1. Introduction
Messenger RNA (mRNA) vaccines have emerged as a transformative force in immunization, offering a versatile platform to provide protection against a variety of pathogens. By harnessing the cell’s natural machinery to produce proteins directly from mRNA molecules, the approach circumvents the need for replicating vectors (bacteria, fungi, viruses), thus reducing biological risks during production and delivery of vaccines as well as enabling faster development times. Their remarkable efficacy in addressing global health challenges emerged during the COVID-19 pandemic and is becoming a cornerstone of pharma technology. The 2023 Nobel prize awarded to Katalin Karikó and Drew Weissman was not for their invention of mRNA vaccines, but for their finding that while delivery of mRNA to mice incited substantial inflammatory responses through activation of Toll-like receptors, inoculation of mRNA that had been modified by changing uridine with pseudouridine strongly abated inflammation [
1,
2]. Contributes of the two scientists are well summarized in two recent articles [
3,
4].
The mRNA platform represents the foundation of preventive vaccines as well as a basis for therapeutics, especially in monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) [
5]. Refinements are in progress with regard to the structure and production of mRNA constructs, the selection of packaging components for mRNA to resist degradation and enter the cells, improved criteria for selecting administration routes.
To date, mRNA vaccines have been administered predominantly via parenteral routes (intramuscular, intradermal, subcutaneous, intravenous, into superficial lymph nodes) [
6]. While these routes have proven effective in enhancing resistance to systemic infection and in mitigating the risk of severe disease, they may fall short in addressing mucosal infections.
In fact, despite systemic immunity, microbes may continue to replicate in mucosal surfaces, evading local defenses and perpetuating community transmission. For a wide range of infectious agents, mucosae serve as a critical interface both for establishing the initial contact with the host and for exiting the body. Given the immune system’s inherent design to elicit a systemic response following superficial infections, leveraging mucosae for vaccination appears a natural strategy capable of triggering local immunity at the right point of pathogen entry. This not only provides mucosal resistance that is critical to thwarting infections but is also followed by a strong systemic response.
In general, vaccination programs need special consideration to another crucial aspect: the capacity to be run also in regions with limited medical infrastructure, particularly in developing countries. Utilizing parenteral vaccination in such contexts may not be optimal due to the invasive nature of the practice, the need of trained personnel and sterile tools. In addition, the practice carries infection risks, needle-stick injuries, and the occasional transmission of diseases other than that being prevented. The proper disposal of used materials is mandatory. In contrast, mucosal vaccines may offer easy administration that favors acceptance by the population, no needle-related risks and, usually, lower costs of production and vaccine delivery.
Developing and successfully testing mucosal vaccine formulations has been limited, primarily because of the scarcity of effective antigen delivery systems as well as mucosal adjuvants [
7]. This review focuses on mRNA vaccines regarding the establishment of mucosal immunity in either industrialized or developing countries.
2. Vaccine Administration through Parenteral Routes
Successful vaccination depends on the correct route of administration of the immunogen. In general, most vaccines are administered by either the subcutaneous (SC) or intramuscular (IM) route. These routes take advantage of the immune surveillance systems for inducing both innate and adaptive responses. They also facilitate the gradual processing of the inoculum by bringing antigens and adjuvants across the epidermal barrier. Importantly, controlled delivery avoids their direct introduction into the bloodstream thus preventing the systemic distribution of these substances and their rapid clearance [
8].
Subcutaneous (SC) injections target the adipose-connective tissue beneath the dermis and above the muscle layer, while Intramuscular (IM) injection stands out as the predominant delivery method by reaching skeletal muscles. Selecting the administration route is tailored to the specific vaccine, the target population, considerations to manufacturing and quality control methods, the possible need of a cold chain, the training required for personnel administering the vaccine. Opting for intramuscular administration enhances the immunogenicity of most vaccines and reduces adverse reactions at the injection site. Muscles, being highly vascularized, facilitate adequate mobilization and distribution of the vaccine to lymphoid cells and lymph nodes. Conversely, injecting a vaccine into the subcutaneous layer, with its lower vascularity, may lead to a slower mobilization of the immunogen and antigen presentation and also poses the risk of local adverse effects or delayed response [
9].
Upon vaccine administration, the innate immune response initiates at the injection site. The adaptive response commences at the local lymph nodes that the vaccine drains into. Studies comparing vaccine routes of administration have yielded mixed results, indicating different speeds of B- or T-cell responses depending on the vaccine and its formulation. Generally, injected vaccines of the same formulation exhibit similar long-term outcomes when injected through different routes [
10].
Vaccinologists have long been concerned with problems posed by parenteral injections, especially in developing countries for reasons of biological safety and costs. The history of the polio vaccine exemplifies the crucial impact of integrated considerations in vaccine development, especially the choice of attenuated versus inactivated platforms, the choice of adjuvants (e.g., aluminum or oil-in-water), the selection of administration routes (oral or intramuscular). Sabin’s attenuated polio vaccine administered orally (OPV), has been widely used due to its convenience, the ability to elicit intestinal immunity, its spread to contacts, cost-effectiveness. The inactivated polio vaccine (IPV) is considered safer, but more expensive and “less effective” since it induces only systemic immunity. Efforts to reduce IPV costs include exploring a variety of adjuvants with the aim of cutting costs. The last three decades have seen advancements in vaccine design and testing that lead to a more engineered approach and the emergence of the distinct field of ‘vaccinology.’ The recent development of COVID-19 vaccines underscores the importance of integrated considerations in vaccinology. Independently and collectively, the choice of vaccine platforms, adjuvants, and delivery routes interact in determining vaccine efficacy and safety. Liquid formulations for injection face challenges due to the need of a ‘cold chain.’ In the realm of nucleic acid vaccines, currently licensed products are administered intramuscularly. Researchers have pursued alternative delivery routes, resulting in innovative tools (e.g., mucosal adjuvants, mRNA encapsulation components, micropatch needles) that may improve vaccine immunogenicity, and stability [
11,
12].
3. Alternative Routes for Vaccine Administration
Mucosal delivery of vaccines is considered highly effective in providing robust protection at mucosal surfaces. leveraging mucosa-associated lymph tissues (MALTs) it leads to antibody secretion into mucus. Despite the advantages of needleless delivery of the immunizing agent, the penetration and retention of immunogens at the mucosal surface is challenged by host’s natural defense mechanisms, including stomach acid, digestive enzymes and the mucus layer. Currently, only five vaccines utilize mucosal delivery through the oral and intranasal routes [
13]. Among those, the Sabin polio vaccine, a cholera vaccine and a rotavirus vaccine represent effective preventive measures against important pathogens. Compared to injectable vaccines, oral vaccination has several advantages that include easy manufacturing, facilitated distribution and affordability. Oral vaccines are also remarkably stable and have long shelf-lives that facilitate distribution. Additionally, the simplicity of administration and the minimal training for sanitary personnel contribute to their success as well as to wider acceptance among the population.
3.1. Expressing Protein Antigens in Plants
It has been about 30 years since the first plant engineering technology was established [
14]. The idea is to express select protein antigens of microbial pathogens in edible plants whose fruits need not to be cooked before eating. Hence, eating the genetically engineered fruits (e.g., bananas, tomatoes) would result in the exposure of humans to antigens of a specific target germ within the digestive system. Since mucosal structures enfold the digestive system, the microbial immunizing protein would encounter mucosal-associated lymphoid tissues. A local immune response would follow and would spread widely in the digestive system leading – among other reactions - to the production of secretory IgA antibodies. Whereas this is desirable, safety consequences might emerge. An example is gluten sensitivity in celiac disease and related disorders [
15].
Edible plant vaccines against influenza viruses [
16], polioviruses [
17] and animal virus pathogens [
18] have been proposed, but no vaccines of this type are currently in use either for animals or humans [
19]. At present, a single plant-made vaccine has been approved by the USDA: the Newcastle disease vaccine for poultry that is produced in suspension-cultured tobacco cells. Adoption of plant-based vaccines takes great methodological efforts, but the regulatory, patenting and safety issues are even more difficult to resolve [
20,
21].
3.2. Administration of mRNA Vaccines within Extracellular Vesicles
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are small membrane-bound particles released by cells into the extracellular space and include exosomes and microvesicles. EVs are proper of most living systems including animals and plants. They play a role in intercellular communication by transporting bioactive molecules such as proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids.
EVs have the potential to be employed for mRNA vaccines thanks to their intrinsic properties [
22] that make them a valid alternative to parenteral administration:
- a)
Natural Cell-to-Cell Communication: EVs are involved in normal physiological processes as mediators of cell-to-cell communication. Exploiting this natural communication system for vaccine delivery may have advantages in terms of the body response to the introduced mRNA. EVs have been shown to modulate immune responses [
23].
- b)
Protection of mRNA: EVs can protect the encapsulated mRNA from degradation and immune system recognition, thus improving the stability and effectiveness of mRNA vaccines [
24,
25,
26,
27,
28,
29].
- c)
Targeted Delivery: EVs can be engineered to express specific surface proteins that allow them to target specific cell types or tissues, thus enhancing the precision of vaccine delivery. Several methods have been developed to engineer EVs by modifying their surface with the purpose of targeting drug delivery [for review see [
30]].
- d)
Reduced Reactogenicity: EVs may help reduce inflammatory reactions associated with mRNA vaccines, making them safer and more acceptable for therapeutic applications.
- e)
Potential for Personalized Medicine: the ability to modify EVs for specific target cells opens up the possibility for personalized medicine, better adapting vaccines to the individual’s unique needs [
31].
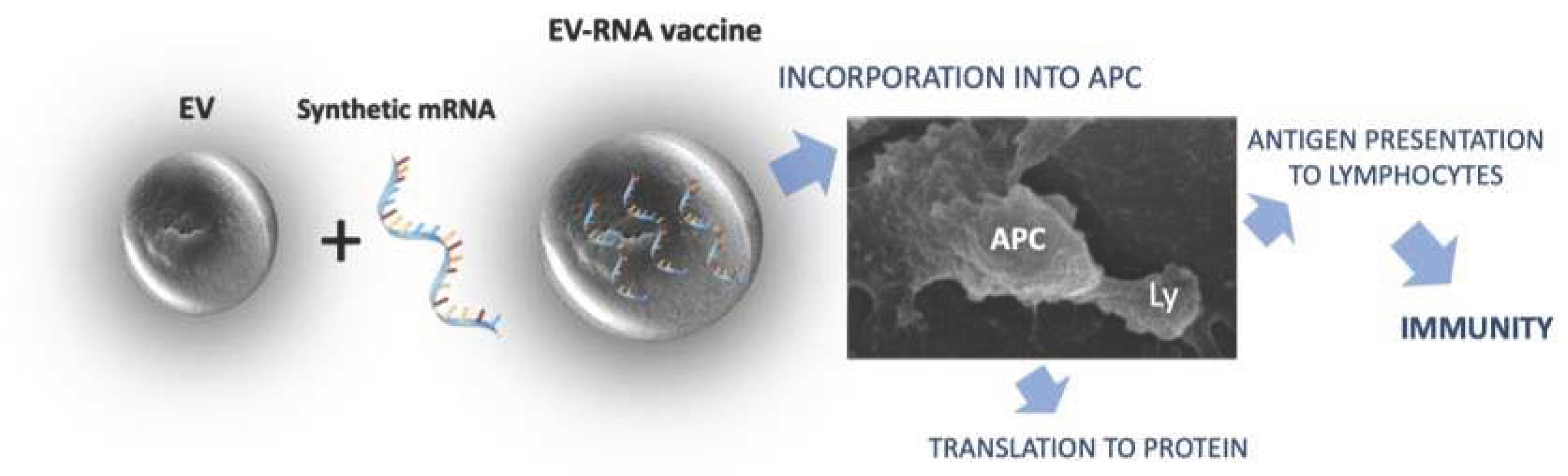
The general procedure for immunization using mRNA constructs loaded into plant derived EVs is summarized in
Figure 1.
While the concept is promising, the implementation of EVs as mRNA carriers requires intensive research. Challenges include optimizing production methods, ensuring optimal loading of mRNA into EVs, addressing regulatory and safety considerations.
Preclinical studies addressed the use of EVs for mRNA-based vaccines. Wang et al. [
32] investigated the intranasal administration of lung cell-derived EVs containing mRNA specific for the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Animals produced IgG and IgA antibodies as well as a T cell-mediated immune response. The EV carrier was shown to be superior to liposomes in terms of immunizing potency. Vaccination of hamsters with the same procedure significantly reduced the severity of pneumonia triggered by SARS-CoV-2. Notably, the lyophilized form of this mRNA vaccine was stable up to three months [
32]. Lung derived EVs containing mRNA encoding the S protein of SARS-CoV-2 was also administered to rodents as inhalable dry powder as well as to non-human primates. The EV vaccine was superior to synthetic liposomes due to better biodistribution in lungs [
33,
34]. A vaccine composed of EVs released by the HEK293 cell line fused with lipid coated mRNA encoding for the S and N proteins of SARS-CoV-2 was developed by Tsai et al. [
35]. Whereas mRNA loaded into synthetic nanoparticles was toxic to the cells, EV-loaded mRNA apparently lacked toxicity and stimulated long lasting immunity [
35].
Since the upscale production of EVs in cultured human cells is laborious, expensive and requires complex quality controls, alternative sources have been explored. EVs from edible plants may represent an appealing alternative. EVs of plant cells closely resemble those of mammalians [
36]. Plant EVs are constituted by a bilayer membrane, and it has been shown that they can be loaded with exogenous nucleic acids, including mRNA, regulatory small RNA, DNA plasmids [
37,
38,
39]. Edible plant-derived EVs are abundant in fruit juice and their production is scalable. In addition, select plants that have been long-term part of human diets are expected to be non-toxic and, in general, little or no immunogenic. Recently, Pomatto et al. [
37,
40] explored the use of plant-derived EVs extracted from orange (Citrus sinensis) as carriers for SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccines. The potential of EVs as a platform for administering mRNA vaccines through the parenteral, oral, and intranasal routes has been evaluated. An efficient loading of mRNA and mRNA protection from degrading enzymes including gastric juice was observed. The loaded mRNA was successfully delivered to antigen-presenting cells and stimulated T lymphocyte activation
in vitro. Mice immunization - via different administration routes - with orange-derived EVs in soluble form stimulated humoral and T cell-mediated immune response [
37]. Rat immunization with lyophilized orange-derived EVs loaded with S1 mRNA encapsulated in gastro-resistant capsules administered by gavage also stimulated mucosal immune response with production of specific IgA and T lymphocyte activation [
40].
The versatility of administration routes and the induction of both humoral and cell-mediated responses by vegetal EV-based vaccines make this approach promising. The formulation of lyophilized mRNA containing EVs may represent an important delivery strategy not only for oral vaccines but also for a dry powder inhalator vaccine. The formulation stability at room temperature adds merits to the proposed vaccination approach.
4. Optimization of mRNA Constructs to Improve Stability and Translation Efficiency
While mRNA vaccines offer numerous advantages, there are notable challenges associated with their delivery. Research is focused on developing improved delivery systems to safeguard mRNA and ensure their entry into cells [
41]. Potential side effects, including heart, renal and microvascular damage, blood clotting as well as allergic reactions have been identified with mRNA vaccines [
42]. These have been traced, in part, to hypersensitivity reactions elicited by LNP-mRNA components, likely the PEGlyated lipid nanoparticles [
43]. Thus, safer technology for mRNA encapsulation is strongly needed. Moreover, the rapid degradation of mRNA in the body after administration [
44] or the risk of triggering great cytokine responses [
45] present considerable obstacles to practical applications.
The successful translation of mRNA into functional proteins is contingent upon optimizing key elements within the mRNA construct. Here we explore strategies for enhancing the stability and translation efficiency of mRNA sequences through targeted optimizations of the 5’ cap, 3′ poly-A tail, and codons for increasing mRNA stability and translation efficiency.
4.1. Cap Structure
Almost all endogenous eukaryotic mRNA contains a 5′ cap structure added during RNA post-transcription modifications. processing. The 5′ cap consists of an N7-methylated guanosine (m
7G) linked to the first nucleotide of the RNA via a reverse 5′ to 5′ triphosphate linkage (the 5′ m
7G cap)) [
46] and is essential for initiating protein synthesis. Furthermore, the cap structure serves as a protective barrier against exonuclease cleavage, thereby enhancing mRNA stability. Notably, the cap structure aids the host’s discrimination between self and non-self mRNA molecules, underscoring its importance in immunogenicity and host-pathogen interactions [
47].
Numerous strategies for mRNA structure optimization have been applied to optimize m
7G to achieve cap analogs with high transcription efficiency and low susceptibility for decapping enzymes [
48]. Modification of m
7G represents another approach to improving mRNA translation. It has been shown that replacing m
7G with 7-benzylated guanosine significantly enhances translation efficiency [
49], further boosted by attaching m
7G with another m
7G via tetraphosphate (m
7Gppppm
7G), resulting in analogs with higher translation efficiency compared to natural eukaryotic 5′ caps. Additionally, synthetic modifications such as anti-reverse cap analogs (ARCA) have been developed to further enhance mRNA stability and translation efficiency. ARCA-capped mRNA exhibits improved translation efficiency and prolonged half-life compared to conventional cap analogs, leading to enhanced protein expression in cultured cells [
50]. This approach offers promising prospects for optimizing mRNA constructs in different biomedical applications, including gene therapy and vaccines.
In contrast to the modified 5′ cap structure present in most endogenous eukaryotic mRNA, prokaryotic mRNA transcripts typically retain their 5′ triphosphate without further modification. While the notion of developing an mRNA vaccine with only an Internal Ribosome Entry Site (IRES) at the 5′ end (thus omitting the need for a cap) appears appealing due to its simplicity, it comes with a significant drawback. Unprotected mRNA lacking both 5′ and 3′ modifications is highly susceptible to degradation by exonucleases, rendering it unstable and prone to rapid degradation. Solodushko et al. borrowed a strategy from
E. coli to protect its 5′ end from exonucleases by forming a 5′-terminal stem-loop structure [
51]. Apparently, this stabilizes the molecule and protects mRNA from exonuclease degradation when delivered to target cells, thus saving time and reducing costs.
4.2. Poly (A) Tail
The poly(A) tail is an essential element in most protein-encoding RNA molecules, providing stability and improving translation efficiency [
52]. The poly(A) tail is added to mRNA in the cell nucleus in a post-transcriptional process downstream of the gene-encoded polyadenylation signal (AATAAA) [
53]. Eukaryotic transcripts usually receive a poly-A tail of approximately 200 nucleotides (nt) in mammals and 70 nt yeast [
54]. For mRNA constructs, an optimal poly(A) tail length of approximately 100 nt has been identified, helping to reduce the degradation of RNA molecules [
55]. Other approaches have been evaluated to improve the transcription efficiency and stability, including the adoption of segmented poly(A) sequences. This method involves the insertion of interspersed smaller spaces length between poly(A) stretches and has been demonstrated to improve the stability of plasmid DNA and the in vivo expression of mRNA [
56,
57]. This technique has been successfully applied to the development of a candidate rabies vaccine (RV021) encoding the rabies virus glycoprotein [
58].
4.3. Codon Usage
When designing a protein that will be expressed from an mRNA counterpart, the protein sequence needs to be converted into nucleotides. This is not a univocal process, as each amino acid can be encoded by multiple nucleotide triplets – called codons. In total there are 64 possible codons expressing the 20 naturally occurring amino acids. The codons composition of a construct does affect the translation efficiency, the mRNA abundance and protein folding. In addition, the result is dependent on the organism and the specific cell type(s) in which the mRNA is expressed [
12]. The composition of codons does not only influence translation efficiency but also affects the mRNA secondary structure, with constructs having higher GC content that translate more efficiently than sequences characterized by lower GC content [
59]. Strategies for codon optimization involve modifying codon usage to match more common tRNA species, substituting rare codons with frequent ones to expedite translation, and considering neighboring nucleotides and codons to enhance translational elongation rate [
60].
Different methodologies have been used in the past to explore the vast range of possible codon combinations. Zhang et al. [
61] adapted the classical concepts of lattice parsing in computational linguistics to develop LinearDesign, an in-silico optimization algorithm that allows to select the optimal mRNA among a vast space of candidates. By defining the mRNA design space using a deterministic finite-state automaton (DFA), the approach successfully selects a vast number of mRNA candidates and allows to explore a number of solutions to identify the one providing the most stable molecules. The method has been applied to optimize the production of SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein, improving both mRNA half-life and protein expression. Rishab et al. introduced a codon optimization tool that leverages deep learning and recurrent neural networks (RNNs) to enhance heterologous expression in synthetic genes [
62]. Specifically, the approach employs Bidirectional Long-Short-Term Memory (BiLSTM) to learn codon usage biases alongside the contextual information surrounding codons. Its algorithm was trained with a non-redundant dataset of genes derived from E. coli genomes, ensuring robustness and relevance among diverse bacterial strains. By understanding the patterns and subsequences in which synonymous codons are employed within genes, ICOR achieves a predictive accuracy that outperforms traditional methods. While this approach is based on E. coli genomes, research aims to extend the concept to other organisms through transfer learning approaches.
To advance research and development in mRNA-based drugs, leveraging AI and advanced high-throughput/high-speed technologies will be essential. These tools can play a crucial role in designing, selecting, and validating a variety of aspects such as the DNA template, sequence composition, structural antigen features, chemical modification, formulation, delivery system, and manufacturing process. Optimization of all these factors does impact mRNA translation efficiency, cellular stability, non-immunogenicity, low toxicity, thermostability, cellular uptake efficiency, targeting to specific organs, immune stimulating effect, biodistribution and expression, as well as cost-effectiveness. Through ongoing advancements, the potential of mRNA vaccines and therapeutics will surely bring significant benefits to global health and the quality of life.
4.4. Self-Amplifying RNA Vaccines (saRNA)
Supposedly, self-amplifying RNA vaccines may offer important advantages over conventional mRNA vaccines [
63,
64]. First, since saRNA vaccines contain a built-in RNA polymerase, their dose can be significantly reduced. When comparing an mRNA vaccine and an saRNA vaccine in mice, it was found that the saRNA preparation could achieve equivalent levels of protection against influenza virus with just 1/64th the dose. Second, saRNA vaccines are expected to induce a more durable immune response since the RNA keeps copying itself and remains for prolonged times in the body. For instance, while mRNA might last for a few days, saRNA vaccines could persist for over a month. The biodistribution of saRNA vaccines has been reviewed recently [
65]. Of course, self-replicating nucleic acids could also entail safety problems linked to mutational changes during repeated replication [
66] and – theoretically – to the possible conversion of the RNA construct into cDNA followed by its integration into the host genome [
67].
5. Needs for Pre-Clinical Research
In all these investigations, the results of extensive pre-clinical data are needed before phase-1 studies [
68]. Important factors to consider when designing and conducting pre-clinical toxicology/immunology studies for vaccines include: a) the need of following good laboratory practice (GLP) guidelines, b) during tests, avoiding any changes to the study protocol that could affect the results by preparing and following quality assurance elements, such as SOPs, instrument validation, and lab certification. Examples of pre-clinical studies for vaccines have been published on Marburg virus [
69] and SARS-CoV-2 [
70], among others.
With regard to vaccine delivery through plant-derived EVs, at least four factors must also be explored: 1) toxicity in experimental animals of vegetal EV preparations (devoid of mRNA cargoes); 2) immunogenicity of proteins in EV preparations; 3) distribution in different organs of select mRNA constructs delivered through vegetal EVs by the oral, nasal or other routes; 4) detectability of mRNA constructs and the encoded proteins in tissues at different times post administration (e.g., 3, 7, 15, 30 days)
6. Possible Vaccine Targets for Future Pandemics
According to official reports and media, animal-derived Ebola, Marburg, SARS, Nipah, Machupo viruses represent threats listed on the World Health Organization’s priority pathogens noted for their potential to cause the next pandemics [
71]. Insect-transmitted epidemic diseases are also of particular concern. Currently approved vaccines against pathogens with pandemic potential include: Covid-19, Japanese encephalitis, Yellow fever, Dengue fever and – most recently – Chikungunya disease (Frelick,
https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/998362).
7. Additional Goals and Perspectives
In addition to Covid-19 vaccines, pharmaceutic companies are envisaging a wide range of applications for mRNA technologies (see:
https://endpts.com/moderna-aims-to-launch-15-new-products-and-50-clinical-candidates-in-the-next-5-years/). For instance, Moderna is aiming at pan-influenza vaccines, a way to divert from yearly injections to classical immunizations that could offer life-long protection. Cancer therapy is an important field growing in parallel with therapeutic approaches to genetic diseases due to proteins that are altered or missing in the liver. In the latter case, mRNAs could be delivered with infusions in the blood (e.g., methylmalonic acidemia, phenylketonuria).
Thus, the art of mRNA therapeutics is indeed promising but still at its dawn. Collaboration between the academy, pharmaceutical companies, and regulatory bodies will be crucial to accelerate the deployment of safe and effective mRNA medications.
Author Contributions
A.T., G.M and G.C. wrote, edited, and approved the manuscript for submission. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable
Acknowledgments
We express gratitude to the Global Virus Network (GVN), Baltimore, MD and to Centro Linceo Beniamino Segre, Accademia dei Lincei, Rome, Italy.
Conflicts of Interest
A.T. and G.M. declare no conflict of interest. G.C. is Scientific Coordinator of EvoBiotech and named as inventor in a related patent (WO2022053485A1).
References
- Karikó, K.; Buckstein, M.; Ni, H.; Weissman, D. Suppression of RNA Recognition by Toll-like Receptors: The Impact of Nucleoside Modification and the Evolutionary Origin of RNA. Immunity 2005, 23, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karikó, K.; Muramatsu, H.; Welsh, F.A.; Ludwig, J.; Kato, H.; Akira, S.; Weissman, D. Incorporation of Pseudouridine Into MRNA Yields Superior Nonimmunogenic Vector With Increased Translational Capacity and Biological Stability. Molecular Therapy 2008, 16, 1833–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatraman, V. The MRNA Enthusiast’s Memoirs Breaking Through: My Life in Science Katalin Karikó Crown, 2023. 336 Pp. Science (1979) 2023, 382, 45–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Offord, C.; Cohen, J. Award Honors Pair for MRNA Work Key to COVID-19 Vaccines. Science (1979) 2023, 382, 22–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoecke, V.; Med, R.J.T.; Van Hoecke, L.; Roose, K. How MRNA Therapeutics Are Entering the Monoclonal Antibody Field. Journal of Translational Medicine 2019 17:1 2019, 17, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Zhang, C.; Walker, P.G.; Dong, Y. Formulation and Delivery Technologies for MRNA Vaccines. In; 2020; pp. 71–110.
- Tada, R.; Yamazaki, H.; Nagai, Y.; Takeda, Y.; Ohshima, A.; Kunisawa, J.; Negishi, Y. Intranasal Administration of Sodium Nitroprusside Augments Antigen-Specific Mucosal and Systemic Antibody Production in Mice. Int Immunopharmacol 2023, 119, 110262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozak, M.; Hu, J. The Integrated Consideration of Vaccine Platforms, Adjuvants, and Delivery Routes for Successful Vaccine Development. Vaccines (Basel) 2023, 11, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuckerman, J.N. The Importance of Injecting Vaccines into Muscle : Different Patients Need Different Needle Sizes. BMJ : British Medical Journal 2000, 321, 1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenbaum, P.; Tchitchek, N.; Joly, C.; Rodriguez Pozo, A.; Stimmer, L.; Langlois, S.; Hocini, H.; Gosse, L.; Pejoski, D.; Cosma, A.; et al. Vaccine Inoculation Route Modulates Early Immunity and Consequently Antigen-Specific Immune Response. Front Immunol 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnelly, R.F. Vaccine Delivery Systems. Hum Vaccin Immunother 2017, 13, 17–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brule, C.E.; Grayhack, E.J. Synonymous Codons: Choose Wisely for Expression. Trends Genet 2017, 33, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakya, A.K.; Chowdhury, M.Y.E.; Tao, W.; Gill, H.S. Mucosal Vaccine Delivery: Current State and a Pediatric Perspective. J Control Release 2016, 240, 394–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eidenberger, L.; Kogelmann, B.; Steinkellner, H. Plant-Based Biopharmaceutical Engineering. Nature Reviews Bioengineering 2023, 1, 426–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio-Tapia, A.; Hill, I.D.; Semrad, C.; Kelly, C.P.; Greer, K.B.; Limketkai, B.N.; Lebwohl, B. American College of Gastroenterology Guidelines Update: Diagnosis and Management of Celiac Disease. American Journal of Gastroenterology 2023, 118, 59–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mardanova, E.S.; Ravin, N. V. Plant-Produced Recombinant Influenza A Vaccines Based on the M2e Peptide. Curr Pharm Des 2018, 24, 1317–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolaños-Martínez, O.C.; Strasser, R. Plant-Made Poliovirus Vaccines – Safe Alternatives for Global Vaccination. Front Plant Sci 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeyama, N.; Kiyono, H.; Yuki, Y. Plant-Based Vaccines for Animals and Humans: Recent Advances in Technology and Clinical Trials. Ther Adv Vaccines 2015, 3, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Márquez-Escobar, V.A.; Rosales-Mendoza, S.; Beltrán-López, J.I.; González-Ortega, O. Plant-Based Vaccines against Respiratory Diseases: Current Status and Future Prospects. Expert Rev Vaccines 2017, 16, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eidenberger, L.; Kogelmann, B.; Steinkellner, H. Plant-Based Biopharmaceutical Engineering. Nature Reviews Bioengineering 2023, 1, 426–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiegel, H.; Nölke, G.; Thangaraj, H.; Schillberg, S. The Concept of an Agroinfiltration Kit for Recombinant Protein Production for Educational and Commercial Use—A Journey through a Forest of Regulatory and Legal Implications. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, T.P.; Golik, M.; Olejnik, J.; Łukaszewska, M.; Markowska, D.; Drożdżyńska, M.; Kotecki, A.; Głowacki, M.; Jagodziński, P.P. Potential Applications of Using Tissue-Specific EVs in Targeted Therapy and Vaccinology. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2023, 166, 115308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, P.D.; Morelli, A.E. Regulation of Immune Responses by Extracellular Vesicles. Nature Reviews Immunology 2014 14:3 2014, 14, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, S.; Cornils, K.; Speiseder, T.; Badbaran, A.; Reimer, R.; Indenbirken, D.; Grundhoff, A.; Brunswig-Spickenheier, B.; Alawi, M.; Lange, C. Indication of Horizontal DNA Gene Transfer by Extracellular Vesicles. PLoS One 2016, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guduric-Fuchs, J.; O’Connor, A.; Camp, B.; O’Neill, C.L.; Medina, R.J.; Simpson, D.A. Selective Extracellular Vesicle-Mediated Export of an Overlapping Set of MicroRNAs from Multiple Cell Types. BMC Genomics 2012, 13, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valadi, H.; Ekström, K.; Bossios, A.; Sjöstrand, M.; Lee, J.J.; Lötvall, J.O. Exosome-Mediated Transfer of MRNAs and MicroRNAs Is a Novel Mechanism of Genetic Exchange between Cells. Nat Cell Biol 2007, 9, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deregibus, M.C.; Cantaluppi, V.; Calogero, R.; Lo Iacono, M.; Tetta, C.; Biancone, L.; Bruno, S.; Bussolati, B.; Camussi, G. Endothelial Progenitor Cell Derived Microvesicles Activate an Angiogenic Program in Endothelial Cells by a Horizontal Transfer of MRNA. Blood 2007, 110, 2440–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratajczak, J.; Miekus, K.; Kucia, M.; Zhang, J.; Reca, R.; Dvorak, P.; Ratajczak, M.Z. Embryonic Stem Cell-Derived Microvesicles Reprogram Hematopoietic Progenitors: Evidence for Horizontal Transfer of MRNA and Protein Delivery. Leukemia 2006 20:5 2006, 20, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, S.J.; Raposo, G. As We Wait: Coping with an Imperfect Nomenclature for Extracellular Vesicles. J Extracell Vesicles 2013, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghav, A.; Jeong, G.B. A Systematic Review on the Modifications of Extracellular Vesicles: A Revolutionized Tool of Nano-Biotechnology. J Nanobiotechnology 2021, 19, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beetler, D.J.; Di Florio, D.N.; Bruno, K.A.; Ikezu, T.; March, K.L.; Cooper, L.T.; Wolfram, J.; Fairweather, D.L. Extracellular Vesicles as Personalized Medicine. Mol Aspects Med 2023, 91, 101155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Popowski, K.D.; Zhu, D.; de Juan Abad, B.L.; Wang, X.; Liu, M.; Lutz, H.; De Naeyer, N.; DeMarco, C.T.; Denny, T.N.; et al. Exosomes Decorated with a Recombinant SARS-CoV-2 Receptor-Binding Domain as an Inhalable COVID-19 Vaccine. Nature Biomedical Engineering 2022 6:7 2022, 6, 791–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popowski, K.D.; López de Juan Abad, B.; George, A.; Silkstone, D.; Belcher, E.; Chung, J.; Ghodsi, A.; Lutz, H.; Davenport, J.; Flanagan, M.; et al. Inhalable Exosomes Outperform Liposomes as MRNA and Protein Drug Carriers to the Lung. Extracellular Vesicle 2022, 1, 100002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popowski, K.D.; Moatti, A.; Scull, G.; Silkstone, D.; Lutz, H.; López de Juan Abad, B.; George, A.; Belcher, E.; Zhu, D.; Mei, X.; et al. Inhalable Dry Powder MRNA Vaccines Based on Extracellular Vesicles. Matter 2022, 5, 2960–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, S.J.; Atai, N.A.; Cacciottolo, M.; Nice, J.; Salehi, A.; Guo, C.; Sedgwick, A.; Kanagavelu, S.; Gould, S.J. Exosome-Mediated MRNA Delivery in Vivo Is Safe and Can Be Used to Induce SARS-CoV-2 Immunity. J Biol Chem 2021, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambrosone, A.; Barbulova, A.; Cappetta, E.; Cillo, F.; De Palma, M.; Ruocco, M.; Pocsfalvi, G. Plant Extracellular Vesicles: Current Landscape and Future Directions. Plants 2023, Vol. 12, Page 4141 2023, 12, 4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomatto, M.A.C.; Gai, C.; Negro, F.; Massari, L.; Deregibus, M.C.; Grange, C.; De Rosa, F.G.; Camussi, G. Plant-Derived Extracellular Vesicles as a Delivery Platform for RNA-Based Vaccine: Feasibility Study of an Oral and Intranasal SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 974–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massaro, C.; Sgueglia, G.; Frattolillo, V.; Baglio, S.R.; Altucci, L.; Dell’aversana, C. Extracellular Vesicle-Based Nucleic Acid Delivery: Current Advances and Future Perspectives in Cancer Therapeutic Strategies. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orefice, N.S. Development of New Strategies Using Extracellular Vesicles Loaded with Exogenous Nucleic Acid. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomatto, M.A.C.; Gai, C.; Negro, F.; Massari, L.; Deregibus, M.C.; De Rosa, F.G.; Camussi, G. Oral Delivery of MRNA Vaccine by Plant-Derived Extracellular Vesicle Carriers. Cells 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhu, Z.; Li, J. Pharmacokinetic Analyses of a Lipid Nanoparticle-Encapsulated MRNA-Encoded Antibody against Rift Valley Fever Virus. Mol Pharm 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, M.; Rosenblum, H.G.; Moulia, D.L.; Broder, K.R.; Shimabukuro, T.T.; Taylor, C.A.; Havers, F.P.; Meyer, S.A.; Dooling, K.; Oliver, S.E.; et al. A Summary of the Advisory Committee for Immunization Practices (ACIP) Use of a Benefit-Risk Assessment Framework during the First Year of COVID-19 Vaccine Administration in the United States. Vaccine 2023, 41, 6456–6467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bitounis, D.; Jacquinet, E.; Rogers, M.A.; Amiji, M.M. Strategies to Reduce the Risks of MRNA Drug and Vaccine Toxicity. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schober, G.B.; Story, S.; Arya, D.P. A Careful Look at Lipid Nanoparticle Characterization: Analysis of Benchmark Formulations for Encapsulation of RNA Cargo Size Gradient. Sci Rep 2024, 14, 2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schramm, C.A.; Moon, D.; Peyton, L.; Lima, N.S.; Wake, C.; Boswell, K.L.; Henry, A.R.; Laboune, F.; Ambrozak, D.; Darko, S.W.; et al. Interaction Dynamics between Innate and Adaptive Immune Cells Responding to SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination in Non-Human Primates. Nat Commun 2023, 14, 7961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warminski, M.; Mamot, A.; Depaix, A.; Kowalska, J.; Jemielity, J. Chemical Modifications of MRNA Ends for Therapeutic. Acc Chem Res 2023, 56, 2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbett, K.S.; Edwards, D.K.; Leist, S.R.; Abiona, O.M.; Boyoglu-Barnum, S.; Gillespie, R.A.; Himansu, S.; Schäfer, A.; Ziwawo, C.T.; DiPiazza, A.T.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 MRNA Vaccine Design Enabled by Prototype Pathogen Preparedness. Nature 2020, 586, 567–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strenkowska, M.; Grzela, R.; Majewski, M.; Wnek, K.; Kowalska, J.; Lukaszewicz, M.; Zuberek, J.; Darzynkiewicz, E.; Kuhn, A.N.; Sahin, U.; et al. Cap Analogs Modified with 1,2-Dithiodiphosphate Moiety Protect MRNA from Decapping and Enhance Its Translational Potential. Nucleic Acids Res 2016, gkw896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasprzyk, R.; Jemielity, J. Enzymatic Assays to Explore Viral MRNA Capping Machinery. ChemBioChem 2021, 22, 3236–3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grudzien-Nogalska, E.; Jemielity, J.; Kowalska, J.; Darzynkiewicz, E.; Rhoads, R.E. Phosphorothioate Cap Analogs Stabilize MRNA and Increase Translational Efficiency in Mammalian Cells. RNA 2007, 13, 1745–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solodushko, V.; Fouty, B. Terminal Hairpins Improve Protein Expression in IRES-Initiated MRNA in the Absence of a Cap and Polyadenylated Tail. Gene Ther 2023, 30, 620–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradrick, S.S.; Dobrikova, E.Y.; Kaiser, C.; Shveygert, M.; Gromeier, M. Poly(A)-Binding Protein Is Differentially Required for Translation Mediated by Viral Internal Ribosome Entry Sites. RNA 2007, 13, 1582–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borodulina, O.R.; Golubchikova, J.S.; Ustyantsev, I.G.; Kramerov, D.A. Polyadenylation of RNA Transcribed from Mammalian SINEs by RNA Polymerase III: Complex Requirements for Nucleotide Sequences. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Gene Regulatory Mechanisms 2016, 1859, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edmonds, M.; Vaughan, M.H.; Nakazato, H. Polyadenylic Acid Sequences in the Heterogeneous Nuclear RNA and Rapidly-Labeled Polyribosomal RNA of HeLa Cells: Possible Evidence for a Precursor Relationship. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 1971, 68, 1336–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linares-Fernández, S.; Lacroix, C.; Exposito, J.-Y.; Verrier, B. Tailoring MRNA Vaccine to Balance Innate/Adaptive Immune Response. Trends Mol Med 2020, 26, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadler, C.R.; Bähr-Mahmud, H.; Celik, L.; Hebich, B.; Roth, A.S.; Roth, R.P.; Karikó, K.; Türeci, Ö.; Sahin, U. Elimination of Large Tumors in Mice by MRNA-Encoded Bispecific Antibodies. Nat Med 2017, 23, 815–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trepotec, Z.; Geiger, J.; Plank, C.; Aneja, M.K.; Rudolph, C. Segmented Poly(A) Tails Significantly Reduce Recombination of Plasmid DNA without Affecting MRNA Translation Efficiency or Half-Life. RNA 2019, 25, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Fang, E.; Wang, Y.; Shi, L.; Li, J.; Peng, Q.; Li, X.; Zhao, D.; Liu, X.; Liu, X.; et al. An MRNA Vaccine against Rabies Provides Strong and Durable Protection in Mice. Front Immunol 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudla, G.; Lipinski, L.; Caffin, F.; Helwak, A.; Zylicz, M. High Guanine and Cytosine Content Increases MRNA Levels in Mammalian Cells. PLoS Biol 2006, 4, e180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannarozzi, G.; Schraudolph, N.N.; Faty, M.; von Rohr, P.; Friberg, M.T.; Roth, A.C.; Gonnet, P.; Gonnet, G.; Barral, Y. A Role for Codon Order in Translation Dynamics. Cell 2010, 141, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.; Lin, A.; Xu, C.; Li, Z.; Liu, K.; Liu, B.; Ma, X.; Zhao, F.; Jiang, H.; et al. Algorithm for Optimized MRNA Design Improves Stability and Immunogenicity. Nature 2023, 621, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.; Jain, A.; Mauro, E.; LeShane, K.; Densmore, D. ICOR: Improving Codon Optimization with Recurrent Neural Networks. BMC Bioinformatics 2023, 24, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Hu, Q. Advances in SaRNA Vaccine Research against Emerging/Re-Emerging Viruses. Vaccines (Basel) 2023, 11, 1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, A.; Mutschler, H. Design Principles and Applications of Synthetic Self-replicating <scp>RNAs</Scp>. WIREs RNA 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pateev, I.; Seregina, K.; Ivanov, R.; Reshetnikov, V. Biodistribution of RNA Vaccines and of Their Products: Evidence from Human and Animal Studies. Biomedicines 2023, 12, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domingo, E.; Soria, M.E.; Gallego, I.; de Ávila, A.I.; García-Crespo, C.; Martínez-González, B.; Gómez, J.; Briones, C.; Gregori, J.; Quer, J.; et al. A New Implication of Quasispecies Dynamics: Broad Virus Diversification in Absence of External Perturbations. Infection, Genetics and Evolution 2020, 82, 104278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volff, J.-N.; Brosius, J. Modern Genomes with Retro-Look: Retrotransposed Elements, Retroposition and the Origin of New Genes. In Gene and Protein Evolution; KARGER: Basel, 2007; pp. 175–190. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Humadi, N. Pre-Clinical Toxicology Considerations for Vaccine Development. Vaccine 2017, 35, 5762–5767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dulin, N.; Spanier, A.; Merino, K.; Hutter, J.N.; Waterman, P.E.; Lee, C.; Hamer, M.J. Systematic Review of Marburg Virus Vaccine Nonhuman Primate Studies and Human Clinical Trials. Vaccine 2021, 39, 202–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbeke, R.; Lentacker, I.; De Smedt, S.C.; Dewitte, H. The Dawn of MRNA Vaccines: The COVID-19 Case. Journal of Controlled Release 2021, 333, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, G.; Kawaoka, Y. Which Virus Will Cause the Next Pandemic? Viruses 2023, 15, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).