Submitted:
12 March 2024
Posted:
12 March 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Experiment
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Experimental Design
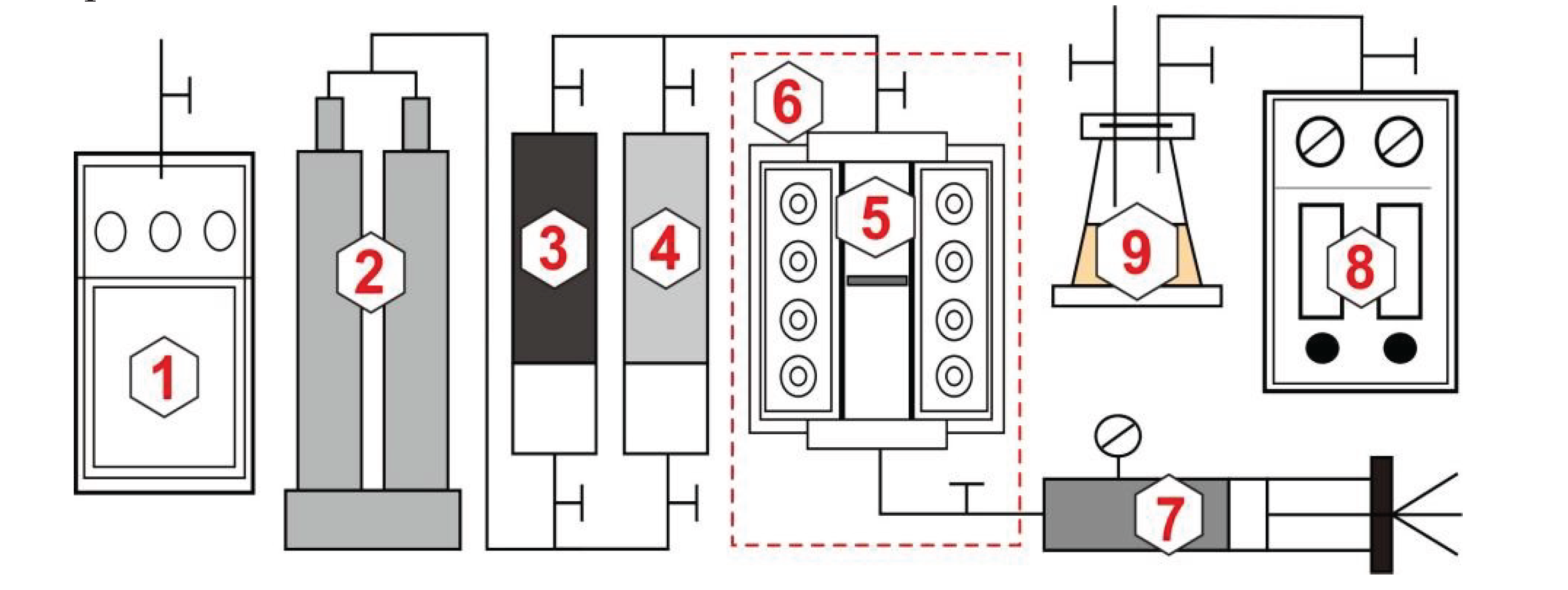
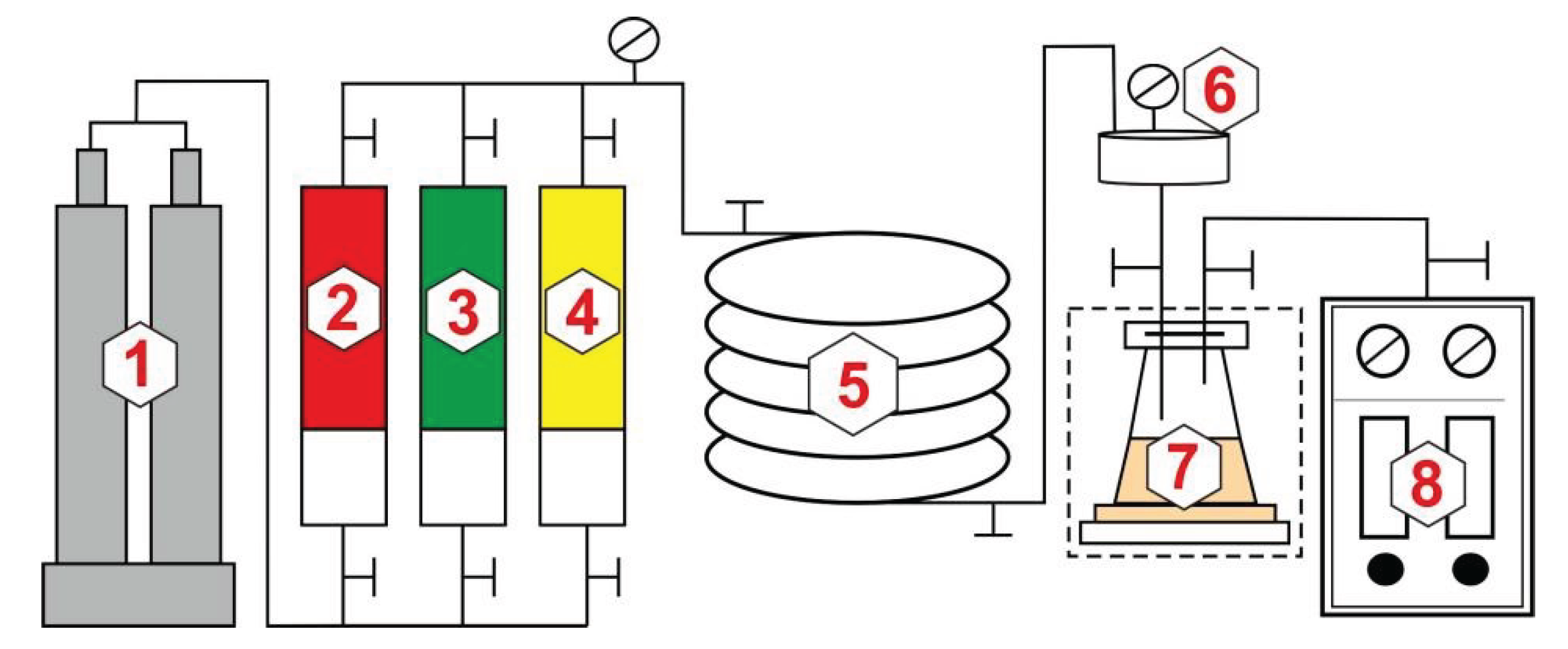
2.2.1. Experiment on Gas Injection Expansion
2.2.2. Experiment on Minimum Miscibility Pressure
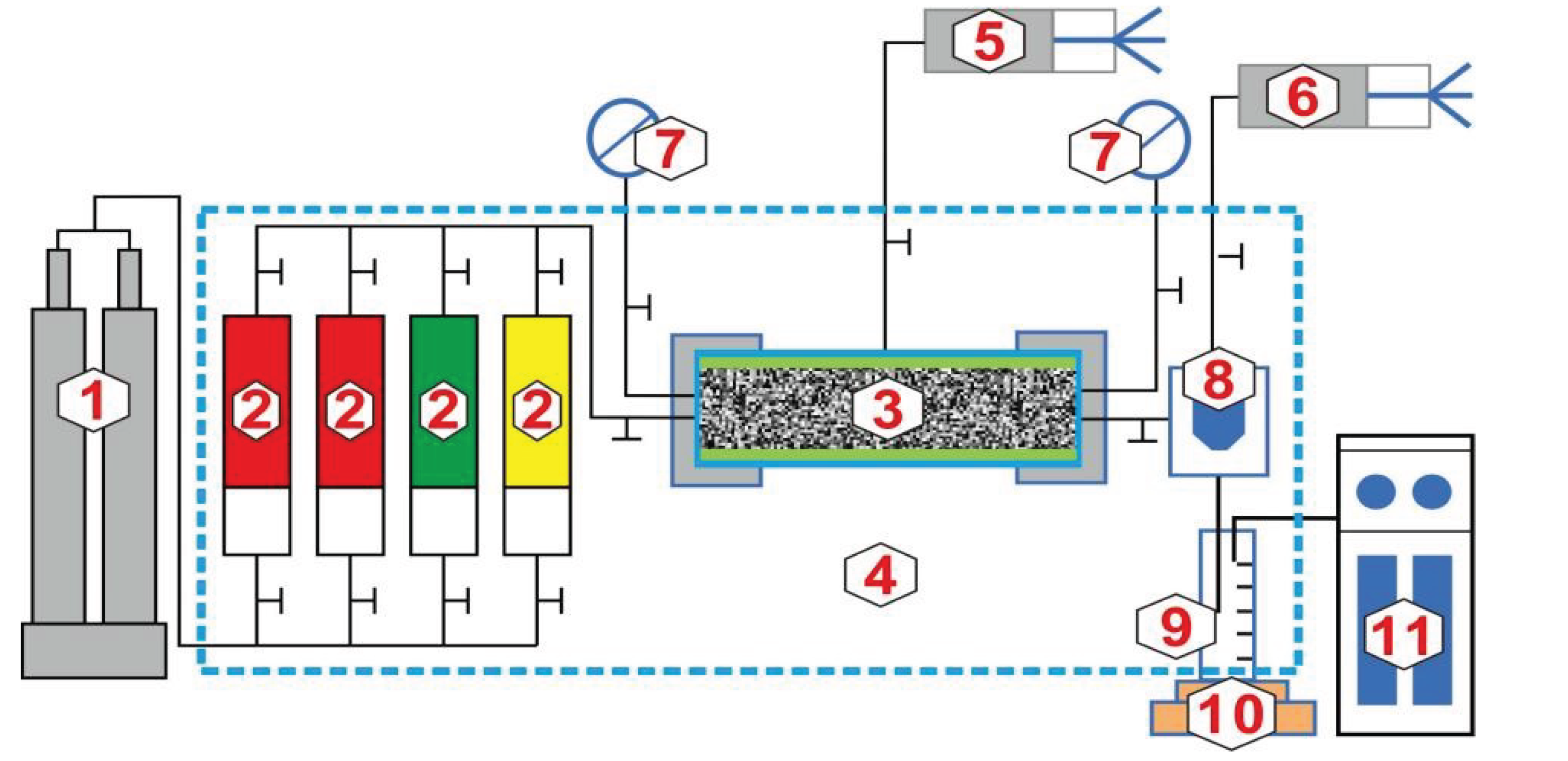
2.2.3. Experiment on CO2 Miscible Fracturing Huff and Puff
3. Experimental Results and Analysis
3.1. Mechanism of Oil Production Increase
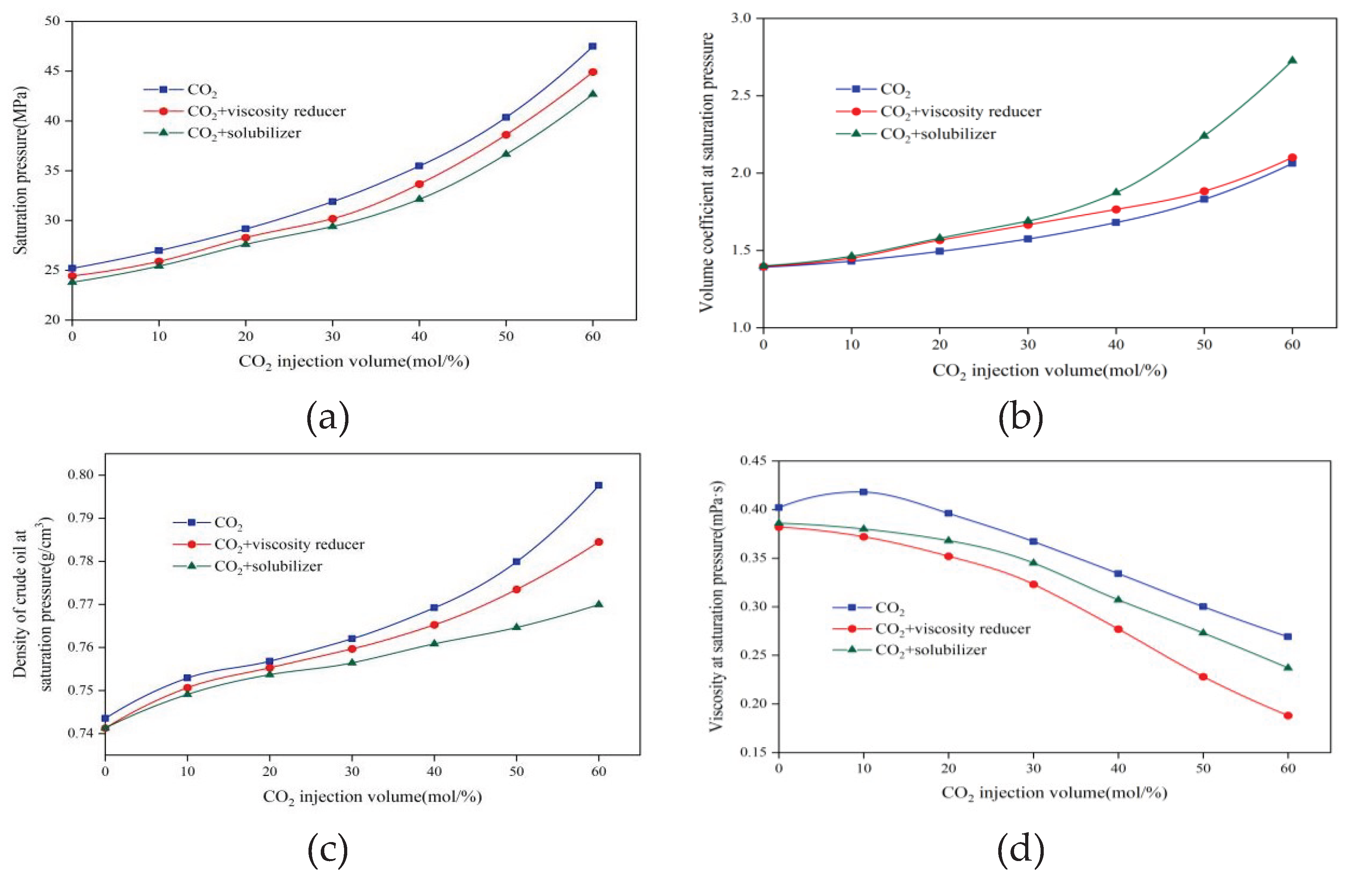
3.1.1. Interaction between CO2 And Crude Oil
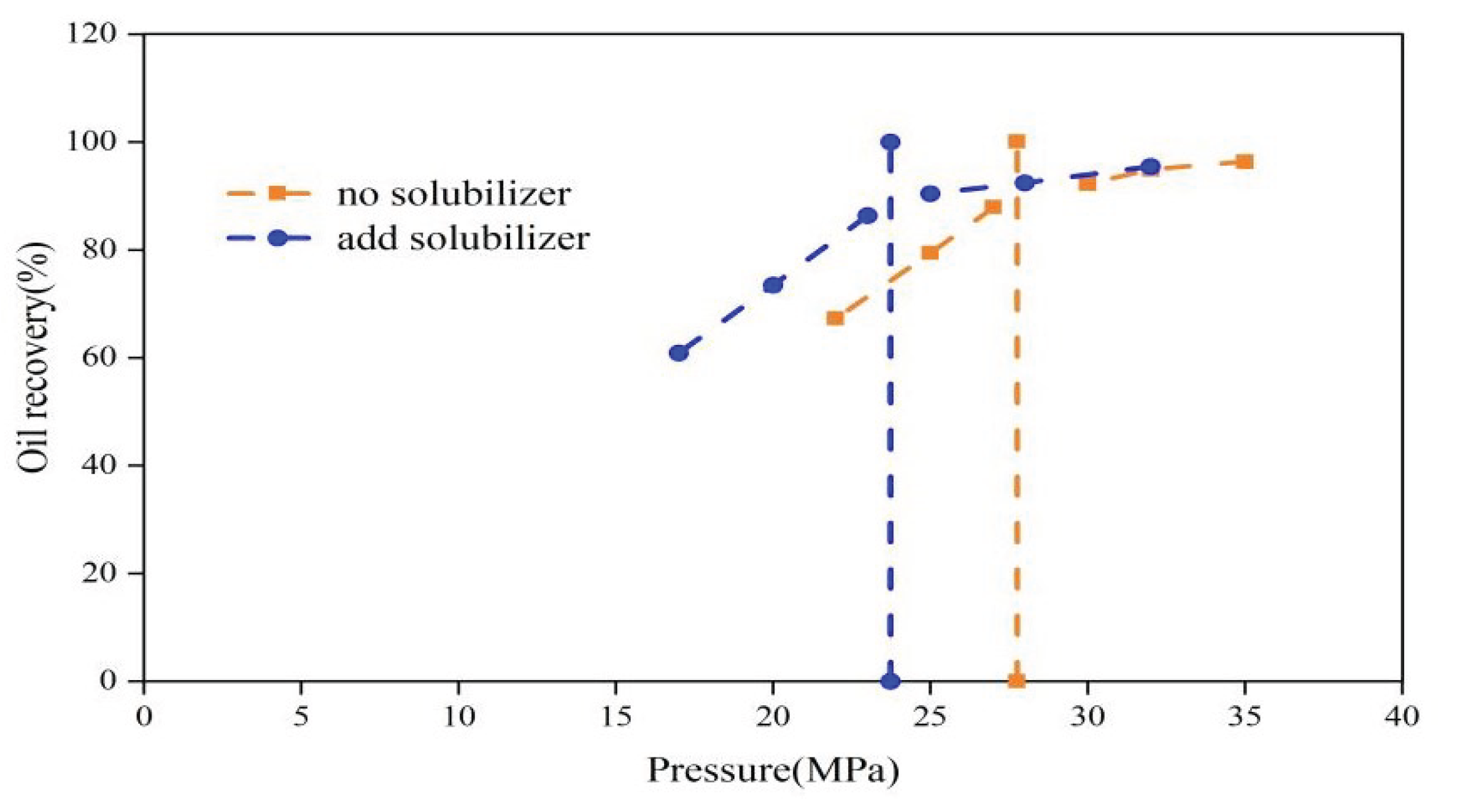
3.1.2. Minimum Miscibility Pressure
3.2. Effect of Huff and Puff
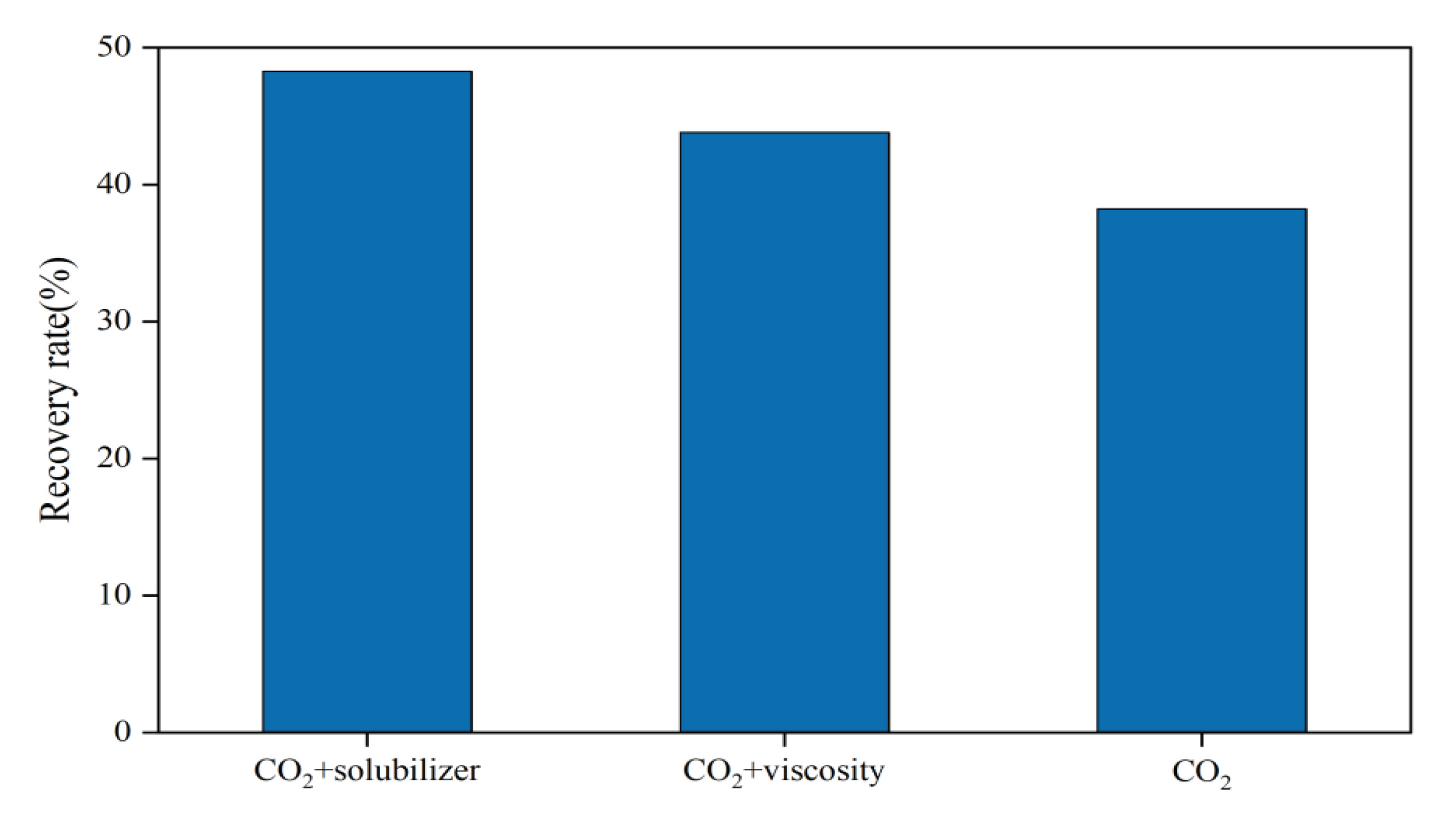
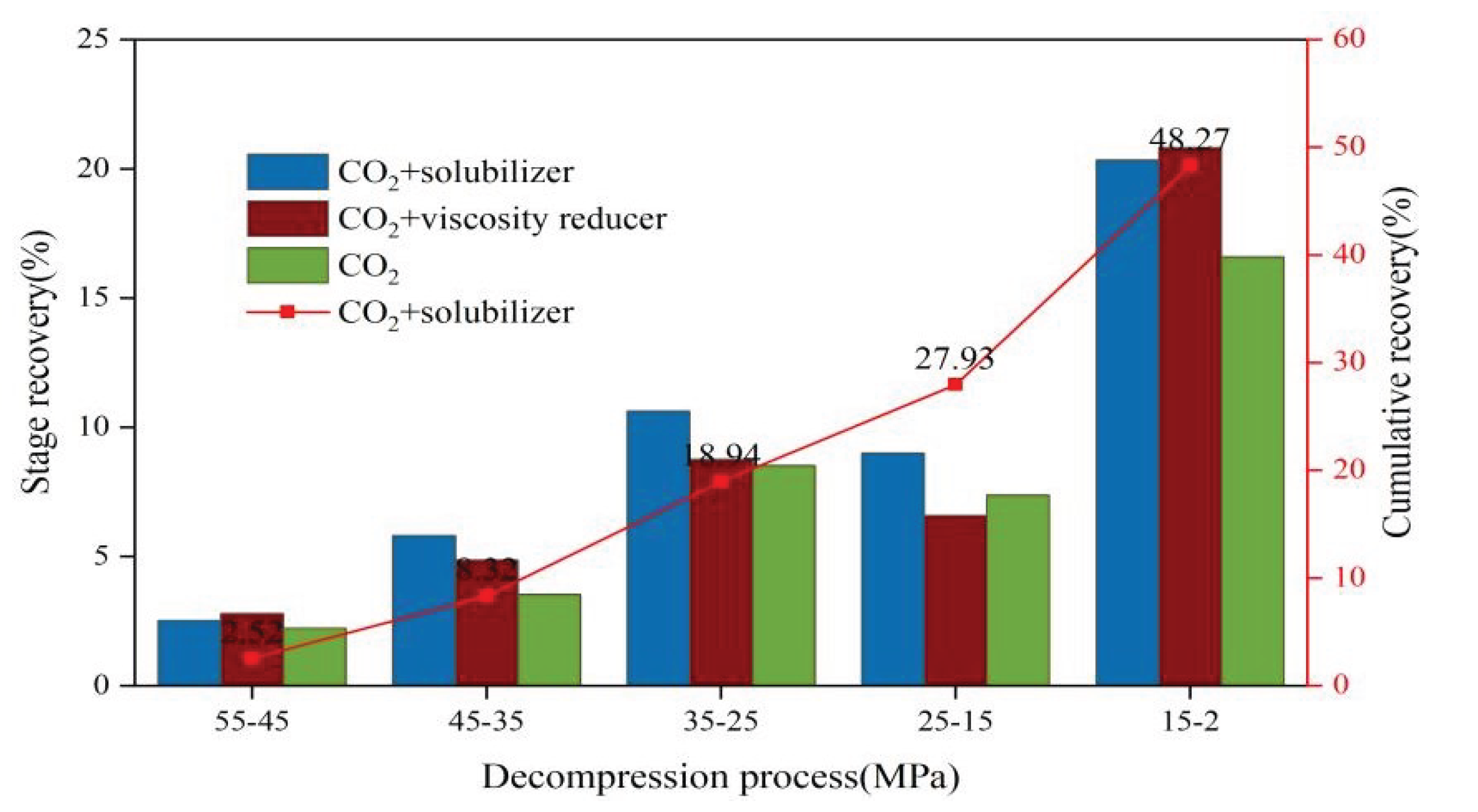
3.2.1. Impact of Fracturing Fluid Additives
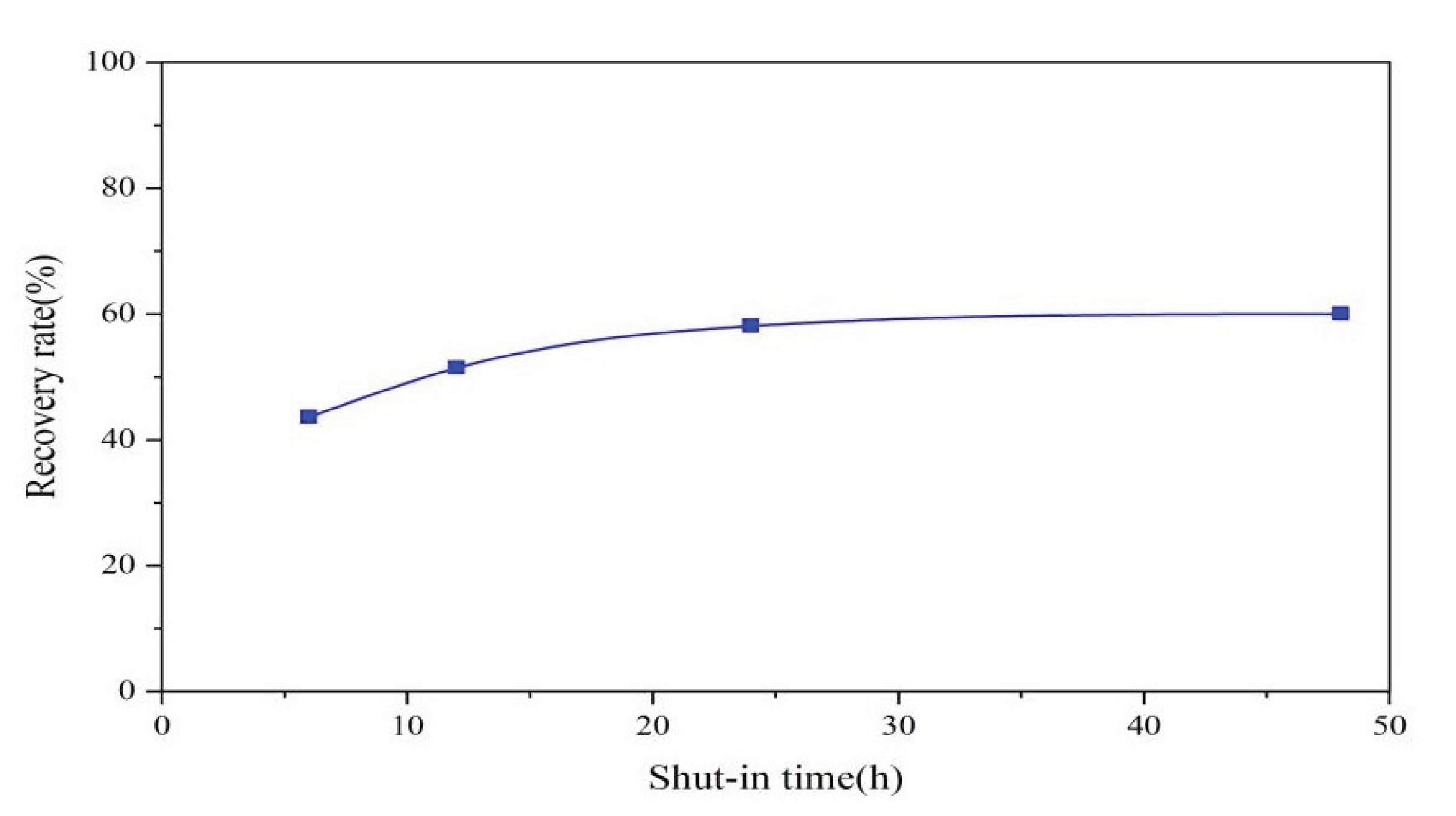
3.2.2. Impact of Shut-in Time
3.2.3. Impact of Permeability
3.2.4. Impact of Huff and Puff Patterns
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yuejun Zhao, Guangjuan Fan, Kaoping Song, Yilin Li, Hao Chen, et al. The experimental research for reducing the minimum miscibility pressure of carbon dioxide miscible flooding. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews 2021, 145, 111091. [CrossRef]
- N. Li, L. S. Cheng, Q. Li, C. Li, W. Sun. Phase change characteristics during carbon dioxide flooding. Energy Sources, Part A: Recovery, Utilization, and Environmental Effects 2012, 34(15), 1400-1406. [CrossRef]
- Seyyedi Mojtaba, Sohrabi Mehran. Assessing the feasibility of improving the performance of CO2 and CO2–WAG injection scenarios by CWI. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research 2018, 57(34), 11617-11624. [CrossRef]
- R. Miscible gas displacement of multicomponent oils. SPE J. 1996, 1(01), 39–50. [CrossRef]
- Angang Zhang, Zifei Fan, Lun Zhao. An investigation on phase behaviors and displacement mechanisms of gas injection in gas condensate reservoir. Fuel 2020, 268, 117373. [CrossRef]
- Tengfei Wang, Liangliang Wang, Xingbang Meng, Yi Chen, Wei Song, Chengdong Yuan. Key parameters and dominant EOR mechanism of CO2 miscible flooding applied in low-permeability oil reservoirs. Geoenergy Science and Engineering 2023, 225, 211724. [CrossRef]
- Maryam Mohdsaeed H., I. Abdulla, Shaligram Pokharel. Analytical models for predicting oil recovery from immiscible CO2 injection: A literature review. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering 2022, 219, 111131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokufe Afzali, Nima Rezaei, Sohrab Zendehboudi. A comprehensive review on enhanced oil recovery by water alternating gas(WAG) injection. Fuel 2018, 227, 218–246. [CrossRef]
- Liping He, Pingping Shen, Xinwei Liao, QiChao Gao, Chengsheng Wang, Fangfang Li. Study on CO2 EOR and its geological sequestration potential in oil field around Yulin city. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering 2015, 134, 199–204. [CrossRef]
- Mohamed Almobarak, Zangyuan Wu, Daiyu Zhou, Kun Fan, Yongbing Liu, Quan Xie. A review of chemical-assisted minimum miscibility pressure reduction in CO2 injection for enhanced oil recovery. Petroleum 2021, 7, 245–253. [CrossRef]
- Hao Chen, Bowen Li, Xiansong Zhang, Quan Wang, Xiaoqiang Wang, Shenglai Yang. Effect of gas contamination and well depth on pressure interval of CO2 near miscible flooding, Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering 2019, 176, 43–50. [CrossRef]
- Ramin Moghadasi, Alireza Rostami, Abdolhossein Hemmati-Sarapardeh. Enhanced oil recovery using CO2. Fundamentals of Enhanced Oil and Gas Recovery from Conventional and Unconventional Reservoirs 2018, 61–99. [CrossRef]
- Hamid, R. Lashgari, Alexander Sun, Tongwei Zhang, Gary A. Pope, Larry W. Lake. Evaluation of carbon dioxide storage and miscible gas EOR in shale oil reservoirs. Fuel 2019, 241, 1223–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng Chen, Matthew Balhoff, Kishore K. Mohanty. Effect of reservoir heterogeneity on primary recovery and CO2 huff ‘n’ puff recovery in shale-oil reservoirs. SPE Reservoir Evaluation & Engineering 2014, 17(3), 404-413. [CrossRef]
- Zeya Li, Yongan Gu. Soaking effect on miscible CO2 flooding in a tight sandstone formation. Fuel 2014, 134, 659–668. [CrossRef]
- Yuejun Zhao, Guangjuan Fan, Yilin Li, Xiaodan Zhang, Hao Chen, He Sun. Research for reducing minimum miscible pressure of crude oil and carbon dioxide and miscible flooding experiment by injecting critic acid isopentyl ester. Arabian Journal of Chemistry 2020, 13(12), 9207–9215. [CrossRef]
- He Liu, Feng Wang, Jian Zhang, Siwei Meng, Yongwei Duan. Fracturing with carbon dioxide: Application status and development trend. Petroleum exploration and development 2014, 41(4), 513-519. [CrossRef]
- Zhengguo He, Shouceng Tian, Gensheng Li, Haizhu Wang, Zhongzhu Shen, Zhengming Xu. The pressurization effect of jet fracturing using supercritical carbon dioxide. Journal of natural gas science and engineering 2015, 27(2), 842–851. [CrossRef]
- Narendra Kumar, Marcio Augusto Sampaio, Keka Ojha, Hussein Hoteit. Ajay Mandal. Fundamental aspects, mechanisms and emerging possibilities of CO2 miscible flooding in enhanced oil recovery: A review. Fuel 2022, 330, 125633. [CrossRef]
- Luis M., C. Pereira, Antonin Chapoy, Rod Burgass, Bahman Tohidi. Measurement and modelling of high pressure density and interfacial tension of (gas + n-alkane) binary mixtures. The Journal of Chemical Thermodynamics 2016, 97, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mingyong Du, Xin Sun, Caili Dai, Hao Li, Tao Wang, Zhongliang Xu, Mingwei Zhao, Baoshan Guan, Ping Liu. Laboratory experiment on a toluene - polydimethyl silicone thickened supercritical carbon dioxide fracturing fluid. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering 2018, 166, 369–374. [CrossRef]
- Houjian Gong, Xuejin Qin, Shengxiang Shang, Chaofan Zhu, Long Xu, Qian San, Yajun Li, Mingzhe Dong. Enhanced shale oil recovery by the huff and puff method using CO2 and cosolvent mixed fluids. Energy & Fuels 2020, 34(2), 1438-1446. [CrossRef]
- Su Yuliang, Wang Chenwei, Li Lei, Hou Zhengxiao, Fan Liyao, Chen Zheng. Behavior of CO2 pre-fracturing fluid in tight reservoir. Science Technology and Engineering 2021, 21(8), 3076-3081.

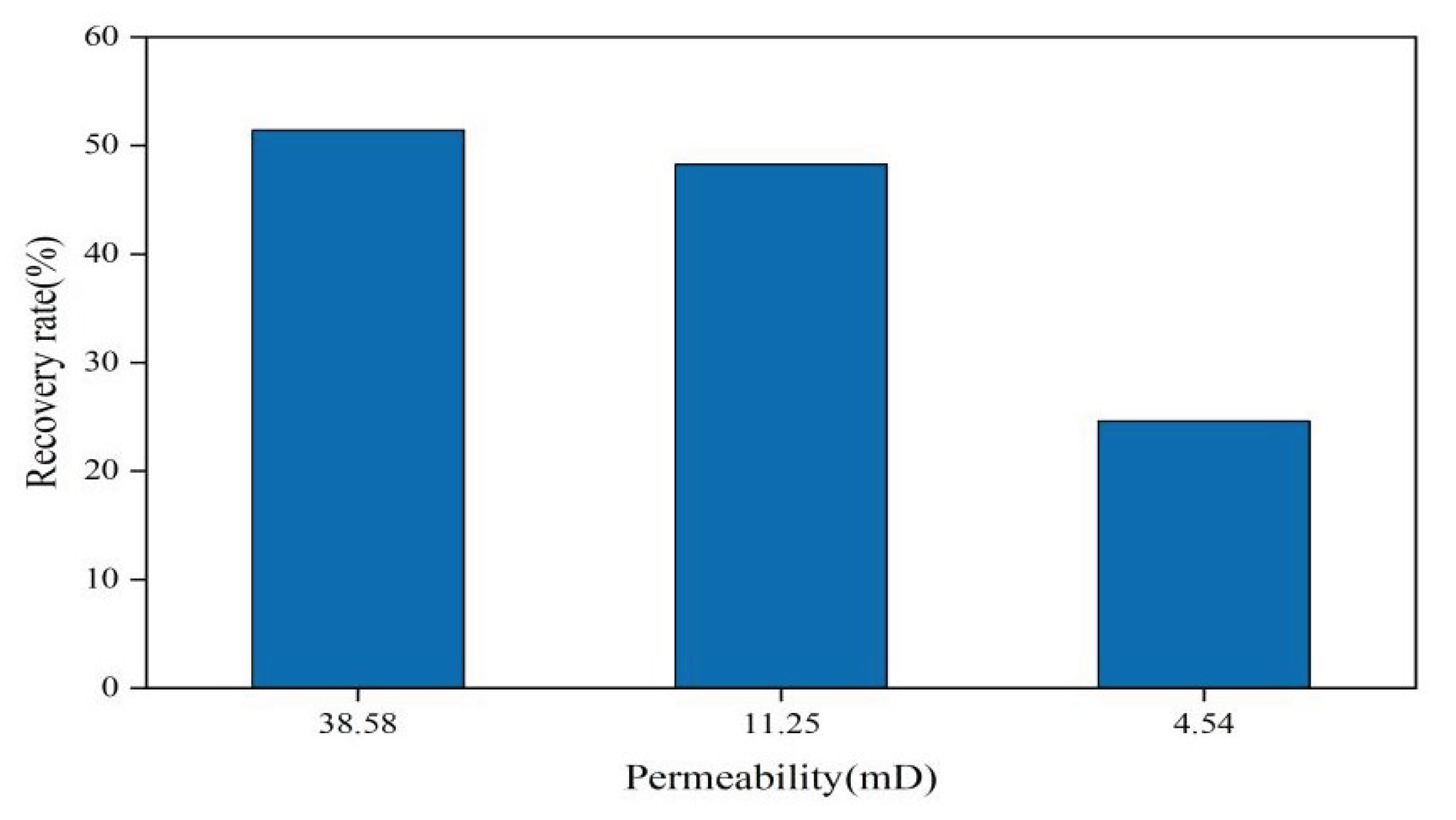
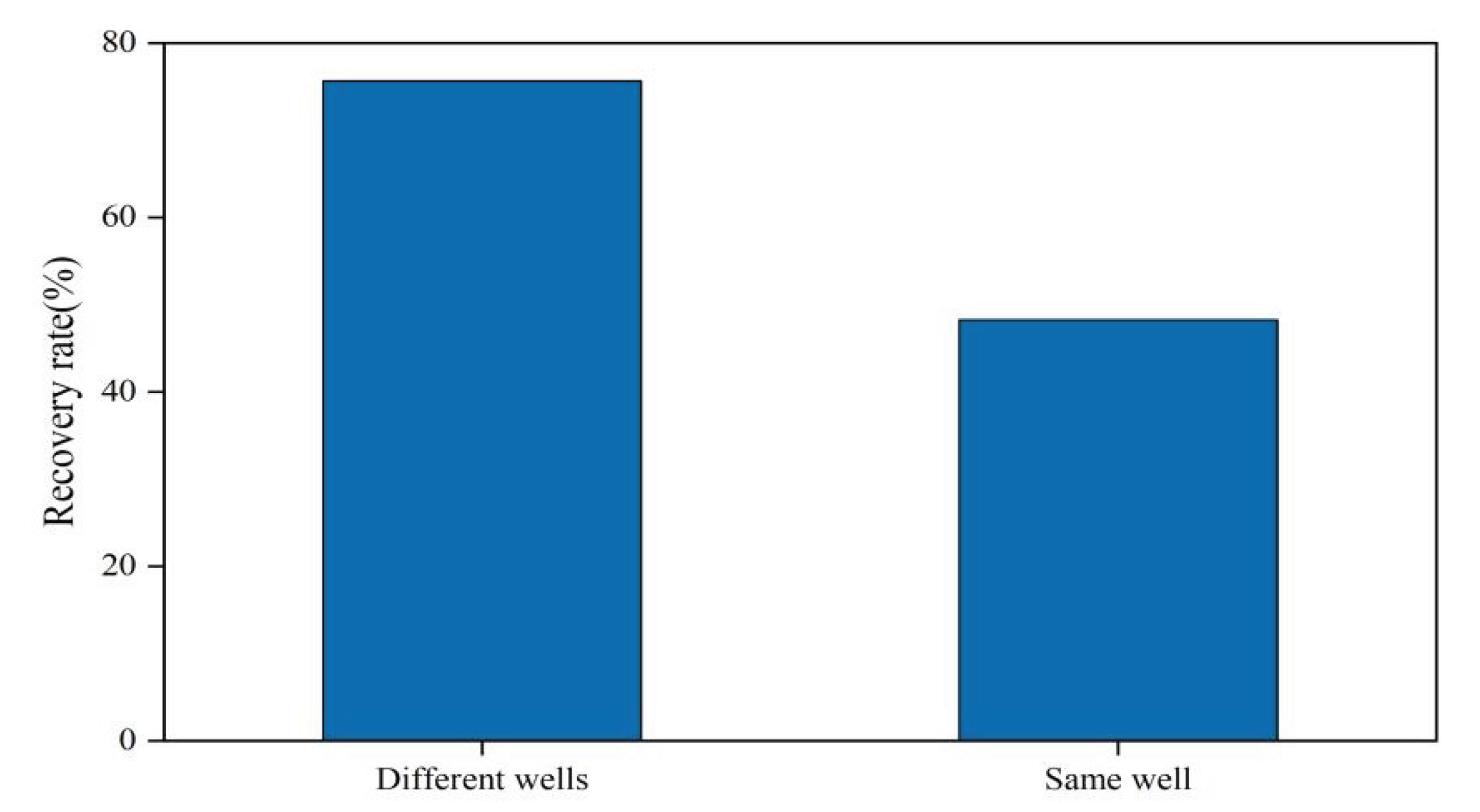
| Core | Length(cm) | Diameter(cm) | Permeability(mD) | Porosity(%) | Injection medium | Shut-in time | Huff and puff mode |
| 1-1 | 9.454 | 2.523 | 39.42 | 19.72 | CO2+solubilizer | 6 | Same well |
| 1-2 | 9.835 | 2.525 | 38.58 | 19.27 | 12 | ||
| 1-3 | 9.637 | 2.521 | 39.15 | 19.31 | 24 | ||
| 1-4 | 9.646 | 2.523 | 38.97 | 18.96 | 48 | ||
| 2-1 | 9.832 | 2.520 | 11.85 | 17.02 | CO2 | 12 | Same well |
| 2-2 | 9.994 | 2.521 | 11.25 | 17.25 | CO2+solubilizer | ||
| 2-3 | 9.705 | 2.522 | 11.48 | 17.31 | |||
| 2-4 | 9.924 | 2.523 | 12.07 | 17.59 | Different well | ||
| 3-1 | 9.841 | 2.532 | 4.54 | 12.72 | Same well |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





