Introduction
The new area of gene engineering could be very helpful to the fields of biology and health. If we could make disease models in cells or in animals, gene therapy for genetic diseases might make a lot of progress [1,2]. Capecchi’s early work in this field made it possible for a method that had previously only been used to change a small number of species because it was hard to do so on a large scale. Genome engineering with homologous recombination took a long time to get better because the targeted and selection steps were hard to figure out. Then, using homologous recombination with phages, recombineering was made possible. This made it easier to make target vectors and change large parts of DNA patterns using genetic engineering. The fact that managed double-strand breaks (DSBs) make it easier to change certain parts of the genome has made genome editing more precise. Double-strand breaks (DSBs) happen more often when homologous recombination is planned than when it happens by chance. [3] In the mid-1990s, this was shown by two different groups using the very rare cutting Saccharomyces cerevisiae restriction endonuclease I-SceI. Two studies done in the late 1990s showed that a unique zinc finger (ZF) domain was joined to a general cleavage domain (FokI). This shows how ZF proteins can be used as building blocks to change recognition sequence regions for a 9-bp or 18-bp target sequence. These two discoveries make it possible to change how current nucleases work by adding ZF domains to their structures. The FokI cleavage domain is joined to a modified ZF DNA-binding domain to make ZFNs. 15 years after the first ZFNs were made, it was found out that Xanthomonas bacteria make and release transcription activator-like effector (TALE) binding proteins. ZFNs are useful because they are made up of groups of 3–6 ZF modules that are joined together to make a 9–18 bp DNA-binding region that is unique to each ZF monomer. TALE sequences that work as DNA-binding motifs, on the other hand, are usually 34 amino acids long. Each time through, the goal is on finding and connecting a single base. Diresidue is a very rare repeat variable because it has two different amino acids. Because the DNA recognition code was found in, it is easier to create and build TALE DNA-binding domains than ZF ones. [4,5]
After that, changes to the DNA happened quickly. After CRISPR-Cas9 was discovered in 2012, it became much easier to change certain parts of the genome. The bacteria’s DNA has been changed in a way that makes its natural defenses useless. Since it was found that bacteria use repeating patterns to protect themselves from viruses and other DNA, they have been used a lot in this field of basic study. [6,10]
CRISPR was made possible by two separate science projects. In the first study, it was found that ribonucleoprotein Cas9 helped break up DNA when it was mixed with crRNA (CRISPR targeting RNA). Doudna and Charpentier showed that the CRISPR-Cas9 Cas9 endonuclease, crRNA, and tracrRNA could be combined to make a single guide RNA (sgRNA). This process is called "trans-activating crRNA." This made it much easier to change the DNA of living things. In 2013, several study groups showed that CRISPR-Cas9 can be used to change animal genes. We suggest reading three in-depth pieces about CRISPR-Cas9 and how it can be used to change the genome. [13,15]
The CRISPR-Cas9 system does not change proteins like ZFNs, meganucleases, and TALE nucleases (TALENs) do in order to find the sgRNA and target DNA. To move CRISPR-Cas9 to a different gene, all you have to do is make a new 20-nt RNA fragment. Because of this, it doesn’t take much work to use the instrument. Using ZFN and TALEN-based methods to make and clone whole protein domains takes a lot of time. Miniaturized components for multiplex uses have made it possible to change many loci at once, as well as to delete and move genes. CRISPR-Cas9 can also be used in high-throughput ways. [14,16]
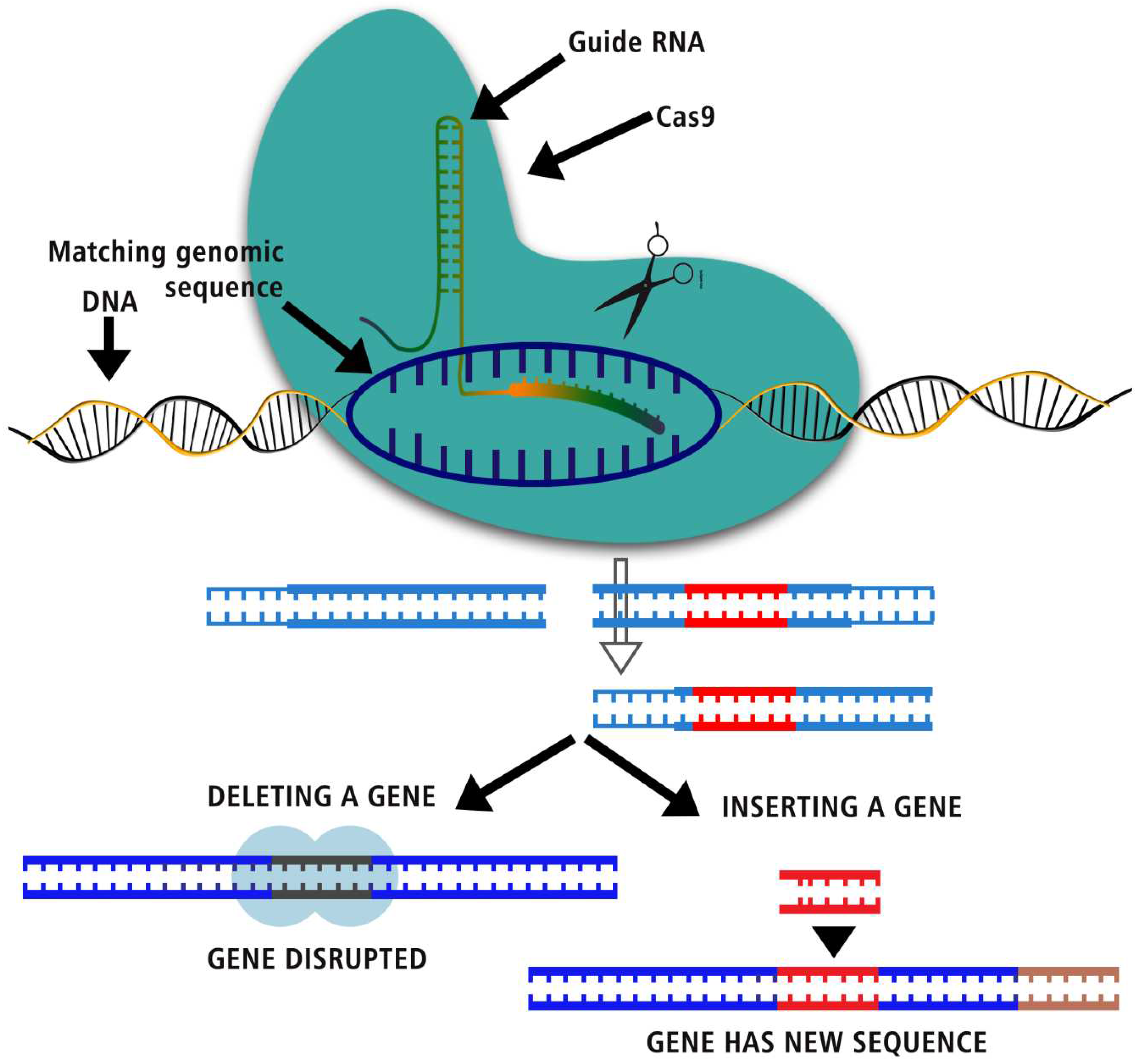
Figure 1.
CRISPR, one of the biggest science stories of the decade, explained.
Figure 1.
CRISPR, one of the biggest science stories of the decade, explained.
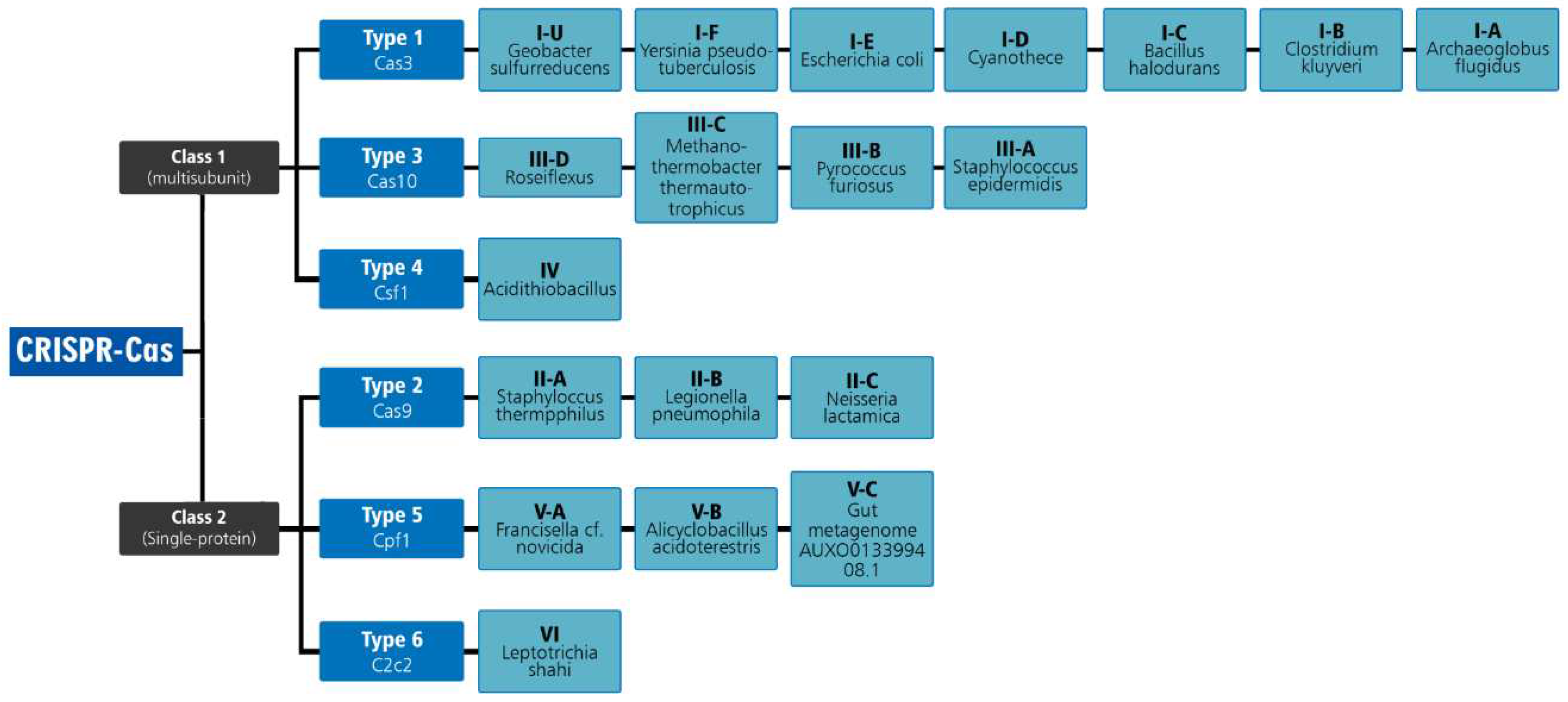
Figure 2.
Classification of CRISPR-Cas technology.
Figure 2.
Classification of CRISPR-Cas technology.
Comparison, Gene function and Benefits
Eliminating a gene’s expression is the best way to figure out what it does. There is more than one right way to do something. RNA interference (RNAi) has been shown to be the best approach over the last 15 years. RNAs with two strands make it easy, cheap, quick, and scalable to turn off genes. Inhibition is rarely used in clinical settings because it is temporary, results vary between studies and labs, and it could have effects that were not intended. Instead of just "knocking down" gene expression, ZFNs and TALENs may be able to totally quiet genes to mimic the loss of all function caused by a DNA mistake. Customized nucleases were helpful, but not the best way to change the genome in an exact way. [7,9] These methods weren’t perfect because protein engineering is hard and the success of targeting depended on choosing the right marks. Because it can be used in many different ways and is easy to use, CRISPR-Cas9 is the best tool for understanding how genes work. Also, as new ways to use CRISPR are found, the value of the technology goes up. [8,11]
Nucleases are tools that scientists use in genome engineering to change DNA in many different ways. Tools like ZFNs, TALENs, and the CRISPR-Cas9 system make genetic editing more exact by making specific double-strand breaks (DSBs) in the genome. (First Time Around) "Homology-directed repair" (HDR) and "non-homologous end joining" (NHEJ) are the two most common ways to fix double-strand breaks. The double-strand break (DSB) is fixed by putting the broken ends of donated DNA templates back together. Using HDR, it is possible to change the DNA of an organism by adding new genes or errors. Even with its flaws, the NHEJ road has a bigger number of members. The process uses frameshift mutations, which can happen during healing and could be used to turn off genes. By changing how we look at things, we might be able to study genes in the context of the whole chromosome and learn more about how they work. This gets rid of the way position can mess up DNA studies. [12,17]
This is how experts usually use CRISPR-Cas9. CRISPR-Cas9 makes DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs), which can be fixed in two ways - with the poor NHEJ repair method and with the better HDR repair method. Because of these holes, some parts of the DNA could be changed. B. Cas9 can be made inactive by putting it together with inactive effectors or domains. So, fluorescent colors can be used to name DNA, control transcription, and change the epigenome. We can move on to other projects now that we know how things work. Pooled screening is easier when whole-genome guide RNA libraries are used. The process of fixing broken DNA is called many different things, such as the joining of different ends, homology-directed repair, insertions and deletions, and double-strand breaks.
CRISPR: Gene Delivery Associated Concerns
Even though CRISPR-Cas9 has many benefits, such as being easy to get and use, some big problems still need to be settled. To make changes to the genome, it is important to get the flexible nuclease to the right place. Whether or not a virus can spread the CRISPR system will depend on how the experiment is set up. Because of how they are built, DNA, mRNA, and ribonucleoproteins (RNPs) are all examples of carriers. Viral vectors are a good way to move CRISPR parts because they can be redirected through almost any tissue or cell type. Additionally, they can be given either locally or throughout the body. So, they are a useful resource that can be used in many different ways. Some vectors that can be used to move enzymes and nucleases are adenoviruses, baculoviruses, and both integrative and non-integrative lentiviruses. AAVs that are safe for people are now a fact. They are the most wanted gene delivery vectors right now because they allow stable transgenic expression without having to put the genome together. Cas9 and DNA templates can be used to fix certain kinds of cells. Their main flaw is that they only have 4.7 kb of storage space, which is not enough to store even the most basic design and management information. In the big picture, this is a small thing to give up. So, Cas9 and the guide sequences for vectors can’t move within them. The need for a secondary carrier has gone away since smaller Cas9 orthologs, like those from Staphylococcus aureus, have been made. Because of their small size, these orthologs are the "editor’s pick" for making changes to the genomes of live things [5,22].
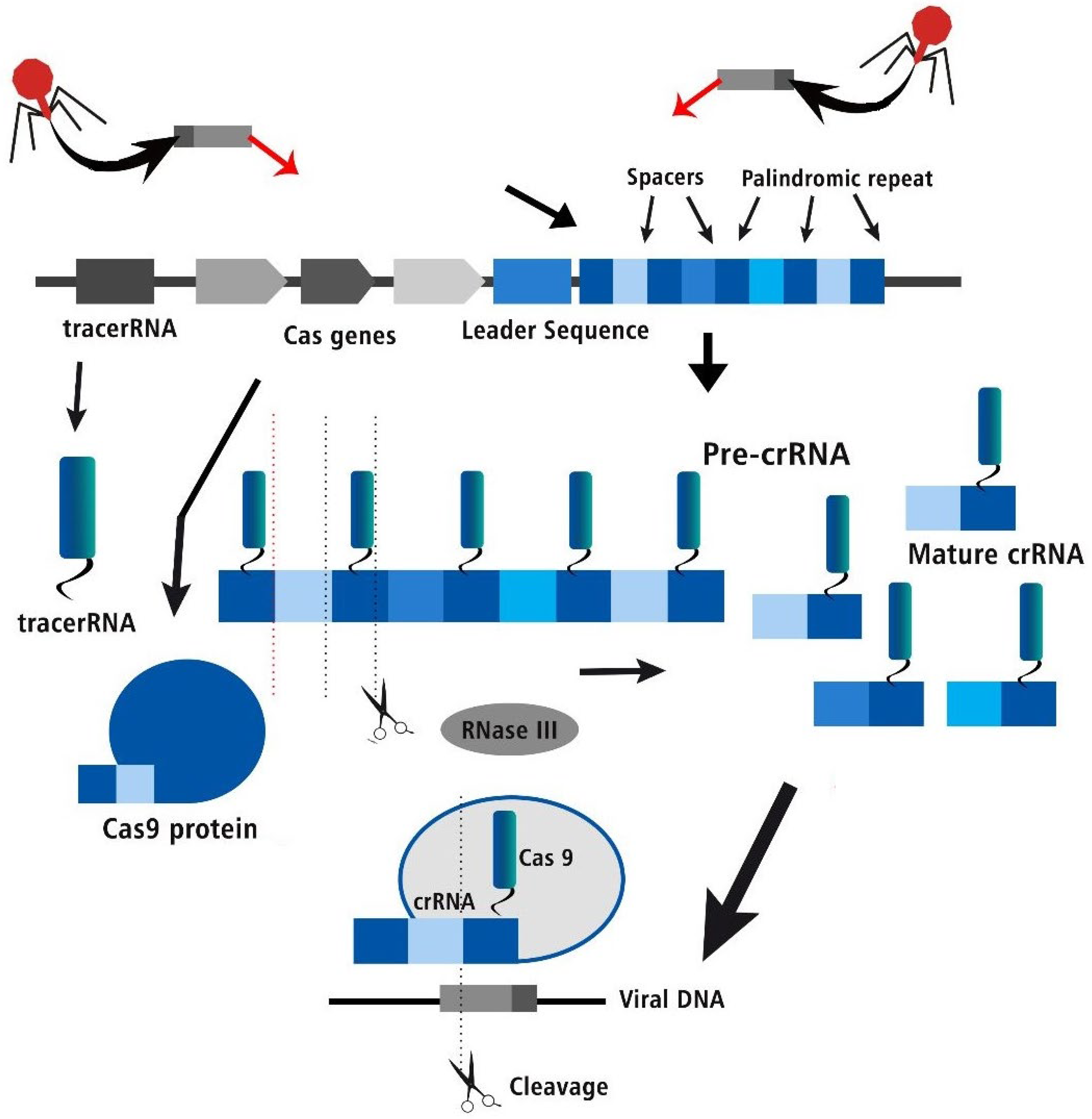
Figure 2.
The three stages of the CRISPR Cas bacterial adaptive immune system- acquisition, crRNA biogenesis and interference of viral DNA.
Figure 2.
The three stages of the CRISPR Cas bacterial adaptive immune system- acquisition, crRNA biogenesis and interference of viral DNA.
Non-viral delivery methods work better than viral vectors and can be used again and again in cell growth. Because these systems only work for a short time, they are better than long-lasting systems like lentiviruses, which have clear problems. Non-viral transfer methods include the use of lipid-based agents for transfection, electroporation, and nucleofection. Electroporation has become the method of choice because it can be used on so many different kinds of cells and even in clinical settings to change the genome outside of the body. Even though this way of changing cells doesn’t always work, it has a lot of possible uses. It is very important to keep this in mind when coming up with ways to spread genetic material. On top of that, it doesn’t do anything. Hydrodynamic injection has recently been put forward as a way to change the DNA in the mouse liver without using viruses. Studies show that it could mess up the way the heart normally works and do a lot of damage to the liver. This makes it risky to use on big animals or store in the liver. [10,15]
CRISPR Specificity and Off-Target Effects
Since the CRISPR-Cas9 system was created, there has been a lot of talk about how often unexpected effects happen. But later study showed that off-target effects might rely on the situation and might not happen in all cells. There aren’t many off-target changes in human embryonic stem cells with good double-strand break (DSB) repair pathways. When compared to human cell types with DSBs, these results are new. Even though the findings are different, we will talk about different ways to reduce off-target affects. The guide sequence can be changed in many ways, such as by making a "truncated guide RNA" by shrinking the sgRNA, adding a nucleotide to the 5’ end, or improving the structure of the sgRNA. When any of these methods are used, off-target mutations are less likely to happen and target selection is improved. [1–3]
Nickases are different kinds of Cas9 that need a second enzyme to cut DNA. Both the D10A mutation and the H840A mutation change how the protein works. This method cut off-target behavior by a lot without hurting its efficiency. Keeping the CRISPR system from getting busy the dose of a drug is more important to how well it works than the drug itself. People have given similar reasons why high amounts of CRISPR/Cas9 could have unintended effects. One way to figure out how much of each CRISPR component is needed for an experiment is to use an appropriate optimization method. Step four is the time of stabilization. By adding dCas9 to the FokI nuclease region, the DNA can be cut with more accuracy. These blends are more accurate than paired nickases, but they can also have effects that were not planned. Using shorter guides and dCa9-FokI, it is also possible to change the DNA of human cell lines in a controlled way. Setting the amount of time between when Cas9 and its guide sequences are released and when they reach the target cell. You could use methods like inducible vectors, split Cas9, or cell cycle alignment to go around the problem. But Cas9 RNP may have mostly replaced plasmid DNA or virus drives, which may be the most important change. This improvement helps both human and animal cells, even those that were already resistant. Cas9 RNP works well because the complexes are already put together. It also breaks down quickly, so it rarely causes unwanted side effects. Human fetal stem cell transplants have shown promise. [2–5,7]
Conclusions
Even though CRISPR technology has come a long way in a short amount of time, many technical problems still need to be solved. The first step is to speed up how quickly CRISPR parts are sent to the target cell. This means that we need to not only improve how we offer services now, but also look into other options. Second, to be as successful as possible, you need to be precise. To avoid off-target effects, it’s important to find new ways to treat localized illnesses. Before CRISPR can be used regularly in science and medicine, a lot more research needs to be done on it. Genome editing technologies based on CRISPR-Cas9, on the other hand, may soon shed light on how diseases work and how well possible treatments might work.
Ethical Approval and Consent to participate
All procedures performed in studies are not involving human participants. Therefore there is no need of the ethical approval of the institutional and/or national research committee and 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. For type of studies no formal consent is required.
Animal rights
Additionally, this research studies no animals involved. The authors indicate the procedures followed are in accordance with the standards set forth in the eighth edition of Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals; published by the National Academy of Sciences, The National Academies Press, Washington, D.C.).
Consent for publication
Authors agree and grant consent to publish this article in this research journal.
Author Contributions
This work was carried out in collaboration among all authors. Taha Nazir designed the study of proposed hypothesis and compile the scientific contents. Nida Taha elaborated study to make it more credible. Whereas, Hameed A Mirza managed the literature searches and citation part of the manuscript. Thus, all authors have read and approved the final manuscript for publication in this journal.
Funding
This project is not-funded from any local and/ or international organization.
Data Availability Statement
All study information and possible research data successfully incorporated for publication.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the technical and scientific support of A.S. Chemical Laboratories Inc., Concord, ON L4K4M4 Canada and Advanced Multiple Inc., Mississauga ON, L5T2M9 Canada.
Conflict of interests
The authors also declare that they are no any potential and/ or completing conflict of interest.
References
- Balon K, Sheriff A, Jacków J, Łaczmański Ł. Targeting Cancer with CRISPR/Cas9-Based Therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 5;23(1):573. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Behan FM, Iorio F, Picco G, Gonçalves E, Beaver CM, Migliardi G, Santos R, Rao Y, Sassi F, Pinnelli M, Ansari R, Harper S, Jackson DA, McRae R, Pooley R, Wilkinson P, van der Meer D, Dow D, Buser-Doepner C, Bertotti A, Trusolino L, Stronach EA, Saez-Rodriguez J, Yusa K, Garnett MJ. Prioritization of cancer therapeutic targets using CRISPR-Cas9 screens. Nature. 2019 Apr;568(7753):511-516. Epub 2019 Apr 10. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatia S, Pooja, Yadav SK. CRISPR-Cas for genome editing: Classification, mechanism, designing and applications. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023 May 31;238:124054. Epub 2023 Mar 17. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhokisham N, Laudermilch E, Traeger LL, Bonilla TD, Ruiz-Estevez M, Becker JR. CRISPR-Cas System: The Current and Emerging Translational Landscape. Cells. 2023 Apr 7;12(8):1103. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chaudhuri A, Halder K, Datta A. Classification of CRISPR/Cas system and its application in tomato breeding. Theor Appl Genet. 2022 Feb;135(2):367-387. Epub 2022 Jan 1. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cheng X, Fan S, Wen C, Du X. CRISPR/Cas9 for cancer treatment: technology, clinical applications and challenges. Brief Funct Genomics. 2020 May 20;19(3):209-214. Erratum in: Brief Funct Genomics. 2020 Dec 4;19(5-6):411. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christie KA, Guo JA, Silverstein RA, Doll RM, Mabuchi M, Stutzman HE, Lin J, Ma L, Walton RT, Pinello L, Robb GB, Kleinstiver BP. Precise DNA cleavage using CRISPR-SpRYgests. Nat Biotechnol. 2023 Mar;41(3):409-416. Epub 2022 Oct 6. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Grand Moursel L, Visser M, Servant G, Durmus S, Zuurmond AM. CRISPRing future medicines. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2021 Apr;16(4):463-473. Epub 2021 Jan 3. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrington LB, Burstein D, Chen JS, Paez-Espino D, Ma E, Witte IP, Cofsky JC, Kyrpides NC, Banfield JF, Doudna JA. Programmed DNA destruction by miniature CRISPR-Cas14 enzymes. Science. 2018 Nov 16;362(6416):839-842. Epub 2018 Oct 18. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Huang J, Wang Y, Zhao J. CRISPR editing in biological and biomedical investigation. J Cell Physiol. 2018 May;233(5):3875-3891. Epub 2017 Sep 7. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang S, Dai R, Zhang Z, Zhang H, Zhang M, Li Z, Zhao K, Xiong W, Cheng S, Wang B, Wan Y. CRISPR/Cas-Based Techniques for Live-Cell Imaging and Bioanalysis. Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 30;24(17):13447. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Karimian A, Azizian K, Parsian H, Rafieian S, Shafiei-Irannejad V, Kheyrollah M, Yousefi M, Majidinia M, Yousefi B. CRISPR/Cas9 technology as a potent molecular tool for gene therapy. J Cell Physiol. 2019 Aug;234(8):12267-12277. Epub 2019 Jan 30. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim DY, Lee JM, Moon SB, Chin HJ, Park S, Lim Y, Kim D, Koo T, Ko JH, Kim YS. Efficient CRISPR editing with a hypercompact Cas12f1 and engineered guide RNAs delivered by adeno-associated virus. Nat Biotechnol. 2022 Jan;40(1):94-102. Epub 2021 Sep 2. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lanigan TM, Kopera HC, Saunders TL. Principles of Genetic Engineering. Genes (Basel). 2020 Mar 10;11(3):291. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Li Y, Li S, Wang J, Liu G. CRISPR/Cas Systems towards Next-Generation Biosensing. Trends Biotechnol. 2019 Jul;37(7):730-743. Epub 2019 Jan 14. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long J, Xu Y, Ou L, Yang H, Xi Y, Chen S, Duan G. Diversity of CRISPR/Cas system in Clostridium perfringens. Mol Genet Genomics. 2019 Oct;294(5):1263-1275. Epub 2019 May 27. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makarova KS, Haft DH, Barrangou R, Brouns SJ, Charpentier E, Horvath P, Moineau S, Mojica FJ, Wolf YI, Yakunin AF, van der Oost J, Koonin EV. Evolution and classification of the CRISPR-Cas systems. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2011 Jun;9(6):467-77. Epub 2011 May 9. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Makarova KS, Wolf YI, Iranzo J, Shmakov SA, Alkhnbashi OS, Brouns SJJ, Charpentier E, Cheng D, Haft DH, Horvath P, Moineau S, Mojica FJM, Scott D, Shah SA, Siksnys V, Terns MP, Venclovas Č, White MF, Yakunin AF, Yan W, Zhang F, Garrett RA, Backofen R, van der Oost J, Barrangou R, Koonin EV. Evolutionary classification of CRISPR-Cas systems: a burst of class 2 and derived variants. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2020 Feb;18(2):67-83. Epub 2019 Dec 19. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Manghwar H, Lindsey K, Zhang X, Jin S. CRISPR/Cas System: Recent Advances and Future Prospects for Genome Editing. Trends Plant Sci. 2019 Dec;24(12):1102-1125. Epub 2019 Nov 11. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz-Pujol G, Ugarteburu O, Segur-Bailach E, Moliner S, Jurado S, Garrabou G, Guitart-Mampel M, García-Villoria J, Artuch R, Fons C, Ribes A, Tort F. CRISPR/Cas9-based functional genomics strategy to decipher the pathogenicity of genetic variants in inherited metabolic disorders. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2023 Nov;46(6):1029-1042. Epub 2023 Oct 3. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nidhi S, Anand U, Oleksak P, Tripathi P, Lal JA, Thomas G, Kuca K, Tripathi V. Novel CRISPR-Cas Systems: An Updated Review of the Current Achievements, Applications, and Future Research Perspectives. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 24;22(7):3327. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Qian Y, Zhou D, Li M, Zhao Y, Liu H, Yang L, Ying Z, Huang G. Application of CRISPR-Cas system in the diagnosis and therapy of ESKAPE infections. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2023 Aug 17;13:1223696. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sahel DK, Mittal A, Chitkara D. CRISPR/Cas System for Genome Editing: Progress and Prospects as a Therapeutic Tool. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2019 Sep;370(3):725-735. Epub 2019 May 23. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuncel A, Qi Y. CRISPR/Cas mediated genome editing in potato: Past achievements and future directions. Plant Sci. 2022 Dec;325:111474. Epub 2022 Sep 26. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).