1. Introduction
Alfalfa (alias lucerne,
Medicago sativa L. subsp.
sativa) is the most grown perennial forage legume in Mediterranean-climate and temperate-climate regions [
1,
2]. As a crop, it is prized for its high nutritional content, serving as a vital feed for various livestock species due to its rich protein, vitamin, and mineral composition. As a legume, alfalfa is capable of fixing atmospheric nitrogen into the soil through symbiosis with nitrogen-fixing bacteria, thus enhancing soil fertility and diminishing the reliance on synthetic fertilizers in crop rotations [
3]. Additionally, its deep root system enables alfalfa to access water and nutrients from deeper soil layers, making it resilient to drought conditions and contributing to soil stabilization and erosion control [
4].
Unfortunately, alfalfa may appear as a less attractive choice for growers when compared to other crops, especially cereals. Indeed, progress in alfalfa variety improvement has been slow, due to a number of concurring factors such as long breeding cycles, low heritability of traits, and complex genetic structure [
2]. More specifically, progress on biomass yield improvement is constrained by a high ratio of non-additive genetic variance due to complementary alleles in the repulsion phase at different loci and intra-locus allelic interactions allowed for by autotetraploidy [
5]. In practical terms, alfalfa suffers heavily from inbreeding depression and does not allow the creation of pure lines or real hybrids [
6]. Since the intrinsic complexity of the genetic architecture appears irreducible, crop improvement could thus benefit from advancements in related topics such as sequencing, genomic parametrization, and genomic regression models. Alfalfa genomic selection through models constructed by genotyping parent plants and phenotyping their half-sib progenies, as required for synthetic variety development (which can only exploit the additive genetic variance), is convenient also in view of the relatively greater efficiency of half-sib progeny-based selection relative to other selection schemes for crop yield improvement in this species [
7]. Indeed, this genomic selection approach has proved promising for improving biomass yield and key forage quality traits in pioneer studies [
8,
9], which, however, used a diploid representation of the tetraploid genome (by pooling the three heterozygous classes Aaaa, AAaa, AAAa into a single class) because of largely insufficient SNP reading depth for a tetraploid parametrization.
Recent technological advancements have spurred the development of second- and third-generation sequencing platforms, which have greatly enhanced the creation of genomic resources for polyploid genomes. Reduced-target next-generation sequencing techniques, such as genotyping-by-sequencing (GBS), have enabled the sequencing of numerous polyploid species and facilitated SNP discovery. Moreover, a variety of software tools and scripts tailored for polyploid crop data analysis has become available. Different SNP calling pipelines for GBS, such as fast-GBS [
10], Ugbs-Flex [
11], and PolyRAD [
12], are being utilized in polyploid research [
13]. However, no clear a priori indication about the best approach for sequencing and genomic parametrization is available. Existing studies provide experimental evidence [
14], but new applications - especially when considering new crops - require dedicated optimization efforts.
The availability of large number of SNP markers allowed for effective implementation of genomic selection, by which phenotyping and genotyping data of a genotype sample representing a target genetic base (reference population) are combined into a model that estimates breeding values for future plant selection [
8]. In this context genomic regressions are used as proxy for the efficacy of genomic selection at large. As such, choices on treatment and representation of genomic data can have effect on the final performance metric of choice, usually the predictive ability of the regression. It is thus possuble to explicitly measure and compare the effect of different strategies, and consequently select the optimal combination.
In this study we investigate the effects on genomic regression of 1) genome parametrization (tetraploid allele dosage vs. diploid vs. observed alleles ratios); 2) subsetting SNPs located only in the genic areas (i.e., coding regions of the genome); 3) filtering genomic data based on missing rate and reading depth. The plant material was a European reference population obtained by intercrossing several elite semi-dormant cultivars bred in different countries, with polycrossing aimed to remove the population structure. The material was grown in a moisture-favorable and a drought-prone environment. Together with the analyses, we released Legpipe2, an open-source SNP calling pipeline that guarantees reproducibility.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material and Phenotyping
The development of the European reference population of semi-dormant alfalfa is briefly described in [
15] . The 10 contributing cultivars were selected according to breeders’ indications on best-performing material in seven countries, envisaging more cultivars for countries with larger alfalfa cropping area. The cultivars were Beatrix, Costanza and Cuore Verde from Italy, Fado and Galaxie from France, Cezara from Romania, Dara from Bulgaria, Mediana from Serbia, Morava from the Czech Republic, and Vanda from Slovakia, which underwent two generations of intercrossing by bumble bees (
Bombus terrestris) under insect-proof cages. A set of 143 genotypes were randomly chosen for this study, genotyping them and phenotyping their half-sib progenies in a two-year experiment carried out in Lodi, northern Italy, in a large phenotypic platform. The platform consisted of six large (24.0 m × 1.6 m × 0.8 m deep) bottomless containers in concrete, filled with local sandy-loam soil, under a rainout shelter provided with a double-rail irrigation boom. Three containers represented as many replications of a managed environment with imposed severe drought stress, and the other three containers as replications of a moisture-favorable managed environment. The experiment was established as an alpha lattice with 16 incomplete blocks of nine plots each within each replication (a ‘filler’ entry was added to the 143 half-sib families). The area of each plot measured 0.24 m2 (0.8 m × 0.3 m) and included four rows of 10 plants, each spaced 7.5 cm within and across rows (plant density = 166.7 m-2). The four front plants of the plot were treated as border plants and discarded from the harvest area. The sowing took place in late winter (early March 2022) in plugtrays kept in a greenhouse, and seedling transplantation was performed in the platform after eight weeks (early May). Mineral fertilisation was incorporated into the seedbed prior to transplantation at the rates of 27 kg ha-1 N, 46 kg ha-1 P2O5, and 50 kg ha-1 K2O. After an initial period of favorable growth implying 180 mm of irrigation to all containers, the two conditions of water availability were applied starting from the beginning of July 2022. The two conditions were meant to represent contrasting environments for semi-dormant material across Italy, namely, a rainfed, stressful environment mostly occurring in Central Italy, and a favorable, irrigated environment mainly occurring in the northern part of the Po Valley. During the first year (July-December 2022), the moisture-favorable condition received 445 mm of irrigation (in two applications per month) while the stressful condition received 230 mm of irrigation (in one application per month). In the second year (January-December 2023), the irrigation amounts were 825 mm and 375 mm, respectively. The dry biomass yield was recorded on a plot basis in both conditions by hand clipping all the living plants within the harvest area at a cutting height of 5 cm from the ground, and immediately oven drying the whole plot biomass at 60 °C for four days to constant weight. Four harvests were made in the first year (between mid-July and late October), and six in the second year (between mid-April and mid-October). However, due to growth impairment caused by the drought stress, only two harvests were made in the stressed treatment in the first year (skipping the harvests in August and September), and three in the second year (skipping the harvests in June, July and early September). The total dry matter yield across years referred, therefore, to 10 harvests for the moisture-favorable condition, and five harvests for the drought-stressed one. Onset of flowering was recorded as number of days from the day of harvest to the date when open flowers were visible on 10% of the plants per plot. The character was assessed on three regrowth after harvests in both years (twice in the first year, once in the second one). Leaf size was recorded in early July of the first year, just before the imposition of the two moisture treatments, by measuring the maximum length and width of the central leaflet of a representative leaf (usually, the third or fourth from the uppermost vegetative node) from four random plants per plot, and computing the leaf area, expressed in cm2, as length × width.
2.2. Experimental Design Solution, BLUPs Computation and Heritability
Broad-sense heritability was estimated [
16] as the ratio of the genetic variance
to the phenotypic variance
:
where
depends on the variance components for genotype
, experimental error
and number of replicates
, according to the formula:
Best Linear Unbiased Predictions (BLUPs) were then used as phenotypic data for genomic regressions [
17]. BLUPs were computed by solving the mixed model equation where varietal effect is included as random,
i.e., by summing the model intercept (overall mean) to the random effects associated to each genotype, as described in [
18]. Heritability and BLUP values computations were carried out using R-package INTI . For total dry matter, recorded in two environments, we verified the occurrence of half-sib progeny × environment interaction in an analysis of variance including the factors environment, progeny and replication, and estimated the genetic correlation coefficient for half-sib progeny response across environments according to [
20].
2.3. DNA Extraction, Library Preparation, Sequencing
Genomic DNA was extracted from young leaves of each plant using the DNeasy Plant Mini Kit (Qiagen, Milan, Italy). Nucleic acid was quantified by a Quant-iT™ PicoGreen™ dsDNA Assay Kit (P7589, Life Technologies, Italy), checking its quality by 1% agarose gel electrophoresis. A trial digestion was carried out on 10% of the DNA samples using the Optizyme EcoRI restriction enzyme (25,000 U, Fisher BioReagents, Rodano, MI, Italy), to compare bands of cut and uncut DNA. The reaction was performed at 37 °C for one hour and the enzyme was deactivated at 65 °C for 20 min. DNA samples were sent to The Elshire Group Ltd. laboratory (Palmerston North, New Zealand) for outsourced library preparation and sequencing. GBS data were generated according to Elshire et al.’s method [
21] with the following changes: we used 100 ng of genomic DNA and 3.6 ng of total adapters and restricted the genomic DNA with ApeKI enzyme (NEB New England Biolabs, R0643L); then, the library was amplified with Kapa Taq polymerase Alpha (KAPA Library Amplification Readymix, Kapa Biosystems KK2611) by 14 PCR cycles.
The library was sequenced at the Elshire Group Ltd. facility (New Zealand) using an Illumina X Ten platform with 150 bp paired end reads. Each sample was repeated three times on three different lanes. The raw reads were collated before demultiplexing.
Raw reads have been deposited to: DATA WILL BE UPLOADED TO NBCI-SRA UPON PAPER ACCEPTANCE.
2.4. SNP Calling, Filtering, Genome Parametrization
SNP calling was executed using the
Legpipe2 pipeline, released together with this paper. The configuration file necessary to reproduce the actual SNP calling is available in Supplementary File 1. As reference genome, we used the sequence obtained from Long et al., 2022 [
22] selecting the longest copy of each chromosome.
Obtained variants were filtered for quality (phred score >= 40), minor allele frequency (MAF >= 5%), several levels of missing per marker (5%, 10%, 20%) and of minimum total reads (10, 20, 30, 40). The combination of the above filtering produced 12 different genomic dataset, to be further analyzed in parallel.
After SNP calling the data were transformed in three different genomic parametrization: allele ratios, tetraploid SNP dosage and diploid SNP dosage.
Allele ratios are defined as:
where
a is the number of reads containing the alternative allele and
A is the number of reads containing the standard allele. The allele ratios are thus defined in the [0,1] interval. Allele ratios were computed using a custom R script.
The second genomic parametrization is tetraploid SNP dosage and aims to model the actual number of alternative alleles present at each SNP site. As such, for each SNP-sample pair the final result is an integer number between zero (homozygote of the same allele found in the reference genome) and four (homozygote of the alternative genome), with the in-between values between one and three representing the three types of heterozygotes possible in an autotetraploid genome. This parametrization was obtained using the
multidog function from the
updog R package [
23] with parameters
ploidy=4 and
model=”norm”. Once the dosages were obtained, the SNPs were further filtered discarding the markers with the
bias parameter outside the [e-1, e1] range.
The third genomic parametrization is diploid SNP dosage and is a simplification of tetraploid SNP dosage obtained collating the three possible heterozygotes in a single bin of intermediate value between the two homozygotes. In practical terms, each SNP-sample pair was represented by an integer value between zero (homozygote of the reference allele) and two (homozygote of the alternative allele). Regardless of the dosage, all the possible heterozygotes were represented by the value one.
SNPs were also qualified as belonging or not to genic regions, using the information available with the reference genome [
22]. As such, we compared the regression results using either the full set of SNPs, or only the SNPs coming from genic regions, or only the SNPs coming from non-genic regions.
2.5. Genomic Regression
Genomic predictions were investigated for all quantitative traits (grain yield in favorable and stressed conditions, onset of flowering and leaf size) by using ridge regression BLUP (rrBLUP) [
24]. We assessed the predictive ability of genomic regression as Pearson’s correlations between true and predicted phenotypes via ordinary 10 folds cross-validation for the four traits using the R package GROAN [
25].
3. Results
3.1. Phenotypic Analysis
Table 1 reports broad sense heritabilities and descriptive statistics for the four focus traits. The highest heritability was found for onset of flowering (0.690) followed by leaf size (0.550) and total dry matter in the favorable environment (0.529). The lowest one (0.302) was computed for total dry matter in the drought stressed environment. Apart from reducing the heritability, drought stress heavily reduced the total dry matter yield, with mean value passing from 16.50 t/ha in favorable conditions to 6.84 t/ha in the stressed ones. The presence of stress also reduced the genetic coefficient of variation for total dry matter yield from 9.2% in the favorable environment to 5.5% in the stressed environment. The coefficient of variation for experimental error was almost identical for yield in the two conditions.
The genetic correlation for half-sib dry matter yield across the two environments was relatively high, namely, rg = 0.82, despite the occurrence of highly significant half-sib progeny × environment interaction (P < 0.001). Total dry matter yield in favorable conditions displayed a modest positive phenotypic correlation with leaf size (r = 0.14) and a negative correlation with onset of flowering (r = –0.25), whereas onset of flowering and leaf size correlated positively (r = 0.27).
3.2. Sequencing, SNP Calling, Filtering
Sequencing produced an average of 7.5 Mreads per sample.
Table 2 reports the resulting number of SNP markers depending on the applied filters on required number of reads per locus, allowed maximum missing rate, and parametrization. As expected, the total number of SNP markers shrank as the filter parameters became stricter (higher required reads, lower accepted missing rates), ranging from 2387 to 19668 markers.
Genome parametrization heavily influenced the final number of markers, since many markers were rejected during the SNP dosage calling due to insufficient number of reads to support proper dosage estimation. This became particularly evident with stricter filtering on missing rate, e.g., minimum reads per locus = 10 and maximum missing rate = 5% resulted in about twice as many ratio markers as dosage markers. For comparison, with maximum missing rate = 20% the number of markers resulted about the same with the two genome parametrizations.
Table 2 also reports the amount of SNP markers located in genic regions. While the absolute values changed with filtering and parametrization, the fraction of markers in genic regions was stable at 73.9% on average.
3.3. Genomic Regressions
Genetic data for genomic regressions were produced to test the effects of different levels of filtering (on missing rate and number of reads), genome parametrization (allele ratio, tetraploid and diploid) and SNP selection (all SNPs, genic regions only, non-genic regions only), for a total of 144 different configurations. For each configuration, the predictive ability of the model was measured as Pearson’s correlation between true and predicted phenotypic values in a ten-fold crossvalidation scheme.
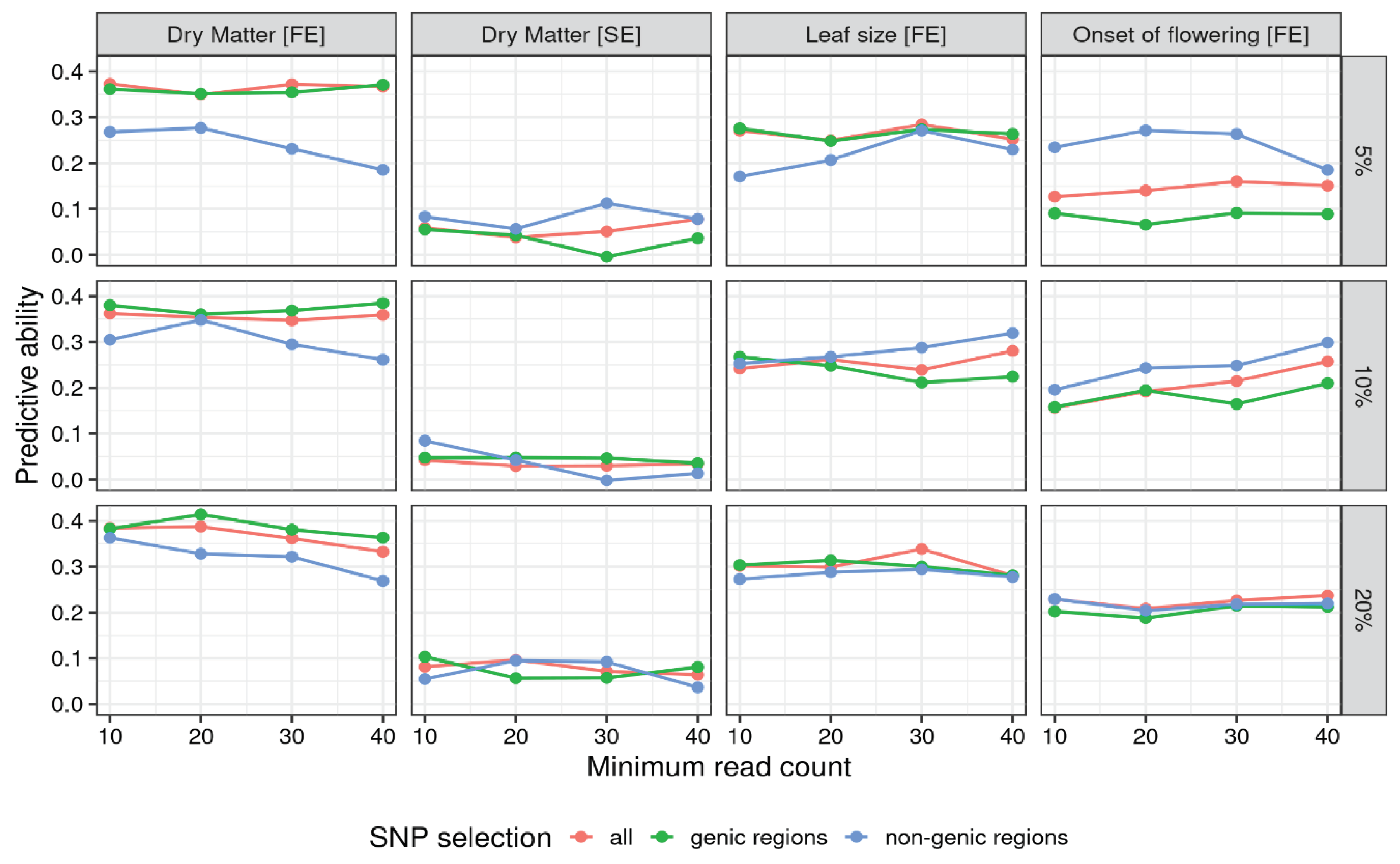
Figure 1 shows the effects on the predictive ability of the choice of filtering and SNP representation for ratios genome parametrization.
Supplementary Figure S1 does the same for the tetraploid parametrization. The full list of results is reported in
Supplementary Table S1.
Figure 1 highlights several trends. The four traits exibit different patterns, with yield in favorable environment showing predictive abilities strictly higher than yield in stressed environment. Leaf size and onset of flowering show values closer to yield in favorable environment, if slightly lower. The use of markers from non genic regions is heavily penalized in yield in favorable condition, where using marker from genic regions yield slightly better results than using all markers. With yield in stressed conditions and leaf size the choice of subsetting doesn’t look influential, with the three lines intewined without a clear advantage. Onset of flowering flips the pattern found with yield in favorable conditions, achieving the highest predictive abilities when subsetting markers from non-genic regions.
Table 3 reports, for each trait, the configuration with the highest predictive ability, ranging from 0.168 (dry matter in stressed environment) to 0.414 (dry matter in favorable environment). Three out of four traits got their best result when using the strictest filtering on missing rate, the exception being dry matter in favorable environment for which the loosest filtering was best. With regards to genome parametrization, yield in stressed conditions and leaf size achieved the best performances with diploid parametrization, while onset of flowering was favoured by tetraploid parametrization and yield in favorable conditions by allele ratio. Regarding SNP selection, two traits (yield in favorable conditions and leaf size) got the best results using SNPs from coding regions, while the other two with SNPs from non-coding regions.
Averaging over all tested configurations it was possible to single out the effect of specific filtering. On average, the allele ratio provided an advantage in terms of average predictive ability (0.232), followed by the tetraploid dosage (0.215) and the diploid dosage (0.206). Averaging over SNP subsets revealed an advantage using all SNPs (0.226) followed by genic regions (0.218) and then non-genic regions (0.210).
3.4. Released Software: Legpipe2
Together with this study we are releasing
LegPipe2, a SNP calling pipeline aimed to reduced representation sequencing (GBS and RAD alike) and freely available at
https://github.com/ne1s0n/legpipe2.
Legpipe2 design is inspired by existing pipelines like dDocent [
26] and UgbS-Flex [
27], with improvement on modularity, log management, and general flexibility. All operations are depending on a single configuration file, which can be shared together with
Legpipe2 version to ensure data reproducibility. Apart from outputting standard .vcf file,
Legpipe2 already contains filtering and data manipulation steps so that the data can easily be imported in other softwares,
e.g., in R/updog [
28].
Internally,
Legpipe2 uses the GVCF workflow from GATK/HaplotypeCaller [
29] suite, thus ensuring low memory requirements. Other steps are implemented with standard state of the art softwares, such as botwie2 [
30] (for alignment), picard and samtools [
31] (for data manipulation and filtering) and fastx [
32] (for trimming).
4. Discussion
Agriculture is a water-intensive activity, and drought exacerbates the competition for water resources, particularly in regions already facing limitations in water availability. Alfalfa is known for its fairly high resilience to drought but also for the difficulties of its genetic improvement, partly arising from autotetraploidy. The definitely lower genomic prediction ability for total dry matter yield observed for this European reference population in the drought-prone environment relative to the moisture-favorable one (0.17 vs. 0.41) agrees with earlier findings [
8,
33] for a Mediterranean alfalfa reference population using a diploid genome representation, for which we reported a progressive decrease of predictive ability across managed environments ranging from moisture-favorable (0.35) to moderately stressed (0.26) to heavily stressed (0.03), as well as prediction abilities in the range of 0.12-0.23 for drought-prone agricultural environments. It was previously found [
33] the decreasing predictive ability on increasing drought stress was paralleled by a progressive increase of experiment error CV (12.6% vs. 19.5% vs. 30.1%) in the presence of similar genetic variance. In this study the same pattern was found in the genetic coefficient of variation, probably because of smaller variation for drought tolerance that one could expect in European germplasm relative to a Mediterranean reference population. Due to the controlled experimental conditions the experiment error CV was however more stable here, with stressed and favorable conditions showing almost exactly the same values (15.2% and 15.4%, respectively).
Our study provided an unprecedented assessment of the potential advantage of allele dosage imputation for alfalfa genomic predictions. The extent of this advantage varied largely in earlier studies on other species. A study on the perennial autotetraploid forage grass
Panicum maximum reported a remarkable advantage of allele dosage imputation over the diploid model pooling the heterozygote classes, with increases of predictive ability of about 50% for leaf dry matter, 42% for crude protein content and 18% for in vitro digestibility [
34]. In contrast, the advantage of allelic dosage imputation was minimal for predicting agronomic traits of interspecific hybrids of the tropical grass
Urochloa spp. [
35], possibly because of the segmental allotetraploid (partly autotetraploid and partly allotetraploid) genome of this material. In this study, the disadvantage of a diploid genome representation relative to a tetraploid genome or its approximation as provided by the allele ratio was not large, suggesting that using a diploid representation as necessarily required when adopting lower sequencing effort may be convenient for some traits in terms of genomic selection cost efficiency in comparison with more expensive albeit more informative genotyping options.
Identifying the optimal combinations of data treatment, filtering and genome representation can be important to maximize the genome-enabled predictive ability of alfalfa. Our comparison of the allele ratio relative to the tetraploid allele dosage based on same sequencing data suggested that the allele ratio could be the preferred alternative, bringing to an average +7.9% increase in predictive ability when compared to tetraploid dosage (+12.6% when compared to diploid). This approach, which is computationally simpler and avoids problems associated with misclassification of genotypic classes, produced genomic selection models about as accurate as those based on estimated genotype classes in a blueberry study [
36]. However, the advantage of the allele ratio held true only on average in our study. In fact, the allele ratio parametrization was selected as the best configuration only in one trait out of four. A similar pattern was found when examining the effect of SNP selection. While using all available markers was preferable on average (+3.7% vs. genic regions, +7.6% vs. non-genic regions), that choice was never selected when looking for the best configuration for each single trait. This finding highlights the layered interaction between data representation, data filtering and genomic regression. From the methodological perspective, we propose, therefore, that genome parametrization and SNP marker selection become part of the options routinely explored when optimizing genomic regressions.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Nelson Nazzicari and Paolo Annicchiarico; Methodology, Nelson Nazzicari, Nicolo Franguelli, Barbara Ferrari, Luciano Pecetti and Paolo Annicchiarico; Software, Nelson Nazzicari; Writing – original draft, Nelson Nazzicari; Writing – review & editing, Barbara Ferrari, Luciano Pecetti and Paolo Annicchiarico.
Funding
The research was carried out within the project GENLEG funded by the Italian Ministry of Agriculture, Food Sovereignty and Forestry and the project AGRITECH funded by the European Union under the Italian National Recovery and Resilience Plan.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Julier, B.; Gastal, F.; Louarn, G.; Badenhausser, I.; Annicchiarico, P.; Crocq, G.; et al. Alfalfa (lucerne) in European cropping systems. Legumes in cropping systems 2017, 168–191. [Google Scholar]
- Annicchiarico, P.; Barrett, B.; Brummer, E.C.; Julier, B.; Marshall, A.H. Achievements and challenges in improving temperate perennial forage legumes. Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences 2015, 34, 327–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanford, G.R.; Jackson, R.D.; Booth, E.G.; Hedtcke, J.L.; Picasso, V. Perenniality and diversity drive output stability and resilience in a 26-year cropping systems experiment. Field Crops Research 2021, 263, 108071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Wu, P.; Feng, H.; Merkley, G.P. Effects of alfalfa coverage on runoff, erosion and hydraulic characteristics of overland flow on loess slope plots. Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering in China 2011, 5, 76–83. [Google Scholar]
- Bingham, E.T.; Groose, R.W.; Woodfield, D.R.; Kidwell, K.K. Complementary gene interactions in alfalfa are greater in autotetraploids than diploids. Crop Science 1994, 34, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Brummer, E.C. Inbreeding depression for fertility and biomass in advanced generations of inter-and intrasubspecific hybrids of tetraploid alfalfa. Crop Science 2009, 49, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annicchiarico, P.; Pecetti, L. Comparison among nine alfalfa breeding schemes based on actual biomass yield gains. Crop Science 2021, 61, 2355–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annicchiarico, P.; Nazzicari, N.; Li, X.; Wei, Y.; Pecetti, L.; Brummer, E.C. Accuracy of genomic selection for alfalfa biomass yield in different reference populations. BMC Genomics 2015, 16, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biazzi, E.; Nazzicari, N.; Pecetti, L.; Brummer, E.C.; Palmonari, A.; Tava, A.; et al. Genome-wide association mapping and genomic selection for alfalfa (Medicago sativa) forage quality traits. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torkamaneh, D.; Laroche, J.; Belzile, F. Fast-GBS v2. 0: an analysis toolkit for genotyping-by-sequencing data. Genome 2020, 63, 577–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, P.; Gimode, D.; Saha, D.; Schröder, S.; Chakraborty, D.; Wang, X.; et al. UGbS-Flex, a novel bioinformatics pipeline for imputation-free SNP discovery in polyploids without a reference genome: finger millet as a case study. BMC Plant Biology 2018, 18, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, L.V.; Lipka, A.E.; Sacks, E.J. polyRAD: Genotype calling with uncertainty from sequencing data in polyploids and diploids. G3: Genes, Genomes, Genetics 2019, 9, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakral, V.; Yadav, H.; Padalkar, G.; Kumawat, S.; Raturi, G.; Kumar, V.; et al. Recent Advances and Applicability of GBS, GWAS, and GS in Polyploid Crops. Genotyping by Sequencing for Crop Improvement 2022, 328–354. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrão, L.F.V.; Amadeu, R.R.; Benevenuto, J.; de Bem Oliveira, I.; Munoz, P.R. Genomic selection in an outcrossing autotetraploid fruit crop: lessons from blueberry breeding. Frontiers in Plant Science 2021, 12, 676326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annicchiarico, P.; Brummer, E.C.; Nazzicari, N. Alfalfa Genomic Selection: Challenges, Strategies, Transnational cooperation. In Breeding in a World of Scarcity: Proceedings of the 2015 Meeting of the Section “Forage Crops and Amenity Grasses” of Eucarpia.; Springer, 2016; p. 145. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, P.; Hartung, J.; Bennewitz, J.; Piepho, H.P. Heritability in plant breeding on a genotype-difference basis. Genetics 2019, 212, 991–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piepho, H.P.; Möhring, J.; Melchinger, A.E.; Büchse, A. BLUP for phenotypic selection in plant breeding and variety testing. Euphytica 2008, 161, 209–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montesinos López, O.A.; Montesinos López, A.; Crossa, J. Preprocessing Tools for Data Preparation. In Multivariate Statistical Machine Learning Methods for Genomic Prediction; Springer, 2022; pp. 35–70. [Google Scholar]
- Lozano-Isla, F. inti: Tools and statistical procedures in plant science. R Package Version 0.6.3. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=inti.
- Itoh, Y.; Yamada, Y. Relationships between genotype x environment interaction and genetic correlation of the same trait measured in different environments. Theoretical and Applied Genetics 1990, 80, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elshire, R.J.; Glaubitz, J.C.; Sun, Q.; Poland, J.A.; Kawamoto, K.; Buckler, E.S.; et al. A robust, simple genotyping-by-sequencing (GBS) approach for high diversity species. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, R.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, Z.; Li, M.; Chen, L.; Wang, X.; et al. Genome assembly of alfalfa cultivar zhongmu-4 and identification of SNPs associated with agronomic traits. Genomics, Proteomics & Bioinformatics 2022, 20, 14–28. [Google Scholar]
- Gerard, D.; Ferrão, L.F.V.; Garcia, A.A.F.; Stephens, M. Genotyping polyploids from messy sequencing data. Genetics 2018, 210, 789–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endelman, J.B. Ridge regression and other kernels for genomic selection with R package rrBLUP. Plant Genome 2011, 4, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazzicari, N.; Biscarini, F. Stacked kinship CNN vs. GBLUP for genomic predictions of additive and complex continuous phenotypes. Scientific Reports 2022, 12, 19889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puritz, J.B.; Hollenbeck, C.M.; Gold, J.R. dDocent: a RADseq, variant-calling pipeline designed for population genomics of non-model organisms. PeerJ 2014, 2, e431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, P.; Gimode, D.; Saha, D.; Schröder, S.; Chakraborty, D.; Wang, X.; et al. UGbS-Flex, a novel bioinformatics pipeline for imputation-free SNP discovery in polyploids without a reference genome: finger millet as a case study. BMC Plant Biology 2018, 18, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerard, D.; Ferrão, L.F.V. Priors for genotyping polyploids. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 1795–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Auwera, G.A.; O’Connor, B.D. Genomics in the cloud: using Docker, GATK, and WDL in Terra. O’Reilly Media 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Langmead, B.; Wilks, C.; Antonescu, V.; Charles, R. Scaling read aligners to hundreds of threads on general-purpose processors. Bioinformatics 2019, 35, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danecek, P.; Bonfield, J.K.; Liddle, J.; Marshall, J.; Ohan, V.; Pollard, M.O.; et al. Twelve years of SAMtools and BCFtools. Gigascience 2021, 10, giab008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, A.; Hannon, G.; et al. Fastx-toolkit, FASTQ/A short-reads preprocessing tools. Available online: http://hannonlab.cshl.edu/fastx_toolkit (accessed on 29 February 2024).
- Annicchiarico, P.; Nazzicari, N.; Bouizgaren, A.; Hayek, T.; Laouar, M.; Cornacchione, M.; et al. Alfalfa genomic selection for different stress-prone growing regions. The Plant Genome 2022, 15, e20264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de CLara, L.A.; Santos, M.F.; Jank, L.; Chiari, L.; Vilela M de, M.; Amadeu, R.R.; et al. Genomic selection with allele dosage in Panicum maximum jacq. G3: Genes, Genomes, Genetics 2019, 9, 2463–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matias, F.I.; Alves, F.C.; Meireles, K.G.X.; Barrios, S.C.L.; do Valle, C.B.; Endelman, J.B.; et al. On the accuracy of genomic prediction models considering multi-trait and allele dosage in Urochloa spp. interspecific tetraploid hybrids. Molecular Breeding 2019, 39, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bem Oliveira, I.; Resende Jr, M.F.; Ferrão, L.F.V.; Amadeu, R.R.; Endelman, J.B.; Kirst, M.; et al. Genomic prediction of autotetraploids; influence of relationship matrices, allele dosage, and continuous genotyping calls in phenotype prediction. G3: Genes, Genomes, Genetics 2019, 9, 1189–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).