Submitted:
04 February 2024
Posted:
05 February 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
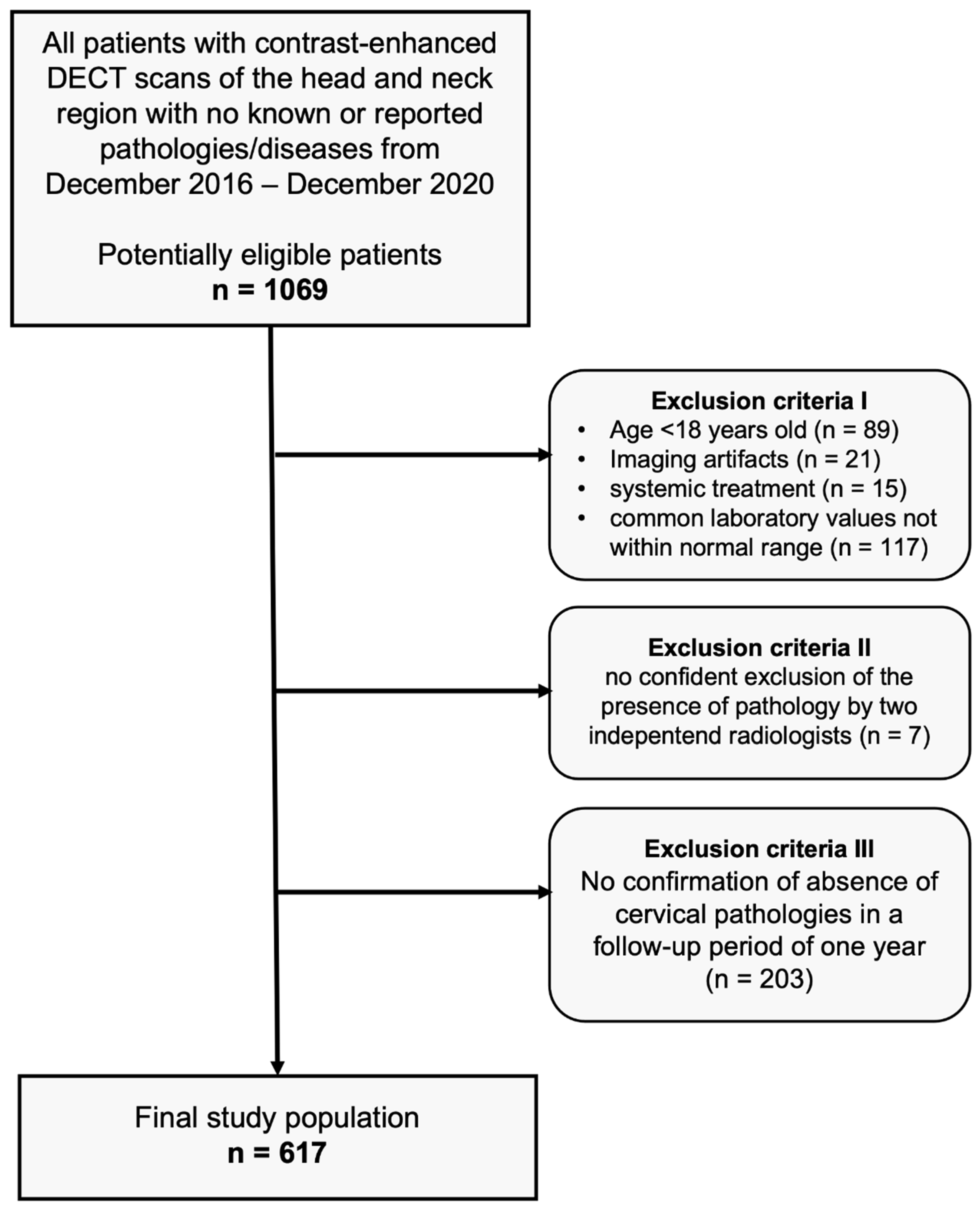
2.1. Study population
2.2. DECT imaging technique
2.3. Iodine mapping and uptake measurements
2.4. Statistical analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient collective
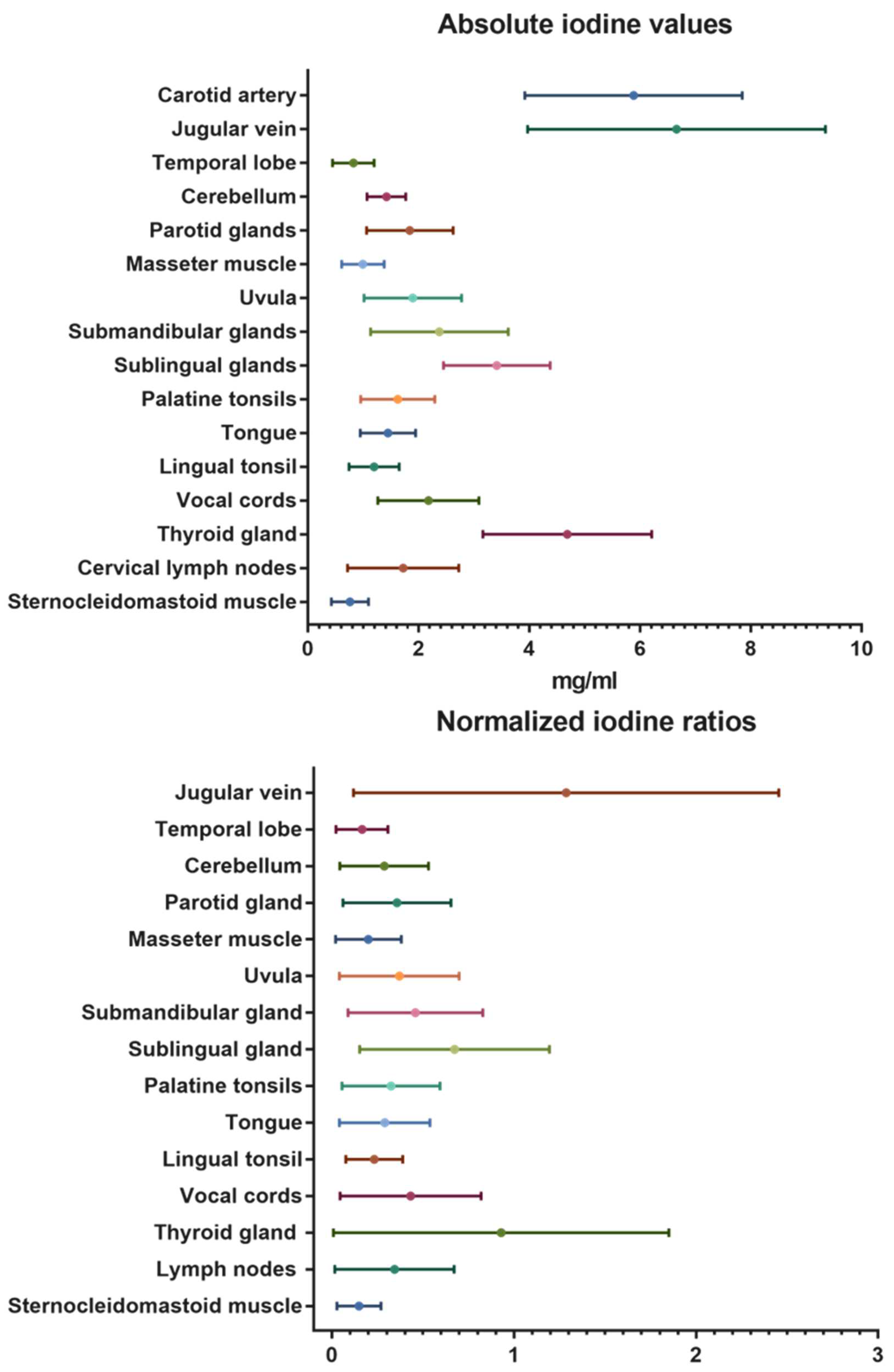
3.2. Overall iodine values
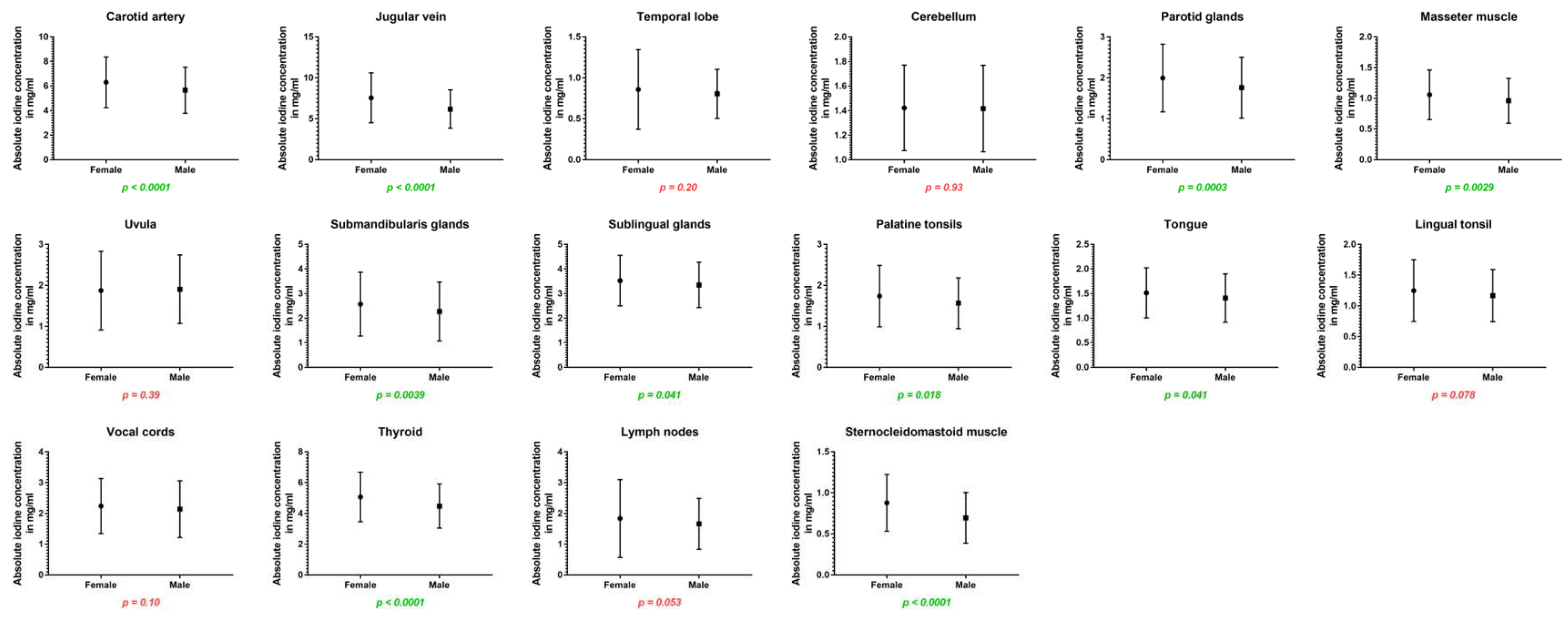
3.3. Impact of sex
3.4. Impact of age
3.5. Impact of BMI
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Abbreviations
| BMI | body mass index |
| CT | computed tomography |
| DECT | dual-energy CT |
| kV | kilovolt |
| mAs | milliampere-seconds |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| ROI | region of interest |
References
- Roele, E.D.; Timmer, V.C.M.L.; Vaassen, L.A.A.; van Kroonenburgh, A.M.J.L.; Postma, A.A. Dual-Energy CT in Head and Neck Imaging. Curr Radiol Rep 2017, 5, 19–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forghani, R. Advanced dual-energy CT for head and neck cancer imaging. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 2015, 15, 1489–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harsaker, V.; Jensen, K.; Andersen, H.K.; Martinsen, A.C. Quantitative benchmarking of iodine imaging for two CT spectral imaging technologies: a phantom study. European Radiology Experimental 2021, 5, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.S.; Weidinger, S.; Czwikla, R.; Kaltenbach, B.; Albrecht, M.H.; Lenga, L.; Vogl, T.J.; Wichmann, J.L. Iodine and Fat Quantification for Differentiation of Adrenal Gland Adenomas From Metastases Using Third-Generation Dual-Source Dual-Energy Computed Tomography. Investigative radiology 2018, 53, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, S.S.; Trapp, F.; Wichmann, J.L.; Albrecht, M.H.; Lenga, L.; Durden, J.; Booz, C.; Vogl, T.J.; D’Angelo, T. Dual-energy CT in early acute pancreatitis: improved detection using iodine quantification. Eur Radiol 2019, 29, 2226–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelgrim, G.J.; van Hamersvelt, R.W.; Willemink, M.J.; Schmidt, B.T.; Flohr, T.; Schilham, A.; Milles, J.; Oudkerk, M.; Leiner, T.; Vliegenthart, R. Accuracy of iodine quantification using dual energy CT in latest generation dual source and dual layer CT. European radiology 2017, 27, 3904–3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenga, L.; Bernatz, S.; Martin, S.S.; Booz, C.; Solbach, C.; Mulert-Ernst, R.; Vogl, T.J.; Leithner, D. Iodine Map Radiomics in Breast Cancer: Prediction of Metastatic Status. Cancers (Basel) 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Kim, S.H.; Ryu, H.S.; Han, J.K. Iodine Quantification on Spectral Detector-Based Dual-Energy CT Enterography: Correlation with Crohn’s Disease Activity Index and External Validation. Korean J Radiol 2018, 19, 1077–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, B.N.; Vernuccio, F.; Meyer, M.; Godwin, B.; Rosenberg, M.; Rudnick, N.; Harring, S.; Nelson, R.; Ramirez-Giraldo, J.C.; Farjat, A.; et al. Dual-Energy CT Material Density Iodine Quantification for Distinguishing Vascular From Nonvascular Renal Lesions: Normalization Reduces Intermanufacturer Threshold Variability. AJR. American journal of roentgenology 2019, 212, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, N.; Su, X.; Li, K.; Yu, D.; Ouyang, A. FORCE dual-energy CT in pathological grading of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Oncol Lett 2019, 18, 6405–6412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.Q.; Xin, Y.K.; Jing, Y.; Li, G.F.; Wang, S.M.; Rong, W.C.; Xiao, G.; Lei, X.B.; Li, B.; Hu, Y.C.; et al. Iodine Quantification Using Dual-Energy Computed Tomography for Differentiating Thymic Tumors. Journal of computer assisted tomography 2018, 42, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasser, E.C. Second Harry Fischer Lecture. Sex, surfaces, sulfation, and sensitivity. Investigative radiology 1991, 26 (Suppl. 1), S16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasser, E.C.; Berry, C.C.; Talner, L.B.; Santini, L.C.; Lang, E.K.; Gerber, F.H.; Stolberg, H.O. Pretreatment with corticosteroids to alleviate reactions to intravenous contrast material. N Engl J Med 1987, 317, 845–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klostranec, J.M.; Rohringer, T.; Gerber, R.; Murphy, K.J. The Role of Biologic Sex in Anaphylactoid Contrast Reactions: An Important Consideration for Women of Reproductive Age and Undergoing Hormone Replacement Therapy. Radiology 2021, 299, 272–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, S.; Gupta, R.; Kelly, H.; Curtin, H.D.; Forghani, R. Multiparametric Evaluation of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Using a Single-Source Dual-Energy CT with Fast kVp Switching: State of the Art. Cancers (Basel) 2015, 7, 2201–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, A.C.; Day, T.A.; Neville, B.W. Oral cavity and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma--an update. CA Cancer J Clin 2015, 65, 401–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Große Hokamp, N.; Abdullayev, N.; Persigehl, T.; Schlaak, M.; Wybranski, C.; Holz, J.A.; Streichert, T.; Alkadhi, H.; Maintz, D.; Haneder, S. Precision and reliability of liver iodine quantification from spectral detector CT: evidence from phantom and patient data. European radiology 2019, 29, 2098–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Wagner-Bartak, N.; Jensen, C.T.; Hui, A.; Wei, W.; Lertdilok, P.; Qayyum, A.; Tamm, E.P. Dual-energy CT of pancreatic adenocarcinoma: reproducibility of primary tumor measurements and assessment of tumor conspicuity and margin sharpness. Abdominal Radiology 2016, 41, 1317–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-H.; Du, Y.-M.; Huang, H.-M. Accuracy of dual-energy computed tomography for the quantification of iodine in a soft tissue-mimicking phantom. Journal of Applied Clinical Medical Physics 2015, 16, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Yan, F.; Pan, Z.; Lin, X.; Luo, X.; Shi, C.; Chen, X.; Wang, B.; Zhang, H. Evaluation of dual energy spectral CT in differentiating metastatic from non-metastatic lymph nodes in rectal cancer: Initial experience. European journal of radiology 2015, 84, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mileto, A.; Marin, D.; Alfaro-Cordoba, M.; Ramirez-Giraldo, J.C.; Eusemann, C.D.; Scribano, E.; Blandino, A.; Mazziotti, S.; Ascenti, G. Iodine Quantification to Distinguish Clear Cell from Papillary Renal Cell Carcinoma at Dual-Energy Multidetector CT: A Multireader Diagnostic Performance Study. Radiology 2014, 273, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarzour, J.G.; Milner, D.; Valentin, R.; Jackson, B.E.; Gordetsky, J.; West, J.; Rais-Bahrami, S.; Morgan, D.E. Quantitative iodine content threshold for discrimination of renal cell carcinomas using rapid kV-switching dual-energy CT. Abdominal Radiology 2017, 42, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, S.; Radice, D.; Femia, M.; De Marco, P.; Origgi, D.; Preda, L.; Barberis, M.; Vigorito, R.; Mauri, G.; Mauro, A.; et al. Metastatic and non-metastatic lymph nodes: quantification and different distribution of iodine uptake assessed by dual-energy CT. European radiology 2018, 28, 760–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Luo, D.; Li, L.; Zhao, Y.; Lin, M.; Guo, W.; Zhou, C. Differentiation of malignant cervical lymphadenopathy by dual-energy CT: a preliminary analysis. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 31020–31020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauter, A.P.; Ostmeier, S.; Nadjiri, J.; Deniffel, D.; Rummeny, E.J.; Pfeiffer, D. Iodine concentration of healthy lymph nodes of neck, axilla, and groin in dual-energy computed tomography. Acta radiologica (Stockholm, Sweden: 1987) 2020, 61, 1505–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
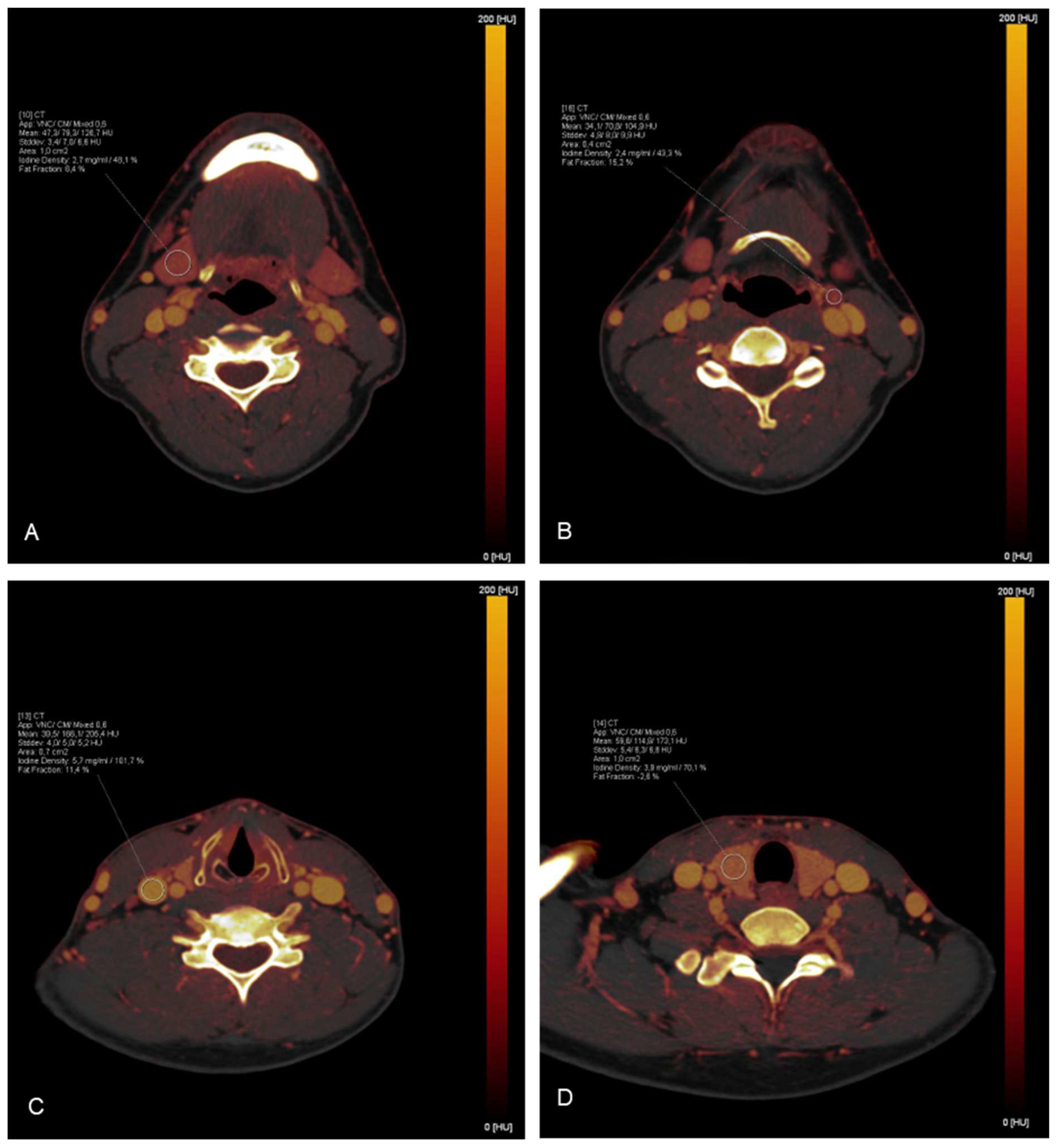
| Structure | Number of ROI | ROI placement |
|---|---|---|
| Carotid artery | 2 | central within the vessel at the level of the thyroid gland |
| Jugular vein | 2 | central within the vessel at the level of the thyroid gland |
| Temporal lobe | 2 | right and left temporal lobe |
| Cerebellum | 2 | right and left cerebellum |
| Parotid glands | 2 | right and left gland, avoiding duct |
| Masseter muscle | 2 | the superficial portion on both sides |
| Uvula | 1 | distal of the soft palatine |
| Submandibular glands | 2 | right and left gland, avoiding duct |
| Sublingual glands | 2 | right and left gland, avoiding surrounding tissue |
| Palatine tonsils | 2 | at the most prominent portion |
| Tongue | 2 | right and left half of the tongue |
| Lingual tonsil | 1 | at the most prominent portion |
| Vocal cords | 2 | at the level of arytenoid cartilage |
| Thyroid gland | 4 | upper and lower portion both sides |
| Cervical lymph nodes | 5 | one on each cervical lymph node level |
| Sternocleidomastoid muscle | 2 | common muscle belly |
| Structure | Absolute iodine concentration in mg/ml (mean ± SD) |
Normalized iodine ratio |
|---|---|---|
| Carotid artery | 5.88 ± 2.0 | 1 |
| Jugular vein | 6.66 ± 2.7 | 1.29 ± 1.2 |
| Temporal lobe | 0.82 ± 0.4 | 0.17 ± 0.1 |
| Cerebellum | 1.41 ± 0.4 | 0.29 ± 0.2 |
| Parotid glands | 1.84 ± 0.8 | 0.36 ± 0.3 |
| Masseter muscle | 0.99 ± 0.4 | 0.21 ± 0.2 |
| Uvula | 1.90 ± 0.9 | 0.37 ± 0.3 |
| Submandibular glands | 2.37 ± 1.2 | 0.46 ± 0.4 |
| Sublingual glands | 3.41 ± 1.0 | 0.67 ± 0.5 |
| Palatine tonsils | 1.62 ± 0.7 | 0.33 ± 0.3 |
| Tongue | 1.45 ± 0.5 | 0.29 ± 0.2 |
| Lingual tonsil | 1.20 ± 0.5 | 0.23 ± 0.2 |
| Vocal cords | 2.18 ± 0.9 | 0.43 ± 0.4 |
| Thyroid gland | 4.68 ± 1.5 | 0.93 ± 0.9 |
| Cervical lymph nodes | 1.72 ± 1.0 | 0.35 ± 0.3 |
| Sternocleidomastoid muscle | 0.76 ± 0.3 | 0.15 ± 0.1 |
| Structure | Absolute iodine concentration in mg/ml (mean ± SD) |
p-values | |
| Female | Male | ||
| Carotid artery | 6.31 ± 2.1 | 5.66 ± 1.8 | <0.001* |
| Jugular vein | 7.56 ± 3.1 | 6.18 ± 2.3 | <0.001* |
| Temporal lobe | 0.86 ± 0.5 | 0.80 ± 0.3 | 0.199 |
| Cerebellum | 1.42 ± 0.3 | 1.42 ± 0.4 | 0.926 |
| Parotid glands | 2.00 ± 0.8 | 1.76 ± 0.7 | <0.001* |
| Masseter muscle | 1.06 ± 0.4 | 0.96 ± 0.4 | 0.003* |
| Uvula | 1.88 ± 1.0 | 1.91 ± 0.8 | 0.387 |
| Submandibular glands | 2.57 ± 1.3 | 2.27 ± 1.2 | 0.004* |
| Sublingual glands | 3.53 ± 1.0 | 3.35 ± 0.9 | 0.041* |
| Palatine tonsils | 1.74 ± 0.7 | 1.57 ± 0.6 | 0.018* |
| Tongue | 1.52 ± 0.5 | 1.41 ± 0.5 | 0.041* |
| Lingual tonsil | 1.25 ± 0.5 | 1.17 ± 0.4 | 0.078 |
| Vocal cords | 2.24 ± 0.9 | 2.14 ± 0.9 | 0.100 |
| Thyroid gland | 5.07 ± 1.6 | 4.48 ± 1.4 | <0.001* |
| Cervical lymph nodes | 1.83 ± 1.3 | 1.66 ± 0.8 | 0.053 |
| Sternocleidomastoid muscle | 0.87 ± 0.3 | 0.70 ± 0.3 | <0.001* |
| Structure | Normalized iodine ratios | p-values | |
| Female | Male | ||
| Jugular vein | 1.38 ± 1.3 | 1.24 ± 1.1 | 0.008* |
| Temporal lobe | 0.17 ± 0.2 | 0.17 ± 0.1 | 0.073 |
| Cerebellum | 0.27 ± 0.2 | 0.30 ± 0.3 | <0.001* |
| Parotid glands | 0.36 ± 0.2 | 0.37 ± 0.4 | 0.54 |
| Masseter muscle | 0.20 ± 0.2 | 0.21 ± 0.2 | 0.99 |
| Uvula | 0.34 ± 0.3 | 0.39 ± 0.3 | 0.001* |
| Submandibular glands | 0.46 ± 0.3 | 0.46 ± 0.4 | 0.53 |
| Sublingual glands | 0.65 ± 0.4 | 0.71 ± 0.6 | 0.049* |
| Palatine tonsils | 0.31 ± 0.2 | 0.34 ± 0.3 | 0.76 |
| Tongue | 0.29 ± 0.3 | 0.29 ± 0.2 | 0.48 |
| Lingual tonsil | 0.23 ± 0.1 | 0.24 ± 0.2 | 0.18 |
| Vocal cords | 0.41 ± 0.3 | 0.45 ± 0.5 | 0.35 |
| Thyroid gland | 0.94 ± 0.9 | 0.93 ± 0.9 | 0.72 |
| Cervical lymph nodes | 0.34 ± 0.3 | 0.36 ± 0.5 | 0.67 |
| Sternocleidomastoid muscle | 0.16 ± 0.1 | 0.15 ± 0.1 | 0.22 |
| Structure | Absolute iodine concentration in mg/ml (mean ± SD) |
p-values | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18-48 years |
49-64 years |
65-98 years |
18-48 vs 49-64 | 18-48 vs 65-98 | 49-64 vs 65-98 | |
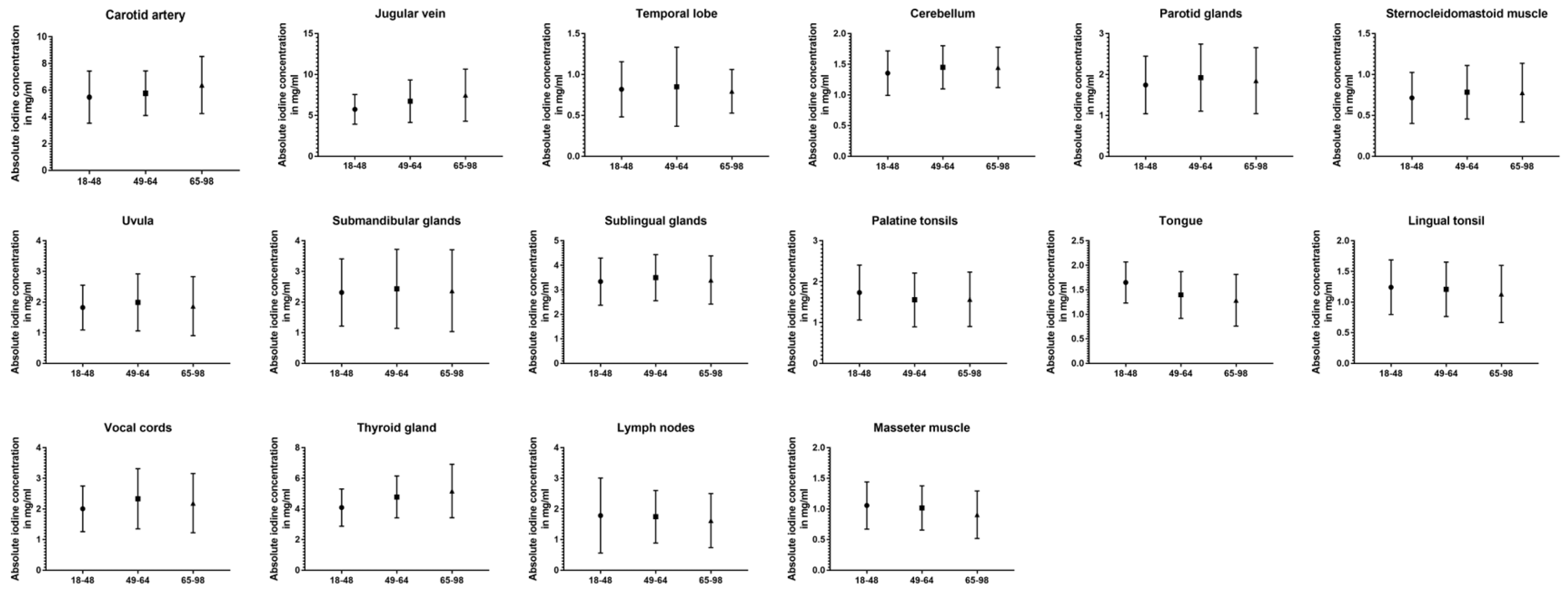
| Carotid artery | 5.48 ± 2.0 | 5.77 ± 1.7 | 6.39 ± 2.1 | 0.027* | <0.001* | 0.008* |
| Jugular vein | 5.75 ± 1.8 | 6.73 ± 2.6 | 7.48 ± 3.2 | <0.001* | <0.001* | 0.024* |
| Temporal lobe | 0.82 ± 0.3 | 0.85 ± 0.5 | 0.80 ± 0.3 | 0.69 | 0.74 | 0.45 |
| Cerebellum | 1.36 ± 0.4 | 1.45 ± 0.4 | 1.45 ± 0.3 | 0.032* | 0.022* | 0.93 |
| Parotid glands | 1.75 ± 0.7 | 1.92 ± 0.8 | 1.85 ± 0.8 | 0.099 | 0.86 | 0.86 |
| Masseter muscle | 1.06 ± 0.4 | 1.02 ± 0.4 | 0.91 ± 0.4 | 0.53 | <0.001* | 0.009* |
| Uvula | 1.83 ± 0.7 | 1.99 ± 0.9 | 1.87 ± 1.0 | 0.35 | 0.83 | 0.26 |
| Submandibular glands | 2.32 ± 1.1 | 2.44 ± 1.3 | 2.37 ± 1.3 | 0.39 | 0.93 | 0.54 |
| Sublingual glands | 3.34 ± 1.0 | 3.50 ± 0.9 | 3.40 ± 1.0 | 0.22 | 0.78 | 0.58 |
| Palatine tonsils | 1.74 ± 0.7 | 1.55 ± 0.7 | 1.57 ± 0.6 | 0.008* | 0.031* | 0.75 |
| Tongue | 1.65 ± 0.4 | 1.39 ± 0.5 | 1.29 ± 0.5 | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.034 |
| Lingual tonsil | 1.24 ± 0.4 | 1.21 ± 0.4 | 1.13 ± 0.5 | 0.94 | 0.015* | 0.22 |
| Vocal cords | 2.01 ± 0.7 | 2.33 ± 1.0 | 2.19 ± 1.0 | 0.003* | 0.43 | 0.21 |
| Thyroid gland | 4.10 ± 1.2 | 4.79 ± 1.4 | 5.18 ± 1.7 | <0.001* | <0.001* | 0.01* |
| Cervical lymph nodes | 1.79 ± 1.2 | 1.75 ± 0.9 | 1.62 ± 0.9 | 0.75 | 0.53 | 0.31 |
| Sternocleidomastoid muscle | 0.71 ± 0.3 | 0.78 ± 0.3 | 0.78 ± 0.4 | 0.083 | 0.28 | 0.61 |
| Structure | Normalized iodine ratio (mean ± SD) |
p-values | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18-48 years |
49-64 years |
65-98 years |
18-48 vs 49-64 | 18-48 vs 65-98 | 49-64 vs 65-98 | |
| Jugular vein | 1.27 ± 1.4 | 1.27 ± 0.9 | 1.32 ± 1.0 | 0.11 | 0.099 | 0.87 |
| Temporal lobe | 0.18 ± 0.2 | 0.17 ± 0.2 | 0.15 ± 0.1 | 0.54 | 0.004* | 0.023* |
| Cerebellum | 0.29 ± 0.2 | 0.30 ± 0.3 | 0.29 ± 0.4 | 0.75 | 0.034* | 0.077 |
| Parotid glands | 0.35 ± 0.2 | 0.37 ± 0.3 | 0.36 ± 0.4 | 0.92 | 0.03* | 0.023* |
| Masseter muscle | 0.22 ± 0.2 | 0.21 ± 0.2 | 0.18 ± 0.3 | 0.041* | <0.001* | 0.001* |
| Uvula | 0.38 ± 0.2 | 0.39 ± 0.4 | 0.34 ± 0.4 | 0.78 | 0.004* | 0.01* |
| Submandibular glands | 0.47 ± 0.3 | 0.47 ± 0.4 | 0.44 ± 0.4 | 0.52 | 0.038* | 0.21 |
| Sublingual glands | 0.68 ± 0.3 | 0.71 ± 0.7 | 0.66 ± 0.7 | 0.86 | <0.001* | 0.004* |
| Palatine tonsils | 0.35 ± 0.2 | 0.32 ± 0.3 | 0.33 ± 0.4 | <0.001* | <0.001* | 0.83 |
| Tongue | 0.36 ± 0.3 | 0.28 ± 0.2 | 0.23 ± 0.2 | <0.001* | <0.001* | <0.001* |
| Lingual tonsil | 0.26 ± 0.2 | 0.24 ± 0.2 | 0.21 ± 0.2 | 0.035* | <0.001* | 0.009* |
| Vocal cords | 0.43 ± 0.4 | 0.46 ± 0.4 | 0.42 ± 0.4 | 0.95 | 0.085 | 0.004* |
| Thyroid gland | 0.94 ± 1.2 | 0.92 ± 0.6 | 0.95 ± 0.9 | 0.035* | 0.12 | 0.69 |
| Cervical lymph nodes | 0.37 ± 0.3 | 0.36 ± 0.4 | 0.33 ± 0.5 | 0.91 | 0.001* | 0.033* |
| Sternocleidomastoid muscle | 0.15 ± 0.1 | 0.16 ± 0.1 | 0.14 ± 0.1 | 0.65 | 0.25 | 0.082 |
| Structure | Absolute iodine concentration in mg/ml (mean ± SD) |
p-values | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No BMI < 25 |
Ov 25 – 29.9 |
Ob BMI > 29.9 |
No vs Ov | No vs Ob | Ov vs Ob | |
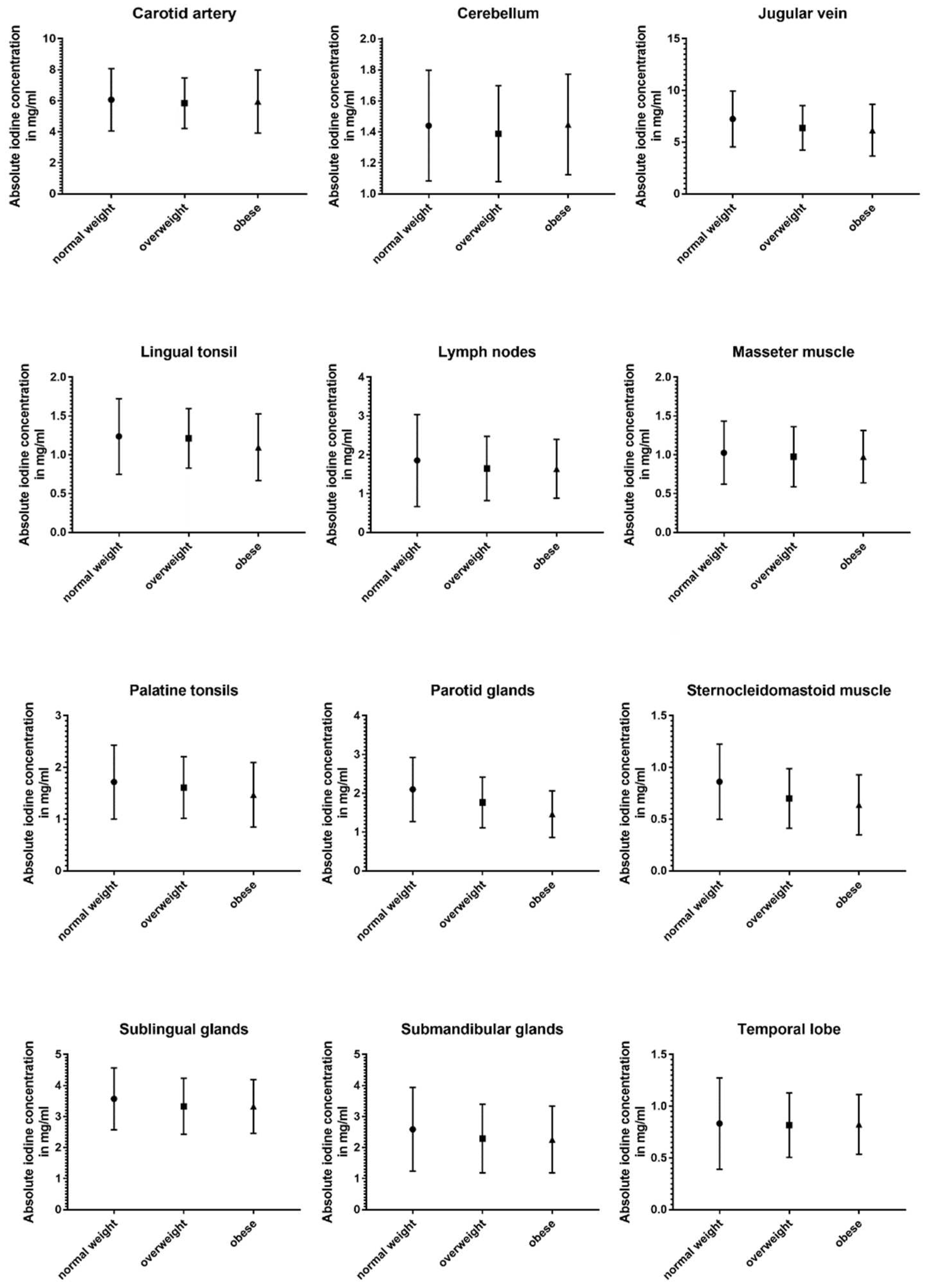
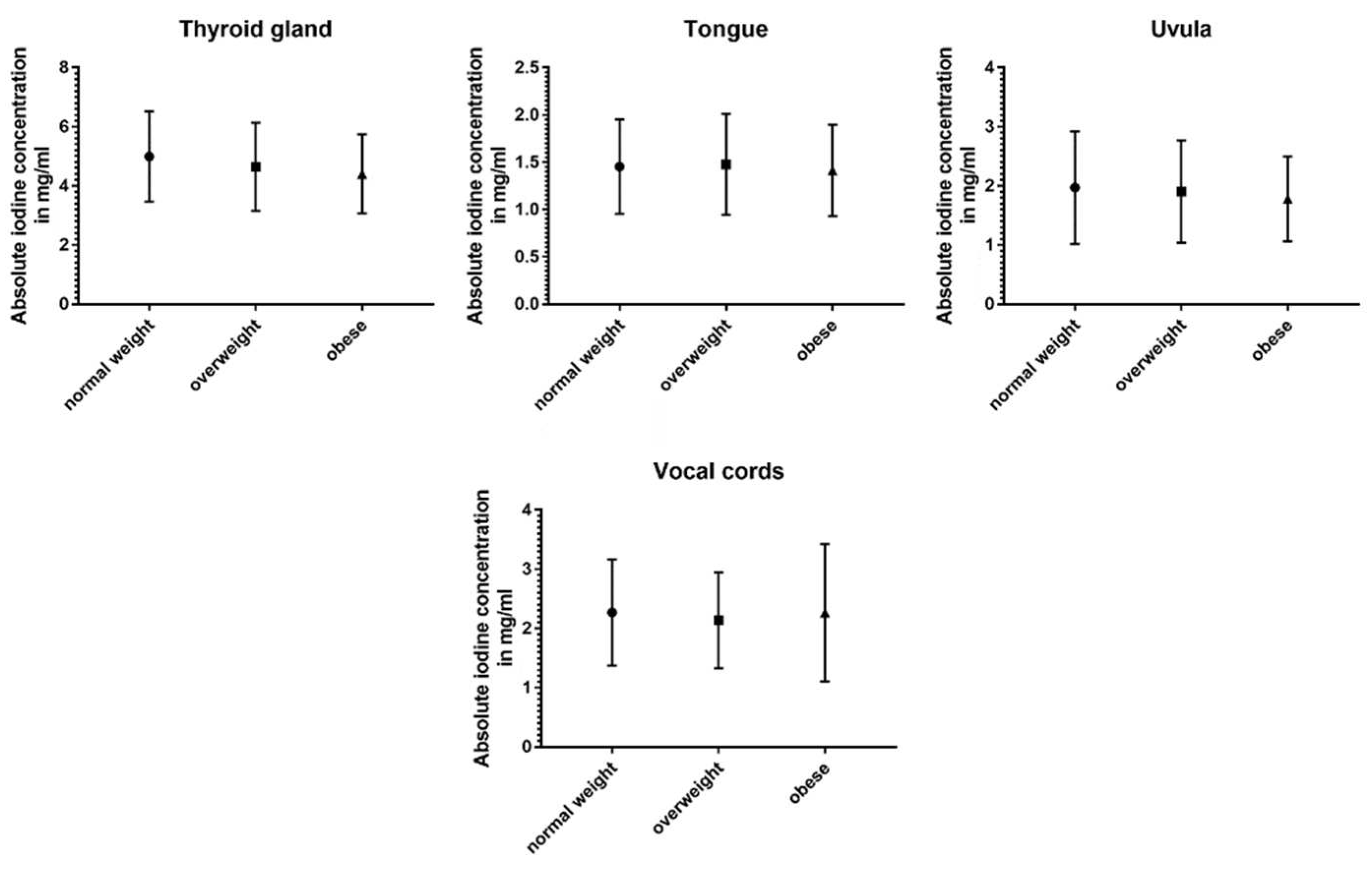
| Carotid artery | 6.1 ± 2.0 | 5.84 ± 1.6 | 5.96 ± 2.0 | 0.91 | 0.59 | 0.84 |
| Jugular vein | 7.24 ± 2.7 | 6.37 ± 2.1 | 6.16 ± 2.5 | <0.001* | <0.001* | 0.87 |
| Temporal lobe | 0.83 ± 0.4 | 0.82 ± 0.3 | 0.83 ± 0.3 | 0.83 | 0.54 | 0.50 |
| Cerebellum | 1.44 ± 0.4 | 1.39 ± 0.3 | 1.45 ± 0.3 | 0.67 | 0.79 | 0.69 |
| Parotid glands | 2.10 ± 0.8 | 1.76 ± 0.7 | 1.46 ± 0.6 | <0.001* | <0.001* | 0.004* |
| Masseter muscle | 1.03 ± 0.4 | 0.98 ± 0.4 | 0.98 ± 0.3 | 0.22 | 0.60 | 0.79 |
| Uvula | 1.97 ± 1.0 | 1.91 ± 0.9 | 1.78 ± 0.7 | 0.56 | 0.51 | 0.39 |
| Submandibular glands | 2.59 ± 1.4 | 2.29 ± 1.1 | 2.26 ± 1.1 | 0.08 | 0.092 | 0.69 |
| Sublingual glands | 3.57 ± 1.0 | 3.33 ± 0.9 | 3.33 ± 0.9 | 0.014* | 0.024* | 0.87 |
| Palatine tonsils | 1.72 ± 0.7 | 1.61 ± 0.6 | 1.47 ± 0.6 | 0.29 | 0.014* | 0.29 |
| Tongue | 1.45 ± 0.5 | 1.48 ± 0.5 | 1.41 ± 0.5 | 0.83 | 0.63 | 0.53 |
| Lingual tonsil | 1.24 ± 0.5 | 1.21 ± 0.4 | 1.10 ± 0.4 | 0.58 | 0.006* | 0.038* |
| Vocal cords | 2.27 ± 0.9 | 2.14 ± 0.8 | 2.27 ± 1.2 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.80 |
| Thyroid gland | 4.99 ± 1.5 | 4.65 ± 1.5 | 4.41 ± 1.3 | 0.068 | 0.002* | 0.52 |
| Cervical lymph nodes | 1.85 ± 1.2 | 1.65 ± 0.8 | 1.64 ± 0.8 | 0.062 | 0.11 | 0.92 |
| Sternocleidomastoid muscle | 0.86 ± 0.4 | 0.70 ± 0.3 | 0.64 ± 0.3 | <0.001* | <0.001* | 0.64 |
| Structure | Normalized iodine ratio (mean ± SD) |
p-values | ||||
| No BMI < 25 |
Ov 25 – 29.9 |
Ob BMI > 29.9 |
No vs Ov | No vs Ob | Ov vs Ob | |
| Jugular vein | 1.39 ± 1.3 | 1.15 ± 0.6 | 1.26 ± 1.3 | 0.051 | 0.017* | 0.70 |
| Temporal lobe | 0.17 ± 0.2 | 0.16 ± 0.1 | 0.18 ± 0.2 | 0.48 | 0.36 | 0.85 |
| Cerebellum | 0.29 ± 0.3 | 0.27 ± 0.3 | 0.32 ± 0.3 | 0.73 | 0.23 | 0.53 |
| Parotid glands | 0.41 ± 0.4 | 0.34 ± 0.3 | 0.32 ± 0.3 | 0.003* | <0.001* | 0.69 |
| Masseter muscle | 0.20 ± 0.2 | 0.20 ± 0.3 | 0.22 ± 0.2 | 0.51 | 0.65 | 0.87 |
| Uvula | 0.39 ± 0.4 | 0.35 ± 0.2 | 0.37 ± 0.3 | 0.99 | 0.99 | 0.97 |
| Submandibular glands | 0.50 ± 0.4 | 0.41 ± 0.2 | 0.45 ± 0.4 | 0.37 | 0.16 | 0.63 |
| Sublingual glands | 0.69 ± 0.5 | 0.64 ± 0.6 | 0.72 ± 0.7 | 0.69 | 0.99 | 0.92 |
| Palatine tonsils | 0.34 ± 0.3 | 0.32 ± 0.4 | 0.33 ± 0.3 | 0.49 | 0.33 | 0.31 |
| Tongue | 0.29 ± 0.3 | 0.27 ± 0.1 | 0.31 ± 0.3 | 0.40 | 0.37 | 0.61 |
| Lingual tonsil | 0.23 ± 0.2 | 0.23 ± 0.1 | 0.24 ± 0.2 | 0.87 | 0.52 | 0.40 |
| Vocal cords | 0.44 ± 0.4 | 0.40 ± 0.3 | 0.46 ± 0.5 | 0.41 | 0.61 | 0.98 |
| Thyroid gland | 0.98 ± 0.9 | 0.87 ± 0.5 | 0.94 ± 0.9 | 0.43 | 0.71 | 0.74 |
| Cervical lymph nodes | 0.36 ± 0.4 | 0.33 ± 0.5 | 0.36 ± 0.4 | 0.34 | 0.75 | 0.75 |
| Sternocleidomastoid muscle | 0.17 ± 0.1 | 0.14 ± 0.1 | 0.14 ± 0.1 | 0.003* | 0.004* | 0.92 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





