Chathuranga, K.; Lee, J.-S. Intracellular sensing of viral genomes and viral evasion. Exp. Mol. Med. 2019, 51, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Wu, J.; Du, F.; Chen, X.; Chen, Z.J. Cyclic GMP-AMP Synthase Is a Cytosolic DNA Sensor That Activates the Type I Interferon Pathway. Science 2013, 339, 786–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ablasser, A.; Goldeck, M.; Cavlar, T.; Deimling, T.; Witte, G.; Röhl, I.; Hopfner, K.-P.; Ludwig, J.; Hornung, V. cGAS produces a 2′-5′-linked cyclic dinucleotide second messenger that activates STING. Nature 2013, 498, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell'Oste, V.; Gatti, D.; Giorgio, A.G.; Gariglio, M.; Landolfo, S.; De Andrea, M. The interferon-inducible DNA-sensor protein IFI16: a key player in the antiviral response. New Microbiol. 2015, 38, 5–20. [Google Scholar]
- Hornung, V.; Ablasser, A.; Charrel-Dennis, M.; Bauernfeind, F.; Horvath, G.; Caffrey, D.R.; Latz, E.; Fitzgerald, K.A. AIM2 recognizes cytosolic dsDNA and forms a caspase-1-activating inflammasome with ASC. Nature 2009, 458, 514–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Yuan, B.; Bao, M.; Lu, N.; Kim, T.; Liu, Y.-J. The helicase DDX41 senses intracellular DNA mediated by the adaptor STING in dendritic cells. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 959–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, Y.-H.; MacMillan, J.B.; Chen, Z.J. RNA Polymerase III Detects Cytosolic DNA and Induces Type I Interferons through the RIG-I Pathway. Cell 2009, 138, 576–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalet, A.; Gatti, E.; Pierre, P. Integration of PKR-dependent translation inhibition with innate immunity is required for a coordinated anti-viral response. FEBS Lett. 2015, 589, 1539–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hornung, V.; Hartmann, R.; Ablasser, A.; Hopfner, K.-P. OAS proteins and cGAS: unifying concepts in sensing and responding to cytosolic nucleic acids. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, C.; Yi, G.; Watts, T.; Kao, C.C.; Li, P. Structure of STING bound to cyclic di-GMP reveals the mechanism of cyclic dinucleotide recognition by the immune system. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2012, 19, 722–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, G.; Zhang, C.; Chen, Z.J.; Bai, X.-C.; Zhang, X. Cryo-EM structures of STING reveal its mechanism of activation by cyclic GMP–AMP. Nature 2019, 567, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Shang, G.; Gui, X.; Zhang, X.; Bai, X.-C.; Chen, Z.J. Structural basis of STING binding with and phosphorylation by TBK1. Nature 2019, 567, 394–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Cai, X.; Wu, J.; Cong, Q.; Chen, X.; Li, T.; Du, F.; Ren, J.; Wu, Y.-T.; Grishin, N.V.; et al. Phosphorylation of innate immune adaptor proteins MAVS, STING, and TRIF induces IRF3 activation. Science 2015, 347, aaa2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.; Ghosh, A.; Kumar, B.; Chandran, B. IFI16, a nuclear innate immune DNA sensor, mediates epigenetic silencing of herpesvirus genomes by its association with H3K9 methyltransferases SUV39H1 and GLP. eLife 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orzalli, M.H.; Broekema, N.M.; Diner, B.A.; Hancks, D.C.; Elde, N.C.; Cristea, I.M.; Knipe, D.M. cGAS-mediated stabilization of IFI16 promotes innate signaling during herpes simplex virus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2015, 112, E1773–E1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
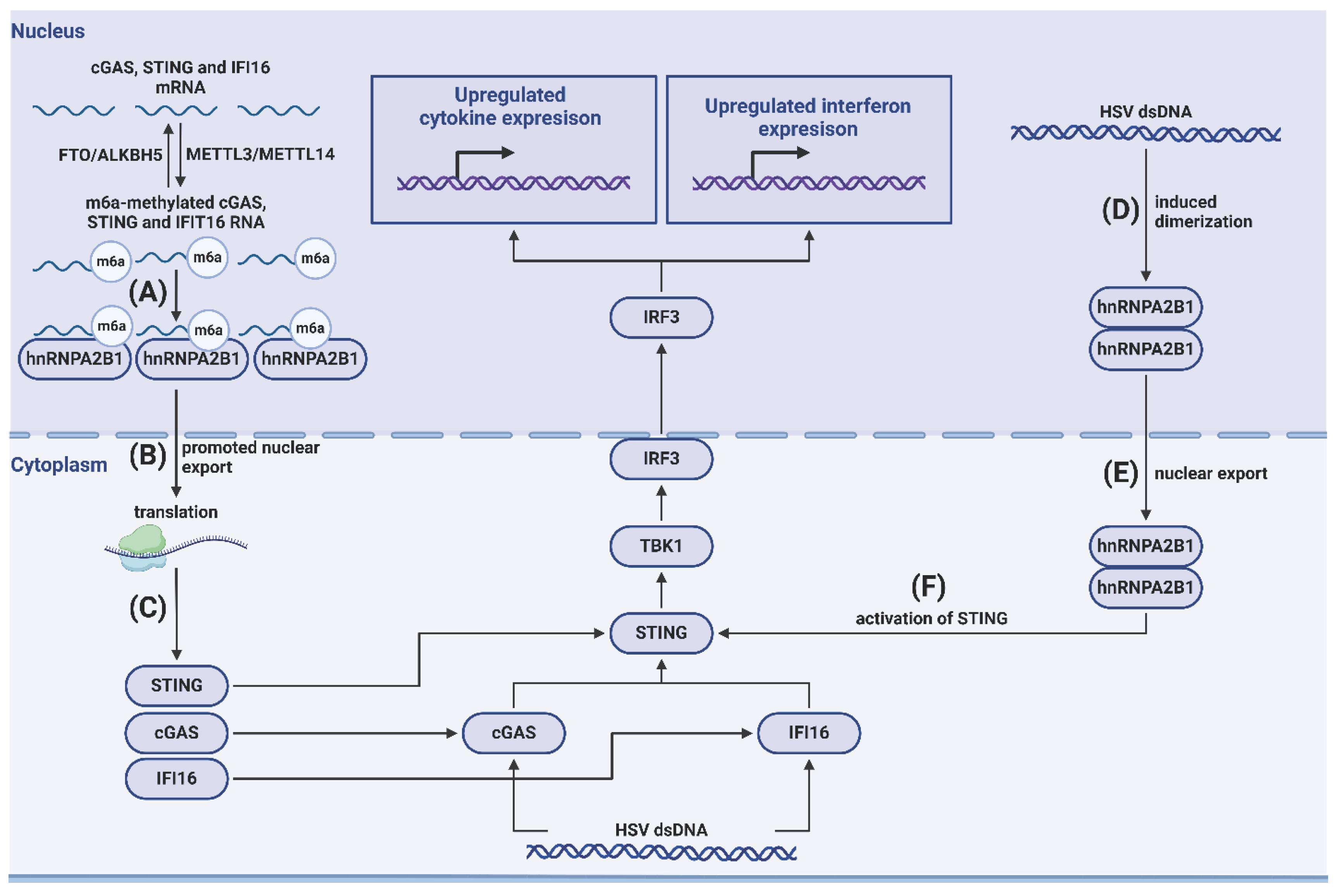
- Wang, L.; Wen, M.; Cao, X. Nuclear hnRNPA2B1 initiates and amplifies the innate immune response to DNA viruses. Science 2019, 365, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, S.; Aiello, D.; Atianand, M.K.; Ricci, E.P.; Gandhi, P.; Hall, L.L.; Byron, M.; Monks, B.; Henry-Bezy, M.; Lawrence, J.B.; et al. A Long Noncoding RNA Mediates Both Activation and Repression of Immune Response Genes. Science 2013, 341, 789–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentili, M.; Lahaye, X.; Nadalin, F.; Nader, G.P.; Lombardi, E.P.; Herve, S.; De Silva, N.S.; Rookhuizen, D.C.; Zueva, E.; Goudot, C.; et al. The N-Terminal Domain of cGAS Determines Preferential Association with Centromeric DNA and Innate Immune Activation in the Nucleus. Cell Rep. 2019, 26, 2377–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Yu, Q.; Chu, L.; Cui, Y.; Ding, M.; Wang, Q.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, C. Nuclear cGAS Functions Non-canonically to Enhance Antiviral Immunity via Recruiting Methyltransferase Prmt5. Cell Rep. 2020, 33, 108490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justice, J.L.; Kennedy, M.A.; Hutton, J.E.; Liu, D.; Song, B.; Phelan, B.; Cristea, I.M. Systematic profiling of protein complex dynamics reveals DNA-PK phosphorylation of IFI16 en route to herpesvirus immunity. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkl, P.E.; Knipe, D.M. Role for a Filamentous Nuclear Assembly of IFI16, DNA, and Host Factors in Restriction of Herpesviral Infection. mBio 2019, 10, e02621–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunphy, G.; Flannery, S.M.; Almine, J.F.; Connolly, D.J.; Paulus, C.; Jønsson, K.L.; Jakobsen, M.R.; Nevels, M.M.; Bowie, A.G.; Unterholzner, L. Non-canonical Activation of the DNA Sensing Adaptor STING by ATM and IFI16 Mediates NF-κB Signaling after Nuclear DNA Damage. Mol. Cell 2018, 71, 745–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crow, M.S.; Cristea, I.M. Human Antiviral Protein IFIX Suppresses Viral Gene Expression during Herpes Simplex Virus 1 (HSV-1) Infection and Is Counteracted by Virus-induced Proteasomal Degradation. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2017, 16, S200–S214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Yang, G.; Luo, Y.; Li, S.; Du, H.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, D.; Chen, J.; et al. The Nuclear Matrix Protein SAFA Surveils Viral RNA and Facilitates Immunity by Activating Antiviral Enhancers and Super-enhancers. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 26, 369–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahaye, X.; Gentili, M.; Silvin, A.; Conrad, C.; Picard, L.; Jouve, M.; Zueva, E.; Maurin, M.; Nadalin, F.; Knott, G.J.; et al. NONO Detects the Nuclear HIV Capsid to Promote cGAS-Mediated Innate Immune Activation. Cell 2018, 175, 488–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morchikh, M.; Cribier, A.; Raffel, R.; Amraoui, S.; Cau, J.; Severac, D.; Dubois, E.; Schwartz, O.; Bennasser, Y.; Benkirane, M. HEXIM1 and NEAT1 Long Non-coding RNA Form a Multi-subunit Complex that Regulates DNA-Mediated Innate Immune Response. Mol. Cell 2017, 67, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, R.M.; Depledge, D.P.; Bianco, C.; Thompson, L.; Mohr, I. RNA m6 A modification enzymes shape innate responses to DNA by regulating interferon β. Genes Dev. 2018, 32, 1472–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Hou, J.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Z.; Cao, X. The RNA helicase DDX46 inhibits innate immunity by entrapping m6A-demethylated antiviral transcripts in the nucleus. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 1094–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesser, C.R.; Walsh, D. YTHDF2 Is Downregulated in Response to Host Shutoff Induced by DNA Virus Infection and Regulates Interferon-Stimulated Gene Expression. J. Virol. 2023, 97, e0175822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
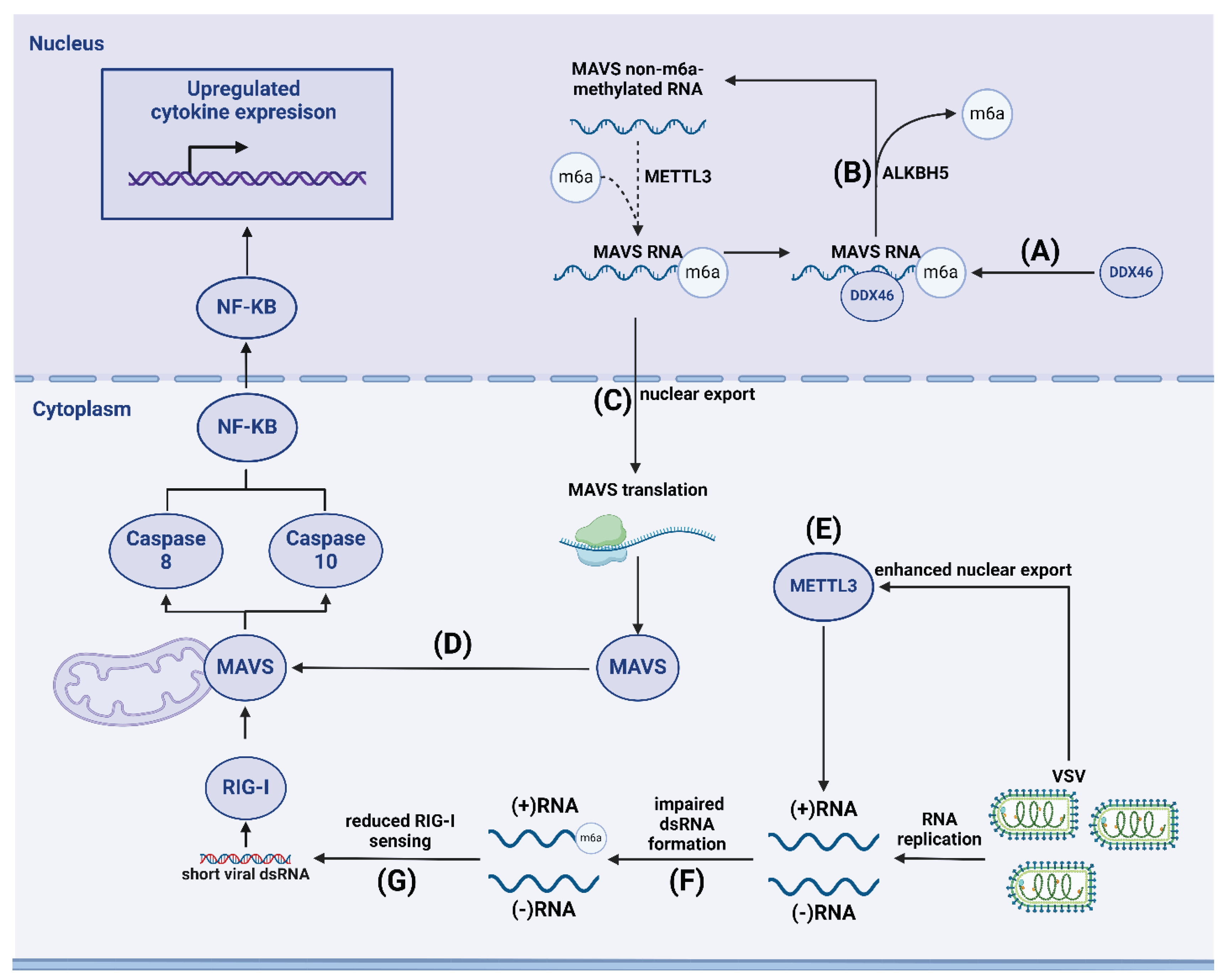
- Qin, F.; Cai, B.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, L.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, B.; Gao, C. Methyltransferase-Like Protein 14 Attenuates Mitochondrial Antiviral Signaling Protein Expression to Negatively Regulate Antiviral Immunity via N6-methyladenosine Modification. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2100606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Hui, H.; Bray, B.; Gonzalez, G.M.; Zeller, M.; Anderson, K.G.; Knight, R.; Smith, D.; Wang, Y.; Carlin, A.F.; et al. METTL3 regulates viral m6A RNA modification and host cell innate immune responses during SARS-CoV-2 infection. Cell Rep. 2021, 35, 109091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, W.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, R.; Lu, Y.; Wang, X.; Tian, H.; Yang, Y.; Gu, Z.; Gao, Y.; Yang, X.; et al. N6-methyladenosine RNA modification suppresses antiviral innate sensing pathways via reshaping double-stranded RNA. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
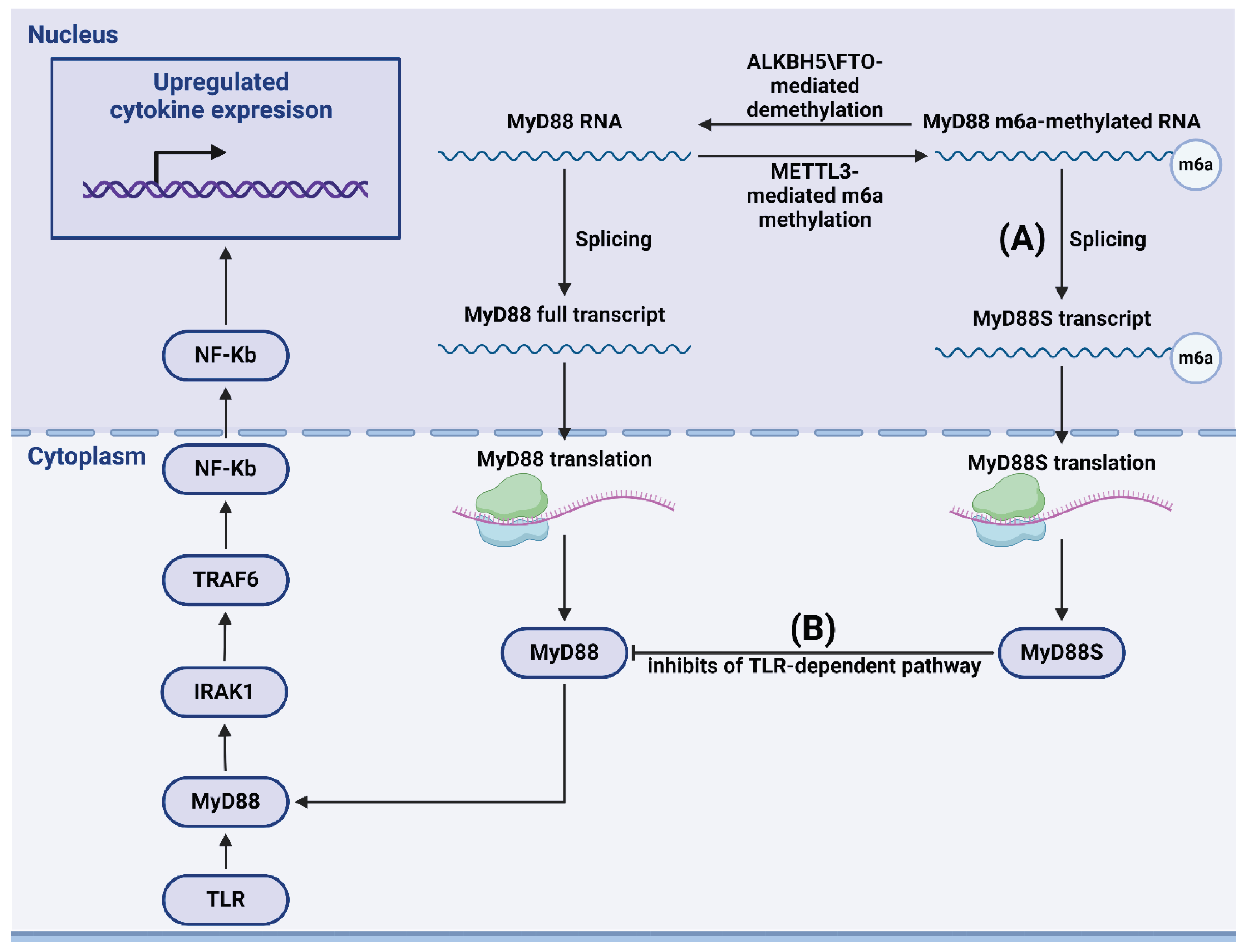
- Feng, Z.; Li, Q.; Meng, R.; Yi, B.; Xu, Q. METTL3 regulates alternative splicing of MyD88 upon the lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response in human dental pulp cells. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 2558–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wu, G.; Wu, Q.; Peng, L.; Yuan, L. METTL3 overexpression aggravates LPS-induced cellular inflammation in mouse intestinal epithelial cells and DSS-induced IBD in mice. Cell Death Discov. 2022, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karikó, K.; Buckstein, M.; Ni, H.; Weissman, D. Suppression of RNA Recognition by Toll-like Receptors: The Impact of Nucleoside Modification and the Evolutionary Origin of RNA. Immunity 2005, 23, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Ren, X.; Wang, A.; Chen, Z.; Yao, J.; Mao, K.; Liu, T.; Meng, F.-L.; et al. Pooled CRISPR screening identifies m 6 A as a positive regulator of macrophage activation. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabd4742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Hu, X.; Huang, M.; Liu, J.; Gu, Y.; Ma, L.; Zhou, Q.; Cao, X. Mettl3-mediated mRNA m6A methylation promotes dendritic cell activation. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, S.; Zheng, W.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, T. METTL3-Mediated m6A Modification of TRIF and MyD88 mRNAs Suppresses Innate Immunity in Teleost Fish, Miichthys miiuy. J. Immunol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balzarolo, M.; Engels, S.; de Jong, A.J.; Franke, K.; Berg, T.K.v.D.; Gulen, M.F.; Ablasser, A.; Janssen, E.M.; van Steensel, B.; Wolkers, M.C. m6A methylation potentiates cytosolic dsDNA recognition in a sequence-specific manner. Open Biol. 2021, 11, 210030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Zhang, L.; Li, C.; Maimaiti, M.; Sun, J.; Hu, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C.; Hu, H. m6A-mediated modulation coupled with transcriptional regulation shapes long noncoding RNA repertoire of the cGAS-STING signaling. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 1785–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Ling, T.; Wang, Y.; Jia, X.; Xie, X.; Chen, R.; Chen, S.; Yuan, S.; Xu, A. Degradation of WTAP blocks antiviral responses by reducing the m 6 A levels of IRF3 and IFNAR1 mRNA. Embo Rep. 2021, 22, e52101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
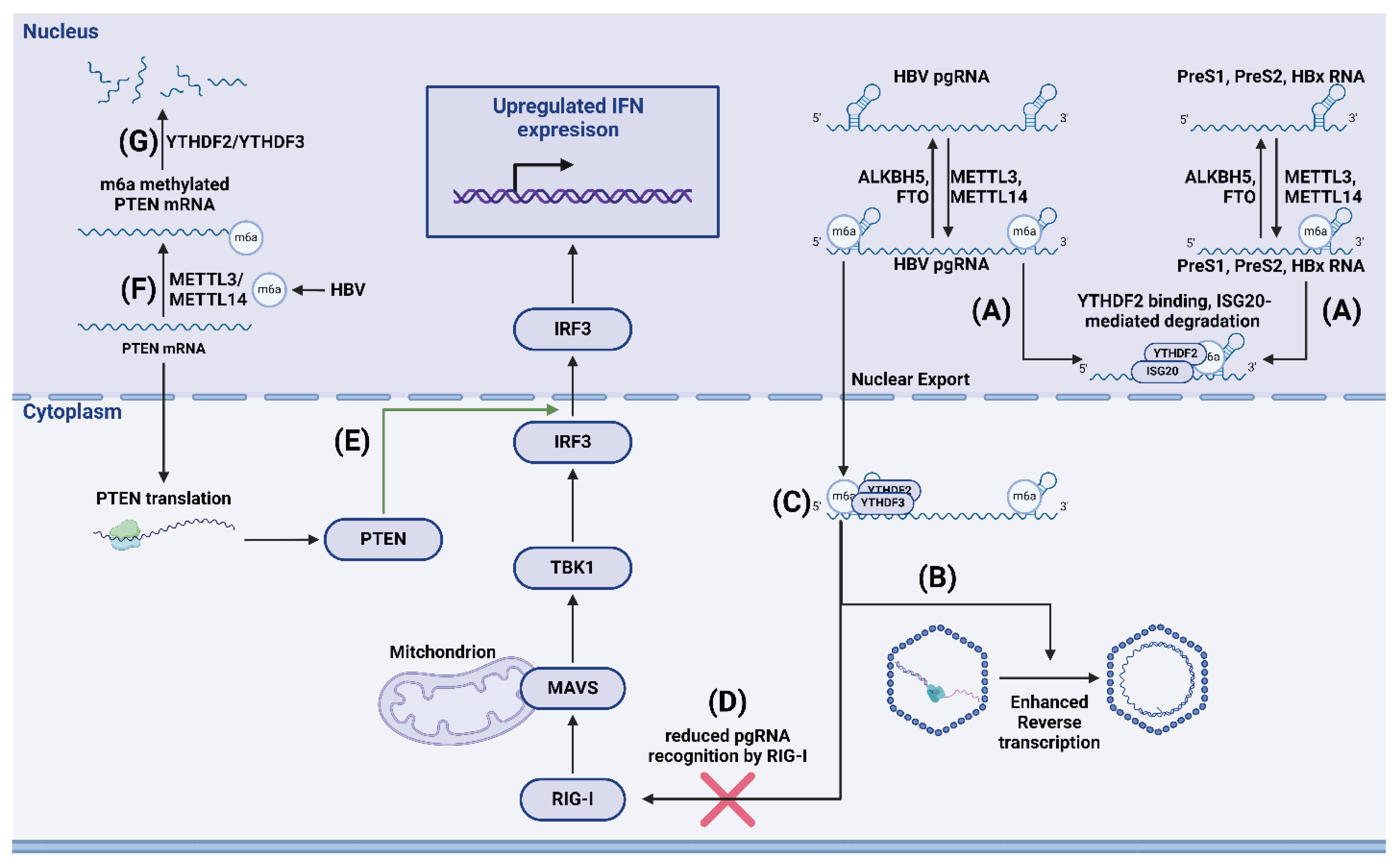
- Imam, H.; Kim, G.-W.; Mir, S.A.; Khan, M.; Siddiqui, A. Interferon-stimulated gene 20 (ISG20) selectively degrades N6-methyladenosine modified Hepatitis B Virus transcripts. PLOS Pathog. 2020, 16, e1008338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.; Imam, H.; Khan, M.; Mir, S.A.; Kim, S.; Yoon, S.K.; Hur, W.; Siddiqui, A. HBV-Induced Increased N6 Methyladenosine Modification of PTEN RNA Affects Innate Immunity and Contributes to HCC. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 533–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, L.; Cao, X. RNA-binding protein YTHDF3 suppresses interferon-dependent antiviral responses by promoting FOXO3 translation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2018, 116, 976–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirumuru, N.; Zhao, B.S.; Lu, W.; Lu, Z.; He, C.; Wu, L. N 6-methyladenosine of HIV-1 RNA regulates viral infection and HIV-1 Gag protein expression. Elife 2016, 5, e15528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.-L.; Pan, C.-Y.; Tseng, Y.-T.; Chen, F.-C.; Chang, Y.-C.; Wang, T.-C. Acute effects of high-intensity interval training and moderate-intensity continuous exercise on BDNF and irisin levels and neurocognitive performance in late middle-aged and older adults. Behav. Brain Res. 2021, 413, 113472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Kumar, S.; Espada, C.E.; Tirumuru, N.; Cahill, M.P.; Hu, L.; He, C.; Wu, L. N6-methyladenosine modification of HIV-1 RNA suppresses type-I interferon induction in differentiated monocytic cells and primary macrophages. PLOS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtney, D.G.; Kennedy, E.M.; Dumm, R.E.; Bogerd, H.P.; Tsai, K.; Heaton, N.S.; Cullen, B.R. Epitranscriptomic Enhancement of Influenza A Virus Gene Expression and Replication. Cell Host Microbe 2017, 22, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichinchi, G.; Zhao, B.S.; Wu, Y.; Lu, Z.; Qin, Y.; He, C.; Rana, T.M. Dynamics of Human and Viral RNA Methylation during Zika Virus Infection. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 20, 666–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokhale, N.S.; McIntyre, A.B.R.; McFadden, M.J.; Roder, A.E.; Kennedy, E.M.; Gandara, J.A.; Hopcraft, S.E.; Quicke, K.M.; Vazquez, C.; Willer, J.; et al. N6 -Methyladenosine in Flaviviridae Viral RNA Genomes Regulates Infection. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 20, 654–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.-W.; Siddiqui, A. The role of N6-methyladenosine modification in the life cycle and disease pathogenesis of hepatitis B and C viruses. Exp. Mol. Med. 2021, 53, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.-W.; Imam, H.; Khan, M.; Siddiqui, A. N6-Methyladenosine modification of hepatitis B and C viral RNAs attenuates host innate immunity via RIG-I signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 13123–13133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Xue, M.; Wang, H.-T.; Kairis, E.L.; Ahmad, S.; Wei, J.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y.; et al. Nonsegmented Negative-Sense RNA Viruses Utilize N 6 -Methyladenosine (m 6 A) as a Common Strategy To Evade Host Innate Immunity. J. Virol. 2021, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Kairis, E.L.; Lu, M.; Ahmad, S.; Attia, Z.; Harder, O.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, J.; et al. Viral RNA N6-methyladenosine modification modulates both innate and adaptive immune responses of human respiratory syncytial virus. PLOS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1010142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Xu, Y.-P.; Li, K.; Ye, Q.; Zhou, H.-Y.; Sun, H.; Li, X.; Yu, L.; Deng, Y.-Q.; Li, R.-T.; et al. The m6A methylome of SARS-CoV-2 in host cells. Cell Res. 2021, 31, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgess, H.M.; Depledge, D.P.; Thompson, L.; Srinivas, K.P.; Grande, R.C.; Vink, E.I.; Abebe, J.S.; Blackaby, W.P.; Hendrick, A.; Albertella, M.R.; et al. Targeting the m6A RNA modification pathway blocks SARS-CoV-2 and HCoV-OC43 replication. Genes Dev. 2021, 35, 1005–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Zhang, Y.-Z.; Yin, H.; Yu, L.-L.; Cui, J.-J.; Yin, J.-Y.; Luo, C.-H.; Guo, C.-X. Identification of SARS-CoV-2 m6A modification sites correlate with viral pathogenicity. Microbes Infect. 2024, 26, 105228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imam, H.; Khan, M.; Gokhale, N.S.; McIntyre, A.B.R.; Kim, G.-W.; Jang, J.Y.; Kim, S.-J.; Mason, C.E.; Horner, S.M.; Siddiqui, A. N6 -methyladenosine modification of hepatitis B virus RNA differentially regulates the viral life cycle. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2018, 115, 8829–8834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, T.; Iwahori, S.; Okuno, Y.; Nishitsuji, H.; Yanagi, Y.; Watashi, K.; Wakita, T.; Kimura, H.; Shimotohno, K. N6-methyladenosine Modification of Hepatitis B Virus RNA in the Coding Region of HBx. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.-W.; Imam, H.; Siddiqui, A. The RNA Binding Proteins YTHDC1 and FMRP Regulate the Nuclear Export of N 6 -Methyladenosine-Modified Hepatitis B Virus Transcripts and Affect the Viral Life Cycle. J. Virol. 2021, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostyusheva, A.; Brezgin, S.; Glebe, D.; Kostyushev, D.; Chulanov, V. Host-cell interactions in HBV infection and pathogenesis: the emerging role of m6A modification. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2021, 10, 2264–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Gao, W.; Liu, Z.; Yu, S.; Jian, H.; Hou, Z.; Zeng, P. Comprehensive analysis of m6A regulators associated with immune infiltration in Hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Gastroenterol. 2023, 23, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, A.M.; Hayer, K.E.; McIntyre, A.B.R.; Gokhale, N.S.; Abebe, J.S.; Della Fera, A.N.; Mason, C.E.; Horner, S.M.; Wilson, A.C.; Depledge, D.P.; et al. Direct RNA sequencing reveals m6A modifications on adenovirus RNA are necessary for efficient splicing. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajikhezri, Z.; Kaira, Y.; Schubert, E.; Darweesh, M.; Svensson, C.; Akusjärvi, G.; Punga, T. Fragile X-Related Protein FXR1 Controls Human Adenovirus Capsid mRNA Metabolism. J. Virol. 2023, 97, e0153922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Zhou, F.; Tan, M.; Wang, T.; Chen, Y.; Xu, W.; Li, B.; Wang, X.; Deng, X.; He, M.-L. Targeting m6A modification inhibits herpes virus 1 infection. Genes Dis. 2021, 9, 1114–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansens, R.J.; Olarerin-George, A.; Verhamme, R.; Mirza, A.; Jaffrey, S.; Favoreel, H.W. Alphaherpesvirus-mediated remodeling of the cellular transcriptome results in depletion of m6A-containing transcripts. iScience 2023, 26, 107310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Ye, W.; Chen, S.; Tang, Y.; Chen, D.; Lu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Huang, Z.; Ge, Y. METTL3-mediated m6A RNA modification promotes corneal neovascularization by upregulating the canonical Wnt pathway during HSV-1 infection. Cell. Signal. 2023, 109, 110784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Qi, Y.; Ju, Q. Promotion of the resistance of human oral epithelial cells to herpes simplex virus type I infection via N6-methyladenosine modification. BMC Oral Heal. 2023, 23, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walther, K.; Schulte, L.N. The role of lncRNAs in innate immunity and inflammation. RNA Biol. 2020, 18, 587–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




