Submitted:
04 February 2024
Posted:
05 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Entropy Applications to Education
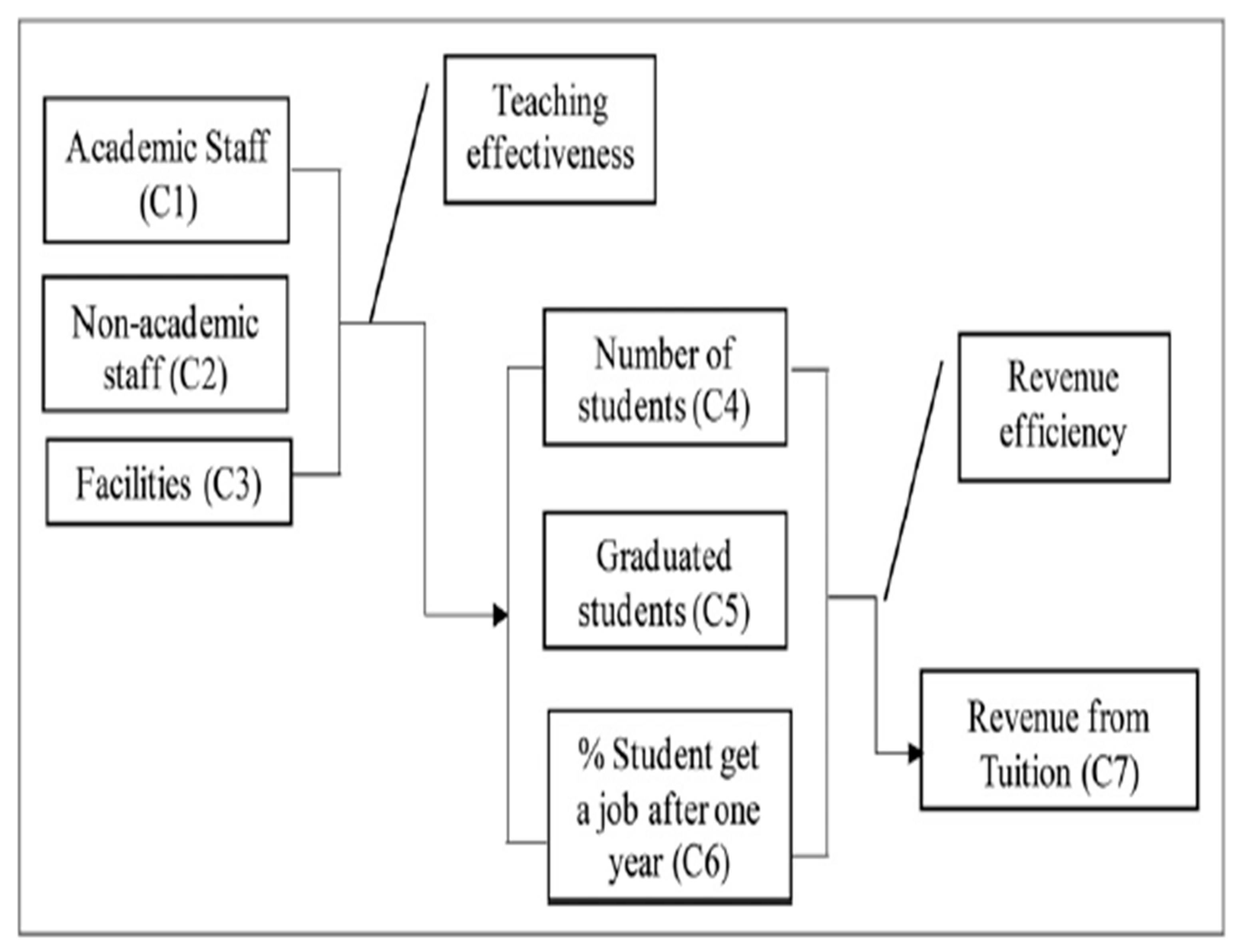
- Teaching effectiveness, which refers to the measure of how well educational instruction is delivered and how effectively students learn and acquire knowledge.
- Revenue efficiency, on the other hand, pertains to the effectiveness of financial resources and expenditures in generating income for the educational institution, particularly through tuition fees.

3. Open Problems
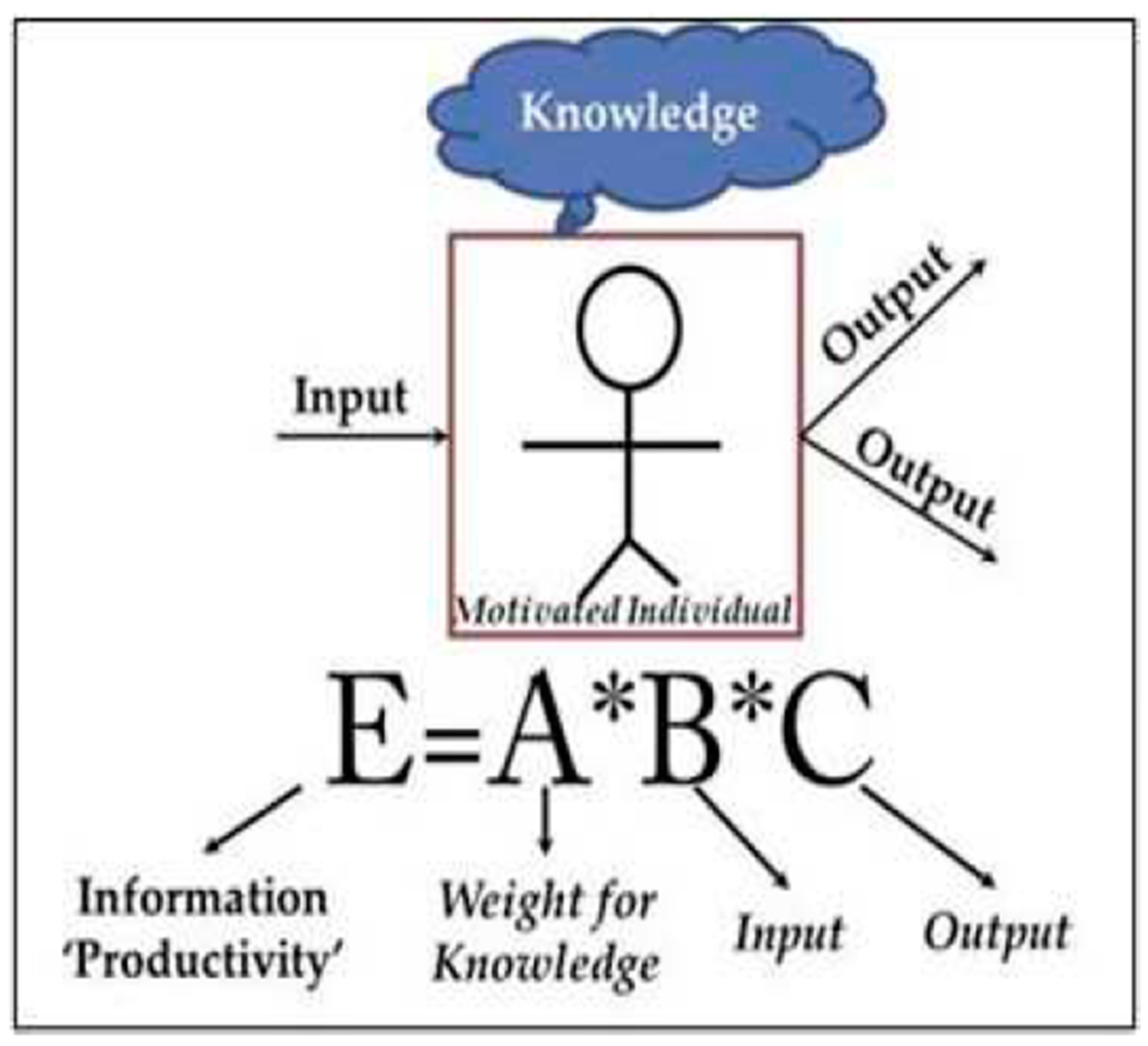
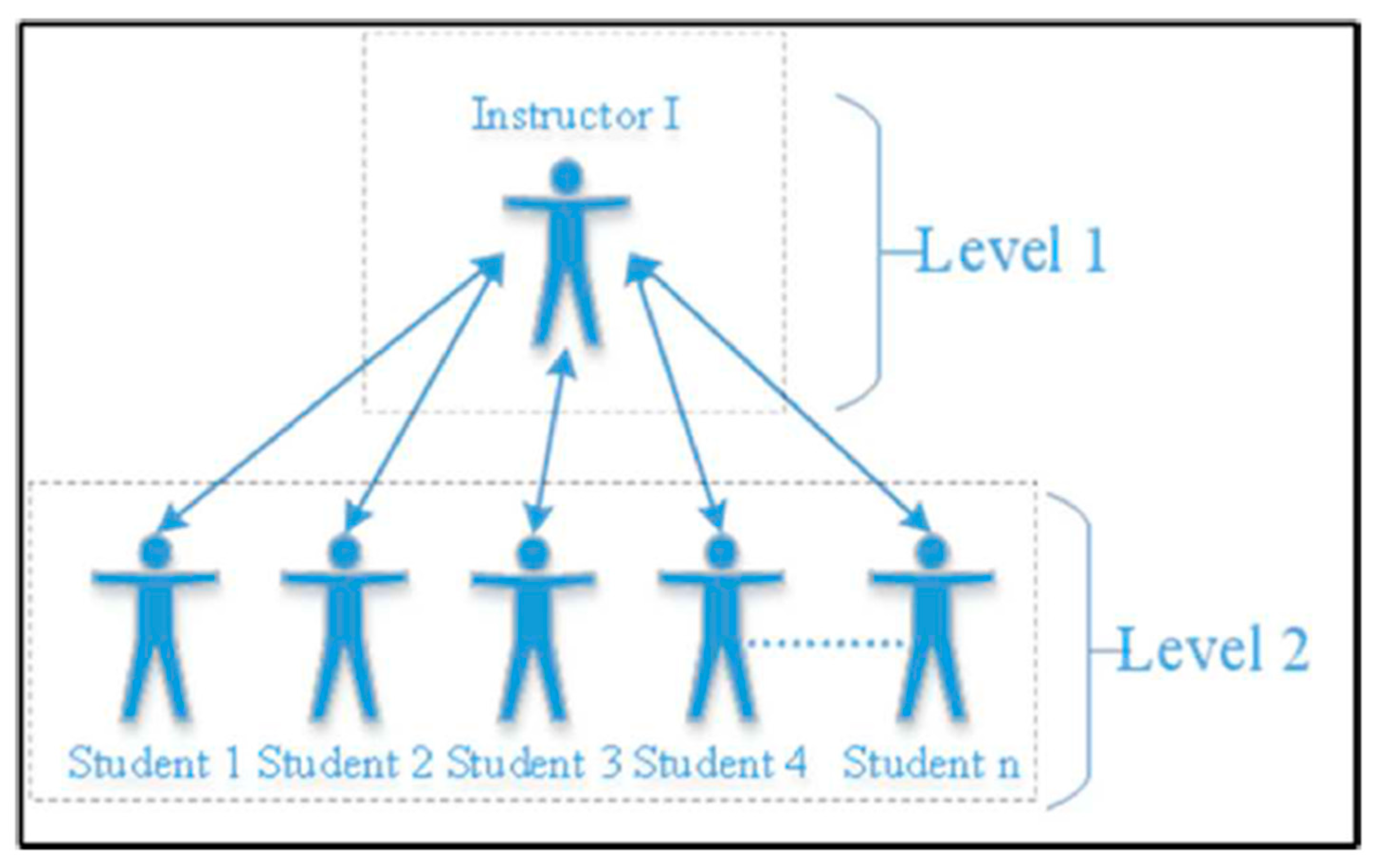
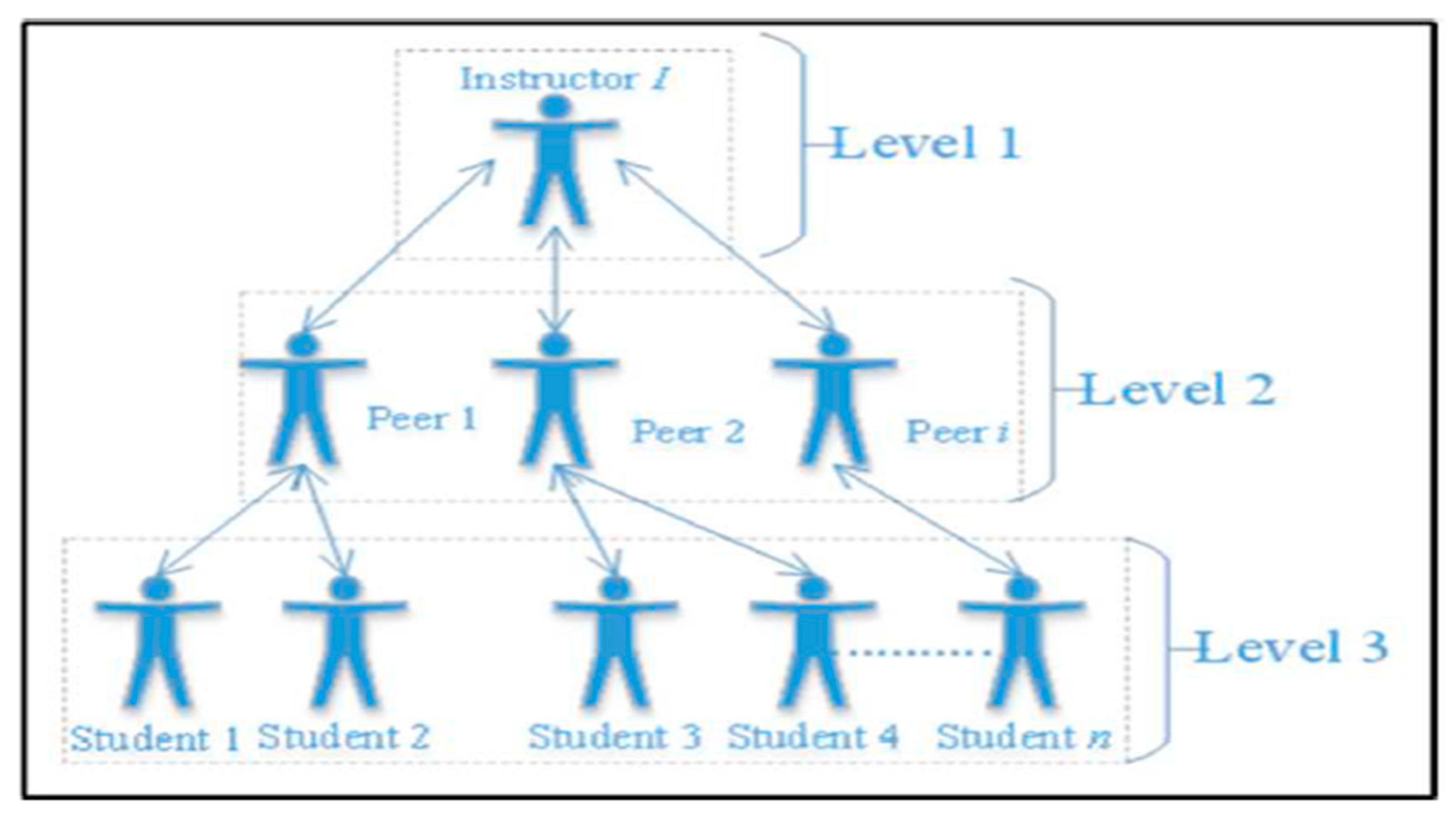
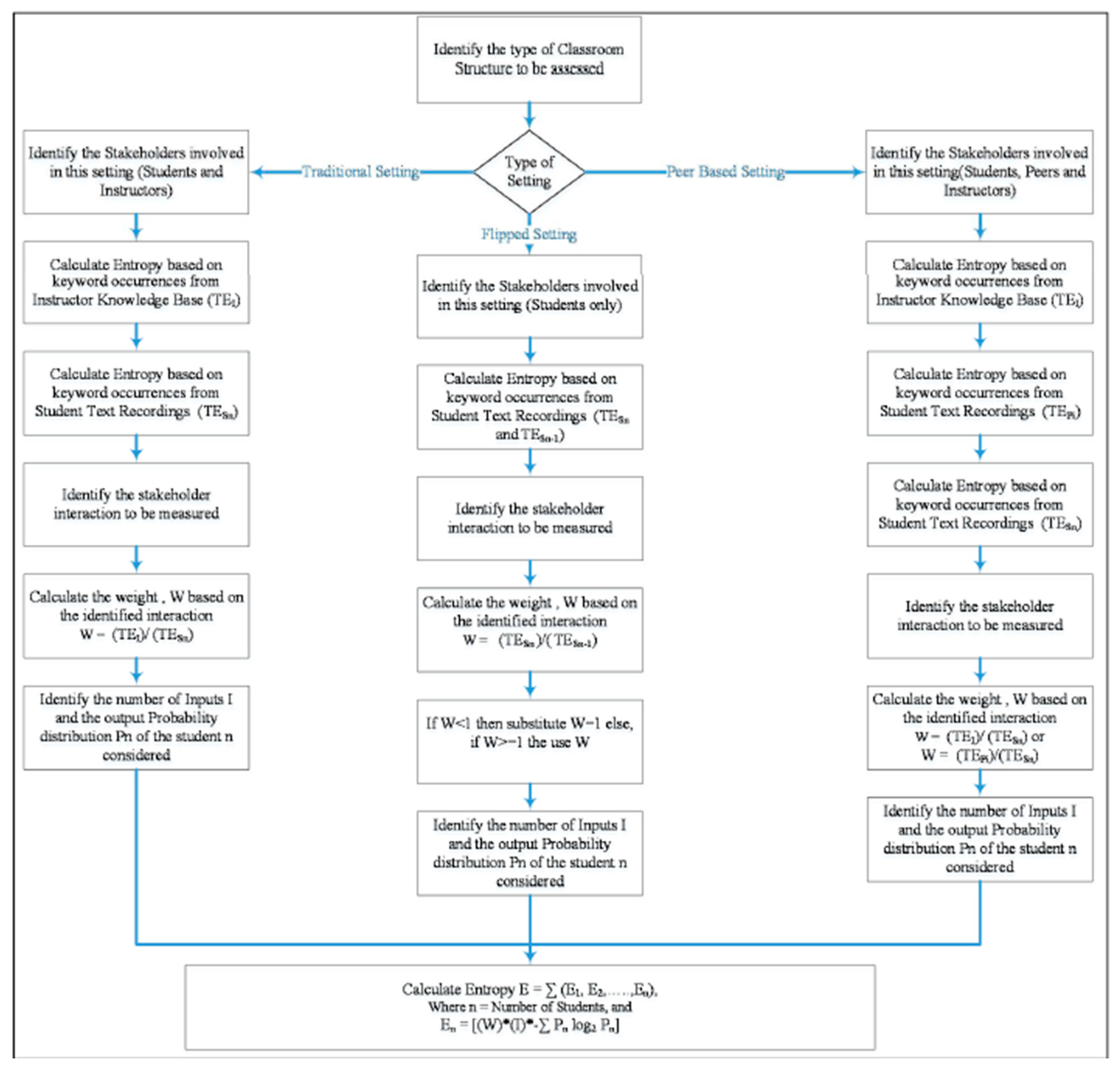
- Following (Akundi et al., 2023), is it possible to propose an entropy-based assessment framework for a classroom the structural setting’s analysis and assessment, considering factors like interaction patterns, knowledge of the actors, number of actors, and types of classroom interfaces. The question is still open.
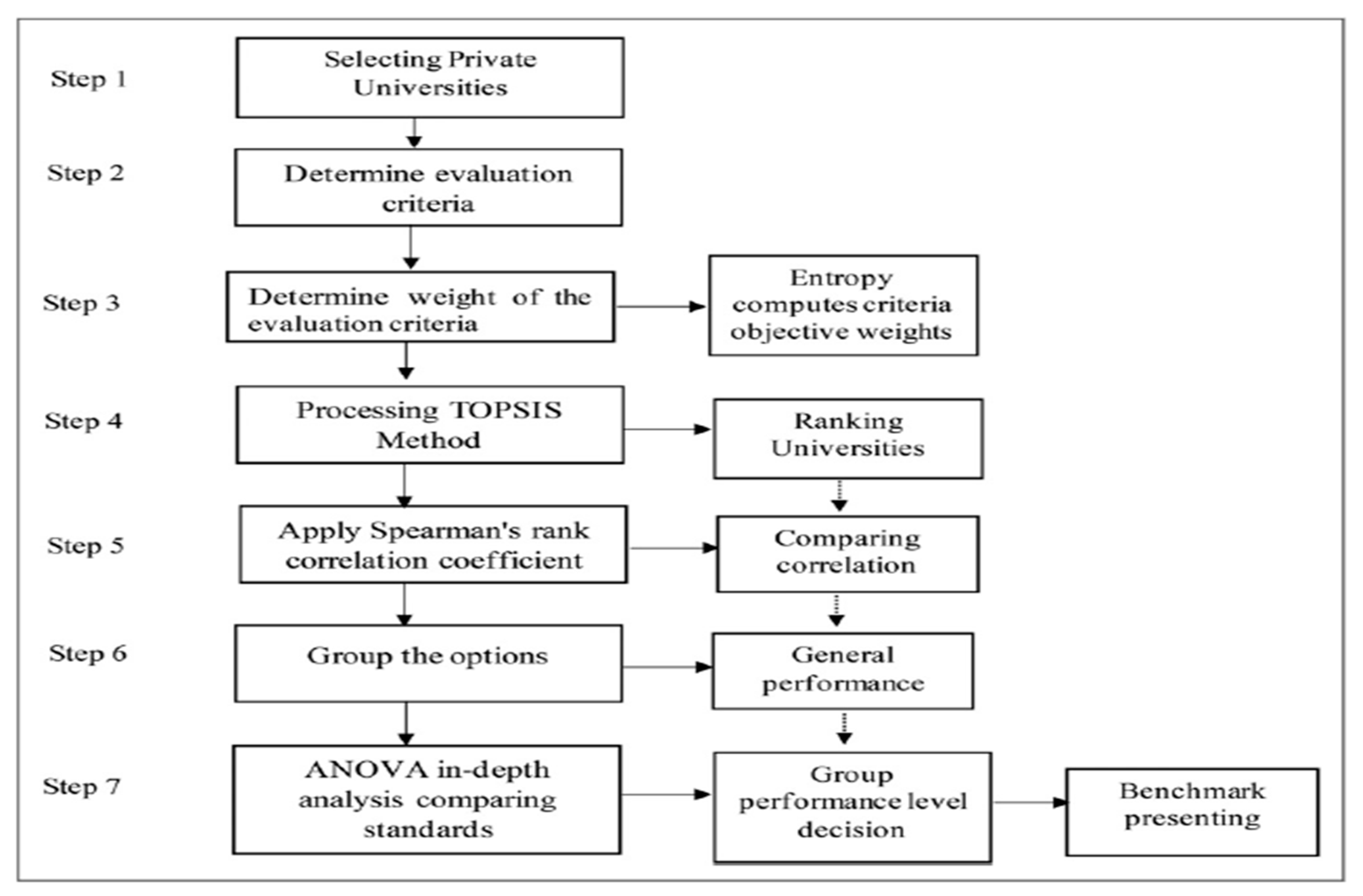
- The proposed model (Wang et al., 2022), does not consider operational efficiency comprehensively or evaluate the impact of scientific research activities, which vary among universities. Additionally, the analysis does not cover all private universities and does not consider factors like reputation, establishment time, or location that can influence rankings. This proposes an open problem that needs to be addressed and applied to various international educational settings.
- Having Shannon’s entropy (c.f., Equation(1)) would be the very basic entropy to employ. On another strong note, the use of Ismail’s innovative entropy forms (Mageed, 2022, 2023(a), 2023(b), 2023(c)) would add more to the stellar fusion of the educational profile on all settings. This is based on the variety of the involved parameters, especially, the information-theoretic parameter that fine tunes LRIs(long-range interactions), while is a unique descriptor of SRIs(short-range interactions). Both LRIs and SRIs will have a significant impact on all educational setting and performance.
4. Closing Moments
References
- Cunha, M.d.Vale,Ribeiro Santos, C.C,Moret, M.A, de Barros Pereira, H.B. 2020. Shannon entropy in time-varying semantic networks of titles of scientific Paper. Appl Net Sci 5, 53. [CrossRef]
- Arbabi, H, Mezic,I. 2017. Ergodic theory, dynamic mode decomposition, and computation of spectral properties of the Koopman operator. SIAM Journal on Applied Dynamical Systems, 16(4):2096-126. [CrossRef]
- Montesinos, Castaldo, R,Pecchia, L. 2018.On the use of approximate entropy and sample entropy with center of pressure time-series. J Neuro Engineering Rehabil 15, 116. [CrossRef]
- Burget, D. 2018. Rescaled entropy and cellular Automata. Available online at: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2005.08585.pdf.
- Zunino,L, Kulp, CW. 2017. Detecting nonlinearity in short and noisy time series using the permutation entropy. Physics Letters A, 13;381(42):3627-35. [CrossRef]
- Gomes, JB, Carneiro, MJ. 2021.Polynomial Entropy for Interval Maps and Lap Number. Qualitative Theory of Dynamical Systems, 20(1):1-6. [CrossRef]
- Donglai, W, Joseph, Zisserman, L, Freeman, A.2018. Learning and Using The Arrow of Time. CVF version and available on IEEE Xplore. Online at: https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_cvpr_2018/papers/Wei_L earning_ and Using CVPR_2018_paper.pdf.
- Zhang, B, Shang, P. 2020. Measuring information transfer by dispersion transfer Entropy. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, Vol 89. [CrossRef]
- Manish, KH. 2020.A Brief History of Entropy, Towards Data Science. Online at: https://towardsdatascience.com/a-brief-history-of -entropy- chapter-1-9a2f1bc0d6de.
- Akundi, A., Lopez, V., & Luna, S.2023. Information entropy as a basis for classroom structural assessment. In 2023 IEEE International Systems Conference (SysCon) (pp. 1-7). IEEE. [CrossRef]
- Wang, T. C., Thu Nguyen, T. T., & Phan, B. N. 2022. Analyzing higher education performance by entropy-TOPSIS method: A case study in Viet Nam private universities. Measurement and Control, 55(5-6), 385-410. [CrossRef]
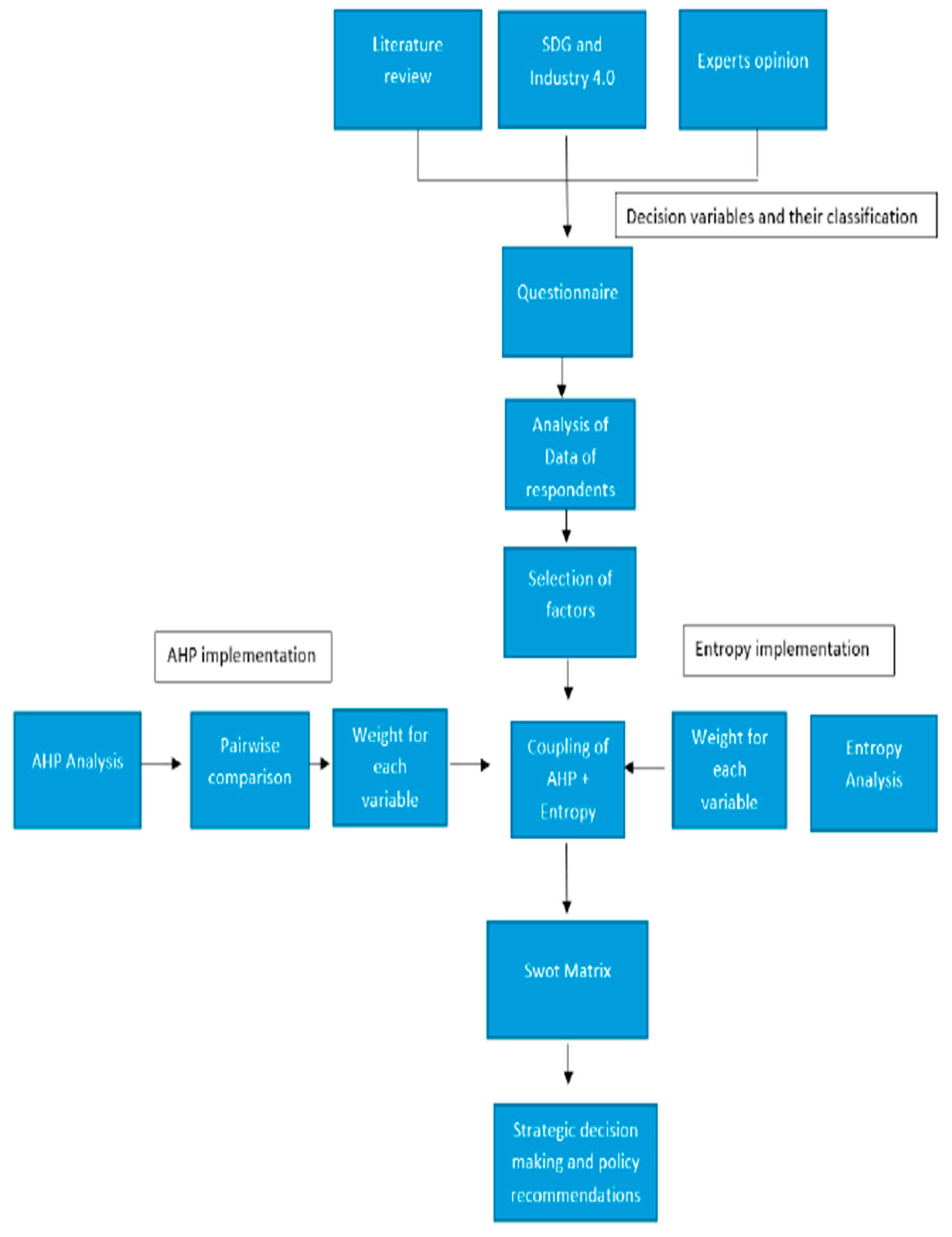
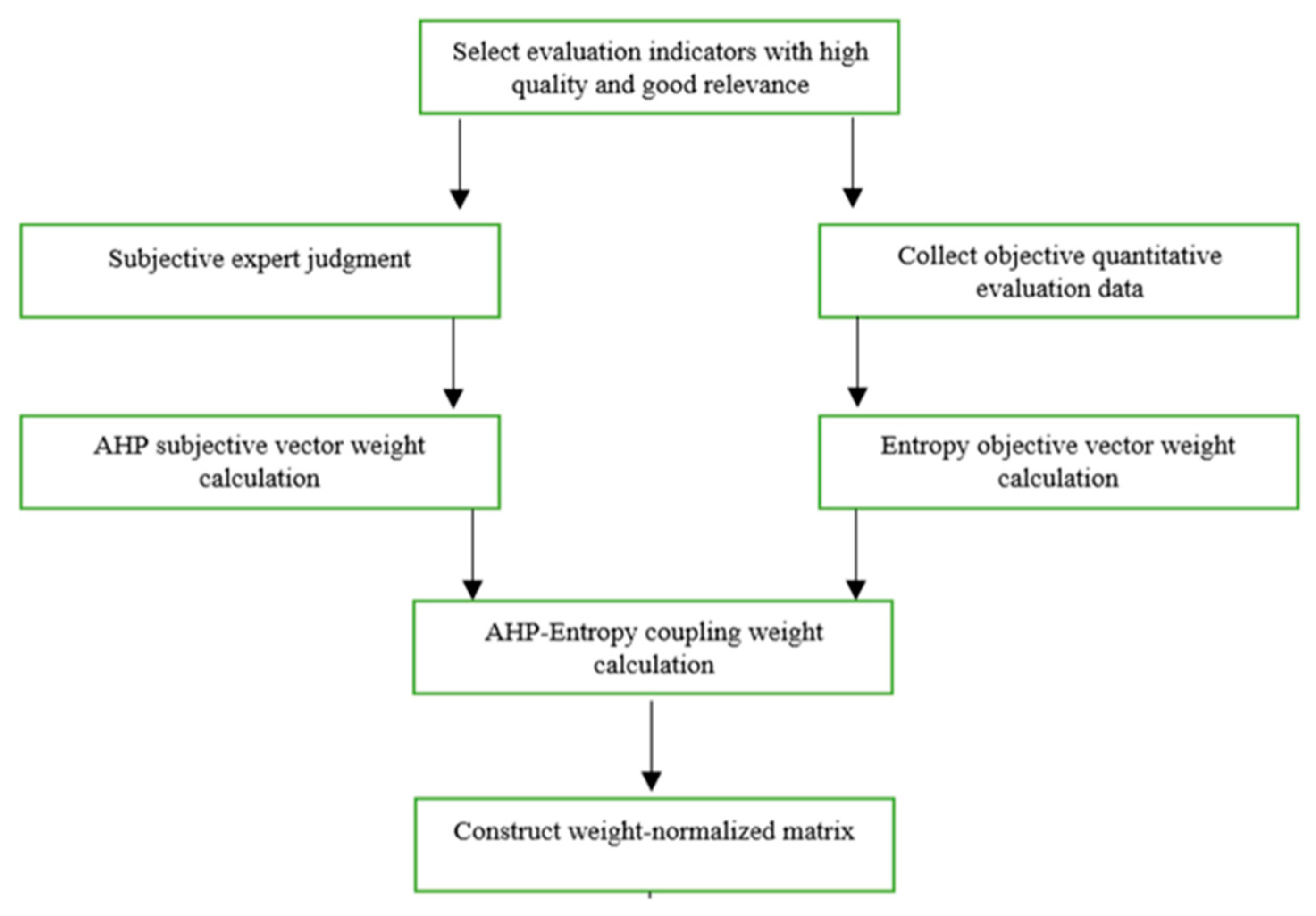
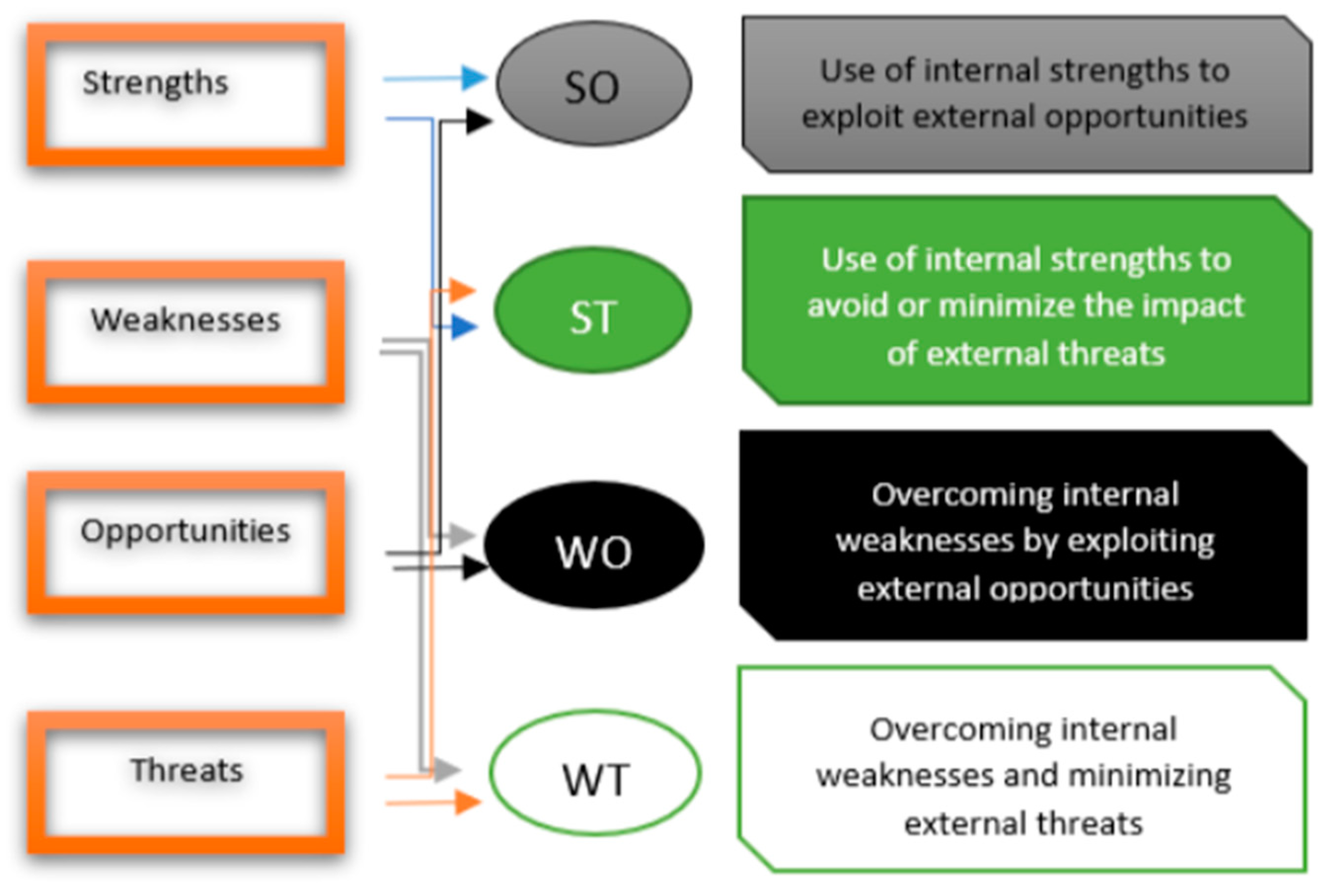
- Fahim, A., Tan, Q., Naz, B., Ain, Q. U., & Bazai, S. U. 2021. Sustainable higher education reform quality assessment using SWOT analysis with integration of AHP and entropy models: A case study of Morocco. Sustainability, 13(8), 4312. [CrossRef]
- Mageed, I.A., and Zhang,Q.2022. An Information Theoretic Unified Global Theory For a Stable M/G/1 Queue With Potential Maximum Entropy Applications to Energy Works. 2022 Global Energy Conference (GEC). Batman, Turkey, 2022, pp. 300-305. [CrossRef]
- Mageed, I.A. 2023(a). Fractal Dimension of Ismail’s Third Entropy with Fractal Applications to CubeSat Technologies and Education. The 2nd International Conference on Applied Mathematics, Informatics, and Computing Sciences (AMICS 2023). Ghent University, Belgium. [CrossRef]
- Mageed, I.A. 2023(b)."Fractal Dimension(Df) Theory of Ismail’s Second Entropy () with Potential Fractal Applications to ChatGPT, Distributed Ledger Technologies(DLTs) and Image Processing(IP). 2023 International Conference on Computer and Applications (ICCA), Cairo, Egypt, 2023, pp. 1-6. [CrossRef]
- Mageed, I.A. 2023(c).Fractal Dimension (Df) of Ismail’s Fourth Entropy with Fractal Applications to Algorithms, Haptics, and Transportation. 2023 International Conference on Computer and Applications (ICCA).Cairo, Egypt, pp. 1-6. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




