Submitted:
15 February 2024
Posted:
16 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
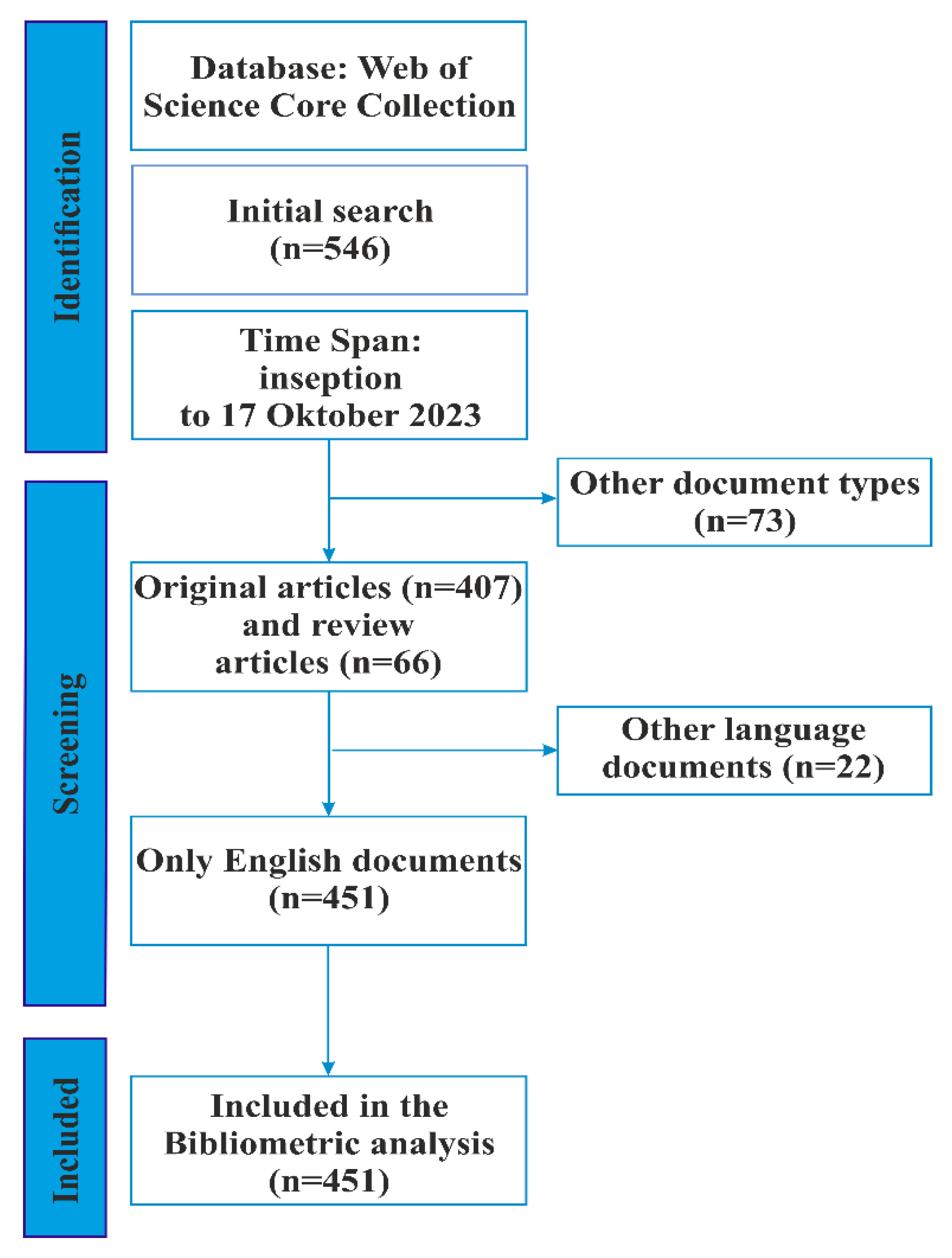
2.1. Data Sourses and Search Strategies
2.2. Bibliometric Analysis and Visualization
3. Results
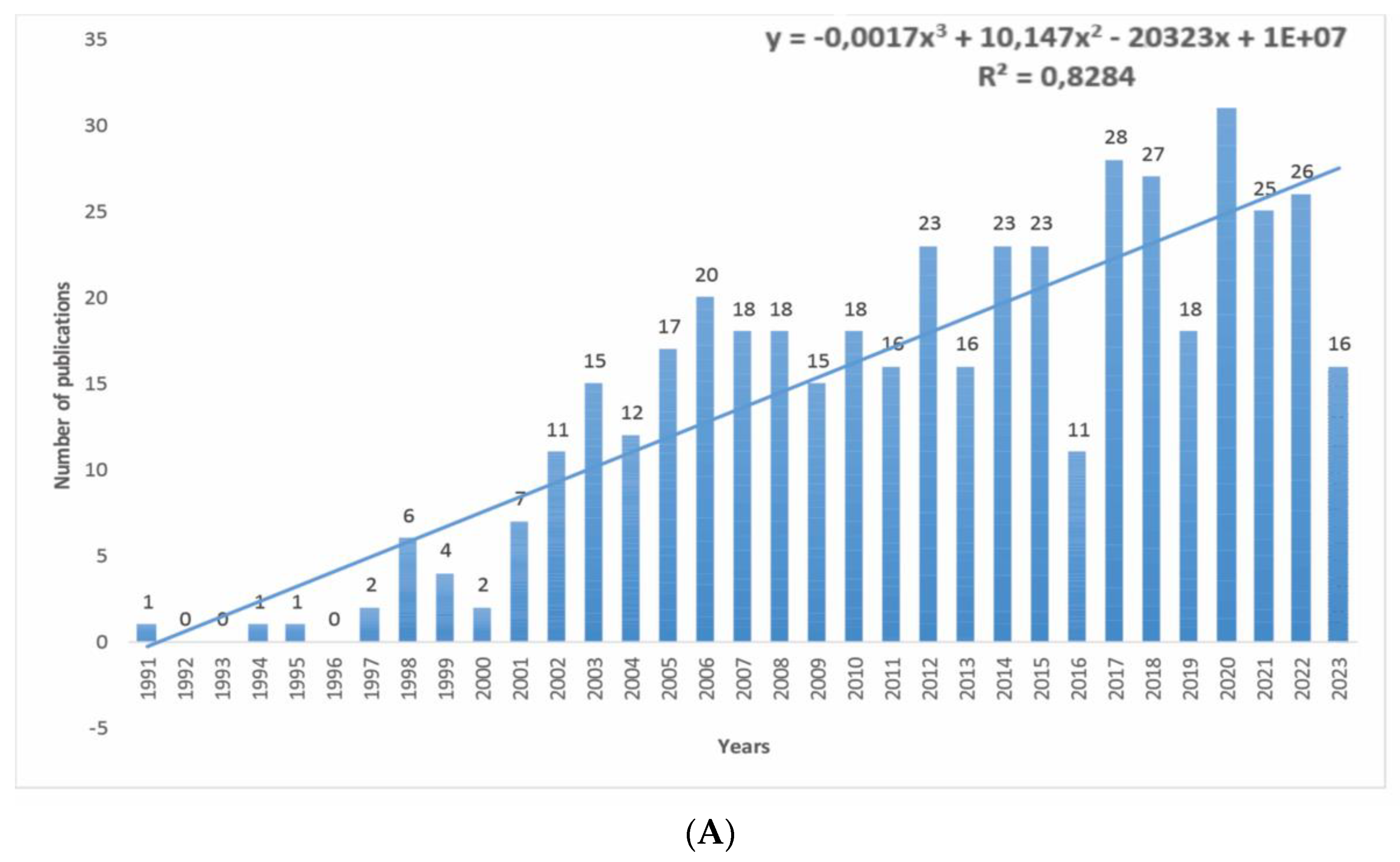
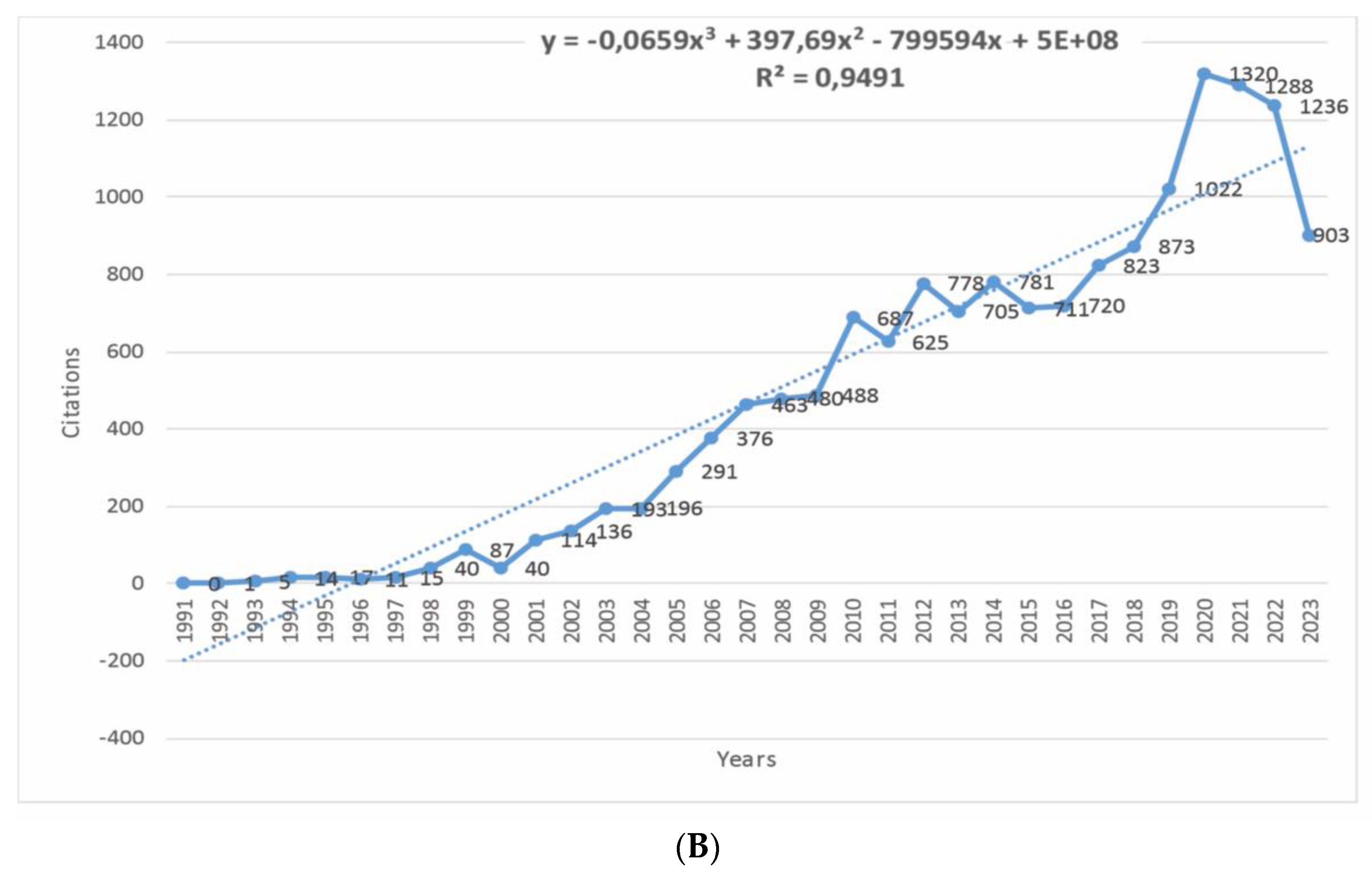
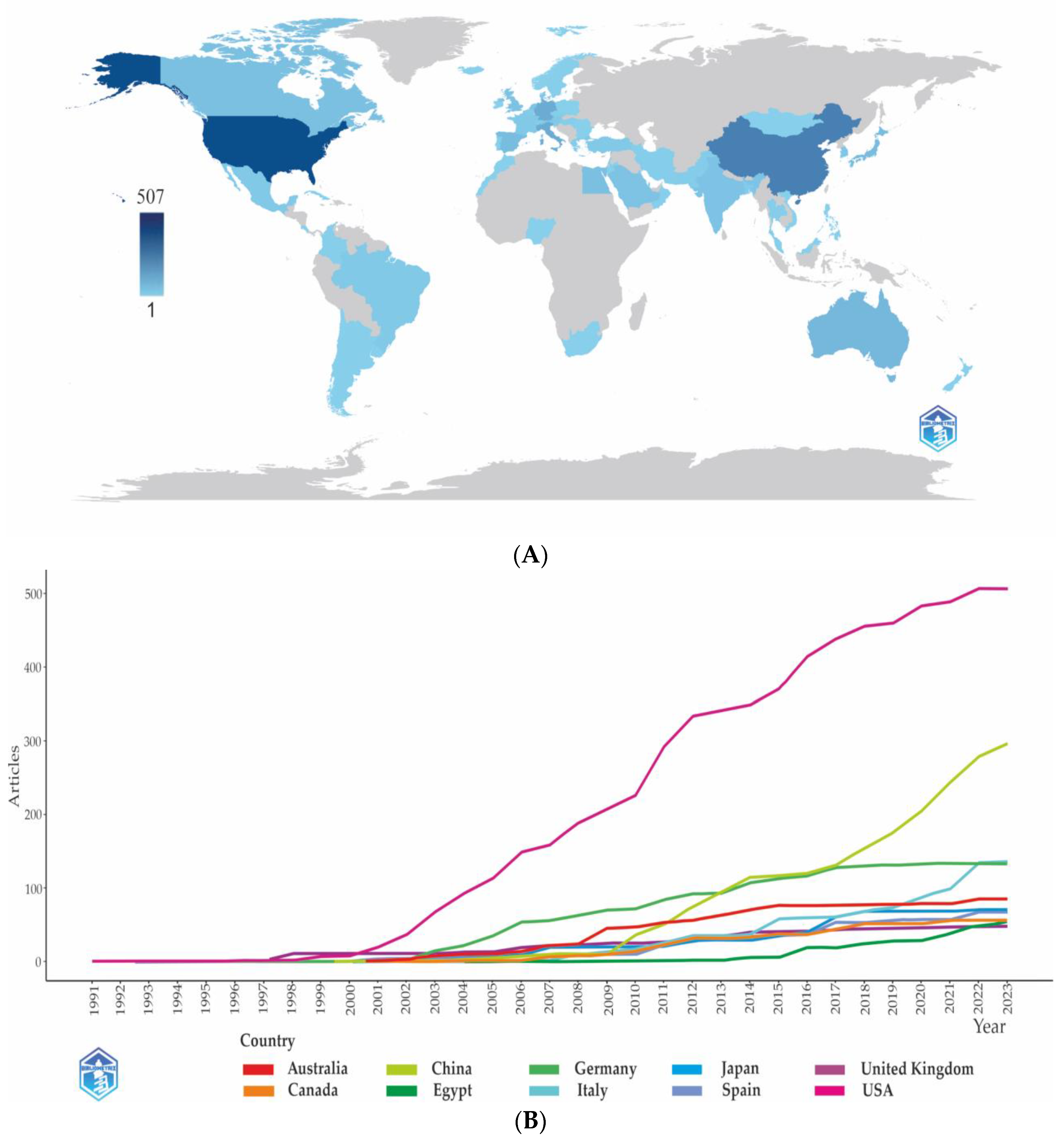
3.1. Publication Trends and Citations
3.2. Analysis of Productivity and Cooperation for Countries, Institutions, and Authors
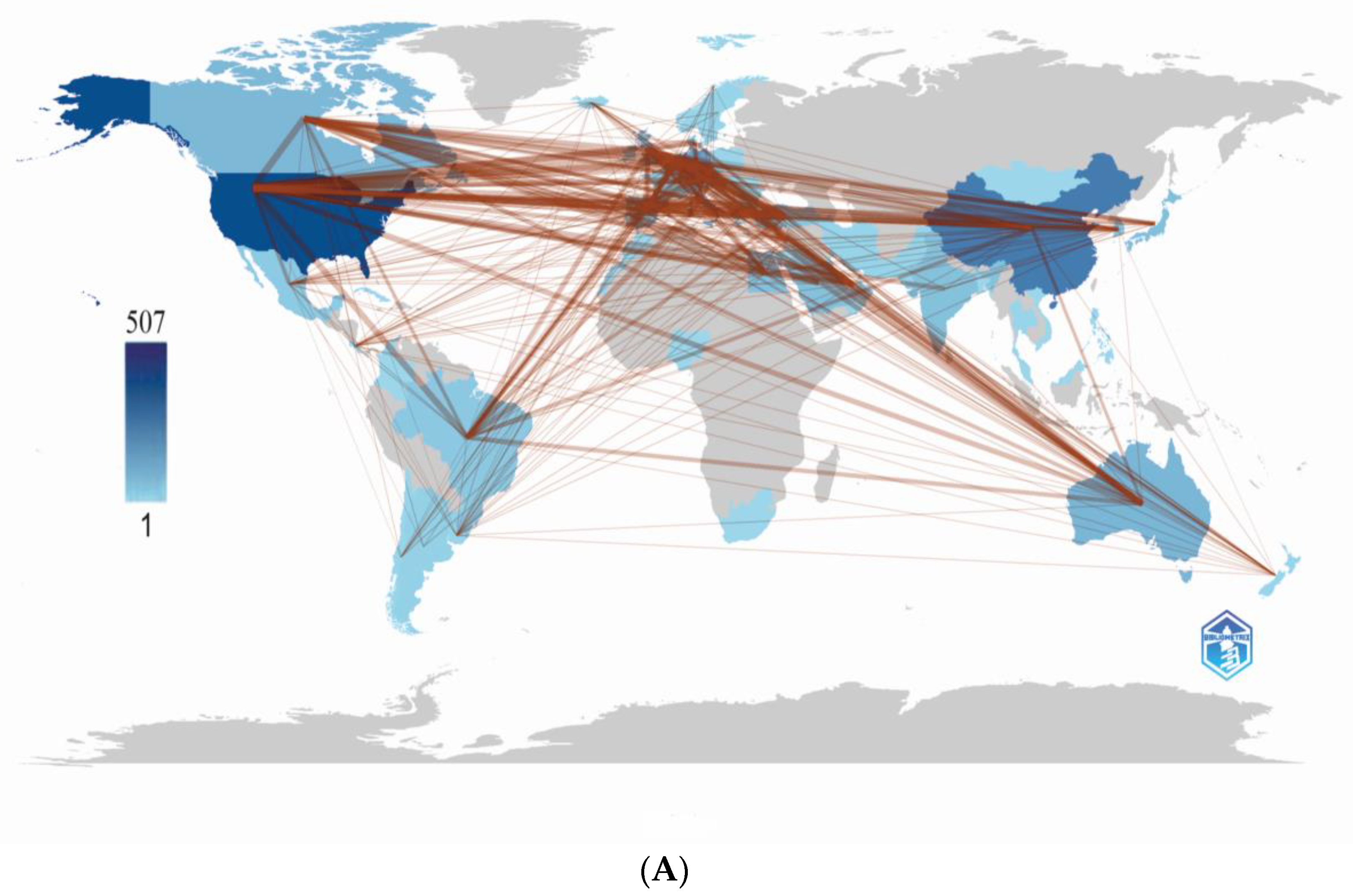
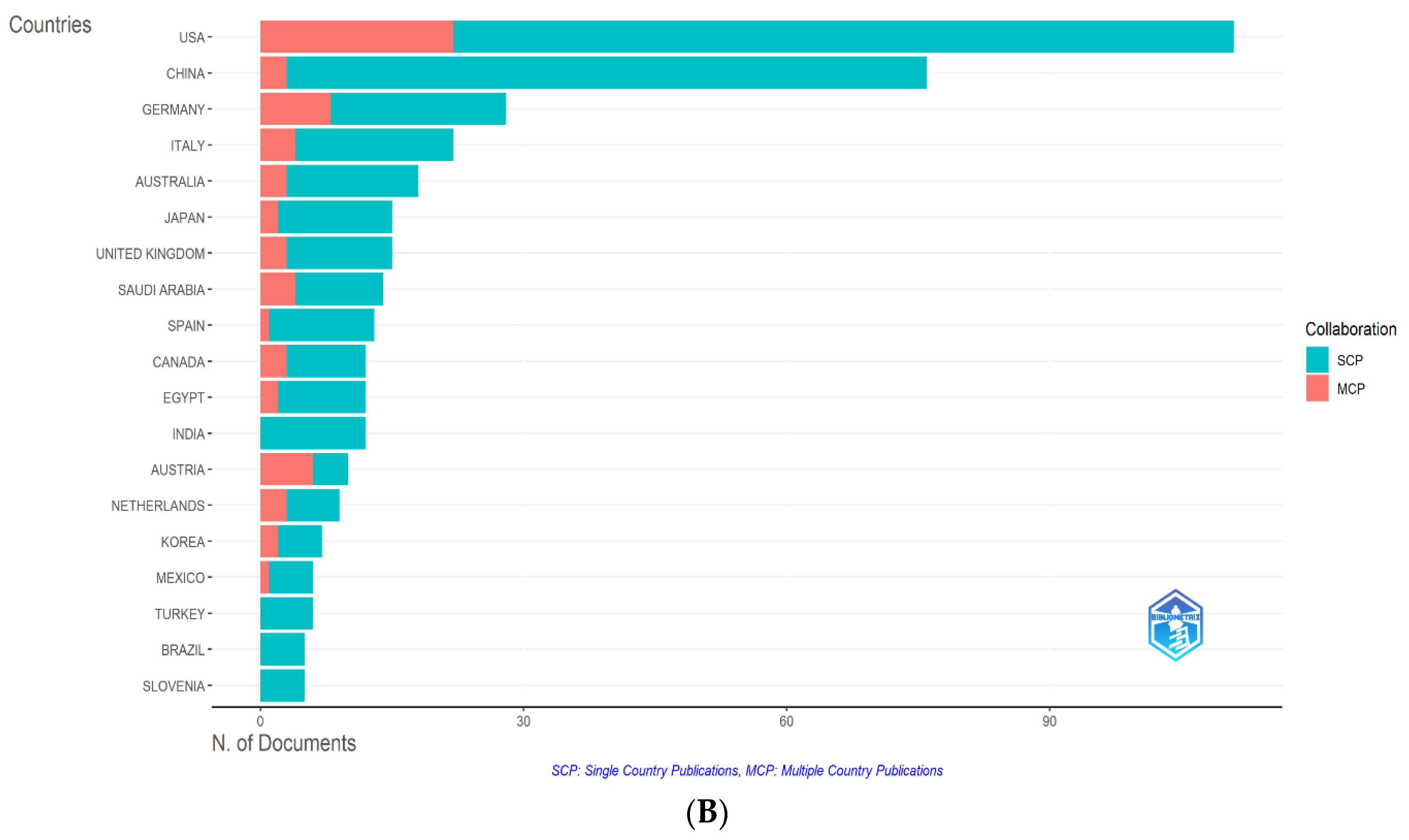
3.2.1. Country Analysis
3.2.1.1. Top Countries within the Countries’ Performance Analysis
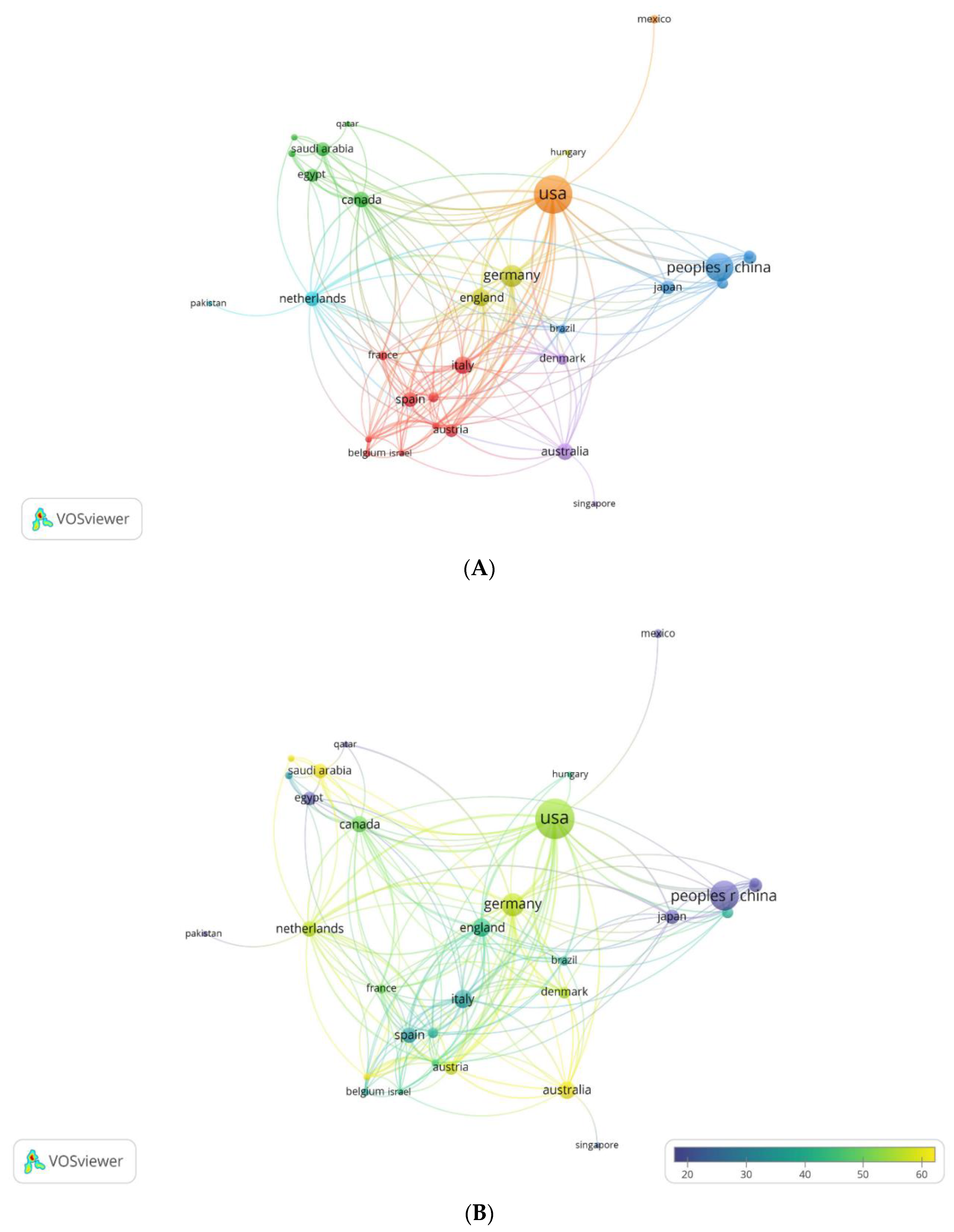
3.2.1.2. Maps of Cooperation between Countries
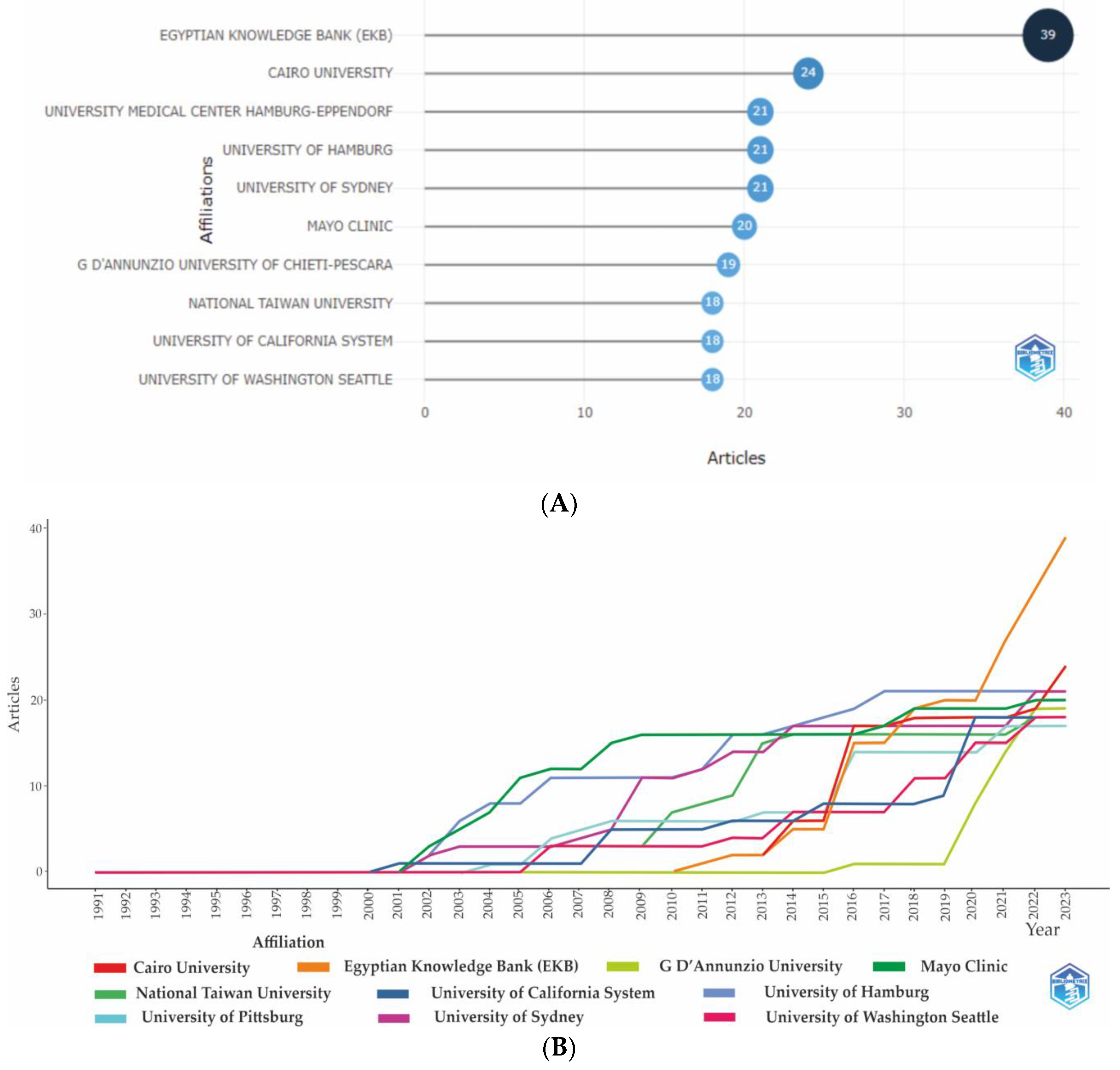
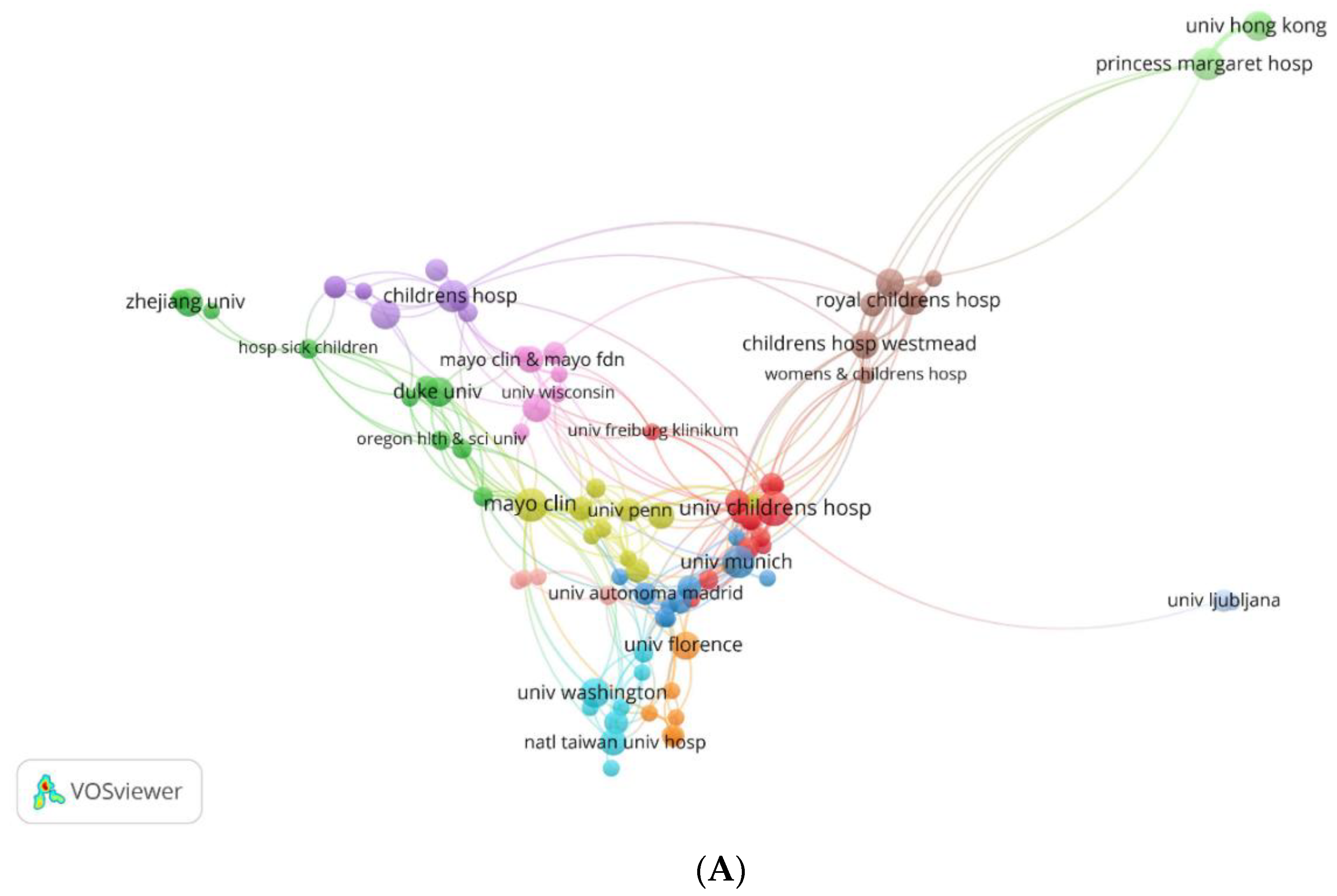
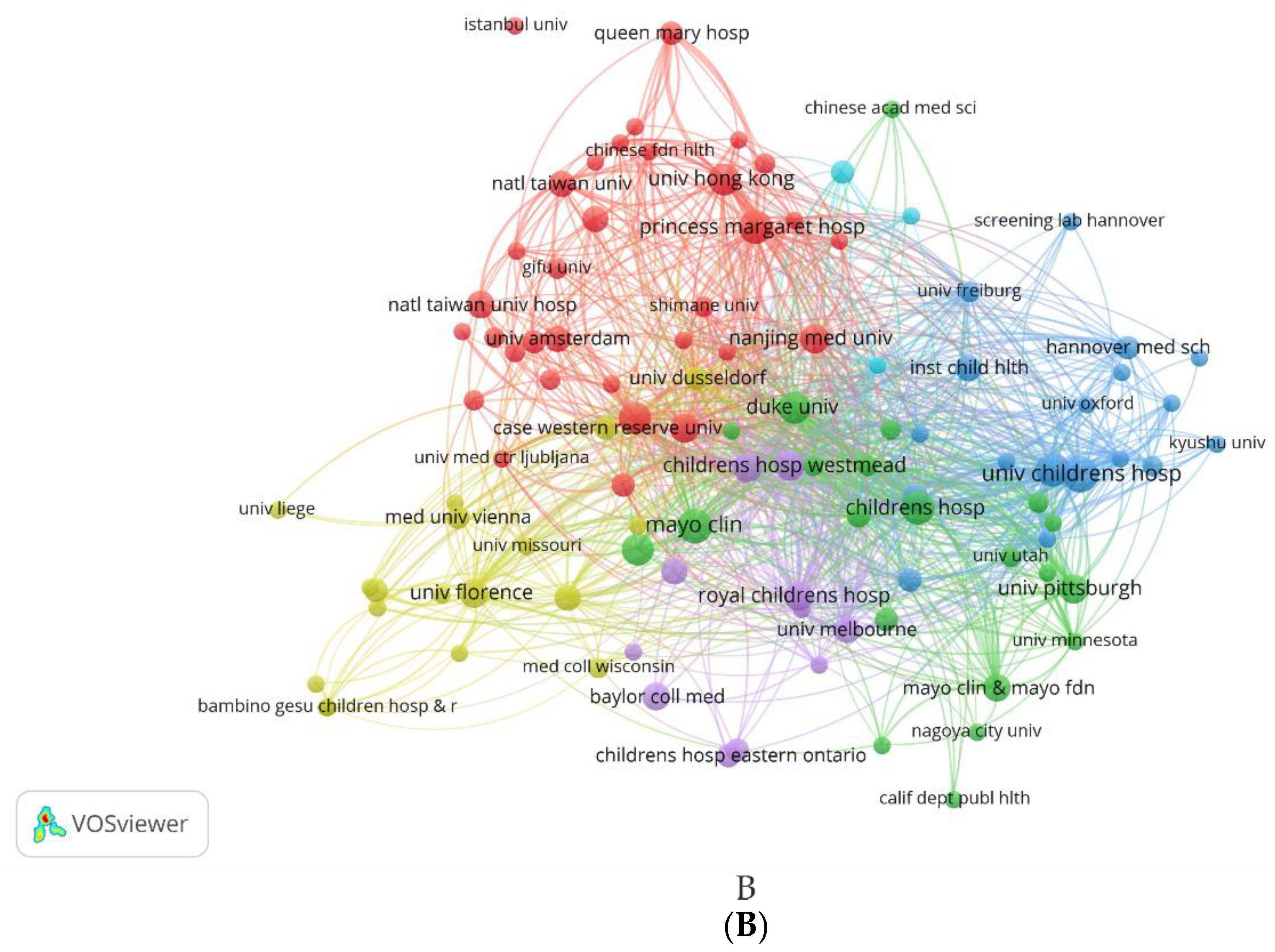
3.2.2. Institutional analysis
3.2.2.1. Leading Institutions
3.2.2.2. Maps of Institutions Cooperation
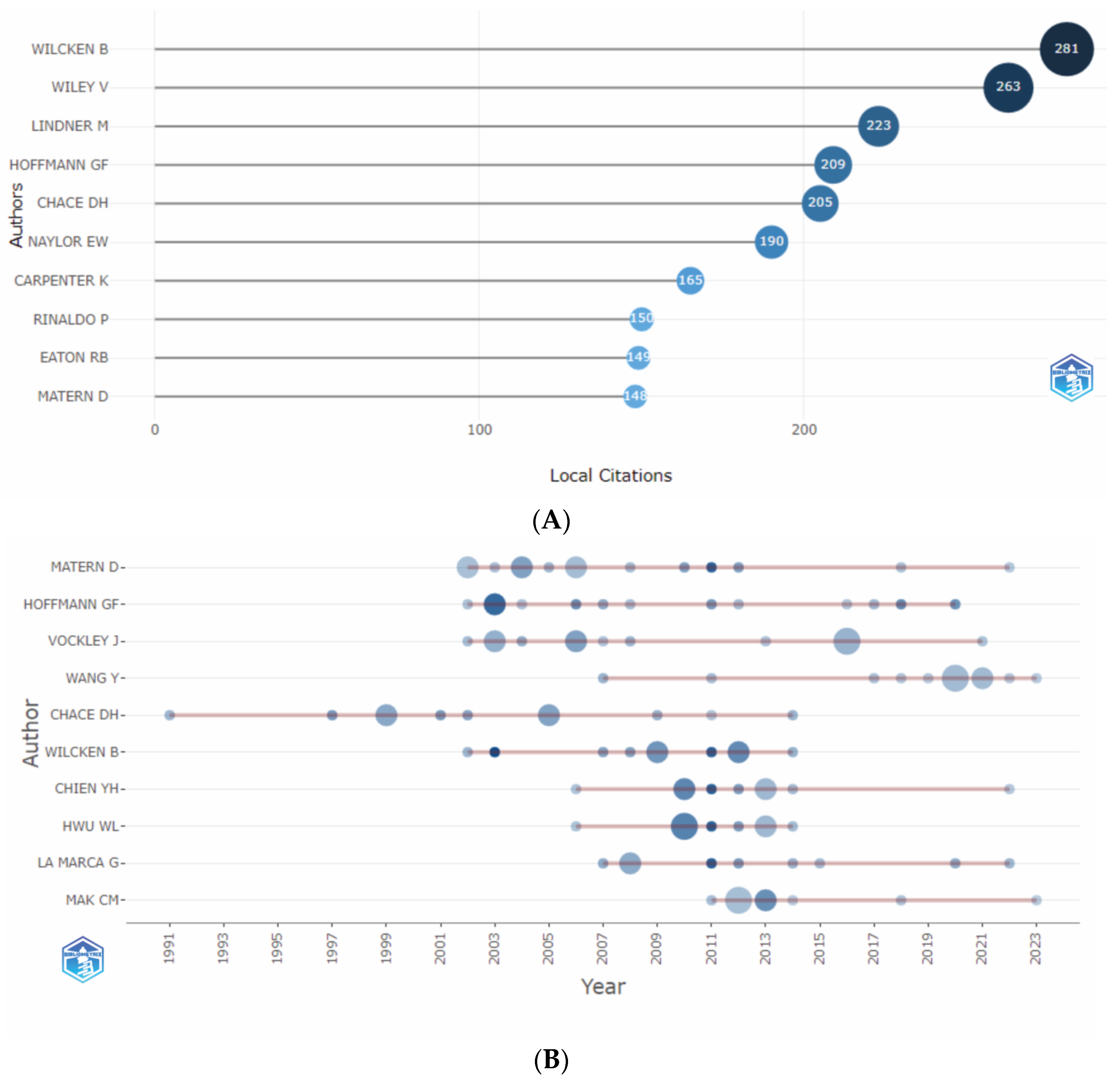
3.2.3. Analysis by Authors
3.2.3.1. Authors’ Productivity Analysis
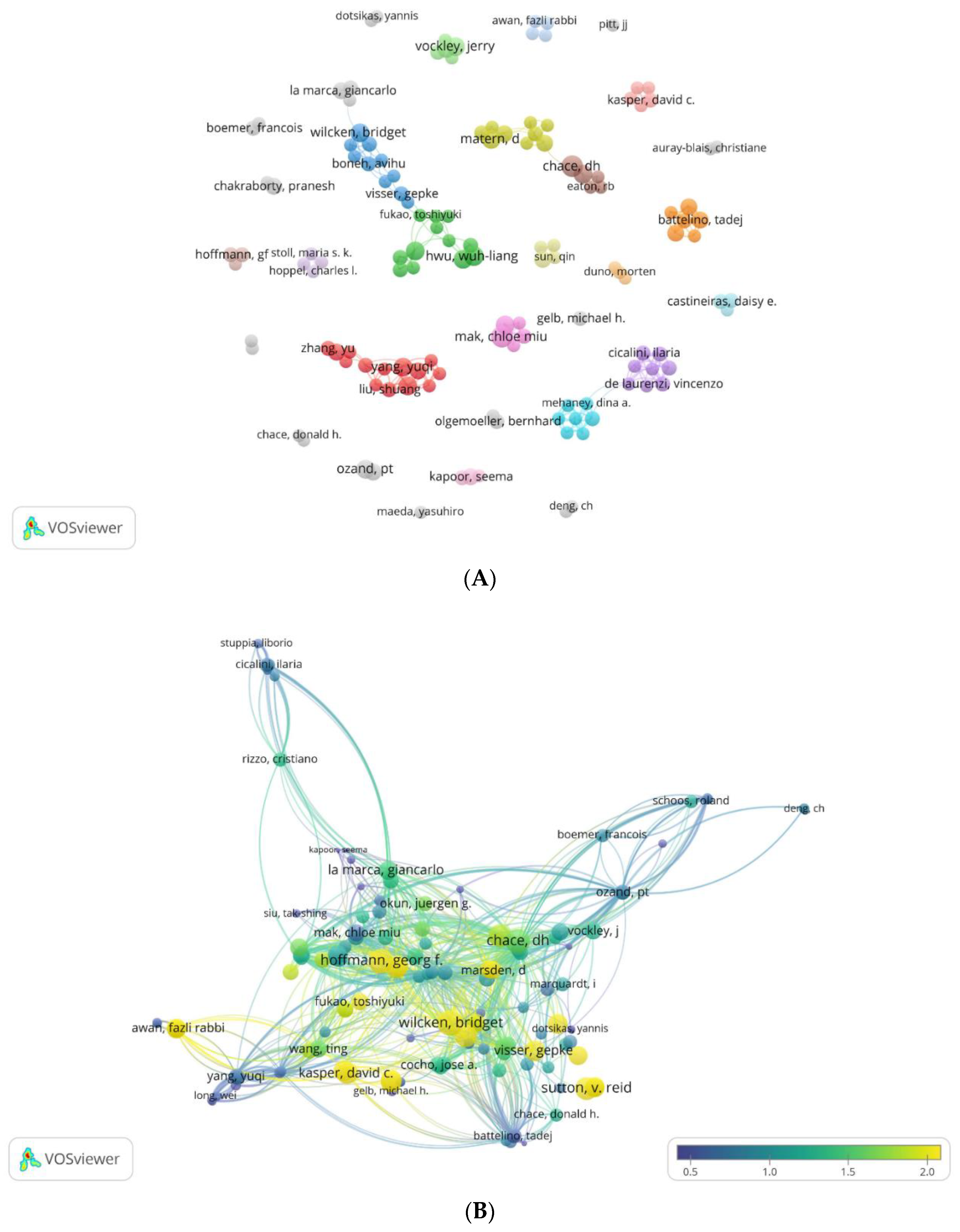
3.2.3.2. Author Collaboration Maps
3.3. Analysis by Journals
3.3.1. Prominent Journals
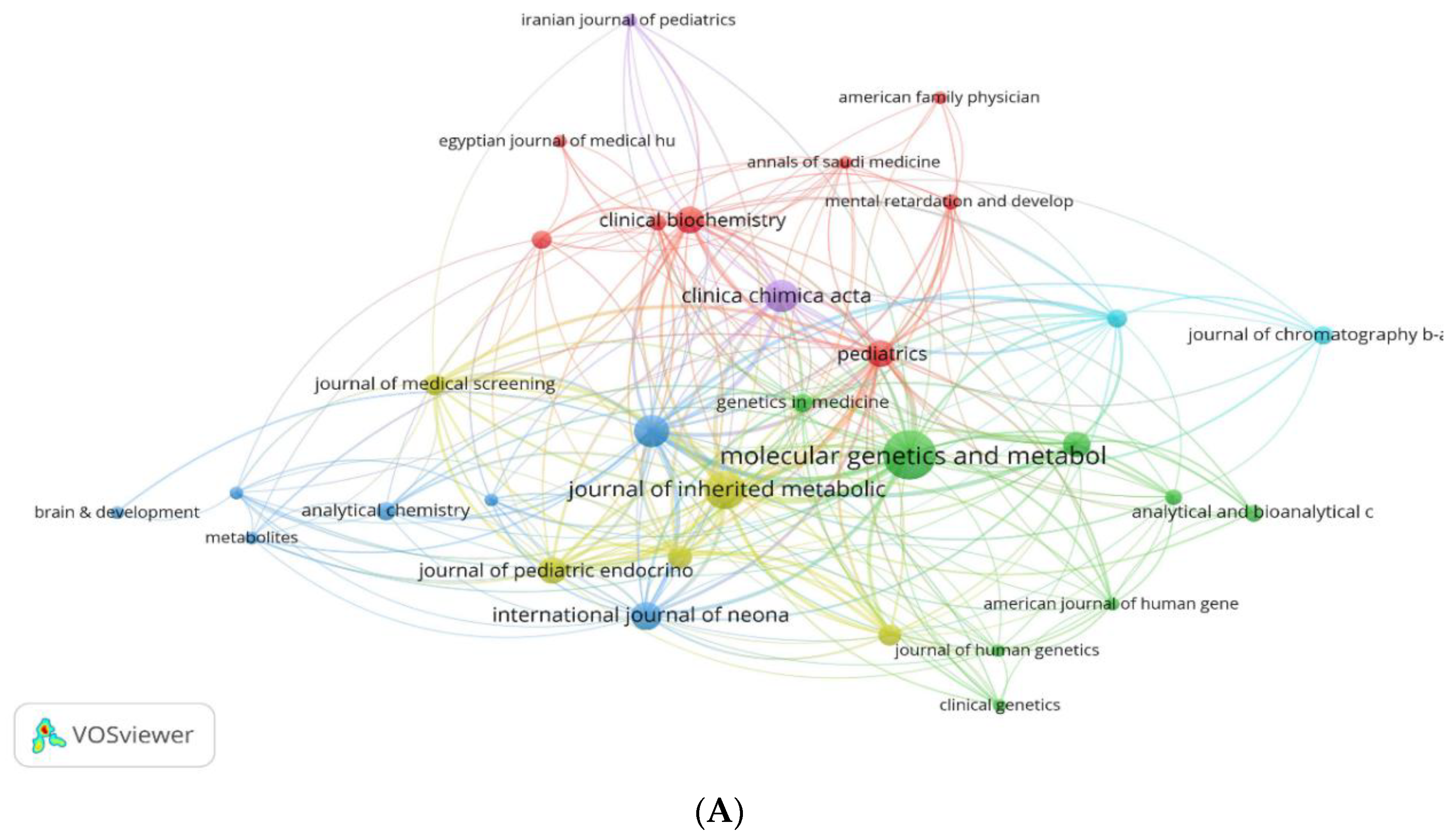
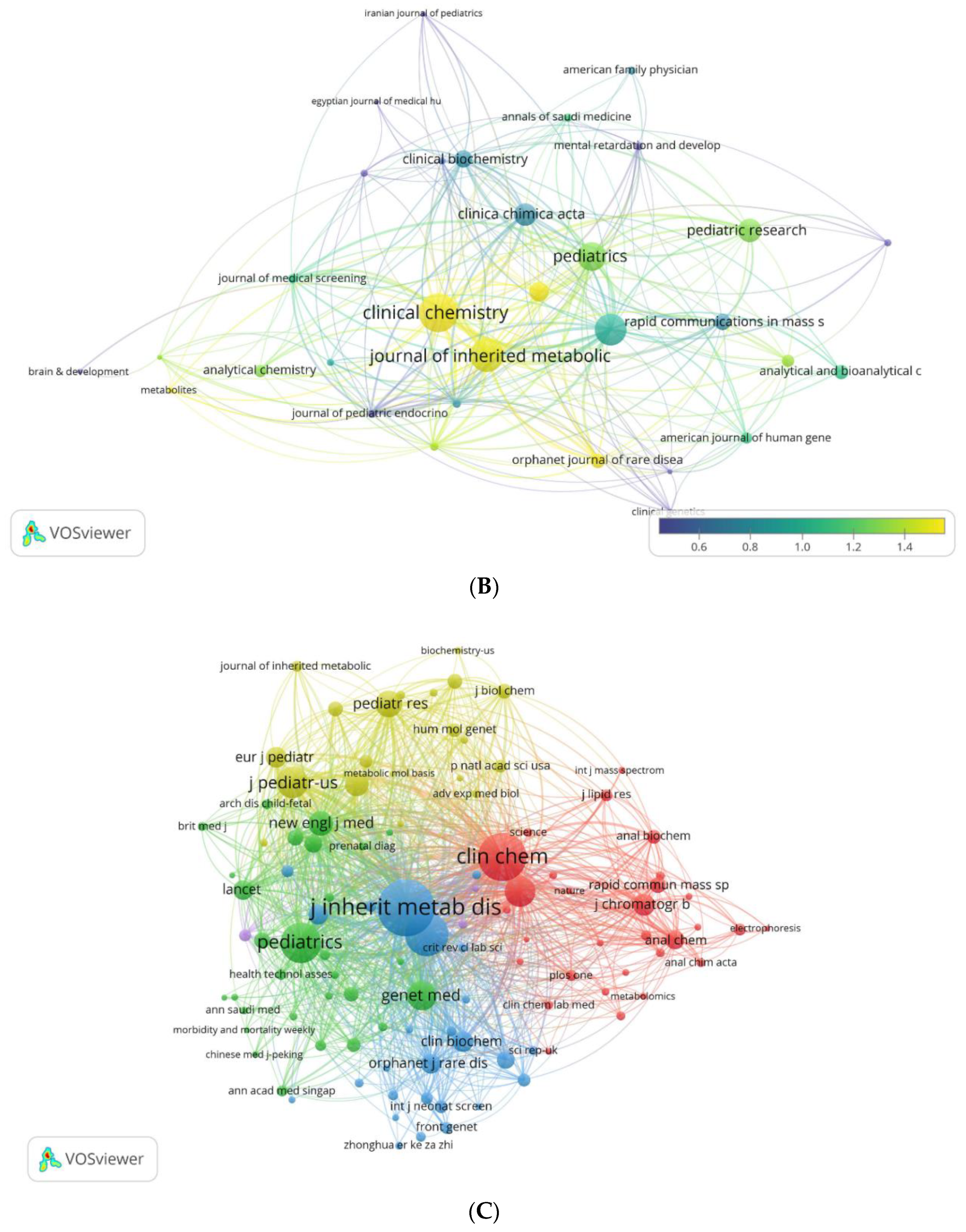
3.3.2. Journal Collaboration Maps
3.4. Analysis by Papers
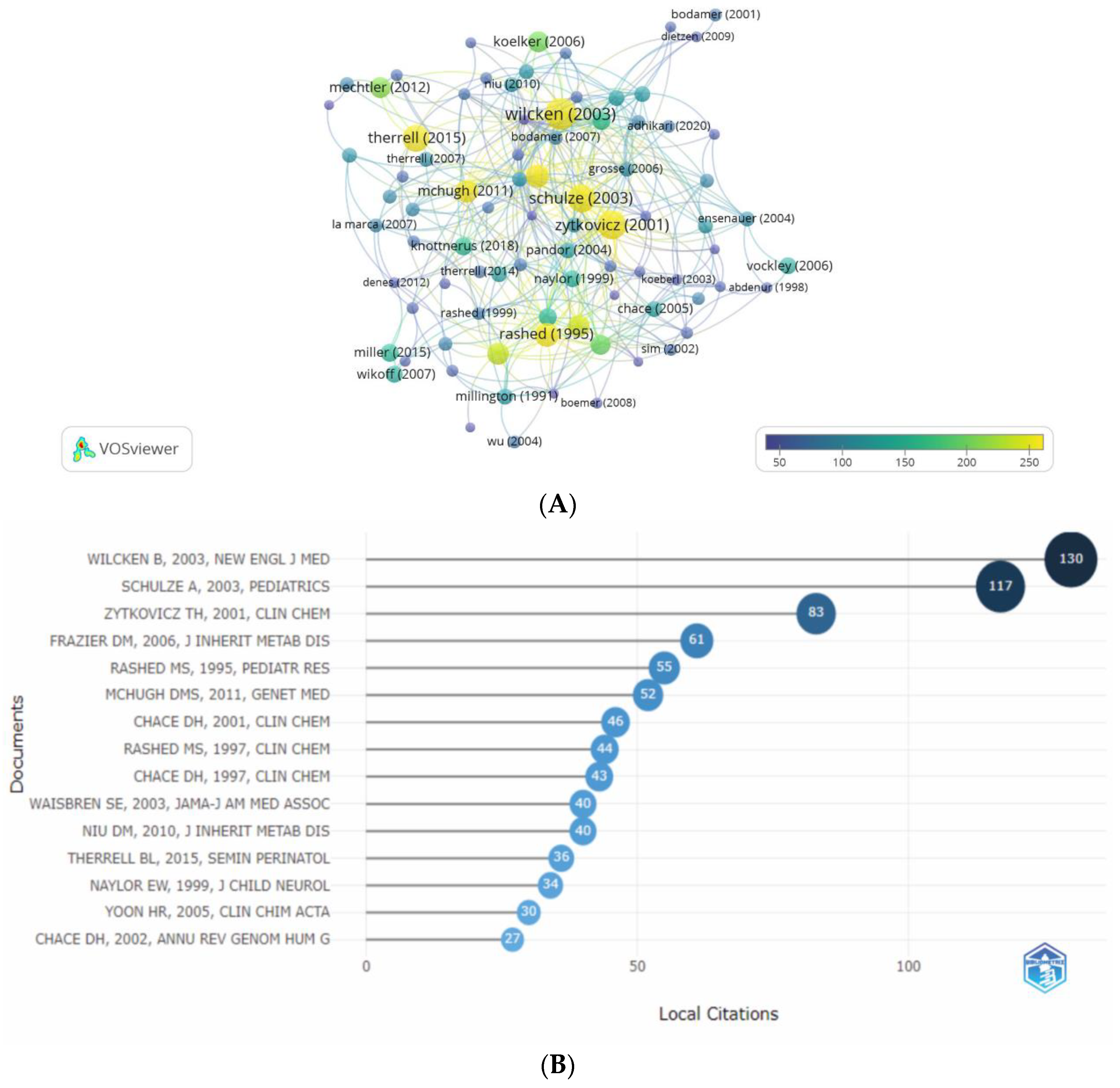
3.4.1. Highly Cited Papers. Analysis of Citation
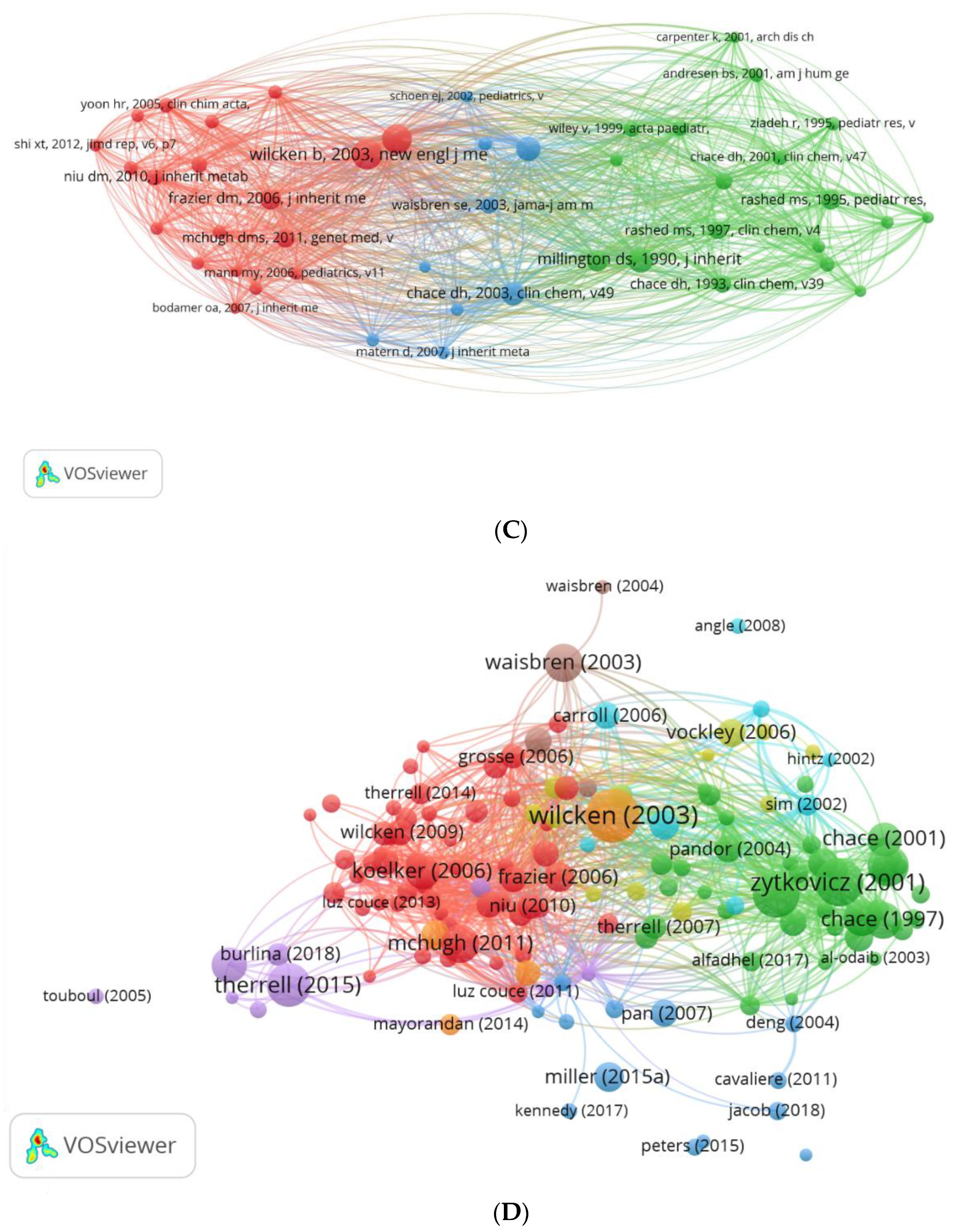
3.4.2. Analysis of Co-Citation
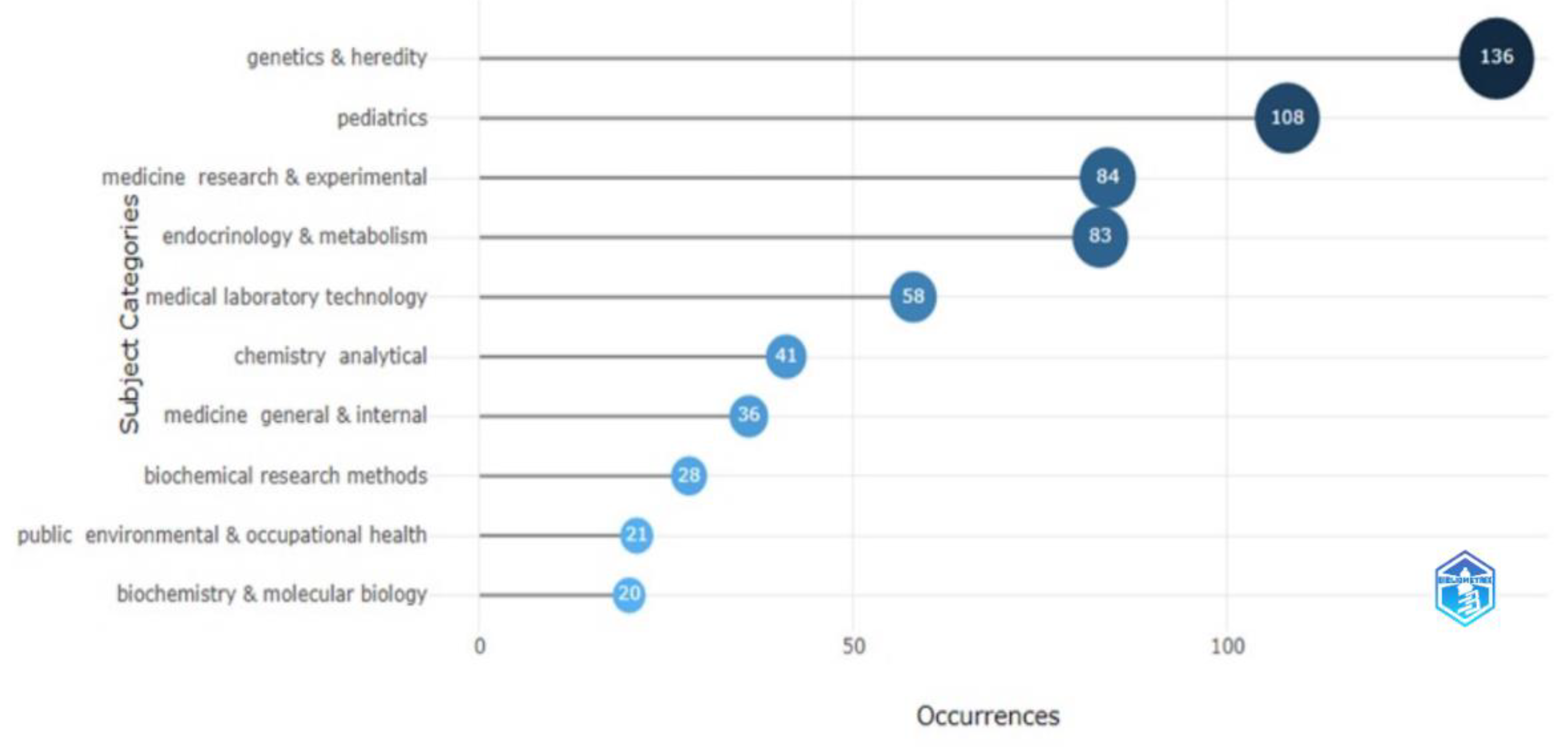
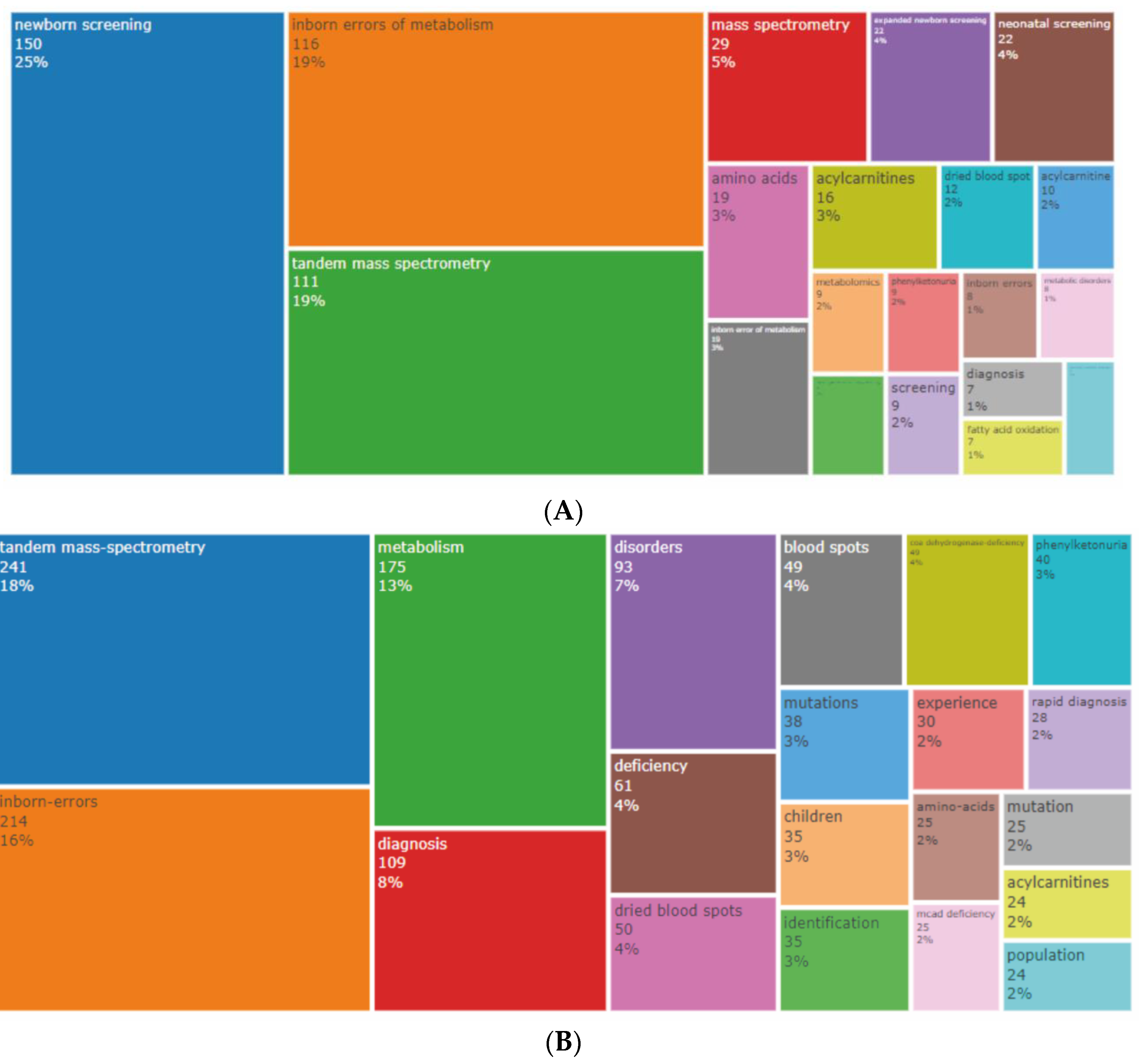
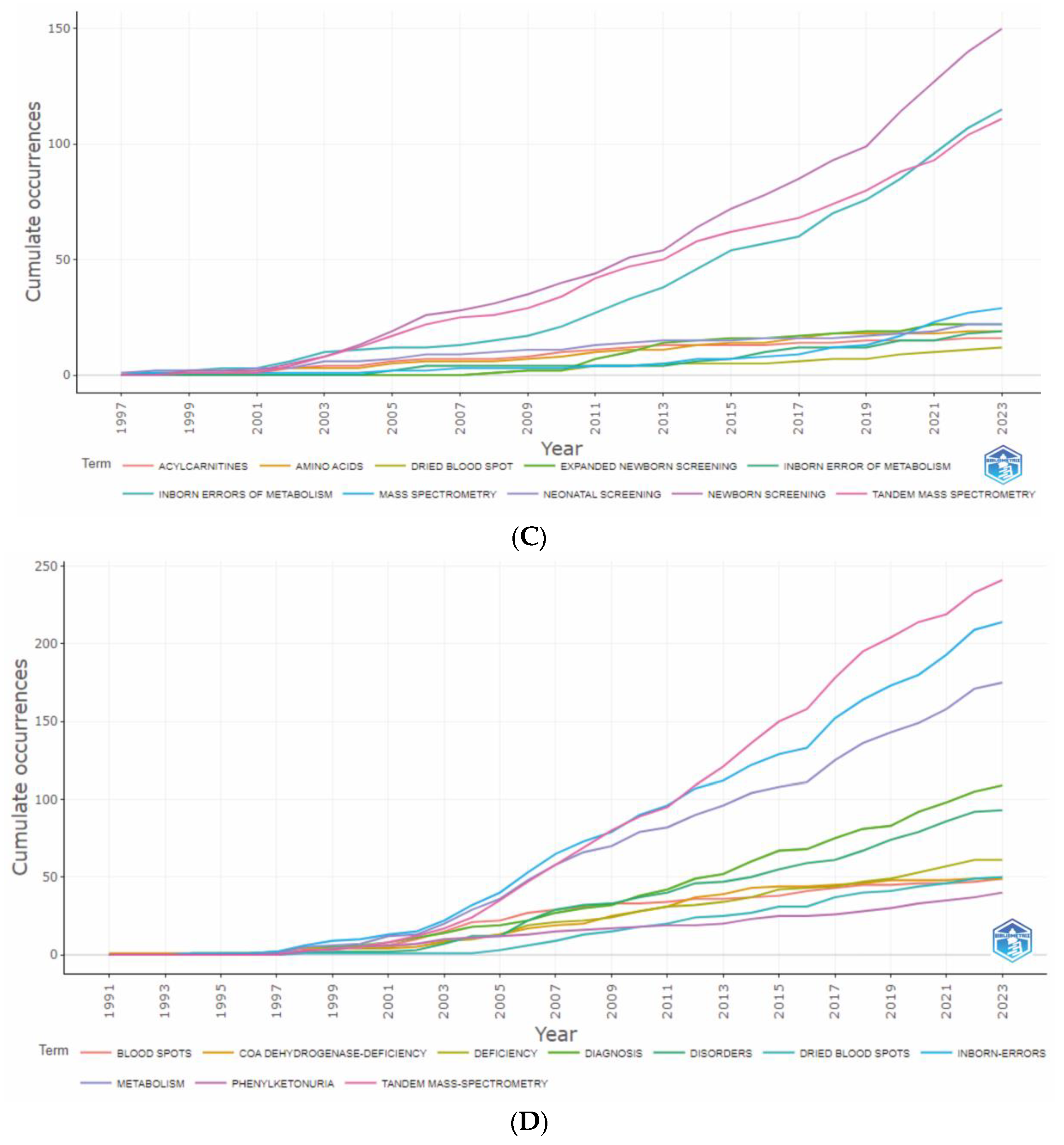
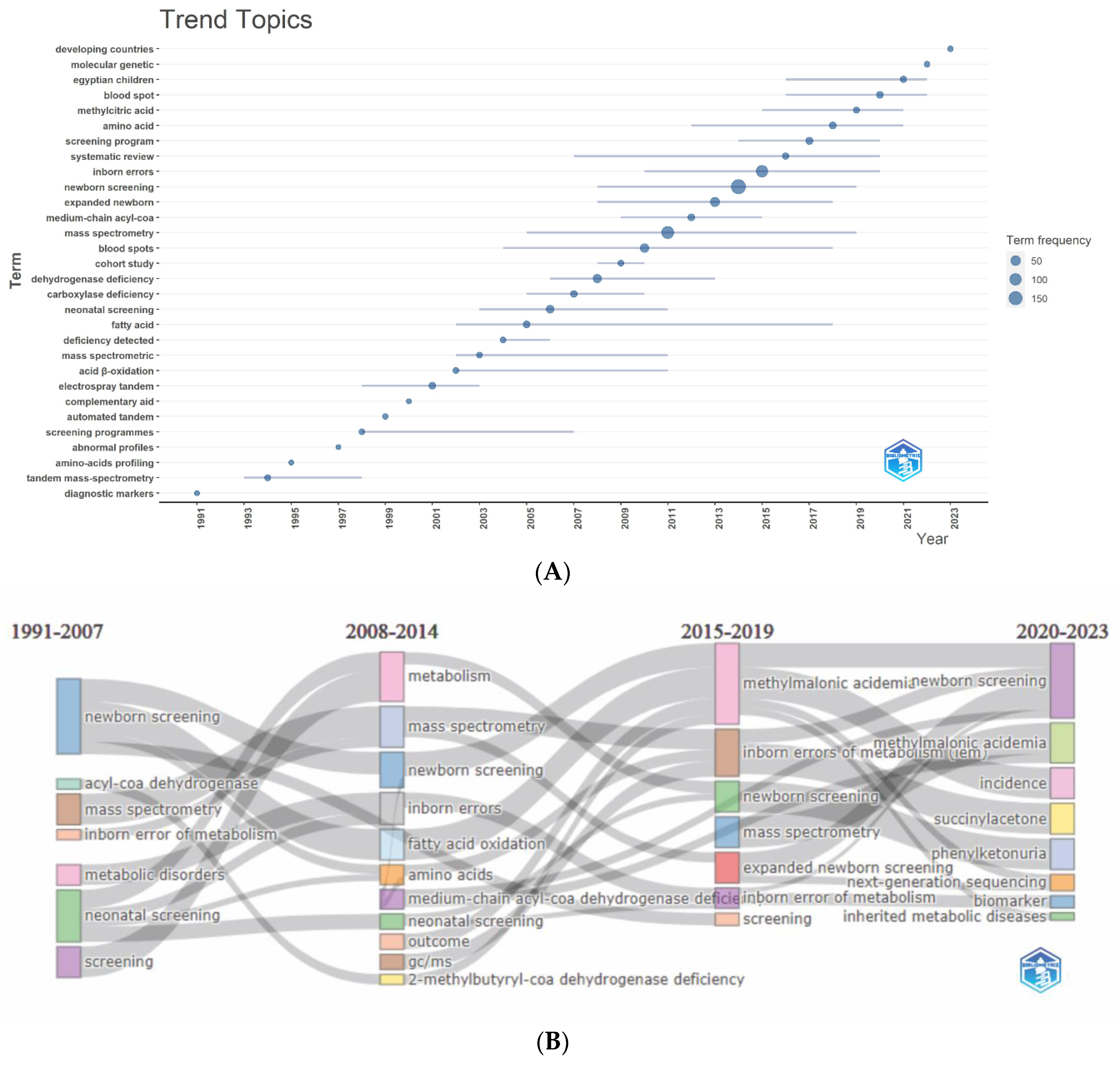
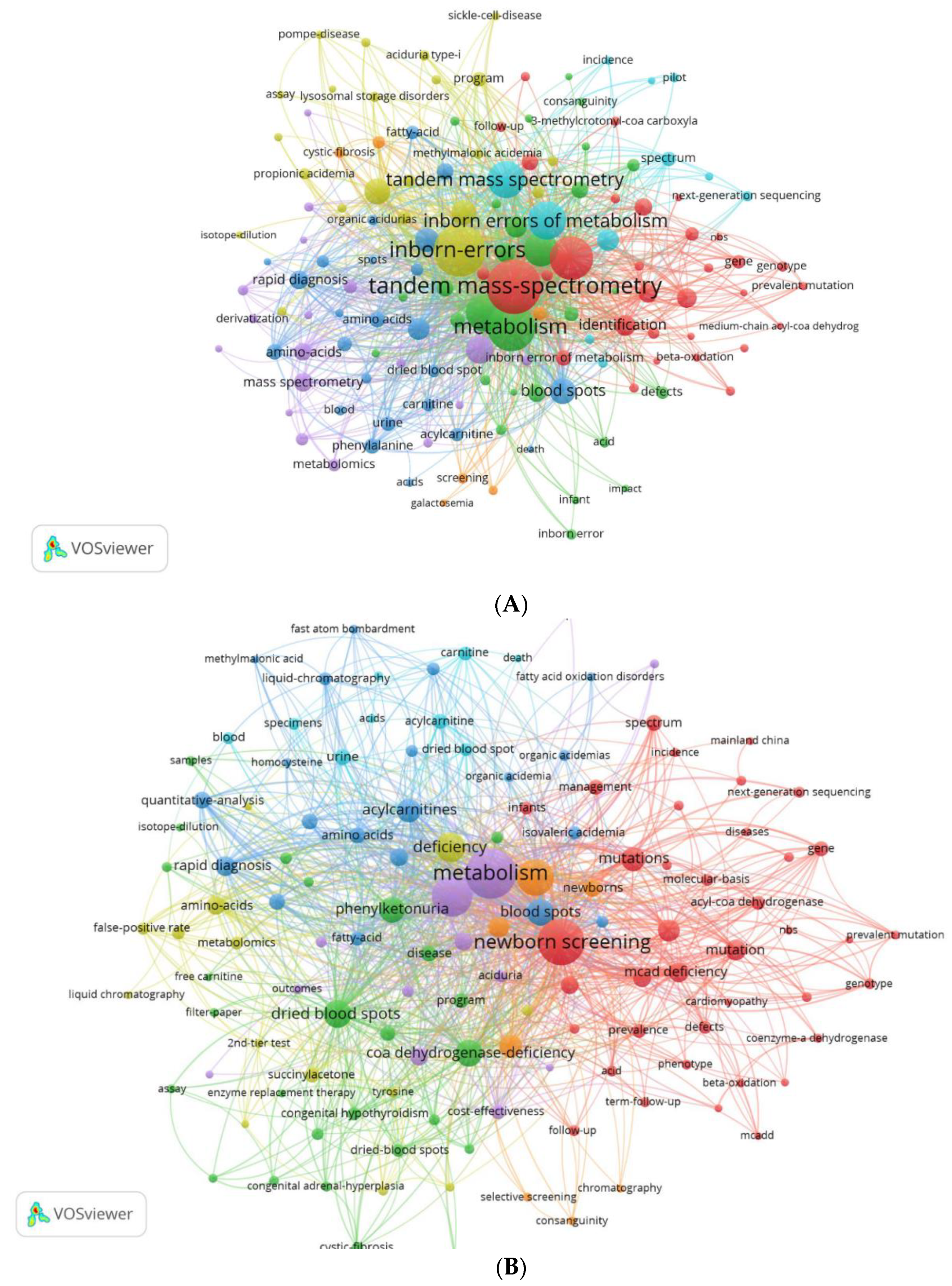
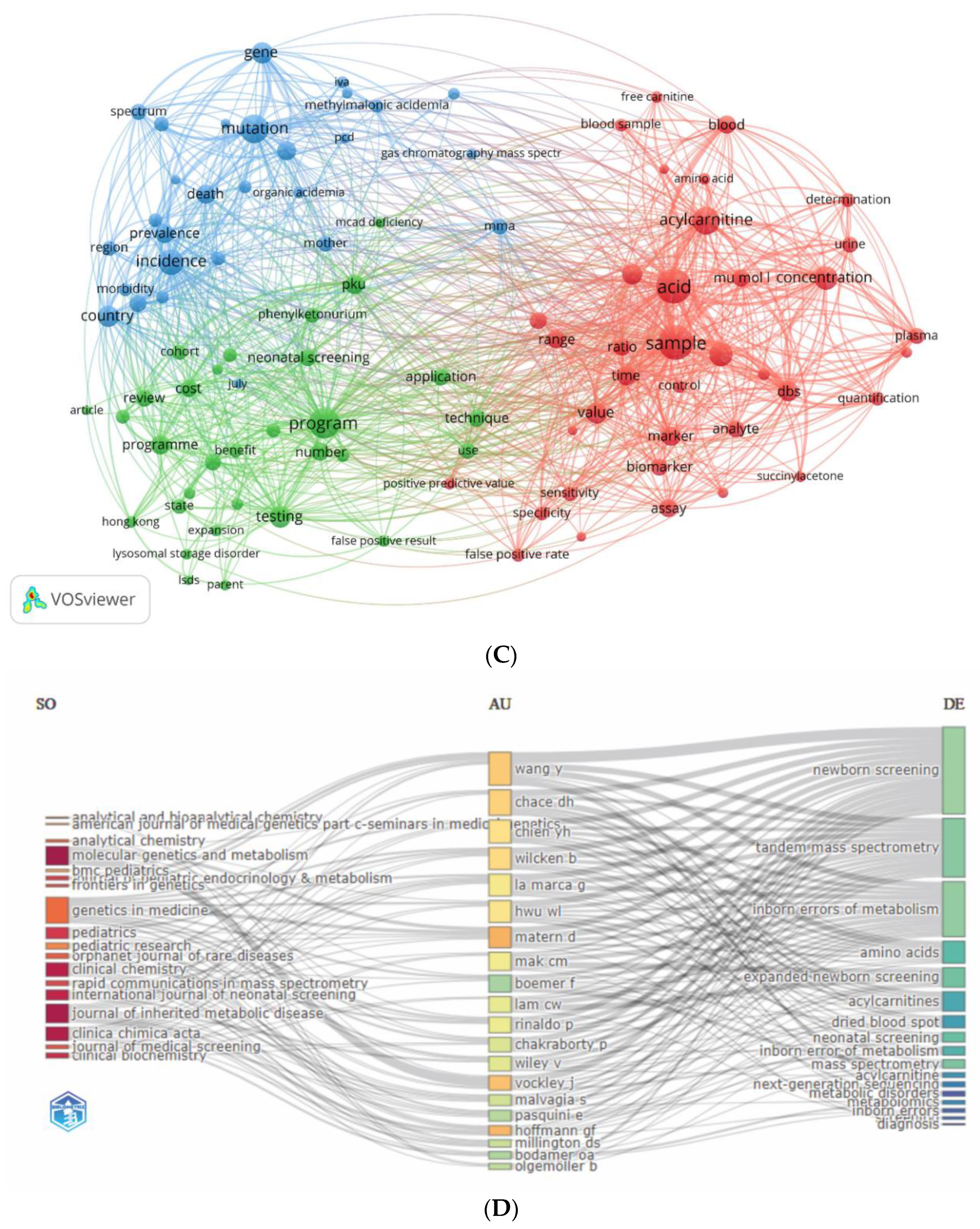
3.5. Analysis of Keywords
3.5.1. Authors’ and Additional (Plus) Keywords
3.5.2. Keywords Co-occurrence Maps and Relationships between Authors, Keywords, and Sources
4. Discussion
- We used only the core WOS collection to search for relevant sources. The current study did not consider other databases, such as Scopus and MEDLINE. WOS is the most commonly used database in scientometrics, and Biblioshiny and VOSviewer have identified a format for recording metadata from WOS.
- Only articles in English were included.
- Proceeding papers, book chapters, meeting abstracts, editorial materials, early access articles, letters, and notes were not included in the study.
- The total citation rate for newer articles is lower, which can be considered a manifestation of the methodological weakness of the bibliometric analysis. However, this is covered by the average citation indicator per period (year).
- Bibliometric and scientometric analysis of articles indexed in the WOS database focused only on metadata, not their content. Analysis of the full text of the included articles and their scientific content was not the purpose of the research as being beyond the scope of this article. Besides, analyzing the textual content of the abstracts was also not the purpose of our study. Article metadata were sources of information about authors and their countries/institutions to assess their productivity, collaboration, and keyword trends.
- The textual content of some images displayed by Biblioshiny and VOSviewer is incomplete.
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
- CIT I, citrullinemia I
- DBS, dry blood spot
- ENBS, expanded newborn screening
- FAOD, fatty acid oxidation disorders
- GA I, glutaric aciduria type I, glutaryl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency
- GC-MS, gas chromatography-mass spectrometry
- НРА, hyperphenylalaninemia
- IEM, inborn errors of metabolism
- IMD, inherited metabolic diseases
- LC-MS/MS, liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry
- MADD, multiple-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency
- MCAD, medium-chain acyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase deficiency;
- MCCD, 3-methylcrotonyl-CoA carboxylase deficiency
- MCP, multiple countries’ publication
- MMA, methylmalonic acidemia
- MS/MS, tandem mass spectrometry
- NGS, next-generation sequencing
- PA, propionic acidemia
- PKU, phenylketonuria
- PCD, primary carnitine deficiency
- SCP, single country publication
References
- Rashed, M.S.; Bucknall, M.P.; Little, D.; Awad, A.; Jacob, M.; Alamoudi, M.; Alwattar, M.; Ozand, P.T. Screening blood spots for inborn errors of metabolism by electrospray tandem mass spectrometry with a microplate batch process and a computer algorithm for automated flagging of abnormal profiles. Clin Chem. 1997, 43(7), 1129–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonsen, H.; Jensen, U.G.; Brandt, N.J.; Christensen, E.; Skovby, F.; Nørgaard-Pedersen, B. Design of a pilot study to evaluate tandem mass spectrometry for neonatal screening. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 1999, 30 (Suppl. 2), 166–169. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Frazier, D.M.; Millington, D.S.; McCandless, S.E.; Koeberl, D.D.; Weavil, S.D.; Chaing, S.H.; Muenzer, J. The tandem mass spectrometry newborn screening experience in North Carolina: 1997-2005. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2006, 29(1), 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seymour, C.A.; Thomason, M.J.; Chalmers, R.A.; Addison, G.M.; Bain, M.D.; Cockburn, F.; et al. Newborn screening for inborn errors of metabolism: a systematic review. Health Technol Assess (Winchester, England) 1997, 1(11), i–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.M.; Bennett, M.J. The changing face of newborn screening: diagnosis of inborn errors of metabolism by tandem mass spectrometry. Clin Chim Acta 2002, 324(1-2), 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chace, D.H.; Kalas, T.A.; Naylor, E.W. The application of tandem mass spectrometry to neonatal screening for inherited disorders of intermediary metabolism. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet. 2002, 3, 17–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, U.; Dasouki, M. Expanded newborn screening of inherited metabolic disorders by tandem mass spectrometry: clinical and laboratory aspects. Clin Biochem. 2006, 39(4), 315–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Therrell, B.L.; Adams, J. Newborn screening in North America. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2007, 30(4), 447–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinaldo, P.; Tortorelli, S.; Matern, D. Recent developments and new applications of tandem mass spectrometry in newborn screening. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2004, 16(4), 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitt, J.J.; Eggington, M.; Kahler, S.G. Comprehensive screening of urine samples for inborn errors of metabolism by electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. Clin Chem. 2002, 48(11), 1970–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, P.; Schulze, A.; Schindler, I.; Ethofer, T.; Buehrdel, P.; Ceglarek, U. Validation of an ESI-MS/MS screening method for acylcarnitine profiling in urine specimens of neonates, children, adolescents and adults. Clin Chim Acta 2003, 327(1-2), 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpenter, K.H.; Wiley, V. Application of tandem mass spectrometry to biochemical genetics and newborn screening. Clin Chim Acta 2002, 322(1-2), 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chace, D.H.; Kalas, T.A.; Naylor, E.W. Use of tandem mass spectrometry for multianalyte screening of dried blood specimens from newborns. Clin Chem. 2003, 49(11), 1797–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandor, A.; Eastham, J.; Beverley, C.; Chilcott, J.; Paisley, S. Clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of neonatal screening for inborn errors of metabolism using tandem mass spectrometry: a systematic review. Health Technol Assess (Winchester, England) 2004, 8(12), iii–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilcken, B.; Wiley, V.; Hammond, J.; Carpenter, K. Screening newborns for inborn errors of metabolism by tandem mass spectrometry. N Engl J Med. 2003, 348(23), 2304–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsden, D. Expanded newborn screening by tandem mass spectrometry: the Massachusetts and New England experience. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health 2003, 34 (Suppl. 3), 111–114. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Raghuveer, T.S.; Garg, U.; Graf, W.D. Inborn errors of metabolism in infancy and early childhood: an update. Am Fam Physician 2006, 73(11), 1981–1990. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mak, C.M.; Lee, H.C.; Chan, A.Y.; Lam, C.W. Inborn errors of metabolism and expanded newborn screening: review and update. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 2013, 50(6), 142–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.; Han, F.; Ye, J.; Qiu, W.; Zhang, H.; Gao, X.; Wang, Y; Ji, W.; Gu, X. Spectrum analysis of common inherited metabolic diseases in Chinese patients screened and diagnosed by tandem mass spectrometry. J Clin Lab Anal. 2015, 29(2), 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmonem, M.A.; and van den Heuvel, L.P. Editorial: Newborn Screening for Inborn Errors of Metabolism: Is It Time for a Globalized Perspective Based on Genetic Screening? Front Genet. 2021, 12, 758142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozben, T. Expanded newborn screening and confirmatory follow-up testing for inborn errors of metabolism detected by tandem mass spectrometry. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2013, 51(1), 157–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Champion, M.P. An approach to the diagnosis of inherited metabolic disease. Arch Dis Child Educ Pract Ed. 2010, 95(2), 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, N.; Hasegawa, Y.; Yamada, K.; Kobayashi, H.; Purevsuren, J.; Yang, Y.; Dung, V.C.; Khanh, N.N.; Verma, I.C.; Bijarnia-Mahay, S.; et al. Diversity in the incidence and spectrum of organic acidemias, fatty acid oxidation disorders, and amino acid disorders in Asian countries: Selective screening vs. expanded newborn screening. Mol Genet Metab Rep. 2018, 16, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarker, S.K.; Islam, M.T.; Biswas, A.; Bhuyan, G.S.; Sultana, R.; Sultana, N.; Rakhshanda, S.; Begum, M.N.; Rahat, A.; Yeasmin, S.; et al. Age-Specific Cut-off Values of Amino Acids and Acylcarnitines for Diagnosis of Inborn Errors of Metabolism Using Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Biomed Res Int. 2019, 2019, 3460902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lampret, B.R.; Murko, S.; Tanšek, M.Ž.; Podkrajšek, K.T.; Debeljak, M.; Šmon, A.; Battelino, T. Selective Screening for Metabolic Disorders in the Slovenian Pediatric Population. J Med Biochem. 2015, 34(1), 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietzen, D.J.; Bennett, M.J.; Lo, S.F.; Grey, V.L.; Jones, P.M. Dried Blood Spot Reference Intervals for Steroids and Amino Acids in a Neonatal Cohort of the National Children’s Study. Clin Chem. 2016, 62(12), 1658–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Karnebeek, C.D.; Stockler-Ipsiroglu, S. Early identification of treatable inborn errors of metabolism in children with intellectual disability: The Treatable Intellectual Disability Endeavor protocol in British Columbia. Paediatr Child Health. 2014, 19(9), 469–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwu, W.L.; Chien, Y.H.; Lee, N.C.; Wang, S.F.; Chiang, S.C.; Hsu, L.W. Application of mass spectrometry in newborn screening: about both small molecular diseases and lysosomal storage diseases. Top Curr Chem. 2014, 336, 177–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chace, D.H.; Kalas, T.A. A biochemical perspective on the use of tandem mass spectrometry for newborn screening and clinical testing. Clin Biochem. 2005, 38(4), 296–309, Erratum in: Clin Biochem. 2005, 38(5), 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chace, D.H. Mass spectrometry in newborn and metabolic screening: historical perspective and future directions. J Mass Spectrom. 2009, 44(2), 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, A.M.; Hougaard, D.M.; Simonsen, H.; Andresen, B.S.; Christensen, M.; Dunø, M.; Skogstrand, K.; Olsen, R.K.; et al. Biochemical screening of 504,049 newborns in Denmark, the Faroe Islands and Greenland--experience and development of a routine program for expanded newborn screening. Mol Genet Metab. 2012, 107(3), 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietzen, D.J.; Rinaldo, P.; Whitley, R.J.; Rhead, W.J.; Hannon, W.H.; Garg, U.C.; Lo, S.F.; Bennett, M.J. National academy of clinical biochemistry laboratory medicine practice guidelines: follow-up testing for metabolic disease identified by expanded newborn screening using tandem mass spectrometry; executive summary. Clin Chem. 2009, 55(9), 1615–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharya, K.; Wotton, T.; Wiley, V. The evolution of blood-spot newborn screening. Transl Pediatr. 2014, 3(2), 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lampret, B.R.; Remec, Ž.I.; Torkar, A.D.; Tanšek, M.Ž.; Šmon, A.; Koračin, V.; Čuk, V.; Perko, D.; Ulaga, B.; Jelovšek, A.M.; et al. Expanded Newborn Screening Program in Slovenia using Tandem Mass Spectrometry and Confirmatory Next Generation Sequencing Genetic Testing. Zdr Varst. 2020, 59(4), 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindner, M.; Gramer, G.; Haege, G.; Fang-Hoffmann, J.; Schwab, K.O.; Tacke, U.; Trefz, F.K.; Mengel, E.; Wendel, U.; Leichsenring, M.; et al. Efficacy and outcome of expanded newborn screening for metabolic diseases--report of 10 years from South-West Germany. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2011, 6, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilcken, B.; Haas, M.; Joy, P.; Wiley, V.; Bowling, F.; Carpenter, K.; Christodoulou, J.; Cowley, D.; Ellaway, C.; Fletcher, J.; et al. Expanded newborn screening: outcome in screened and unscreened patients at age 6 years. Pediatrics 2009, 124(2), e241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norman, R.; Haas, M.; Chaplin, M.; Joy, P.; Wilcken, B. Economic evaluation of tandem mass spectrometry newborn screening in Australia. Pediatrics 2009, 123(2), 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 38. Medical Advisory Secretariat. Neonatal screening of inborn errors of metabolism using tandem mass spectrometry: an evidence-based analysis. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser 2003, 3(3), 1–36.
- Schulze, A.; Lindner, M.; Kohlmüller, D.; Olgemöller, K.; Mayatepek, E.; Hoffmann, G.F. Expanded newborn screening for inborn errors of metabolism by electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry: results, outcome, and implications. Pediatrics 2003, 111 Pt 1, 1399–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dionisi-Vici, C.; Deodato, F.; Röschinger, W.; Rhead, W.; Wilcken, B. ‘Classical’ organic acidurias, propionic aciduria, methylmalonic aciduria and isovaleric aciduria: long-term outcome and effects of expanded newborn screening using tandem mass spectrometry. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2006, 29(2-3), 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messina, M.; Meli, C.; Raudino, F.; Pittalá, A.; Arena, A.; Barone, R.; Giuffrida, F.; Iacobacci, R.; Muccilli, V.; Sorge, G.; et al. Expanded Newborn Screening Using Tandem Mass Spectrometry: Seven Years of Experience in Eastern Sicily. Int J Neonatal Screen. 2018, 4(2), 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filiano, J.J.; Bellimer, S.G.; Kunz, P.L. Tandem mass spectrometry and newborn screening: pilot data and review. Pediatr Neurol. 2002, 26(3), 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 43. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). CDC Grand Rounds: Newborn screening and improved outcomes. MMWR. Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2012, 61(21), 390–393.
- Landau, Y.E.; Waisbren, S.E.; Chan, L.M.; Levy, H.L. Long-term outcome of expanded newborn screening at Boston children’s hospital: benefits and challenges in defining true disease. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2017, 40(2), 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khneisser, I.; Adib, S.; Assaad, S.; Megarbane, A.; Karam, P. Cost-benefit analysis: newborn screening for inborn errors of metabolism in Lebanon. J Med Screen. 2015, 22(4), 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, Z.; He, Z.; Yue, A.; Song, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, X.; Sun, R. Expanded newborn screening for inborn errors of metabolism by tandem mass spectrometry in newborns from Xinxiang city in China. J Clin Lab Anal. 2020, 34(5), e23159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Zhou, C.; Xu, P.; Jin, X.; Liu, W.; Wang, W.; Huang, C.; Jiang, M.; Chen, X. Newborn screening and diagnosis of inborn errors of metabolism: A 5-year study in an eastern Chinese population. Clin Chim Acta 2020, 502, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Therrell, B.L.; Padilla, C.D.; Loeber, J.G.; Kneisser, I.; Saadallah, A.; Borrajo, G.J.; Adams, J. Current status of newborn screening worldwide: 2015. Semin Perinatol. 2015, 39(3), 171–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zupic, I.; Čater, T. Bibliometric methods in management and organization. Organ Res Methods 2015, 18(3), 429–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, W.; Bornmann, L. On the causes of subject-specific citation rates in Web of Science. Scientometrics 2015, 102(2), 1823–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, T.H.; Kouropalatis, Y.; Morgan, R.E.; Karhu, P. Mapping knowledge and innovation research themes: Using bibliometrics for classification, evolution, proliferation and determinism. Int J Entrep Innov Manag. [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Costas, R.; Tian, W.; Wang, X.; Wouters, P. An extensive analysis of the presence of altmetric data for Web of Science publications across subject fields and research topics. Scientometrics 2020, 124(3), 2519–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millington, D.S.; Kodo, N.; Terada, N.; Roe, D.S.; Chace, D.H. The analysis of diagnostic markers of genetic disorders in human blood and urine using tandem mass spectrometry with liquid secondary ion mass spectrometry. Int J Mass Spectrom Ion Processes 1991, 111, 211–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aria, M.; Cuccurullo, C. Bibliometrix: An R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. J Informetr. 2017, 11, 959–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics 2010, 84(2), 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zytkovicz, T.H.; Fitzgerald, E.F.; Marsden, D.; Larson, C.A.; Shih, V.E.; Johnson, D.M.; Strauss, A.W.; Comeau, A.M.; Eaton, R.B.; Grady, G.F. Tandem mass spectrometric analysis for amino, organic, and fatty acid disorders in newborn dried blood spots: a two-year summary from the New England Newborn Screening Program. Clin Chem. 2001, 47(11), 1945–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollitt, R.J. International perspectives on newborn screening. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2006, 29(2-3), 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sander, J.; Janzen, N.; Sander, S.; Steuerwald, U.; Das, A.M.; Scholl, S.; Trefz, F.K.; Koch, H.G.; Häberle, J.; Korall, H.; et al. Neonatal screening for citrullinaemia. Eur J Pediatr. 2003, 162(6), 417–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shigematsu, Y.; Hirano, S.; Hata, I.; Tanaka, Y.; Sudo, M.; Sakura, N.; Tajima, T.; Yamaguchi, S. Newborn mass screening and selective screening using electrospray tandem mass spectrometry in Japan. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2002, 776(1), 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, H.R.; Lee, K.R.; Kang, S.; Lee, D.H.; Yoo, H.W.; Min, W.K.; Cho, D.H.; Shin, S.M.; Kim, J.; Song, J.; et al. Screening of newborns and high-risk group of children for inborn metabolic disorders using tandem mass spectrometry in South Korea: a three-year report. Clin Chim Acta 2005, 354(1-2), 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, S.N.; Venugopalan, P. Clinical characteristics of neonates with inborn errors of metabolism detected by Tandem MS analysis in Oman. Brain Dev. 2007, 29(9), 543–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golbahar, J.; Al-Jishi, E.A.; Altayab, D.D.; Carreon, E.; Bakhiet, M.; Alkhayyat, H. Selective newborn screening of inborn errors of amino acids, organic acids and fatty acids metabolism in the Kingdom of Bahrain. Mol Genet Metab. 2013, 110(1-2), 98–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Therrell, B.L. Jr.; Padilla, C.D. Newborn screening in the developing countries. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2018, 30(6), 734–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahai, I.; Zytkowicz, T.; Rao Kotthuri, S.; Lakshmi Kotthuri, A.; Eaton, R.B.; Akella, R.R. Neonatal screening for inborn errors of metabolism using tandem mass spectrometry: experience of the pilot study in Andhra Pradesh, India. Indian J Pediatr. 2011, 78(8), 953–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, I.C.; Bijarnia-Mahay, S.; Jhingan, G.; Verma, J. Newborn screening: need of the hour in India. Indian J Pediatr. 2015, 82(1), 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollitt, R.J. Newborn mass screening versus selective investigation: benefits and costs. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2001, 24(2), 299–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selim, L.A.; Hassan, S.A.; Salem, F.; Orabi, A.; Hassan, F.A.; El-Mougy, F.; Mahmoud, I.G.; El-Badawy, A.; Girgis, M.Y.; Elmonem, M.A.; et al. Selective screening for inborn errors of metabolism by tandem mass spectrometry in Egyptian children: a 5 year report. Clin Biochem. 2014, 47(9), 823–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magdy, R.M.; Abd-Elkhalek, H.S.; Bakheet, M.A.; Mohamed, M.M. Selective screening for inborn errors of metabolism by tandem mass spectrometry at Sohag University Hospital, Egypt. Arch Pediatr. 2022, 29(1), 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Visualizing bibliometric networks. In Measuring scholarly impact: Methods and practice; Ding, Y., Rousseau, R., Wolfram, D., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 285–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millington, D.S.; Kodo, N.; Norwood, D.L.; Roe, C.R. Tandem mass spectrometry: a new method for acylcarnitine profiling with potential for neonatal screening for inborn errors of metabolism. J Inherit Metab Dis. 1990, 13(3), 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naylor, E.W.; Chace, D.H. Automated tandem mass spectrometry for mass newborn screening for disorders in fatty acid, organic acid, and amino acid metabolism. J Child Neurol. 1999, 14 Suppl 1, S4–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashed, M.S.; Özand, P.; Harrison, M.E.; Watkins, P.J.; Evans, S.; Baillie, T.A. Electrospray tandem mass spectrometry in the diagnosis of organic acidemias. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 1994, 8(1), 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashed, M.S.; Özand, P.T.; Bucknall, M.P.; Little, D. Diagnosis of inborn errors of metabolism from blood spots by acylcarnitines and amino acids profiling using automated electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. Pediatr Res. 1995, 38(3), 324–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashed, M.S.; Rahbeeni, Z.; Özand, P.T. Application of electrospray tandem mass spectrometry to neonatal screening. Semin Perinatol. 1999, 23(2), 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfadhel, M.; Benmeake, M.; Hossain, M.A.; Al Mutairi, F.; Al Othaim, A.; Alfares, A.A.; Al Balwi, M.; Alzaben, A.; Eyaid, W. Thirteen year retrospective review of the spectrum of inborn errors of metabolism presenting in a tertiary center in Saudi Arabia. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2016, 11(1), 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirelce, Ö.; Aksungar, F.B.; Saral, N.Y.; Kilercik, M.; Serteser, M.; Unsal, I. Institutional experience of newborn screening for inborn metabolism disorders by tandem MS in the Turkish population. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2020, 33(6), 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomason, M.J.; Lord, J.; Bain, M.D.; Chalmers, R.A.; Littlejohns, P.; Addison, G.M.; Wilcox, A.H.; Seymour, C.A. A systematic review of evidence for the appropriateness of neonatal screening programmes for inborn errors of metabolism. J Public Health Med. 1998, 20(3), 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parini, R.; Corbetta, C. Metabolic screening for the newborn. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2011, 24 Suppl 2, 6–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chace, D.H.; Hillman, S.L.; Van Hove, J.L.; Naylor, E.W. Rapid diagnosis of MCAD deficiency: quantitative analysis of octanoylcarnitine and other acylcarnitines in newborn blood spots by tandem mass spectrometry. Clin Chem. 1997, 43(11), 2106–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcken, B.; Wiley, V. Newborn screening. Pathology 2008, 40(2), 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loukas, Y.L.; Soumelas, G.S.; Dotsikas, Y.; Georgiou, V.; Molou, E.; Thodi, G.; Boutsini, M.; Biti, S.; Papadopoulos, K. Expanded newborn screening in Greece: 30 months of experience. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2010, 33 Suppl 3, S341–S348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensenauer, R.; Vockley, J.; Willard, J.M.; Huey, J.C.; Sass, .J.O.; Edland, S.D.; Burton, B.K.; Berry, S.A.; Santer, R.; Grünert, S.; et al. A common mutation is associated with a mild, potentially asymptomatic phenotype in patients with isovaleric acidemia diagnosed by newborn screening. Am J Hum Genet. 2004, 75(6), 1136–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasquali, M.; Monsen, G.; Richardson, L.; Alston, M.; Longo, N. Biochemical findings in common inborn errors of metabolism. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2006, 142C(2), 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, D.M.; Chien, Y.H.; Chiang, C.C.; Ho, H.C.; Hwu, W.L.; Kao, S.M.; Chiang, S.H.; Kao, C.H.; Liu, T.T.; Chiang, H.; et al. Nationwide survey of extended newborn screening by tandem mass spectrometry in Taiwan. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2010, 33 Suppl 2, S295–S305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.T.; Cai, J.; Wang, Y.Y.; Tu, W.J.; Wang, W.P.; Gong, L.M.; Wang, D.W.; Ye, Y.T.; Fang, S.G.; Jing, P.W. Newborn screening for inborn errors of metabolism in mainland china: 30 years of experience. JIMD Rep. 2012, 6, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, W.E.; Millington, D.S.; Koeberl, D.D.; Lesser, P.S. Glutaric acidemia, type I, missed by newborn screening in an infant with dystonia following promethazine administration. Pediatrics 2001, 107(5), 1184–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.S.; Ye, J.; Qiu, W.J.; Gao, X.L.; Wang, Y.; Gu, X.F. Selective screening for inborn errors of metabolism on clinical patients using tandem mass spectrometry in China: a four-year report. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2007, 30(4), 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Yang, L.; Tong, F.; Yang, R.; Zhao, Z. Screening for inborn errors of metabolism in high-risk children: a 3-year pilot study in Zhejiang Province, China. BMC Pediatr. 2012, 12, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moorthie, S.; Cameron, L.; Sagoo, G.S.; Bonham, J.R.; Burton, H. Systematic review and meta-analysis to estimate the birth prevalence of five inherited metabolic diseases. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2014, 37(6), 889–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fingerhut, R.; Olgemöller, B. Newborn screening for inborn errors of metabolism and endocrinopathies: an update. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2009, 393(5), 1481–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CDC. Using tandem mass spectrometry for metabolic disease screening among newborns. A report of a work group. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2001, 50(RR-3), 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Vist, G.E.; Frønsdal, K.B.; Johansen, M.; Hofmann, B.; Fretheim, A. Newborn Screening for Inborn Errors of Metabolism [Internet]. Oslo, Norway: Knowledge Centre for the Health Services at The Norwegian Institute of Public Health (NIPH), 2007, Report from Norwegian Knowledge Centre for the Health Services (NOKC) No. 22-2007. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK464885/ (accessed on 20 December 2023).
- Lindner, M.; Hoffmann, G.F.; Matern, D. Newborn screening for disorders of fatty-acid oxidation: experience and recommendations from an expert meeting. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2010, 33(5), 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCandless, S.E. A primer on expanded newborn screening by tandem mass spectrometry. Prim Care 2004, 31(3), 583–604,ix-x. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American College of Medical Genetics Newborn Screening Expert Group. Newborn screening: toward a uniform screening panel and system--executive summary. Pediatrics 2006, 117 Pt 2, S296–S307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Lainez, C.; Aguilar-Lemus, J.J.; Vela-Amieva, M.; Ibarra-González, I. Tandem mass spectrometry newborn screening for inborn errors of intermediary metabolism: abnormal profile interpretation. Curr Med Chem. 2012, 19(26), 4511–4522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumgartner, C.; Baumgartner, D. Biomarker discovery, disease classification, and similarity query processing on high-throughput MS/MS data of inborn errors of metabolism. J Biomol Screen. 2006, 11(1), 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasper, D.C.; Ratschmann, R.; Metz, T.F.; Mechtler, T.P.; Möslinger, D.; Konstantopoulou, V.; Item, C.B.; Pollak, A.; Herkner, K.R. The national Austrian newborn screening program - eight years experience with mass spectrometry. past, present, and future goals. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2010, 122(21-22), 607–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitusong, R.; Japaer, R.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Yang, R.L.; Huang, X.L.; Mao, H.Q. Newborn screening in Zhejiang, China. Chin Med J. 2012, 125(4), 702–704. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Harms, E.; Olgemöller, B. Neonatal screening for metabolic and endocrine disorders. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2011, 108(1-2), 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollak, A.; Kasper, D.C. Austrian Newborn Screening Program: a perspective of five decades. J Perinat Med. 2014, 42(2), 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- la Marca, G.; Malvagia, S.; Casetta, B.; Pasquini, E.; Donati, M.A.; Zammarchi, E. Progress in expanded newborn screening for metabolic conditions by LC-MS/MS in Tuscany: update on methods to reduce false tests. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2008, 31 (Suppl. 2), S395–S404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Focardi, M.; Pinchi, V.; Defraia, B.; Gualco, B.; Varvara, G.; Norelli, G.A. Newborn screening of inherited metabolic disorders: the Italian situation. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents 2016, 30(3), 909–914. [Google Scholar]
- Couce, M.L.; Castiñeiras, D.E.; Bóveda, M.D.; Baña, A.; Cocho, J.A.; Iglesias, A.J.; Colón, C.; Alonso-Fernández, J.R.; Fraga, J.M. Evaluation and long-term follow-up of infants with inborn errors of metabolism identified in an expanded screening programme. Mol Genet Metab. 2011, 104(4), 470–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilarinho, L.; Rocha, H.; Sousa, C.; Marcão, A.; Fonseca, H.; Bogas, M.; Osório, R.V. Four years of expanded newborn screening in Portugal with tandem mass spectrometry. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2010, 33 Suppl 3, S133–S138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.P.; Chu, K.L.; Chien, Y.H.; Wei, M.L.; Wu, S.T.; Wang, S.F.; Hwu, W.L. Tandem mass neonatal screening in Taiwan--report from one center. J Formos Med Assoc. 2006, 105(11), 882–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.S.; Tan, E.S.; John, C.M.; Poh, S.; Yeo, S.J.; Ang, J.S.; Adakalaisamy, P.; Rozalli, R.A.; Hart, C.; Tan, E.T.; et al. Inborn Error of Metabolism (IEM) screening in Singapore by electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry (ESI/MS/MS): An 8 year journey from pilot to current program. Mol Genet Metab. 2014, 113(1-2), 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüders, A.; Blankenstein, O.; Brockow, I.; Ensenauer, R.; Lindner, M.; Schulze, A.; Nennstiel, U. screening laboratories in Germany. Neonatal Screening for Congenital Metabolic and Endocrine Disorders–Results From Germany for the Years 2006–2018. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2021, 118(7), 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiekerkoetter, U.; Krude, H. Target Diseases for Neonatal Screening in Germany. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2022, 119(17), 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smon, A.; Repic Lampret, B.; Groselj, U.; Zerjav Tansek, M.; Kovac, J.; Perko, D.; Bertok, S.; Battelino, T.; Trebusak Podkrajsek, K. Next generation sequencing as a follow-up test in an expanded newborn screening programme. Clin Biochem. 2018, 52, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villani, G.R.D.; Albano, L.; Caterino, M.; Crisci, D.; Di Tommaso, S.; Fecarotta, S.; Fisco, M.G.; Frisso, G.; Gallo, G.; Mazzaccara, C.; et al. Hypermethioninemia in Campania: Results from 10 years of newborn screening. Mol Genet Metab Rep. 2019, 21, 100520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruoppolo, M.; Malvagia, S.; Boenzi, S.; Carducci, C.; Dionisi-Vici, C.; Teofoli, F.; Burlina, A.; Angeloni, A.; Aronica, T.; Bordugo, A.; et al. Expanded Newborn Screening in Italy Using Tandem Mass Spectrometry: Two Years of National Experience. Int J Neonatal Screen. 2022, 8(3), 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Rivada, Á.; Palomino Pérez, L.; Ruiz-Sala, P.; Navarrete, R.; Cambra Conejero, A.; Quijada Fraile, P.; Moráis López, A.; Belanger-Quintana, A.; Martín-Hernández, E.; Bellusci, M.; et al. Diagnosis of inborn errors of metabolism within the expanded newborn screening in the Madrid region. JIMD Rep. 2022, 63(2), 146–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, A.; Wang, Q.; Li, H.; Xiang, J.; Wang, B. Expanded Newborn Screening for Inborn Errors of Metabolism by Tandem Mass Spectrometry in Suzhou, China: Disease Spectrum, Prevalence, Genetic Characteristics in a Chinese Population. Front Genet. 2019, 10, 1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, K.; Zhou, X.; Chen, X.; Wu, Y.; Liu, C.; Kong, Q. Expanded Newborn Screening for Inborn Errors of Metabolism and Genetic Characteristics in a Chinese Population. Front Genet. 2018, 9, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, B.; Liu, S.; Yu, B.; Wang, T. Application of Next-Generation Sequencing Following Tandem Mass Spectrometry to Expand Newborn Screening for Inborn Errors of Metabolism: A Multicenter Study. Front Genet. 2019, 10, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Zheng, T.; Zheng, Z.; Lin, W.; Fu, Q. Expanded newborn screening for inherited metabolic disorders and genetic characteristics in a southern Chinese population. Clin Chim Acta 2019, 494, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Gong, L.F.; Zhao, J.Q.; Yang, H.H.; Ma, Z.J.; Liu, W.; Wan, Z.H.; Kong, Y.Y. Inborn errors of metabolism detectable by tandem mass spectrometry in Beijing. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2020, 33(5), 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, K.; Zhu, J.; Yu, E.; Xiang, L.; Yuan, X.; Yao, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, H. Incidence of inborn errors of metabolism detected by tandem mass spectrometry in China: A census of over seven million newborns between 2016 and 2017. J Med Screen. 2021, 28(3), 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; He, J.; He, L.; Zeng, Y.; Huang, X.; Luo, Y.; Li, Y. Spectrum Analysis of Inherited Metabolic Disorders for Expanded Newborn Screening in a Central Chinese Population. Front Genet. 2022, 12, 763222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaku, N.; Ihara, K.; Hirata, Y.; Yamada, K.; Lee, S.; Kanemasa, H.; Motomura, Y.; Baba, H.; Tanaka, T.; Sakai, Y.; et al. Diagnostic potential of stored dried blood spots for inborn errors of metabolism: a metabolic autopsy of medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency. J Clin Pathol. 2018, 71(10), 885–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Liu, X.; Lin, Y. Newborn screening for inborn errors of metabolism in a northern Chinese population. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2023, 36(3), 278–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.J.; Wei, N.; Li, M.; Xie, K.; Li, J.Q.; Huang, C.G.; Xiao, Y.S.; Liu, W.H.; Chen, X.G. Diagnosis and therapeutic monitoring of inborn errors of metabolism in 100,077 newborns from Jining city in China. BMC Pediatr. 2018, 18(1), 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.C.; Mak, C.M.; Lam, C.W.; Yuen, Y.P.; Chan, A.O.; Shek, C.C.; Siu, T.S.; Lai, C.K.; Ching, C.K.; Siu, W.K.; et al. Analysis of inborn errors of metabolism: disease spectrum for expanded newborn screening in Hong Kong. Chin Med J (Engl). 2011, 124(7), 983–989. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Cao, Y.; Luo, F.; Lu, W.; Peng, Y.; Yao, H.; Qiu, P. The screening of inborn errors of metabolism in sick Chinese infants by tandem mass spectrometry and gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Clin Chim Acta 2011, 412(13-14), 1270–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Dai, W.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, X.; Cui, Y. Screening for inherited metabolic diseases using gas chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (GC-MS/MS) in Sichuan, China. Biomed Chromatogr. 2017, 31(4). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.; Chen, D.; Chang, R.; Pan, L.; Yang, J.; Yuan, D.; Huang, L.; Yan, T.; Ning, H.; Wei, J.; Cai, R. Tandem Mass Spectrometry Screening for Inborn Errors of Metabolism in Newborns and High-Risk Infants in Southern China: Disease Spectrum and Genetic Characteristics in a Chinese Population. Front Genet. 2021, 12, 631688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, F.A.; El-Mougy, F.; Sharaf, S.A.; Mandour, I.; Morgan, M.F.; Selim, L.A.; Hassan, S.A.; Salem, F.; Oraby, A.; Girgis, M.Y.; et al. Inborn errors of metabolism detectable by tandem mass spectrometry in Egypt: The first newborn screening pilot study. J Med Screen. 2016, 23(3), 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groselj, U.; Tansek, M.Z.; Smon, A.; Angelkova, N.; Anton, D.; Baric, I.; Djordjevic, M.; Grimci, L.; Ivanova, M.; Kadam, A.; et al. Newborn screening in southeastern Europe. Mol Genet Metab. 2014, 113(1-2), 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rama Devi, A.R.; Naushad, S.M. Newborn screening in India. Indian J Pediatr. 2004, 71(2), 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patial, A.; Saini, A.G.; Kaur, R.; Kapoor, S.; Sharda, S.; Kumar, P.; Singhi, S.; Singhi, P.; Dwivedi, I.; Malik, V.S.; et al. Detection of IEMs by Mass Spectrometry Techniques in High-Risk Children: A Pilot Study. Indian J Pediatr. 2022, 89(9), 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagaraja, D.; Mamatha, S.N.; De, T.; Christopher, R. Screening for inborn errors of metabolism using automated electrospray tandem mass spectrometry: study in high-risk Indian population. Clin Biochem. 2010, 43(6), 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunus, Z.M.; Rahman, S.A.; Choy, Y.S.; Keng, W.T.; Ngu, L.H. Pilot study of newborn screening of inborn error of metabolism using tandem mass spectrometry in Malaysia: outcome and challenges. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2016, 29(9), 1031–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamrakar, A.; Kale, A.; Magar, S.; Kale, A.; Ingale, V.; Shewale, N.; Engade, M.; Shelke, M. Spectrum of Common and Rare Small Molecule Inborn Errors of Metabolism Diagnosed in a Tertiary Care Center of Maharashtra, India. Cureus 2022, 14(7), e27104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla, C.D.; Therrell, B.L. Newborn screening in the Asia Pacific region. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2007, 30(4), 490–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meiouet, F.; El Kabbaj, S.; Abilkassem, R.; Boemer, F. Moroccan Experience of Targeted Screening for Inborn Errors of Metabolism by Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Pediatr Rep. 2023, 15(1), 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcken, B. Newborn screening: how are we travelling, and where should we be going? J Inherit Metab Dis. 2011, 34(3), 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narravula, A.; Garber, K.B.; Askree, S.H.; Hegde, M.; Hall, P.L. Variants of uncertain significance in newborn screening disorders: implications for large-scale genomic sequencing. Genet Med. 2017, 19(1), 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhikari, A.N.; Gallagher, R.C.; Wang, Y.; Currier, R.J.; Amatuni, G.; Bassaganyas, L.; Chen, F.; Kundu, K.; Kvale, M.; Mooney, S.D.; et al. The role of exome sequencing in newborn screening for inborn errors of metabolism. Nat Med. 2020, 26(9), 1392–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojcik, M.H.; Zhang, T.; Ceyhan-Birsoy, O.; Genetti, C.A.; Lebo, M.S.; Yu, T.W.; Parad, R.B.; Holm, I.A.; Rehm, H.L.; Beggs, A.H.; et al.; BabySeq Project Team Discordant results between conventional newborn screening and genomic sequencing in the BabySeq Project. Genet Med. 2021, 23(7), 1372–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Zhong, J.; Le, Y.; Melchior Tellier, L.C.A.; Liu, C.; Jiang, P.; Gao, R.; Wang, Y. Applying targeted next generation sequencing to dried blood spot specimens from suspicious cases identified by tandem mass spectrometry-based newborn screening. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2017, 30(9), 979–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Kuang, J.; Lai, J.; Huang, J.; Wang, Y.; Lan, G.; Xie, Y.; Shi, X. A retrospective analysis of MS/MS screening for IEM in high-risk areas. BMC Med Genomics 2023, 16(1), 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golbahar, J.; Altayab, D.D.; Carreon, E. Short-term stability of amino acids and acylcarnitines in the dried blood spots used to screen newborns for metabolic disorders. J Med Screen. 2014, 21(1), 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strnadová, K.A.; Holub, M.; Mühl, A.; Heinze, G.; Ratschmann, R.; Mascher, H.; Stöckler-Ipsiroglu, S.; Waldhauser, F.; Votava, F.; Lebl, J.; Bodamer, O.A. Long-term stability of amino acids and acylcarnitines in dried blood spots. Clin Chem. 2007, 53(4), 717–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimada, Y.; Kawano, N.; Goto, M.; Watanabe, H.; Ihara, K. Stability of amino acids, free and acyl-carnitine in stored dried blood spots. Pediatr Int. 2022, 64(1), e15072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Rijt, W.J.; Schielen, P.C.J.I.; Özer, Y.; Bijsterveld, K.; van der Sluijs, F.H.; Derks, T.G.J.; Heiner-Fokkema, M.R. Instability of Acylcarnitines in Stored Dried Blood Spots: The Impact on Retrospective Analysis of Biomarkers for Inborn Errors of Metabolism. Int J Neonatal Screen. 2020, 6(4), 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Morillo, E.; Prieto García, B.; Álvarez Menéndez, F.V. Challenges for Worldwide Harmonization of Newborn Screening Programs. Clin Chem. 2016, 62(5), 689–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabie, N.A.V.; Pappas, K.B.; Feldman, G.L. The Current State of Newborn Screening in the United States. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2019, 66(2), 369–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajares, S.; Arranz, J.A.; Ormazabal, A.; Del Toro, M.; García-Cazorla, Á.; Navarro-Sastre, A.; López, R.M.; Meavilla, S.M.; de Los Santos, M.M.; García-Volpe, C.; et al. Implementation of second-tier tests in newborn screening for the detection of vitamin B12 related acquired and genetic disorders: results on 258,637 newborns. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2021, 16(1), 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarra-González, I.; Rodríguez-Valentín, R.; Lazcano-Ponce, E.; Vela-Amieva, M. Metabolic screening and metabolomics analysis in the Intellectual Developmental Disorders Mexico Study. Salud Publica Mex. 2017, 59(4), 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Céspedes, N.; Valencia, A.; Echeverry, C.A.; Arce-Plata, M.I.; Colón, C.; Castiñeiras, D.E.; Hurtado, P.M.; Cocho, J.A.; Herrera, S.; Arévalo-Herrera, M. Reference values of amino acids, acylcarnitines and succinylacetone by tandem mass spectrometry for use in newborn screening in southwest Colombia. Colomb Med (Cali) 2017, 48(3), 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Márquez-Caraveo, M.E.; Ibarra-González, I.; Rodríguez-Valentín, R.; Ramírez-García, M.Á.; Pérez-Barrón, V.; Lazcano-Ponce, E.; Vela-Amieva, M. Brief Report: Delayed Diagnosis of Treatable Inborn Errors of Metabolism in Children with Autism and Other Neurodevelopmental Disorders. J Autism Dev Disord. 2021, 51(6), 2124–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wajner, M.; Sitta, A.; Kayser, A.; Deon, M.; Groehs, A.C.; Coelho, D.M.; Vargas, C.R. Screening for organic acidurias and aminoacidopathies in high-risk Brazilian patients: Eleven-year experience of a reference center. Genet Mol Biol. 2019, 42(1 suppl 1), 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, C.R.; Ribas, G.S.; da Silva, J.M.; Sitta, A.; Deon, M.; de Moura Coelho, D.; Wajner, M. Selective Screening of Fatty Acids Oxidation Defects and Organic Acidemias by Liquid Chromatography/tandem Mass Spectrometry Acylcarnitine Analysis in Brazilian Patients. Arch Med Res. 2018, 49(3), 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiboonboon, K.; Leelahavarong, P.; Wattanasirichaigoon, D.; Vatanavicharn, N.; Wasant, P.; Shotelersuk, V.; Pangkanon, S.; Kuptanon, C.; Chaisomchit, S.; Teerawattananon, Y. An Economic Evaluation of Neonatal Screening for Inborn Errors of Metabolism Using Tandem Mass Spectrometry in Thailand. PLoS ONE 2015, 10(8), e0134782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howson, C.P.; Cedergren, B.; Giugliani, R.; Huhtinen, P.; Padilla, C.D.; Palubiak, C.S.; Santos, M.D.; Schwartz, I.V.D.; Therrell, B.L.; Umemoto, A.; Wang, J.; Zeng, X.; et al. Universal newborn screening: A roadmap for action. Mol Genet Metab. 2018, 124(3), 177–183, Erratum in: Mol Genet Metab. 2019, 127(3), 216–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Country | Total Citations | Average Article Citations |
|---|---|---|
| USA | 6,057 | 54.60 |
| Germany | 1,486 | 53.10 |
| Australia | 1,266 | 70.30 |
| China | 1,236 | 16.30 |
| Saudi Arabia | 971 | 69.40 |
| Italy | 616 | 28.00 |
| Austria | 577 | 57.70 |
| United Kingdom | 562 | 37.50 |
| Netherlands | 379 | 42.10 |
| Japan | 279 | 18.60 |
| Rank | Author | Articles / % of 451 |
Articles Fractionalized | Total number of citations | H- index | G- index | M- index | Publishing since |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Matern D. | 14 (3.104%) | 2.72 | 865 | 11 | 14 | 0.5 | 2002 |
| 2 | Hoffmann G.F. | 13 (2.882%) | 1.65 | 1,024 | 12 | 13 | 0.545 | 2002 |
| 3 | Vockley J. | 13 (2.882%) | 2.27 | 528 | 10 | 13 | 0.455 | 2002 |
| 4 | Wang Y. | 12 (2.661%) | 1.66 | 136 | 5 | 11 | 0.294 | 2007 |
| 5 | Chace D.H. | 11 (2.439%) | 4.45 | 1,103 | 11 | 11 | 0.333 | 1991 |
| 6 | Wilcken B. | 10 (2.217%) | 1.68 | 1,372 | 10 | 10 | 0.455 | 2002 |
| 7 | Chien Y.H. | 9 (1.996%) | 0.83 | 610 | 8 | 9 | 0.444 | 2006 |
| 8 | Hwu W.L. | 9 (1.996%) | 0.85 | 621 | 9 | 9 | 0.5 | 2006 |
| 9 | La Marca G. | 9 (1.996%) | 1.82 | 625 | 8 | 9 | 0.471 | 2007 |
| 10 | Mak C.M. | 9 (1.996%) | 1.10 | 185 | 6 | 9 | 0.462 | 2011 |
| Rank | Journal | N of Publications / % of 451 | Total N of citations | H-index | G-index | M-index | Publishing since |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Molecular Genetics and Metabolism | 41 (9.09) | 1,226 | 23 | 34 | 1.045 | 2002 |
| 2 | Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease | 24 (5.32) | 1,397 | 21 | 24 | 0.808 | 1998 |
| 3 | Clinical Chemistry | 18 (3.99) | 1,865 | 15 | 18 | 0.556 | 1997 |
| 4 | Clinica Chimica Acta | 18 (3.99) | 619 | 14 | 18 | 0.609 | 2001 |
| 5 | International Journal of Neonatal Screening | 14 (3.10) | 88 | 7 | 8 | 1.167 | 2018 |
| 6 | Clinical Biochemistry | 13 (2.88) | 368 | 9 | 13 | 0.375 | 2000 |
| 7 | Pediatrics | 13 (2.88) | 1,054 | 12 | 13 | 0.522 | 2001 |
| 8 | Journal of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism | 12 (2.66) | 89 | 6 | 9 | 0.545 | 2013 |
| 9 | Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry | 11 (2.44) | 360 | 10 | 11 | 0.333 | 1994 |
| 10 | Frontiers in Genetics | 9 (1.99) | 85 | 4 | 9 | 0.667 | 2018 |
| 11 | Journal of Medical Screening | 8 (1.77) | 112 | 6 | 8 | 0.6 | 2014 |
| 12 | Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases | 8 (1.77) | 279 | 6 | 8 | 0.462 | 2011 |
| 13 | Analytical Chemistry | 6 (1.33) | 194 | 6 | 6 | 0.4 | 2009 |
| 14 | Genetics in Medicine | 6 (1.33) | 490 | 6 | 6 | 0.333 | 2006 |
| 15 | Indian Journal of Pediatrics | 6 (1.33) | 78 | 5 | 6 | 0.385 | 2011 |
| Rank | Article Title | Journal | Year | First Author | Total Cita- tions |
TC per Year | Norma-lized TC | Local Cita- tions |
LC/GC Ratio (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Screening newborns for inborn errors of metabolism by tandem mass spectrometry |
New England Journal of Medicine | 2003 | Wilcken, B | 483 | 23.0 | 4.66 | 130 | 5.48 |
| 2 | Tandem mass spectrometric analysis for amino, organic, and fatty acid disorders in newborn dried blood spots: A two-year summary from the New England newborn screening program |
Clinical Chemistry |
2001 | Zytkovicz, TH | 394 | 17.13 | 3.56 | 83 | 21.07 |
| 3 | Expanded newborn screening for inborn errors of metabolism by electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry: Results, outcome, and implications |
Pediatrics |
2003 | Schulze, A | 355 | 16.90 | 3.42 | 117 | 32.96 |
| 4 | Current status of newborn screening worldwide: 2015 |
Seminars in Perinatology | 2015 | Therrell, BL | 329 | 36.56 | 8.30 | 36 | 10.94 |
| 5 | Diagnosis of inborn-errors of metabolism from blood spots by acylcarnitines and amino-acids profiling using automated electrospray tandem mass spectrometry | Pediatric Research |
1995 | Rashed, MS | 277 | 9.55 | 1.00 | 55 | 19.86 |
| 6 | Clinical validation of cutoff target ranges in newborn screening of metabolic disorders by tandem mass spectrometry: A worldwide collaborative project |
Genetics in Medicine |
2011 | McHugh, DMS | 253 | 19.46 | 5.73 | 52 | 2.55 |
| 7 | Effect of expanded newborn screening for biochemical genetic disorders on child outcomes and parental stress |
Jama - Journal of the American Medical Association | 2003 | Waisbren, SE | 253 | 12.05 | 2.44 | 40 | 15.81 |
| 8 | Rapid diagnosis of MCAD deficiency: quantitative analysis of octanoylcarnitine and other acylcarnitines in newborn blood spots by tandem mass pectrometry |
Clinical Chemistry |
1997 | Chace, DH | 233 | 8.63 | 1.01 | 43 | 18.45 |
| 9 | Screening blood spots for inborn errors of metabolism by electrospray tandem mass spectrometry with a microplate batch process and a computer algorithm for automated flagging of abnormal profiles |
Clinical Chemistry |
1997 | Rashed, MS | 229 | 8.48 | 0.99 | 44 | 19.21 |
| 10 | Neonatal screening for lysosomal storage disorders: feasibility and incidence from a nationwide study in Austria |
Lancet |
2012 | Mechtler, TP | 205 | 17.08 | 6.85 | 8 | 3.90 |
| 11 | Natural history, outcome, and treatment efficacy in children and adults with glutaryl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency | Pediatric Research |
2006 | Koelker, S | 197 | 10.94 | 2.68 | 9 | 4.57 |
| 12 | Electrospray tandem mass spectrometry for analysis of acylcarnitines in dried postmortem blood specimens collected at autopsy from infants with unexplained cause of death |
Clinical Chemistry |
2001 | Chace, DH | 192 | 8.32 | 1.74 | 46 | 23.96 |
| 13 | The tandem mass spectrometry newborn screening experience in North Carolina: 1997-2005 |
Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease | 2006 | Frazier, DM | 154 | 8.56 | 2.10 | 61 | 39.61 |
| 14 | Disorders of mitochondrial long-chain fatty acid oxidation and the carnitine shuttle |
Reviews in Endocrine & Metabolic Disorders | 2018 | Knottnerus, SJG | 151 | 25.17 | 5.44 | 0 | 0 |
| 15 | Untargeted metabolomic analysis for the clinical screening of inborn errors of metabolism |
Journal of Inherited Metabolic Disease | 2015 | Miller, MJ | 148 | 16.44 | 3.73 | 8 | 5.41 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





