1. Introduction
The probabilistic dance of particles governed by the laws of quantum mechanics and the elegant curvature of spacetime dictated by gravity have long stood as two separate realms in the landscape of physics. While each theory has provided remarkable insights into the fundamental nature of the universe, the elusive bridge connecting these two pillars of modern physics continues to evade our grasp. The dichotomy between the microscopic world of quantum mechanics, where particles exist in superpositions and exhibit wave-particle duality, and the macroscopic realm of gravity, where massive bodies warp the very fabric of spacetime, poses one of the most profound puzzles in contemporary physics.
For decades, physicists have strived to reconcile the seemingly irreconcilable: the quantum realm described by the successful framework of quantum field theory and the gravitational domain governed by Einstein’s general relativity. While both theories have stood the test of time in their respective domains, attempts to seamlessly integrate them into a unified framework have encountered formidable challenges. The inherent incompatibility between the probabilistic nature of quantum mechanics and the deterministic nature of gravity has fuelled a quest for a more encompassing theory.
In this paper, we expand upon a theory proposed in our earlier study that time progresses as an expansion wave from the time of the big bang, and that all objects in the universe expand and move apart as this time sphere expands that allows us to experience time [
1].
We review and refine the model we use to fit to cosmic luminosity data based on this theory and review the implications, one being that this new understanding leads us to believe the universe expansion is not accelerating as was previously thought [
2,
3]. It also gives us an explanation for dark matter and why it is so hard to observe, as well as allowing for black holes to exist without creating a singularity. Perhaps most importantly, the theory allows us to draw further conclusions about the subatomic world. The extension to the concept put forward by general relativity that time and space are linked, but linked through the universe’s expansion, has far reaching consequences that we believe allows us to garner a unified understanding of the cosmic universe governed by both gravity and quantum mechanics.
Theory in Brief
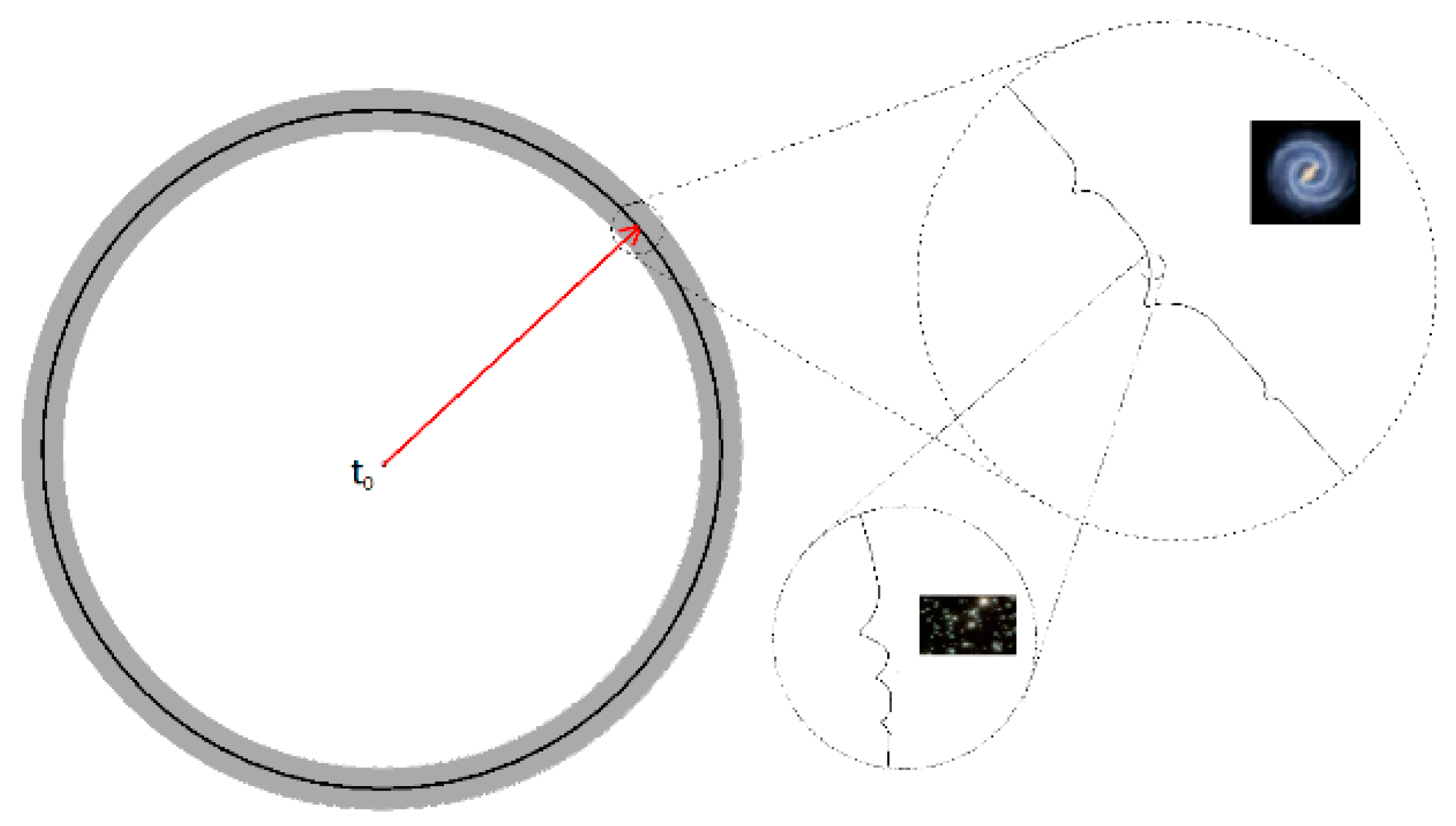
The theory, as proposed in our first paper, is that time is a spatial dimension that obeys the same laws of physics as other spatial dimensions but is largely invisible to us. Time does not progress in a single direction but rather in all directions at once. Each particle is caught up in the expansion wave and is consequently moving in time—a spatial dimension over which we can appreciate only a small, but finite sized, sliver of a sphere at any one moment. If we consider a cross section through the centre of the expansion sphere showing one normal space dimension and one of the time space dimensions, then time will progress outwards, as shown in
Figure 1, away from time t
0. Overall, the expansion wave front will be isotropic, but where large masses have amalgamated, dimples will form in the wave front, as shown in the figure. A galaxy would form a large dimple, and the stars would form smaller dimples as you zoom in further.
We ourselves will predominantly follow a single time path governed by the mass on which we “ride”, but we will interact with objects on a different time path as they expand at different velocities/arrive from different parts of the wave front.
The time dimension can, in a sense, be thought of as a dimension over the top of all the other dimensions that is equally stretching in all directions when viewed as an isotropic universe expansion. In a sense the theory is an extension to general relativity. Einstein identified that space and time were interchangeable or part of a single space-time entity. By taking this a step further and saying that time is the expansion effect we see and that stretches all the other 3 dimensions, then this simplifies the mathematics and provides explanations that are otherwise absent as we shall explain later in this paper.
Another artefact of the theory ties in the subatomic realm. As the slice of time in which we exist must have a finite size then particles/photons on the atomic-to-nothing size level have the freedom to rotate within this space and consequently can move forwards and backwards in time relative to ourselves. We will expand upon this part of the theory here.
Figure 1.
Visualisation of Time expansion wave cross section cutting through a single time dimension (as shown by the radius) and a single space dimension (as shown by the circumference). This expansion wave started at time t0 and has reached time t1 signified by the dark black line. Two gravitationally distinct objects would expand away from each other in space as the time expansion wave increases. Where objects have clumped together then dimples in the wavefront would show up as you zoom in. The thin black line shows the observable slice of time with the grey areas showing the possibility of matter existing outside of our observable time window.
Figure 1.
Visualisation of Time expansion wave cross section cutting through a single time dimension (as shown by the radius) and a single space dimension (as shown by the circumference). This expansion wave started at time t0 and has reached time t1 signified by the dark black line. Two gravitationally distinct objects would expand away from each other in space as the time expansion wave increases. Where objects have clumped together then dimples in the wavefront would show up as you zoom in. The thin black line shows the observable slice of time with the grey areas showing the possibility of matter existing outside of our observable time window.
Luminosity Model and Fit
Stellar luminosity data were modelled in our earlier paper to fit the observed data. As all historical light reaching us from distant luminous objects must have travelled at the speed of light and in a straight line from its point of origin to reach us, we need to consider only one spatial dimension and one temporal expansion dimension to model it. It is assumed that the light that reaches us must have travelled within one of the space dimensions perpendicular to the origin point at t
0 as visualised in
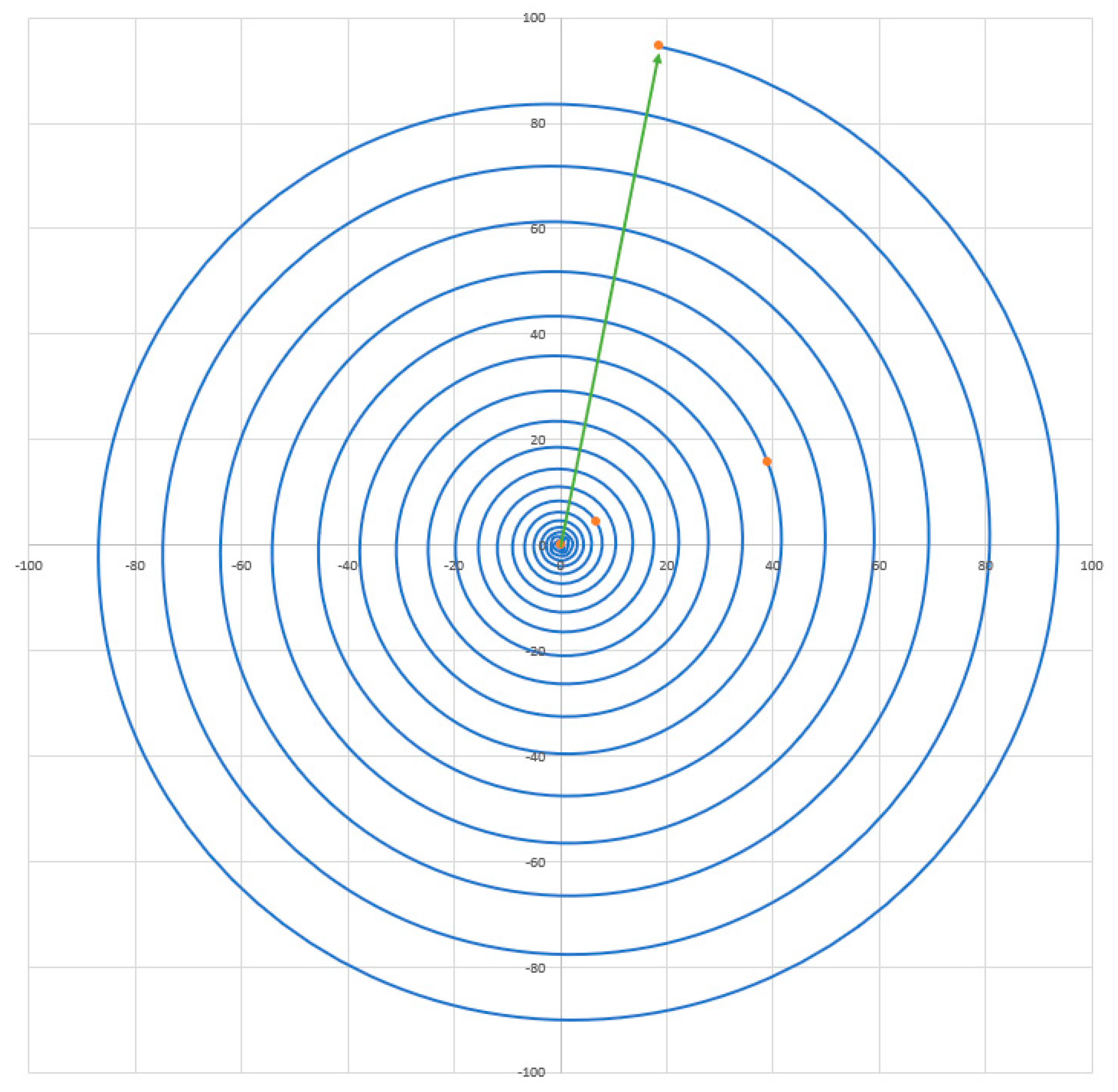
Figure 1. It is also assumed that bending of any of these light ray paths as caused by gravity effects of objects that the light passes will be random and equalise out when considering the universe as a whole. This would mean that to reach us, each light beam has taken a path along the surface of the expanding sphere. Although other light beams will have taken completely different paths, each light pinpoint can be dealt with similarly. Therefore, for each photon, if we take a slice through the temporal dimension and the straight-line spatial path that each photon takes, then you will end up with a spiral path (in time) consistent with the expansion of the universe.
A different photon would require a different cross section/alignment, but the spiral path would simplify to be the same assuming that the expansion of the universe has been isotropically similar and dependent only on the distance from the Earth to the object being observed.
The magnitude of the observed light (expressed as the distance modulus m-M) of any object is related to the luminosity distance by:
where
is the luminosity distance in Mpc and can be defined as
Figure 2.
Visualisation of the spiral effect of a time wave expanding universe caused by the speed of light having a fixed value. Scale for both x and y is in Mpc. Distant, and therefore historic, objects in the universe, if observed from point A will appear as if on a spiral path reaching back to time zero. The above figure was generated using the complex decay model mentioned later in this paper against luminosity data of Betoule et al. (2016) and Reis et al. (1998). Points highlighted, emanating from the centre of the spiral are, respectively as follows: Time zero, most distant observed object at z of 11.09, Most distant fitted data point, Earth.
Figure 2.
Visualisation of the spiral effect of a time wave expanding universe caused by the speed of light having a fixed value. Scale for both x and y is in Mpc. Distant, and therefore historic, objects in the universe, if observed from point A will appear as if on a spiral path reaching back to time zero. The above figure was generated using the complex decay model mentioned later in this paper against luminosity data of Betoule et al. (2016) and Reis et al. (1998). Points highlighted, emanating from the centre of the spiral are, respectively as follows: Time zero, most distant observed object at z of 11.09, Most distant fitted data point, Earth.
L is the intrinsic luminosity of the object, and F is the observed flux. For nearby objects (those for which the time that has passed is minimal and there has been little increase in radius), this would approximate to the distance around an arc of our spiral model, . For objects that are further away, then distortion will occur through two effects:
As the light stretches, the energy of the light diminishes, which causes a reduction in intensity. The wavelength of light will increase relative to as the circumference becomes proportionally larger for the same angle, so consequently, the energy of the light will drop in intensity relative to /.
Second, the stretch will mean that the photon arrival rate within a beam of photons will be reduced again according to /.
The consequence of this is shown below:
And
where z is the observed redshift. The redshift observed for any point around the spiral will be directly related to the size of the universe at that point, i.e., the circumference. As the circumference of our expansion sphere is directly proportional to the radius, the stretching effect or redshift is:
The spiral distance of a light beam’s origin to earth can be seen to be the integral of the light travel distance:
where
is the observed rate of increase in r or the resultant velocity over time (we have used
H in
to denote that this is the observed expansion velocity derived from Hubble expansion) and
r is the radius of the time expansion sphere.
If the rate of expansion was constant (i.e.,
is a constant and independent of r), then:
Note, at this point in the theory, we are not reliant on the expansion wave being linked to time directly as a basic assumption – this idea is brought out rather from the conclusions drawn later.
2. Results
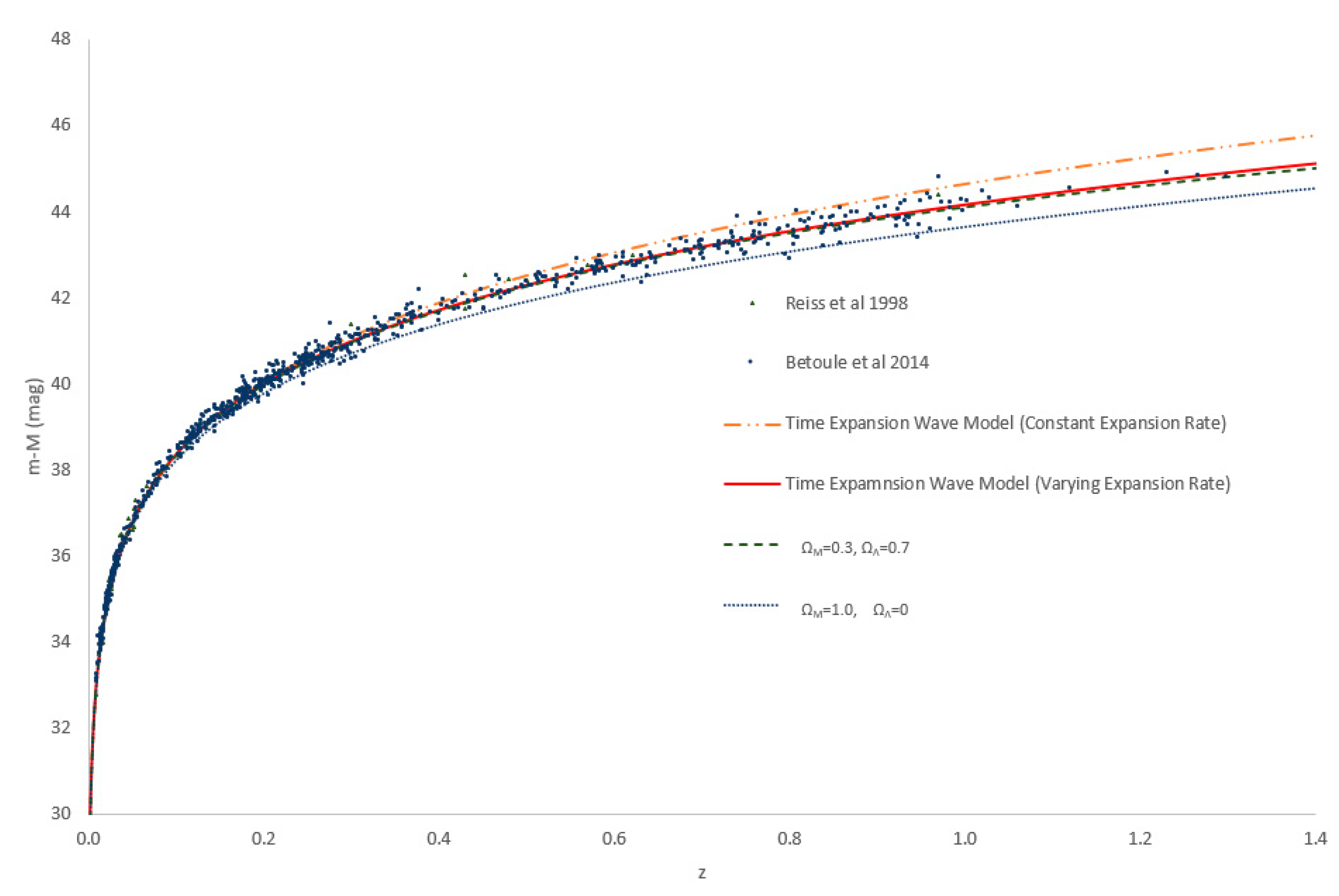
Figure 3.
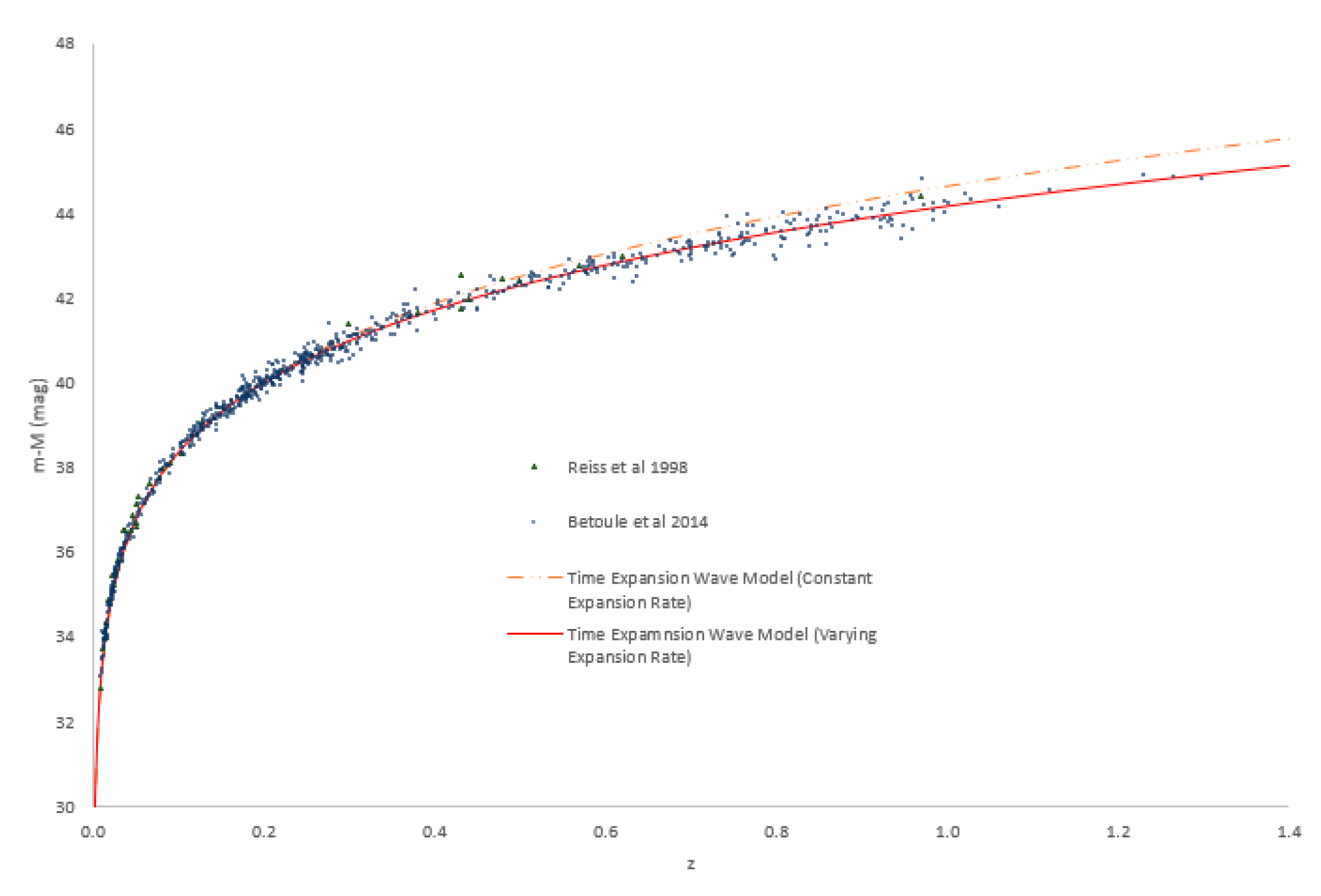
Best fit modelled time expansion wave allowing a fixed speed of expansion (orange solid line) and a varying speed of expansion (red solid line) versus observational data taken by Reiss et al. (1998) and Betoule et al. (2014) (points).
Figure 3.
Best fit modelled time expansion wave allowing a fixed speed of expansion (orange solid line) and a varying speed of expansion (red solid line) versus observational data taken by Reiss et al. (1998) and Betoule et al. (2014) (points).
Figure 4 shows the results of our fit to the luminosity data of Reiss et al. [
2] and Betoule et al. [
3].
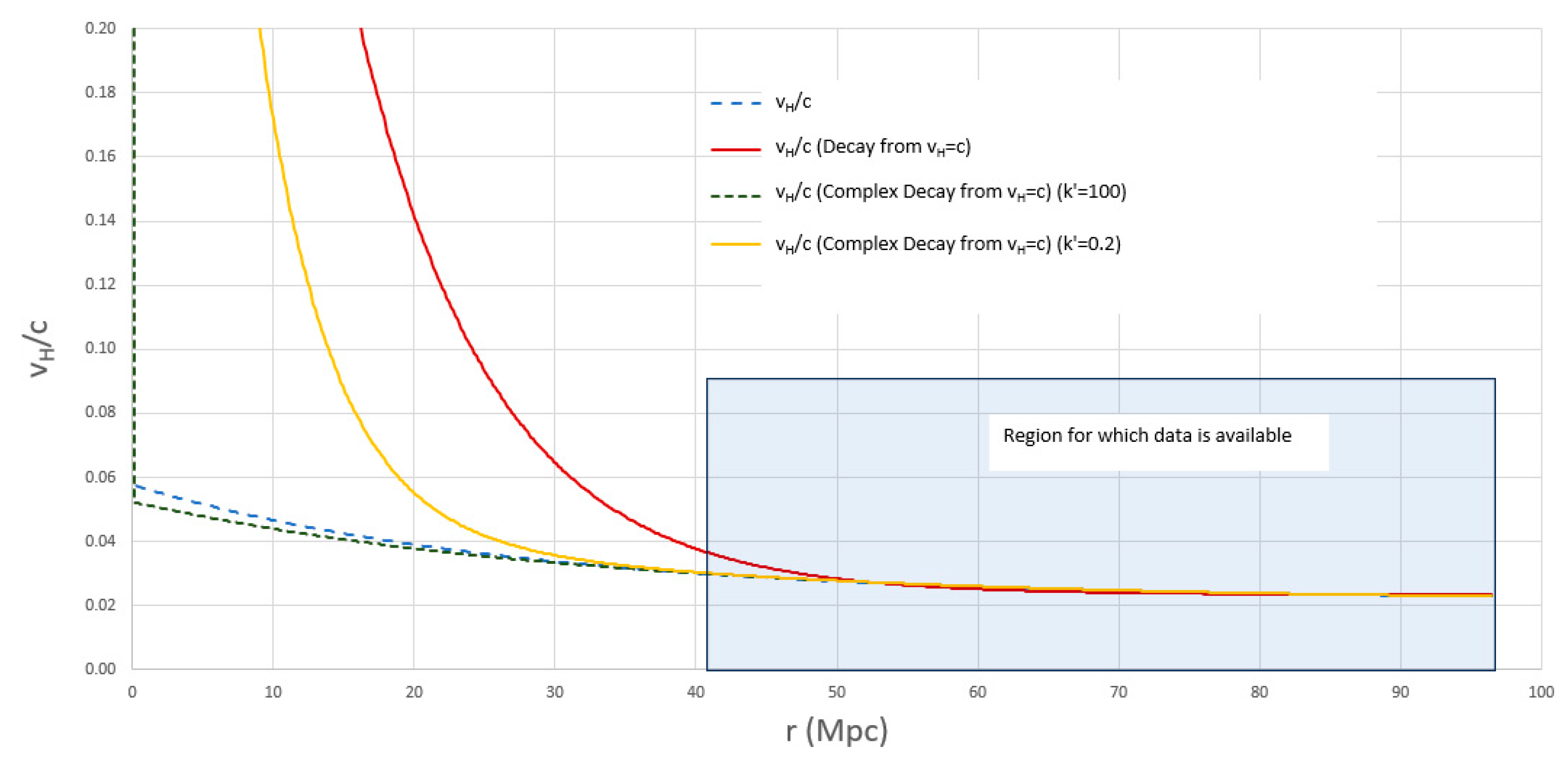
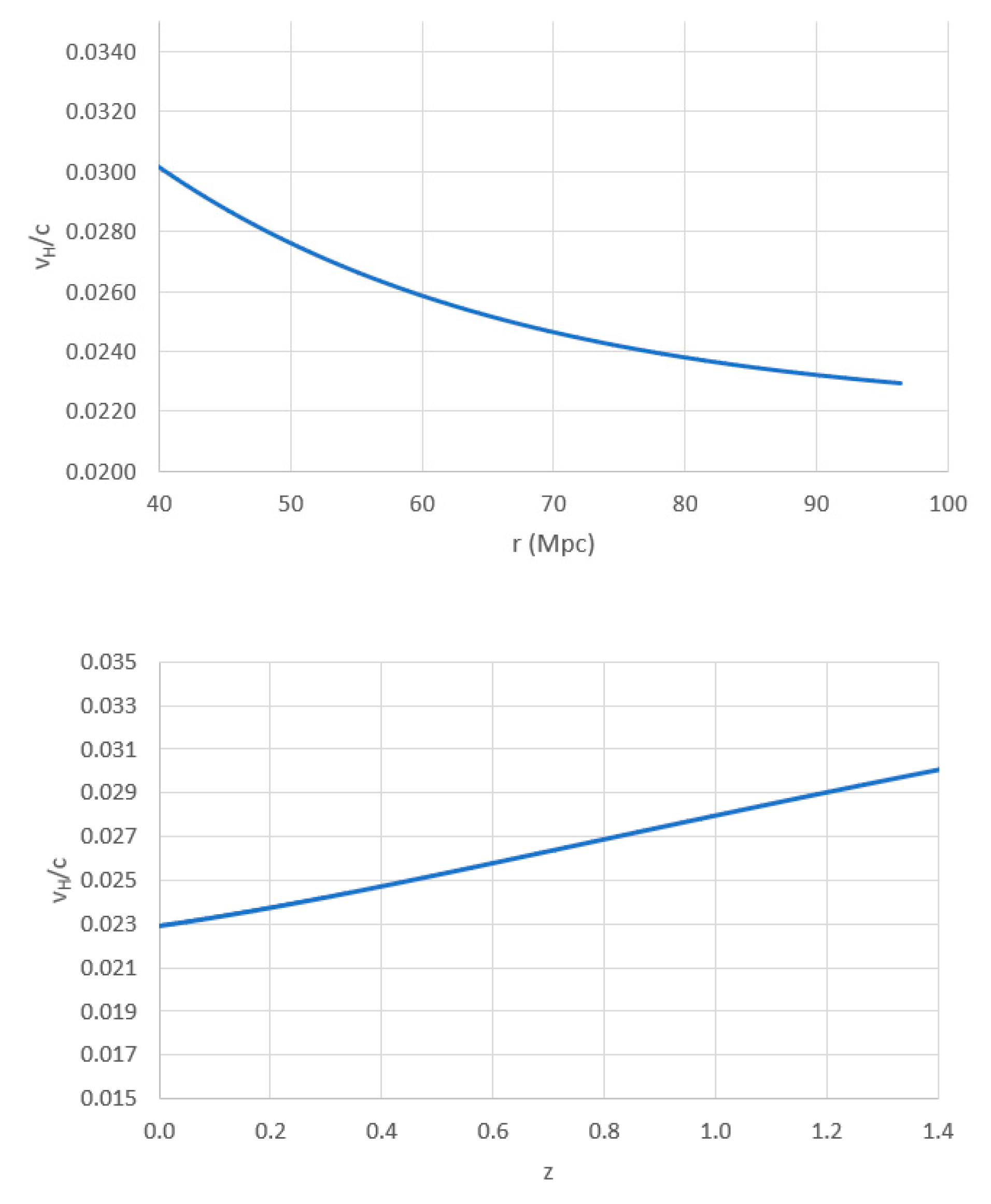
Although a constant velocity of expansion (as shown by the orange dashed line) can be seen to fit reasonably well for nearby objects, the best fit is obtained by allowing the velocity of expansion to vary with time. We fitted the speed of time using a simple exponential decay function of the expansion velocity from time zero, as we wanted a function that could allow the velocity to behave naturally, and we found this to correlate accurately in the region (for z<1.3 and r>45 Mpc) for which we had data available.
The expansion velocity versus the radius of the expansion sphere used in this model can be seen below over the range for which data are available:
Please be aware that the utilization of the exponential decay function in this context is not intended to represent an exact mathematical depiction of reality. Instead, it functions as an algorithm employed to ascertain the pattern of changes in the expansion speed within the specified region of interest. However, what is definitive from the results is that the average velocity over time (or the velocity of expansion of the universe) is slowing down.
To explain the results, it is surmised that the expansion had an initial dramatic increase, but then all “particles” in the universe moved and interacted to such an extent that they slowed in their expansion over billions of years to the current resultant average velocity and that we now exist in the tail of the expansion wave. From our discussion in the first paper, we deduced that the initial speed of time at r=0 must be the speed of light (explained later), which has decayed away from the current speed we observe today.
We therefore also fit the data restricting
from equation 8 to achieve this. The imposed restriction yields a satisfactory fit, particularly for the accessible data within the z<1.2 range. However, when dealing with high-z data, the basic exponential fit encounters challenges, hinting at its limitations as a representation of the decline in the expansion rate. In response to this, we have introduced an extra exponential term to accommodate two distinct decay rates: an initial swift decay succeeded by a less abrupt decline:
The restriction is applied. The different types of models of expansion speed discussed above can be seen in the figure below:
Figure 5.
Exponential decay curves showing various different possible fits.
Figure 5.
Exponential decay curves showing various different possible fits.
As mentioned previously, the use of an exponential decay is simply a tool for mirroring the observed data, but it does at least give us the suggestion of at least two decay processes - one of rapid expansion followed by a less rapid tail. This is consistent with the idea that the universe had a rapid cosmic inflationary period at its inception [
4]. We cannot determine from the data at hand whether rapid expansion happened close to
r=0 or was more spread out. The parameters obtained for our complex decay were as follows:
= 0.9476,
=0.0309,
C=0.0215 (expressed as fractions of
c, the speed of light),
r=96.411 Mpc,
k=0.0318. A value of
k’>0.18 needs to be used to achieve accurate results against the
r<50 Mpc data. The value used in
Figure 5 in yellow is for
k’=0.2, but there is no significance in this value other than to visually show the effect of two decay mechanisms.
k’=100 is shown for comparison which shows the extreme case where the initial expansion is extremely rapid. Again the 100 is just a arbitrary high number which has no actual significance.
The fit using our refined exponential decay with results in a current average expansion rate,
=6.87 ± 0.36 × 10
6 ms
-1, which results in a Hubble expansion rate constant of 71.3 ± 3.7 km/s/Mpc, in broad agreement with previous figures [
5,
6]. This is a similar
that we reported for the single decay from c model reported in our first paper; the high z fits do not really change the resultant
. They merely provides a more accurate fit at higher z and therefore can lead us to imply at least two types of decay were present. The extreme high
k’ case is more consistent with inflationary theory. This is believed to be required to achieve the roughly equal distribution in temperature of the cosmic microwave background that is seen no matter where you look in the universe [
7]. Consequently, we have used this fit throughout the rest of this paper and is the model presented in
Figure 2 and
Figure 3.
Previous theories fitted to the luminosity data using the Friedmann-Lemaître-Robertson-Walker (FLRW) cosmological models [
2,
3] suggested that the rate of expansion is increasing, contrary to our findings.
The realisation that time is a spatial dimension upon which we travel “in time” simplifies the mathematics significantly and provides a result that is perhaps more consistent with what was previously and intuitively expected prior to the FLRW conclusions. The Freidman equation can be derived using our theory, and although it is simplified, the time expansion model does not disagree with the basic principles of the FLRW model—this analysis was presented in our first paper. To summarise our model makes these assumptions to measure the speed of expansion:
The universe is expanding with velocity .
The expansion dimension is treated as a 4th space dimension.
All light reaching us has travelled at the speed of light.
The light we observe is distorted by or to account for the stretch in the universe causing a decrease in photon rate and photon energy.
If any of the above were untrue or distorted, then we should be able to see this as we try to model the observed data. From the above simple premises, we can determine the luminosity that should be observed for known candles at certain distances (or red shift z) from earth. We can then vary the velocity of expansion until a good fit is achieved versus observational data and from this determine its value as a function of the radius of our expansion sphere. The FLRW model analysis by contrast is far more complex and in seeking results starts off with various assumptions about the makeup of the universe. It relies heavily on dark energy to make it balance with the observations. We shall return to this shortly and try and reconcile the two theories but to do so, first we need to explain how mass and gravity come about within our theory.
3. Discussion
Mass out of time
If we accept for a moment that the universe has always been expanding since the time of the big bang and behaves according to Newtons laws of motion and would therefore continue to expand at constant speed unless something slowed it down, what is it that is causing the slowing effect? There are a few effects in play which reveal themselves in different ways.
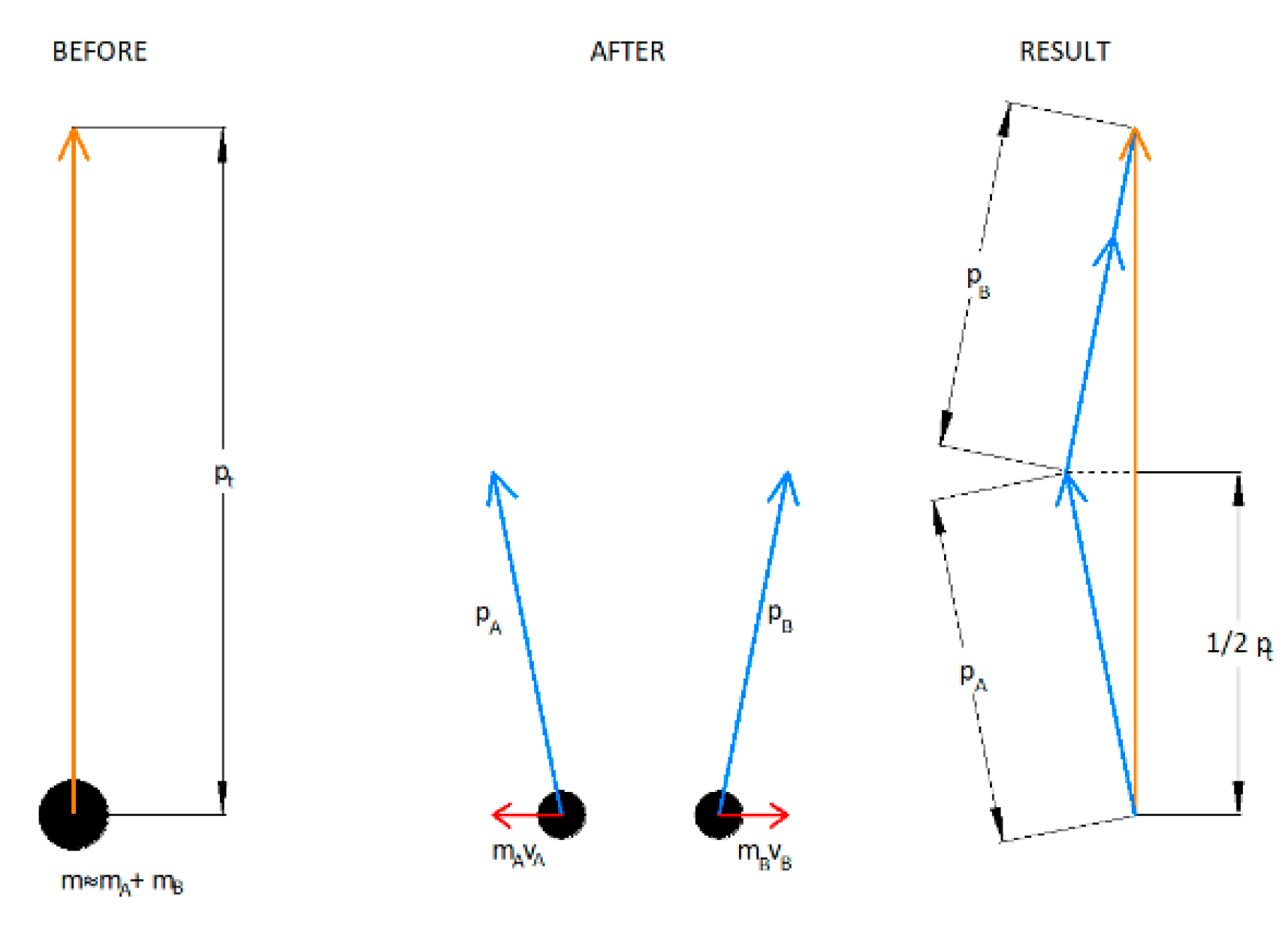
In our first paper, we showed that the interactions of “matter” can cause the general slowing of the expansion to conserve overall momentum by increasing the mass of objects once they deviate from their expansion trajectory. This means that the velocity of any particle remains unchanged at the speed of expansion, but the momentum is conserved by changing the apparent mass that objects possess in 3-dimensional space. This results in the effect on velocity shown in
Figure 6. The vertical direction signifies the direction of time expansion, the horizontal direction represents movement in the spatial dimension, and the blue line represents the resultant trajectory. The orange line indicates the movement of a particle system prior to the sideways movement (the movement may have been caused by, for example, objects splitting apart due to nuclear decay or even two astronauts pushing each other apart in space).
Consequently, using this mechanism, we deduce that sideways movements of particles away from the direction of expansion, caused by particles bumping into each other or decaying, creates a mechanism by which mass can apparently increase in our perceived 3-dimensional space. To conserve momentum following a deviation from the time trajectory, we showed that mass increases by
where
is the unperturbed speed of time,
is the velocity of a particle in normal space,
is the mass of the particle hidden in the time dimension and
is the resultant mass. Rearranging for
, we obtain:
This parameter is the sideways or deflection (from complete expansion) velocity, which can be used to calculate the energy gained or released from the expansion dimension by mass production. This energy of deflection is simply the momentum squared divided by twice the average mass before and after the reaction:
where and are the masses before and after the interaction/reaction, respectively.
In other words, we say that by time dilation, mass energy is brought into the 3D world from the expansion dimension. Conversely, you could say that the expansion of an object has slowed, adding to the overall decrease in expansion and increase in observed mass. By combining equations 12 and 13 and simplifying, we can express this expression in terms of
:
Now, considering a scenario where the initial mass is zero (equivalent to dealing with a delta in mass), then:
The above equation is obviously well known from special relativity, and we can conclude from this that is in fact the speed of light, c and that time expansion wave theory provides a good explanation of why this limit exists, and consequently why the phenomenon occurs. If anything were able to travel any faster, then it would break away from our timeline and escape the universe we know.
What this means is that everything is travelling at the speed of light in one of 4 dimensions. If it is travelling perpendicular to the time path, we see the object travelling at c, and it appears as light. If it is travelling with the timeline, we will not observe it. Any direction in between, and we observe the object to be travelling along our timeline, and it will appear to have mass.
From this, the expansion of the universe might be thought of like a series of fireworks forever going off. There is immediate expansion, which then slows before then exploding and exploding again. In our analogy, however, a new firework can be created from the coming together of previous debris to subsequently explode again and again. The overall initial trajectory continues away from the epicentre, and although, on the whole, it slows, every so often, there is a burst of expansion in different directions. If something is travelling at the speed of light, then it is contributing to the universe’s expansion, although not necessarily in the same direction as us. If it is travelling at a different trajectory to our expansion trajectory, then we will not view it as an expansion.
Light beams that reach us at Earth are expanding from their own origin and will effectively follow their own time path. From our point of view, they will reach us perpendicular to our own expansion along the surface of the expanding sphere. They will have an element of oscillation in the expansion dimension and perpendicular to this, as will be described in a later section and they will contribute to the overall isotropic expansion if taken as a whole, but from our point of view, they will arrive through 3D space.
The other implication that can be drawn from this thought process is that at the time of the big bang, the universe was composed entirely of radiation consequently travelling at the speed of light. So, the above is a mechanism for mass generation. Mass is created – or rather transformed out of - the expansion wave. In our theory, the presence of mass represents that the particle has some presence in all 3 dimensions of “real” space. A “massless” particle like the photon has presence in only 2, so has zero mass from our point of view.
Gravity
According to our theory, every distinct object in the universe has its own expansion trajectory within the expansion wave. As objects clump together and create a more massive single entity, by definition, they are not expanding away from each other as they coalesce. This movement toward each other will cause a time dilation (the universe expansion will be distorted), meaning that heavier objects will end up further back within the expansion wave. The more massive the object becomes because of this coalescence, the more dilated the space will be. In effect, a dimple will be created in the expansion sphere wave front, as shown in
Figure 1, slowing the time in this region of space, which will mean that any object passing will accelerate toward the clump. In addition, those objects that have accelerated toward the massive object will in turn add to the combined mass of the object. Where more clumping has taken place, these areas of the expansion wave will sit closer to time zero than areas that have not clumped together. Note that this effect is subtly different from the “mass out of time” effect of radiation being slowed from expansion and creating mass. Gravity is an accumulation effect whereby two or more items that have mass coalesce and consequently are forced to follow the same trajectory, which has an overall effect of slowing down the expansion in that area, creating a time dilation, and consequently creating an attractive force for any object with mass in the vicinity.
The above leads us to the profound conclusion that the expansion of the universe causes the phenomenon we call time. The theory of general relativity linked time and space. We have perhaps taken a further step saying that the time dimension is no different to any space dimension – it is a spatial dimension, but one on which we travel in time and can therefore only appreciate a small sliver of it. But, without expansion, we would not perceive time. This is why time is not actually a constant in the universe – it is different for everyone. The expansion sphere, as the title of the paper suggest, is a time expansion wave.
Returning to general relativity – Einstein’s theory suggested that the observed gravitational effect comes about due to a warping of spacetime. The warping of spacetime creates a curvature in spacetime which then means any object close to the warping will be attracted or rather accelerated towards its centre. Time expansion theory suggests that the warping is in the time expansion wave front on which we ride and is simply caused by a retardation of the expansion due to mass build up in that region of the wave front. It is therefore easy to understand in our theory why the effects of gravity are indistinguishable from acceleration. In our model we are talking about differences in the rate of expansion causing the distortion, so any object nearing the distortion will consequently experience a time dilation which will have the result that it will in effect accelerate towards it.
Black Holes
In general relativity, singularities, where spacetime curvature and density become infinitely large, exist at the heart of every black hole. Time expansion theory by contrast sees a black hole as a deep dimple on the blast wave front where matter has conglomerated to such a density that it appears to occupy a volume of spacetime that is out of sight. In physical terms, we know this to be where the matter is compacted into a region smaller than the object’s Schwarzschild radius. In other words, the dimple is so deep that light travelling across the blast wave front will disappear into the dimple and stay there – effectively entering a “time” zone that we would no longer have access to. But time expansion theory does not predict a singularity – it is just a dimple that we can’t see the bottom of. Information that has entered the black hole still exists, but it has travelled to a part of the time dimension that we cannot reach. If no matter ever enters the black hole again, then as the universe expands and the blast wave front stretches, the dimple will diminish in density as it is stretched out and the matter and information that disappeared within it would be able to radiate out again once it is stretched beyond its Schwarzschild radius. The idea of a blackhole radiating is not new although it has never been experimentally observed. It is an idea that came about to address a principle in quantum mechanics that information must be conserved. Steven Hawkings came up with an idea that virtual particles created at the event horizon could radiate if one half of the split pair fell into the black hole and the other escaped [
8]. The resolution to the information paradox, as provided by Hawking radiation, addresses the concerns about information loss associated with particles created near the event horizon. However, it does not extend a solution to the fate of particles that have already crossed the event horizon. Time expansion theory however allows for a mechanism by which the information is conserved.
Dark Matter
Although dark matter and dark energy are not needed to explain the luminosity data using our model – our model has no bias on the type of energy density in the universe - we believe they may still have a role to play. We believe dark matter and dark energy may be the matter (or energy) of the time expansion wave shown in the light grey bands of
Figure 1 immediately before and after the point where we are respectively in time. Spiral arms of galaxies have been observed spinning with greater velocity than they should at large distances from the galaxy centre if visible matter alone were present in the universe [
9]. Dark matter has been proposed as the answer to balance this observation. It is easy to believe that there may be matter behind us in the expansion wave that we cannot see or interact with unless we were a super massive object which has dipped the wavefront backwards to overlap this matter; the larger the object the more it will dip back in time on the blast wave front and interact with matter behind us on the time expansion wave. This would explain the observations but also why we are struggling to identify or observe dark matter.
Dark energy may well be matter of the universe ahead of us. The evidence for the existence of dark energy currently lies with the FLRW model and our model by contrast does not require a repulsive pressure speeding up expansion as this is not what we see. The only expansion effect we think we need in our model is the initial burst of energy that created the universe and continues to push us on from the big bang.
Dark Energy and FLRW model
The FLRW model of the universe in basic terms uses a total density parameter
Ωtotal which can be split up into constituents of matter and dark matter (combined as
ΩM), radiation (
Ωrad) and “dark energy” (
ΩΛ), such that
Ω= ΩM+ Ωrad+ ΩΛ= ρ/ ρcritical, where
ρ is density and
ρcritical is the density at which the universe is spatially flat. The current consensus with this model is that the universe is flat, i.e.,
Ωtotal=1 and that the radiation term can be excluded at least to model the later universe so that we need consider only matter and “dark energy”. The currently accepted best fit values using this model are where
ΩM=0.3,
ΩΛ=0.7. The various fits to this model can be seen in
Figure 7 alongside our current models.
As can be seen the
ΩM=1,
ΩΛ=0, matter dominated model, falls below the observations – i.e., predictions are that the objects should be brighter and closer (lower modulus) than they are. Mathematically
ΩM can be deemed a deceleration term,
ΩΛ an acceleration term. So, to balance against observation, more acceleration is required and
ΩM=0.3,
ΩΛ=0.7 is the best fit. The full Freidman equation can be seen below:
Where H is the time dependent Hubble constant, a is the scale factor of the universe relative to today, ρ is the density, G is the gravitational constant, and k is a constant and can be +1, 0 or -1. k defines the curvature of the cosmological model, with 0 signifying a flat universe. and is the cosmological constant. Einstein originally added the cosmological constant to allow the equation to predict a static universe, but when the universe was seen to be expanding, he realized it was no longer required. Ironically the term has been revived to do the opposite and provide a repulsive term which is believed to be associated with dark energy. We can derive the Freidman equation from our model, as we did in our first paper, but when we do this then we do not derive the cosmological constant. Also, if the universe is flat, then we are only left with the first term of equation 10. This would be consistent with a universe that expands indefinitely with the rate of expansion dictated by the distribution of energy and matter.
Figure 7.
Duplication of
Figure 4 with addition of Friedman fits for Cosmological models Ω
M=0.3, Ω
Λ=0.7 and Ω
M=1 for comparison.
Figure 7.
Duplication of
Figure 4 with addition of Friedman fits for Cosmological models Ω
M=0.3, Ω
Λ=0.7 and Ω
M=1 for comparison.
In FLRW theories, the assumption is that the initial impetus from the big bang has diminished and no longer influences the dynamics. Consequently, only the terms related to the density of matter and other contemporary energy types are considered. In a flat universe, the kinetic energy term vanishes, leaving only the density-dependent terms. The model used in time expansion theory assumes that the universe has always been expanding and works out the shape of the universe and the way light would arrive with us if the rate of expansion were constant based on the universe having a fourth expansion dimension and then from that derives how the expansion rate has varied.
From our model we can calculate
as a function of
r, the radius of the expansion sphere. Then ignoring the curvature (which FLRW theories assume is zero after inflation) and the cosmological constant from equation 10 for a moment we can use this to determine the density of the matter from the Friedman equation as a function of radius:
We can also work out the volume of the universe in 3D space - the circumference of our sphere would be the extent of 3D space in all directions. Multiplying the density and volume you can determine the mass contained within the universe as a function of radius. We also know that if every deflection from expansion in the universe leads to a time dilation and creation of mass, and if we assume for a moment this is the only retardation mechanism, then it follows that the mass of the universe,
We can then set the value today of in equation 17 from the value in equation 16 and see how the two compare over radii of the expansion sphere and use the difference to give us insight on how the two theories compare.
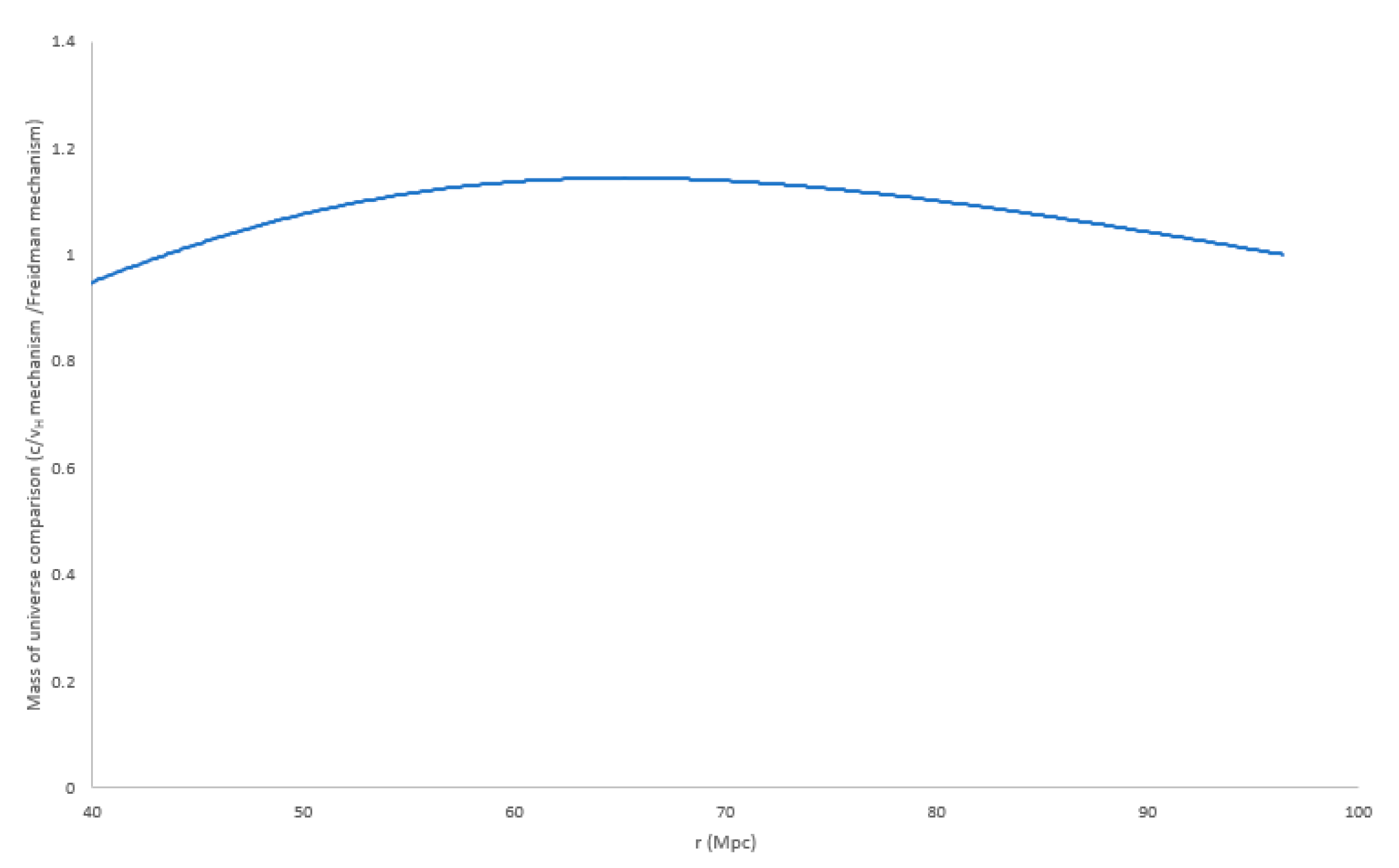
Results can be seen in
Figure 8 over the range for which luminosity data is available. The plot shows that the mass of the universe derived by the simple
mechanism predicts a larger mass compared to simple Freidman derivation in the radius of expansion sphere since r=45 Mpc with a peak at around 65 Mpc diminishing to today. What this tells us is that if we were to analyse the data using the Freidman equations then a repulsive expansion term would be required to match the data in the recent universe. In our model we are getting at the velocity of expansion more directly by allowing the expansion dimension to behave in the same way as the other 3 dimensions and when we do this, we see the velocity of expansion continue to slow.
So, with this simple exercise linking the two theories, we now have a reason for the inconsistency between conclusions. We reach our conclusions as our model directly extracts a speed of expansion in contrast to FLRW which relies on linking to the Friedman equation from the start.
However, the results of the above comparison are perhaps valid beyond providing an explanation for the discrepancy.
Figure 8.
Mass of universe comparison using simple divided by Freidman calculation derived from our results as described in the text.
Figure 8.
Mass of universe comparison using simple divided by Freidman calculation derived from our results as described in the text.
The implications of the variation of mass on our theory can be interpreted in a few ways. First off, the comparison may be over simplified, and the mass of the universe may not be directly related to the speed of expansion or there may be other factors to consider. Another conclusion might be that the universe is not completely flat after inflation. Lastly, gravity itself might vary over time. A flat universe would basically mean that the kinetic energy of expansion always balances the gravitational pull back. The large-scale structure of galaxies and the uniform CMB data do indicate that the post inflationary universe points towards a flat universe. It could just be that the universe is almost flat but the small percentage has this effect on the universe. Alternatively, in our model, as gravity comes about because of the slowing down of the universe from the speed of light, then it follows that the force of gravity experienced by all objects in the universe may indeed vary over time. There is no observational evidence of this. But the fact that the balance between density, size and speed of expansion of the universe (in our simple calculation at least) leads to a variation of mass of only between 5 and 10% in the last 10 billion years might prompt alternative theories to posit it as a genuine constant when it is in fact varying by this degree over billions of years. If gravity is fluctuating though, it might indicate that after the inflation period, the universe has existed at the critical density balanced by variation in the gravity constant which comes about due the balance of matter in the universe.
Age of the Universe
Carrying out a simple calculation of from our model results in an age of the universe of 13.7 billion years. This is consistent with other predictions. But note also that in our model varies over “time” – so the actual age of the universe must be < 13.7 billion years if we measured using today’s concept of a second. The actual age may be substantially smaller depending on the duration of the primary expansion. If the inflationary period were almost instantaneous to the extent that only the second term of our exponential decay dominated for most of time, then the actual age of the universe might be 10.6 billion years. But of course, if the universe’s perception of a second changes according to the speed we are expanding – then the 13.7 billion years would be the time expansion corrected value we observe.
Cosmic Microwave Background
Although our theory does not dispel the current thinking as to the origins of the CMB radiation it does allow for an alternate interpretation. It is worth noting that as the early universe was just radiation then for the photons that did not interact or slow down, it would have created a very bright all-encompassing light and because of the spherical nature of the universe the light would have rotated around the universe again and again. In the very early universe with the radius in time expanding at the speed of light then the circumference would have been increasing even faster and that it would be impossible for light to circumnavigate the universe. But as the expansion slowed there was a point where the light could rotate around the whole universe. This would mean that we would get to see the light of the early universe all around us as indeed we do through the CMB data. Further to this it might be possible to distinguish the reflections of earlier times with perhaps a pattern that might resemble the repeats as seen with the “spiral” expansion path seen in
Figure 2. If the light were slightly isotropic and had temperature fluctuations, then a pattern similar to the angular power spectrum seen in the CMB data might be observed. Further analysis of that data would need to be made to confirm this possibility.
To this point we have concentrated on the macroscopic universe to justify our theory. However, for it to be valid it must also be able to justify phenomenon at all scales.
Wave‒Particle Duality
The classical Young’s double-slit [
10] experiment carried out originally with sunlight proved that light behaves as a wave upon passing through a double slit, and an interference pattern emerges from the light coming out of the two slits. However, within his theory on the photoelectric effect, Einstein proved that a photon must have a physical or particle-like presence [
11]. In the original Young’s double-slit experiment, one would therefore believe that this interference pattern occurs because photons interfere with other photons. To investigate this phenomenon, more recently, a double-slit experiment was carried out in which a single photon passed through the slits at a time [
12]. However, the interference pattern is still observed. To date, despite being a well-established and experimentally verified aspect of quantum mechanics, the philosophical and interpretational aspects of this duality, along with the broader issues of quantum mechanics, continue to be the subject of debate and discussion in the physics community. We believe, however, that time expansion theory holds a reasonably neat and logical explanation.
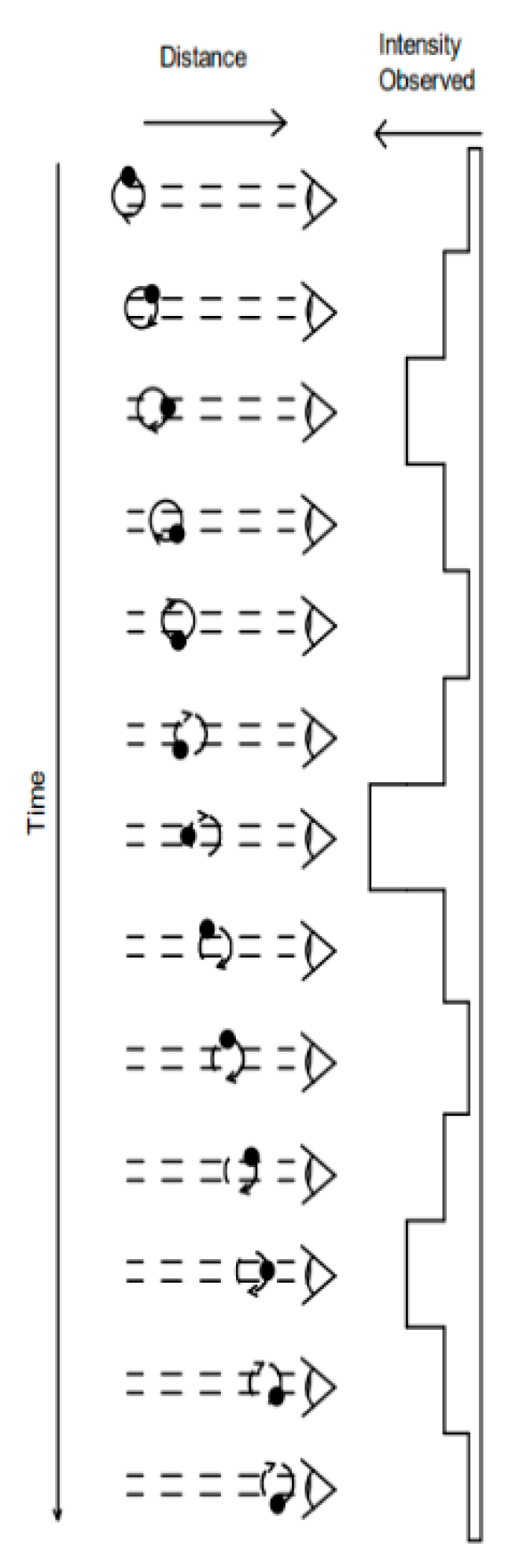
To reiterate, in our theory, the time dimension is a spatial dimension that is no different from any other space dimension except that it reveals itself only through the passage of time, as we are propelled along it. The world around us must have a window of finite size with which it can view the time dimension. This finite size width then effectively allows for a certain degree of freedom regarding interactions between particles. For macroscopic objects much larger than this window, we do not notice any variation in the position of the object within the time window when the interaction occurs. However, if an object is smaller than the window, then this degree of freedom becomes important. We believe that a photon passing along the surface of the expansion sphere resonates or rotates within the time expansion dimension much like a water molecule would if it were caught in a water wave. In other words, photons or subatomic particles can travel back and forward ever so slightly in time from our point of view; therefore, we believe that they can be in multiple places at once and exhibit wave-like behaviour.
If the photon is indeed a particle or at least a packet of energy, it is largely hidden in the temporal dimension and phases in and out of intensity as its presence or overlap with the observer’s time window comes into focus.
Figure 9 represents how this effect may occur. In our theory, the photon is rotating in time which has the effect that it is present over a range of times, blurring its existence at any one point and allowing it to interfere with itself as in the single photon slit experiment. Therefore, prior to interaction, the photon is mostly hidden in the temporal dimension. Only when a photon encounters something wholly in 3D space, as revealed by the photoelectric effect, is the photon oscillation in time halted with the energy of the oscillation being absorbed by the object it interacts with.
The double-slit experiment was further enhanced so that it could be determined which slit the photon went through. When this occurs, the interference pattern disappears. It appears as though the photon, upon being observed, promptly acknowledges its observation, aligns itself, and exhibits characteristics more reminiscent of a particle. This effect has no current explanation beyond being a quantum effect. However, time expansion wave theory allows for this outcome. Basically, the “observation” point locks the photon into the current time zone in much the same way as with the photoelectric effect.
Since our first paper, an interesting experiment has been carried out allowing for the double-slit experiment to be carried out in time rather than space by using a film of iridium tin oxide to open and close the time slot. The results of this experiment showed that the beam seems to interfere across time with the beam from earlier and later times [
13]. Again, this thus far has no explanation and seems counterintuitive until now. In contrast, if we think of oscillating time expansion theory, this result provides strong evidence and support that our theory is correct, as if the light is rotating backwards and forwards in time, as we believe, then it will of course be able to interfere across time.
Therefore, we have described through simple logic a mechanism that explains why a photon can behave as both a wave as it phases in and out of existence by rotating in time and as a particle; if it encounters something, it will then be locked into that time path and add mass to the object it interacts with.
Electron Spin
The above effect will continue for subatomic particles that have mass in the 3D world. Support for this idea is that subatomic particles exhibit wave-like behaviour with electrons exhibiting interference patterns when passed through a slit [
14]. If the electron is also able to oscillate within the time spatial dimension, then it will oscillate and have wave-like properties similar to those of a photon. Again, our theory supports this. The wave‒particle duality observed basically occurs where particles slip in and out of the 4th temporal dimension. A photon is an extreme example restrained to the temporal dimension and 2 other spatial dimensions, but other subatomic particles can still resonate within the narrow time window because of their size relative to the window. The size of the window itself being finite may lead to quantization of the energy stored in the time dimension but the simple step of opening up a spin in time opens up explanations for other quantum effects.
Many texts often quote that the spin associated with electrons is a quantum property. This leads to many important quantum effects, such as Pauli’s exclusion principle—no two electrons occupy the exact same state, which leads to all the chemistry we see around us. However, for the electron, it is at least believed that the quantum spin is different from the actual spin. It has all the hall marks of spin, appears to possess angular momentum and yet is not spin, as there is nothing that can spin. An electron, a charged particle, has a magnetic field that it would indeed have if it were allowed to spin. Previously, this has been described as a basic quantum mechanical property of all fundamental particles without, in our opinion, satisfactory explanation. However, our theory allows for actual spin—a spin within the time dimension—to exist. This simple concept has far-reaching consequences. Having a fourth spatial dimension available means that there is an extra degree of freedom. Therefore, an electron (or other particle) that rotates in time will also move in 3 other dimensions. It may rotate clockwise or anti-clockwise relative to the expansion direction. If we narrow it to spin in time and one other space dimension, we can either spin forward and backwards in time or spin perpendicular to the direction of expansion. This artefact of spin — that at any one specific point in time, the electron must be travelling one way or another and that this spin direction might cause a slightly different real-world effect means it can potentially be defined by a quantum number. The Stern–Gerlach experiment showed that the electron only possesses two possible spin states [
15]. If we allow for a spin in the time dimension, then this spin can be categorised as going clockwise or anti-clockwise to the direction of travel (expansion in time). We believe that the spin, as displayed in the Stern–Gerlach experiment, is the result of this perpendicular spin. Spin forwards and backwards, we believe leads to the charge of the electron, as explained below.
First Light and the Creation of Charged Matter
As described above the evidence suggests that at the point of the big bang, everything was travelling at the speed of light and therefore must have existed only as radiation, i.e., photons – so nothing else existed. Therefore, the photon must be the building block of all the other particles or be able to energise something to create all the other particles. The photon itself is only ever present in our world in 2D – choosing to hide its third side in the time dimension. However, by slowing down and moving into the 3 physical space dimensions, it forms every other particle type with all their properties—or it at least creates the “fundamental” particles that go on to create the others.
It seems that the speed of light is limited by the fact that as soon as a dimension is achieved, the particle collapses entirely into only 2 dimensions and time. We see light travelling toward us; then, at right angles, we will see the electric field and magnetic field. These two “fields” are the remnants left over to the 3D world revealing the presence of something that is “hiding” in the time dimension. The electron also possesses these fields, but as it has mass, it is present in all 4 dimensions at the same time, with only some of its mass blurring into the time dimension.
It has been shown at least indirectly that an electron (and positron as a pair) can be created by crashing together two high-energy photons [
16]. This process, or similar processes, must have therefore occurred in the early universe. We know that an electron and a positron have a characteristic called a charge that the photon does not have. We believe that when they create, they create pairs of opposites so that the charge effectively cancels. What this must mean is that at the point of creation, the split causes an asymmetry of the resultant particles. What could cause this asymmetry?
If we consider this in terms of time expansion theory, then at the point of collision, the photon is either on the forwards part of its spin or on the backwards part of its spin. We propose that this phenomenon causes asymmetry in the particles that are produced. As we believe that electrons and positrons are always created in pairs, then the intimate part of the collision may cause the two particles to leave the interaction zone in an opposing time direction. However, if this assumption is correct, then once separated, this property is frozen within the newly created particles.
Therefore, if the charge is simply concerning whether a particle spins in a way that means, on average, it is dipping back in time from its mass baseline or is spinning forwards, a neutral particle would be one that has stabilised such that the forward and back motion is cancelled.
If the above is true and we assume that the electron reaches back in time and the positron forward, then this might explain why the universe in which we exist seems to be electron biased. By reaching back in time, toward the heavier mass bass line, the electron will be forever tied or drawn toward the mass in the expansion wave that we inhabit. In contrast, the positron will be attracted toward a part of the expansion wave just out of reach. We now live in a different place than the early universe. When the first electrons were created, there would have been no mass to be attracted towards and most positrons would escape only momentarily from their electrons to end up combining with a different electron. However, if the positrons from a zone that is historically and therefore gravitationally behind the current time zone come together, then on the subatomic level, a new electron may encounter the “positron” from a heavier gravitational zone and consequently see a heavier particle. This process is not likely to be happening in today’s universe, but we could conceive of such a mixing in the chaotic early universe.
In our model, a negative charge can therefore be described as a particle that is able to rotate backwards in time from its centre of mass, and a positive charge is one that can reach forward. As the two types of particles obtain this ability via spin in the time dimension moving backwards and forward, they overlap and “see” the other particle before they come into physical contact. If the resultant combination is energy efficient, i.e., results in a loss of mass and more expansion, then the overlap would be favourable, and there would be an effective gradient of attraction. If the opposite is true, then they repel each other. Therefore, the spin in the dimension of time gives particles the ability to look ahead and see what they might become if they combine as they approach. It would therefore explain how attraction or repulsion can happen across empty space forming a field effect in normal 3D space. A positive particle spinning up and negative particle spinning down would result in a neutral particle that spins equally in both directions or may not spin at all. The result of such a combination would likely be beneficial overall from a symmetry point of view—the positive ion would perhaps be drawn away slightly from the time baseline, and the negative electron would be drawn down but overall—because of the mobility of the electron and its relative mass, the overall effect results in a lighter overall product. Basically, the universe appears to be forever trying to repair the expansion and return to a higher expansion rate—i.e., a lighter, more expanding state is favourable. The likely reason for favouring returning to expansion is simple entropy. Effectively, the universe would prefer to be much more spread out than clumped together. A hydrogen atom is lighter than the sum of a proton and electron combined because some of the mass is due to the energy of the electrostatic attraction of the two particles, and upon interaction, this energy is allowed to return to the time dimension.
The blurring of time that allows the electron to look forward and backwards basically explains why it and other subatomic particles can be described only by probability wave functions and not by classical mechanics. The force of attraction or repulsion must therefore be closely linked to the energy of the oscillation in time produced by this resonant effect.
Resonance in Time
The theory results in one quantified result that we can compare to observations, and that is the current average expansion speed of the time dimension. The best value for this speed, , is 6.87 ± 0.36 × 106 ms-1, as discussed earlier. In a universe that is created from such simple building blocks then it seems likely this rate is responsible for other “constants” in the universe.
Water molecules confined within a wave exhibit a tendency to rotate at a velocity consistent with the traveling speed of the wave. Therefore, if we are all caught up on a wave of time travelling at
, the particles caught up within the wave will perhaps try and spin at this velocity. If this were the case, the time to repeat a spin cycle in time would be
, where
is the radius of the “particle” orbit within the time wave and
is the current velocity of time. In the 3D world from which we observe this, we cannot perceive the width of the time dimension, so all we see within 2 of the 3 dimensions of “real” space would be a repeating phase of
. That is, the wavelength at which we observe “radiation” should be
. The frequency of repeat would therefore be:
Therefore, if a particle spins in time, it will have an apparent spin speed in the 3D world of 2.19 × 106 ms-1. This velocity is approximately 1/137 times the speed of light. This is the value of the fine structure constant, which is known to be responsible for quantifying the strength of electromagnetic interaction. This finding ties together with our qualitative argument that this rotation in time is what causes the electromagnetic effect.
The velocity is also the most likely velocity (or Bohr model velocity) at which the electron travels in the first orbit of the hydrogen atom. Therefore, perhaps the speed of time effectively creates a resonant speed of rotation of the electron that matches the speed we see.
The oscillation in time gives us the energy stored in the time dimension as spin, which is then available to be brought into the 3D world we know upon interaction. The presence of electrons in the real world might be the result of this resonance with respect to the time dimension. The ideal lining up of the time dimension with an idealised spin generated from the passing of time would lead to the perfect Bohr model orbital. This would then answer one of the mysteries of the world about why the fine structure constant has its value. It would also indicate that as the speed of time slows – then the fine structure constant would decrease accordingly indicating it was different in the past.
Once you have the fine structure constant, then the value of Planck’s constant, and electric charge are consequently set. If the energised particle takes on spin speed of
, the current velocity of time and we assume all the energy available is twice the kinetic energy (potential energy is negligible or mirrored in the kinetic energy originating from the wave)
If we take the particle to be an electron and radius to be the Bohr radius then we find that 6.624 x 10-34 which is the Planck Constant. Other particles such as the photon may be affected and be allowed to spin at different rates, but it seems from above that they are somehow tied to the energy above.
We now have compelling evidence that our theory can accurately account for gravity and the electromagnetic force —the oscillation in time of charged particles will create an attractive or repulsive force which will interact with other charged particles with a force related to the fine structure constant which in turn appears to be related to the velocity of time. Once combined then the overlap of this oscillation releases a favourable amount of energy back to the expansion dimension. We will now for completeness touch on the strong and weak nuclear interactions.
Strong interaction
The strong interaction is responsible for producing nucleons, the resultant object being heavier than the proposed quantum particles, quarks, which are believed to be the original building blocks. Therefore, the energy mechanism for producing this mass is basically as described in the “mass out of time”. In crude terms, it is the trapping of energy as mass. The electromagnetic effect described above by contrast releases some of this mass back to the temporal dimension. The residual strong interaction (or strong nuclear force), which holds neutrons and protons together again, generally releases energy back to the temporal dimension. The mass that is created out of “nothing” may have many stepping stones to get there—it might be that quarks come about because of some other resonance in time similar to how electrons are created or some quirk about the way they are initially produced. It is generally believed that protons, at least, were created in the early universe and are no longer being produced anywhere. Therefore, initial extreme collisions/interactions in the early universe may have resulted in these protons being created and the mass being trapped. The strong nuclear force – often considered to be one of the same as the strong force – still occurs today as in star formation to bind nucleons together, producing a less stable product. In a sense, this comes about and is favourable, as it enables a route to release some of the “strong interaction” as energy.
Another possibility for proton production is touched upon in the section on the creation of charged matter—it might be that this lockdown in mass came about in the early universe due to an overlap or the universe we now know with an older gravitational zone. Positrons from the older zone would appear heavier and perhaps become protons in our universe. This effect may have happened only in the early universe when there may have been a larger blurring of time relative to the size of the universe. This pairing with positrons from an older time slice may have caused the asymmetry which led to these charged particles remaining in existence today and once bonded they became trapped and generated the layer of matter we now exist in today. It is interesting that the ratio of with being mass of the proton and being the mass of the electron. This might indicate some relationship between the two particles at an earlier time of the universe, but this conclusion is tenuous at best.
Weak Nuclear Interaction
If a proton and electron come together, then they may end up forming a hydrogen atom, which will be held together by electrostatic forces with the electron reaching back in time and the proton reaching forward in time. However, in extreme pressure circumstances such as within stars, electrons and protons can combine more intimately and create neutrons by electron capture. This neutron is effectively held together by the overlap between the electrostatic forces of a proton and an electron in close proximity. This overlap appears to have some stability but will decay as the neutron is heavier than the proton plus electron. If it happens to collide with a proton before it decays and form a heavier atom, then this may stabilise by releasing energy.
However, the fact that neutrons stay together for a period of time must mean that close overlap has some inherent stability, which means that they stick together for a period of time. The overlap of the electrical part of the proton and electron over the expansion dimension might be largely favourable even when overlapping closely, but certain orientations or distributions of the opposite charge in close proximity seem to not be favourable. The neutron would experience these unfavourable distributions only some of the time, and this would consequently lead to decay after a period as is seen. This decay is called beta decay and is normally described as coming about due to the weak nuclear force.
Quantum Entanglement
In quantum mechanical terms, if two particles exist in a single wave function, they are said to be quantum entangled. Basically, if you know the quantum property of one entangled partner, you should be able to infer the property of the other. There were two schools of thought, at least theoretically, on how the properties are revealed by the two entangled partners. One idea was that the partners decide at the point of splitting which property they have—this is the classical view called hidden variables put forward initially by Einstein. The other idea, as defined by quantum mechanics, is much harder to understand because the properties are decided only at the point where they were measured. Faster than light travel would need to occur to pass the message from one entangled entity to the other such that it should behave in a certain way. Bell [
17] derived what is now known as Bell’s inequality, establishing a theoretical framework for testing the predictions of quantum mechanics in comparison to classical theories, particularly in the context of quantum entanglement. Bell’s work laid the foundation for the initial experimental tests of quantum entanglement, conducted by Aspect [
18] on photons. These experiments ultimately confirmed the results predicted by quantum mechanics.
This result seems counterintuitive unless, of course, you consider that the wave form of the entangled partners resonates in the time spatial dimension. This basically gives it the opportunity to time travel and pass information in a way that seems to move faster than light. However, the complete quantum theory posits that entangled partners could be located on opposite sides of the universe and still convey information at the moment of measurement. Yet in our theory, if the waveform has only a slight oscillation in time, the opportunity for communication will be extended but not indefinitely. Therefore, what we end up with in our oscillating time expansion wave theory effectively is a delay or blurring in the separation of entangled partners which leads to the opportunity for information to be passed after the perceived point of splitting.
Although later experiments increased the distance between source and decision points [
19] they were only attempting to overcome the locality loophole thus ensuring only that they beat the speed of light. Thus, if the entangled partners are resonating in time as we believe, i.e., can look ahead, then this does not preclude the decision point being made at the point of separation but its realisation being blurred by this time travelling property. If the entangled partners were separated by a significant amount of time beyond the blurring window, then the decision would indeed be locked if our theory is correct. Therefore, it is our belief that the answer might lie somewhere between the two extremes of quantum mechanics and hidden variables. Hopefully, this can be confirmed experimentally in the future.
In a sense our theory is giving a reason for the quantum effect observed but also stating that there must be a limit as a particle’s ability to look ahead cannot be infinite.
The Nature of Matter
As a final thought, we would like to return to our analogy about water molecules caught in a water wave, which would create a specific spin of time and, again, question exactly what is spinning. We think that a photon is an energy packet that might have real substance but be hidden in the temporal dimension, and it is this that spins. However, if this energising of the particles is anything like the water molecules in our analogy, then the molecules stay put, and it is just the overall wave that moves. The analogy is likely lacking, but there is the possibility that it is similar and that what the time wave is doing is energising the field or whatever exists in the universe before our wave front reaches it. So, it is possible that the expansion wave is merely energising a field or fields that exists across the universe as it passes to generate the mass we see today. This would allow our theory to sit alongside or provide a physical representation to quantum field theory.