1. Introduction
Cerebral cavernous malformations (CCM), also called cavernous angiomas, or cerebral cavernomas are vascular alterations consisting of clusters of abnormal blood vessels in the form of thin-walled caverns with no intervening stroma.
This type of malformations are originated between veins and capillaries, with a lobulated appearance which, at histological level, result in hypertrophied channels of endothelial cells (ECs). However, these lesions neither invade other tissues, nor involve nervous cells. These abnormal structures have been described mainly in components of the central nervous system (CNS) such as brain, retina, and spinal cord and sometimes, in other locations, such as ocular orbit, skin and liver [
1].
There are two forms of cavernomatosis: sporadic and familial. Sporadic cavernomas is not considered a rare disease since it affects 1 in 200-300 people [
2]. It is not hereditary and appears in isolation. The familial form (FCCM), which accounts for about 20% of total cavernoma cases has a genetic basis and three genes ara affected:
CCM1,
CCM2 and
CCM3. FCCM shows an autosomal dominant inheritance with variable penetrance, and an estimated prevalence of 1 in 5,000-10,000 cases [
2], becoming a rare disease.
Clinical manifestations are variable. While some of the patients are asymptomatic, in other cases, cavernomas are detected by MRI in medical screenings following seizures, migraines, epileptic episodes, or other neurological problems [
3,
4]. The most severe cases occur due to bleeding from cavernomatous lesions, which interfere with the functions of the CNS. Common symptoms are epileptic seizures and intracerebral hemorrhages, which in some cases derive in brain infarctions, and neurological deficits [
5].
The molecular mechanisms causing the malformations are not yet completely elucidated. Cells from FCCM patients are heterozygous for the inherited mutation, but when a second mutation occurs in the normal allele, with loss of heterozygosity, the cavernoma lesions arise. Therefore, at the lesion site, mutations affect both alleles resulting a lack, either physical or functional of the protein encoded by the mutated gene.
Up to now, FCCM 1 bear mutations in
CCM1/Krit (7q21-22) and accounts for 53- 65% of all cases;
CCM2/malcavernin (7p13) accounts for 20% and
CCM3/PDCD10 (3q26.1) for the 10-16% [
6].
The proteins encoded by these genes (CCM1-3) form the CCM Signaling Complex (CSC), which interacts with different processes such as angiogenesis, endothelial cell-cell junctions, (which seem to be the origin of the disease malformations) and different signaling pathways. Furthermore, CSC also interacts with proteins involved in the regulation of endothelial structure such as Rap1 and HEG1 [
7]. It also associates with proteins such as VE-Cadherin and β-catenin, interfering with intercellular junctions [
8].
The CSC complex actively participates in the RhoA-ROCK pathway. This pathway is involved in the anchoring between cells and with the extracellular matrix. It has been reported that CCM malformations are characterized by altered and unstable cell-cell junctions [
9].
When the RhoA-ROCK pathway is active, ROCK phosphorylates MLC ("myosin light chain") and triggers a cascade of events, including the formation of stress fibers composed of actin filaments involving intercellular junctions. This process occurs in cell migration, angiogenesis, and cell proliferation [
10]. Several studies support the idea that the CSC complex is directly involved in this process. Specifically, CCM1 associates with proteins that form cell-cell junctions such as β-catenin, which ultimately prevents the increase in ROCK activity. CCM2 inhibits this pathway as it favors RhoA degradation, and CCM3 recruits proteins involved in cell migration and adhesion, such as STK25 or Cdc42. In in vitro assays on altered CCM proteins from endothelial cells, incubation with ROCK inhibitory drugs, the stress fibers decreased and the wild-type phenotype has been recovered [
9].
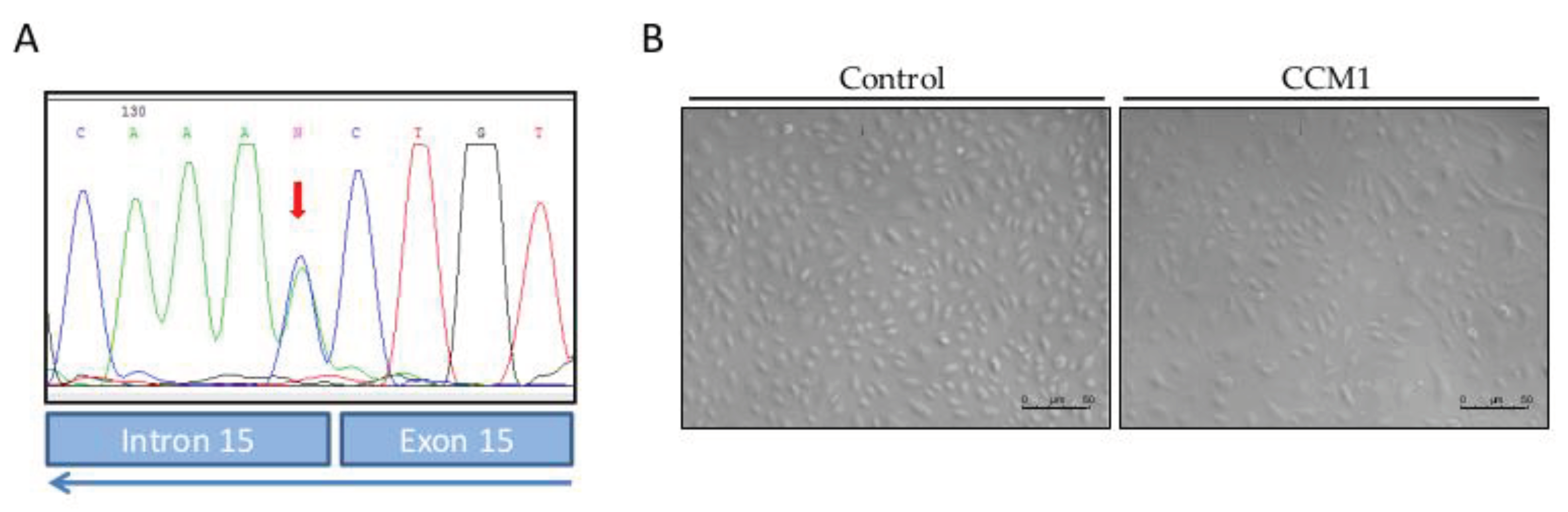
The present work constitutes a first study of molecular and functional characterization of ECs derived from endothelial peripheral blood precursors (EPCs) from a patient with familial cavernomatosis, in
CCM1/Krit harboring the mutationc.1563+1G>T; p.521sp (
Figure 1).
The starting hypothesis is that familial cavernomatosis affects the expression pattern and the functionality of ECs, even in heterozgyous condition.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics
The entire procedure was approved by the ethical committee of the National Agency of Research in Spain (CSIC), with the reference 075/2017. Previous to the extraction the patient (previously diagnosed with CCM1, mutation (CCM1/Krit1 gene: c. 1563 + 1G>T p.521 sp) signed an informed consent.
2.2. Human Samples: Blood Outgrowth Endothelial Cells Isolation and Cultivation
Blood outgrowth endothelial cells (BOECs) were grown from 50 ml peripheral blood, culturing buffy coat mononuclear cells on collagen I-coated culture plates using EBM/EGM-2 culture medium (Promocell, Heidelberg, Germany), as described [
11]. Briefly, cells from mononuclear layers were pelleted and resuspended in 5 ml of EBM/EGM-2 medium. Cells were centrifuged and the pellet washed twice in culture medium. Then, cells were resuspended in 5 ml of culture medium and plated on collagen I coated P-6 wells plate. Cells were incubated in 5% CO
2 at 37 °C and humidity. Medium was replaced daily for the first week and thereafter, every two days. BOECs were established as pure endothelial cultures, being the only surviving cell type covering the wells after 30–45 days of growth. For characterization and functional studies, BOECs from 2
nd to 6
th passage were used. From now on we will refer to them as CCM1-BOECs.
At the same time, BOECs from a healthy donor were used as control for comparison, using the same range of passages as for CCM1- BOECs. We will name these as C-BOECs.
Bright field and fluorescence microscopy images from the same samples were taken using a Zeiss Axiovert 135 microscope (Germany). FIJI-Image J software tool (NIH, Bethesda, MD, USA) was used to process and quantify the fluorescence intensities.
2.3. RNA Extraction, Reverse Transcription and Quantitative PCR
The pellet corresponding to around 3x105 cells was subjected to RNA extraction using the NucleoSpin RNA purification kit (Macherey-Nagel GmbH&Co, Düren, Germany), following the manufacturer protocol. Around 1 μg of RNA was retrotranscribed using the Applied Biosystems kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, MA, USA).
Quantitative PCR was performed by FastStart Essential DNA Green Master (Roche, Basel, Switzerland) to amplify the following genes using the primers shown on
Table 1. As housekeeping genes, 18S and
-actin were used. Samples were run in triplicate. Experiments were repeated at least three times.
2.4. Proliferation Assay
Proliferation of the C and CCM1 BOECS was measured following the “Luminescent Cell Viability Assay” (Promega, Madison, WI, USA) instructions. This is a homogeneous quantitative method to determine the number of viable cells in culture based on quantitation of the ATP presence, which indicates metabolically active cells. Briefly, 5,000 cells per well were seeded by quadruplicates in a collagen-coated P-96 plate. Cell Titer-Glo reagent (Lysis buffer, Ultra-Glo Recombinant Luciferase, Luciferine, and Mg2+) was added to wells to a final proportion of 1:1, and gently mixed for 30 min at room temperature (RT). Next, luminescence was measured in three independent measurements using a Glomax Multidetection System (Promega).
2.5. Western Blot
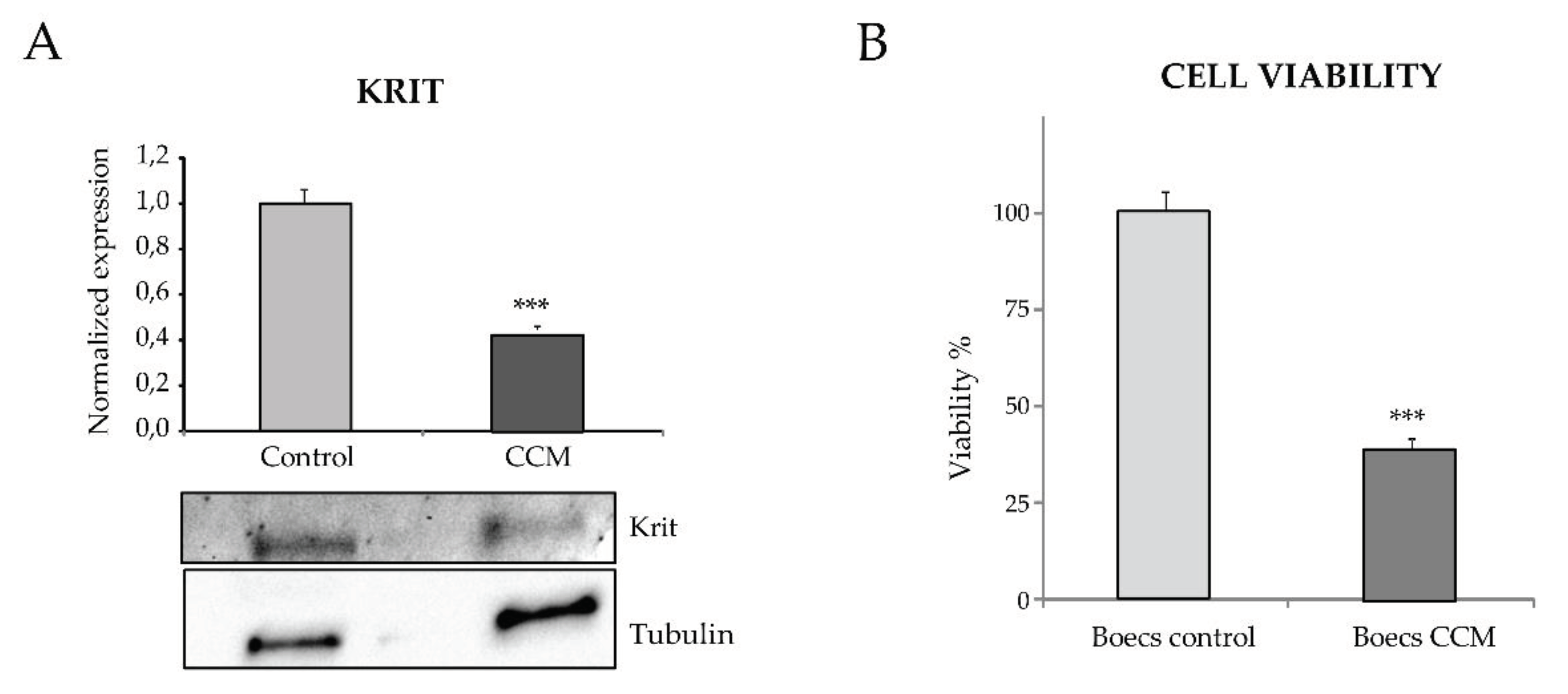
For protein extraction, BOECs either C or CCM1 from 3 confluent p6 wells were lysed on ice for 30 min in TNE buffer (50 mM Tris, 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA, and 0.5% Triton X100) supplemented with wide-range protease inhibitors (Roche) and lactacystin (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA), a specific proteasome inhibitor. Lysates were centrifuged at 14,000×g for 5 min. Similar amounts of protein from cleared cell lysates were boiled in SDS sample buffer and analyzed by 4–20% SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions (BioRad, Hercules, CA, USA). Proteins from gels were electro-transferred to nitrocellulose membranes (Amersham, Little Chalfont, UK) followed by immunodetection with a rabbit monoclonal anti-Krit1 (Santa Cruz Biotechnology), and anti-tubulin (Sigma-Aldrich). Following primary antibody incubation overnight at 4 °C, samples were washed and incubated with the corresponding horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibodies from Dako (Glostrup, Denmark) at RT for 1 h. All antibodies were used at the dilution recommended by the manufacturer. Membranes were developed by chemiluminescence (SuperSignal West Pico Chemiluminescent Substrate, Thermo Scientific).
2.6. Immunofluorescent Microscopy
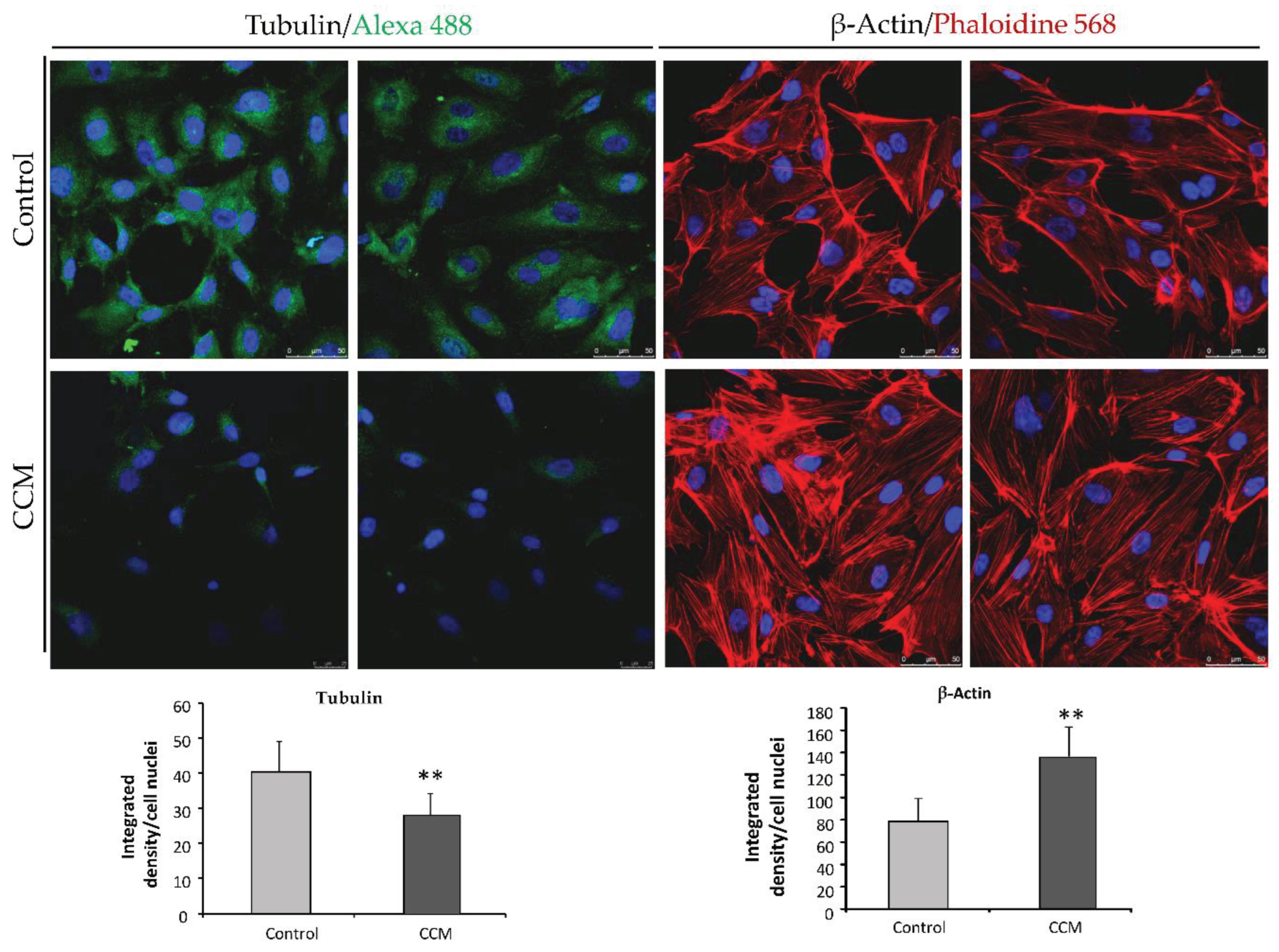
Immunofluorescence analyses were performed to visualize cytoskeleton in Cand CCM1 BOECs. To this purpose a total of 50,000 cells were seeded on collagen-coated sterile coverslips (VWR international, Radnor, PA, USA) placed at the bottom of a 24-well plate. On the next day, cells were previously washed with PBS. Then, for staining actin filaments, cells were fixed, stained, and permeabilized in a single step by addition of 5 units/ml Alexa-546 phalloidin (Molecular Probes, Eugene, OR, USA), 100 μg/ml L-α-lysophosphatidylcholine, and 3.5% formaldehyde in cold PBS. Coverslips were mounted with Prolong+DAPI mounting media (Molecular Probes). Fluorescence images were taken using a confocal SP5 (DMI6000 CS Leica Microsystems, Wetzlar, Germany).
For tubulin/VE-cadherin staining, cells were fixed with 3.5% formaldehyde in PBS, washed and blocked with 1% BSA in PBS for 1 h at 4 °C. Cells were incubated for 1 h at 4 °C with mouse anti-human tubulin/anti-VE-cadherin (1:100) (Sigma Aldrich). Following this, cells were washed thoroughly four times with PBS and incubated for 1 h at RT with goat anti-Mouse IgG (H+L)-Alexa fluor 568-conjugated antibody (1:200) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). Finally, cells were washed with PBS and mounted and observed as described for actin.
2.7. Tubulogenesis: Endothelial Cell Tube Formation Assay
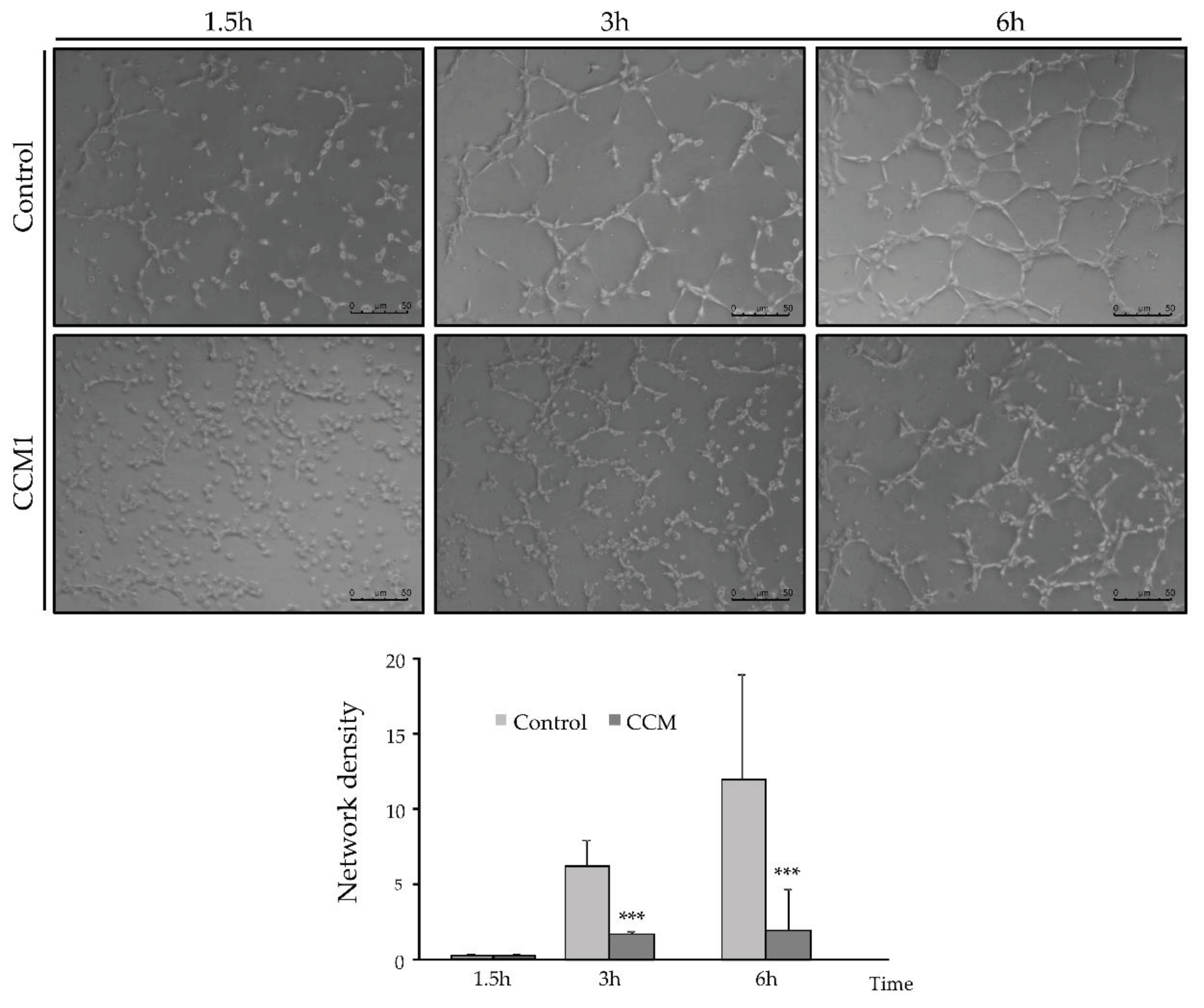
For this purpose, 50,000 cells per well, resuspended in 500 µl of EBM/EGM-2 medium, were seeded in a Matrigel-coated P-24 well (Thermo Fisher Scientific). . Brightfield photographs were taken at different times between 0 and 6h, to count the number of completely closed cells.
2.8. Wound Healing
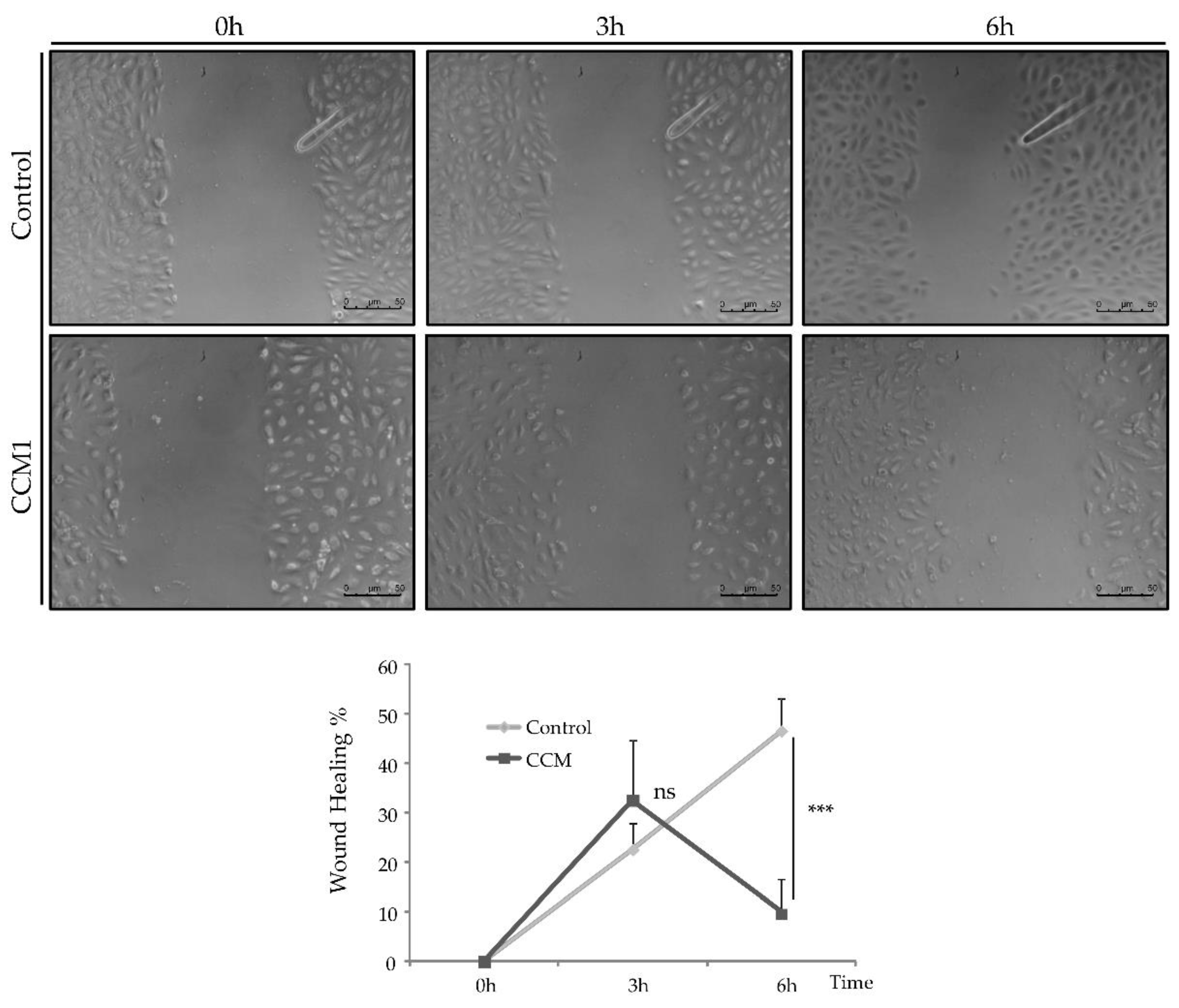
To study the migratory activity of ECs, we performed the wound-healing assay. For this purpose, 50,000 cells per well were seeded in a collagen-coated P-24 plate. Cells were incubated until confluence and, once a confluent monolayer was perceived, a "wound" (discontinuity) was made in the central area of the well. Then bright-field images were taken at different times (0h-6h) to observe the advance of the front delimiting the initial discontinuity.
4. Discussion
CCM1 and its partners in the CSC are proteins involved in different signaling pathways/functions such as cell shape, cell proliferation, migration/wound-healing, angiogenesis and blood barrier permeability [
14]. Therefore, the lack of CCM1/KRIT function leads to disruption of these signaling pathways and the already known clinical/pathological consequences.
The morphology and function of ECs is crucial as they are the first barrier between the blood and the different tissues. Despite biological and clinical studies, many questions remain unsolved about the dynamic biology of the endothelium and vasculature, as it is involved in a multitude of physiological processes in the whole organism.
In our work, by culturing primary ECs (BOECs) from a healthy donor and from a patient with CCM1, we have tried to ascertain morphological, molecular, and functional differences in FCCM disease. These heterozygous cells from a CCM1 patient constitute the vessels of the body, excluding the cavernous lesions, where, after the second hit, no functional CCM1 protein is expressed. However, already in a heterozygous condition we can see differences with control cells. Thus, in the confluent state, control ECs hardly leave any empty intercellular space. They are held together by tight adherent junctions, which may be flexible to change in the process of modulating endothelial permeability and homeostasis. On the contrary, looking at the heterozygous CCM1 cells, it is apparent that some cells adopt a more irregular and elongated morphology, being stretched at one of the cell poles and oval at the other (
Figure 1). These cells divide slower than control cells and do not reach complete confluence, leaving intercellular spaces among them. This observation suggests that the cell-cell junctions are somehow altered, and that the partial lack of CCM1 protein is involved in this alteration.
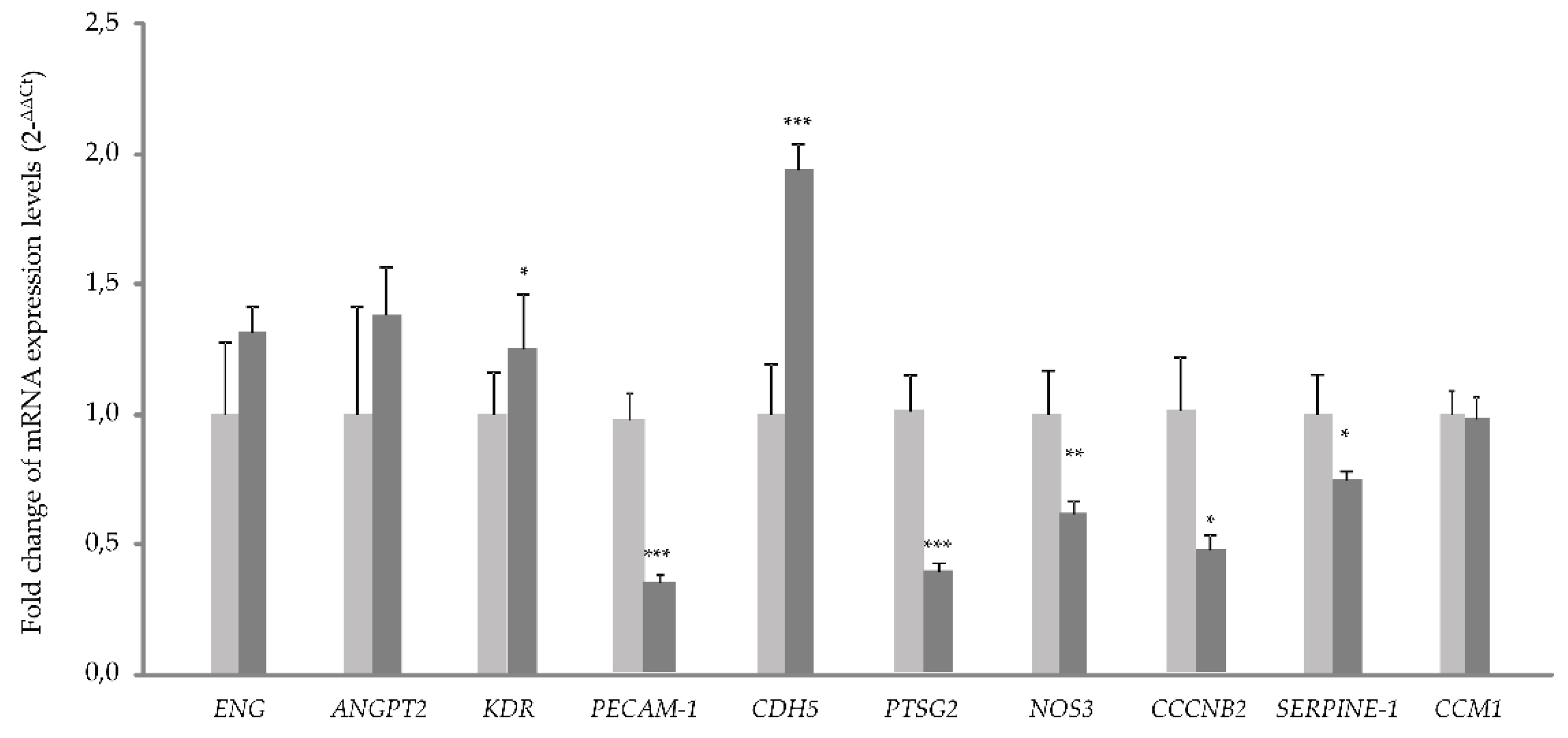
The RNA expression analysis by quantitative PCR, shows a significant increase in the expression of
CDH5. This fact could be connected to the deficit in the CCM1 protein (
Figure 2). If CCM1 is decreased, its interactions with proteins involved in cell-cell junctions such as β-catenin and VE-cadherin result impaired. In such a situation, β-catenin would sense lack of interaction with its partners, VE-cadherin and CCM1/KRIT. As a result, β-catenin could migrate to the nucleus, acting as a transcription factor to try to compensate for the lack of it on the membrane. Therefore, the increase in VE-Cadherin transcription could be a way to compensate for the lack of CCM1, which through its interaction with β-catenin participates in intercellular junctions [
15].
The decrease observed in the expression of
PAI-1 (Serpine 1) gene is explained by the increased signaling of KLF2/4. In fact, following the decrease of CCM1/KRIT1 [
13]. KLF2/4 downregulates
PAI-1 (Serpine 1), as described [
16].
On the other hand, the alteration of intercellular junctions that we have seen in vitro, would affect the permeability of the vasculature and its homeostasis in vivo. ECs act as a selective barrier that control the movement of fluids, ions and other macromolecules between blood and adjacent tissues by regulating junctional complexes. In addition, the endothelium regulates blood flow and tissue perfusion by modifying the diameter of blood vessels as well as vascular tone. ECs control vascular tone by producing NO, prostacyclin, and endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factors, all of which are vasodilators. As evidenced by qPCR, NOS-3 expression is significantly decreased in CCM1 cells, which would result in reduced NO production and, ultimately, impaired modulation of vascular tone.
Goitre et al. (2020) have shown that KRIT is part of the intracellular machinery that controls the redox balance [
17]. In particular, these authors proved that the loss of KRIT1 led to a significant increase in the intracellular ROS levels, Importantly, KRIT1 regulates the expression of the superoxide anion (O
2-) scavenging protein SOD
2. Since O
2- can spontaneously react with nitric oxide (NO) to form OONO
2, a decrease in KRIT may result in two deleterious effects, such as, i) a great reduction of NO bioavailability, with the consequence of impaired vascular tone and ii) an increased formation of OONO
2, a strong oxidant specie with the potential to produce multiple cytotoxic effects, damaging the vasculature.
In the tubulogenesis assays, endothelial CCM1 heterozygous cells take longer to align forming tubes and to form closed structures compared to control cells. Since stabilization of intercellular junctions is required to form a closed tube, the delayed and defective angiogenesis may be a direct consequence of impaired cell junctions. The loss of at least half of the CCM1 protein is preventing the CCM1 interaction with β-catenin/VE-Cadherin. In fact, published molecular studies show that KRIT1 can regulate VE-cadherin-mediated endothelial cell-cell junction integrity [
18].
Whitehead et al. (2009) [
19], provided the first in vivo evidence that any of the genes causing CCM were required in the endothelium. In CCM depleted ECs, a loss of cortical actin with increased actin stress fibers was observed. In our experiments, heterozygous ECs for CCM1 show an increase in actin stress fibers. As discussed by Whitehead et al., these changes are typical of activated RHOA GTPase pathway, which could be reversed by inhibitors of RHOA signaling. Cell culture data from (Whitehead et al) indicate that CCM2 regulates key aspects of the stabilized endothelium, including cellular architecture, barrier function, migration, and tube morphogenesis. Loss of CCM2 favors the destabilized phenotype. Normally, with two functioning alleles of CCM2, the intensity and duration of instability following an endothelial insult is limited. As seen in the heterozygous mice for CCM2 [
19] and likely in our heterozygous endothelial CCM1 cells, with only one functioning allele, there is a greater disruption of the stable state with increased permeability. The formation and maintenance of strong cell-cell contacts is a favorable characteristic of ECs in a stable blood vessel. However, when injury, inflammation, or oxidative stress alter the endothelium, cell-cell junctions are temporarily disrupted, and ECs initiate both migration and angiogenesis to repair de vessel. In this situation, CCM proteins will be required to recover the endothelium stability that will be mediated by limiting the RHOA activation [
20].
The present work is exploring the possibilities of new avenues to personalize treatment for CCM patients. Personalized cultures from CCM patients would allow the study, not only the molecular characteristics of the culture-derived from each patient, but also the use the primary cultures for screening of drugs currently under o trial for familiar CCM [
14] like fasudil or temol, inhibitors of ROCK/Rho A pathway and of inflammatory processes, autophagy, and of the oxidative stress, respectively. Vitamin D has also been proposed as a therapeutical option [
21]. Peripheral plasma vitamin D and non-HDL cholesterol reflect the severity of cerebral cavernous malformation disease. Atorvastatin (statins) is also a ROCK inhibitor, that contributes to normalize actin cytoskeleton. [
22,
23]. Propranolol has been also used in vitro and in clinical trials to avoid bleeding, normalize blood pressure, and normalize vasculature avoiding prothrombotic events [
14,
24,
25].
In conclusion the use of primary cultures of EC from CCM patients would help to expand the idea of introducing personalized medicine in the study and characteristics of rare diseases, in particular when it is necessary a treatment, which could be assayed in vitro, using either BOECs, or/and cultures derived from surgery surplus of cavernous lesions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, V.A., A.M.C. and L.M.B.; methodology, J.G., L.R.-P.; software, V.A. and J.G.; validation, J.G., V.A. and L.M.B.; formal analysis, V.A., J.G., and L.M.B.; investigation, L.L.-H., L.R.-P., V.A. and J.G..; resources, L.M.B; writing—original draft preparation, J.G. and L.M.B.; writing—review and editing, V.A., A.M.C., and L.M.B.; funding acquisition, L.M.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.