Submitted:
29 February 2024
Posted:
29 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Material Preparation
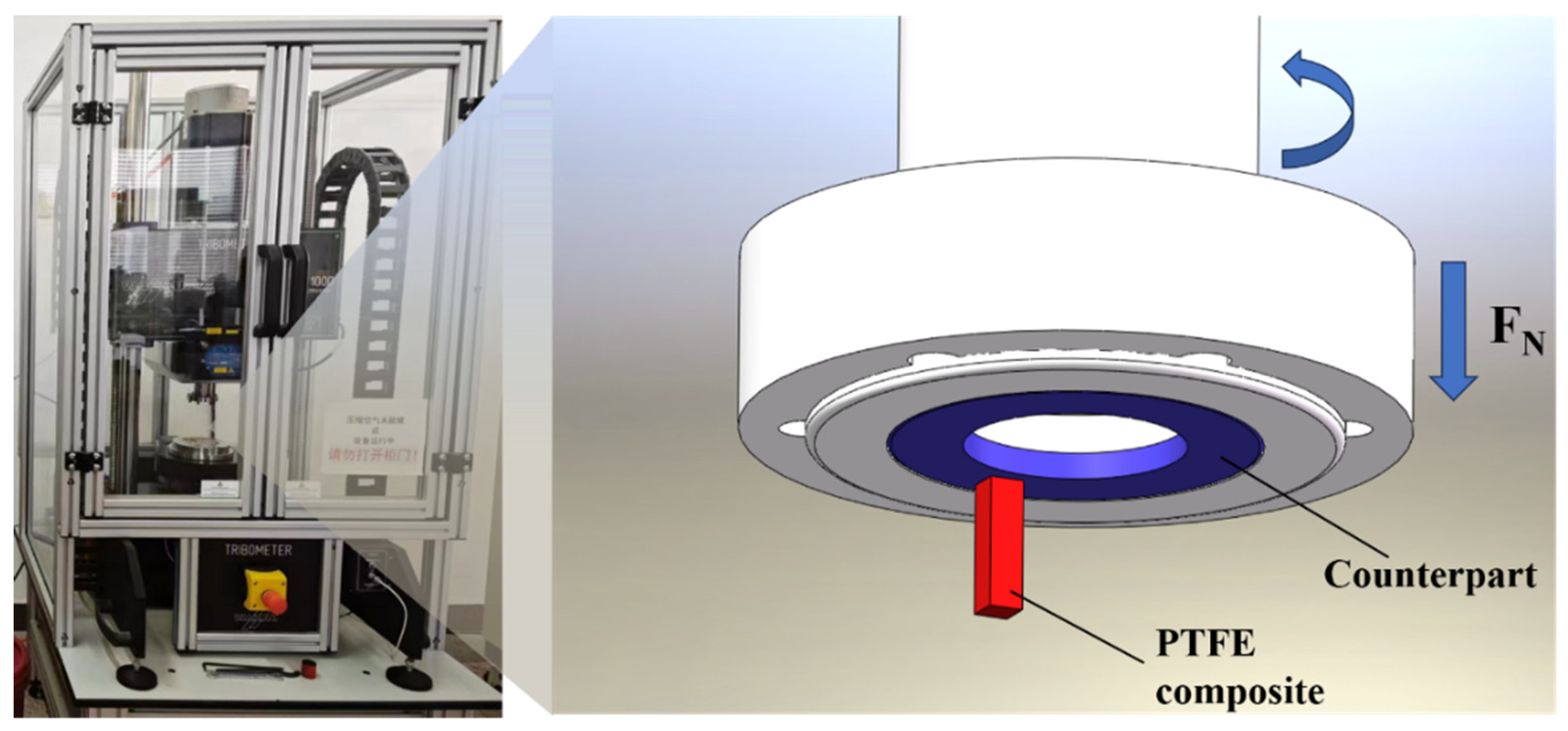
2.2. Tribological Tests
2.3. Characterization of Tribofilm
3. Results and Discussion
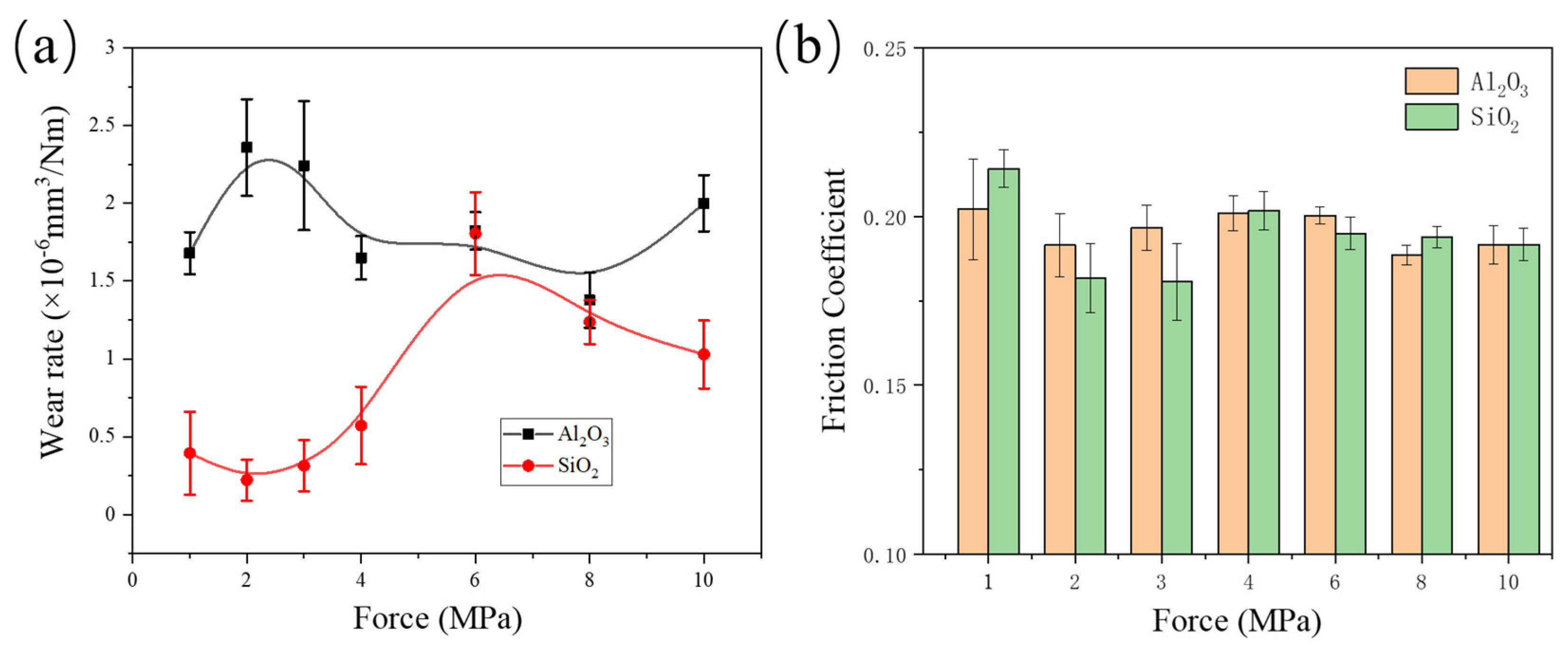
3.1. Friction Test Results
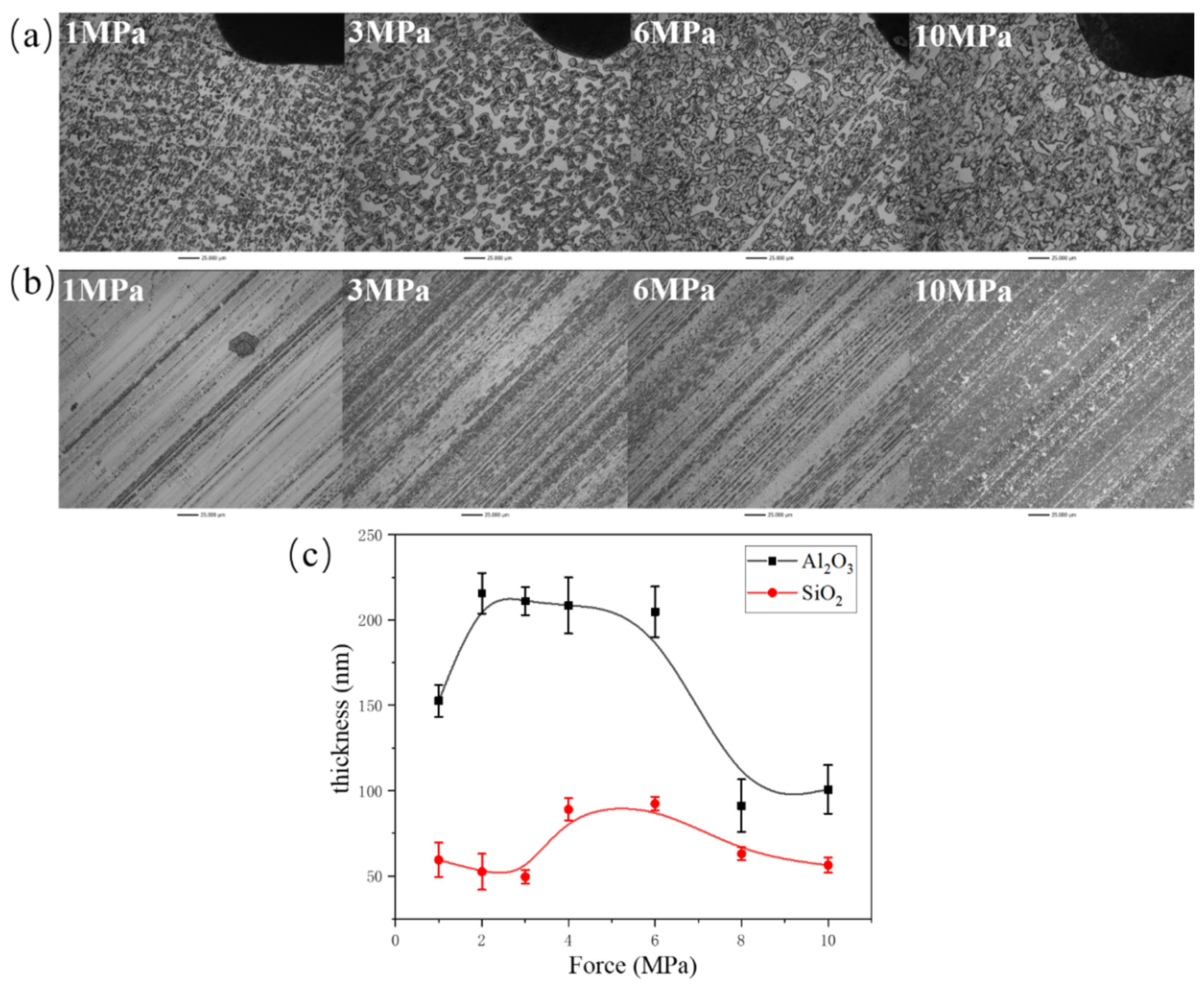
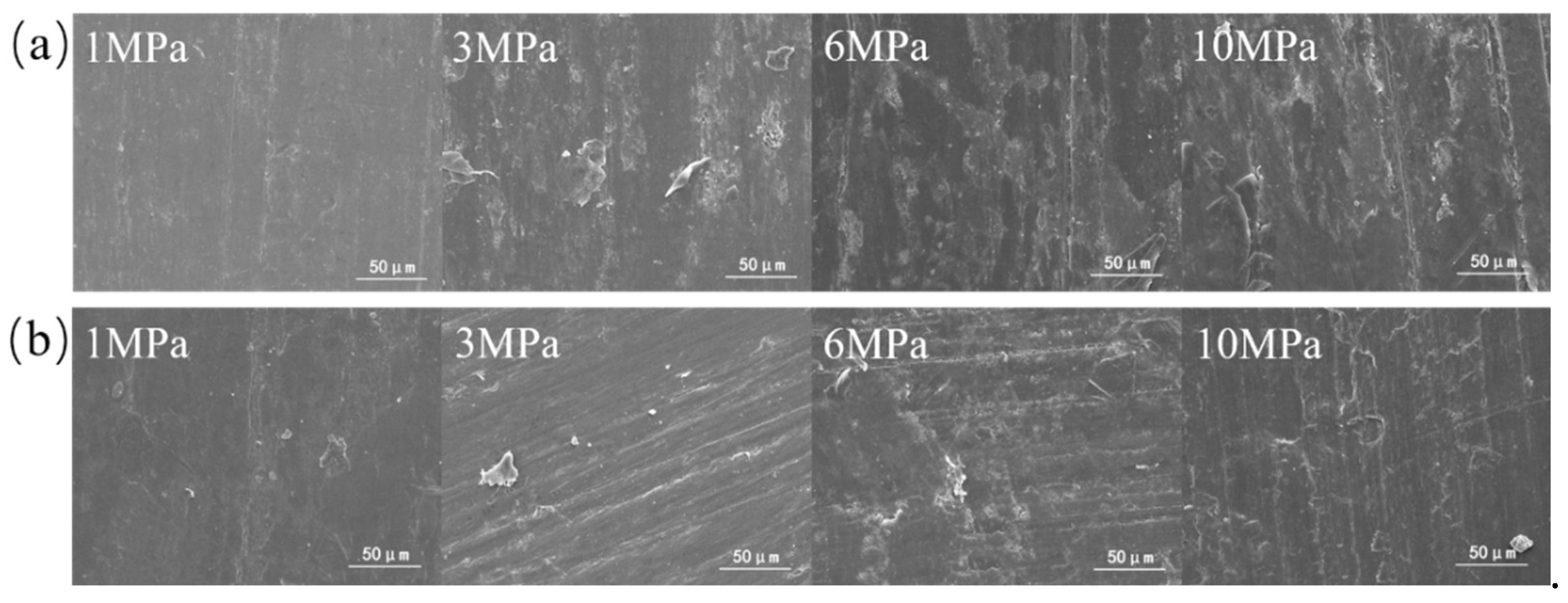
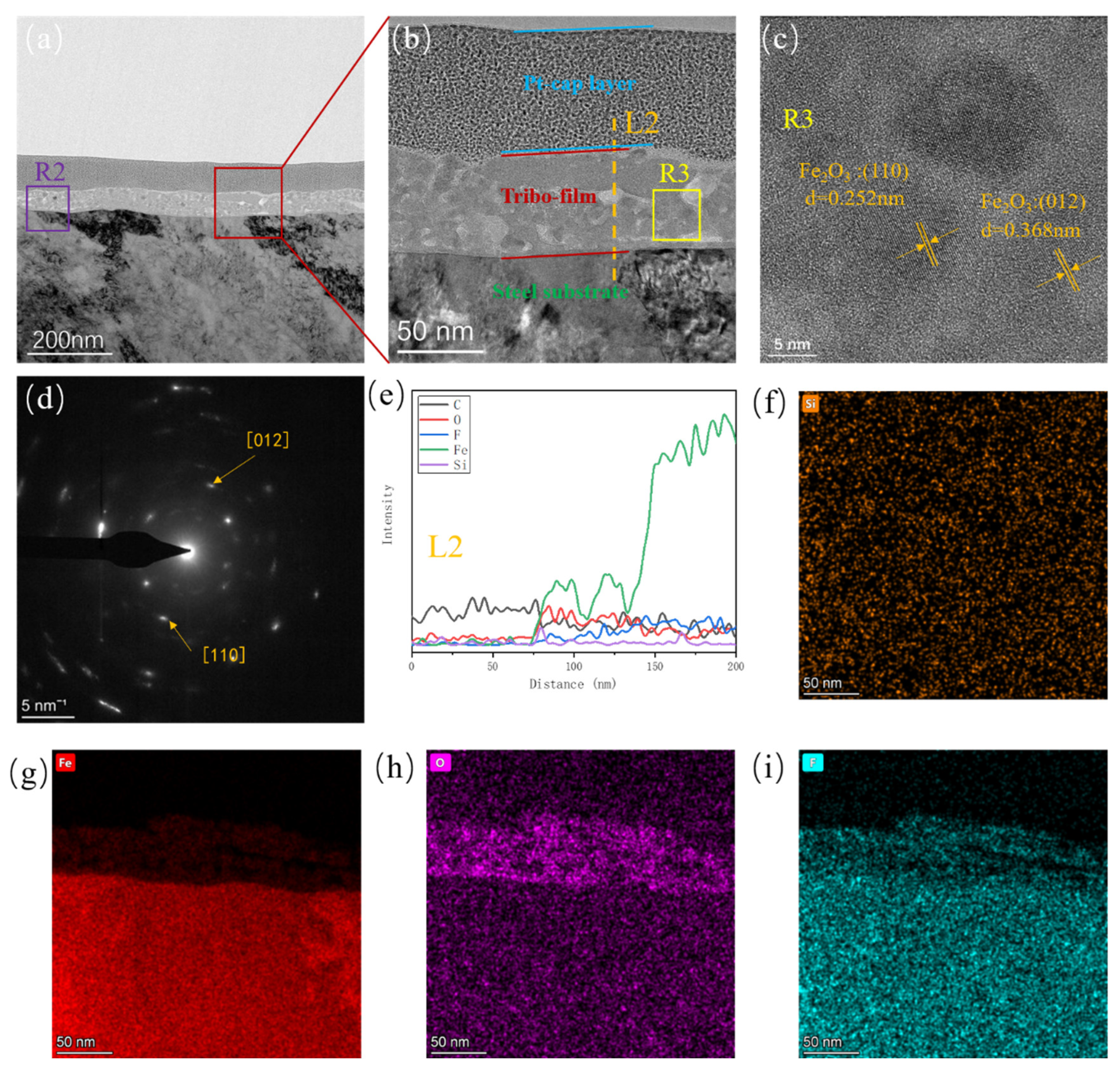
3.2. Tribofilm Morphology
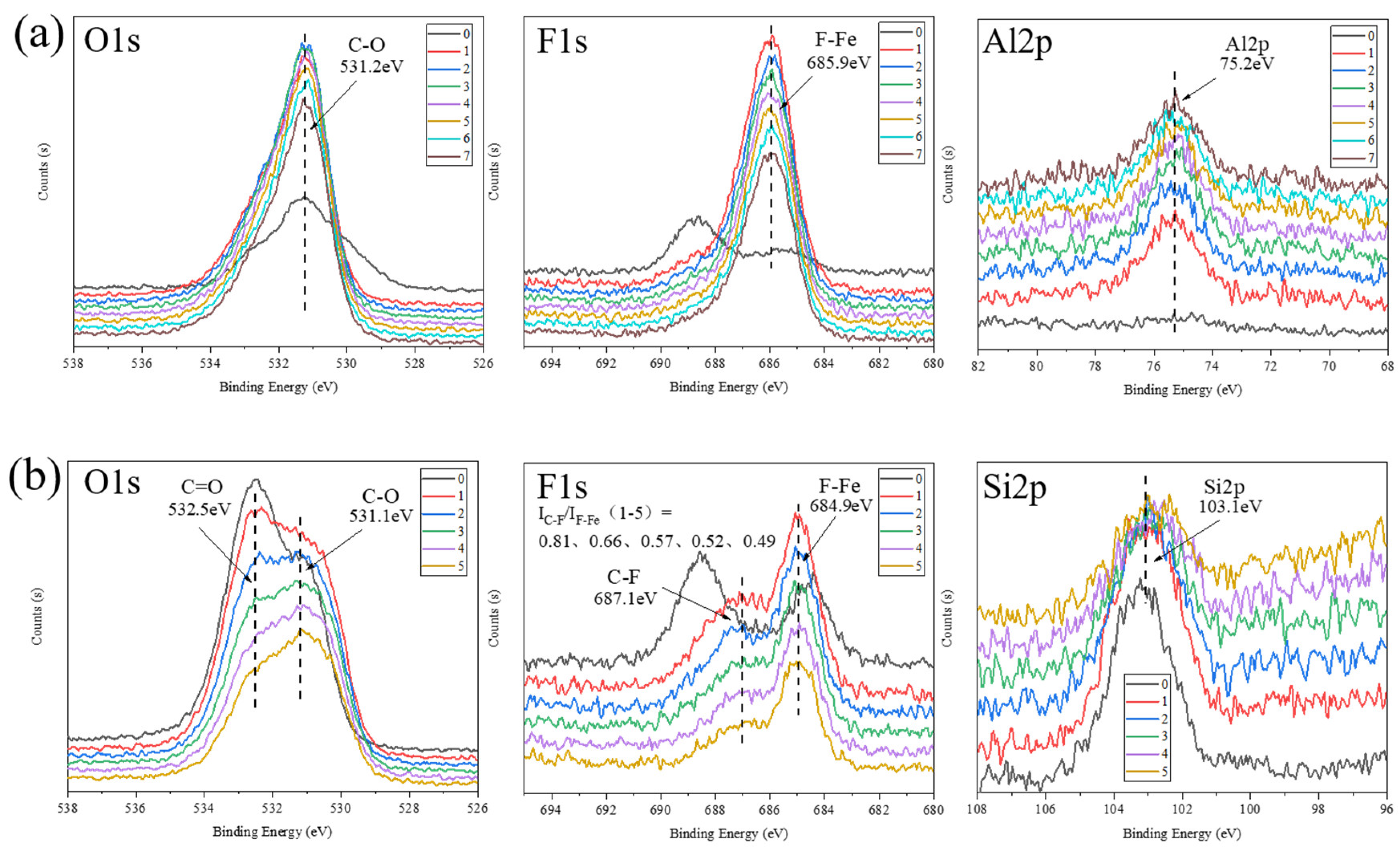
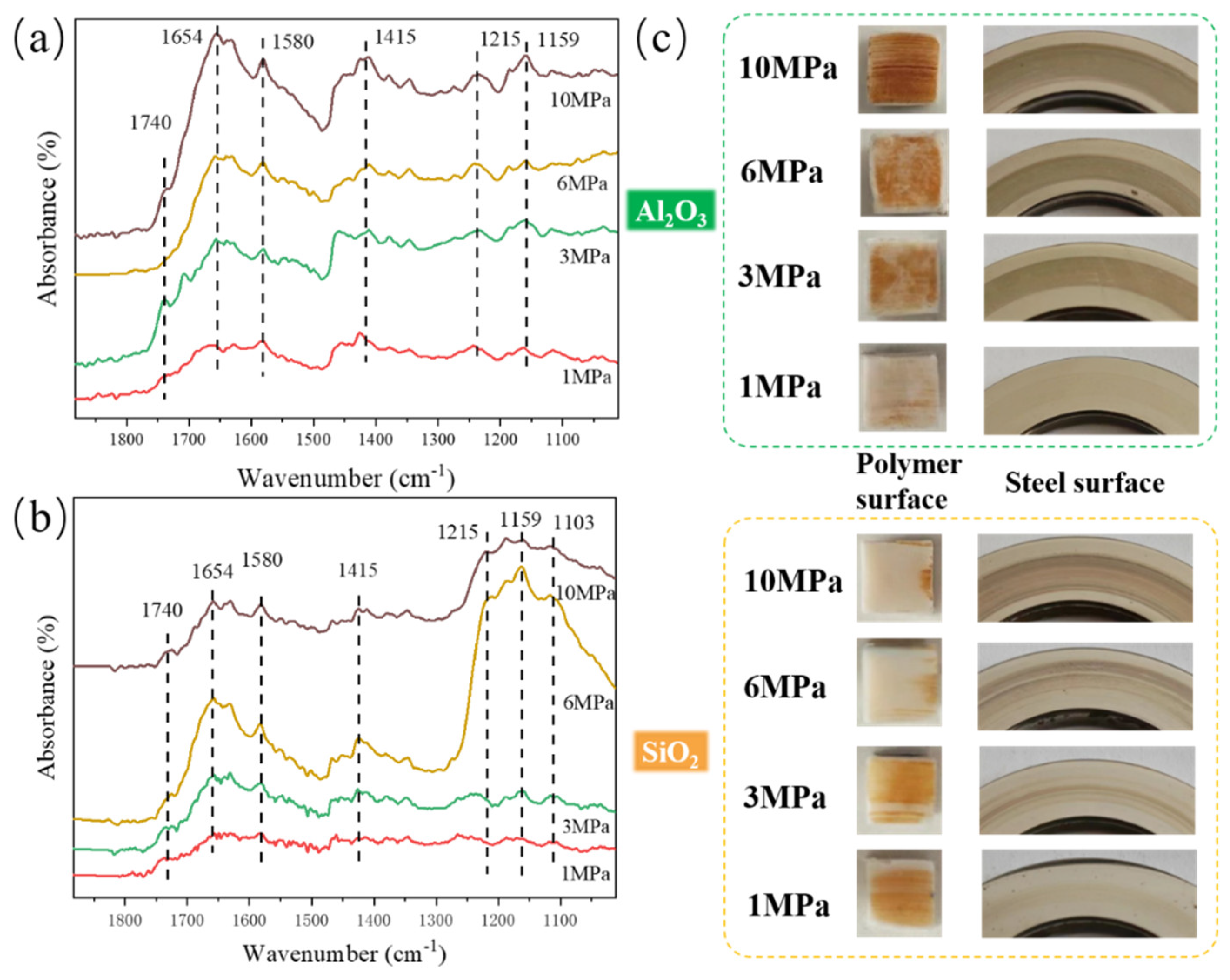
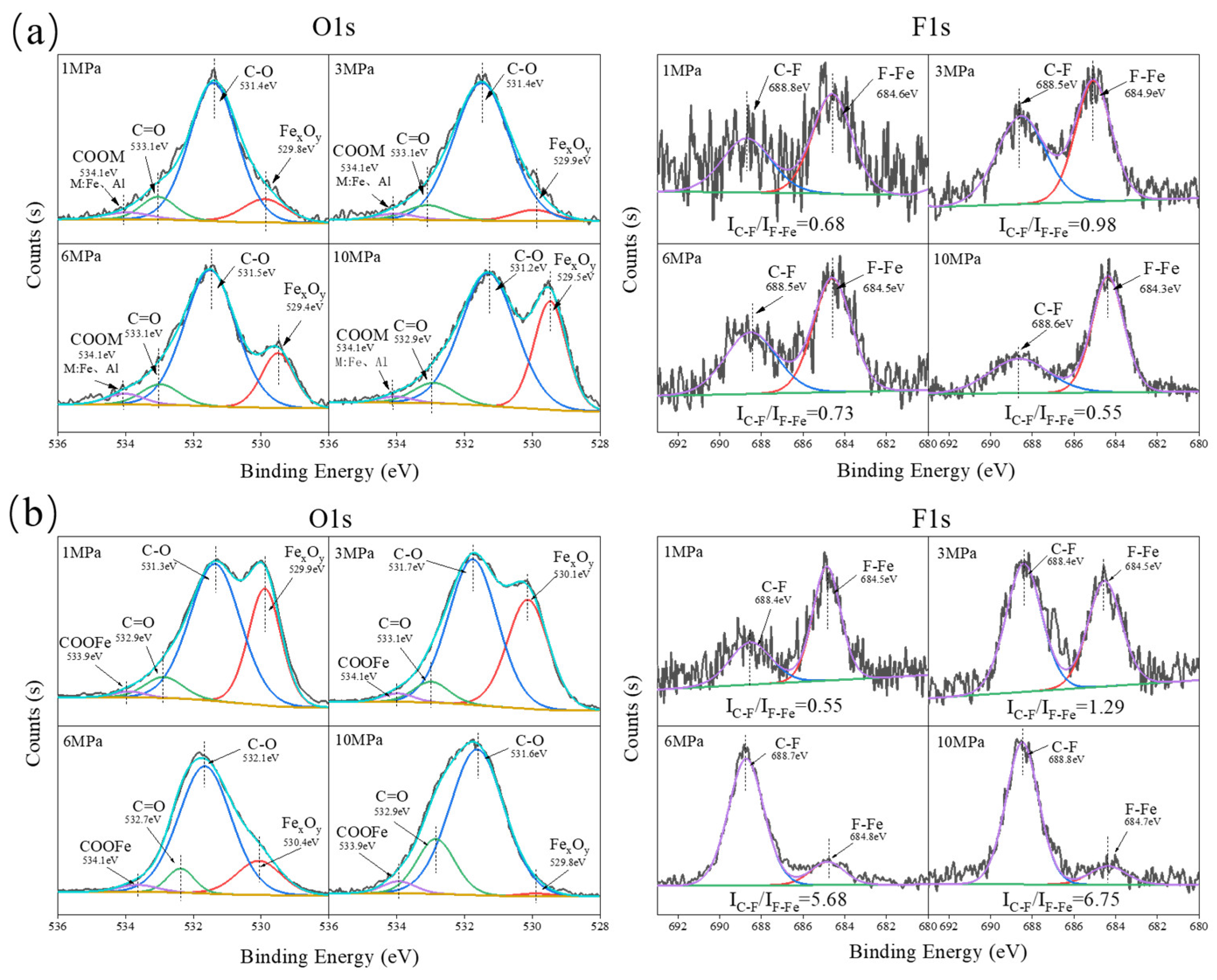
3.3. Analysis of Tribochemical Reactions
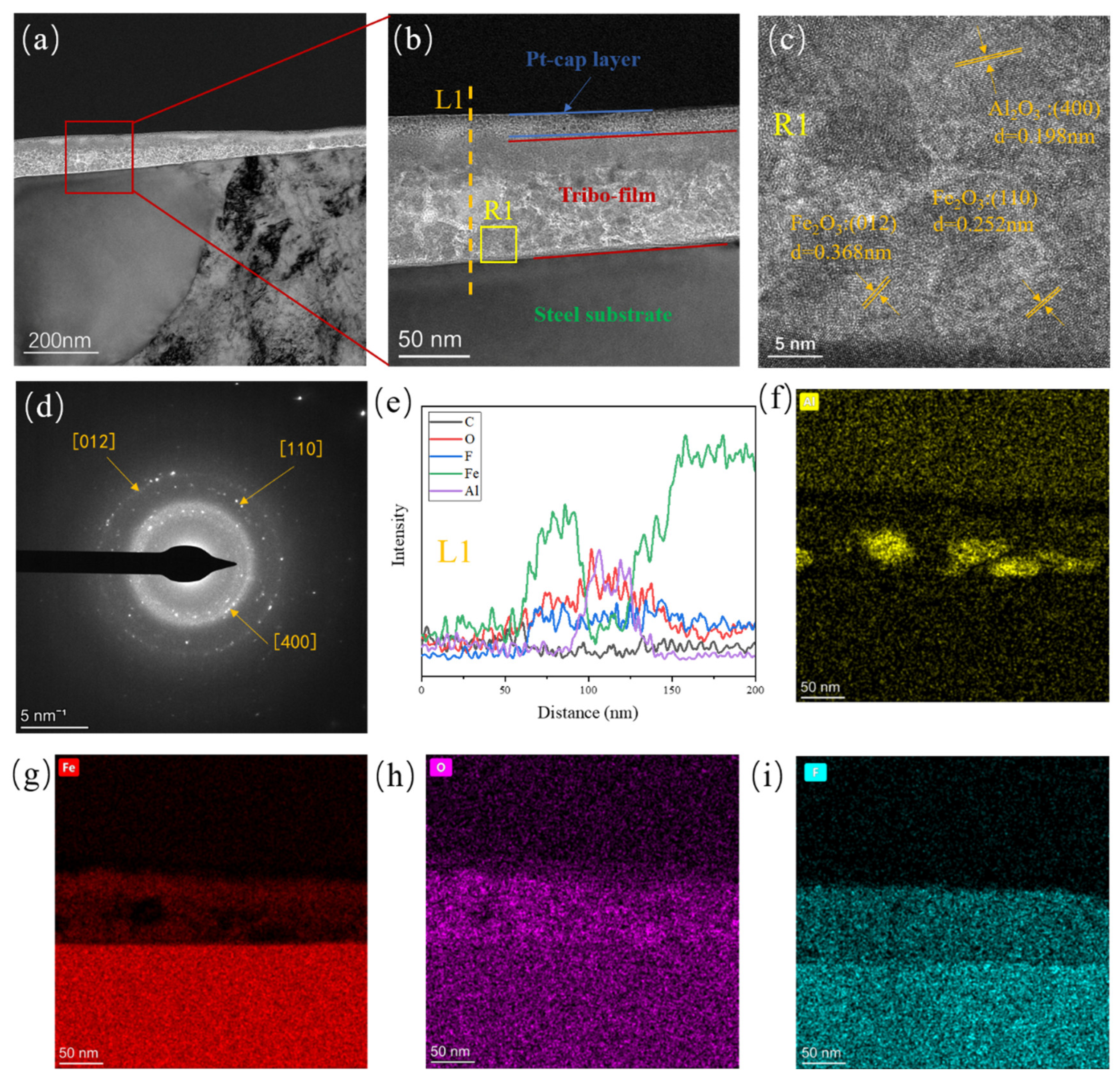
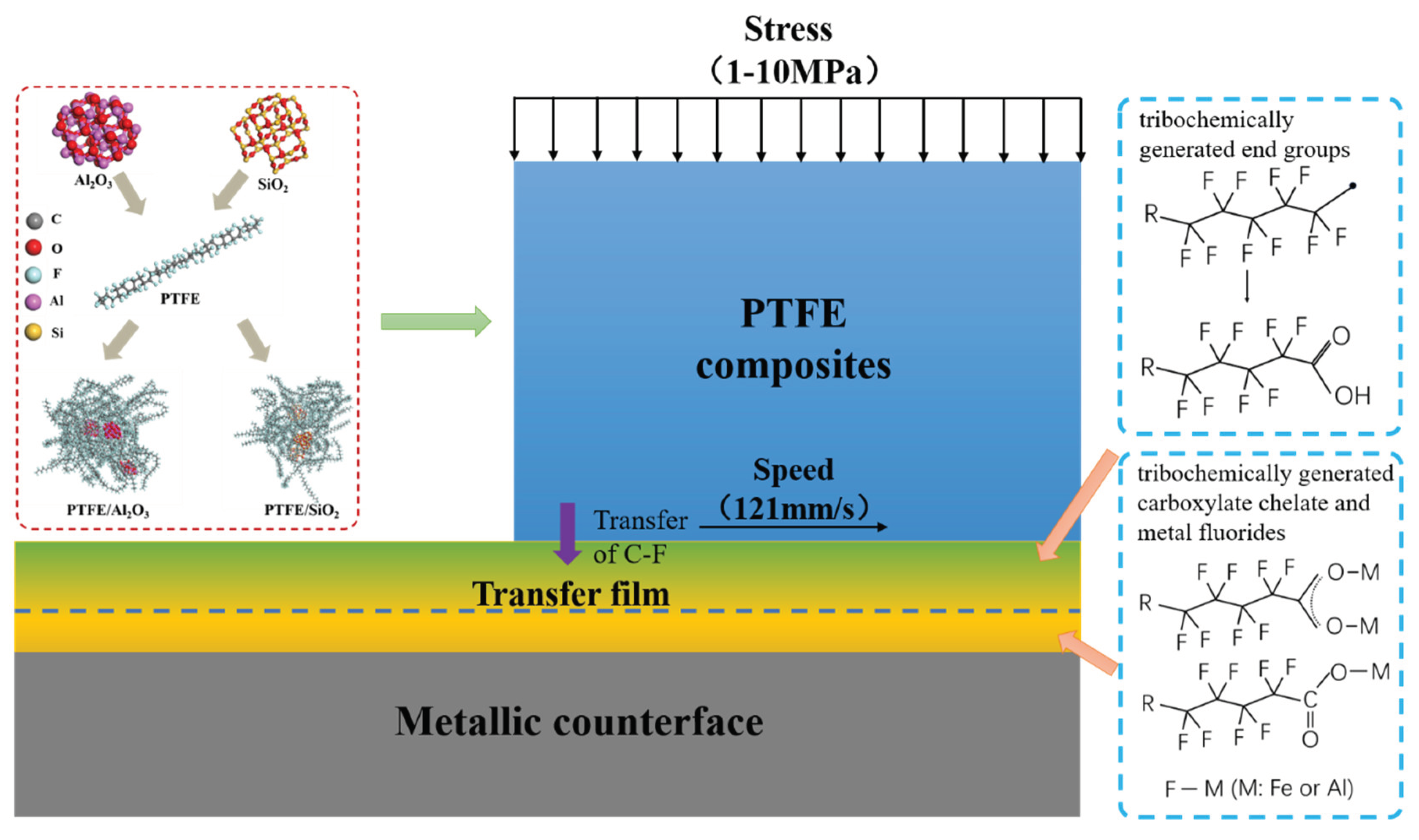
3.4. Tribofilm Formation Mechanism
4. Conclusion
- Both composites exhibit good wear resistance under the pressure ranging from 1 MPa to 10 MPa. The wear rate of the SiO2/PTFE composite is generally lower than that of the α-Al2O3/PTFE, however, the α-Al2O3/PTFE composite demonstrates better performance stability compared to the SiO2/PTFE. For the α-Al2O3/PTFE, an island-like tribofilm is formed with a thickness of 100 to 200 nm, while the tribofilm of SiO2/PTFE composite is thinner, approximately 50 to 100 nm, and displays a striped pattern.
- For the α-Al2O3/PTFE composite, the degree of tribochemical reactions shows a positive correlation with the load. Conversely, in the case of the SiO2/PTFE composite, the degree of tribochemical reactions gradually decreases as the load increases. For α-Al2O3/PTFE, the transfer film exhibits a dual-layer structure across depth, where the upper layer comprises a mixture of PTFE transfer and products of tribochemical reaction, while the lower layer mainly consists of uniform products of tribochemical reaction without obvious PTFE transfer. In contrast, for SiO2/PTFE, the transfer film presents a gradient structure. As the depth increases, there is progressively less PTFE transfer, while the amount of tribochemical reaction products gradually increases.
- The difference in thickness and microstructure evolution of the tribofilms for the two composites is mainly attributed to the tribochemistry of the nanoparticles. α-Al2O3 nanoparticle plays a “cohesion” role during the formation of the tribofilm. which facilitates the formation of a thicker, more uniform, and stronger adhered tribofilm on the metal counterpart, making it more robust against shear stress.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hudec, T.; Roch, T.; Gregor, M.; Orovčík, Ľ.; Mikula, M.; Polcar, T. Tribological behaviour of Mo-S-N solid lubricant coatings in vacuum, nitrogen gas and elevated temperatures. Surface and Coatings Technology 2021, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R. Progress of environment friendly cutting fluids/solid lubricants in turning-A review. Materials Today: Proceedings 2021, 37, 3577–3580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas S K, V.K. Friction and wear of PTFE: A review. 1992.
- Shen, Z.Z.Q.X.W.L.W. Friction and wear properties of metal powder filled PTFE composites under oil lubricated conditions. 1997.
- S, T.K.K. Effect of various fillers on the friction and wear of polytetrafluoroethylene-based composites. 1982.
- Zhao-Zhu Zhang, W.-C.S., Wei-Min Liu, Qun-Ji Xue, Tong-Sheng Li. Tribological properties of polytetrafluoroethylene-based composite in different lubricant media. 1995.
- Myshkin, N.; Kovalev, A. Adhesion and surface forces in polymer tribology—A review. Friction 2018, 6, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E, B.T.A.K.F. Sliding wear mechanism of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) and PTFE composites. 1992.
- Blanchet, T.A. A Model for Polymer Composite Wear Behavior Including Preferential Load Support and Surface Accumulation of Filler Particulates. Tribology Transactions 1995, 38, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burris, D.L.; Sawyer, W.G. Improved wear resistance in alumina-PTFE nanocomposites with irregular shaped nanoparticles. Wear 2006, 260, 915–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandanur, S.S.; Rafiee, M.A.; Yavari, F.; Schrameyer, M.; Yu, Z.-Z.; Blanchet, T.A.; Koratkar, N. Suppression of wear in graphene polymer composites. Carbon 2012, 50, 3178–3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krick, B.A.; Ewin, J.J.; McCumiskey, E.J. Tribofilm Formation and Run-In Behavior in Ultra-Low-Wearing Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) and Alumina Nanocomposites. Tribology Transactions 2014, 57, 1058–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargava, S.; Makowiec, M.E.; Blanchet, T.A. Wear reduction mechanisms within highly wear-resistant graphene- and other carbon-filled PTFE nanocomposites. Wear 2020, 444–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S, B. The development of transfer layers and their role in polymer tribology. 2000.
- Myshkin, N.K.; Petrokovets, M.I.; Kovalev, A.V. Tribology of polymers: Adhesion, friction, wear, and mass-transfer. Tribology International 2005, 38, 910–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padhan, M.; Marathe, U.; Bijwe, J. Surface topography modification, Film transfer and Wear mechanism for fibre reinforced polymer composites-An Overview. Surface Topography-Metrology and Properties 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Pei, X.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, G. Tribofilm growth at sliding interfaces of PEEK composites and steel at low velocities. Tribology International 2020, 151, 106456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Feng, S.; Qi, Y.; Cui, A. Effect of Self-Generated Transfer Layer on the Tribological Properties of PTFE Composites Sliding against Steel. Coatings 2018, 8, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onodera, T.; Park, M.; Souma, K.; Ozawa, N.; Kubo, M. Transfer-Film Formation Mechanism of Polytetrafluoroethylene: A Computational Chemistry Approach. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C 2013, 117, 10464–10472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Khare, H.S.; Burris, D.L. Transfer film evolution and its role in promoting ultra-low wear of a PTFE nanocomposite. Wear 2013, 297, 1095–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.; Wei, J.; Zeng, J.; Alam, K.I.; Sun, W.; Liu, X.; Liu, K.; Burris, D.L. Interfacial Gradient and Its Role in Ultralow Wear Sliding. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C 2020, 124, 6188–6196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.X.; Sun, W.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.J.; Liu, K. Measuring Evolution of Transfer Film-Substrate Interface Using Low Wear Alumina PTFE. Tribology Letters 2018, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onodera, T.; Kawasaki, K.; Nakakawaji, T.; Higuchi, Y.; Ozawa, N.; Kurihara, K.; Kubo, M. Chemical Reaction Mechanism of Polytetrafluoroethylene on Aluminum Surface under Friction Condition. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C 2014, 118, 5390–5396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, K.L.; Pitenis, A.A.; Sawyer, W.G.; Krick, B.A.; Blackman, G.S.; Kasprzak, D.J.; Junk, C. PTFE Tribology and the Role of Mechanochemistry in the Development of Protective Surface Films. Macromolecules 2015, 48, 3739–3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khare, H.S.; Burris, D.L. The extended wedge method: atomic force microscope friction calibration for improved tolerance to instrument misalignments, tip offset, and blunt probes. Rev Sci Instrum 2013, 84, 055108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, K.L.; Sidebottom, M.A.; Atkinson, C.C.; Babuska, T.F.; Kolanovic, C.A.; Boulden, B.J.; Junk, C.P.; Krick, B.A. Ultralow Wear PTFE-Based Polymer Composites—The Role of Water and Tribochemistry. Macromolecules 2019, 52, 5268–5277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurizio Pianca, E.B. , Giuseppe Esposto, Stefano Radice. End groups in fluoropolymers. 1999.
- Lauer, J.L.; Bunting, B.G. High Temperature Solid Lubrication by Catalytically Generated Carbon. Tribology Transactions 1988, 31, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligang; Zhang; Huimin; Qi; Guitao; Li; Daoai; Wang; Tingmei; Wang. Significantly enhanced wear resistance of PEEK by simply filling with modified graphitic carbon nitride. Materials & Design 2017.
- Luiz, N.F., D. Adsorption at Silica Alumina and Related Surfaces. 2006.
- Przedlacki, M.; Kajdas, C. Tribochemistry of Fluorinated Fluids Hydroxyl Groups on Steel and Aluminum Surfaces. Tribology Transactions 2006, 49, 202–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Zhang, G.; Wang, T.; Wang, Q. Enhancing the tribological performance of PEEK exposed to water-lubrication by filling goethite (α-FeOOH) nanoparticles. RSC Advances 2016, 6, 51247–51256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).