1. Introduction
Apocynaceae is a family of plants that includes the herb
Gymnema spp. It is extensively dispersed in tropical and subtropical areas of Asia and Africa, and currently, more than 50 species are listed [
1].
Gymnema inodorum, a medicinous plant locally known as Chiang-da in Northern Thailand [
2], has a wide range of therapeutic uses. In northern Thailand, Chiang-da is mainly used as a vegetable for cooking and as a key botanical ingredient in various dishes, undergoing essential preparation methods like boiling and stir-frying. It is also air-dried for tea production, especially in the countryside. Traditionally, it has been used for treating diabetes and obesity. Because of the plant’s numerous therapeutic benefits, including its possible antioxidant action, Ayurvedic medicine has since long been used [
3].
G. sylvestre, a common gymnema species found in Asia, has been extensively researched for its antioxidant and medicinal properties [
4]. Many studies have reported the medical usage of this species. This gymnema species is also studied for potential phytoconstituents, including triterpene saponins known as gymnemic acids, gymnemasaponins, and polyphenols [
5].
G.
inodorum, share genus with
G. sylvestre and same niche. However, despite its frequently grown in the same regions of
G. sylvestre, G.
inodorum has received relatively less attention. Research has demonstrated that
G. inodorum extract possesses glucose absorption inhibiting properties, with gymnemic acids being its primary constituent [
6]. Further,
G. inodorum leaf extracts contain gymnemic acid and ginsenosides responsible for antifungal and antioxidant activity [
7]. Additionally,
G. inodorum has been investigated for phytoconstituents and gymnemic acid is believed as one of the potential phytochemicals act as a blood sugar regulator [
8,
9] along with antimalarial properties [
10].
Plants' phenolic chemicals have been suggested to be the source of their antioxidant action [
11]. Phenolic compounds have been extensively researched due to their non-toxic nature, efficacy at low concentrations across various biological activities, eco-friendly extraction methods at low cost, showcase diverse pharmacological benefits [
12]. They exhibit potent antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory properties, and robust inhibition against cardiovascular diseases, cancer, and diabetes [
13]. Phytochemicals have been widely utilized in healthcare and studied for their antioxidant potential, reactive ability of compounds to stop the oxidation of free radicals [
14]. Exploration into extracting antioxidants from plant tissues has garnered significant interest due to their natural availability and cost efficiency. Enhancing foods, beverages, or medicinal items with additional antioxidants presents a promising approach to mitigating the adverse impacts of oxidative stress [
15]. The limited prior research on the active polyphenols of
G. inodorum responsible for antioxidant activity underscores the importance of our current study.
As far as we know our study is the first to explore fractions of
G. inodorum extract because most literature received is of crude extract. The crude extract provides limited information about phenols activity and fractionation is done to enhance the activity of extract as well as to identify the essential phenols responsible for higher activity. Hence, the screening and investigation of the
G. inodorum extract, which bears a resemblance to the well-known
G. sylvestre, along with limited information on its phenolic profile, becomes imperative. The detection and measurement of phenolic compounds in the leaf extract of
G. inodorum can shed light on the compound's potential health benefits, as phenolic compounds have considerable antioxidant qualities [
16].
Various extraction methods have been studied for the purification of phytoconstituents, but gymnema leaf contains various other compounds, creating difficulty in screening specific phytochemicals. An additional column separation technique was applied to overcome this shortcoming and find targeted polyphenols, which assisted in screening polyphenols in gymnema leaf extract.
The primary objective of this study was to investigate the phenolic profile and antioxidant activity of G. inodorum leaf extract. The study focused on specific column separation technique for fractionation of crude extract to find out potential phenolic compounds, for the analysis of antioxidant capacity, as well as quantification of the total phenolic compounds, total flavonoid contents, and gymnemic acid levels. The results support the plant's potential polyphenols as specific phytochemical constituents in the extract and antioxidant potential, highlighting the prospective use in pharmaceutical and nutraceutical applications.
2. Results
The preliminary screening of ethanol reflux extract based on Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC) indicated active compounds in the G. inodorum leaf extract. The active compounds in the extract were separated on the TLC plate and compared with the Rf values of employed standards (Quercetin, Gallic Acid, Caffeine, and Trolox). The column chromatographic fractionation of crude extract yielded 12 fractions in the best-suited solvent system of TLC as a mobile phase and silica gel as a stationary phase. The 12 fractions were assessed by using a UV spectrophotometer and produced 3 pool fractions based on UV absorbance values. Newly named as Fraction A (fraction 1 - 4 of column chromatography), Fraction B (fraction 5 – 10), and Fraction C (fraction 11 – 12).
The phenolic and flavonoid content of the three fractions derived from the leaf extract of
G. inodorum were examined. The
G. inodorum leaf extract’s total phenolic content revealed that fraction A has the highest phenolic content at 0.294 ± 0.056 mg QE/mL, followed by fraction C (0.227 ± 0.041 mg QE/mL) and fraction B (0.085 ± 0.039 mg QE/mL), as shown in (
Table 1).
The analysis of total flavonoid content in the fractions of
G. inodorum found that fraction C has the highest flavonoid content at 0.384 ± 0.007 mg QE/mL, followed by fraction B and A (0.309 ± 0.110 mg QE/mL, 0.274 ± 0.050 mg QE/mL), respectively (
Table 1).
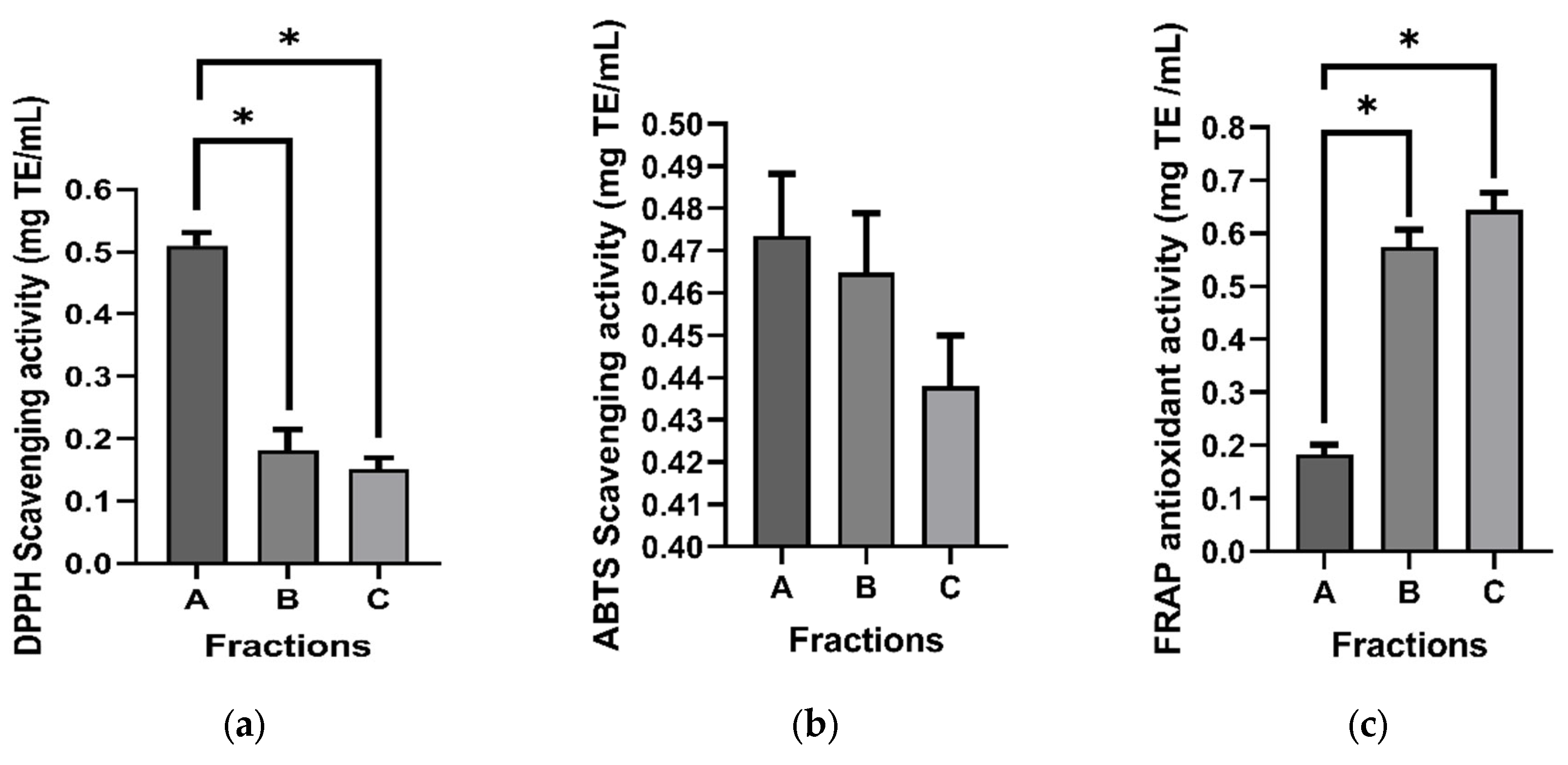
The antioxidant activity of the three fractions received from the leaf extract of G. inodorum was assessed by employing DPPH, ABTS, and FRAP assays. In the DPPH assay, it was observed that fraction A exhibited the most pronounced antioxidant activity (71.25 ± 3.15 mg TE/mL), followed by fraction B (31.57 ± 6.42 mg TE/mL), with the lowest activity observed in fraction C (27.92 ± 3.64 mg TE/mL).
Likewise, the ABTS assay yielded results indicating that fraction A displayed the highest radical scavenging activity (95.45 ± 0.89 mg TE/mL), closely followed by fraction B (93.46 ± 1.43 mg TE/mL), whereas fraction C demonstrated activity of a comparable magnitude (87.29 ± 0.45 mg TE/mL).
Conversely, the assessment of reducing properties using the FRAP assay unveiled that fraction C exhibited the most robust antioxidant activity (2.97 ± 0.25 mg TE/mL). In comparison, fractions B and A demonstrated considerably lower ferric ion reducing power (2.65 ± 0.26 mg TE/mL and 0.85 ± 0.14 mg TE/mL, respectively) (
Figure 1).
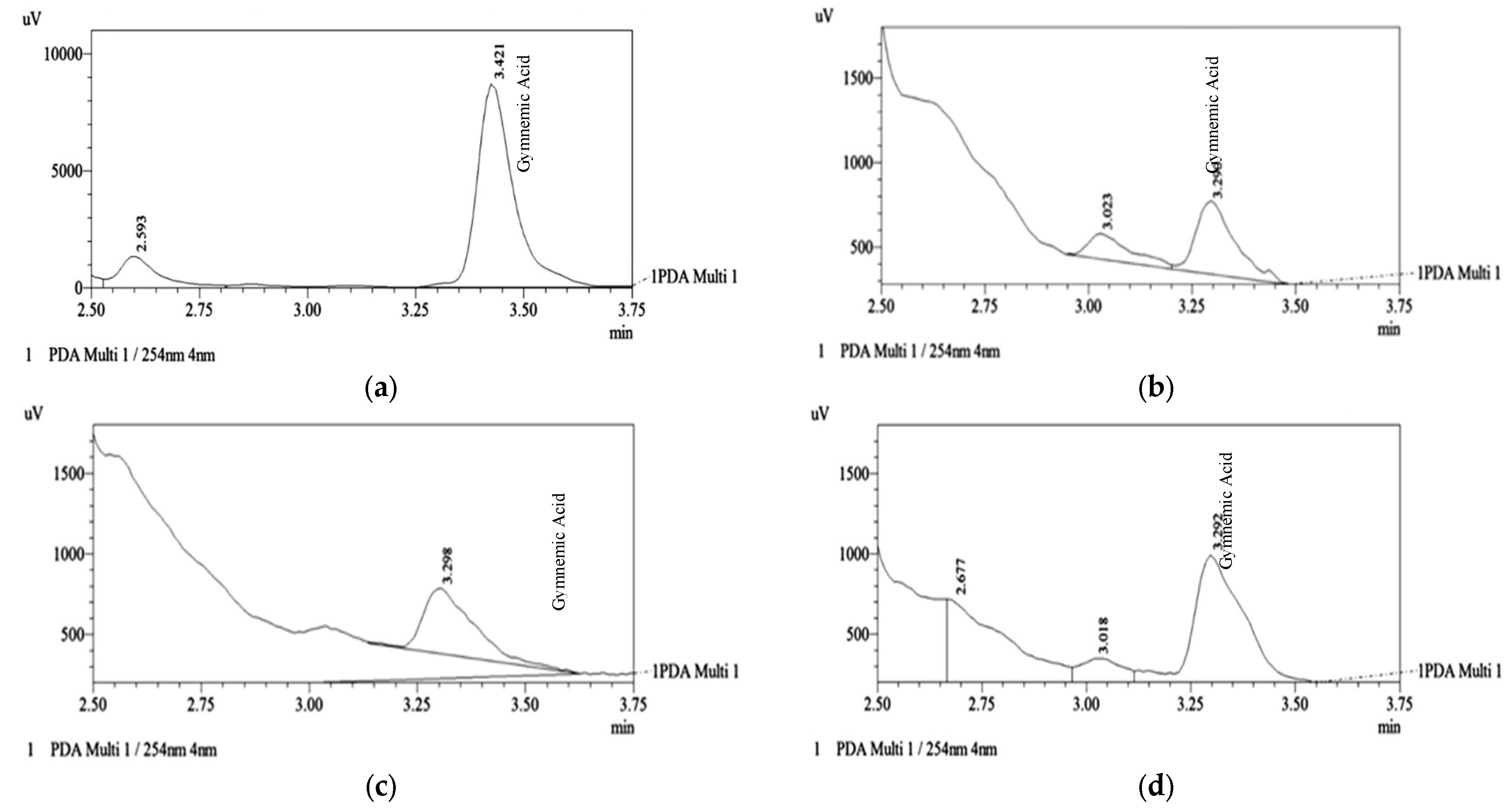
The three fractions were analyzed through HPLC with C18 column to quantify the Gymnemic acid level. After analyzing the sample, fraction C showed the highest gymnemic acid concentration at 0.393 ± 0.003 mg/g, followed by fractions B and A at 0.159 ± 0.003 mg/g and 0.142 ± 0.000 mg/g, respectively (
Table 2). The HPLC-C18 chromatogram in
Figure 2 shows the extract's standard and gymnemic acid peaks.
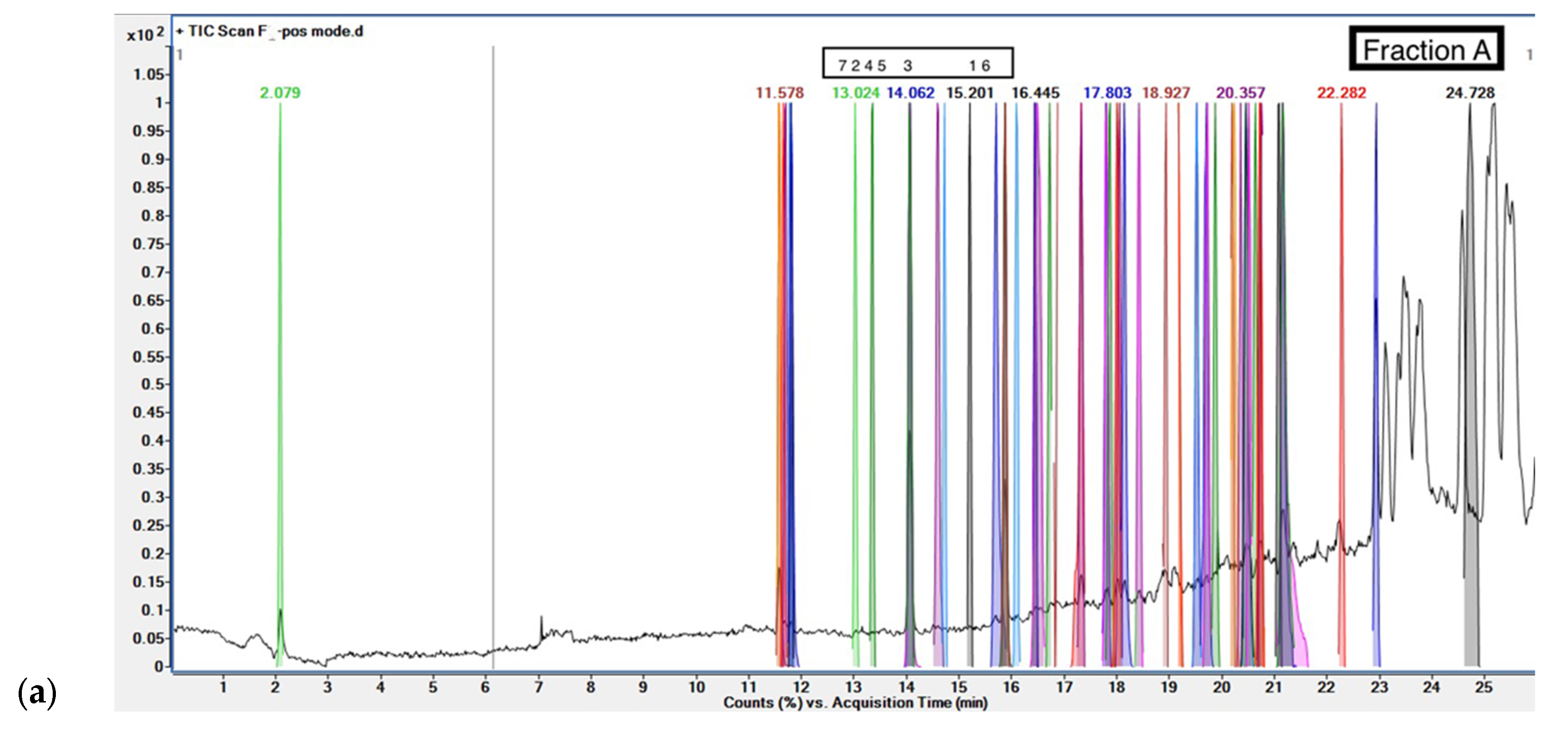
Phenolic compounds were screened in fractions of
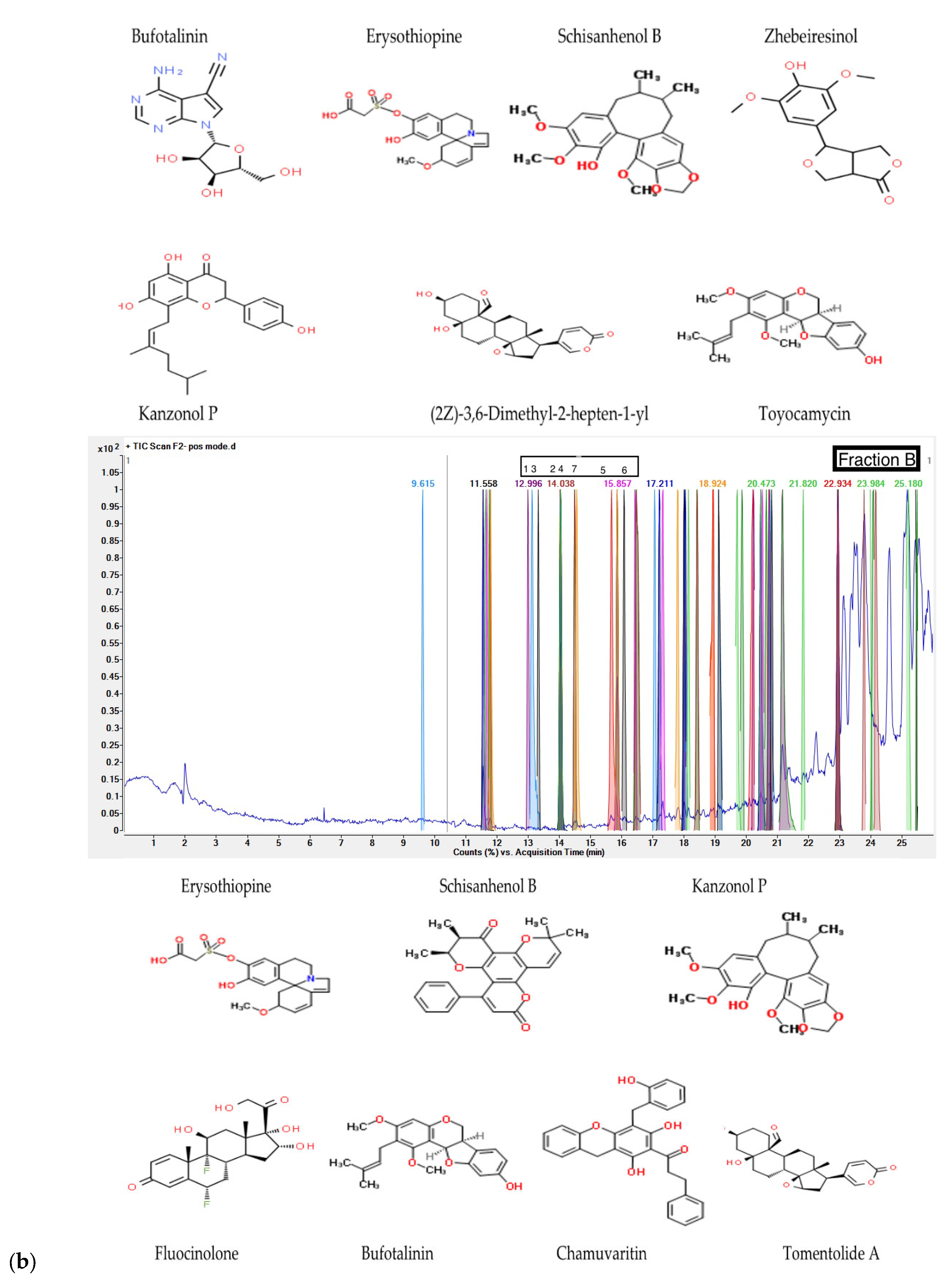
G. inodorum leaf reflux extract by LC-QTOF/MS. The LC-QTOF/MS analyses revealed phytochemical compounds in fractions. From the LC-QTOF/MS result for each fraction, the compounds were analyzed for active phenolic compound screening and the database EMBL – EBI and ChemSpider by Royal Society of Chemistry was used to authenticate the compounds. Fraction A identified Bufotalinin, Erysothiopine, Schisanhenol B, Zhebeiresinol, Kanzonol P, 8-[(2Z)-3,6-Dimethyl-2-hepten-1-yl]-5,7-dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2,3-dihydro-4H-chromen-4-one, and Toyocamycin as a phenolic compounds; other potential antioxidants listed include fatty acids and drugs. The fraction B of
G. inodorum leaf reflux extract showed seven phenolic compounds including Erysothiopine, Schisanhenol B, Kanzonol P, Fluocinolone, Bufotalinin, Chamuvaritin and Tomentolide A in the active compounds. The 6 H Reflux extract of
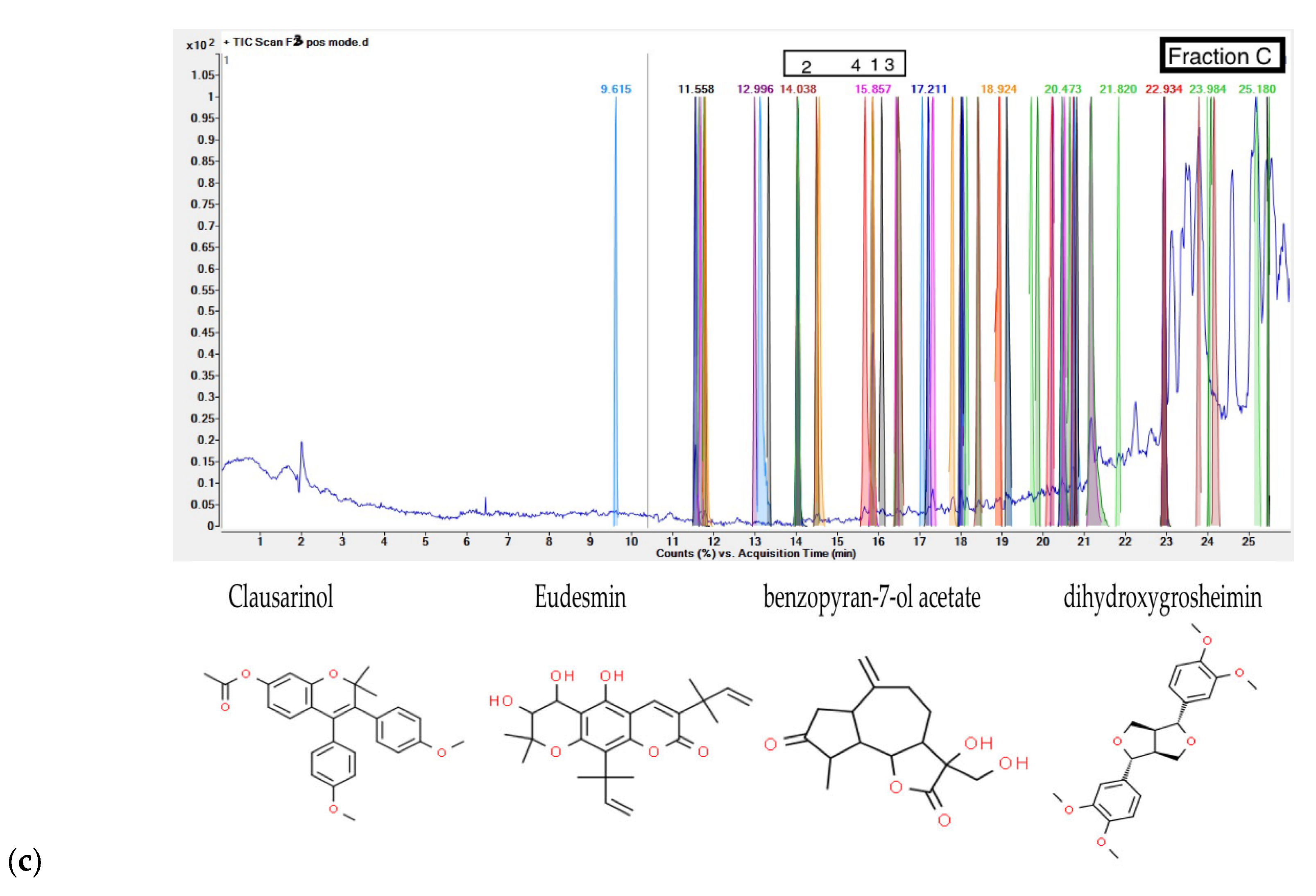
G. inodorum leaf, fraction C, screened for four potential phenolic compounds, namely 2,2-Dimethyl-3,4-bis(4-methoxyphenyl)-2H-1-benzopyran-7-ol acetate, Clausarinol, Psilostachyin, and Eudesmin. The catalog of these phenolic compounds is mentioned in
Table 3. The Phenolic compounds in a fraction of
G. inodorum leaf identified by LC-QTOF/MS, and
Figure 3 shows chromatograms for LC-QTOF/MS of phenolic compounds.
3. Discussion
This investigation studied different methods for determining the antioxidant potential, screening phenolic compounds, and analyzing the gymnemic acid level using other compound extraction laboratory techniques. Column chromatography and thin-layer chromatography have been used to detect and separate active compounds in the extract [
17]. Our results suggest that column separation is a good technique for obtaining the active compound in the extract. Interestingly, preliminary thin-layer chromatography results were similar for column separation, which facilitated selecting the solvents for the best separation of fractions.
Various phenolic classes of Apocynaceae family have attracted significant interest due to their physiological roles, encompassing activities such as scavenging free radicals, preventing mutations, inhibiting carcinogenesis, and reducing inflammation [
18]. The antioxidative efficacy of phenolic compounds is primarily due to their redox properties, enabling them to function as reducing agents, hydrogen donors, quenchers of singlet oxygen, and potential metal chelators [
19].
Further, based on the results, a notably elevated concentration of phenolic compounds was detected in the fractions of column separation reflux extract obtained from the leaves of
G. inodorum as compared to 0.0021 mg/g of crude extract documented by Jeytawan, N. et al [
8]. This finding could provide a scientific basis for the extensive historical utilization of this plant in traditional folk medicine practices as well as evidence for high antioxidant activity.
The antioxidant activities of the phytochemical compounds are essential to scavenging free radicals and have a beneficial effect against oxidative-related disorders [
20]. Many studies have reported that plant extracts' bioactive compound possesses a strong antioxidative capacity, possibly enhancing human health [
21]. The DPPH assay has been employed for radical scavenging activity that revealed the antioxidant activity of each fraction. This assay revealed that the separation of fractions via column chromatography showed increased radical scavenging activity of the DPPH radical, which may indicate an increased ability of purified compounds in fractions to donate hydrogen ions [
22]. Therefore, it may be postulated that fraction A of
G. inodorum leaf extract contains higher potent DPPH and ABTS radical scavenging activity due to abundant purified phytochemicals that reduce the radical due to their hydrogen-reducing ability. However, fraction B and C show lower capacity to scavenge such radicals, which may be due to the compound's light affinity, temperature, and solubility of extracts in the solvent system, which were reported as factors affecting the capacity of compounds to quench the radical [
23].
The antioxidant capacity evaluated by ABTS assay [
24] revealed that fraction A has high ABTS
+ radical scavenging activity as the same level as Trolox standard at 1 mg/mL concentration. This indicated the capability of active compounds in the extract to scavenge free radicals, indicating the potential presence of specific phenolic compounds within the extract that may be useful as therapeutic agents for mitigating pathological damage associated with radicals.
The FRAP assay measures the antioxidative capacity of an antioxidant by its reaction with a ferric tripyridyltriazine (Fe
3+-TPTZ) complex, resulting in the formation of a colored ferrous tripyridyltriazine (Fe
2+-TPTZ) product [
25]. Based on the FRAP assay results, fraction C has reported the highest antioxidant activity with inversely trend to DPPH and ABTS results. It may be due to the higher concentration of antioxidant compound in fraction A are more favorable to DPPH and ABTS regent. On the other hands, antioxidant activity of compounds in FRAP assay involves the reduction of ferric to ferrous ion by donating electrons to antioxidants instead of directly scavenged free radicals [
26]. Our results are supported by a previous study on
G. inodorum for high antioxidant activity in crude extract [
27].
The results for quantification of gymnemic acid level in each fractions were 0.1417 ± 0.000 mg/g, 0.1591 ± 0.003 mg/g and 0.3933 ± 0.003 mg/g for fraction A, B, and C, respectively. The gymnemic acid quantities observed in these fractions, as reported in this study, surpass the previously recorded value of 0.0194 mg/g gymnemic acid in crude
G. inodorum extract. This elevation holds true across various extraction methods [
28], and is supported our applied column chromatography method for separation of active compounds in
G. inodorum leaf extract. Furthermore, the extraction method's efficiency is bolstered by the determination of high gymnemic acid levels.
The current study has shown that the fractions of
G. inodorum leaf extract contains high concentrations of phenols and flavonoids as active compounds; thus, it is inferred that these active compounds are responsible for high antioxidant activity [
29]. The correlation between antioxidant activity and total phenolic contents of
G. inodorum extract is consistent with several reports. The antioxidant activity of fractions revealed that the fractions have higher activity as compared to crude extract. The previous study [
30] has published 0.13506 mg TE/g as the highest DPPH antioxidant activity for
G. inodorum leaf extract, which is lower in comparison to the activity of our fractionated extracts. Furthermore, the fractionation showed better activity for FRAP and ABTS as compared to crude extract. Moreover the results showed the connection between the total phenolic contents of the fractions of
G. inodorum leaf extract and the antioxidant activity as assessed by the DPPH or ABTS assay. The findings demonstrated a direct relationship between total phenolic levels and DPPH (r
2 = 0.69) radical scavenging activity also same relation was found between gymenmic acid level and FRAP activity (r
2 = 0.66). Both the DPPH and FRAP tests indicated the high antioxidant capacity of the fractions with high total phenolic contents and gymnemic acid respectively. Therefore, the fractions of
G. inodorum leaf extract have considerable phenolic compounds with antioxidant properties.
Interestingly, LC-QTOF/MS analysis results supported that, fractions with higher phenolic compound contents showed greater antioxidant activity. There may be a relationship between phenolic compounds and bioactivity, particularly in terms of scavenging free radicals, as evidenced by the higher quantities of these compounds found in fractions with increased antioxidant activity. Nonetheless, a thorough statistical analysis that definitively establishes this association can support the study's conclusions even more and call for further investigation in the future. The difference in concentration of phenolics and flavonoids was reported by other gymnema studies [
31]. Moreover, the screened active phenolic compound, Schisanhenol B was found in Schisandra chinensis and magnolia vine or five-flavor berry, which had never been previously reported as the active phenolic compounds in
G. inodorum leaf extract. These active compounds have been shown to have an antioxidative effect in human low-density lipoprotein [
32]. Among the identified phenolic compounds, Zhebeiresinol a phenolic lignan has potential health benefits, including antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties [
33]. The compound Fluocinolone has been studied for treating localized psoriasis [
34]. Furthermore Eudesmin is found in LC-QTOF/MS result, which is natural phenolic lignan having specific antioxidant and anti-inflammatory potential [
35], while Clausarinol, Chamuvaritin and To-mentolide A seemed to be a new compounds with limited or no prior study. The consumption of this plant may play a vital role due to active phenolic compounds for various disease treatments such as diabetes, hyperglycemia, and premature aging. Nevertheless, additional antioxidant potential in vivo models and various antioxidant mechanisms should be comprehensively studied.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Regents
The solvent methanol, chloroform, acetonitrile, Chemicals and gymnemic acid standard of analytical grade (AR) were obtained from Sigma Chemical Company (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis MO, USA).
4.2. Plant Material and Prepartion of Extract
The shoot and the first three pairs of
G. inodorum leaves were harvested from Sanmahaphon Organic Herbs Community Enterprise, Chiang-da Garden, Chiang Mai, Thailand. Subsequently, the leaves were meticulously purified and air-dried. The dried leaves were ground and sieved through a sieve shaker using 60-mesh sieve size to yield the particle size 250 μm. The dried leaves were finely powdered, and 10 grams of this powdered material from
G. inodorum was packed into a cellulose thimble. Next, a 95 percent ethanol solution (100 mL) was added to the thimble at a ratio of 1:10 (weight to volume). The extraction process was performed thrice at 80 °C using an automatic Soxhlet extractor, each running for 2 hours. After this extraction, the resulting solution was subjected to evaporation using a rotary evaporator to yield the crude extract. Subsequently, the extract was desiccated in a chemical hood, reweighed, and stored at 4°C for further analysis [
36].
4.3. Column Chromatographic Fractionation of Extract
The crude extract was subject to column chromatography for fraction separation using slurry method for column packing. 20 g of Silica gel 60 was packed into transparent (80 cm long, 5 cm diameter) glass column, as a stationary adsorbent without introducing air bubbles along with petroleum ether and methanol (2:1) as mobile phase in the column. The column was passed with the mobile phase before adding silica slurry, and then the mobile phase was gradually increased to develop a packed solid column. Subsequently 2 g of crude extract was added from top without disturbing the solid phase. Sea sand was used to settle the layers properly, separating the crude extract and mobile phase. After proper layer formation between the sample and mobile phase, the stopcock was opened to run the mobile phase down through column. The mobile solvent was gradually added to column to develop gradient elution. Fractions of the extract were received 4 ml, each with specific time interval. 12 fractions were collected in glass tubes with a flow rate of 0.99 mL/min [
37]. The 12 fractions were pooled on the basis of absorbance and the final 3 fractions were passed through rotary evaporator to remove the organic solvent, followed by lyophilization to dry for further analysis.
4.4. Phytochemical Analysis
The fresh fractions extract was analyzed for detecting phytochemicals, Total phenolic content (TPC) and total flavonoid content (TFC) through spectroscopy.
4.4.1. Total Phenolic Content
Quantitative analysis of phenolic content was analyzed using the Folin-Ciocalteu colorimetric method [
38], using Quercetin as the standard reference. To perform the analysis, a mixture of 20 µL of
G. inodorum fraction extract and 20 µL of the diluted (10 times in distilled water) Folin-Ciocalteu solution was prepared. The mixture was then combined with 80 µL of 7% Na₂CO₃ and 200 µL of DW. The plate was observed for any turbidity, and immediately at 760 nm, the absorbance was recorded by spectrophotometer to calculate total phenolic content. The findings were expressed in mg of quercetin equivalents (mg QE/g sample) or milligrams per gram of sample.
4.4.2. Total Flavonoid Content
Total flavonoid content was determined by using quercetin as standard through colorimetric assays [
39]. To perform this 25 µL of the sample, blank or various concentrations of standard solution were added in a 96-well microtiter plate with 12.5 µL of DW and 7.5 µL of 7% NaNO₃ solution. The mixture was allowed to sit at ambient temperature for 5 minutes. Afterwards, 10% AlCl
3 15 µL solution was added and thoroughly mixed. The plate was stored for another 5 minutes at room temperature. Finally, 27.5 µL of distilled water and 50 µL of 1 M NaOH solution were added and incubated at room temperature for an additional 5 minutes. At 510 nm, the absorbance was measured using water as a reference, and the results were reported in terms of the amount of quercetin equivalents per gram of sample (mg QE/g sample).
4.5. Antioxidant Analysis
The fractions of G. inodorum leaf extract were evaluated for their potential antioxidant capacity and free radical scavenging activities.
4.5.1. DPPH Radical Scavenging Activity
The DPPH assay was used to assess the free radical scavenging capabilities of
G. inodorum extracts. The procedure involved creating a DPPH stock solution in methanol and adding 195 µL of the DPPH solution with 10 µL of
G. inodorum extract in a 96-well microtiter plate. After a 30-minute dark incubation period, the absorbance at 517 nm was obtained using a SPECTROstar nano microplate reader (BMG LABTECH) [
40].
4.5.2. ABTS Decolorization Assay
Arnao’s described method [
41] was used to evaluate the antioxidant potential of
G. inodorum fraction extract using ABTS assay. The method involved preparing a 7mM ABTS reagent using 2,2-azino-bis-6-sulfonic acid, diammonium salt in H
2O and 2.45 mM of K
2S
2O
8 (potassium persulfate), which was kept in dark incubation for 12 hours at room temperature. 80% ethanol was added to dilute the solution in a 96-well microtiter plate along with 10 µL of
G. inodorum fraction extract. After a 30-minute dark incubation at 734 nm wavelength, the absorbance was measured and reported as the 50% inhibition concentration value, which reflects the correlation between the % inhibition of the test sample concentration and ABTS. The inhibition was measured at 734 nm absorbance, determined as a percentage and calculated by comparison with Trolox as a standard reference.
4.5.3. FRAP Assay
The method described by Aljadai [
42] was used to determine the ferric-reducing antioxidant power (FRAP) value of
G. inodorum extract. The process involved preparing the FRAP reagent by mixing 2.5 mL of 10 mM 2,4,6-tripyridyl-s-triazine (TPTZ) with 2.5 mL of 20 mM ferric chloride (FeCl
3), 40 mM HCl, and 25 mL of 300 mM acetate buffer at pH 3.6. The
G. inodorum fraction extract was then diluted two times with DW (distilled water), and ten microliters of the
G. inodorum fraction extract was added with 190 microliters of the FRAP standard reagent in a 96-well microtiter plate for a 30-minute dark incubation period. Finally, at 593 nm, the sample's absorbance was observed using a SPECTROstar nano microplate reader and calculated by comparison with Trolox as a standard reference.
4.6. Detection and Quantification of Gymnemic Acid
For the detection of gymnemic acid, 10 mg of the crude gymenema extract was dissolved in 50 mL of a 50% (V/V) methanol solution for chromatographic analysis. To this solution, after adding 10 mL of 11% KOH, heated under reflux for one hour in a boiling water bath before being cooled. After that, 9 mL of 12 N hydrochloric acid (HCl) was mixed and refluxed for another hour in the water bath. After lowering the temperature, the solution was mixed with 50% (V/V) methanol marked 100 mL final volume and further subjected to analyzation with HPLC (Shimadzu LC, Kyoto, Japan). The percentage of gymnemic acid was calculated using the sample's area under the curve, and it was compared to the standard value of deacyl gymnemic acid. Chromatography was conducted using LC systems, HPLC with analytical C18 column (250 x 4.60 mm i.d. x 5.0 μm), mobile phase consisting of (A) Acetonitrile solution and (B) Type 1 water (50:50) at 30°C column temperature, a flow rate of 2.0 mL/min, and detected at the wavelength of 218 nm. Deacyl gymnemic acid was used as a standardization concentration (3.91-500 μg/mL), and a duplicate sample was injected along with 20 μl of the sample solution to perform the HPLC estimation [
43].
4.7. Characterization of Active Phytochemicals
The characterization of active phytoconstituents from
G. inodorum leaf extract fractions was performed by a quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometer, following the method described by Chiwat [
44]. Initially, the collected fractions were dissolved in methanol, followed by cleaning with dispersive C18 SPE. Before analysis, the solution was filtered through HPLC micro-filters (0.22 μm). Further analysis was conducted by utilizing the series of Agilent 1290 Infinity II in conjugation with a 6546 LC-QTOF/MS apparatus with resolution 1.3 Da and 3 ppm accuracy of m/z determination. The LC conditions involve the use of a ZORBAX Eclipse Plus C18 column Shimadzu (HPLC-UV) with an injection quantity of 10 μL, a flow rate of 0.2 mL/min, and a mobile gradient system starting with a mixture of 95% water (1% formic acid) and 5% acetonitrile, gradually increasing to a final composition of 95% acetonitrile. Chromatographic separation was achieved through mass spectrometry conditions that include a positive mode electrospray ionization (ESI) probe, a nebulizer pressure of 20 psi, a flow rate of 7 L/min of N
2, a capillary temperature of 300°C, a flow rate of 8 μL/min, a mass-to-charge ratio range of 50-1000 m/z, a capillary voltage of 4500 V, and a temperature of 280°C dry heater. The phenolic compounds were identified using the database EMBL – EBI [
45].
4.8. Statistical Analysis
The statistical data were expressed as mean ± SEM of three replicates antioxidant activity. The results were statistically analyzed via Graph Pad Prism 9; where applicable, the data were subjected to descriptive analysis SPSS data package 22. Additionally, Microsoft Excel 2013 was used to find the differences between fractions. The results were expressed as mean ± SD for phytochemical analysis with a significance value set at p < 0.05.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, the fractions of extract of the plant G. inodorum showed significant antioxidant activity and phenolic compounds. This suggests the presence of additional beneficial active phenolic compounds within the plant extract, indicating further potential effects that could be beneficial from its use. The different level of antioxidant activity observed from each fraction are probably due to variation of active phytochemicals. Fraction A exerted the highest radical scavenging capacity as well as highest total phenolic content. The study supported that phenolic compounds may be responsible to antioxidant capacity of G. inodorum leaf extract. Our findings further indicate that the column chromatography technique is capable of providing effective purification for these active compounds. Moreover, the results of this study have promising implications across various fields.
Primarily, the endorsement of conventional medical approaches is substantiated by the identification of numerous phenolic components in the leaf extract of G. inodorum, coupled with their correlation to potent antioxidant activity. This implies that G. inodorum may have a therapeutic role in treating oxidative stress-related disorders. Moreover, this investigation illuminates neglected phytochemical compounds, prompting additional research to unveil the concealed therapeutic potential of this locally edible plant. Utilizing column chromatography for their purification offers promise in isolating and studying these valuable compounds. Nonetheless, future research focusing on characterization and identification of active compounds, and its health effect especially through in vivo models and clinical studies, is imperative to translate these findings into practical applications for human health.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.H., S.O., K.B. and S.H.; methodology, M.H., S.O., K.B. and S.H.; software, M.H. and W.K.; formal analysis, M.H. and T.P.; investigation, M.H. and T.P.; resources, S.O., K.B. and S.H.; data curation, W.K; writing—original draft preparation, M.H.; writing—review and editing, M.H., J.L., S.O., S.H., K.B. and W.K.; supervision, S.O.; project administration, S.O., K.B.; funding acquisition, S.O., K.B. and S.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research was funded by the Presidential Scholarship (Ref. No. 8393(25)/1890), Graduate School Chiang Mai University and Research Institute for Health Sciences, Chiang Mai University Research fund (Ref. No. 008/2566).
Institutional Review Board Statement
No applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Graduate School of Chiang Mai University and the Research Institute for Health Sciences, Chiang Mai University, for funding the research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Sample Availability
Not applicable.
References
- Plants of the World Online. Gymnema inodorum(Lour.) Decne. Available online: https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:98176-1 (accessed on 18 October 2022).
- Dunkhunthod, B.; Talabnin, C.; Murphy, M.; Thumanu, K.; Sittisart, P.; Eumkeb, G. Gymnema inodorum(Lour.) Decne. Extract Alleviates Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Mediators Produced by RAW264.7 Macrophages. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2021, 4, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasote, D.M.; Katyare, S.S.; Hegde, M.V.; Bae, H. Significance of Antioxidant Potential of Plants and its Relevance to Therapeutic Applications. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2015, 11, 982–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Plant List. 2013. Available online: http://www.theplantlist.org/1.1/browse/A/Apocynaceae/Gymnema. (accessed on 23 October 2023).
- Dai, J.; Mumper, R.J. Plant Phenolics: Extraction, Analysis and Their Antioxidant and Anticancer Properties. Molecules 2010, 15, 7313–7352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ounjaijean, S.; Romyasamit, C.; Somsak, V. Evaluation of Antimalarial Potential of Aqueous Crude Gymnema inodorum Leaf Extract against Plasmodium berghei Infection in Mice. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat Med. 2021, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suwan, N.; Baison, W.; Chuajedton, A. Purification of Gymnema inodorum Leaf Extract and Its Antifungal Potential Against Colletotrichum gloeosporioides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. India, Sect. B Biol. Sci. 2022, 92, 667–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeytawan, N.; Yadoung, S.; Jeeno, P.; Yana, P.; Sutan, K.; Naksen, W.; Wongkaew, M.; Sommano, S. R.; Hongsibsong, S. Antioxidant and Phytochemical Potential of and Phytochemicals in Gymnema inodorum(Lour.) Decne in Northern Thailand. Plants 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiabchalard, A.; Tencomnao, T.; Santiyanont, R. Effect of Gymnema inodorum on postprandial peak plasma glucose levels in healthy human. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 9, 1079–1085. [Google Scholar]
- Boonyapranai, K.; Sarakul, O.; Somsak, V.; Sukati, S. Effects of Gymnema inodorum Leaf Extract on the Alteration of Blood Coagulation Parameters and Platelet Count in Plasmodium berghei-Infected Mice. J. Parasitol. Res. 2022, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, NC.; Samman,S. Flavonoids- chemistry, metabolism, cardio-protective effects, and dietary sources. Nutritional effects and dietary sources. Nutr. Biochem. 1996, 7, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cianciosi, D.; Forbes-Hernández, T.; Afrin, S.; Gasparrini, M.; Reboredo-Rodriguez, P.; Manna, P.; Quiles, J. Phenolic compounds in honey and their associated health benefits: A review. Molecules. 2018, 23, 2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, S.A.; Malik, S.A. Determination of total phenolic and flavonoid content, antimicrobial and antioxidant activity of a root extract of Arisaema jacquemontii Blume. JTUSCI. 2015, 9, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, M.I.; Tomás-Barberán, F.A.; Hess-Pierce, B.; Kader, A.A. Antioxidant capacities, phenolic compounds, carotenoids, and vitamin C contents of nectarine, peach, and plum cultivars from California. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 4976–4982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasote, D.M.; Katyare, S.S.; Hegde, M.V.; Bae, H. Significance of antioxidant potential of plants and its relevance to therapeutic applications. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2015, 11, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, P.; Mishra, B.N.; Sangwan, N.S. Phytochemical and pharmacological properties of Gymnema sylvestre: An important medicinal plant. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajpai, V.K.; Majumder, R.; Park, J.G. Isolation and purification of plant secondary metabolites using column-chromatographic technique. Bangladesh J. Pharmacol. 2016, 11, 844–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manthey, J.A. Biological properties of flavonoids pertaining to inflammation. Microcirculation. 2000, 7 (6 Pt. 2), 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietta, P.G. Flavonoids as antioxidants. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 1035–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Gan, R.Y.; Li, S.; Zhou, Y.; Li, AN.; Xu, D.P. Antioxidant Phytochemicals for the Prevention and Treatment of Chronic Diseases. Molecules. 2015, 20, 21138–21156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeyrathne, E.D.N.S.; Nam, K.; Huang, X.; Ahn, D.U. Plant- and Animal-Based Antioxidants’ Structure, Efficacy, Mechanisms, and Applications: A Review. Antioxidants. 2022, 11, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand-Williams, W.; Cuvelier, M.E.; Berset, C. Use of a free radical method to evaluate antioxidant activity. LWT - Food Sci. Technol. 1995, 28, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Haley, S.; Perret, J.; Harris, M.; Wilson, J.; Qian, M. Free Radical Scavenging Properties of Wheat Extracts. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 1619–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L. chen.; Hsu, H.W.; Chen, Y.C.; Chiu, C.C.; Lin, Y.I.; Ho, J.A. Antioxidant and antiproliferative activities of red pitaya. Food Chem. 2006, 95, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onanong, N.; Wanwisa, S.; Chaisak, C.; Uthaiwan, S.; Piya, T.; Nitra, N.; Uracha, R. Relationship of phytochemicals and antioxidant activities in Gymnema inodorum leaf extracts. Heliyon. 2023, 10, 23175. [Google Scholar]
- Benzie, I.F.F.; Strain, J.J. The Ferric Reducing Ability of Plasma (FRAP) as a Measure of “Antioxidant Power”: The FRAP Assay. Anal. Biochem. 1996, 239, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.; Ou, B.; Prior, R.L. The Chemistry behind Antioxidant Capacity Assays. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 1841–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nwozo, O.S.; Effiong, E.M.; Aja, P.M.; Awuchi, C.G. Antioxidant, phytochemical, and therapeutic properties of medicinal plants: a review. Int. J. Food Prop. 2023, 26, 359–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinuanchai, W.; Nooin, R.; Jarussophon, S.; Kasemwong, K.; Nuchuchua, O. Determination of gymnemic acid level in Gymnema inodorum leaves using multiple reaction monitoring mass spectrometry. J. Chem. Metrol. 2019, 13, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinuanchai, W.; Nooin, R.; Pitchakarn, P.; Karinchai, J.; Suttisansanee, U.; Chansriniyom, C. Inhibitory effects of Gymnema inodorum(Lour.) Decne leaf extracts and its triterpene saponin on carbohydrate digestion and intestinal glucose absorption. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 266, 113398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuchuchua, O.; Srinuanchai, W.; Chansriniyom, C.; Suttisansanee, U.; Temviriyanukul, P.; Nuengchamnong, N.; Raktanonchai, U. Relationship of phytochemicals and antioxidant activities in Gymnema inodorum leaf extracts. Heliyon 2023, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.H.; Liu, G.T.; Sun, Y.M.; Zhang, H.Y. Antioxidative effect of schisanhenol on human low-density lipoprotein and its quantum chemical calculation. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2004, 25, 1038–1044. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Ma, S.; Lai, F.; Wang, Y.; Lou, C. Traditional Applications, Phytochemistry, and Pharmacological Activities of Eupatorium lindleyanum DC.: A Comprehensive Review. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 8, 577124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoro, V.; Asensio, C.; Martínez, Á., et al; et al. Efficacy and safety of fluocinolone acetonide 0.025% otic solution in patients with otic eczema: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. J. Int. Med. Res. 2018, 46, 4050–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, D. Lignans. Molecules 2019, 24, 1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu, F.; Mat Taib, C.N.; Mohd Moklas, M.A.; Mohd Akhir, S. Antioxidant Properties of Crude Extract, Partition Extract, and Fermented Medium of Dendrobium sabin Flower. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat Med. 2017, 2017, 2907219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miliauskas, G.; Venskutonis, P.R.; Van Beek, T.A. Screening of radical scavenging activity of some medicinal and aromatic plant extracts. Food Chem. 2004, 85, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gini, T.G.; Jeya Jothi, G. Column chromatography and HPLC analysis of phenolic compounds in the fractions of Salvinia molesta mitchell. Egypt. J. Appl. Sci. 2018, 5, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewanto, V.; Wu, X.; Adom, K.K.; Liu, R.H. Thermal Processing Enhances the Nutritional Value of Tomatoes by Increasing Total Antioxidant Activity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 3010–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.; Prottay, A.A.S.; Sultana, I.; Al Faruq, A.; Bappi, M.H.; Akbor, M.S. Phytochemical screening and evaluation of antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and membrane-stabilizing activities of different fractional extracts of Grewia nervosa (Lour.) Panigrahi. Food Biosci. 2023, 1, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeeno, P.; Tongban, S.; Yana, P.; Wongta, A.; Sutan, K.; Yadoung, S. Tentative Identification of Phytochemicals from Smilax glabra and Smilax corbularia Extracts by LC-QTOF/MS and Their Bioactive Potential. Plants. 2022, 11, 2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnao, M.B.; Cano, A.; Acosta, M. The hydrophilic and lipophilic contribution to total antioxidant activity. Food Chem. 2001, 73, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, N.; Santiago, A.; Alías, J.C. Quantification of the Antioxidant Activity of Plant Extracts: Analysis of Sensitivity and Hierarchization Based on the Method Used. Antioxidants. 2020, 9, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devi, K.; Jain, N. A validated HPLC method for estimation of Gymnemic acids as Deacyl gymnemic acid in various extracts and formulations of Gymnema sylvestre. Int. J. Phytomedicine. 2014, 6, 78–88. [Google Scholar]
- Arjin, C.; Hongsibsong, S.; Pringproa, K.; Seel-audom, M.; Ruksiriwanich, W.; Sutan, K. Effect of Ethanolic Caesalpinia sappan Fraction on In Vitro Antiviral Activity against Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).