1. Introduction
Communicable disease surveillance systems are essential in understanding the prevalence, and characterising the transmission of pathogens in the community. Traditional surveillance systems rely heavily on the continuous and systematic collection of clinical case data (clinical surveillance). This includes diagnostic test results, patient-reported symptoms, and information from healthcare providers, including hospitalisations [
1]. Clinical surveillance is essential in tracking the spread of respiratory pathogens such as influenza, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), and severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). However, passive surveillance systems that rely solely on individuals seeking healthcare underrepresent the true disease prevalence in the community, particularly when symptoms are either mild or completely absent [
2].
The effectiveness of clinical surveillance systems is dependent on the timing and completeness of the system end-to-end. Where prompt public health responses are critical, such as during the initial stages of an outbreak, delays in notifications, data collection, analysis and reporting can impact the ability to undertake effective and timely public health action [
3]. These challenges were highlighted during the COVID-19 pandemic [
4], underlining the necessity for timely and representative surveillance systems. This is exacerbated with self-testing which bypasses communicable disease notification systems, such as the use of rapid antigen testing (RAT) on self-collect specimens for respiratory viruses [
5].
Wastewater-based epidemiology (WBE) has emerged as a significant complementary addition to traditional clinical surveillance systems. WBE involves the analysis of raw wastewater to detect markers of disease at a population level, and offers insights independent of individual healthcare-seeking behaviours and medical practitioner testing practices [
1]. WBE for SARS-CoV-2 evolved rapidly due to the requirement for improved surveillance driven by the COVID-19 pandemic [
6]. Studies have demonstrated a positive correlation between SARS-CoV-2 viral concentrations in wastewater to associated clinical metrics in the corresponding region [
7,
8,
9]. Recently, this has also been demonstrated for a range of other respiratory viruses including other seasonal coronaviruses, rhinovirus, human metapneumovirus, parainfluenza virus, RSV, and influenza [
10,
11,
12]. This suggests that WBE is able to provide an understanding of transmission of diseases at the community-level that is less prone to biases, which often implicate clinical surveillance systems. Furthermore, there is emerging evidence of WBE’s ability to act as an early warning system ahead of increases in clinical case numbers [
13] or hospitalisations [
14].
Recent advancements in next-generation sequencing and bioinformatic analysis have enabled the monitoring of intra-species viral lineages in wastewater samples [
15,
16]. This capability has the potential to provide a genomic epidemiological understanding of viral dynamics at a community level, permitting a better understanding of the progression and burden of communicable diseases cost-effectively. Given that wastewater matrices are a mixed sample from diverse individuals, the SARS-CoV-2 sequencing data generated from wastewater requires deconvolution into interpretable data. This process has been primarily applied to SARS-CoV-2 for assessing community-wide genomic epidemiology, utilizing bioinformatics tools such as Freyja [
16] which recovers relative lineage abundances from mixed SARS-CoV-2 samples. Research has shown that these methods support the early detection of emerging variants within communities [
9,
17] and have also established a significant positive correlation between the variants of concern in wastewater and clinical cases in corresponding communities [
18,
19,
20]. While SARS-CoV-2 lineage proportion data in wastewater has been publicly available in many jurisdictions since 2022 [
21,
22,
23], the temporal correlation analysis between Omicron and recombinant sub-lineages detected in wastewater and clinical cases has been limited [
18,
24].
This study demonstrates that WBE of SARS-CoV-2 correlates with clinical metrics such as COVID-19 case notifications and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test positivity rates in Perth, Western Australia (WA) - a city with approximately 2,100,000 residents [
25]. Our approach involves a detailed examination of the relative abundance of key Omicron and recombinant SARS-CoV-2 lineages in wastewater and their correlation to the percentage of clinical cases identified with these specific lineages in the corresponding region. The data produced was available in real-time to public health agencies and was used to inform disease prevention and control.
2. Materials and Methods
Wastewater Sample Collection
Since July 2022, bi-weekly wastewater samples were collected from three metropolitan wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) in Perth, WA as part of a SARS-CoV-2 wastewater surveillance program; these included Subiaco (approximate population 250,000), Woodman Point (approximate population 750,000) and Beenyup (approximate population 700,000). The three catchments represent approximately 79% of metropolitan Perth’s population [
25].
Sample collection involved flow-paced, continuous auto-samplers at each plant. Hourly, 400mL samples were pooled to form a 24-hour composite sample which was retained at 4°C during the sampling window. These composite samples were homogenised, and 250mL aliquots were sampled and transported on ice to the laboratory on the day of collection. Samples were stored between 2°C and 8°C until testing, which occurred within seven days of collection.
From 4 July 2022 to 31 December 2023, a total of 447 composite wastewater samples were collected from these WWTPs.
Wastewater Concentration and Extraction
Each wastewater sample was pre-treated, concentrated, and nucleic acid purified using 50mL aliquots, as per a previously described procedure [
26]. Briefly, sample aliquots were pre-treated with MgCl
2 and centrifuged to remove solids. The supernatant was concentrated on an electronegative filter membrane and nucleic acid purification was performed on the filter membrane using the MagMAX Microbiome Ultra Nucleic Acid Isolation Kit (ThermoFisher, United States). All samples were spiked with MS2 bacteriophage, an internal process control prior to nucleic acid purification.
SARS-CoV-2 Real-Time PCR
SARS-CoV-2 PCR analysis was performed on all wastewater samples collected between 4 July 2022, and 31 December 2023 (N = 447). Quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR) was employed for SARS-CoV-2 quantitation, using the PerkinElmer SARS-CoV-2 Real-time RT-PCR assay (PerkinElmer, United States). This assay targets the nucleocapsid and ORF1ab genomic regions of SARS-CoV-2. Additionally, MS2 bacteriophage is targeted as an internal process control. Following initial verification, the volume of reagents used in each qPCR reaction was halved. Each wastewater sample, alongside negative template controls, were assayed in duplicate technical replicates. Purified SARS-CoV-2 RNA was included as a positive amplification control. Pre-established expected cycle threshold (Ct) values and their 95% confidence intervals were used as benchmarks for the positive control, with repeat batch analysis when the control results did not fall within these confidence intervals.
The limits of detection (LoD) and quantification (LoQ) were established at 5 copies/reaction (equivalent to 200 copies/50mL) and 12.5 copies/reaction (equivalent to 500 copies/50mL), respectively for both SARS-CoV-2 targets.
Molecular Inhibition Assessment
MS2 Ct values served as indicators of extraction issues and to monitor for PCR inhibition. The 95% confidence limits for these values in negative template controls were established. Samples that yielded MS2 Ct values outside these established limits were repeated. In the repeat analysis, both 5µL and 2µL aliquots of purified nucleic acid were used per reaction. Sample results with MS2 Ct values within the 95% confidence limits were considered valid. Those that consistently fell outside these limits were excluded from further quantification and the result was reported as indeterminate.
Wastewater SARS-CoV-2 Viral Quantification
Commercially acquired, quantified SARS-CoV-2 RNA (Twist Bioscience, United States) was used to generate standard curves in the PerkinElmer SARS-CoV-2 Real-time RT-PCR assay. Upon receipt, the RNA stock, transported on dry ice, was promptly stored at -80°C. For assay preparation, the RNA was thawed and serially diluted to create a range of concentrations from 10-2 to 10-5 (equivalent to 10 to 10,000 copies/µL). These dilutions were then dispensed into 20µL volumes, maintained on ice during the process, and subsequently stored at -80°C. Individual aliquots were thawed for each analytical batch to ensure consistency across different runs.
Triplicate 5µL template volumes of four serial dilution levels (50 to 50,000 copies/reaction) were used. Each PCR batch used fresh aliquots of RNA for standard curve production.
To express the sample quantitation results as genome copies per 50mL of wastewater, the concentrations deduced from the standard curve were multiplied by the concentration factor of 40. qPCR assays were executed using the CFX96 Touch Real-Time PCR Detection System (Bio-Rad Laboratories, United States), with quantification calculated through CFX Maestro Software (Bio-Rad Laboratories, United States). The final quantified outcome for each specimen, denoted as genome copies/50mL, represented the mean of the values from dual replicates across both the ORF1ab and nucleocapsid targets. Results from templates diluted below 5µL were manually recalibrated by the corresponding dilution factor.
All samples collected after the 9th of October 2023 were quantified exclusively using the average results from the ORF1ab target due to a mutation identified in all BA.2.86 sub-lineages, which impacted the nucleocapsid assay performance (data not shown).
Results below the LoQ were considered in the correlation analysis.
SARS-CoV-2 Genome Sequencing
SARS-CoV-2 genome sequencing (GS) was performed weekly on one wastewater sample from each WWTP for the complete study period (N = 239).
Upon completion of the SARS-CoV-2 quantification, cDNA synthesis was performed on each purified nucleic acid extract using SuperScript VILO mastermix (ThermoFisher, United States) or LunaScript RT SuperMix (New England Biolabs, United States). These reverse transcription chemistries were validated to ensure comparable results (data not shown). The genome of SARS-CoV-2 was amplified using a modified ARTIC V3 primer set (400 bp) in combination with Q5 Hot Start DNA Polymerase (New England BioLabs, United States), following the manufacturers recommended protocol. Weekly sequencing included a positive control of a known lineage, a non-template control that underwent parallel nucleic acid purification and a non-template control of Ultra-Pure H2O.
Libraries for sequencing were prepared using the Illumina Nextera XT kit (Illumina, United States), adhering to the manufacturer's recommendations but with a half-volume of reagents and employing unique dual indexing. Sequencing was conducted on Illumina platforms (iSeq, 150 bp reads; MiniSeq 150 bp reads; and MiSeq, 300 bp reads) (Illumina, United States). Quality control of the sequencing runs was carried out using a custom in-house pipeline involving mapping of trimmed reads to ref strain Wuhan-Hu-1 (accession NC_045512.2) and SARS-CoV-2 lineage assignment with Pangolin v4.3.1 (
https://github.com/cov-lineages/pangolin) in clinical cases.
Before January 24, 2023, a custom in-house pipeline was employed for the routine reporting of SARS-CoV-2 lineage abundance in wastewater. On January 24, 2023, all historical wastewater sequencing data were reanalysed using Freyja v1.3.9 [
16], applying the most recent lineage-determining mutational "barcodes" available at that time which are derived from the Ultrafast Sample placement on Existing tRees (UShER) global phylogeny (
https://github.com/andersen-lab/Freyja/). From this date, Freyja was used as detailed in Supplementary Material S1,
Table S1. SARS-CoV-2 genome coverage was calculated for each sample using a 10x depth. Samples with a genome coverage of <60% were not reported or used for subsequent correlation analysis. Sub-lineages were condensed into their respective parent lineages to facilitate result presentation and data analysis as per Supplementary Material S1,
Table S4.
Clinical Data
PathWest Laboratory Medicine WA (PathWest) is the sole public pathology provider in WA, offering clinical and environmental microbiology testing. For this study, we calculated the clinical PCR test positivity rate, defined as the number of positive molecular clinical tests divided by the total number of molecular tests conducted for SARS-CoV-2 at PathWest. The tests used to calculate the PCR positivity were restricted to residents from metropolitan Perth, enabling comparison with SARS-CoV-2 wastewater concentrations from the three metropolitan WWTPs.
PathWest is the sole laboratory in WA undertaking clinical whole-genome sequencing (WGS) for SARS-CoV-2. This study incorporates data from all sequenced SARS-CoV-2 cases in the metropolitan Perth metropolitan area throughout the duration of the analysis including the assigned Pangolin designation [
27]. Sub-lineages designated by Pangolin were condensed into their respective parent lineages to facilitate result presentation and data analysis as per Supplementary Material S1,
Table S5.
In WA, COVID-19 is a notifiable infectious disease under the
Public Health Act 2016 [
28], mandating all pathology laboratories and medical or nursing practitioners to report any detections of COVID-19 to the WA Department of Health. From 7 February 2022, under the provisions of the
Emergency Management Act 2005 [
29], individuals with a positive RAT for SARS-CoV-2 were mandated to self-report their results to the WA Department of Health via an online portal. The portal to report RATs to the WA Department of Health ceased operations on 9 October 2023. This study utilises notification data of only PCR-confirmed COVID-19 clinical cases with a residential address in metropolitan Perth, notified to the WA Department of Health to allow for comparison with wastewater concentration levels from the three metropolitan WWTPs.
Data Processing, Correlation and Statistical Significance
Each week, the average SARS-CoV-2 concentrations in wastewater were calculated by aggregating quantified results from samples across all three WWTPs, excluding indeterminate results. Concurrently, the corresponding rate of clinical PCR positivity and the total number of weekly PCR-positive clinical notifications were collated (Supplementary Material S2,
Table S1).
The weekly relative abundance of SARS-CoV-2 parent lineages in both clinical and wastewater samples was determined (Supplementary Material S2,
Table S2 and
Table S3). Information on the number of wastewater samples used each week for calculating the average concentrations and relative lineage abundances is available in Supplementary Material S2,
Table S4. The quarterly number of clinical cases undergoing WGS decreased during the study period (
Table 1).
To analyse the relationship between the wastewater and clinical datasets, Spearman's rank correlation coefficient (
rs) was employed. Additionally, the statistical significance of the correlation was determined (
p) [
30].
4. Discussion
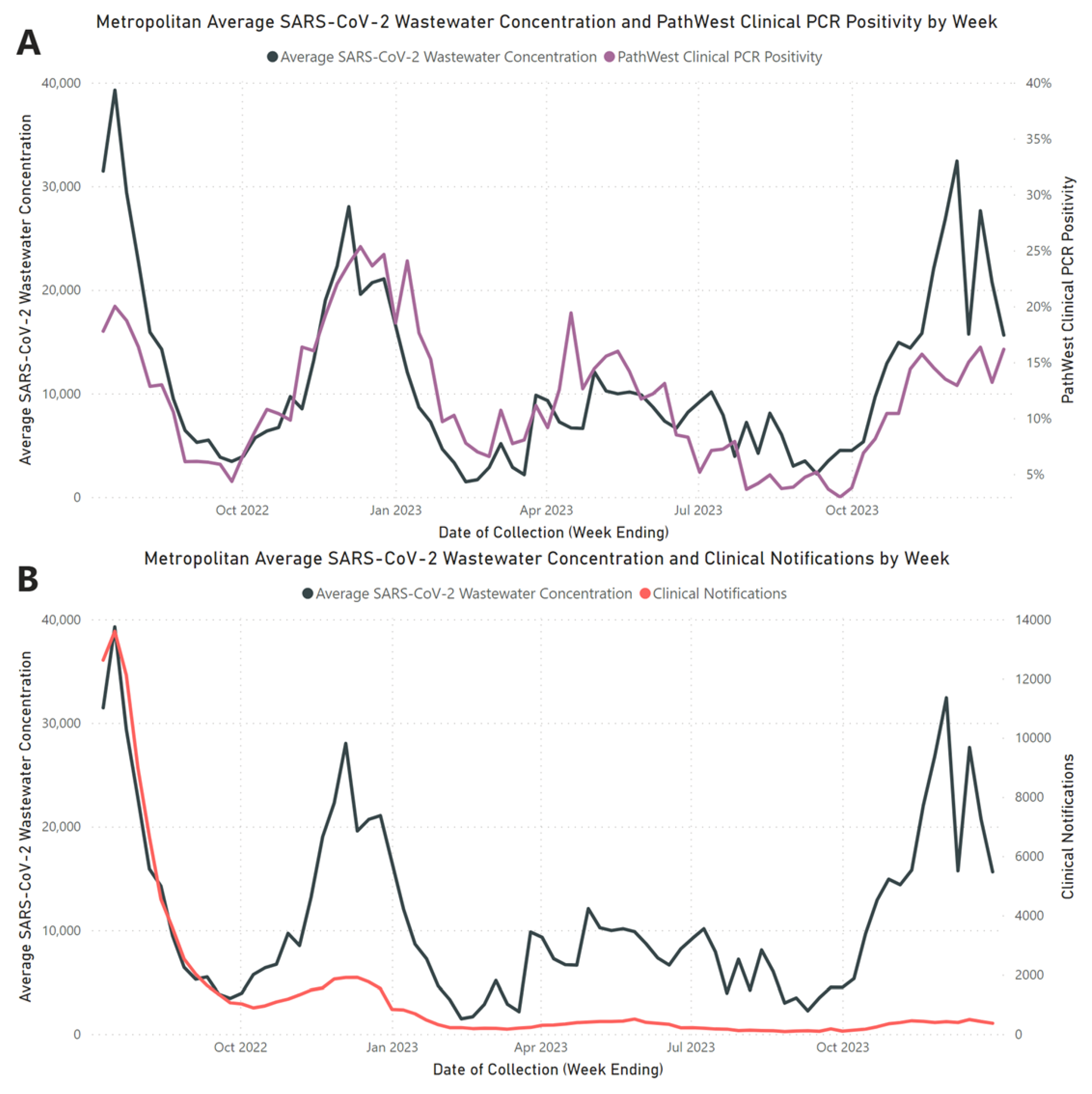
Our 18-month investigation establishes a strong positive correlation between average wastewater viral loads and PathWest clinical PCR positivity rates (
rs = 0.772,
p <0.001). However, this correlation was weaker when compared to confirmed PCR case notifications (
rs = 0.577,
p < 0.001) which can be expected due to reporting bias and shifts in testing modality. This finding supports the globally recognised observation that SARS-CoV-2 concentrations in wastewater are indicative of the prevalence of clinical cases within the associated community [
31] and reinforces the role of WBE as a complementary surveillance tool to clinical epidemiology in enhancing public health surveillance efforts, especially when clinical data may be limited.
As our study progressed, there was an increasing divergence between wastewater SARS-CoV-2 concentrations and PCR COVID-19 clinical case notifications, as illustrated in
Figure 1B. The divergence can be primarily attributed to decreased COVID-19 clinical testing, with a notable shift from higher rates of PCR testing in Q3-2022 to the increased adoption of self-conducted RATs as the predominant testing modality throughout the remaining quarters [
32]. This shift was contributed to by state and workplace-led programs that offered free RATs [
33], making them more accessible and affordable compared to PCR testing. The attenuation in PCR testing was further influenced by several factors, including the rescindment of testing mandates for clinical cases and close contacts, the closure of independent and free COVID-19 testing clinics (which reduced access to PCR testing centres) [
34], and changes in community attitudes towards COVID-19, leading to decreased testing and reduced medical attendance for COVID-19 symptoms. Over the period of July 2022 to December 2023, the decrease in PCR testing and notification for COVID-19 highlights major limitations in traditional clinical surveillance systems in understanding the true community burden of disease, due to the factors discussed above. In the context of our study, WBE continued to provide a strong understanding of the population-wide burden of COVID-19 despite reduced PCR testing, demonstrating a significant benefit of WBE over traditional clinical surveillance systems in its representativeness and ability to provide additional surveillance information.
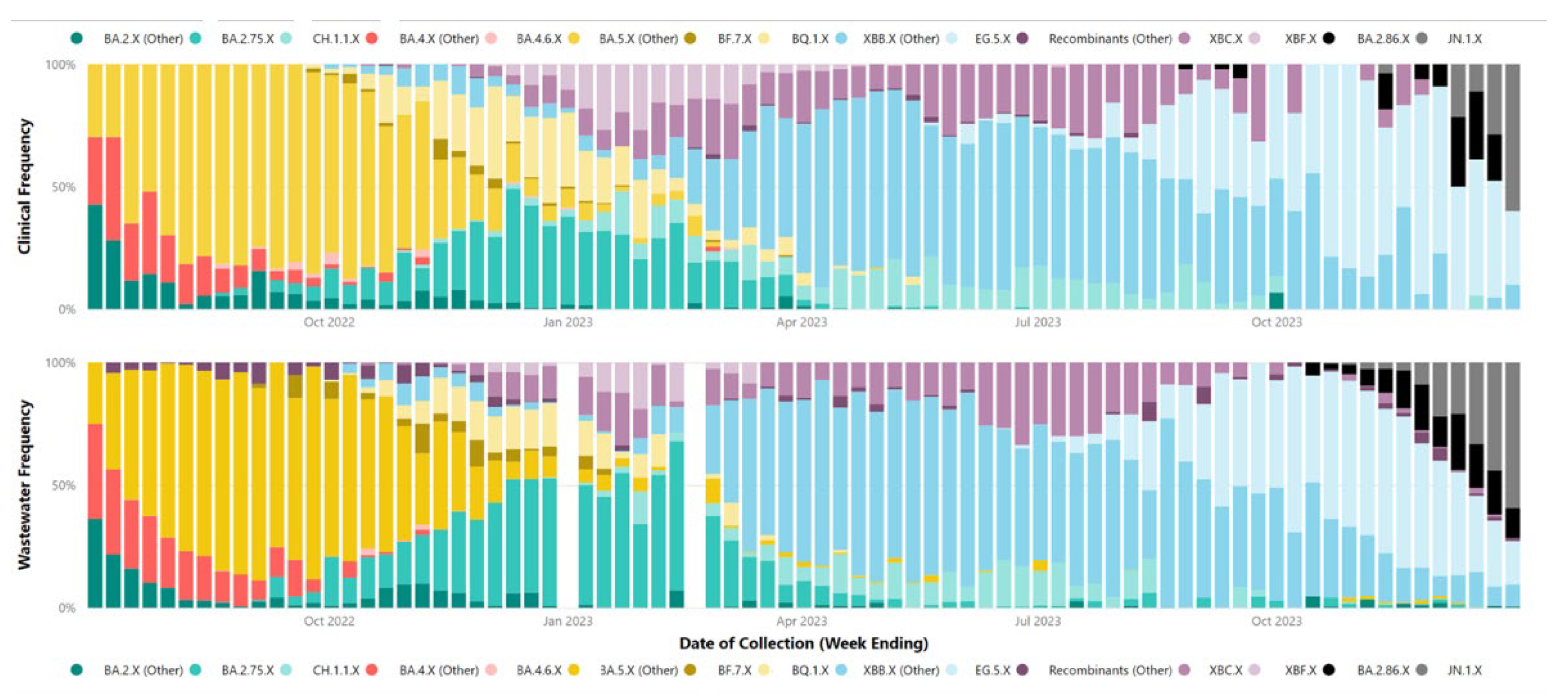
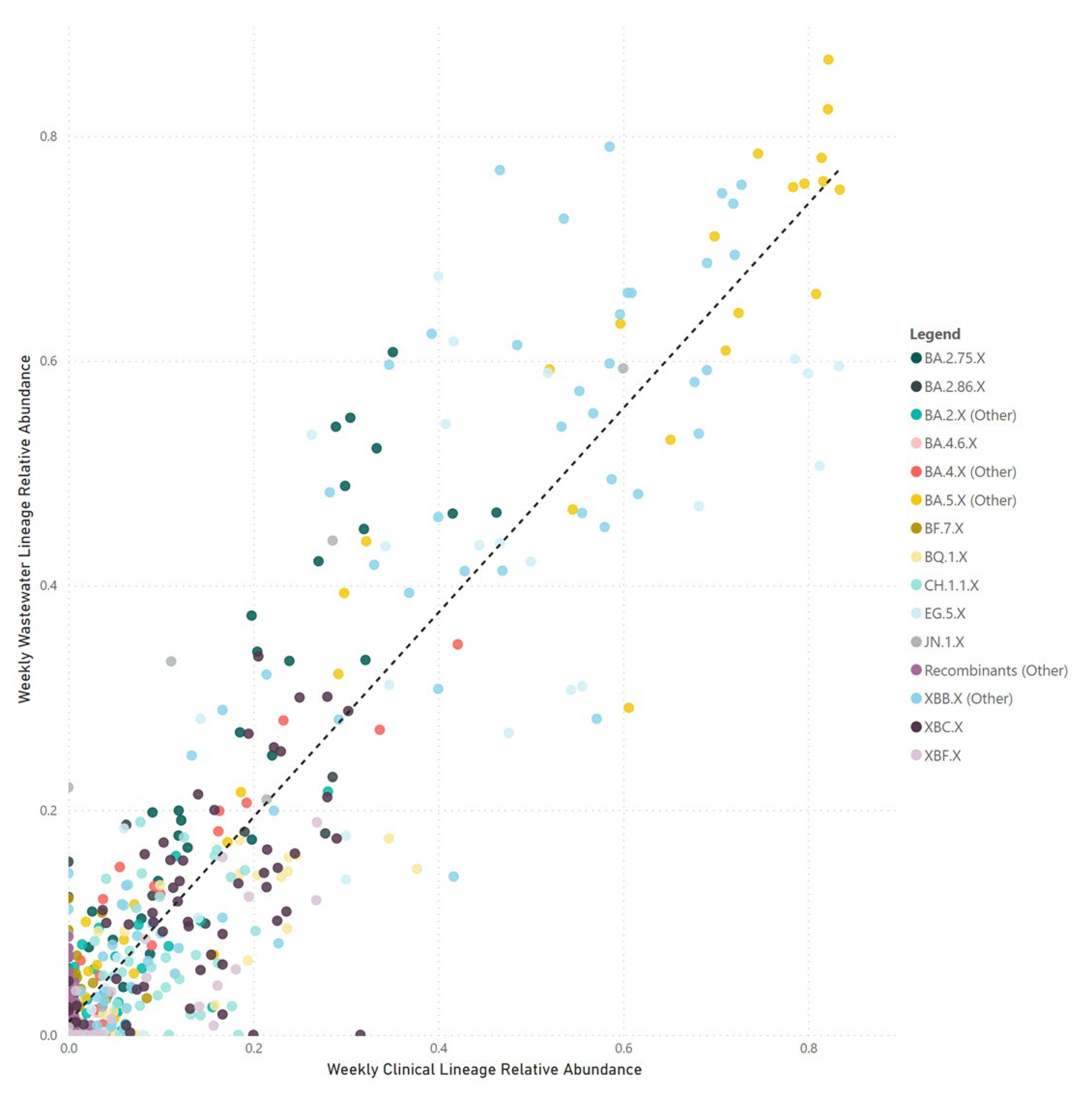
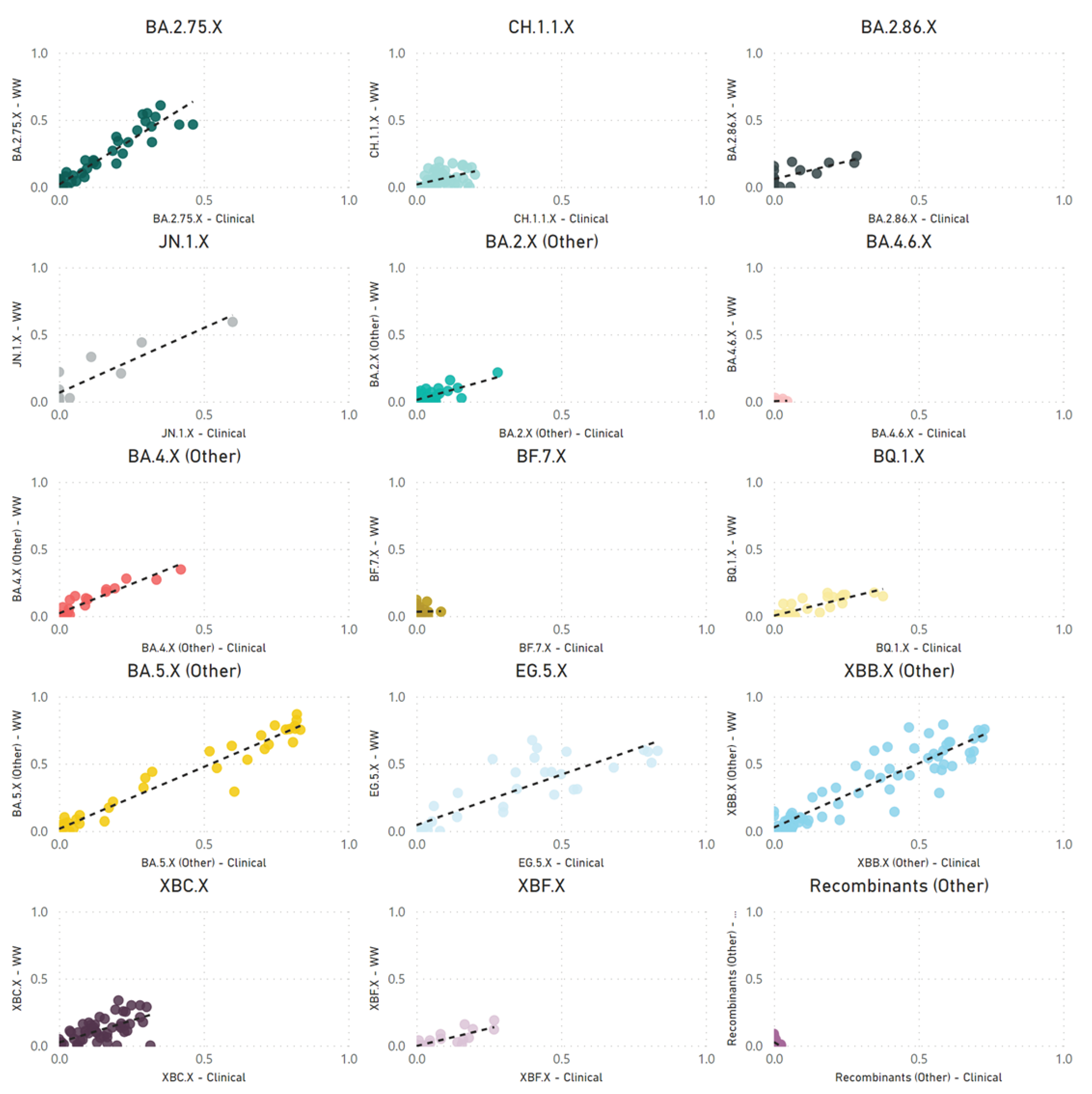
Our correlation between SARS-CoV-2 parent lineage proportions in wastewater and clinical cases over an 18-month period (
rs = 0.728,
p < 0.001) underscores the effectiveness of wastewater GS in accurately measuring the prevalence of Omicron and recombinant lineages within a community. By condensing lineages into their respective parent lineages, we navigated the challenges posed by identifying numerous low-frequency sub-lineages. This approach made the data more accessible to audiences with limited genomic epidemiology expertise, facilitating a clearer understanding of virus dynamics in the population.
Table 1 demonstrates a trend in decreasing number of clinical samples undergoing GS from Q3 2022 to Q4 2023, primarily attributed to decreased funding towards clinical WGS of PCR samples. The reduction in clinical WGS of SARS-CoV-2 has also led to reduced strength of correlation between the lineages identified in clinical WGS and wastewater GS. As the denominator for clinical WGS (number of samples sequenced) reduces, the overall scale for comparison is also reduced. This means that smaller changes in the numerator (each individual clinical WGS result) have a greater and more pronounced effect on the overall frequency or proportion identified. This numerator-denominator bias does not affect the results from wastewater GS. This is because the wastewater GS results rely on the proportion of lineages identified in a sample, which is inherently representative of the population. The wastewater GS denominator encompasses all lineages identified in that specific sample, mitigating potential biases associated with variations in the sample size.
Despite efforts, challenges were encountered in accurately correlating wastewater data with clinical metrics for closely related sub-lineages within the same parent lineage, such as XBB.1.5, XBB.1.9, and XBB.1.16. These difficulties likely stem from a small number (<5) of single nucleotide polymorphisms between these highly related sub-lineages. Additionally, reduced sequencing depth in important genomic regions and the limitations of short-read sequencing technologies may hinder bioinformatics tools' ability to distinguish between these lineages at the read level. Long-read sequencing holds the potential to improve the differentiation between closely related sub-lineages, due to its capacity to identify a greater number of mutations within a single read. However, the fragmentation of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in wastewater could impede the success of long-read sequencing.
The representative identification of SARS-CoV-2 lineages in wastewater provides a foundation for applying similar genomic techniques to characterise other pathogens present in wastewater, as has been recently demonstrated for polioviruses [
15], RSV [
35] and influenza [
36]. This methodological approach not only reinforces the utility of WBE for SARS-CoV-2 surveillance but also underscores its potential for broader pathogen detection and characterisation [
37], offering a scalable and non-invasive tool for public health monitoring and response planning.
Our research highlights the potential of WBE to preemptively identify SARS-CoV-2 variants in the community, with wastewater surveillance occasionally detecting variants before clinical confirmation (
Table 2). In WA, clinical PCR testing predominantly targets symptomatic individuals, with GS performed on a select group of these samples. Conversely, our wastewater surveillance sampling involved bi-weekly collections of two 24-hour composite samples from three WWTPs, each representing the same weekly timeframe. This bi-weekly sampling schedule, while systematic, limits the timeliness of WBE as an early detection tool due to the frequency of data points. Enhancing wastewater sampling frequency or adopting continuous surveillance could markedly improve early variant detection capabilities.
In our correlation analyses, we aligned the week of sample collection for both clinical and wastewater specimens to ensure comparability. However, the inherent delay in laboratory analysis and result reporting presents a barrier to the immediate utility of WBE as an early warning system. Although samples are collected systematically, GS on both clinical and wastewater specimens was conducted weekly in WA, with wastewater GS results reported approximately seven days post-collection. Addressing these reporting delays is critical for maximizing WBE's effectiveness as a proactive tool in public health surveillance. Reducing lag times, while mindful of logistical and economic limitations, could significantly enhance public health response agility by offering timely insights into emergent trends, thereby optimising early detection and intervention strategies for infectious diseases. Additional correlation analyses ,incorporating reporting dates, are required to gain a clearer understanding of the utility of WBE as an early predictor in WA.
Despite the advantages of WBE, the importance of maintaining clinical sequencing alongside wastewater surveillance should not be overstated. Ultimately, WBE provides information at the population level. Clinical sequencing, however, offers insights into the clinical implications of new lineages [
38], including their implications on disease severity, antiviral suitability, and vaccine efficacy [
39]. Moreover, it allows confirmation of the presence and effects of specific sub-lineages in individual patients, a dimension beyond the scope of wastewater analysis. Clinical sequencing also validates and complements wastewater findings, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of the virus’s behaviour and evolution. Thus, integrating both wastewater and clinical sequencing approaches is fundamental to a robust, holistic surveillance strategy in the context of COVID-19. The strong and significant correlations noted throughout this study indicate that the relative abundances of lineages in wastewater may continue to reflect community clinical trends, despite the evolving dynamics of clinical surveillance strategies.
The implementation of WBE provides significant benefits for public health monitoring, yet it faces numerous challenges. Accurate quantification of viral concentrations in wastewater is complicated by its heterogeneity and PCR inhibition from various compounds [
40]. The interpretation of WBE data is further complicated by limitations in understanding pathogen faecal shedding kinetics and the critical role of sampling site and method selection in influencing the accuracy of epidemiological analyses [
41]. Although external factors like stormwater ingress can dilute viral concentrations, necessitating normalisation techniques for accurate measurement [
41], such methods were not performed in this study. The reason for this omission is attributed to the moderate to strong positive correlation observed between clinical outcomes and WBE data throughout the study period, suggesting that, despite these challenges, WBE can still provide valuable insights into disease prevalence in WA. Moreover, the separation of stormwater and wastewater systems in WA minimises the impact of rainfall on the wastewater analysis, though normalization markers like pepper mild mottle virus (ppMoV) could enhance quantification data interpretation by accounting for population dynamics and changes in water use.
Our study encountered specific challenges, notably during the week ending 19 February 2023, when all wastewater samples failed GS due to SARS-CoV-2 genome coverage below 60%, attributed to low SARS-CoV-2 wastewater concentrations. However, these instances were relatively rare, mitigated by our testing protocols designed for low viral concentrations in response to stringent border controls in WA [
42] and the need to detect and characterise virus importation events [
26]. Collaboration with the Australian WBE consortium (ColoSSoS, WaterRA) enabled the selection of a qPCR kit resistant to common wastewater inhibitors, enhancing the reliability of SARS-CoV-2 RNA quantification. This approach effectively addressed most challenges associated with WBE, demonstrating the critical dependency of GS efficacy on sufficient viral load and highlighting the importance of overcoming molecular assay inhibitors to generate reliable results.
Maximising the effectiveness of WBE necessitates the facilitation of data exchange and integration between wastewater surveillance networks and healthcare systems. The ability to efficiently share data is vital for aligning WBE insights with clinical data. However, this process can be hindered by logistical and regulatory barriers, which may result in delays in data comparison and introduce gaps in the overall epidemiological understanding. Overcoming these data-sharing obstacles is essential for improving the precision and applicability of WBE in public health monitoring and intervention strategies. In WA, the presence of a well-established environmental microbiology unit within the state public health laboratory, PathWest, facilitated simple and rapid data exchange between the laboratory and state public health authorities. This arrangement helped to overcome numerous data-sharing challenges and regulatory constraints, attributable to the laboratory's status as a government health service provider.
The proactive use of this WBE surveillance program by the WA Department of Health exemplifies a forward-thinking approach to pandemic and public health management. The department used wastewater data to facilitate a better understanding of COVID-19 prevalence and trends within the community, guiding public health decisions and strategies. The decision to make this data publicly accessible via an online dashboard [
23], updated weekly, ensured transparent communication of the latest trends to the public and the media. This initiative not only facilitated timely information dissemination but also enabled individuals to make informed personal risk assessments, contributing to a more informed public discourse during the pandemic. This strategy, blending advanced genomic surveillance with traditional epidemiological methods, significantly bolstered the overall response to COVID-19, fostering an environment of informed decision-making crucial for effectively managing a public health challenge of this scale.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Jake Gazeley, Terence Lee, and Avram Levy. Methodology & Validation, Jake Gazeley, Terence Lee, Daniel R Knight, and Avram Levy. Bioinformatics Software Development and Implementation, Terence Lee, and Daniel R Knight. Data Provision, Dylan Barth, Alex Shivarev, Jelena Maticevic, Paul Knight, and Paul Armstrong. Data Analysis & Visualization, Jake Gazeley, Dylan D Barth, and Paul Knight. Writing – Original Draft preparation, Jake Gazeley. Writing – Review and Editing, Jake Gazeley, Terence Lee, Avram Levy, Daniel R Knight, Meredith Hodge, Sandra Sjollema, David Speers, Dylan D Barth, Alex Shivarev, Jelena Maticevic, Paul Knight, Paul Armstrong. Sample Collection Coordination, Cameron Gordon. Supervision, Avram Levy, Sandra Sjollema, Meredith Hodge, David Speers, Cameron Gordon, Jelena Maticevic, and Paul Armstrong. Project Administration, Avram Levy, Sandra Sjollema, Meredith Hodge, David Speers, Cameron Gordon, Jelena Maticevic, and Paul Armstrong.