1. Introduction
Cervical cancer, ranking second in terms of mortality among malignancies and standing as the fourth most prevalent cancer in women, reported 528,000 incident cases and 311,000 fatalities globally in 2018. This epidemiological profile underscores its persistent status as a substantial public health concern1-3.
There is considerable regional variation in incidence, which depends on the status of Human Papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination and the feasibility of cervicovaginal smear (CVS) screening4.
In spite of the advent of vaccination and screening initiatives, the challenges associated with their implementation persist, thereby regrettably perpetuating the deleterious impact of cervical cancer in certain regions of the world. Cervical cancer screening guidelines exhibit considerable heterogeneity globally, necessitating comprehensive and recurrent examinations for women from an early age into adulthood. The practical execution of these guidelines encounters obstacles, notably when adequate resources are available and becomes nearly unattainable in resource-constrained settings5.
The theoretically optimal screening approach involves the amalgamation of HPV molecular testing and cytologic examination of cervical specimens. This strategy not only attains the highest sensitivity for cancer detection but also exhibits the highest negative predictive value, enabling longer intervals between negative test results6,7.
The American Society for Colposcopy and Cervical Pathology (ASCCP) advocates the screening of women for cervical lesions through the integration of both smear and HPV-DNA co-testing methodologies. Co-testing has demonstrated superior diagnostic performance compared to CVS alone, specifically in the detection of cervical abnormalities8.
In select European nations, a prevailing cervical cancer screening protocol involves the systematic testing of all women within the age bracket of 30 to 65 for the presence of HPV DNA at five-year intervals9.
Subsequently, solely positive HPV results undergo confirmation via cytological examination. This strategic approach serves to optimize the testing interval while substantially diminishing the frequency of cytology tests, achieving a notable reduction by 90%, all without a substantial compromise in the overall efficacy of the screening program7,10.
Human Papillomavirus (HPV), a DNA virus, assumes a pivotal role in cervical carcinogenesis by infiltrating basal epithelial cells. Its status as the predominant etiological factor underscores its significance in the pathogenesis of cervical cancer. The intricate molecular interactions between HPV and host cells contribute to the dysregulation of cellular processes, ultimately fostering the development of malignancy within the cervix8.
The early detection of HPV through cervical smear screening emerges as a linchpin in the preventive paradigm against cervical cancer, particularly during its nascent stages. Cervical smear screening serves as an indispensable tool in identifying the presence of HPV infections and associated abnormalities in cervical cells. This proactive screening approach allows for the timely identification of viral infections and precancerous changes, enabling early intervention strategies to impede the progression toward cervical cancer11.
Cervical cancer, a preventable cancer, remains the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths among women aged 20-39 years. Nonetheless, the implementation of cotest screening, in conjunction with HPV vaccination, has yielded a decline in prevalance of cervical cancer owing to their widespread adoption4.
Epidemiological investigations have led to the categorization of HPV types based on their respective risks in cancer development. Specifically, HPV types 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59, and 68 are recognized as members of the high-risk group. Among these, HPV types 16, 18, 31, 33, 45, 52, and 58 stand out as the major contributors, being responsible for more than 90% of cervical cancer patients12.
The main purpose of our study was to make a comparative analysis between the outcomes of CVS and HPV-DNA cotest and the results obtained from colposcopic biopsy.
2. Methods
In the retrospective cohort study conducted, a total of 225 cases were subjected to cotest screening, involving cervicovaginal smear (CVS) along with HPV-DNA testing, followed by either colposcopic cervical biopsy or a subsequent CVS test. The evaluation encompassed cases diagnosed within the temporal span from 2014 to 2022. Notably, no instances of conization subsequent to abnormal CVS and HPV-DNA test results were recorded within our department. The comprehensive analysis involved the electronic scanning of cervical cytology and colposcopic biopsy results, as well as HPV-DNA analysis outcomes, all of which were documented in our medical record system.
Cytologic examinations were performed on smear samples utilizing both Papanicolaou (PAP) staining techniques, with 59.2% utilizing the conventional smear method and 40.8% employing liquid-based cytology (LBC). Colposcopic biopsies underwent classical hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) evaluation. The re-evaluation and comparative analysis of biopsy and smear results were conducted, with smear samples assessed according to the Bethesda 2014 system.
Exclusion criteria for the study encompassed patients in whom HPV-DNA analysis was not conducted or those lacking a biopsy report in our department following abnormal smear results coupled with cotest HPV-DNA. These criteria ensured a focused examination of cases with complete diagnostic data for a comprehensive understanding of the screening outcomes.
Ethical considerations were paramount in the study’s design and execution. The research adhered to the principles outlined in the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2000, and was in compliance with the committee on human experimentation, whether institutional or regional. The study received ethical approval from the relevant ethics committee, and the approval certificate is annexed to this communication. The approval was granted on the 22nd of March 2022, reaffirming the commitment to ethical standards and guidelines in the conduct of this research.
Statistical Method
SPSS 25.0 package programme was used for statistical analysis of the data. Categorical measurements were summarized as number and percentage, and continuous measurements were summarized as mean and standard deviation (median and minimum-maximum where necessary).
The agreement between the diagnoses was evaluated by Kappa Concordance Analysis. The correlation between the diagnoses was evaluated by intraclass correlation method. Kappa statistic takes a value between -1 and +1. Positive values of κ indicate that the agreement between raters is higher than the expected agreement by chance, negative values of κ indicate that the agreement between raters is less than expected by chance14.
Sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV) and negative predictive value (NPV) were calculated.
Kruskal Wallis test was used to compare the diagnostic groups and age. Statistical significance level was taken as 0.05 in all tests.
3. Results
In our retrospective investigation, the age of the participants ranged from 21 to 86 years, with a mean age of 44.8 years and a standard deviation of 12.7. The median age of the study population was 46 years.
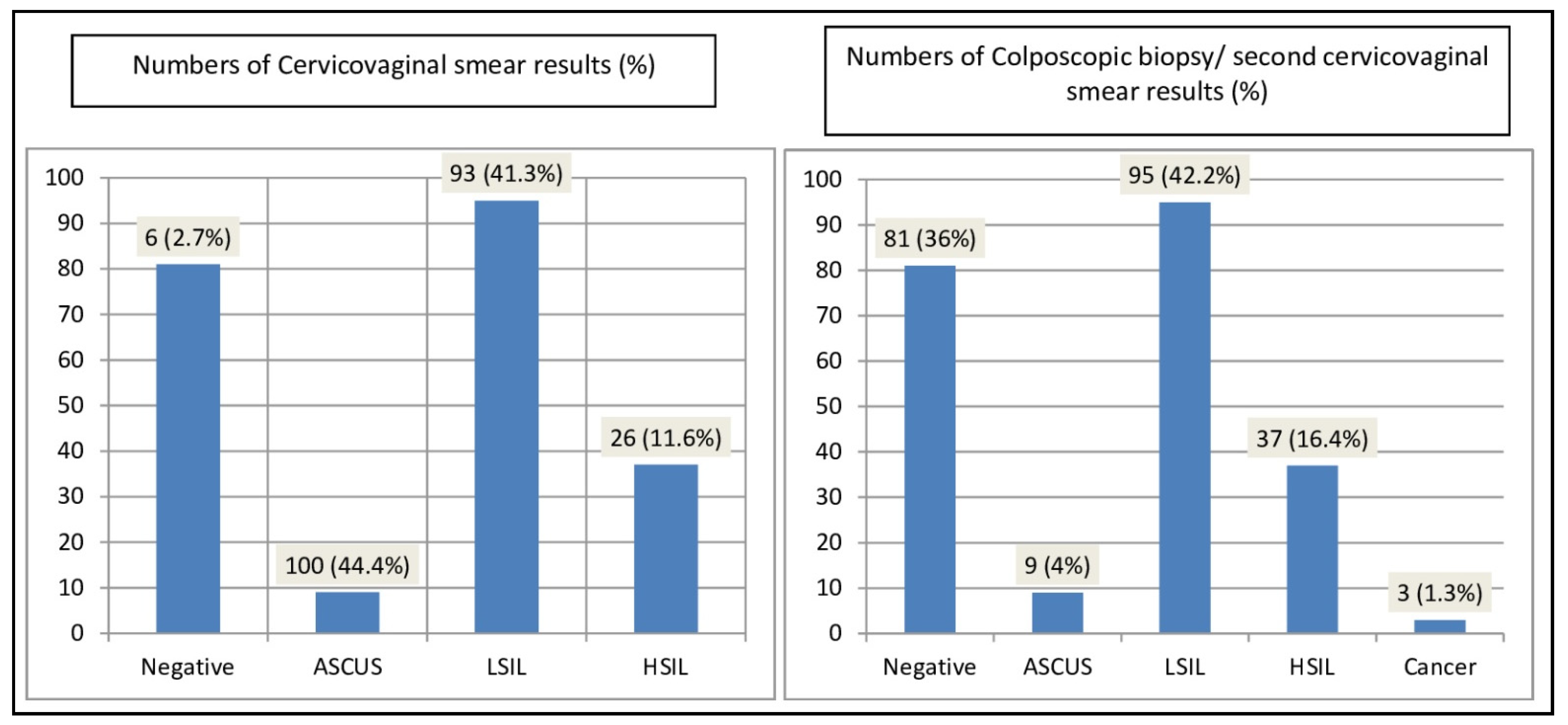
CVS samples consisted of conventional smears (59.2%) and LBC (40.8%) material. CVSs were diagnoses as negative for intraepithelial lesions (negative), Atypical Squamous Cells of Undetermined Significance (ASCUS), Low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (LSIL), High-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL) (2.7%, 44.4%, 41.3%, 11.6%, respectively) [
Figure 1]. Colposcopic biopsies or a second cervicovaginal smears were diagnosed as negative for intraepithelial lesions, ASCUS, LSIL- Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN)-1, HSIL-CIN 2-3, cervical cancer (36%, 4%, 42.2%, 16.4%, 1.3%, respectively) [
Figure 1].
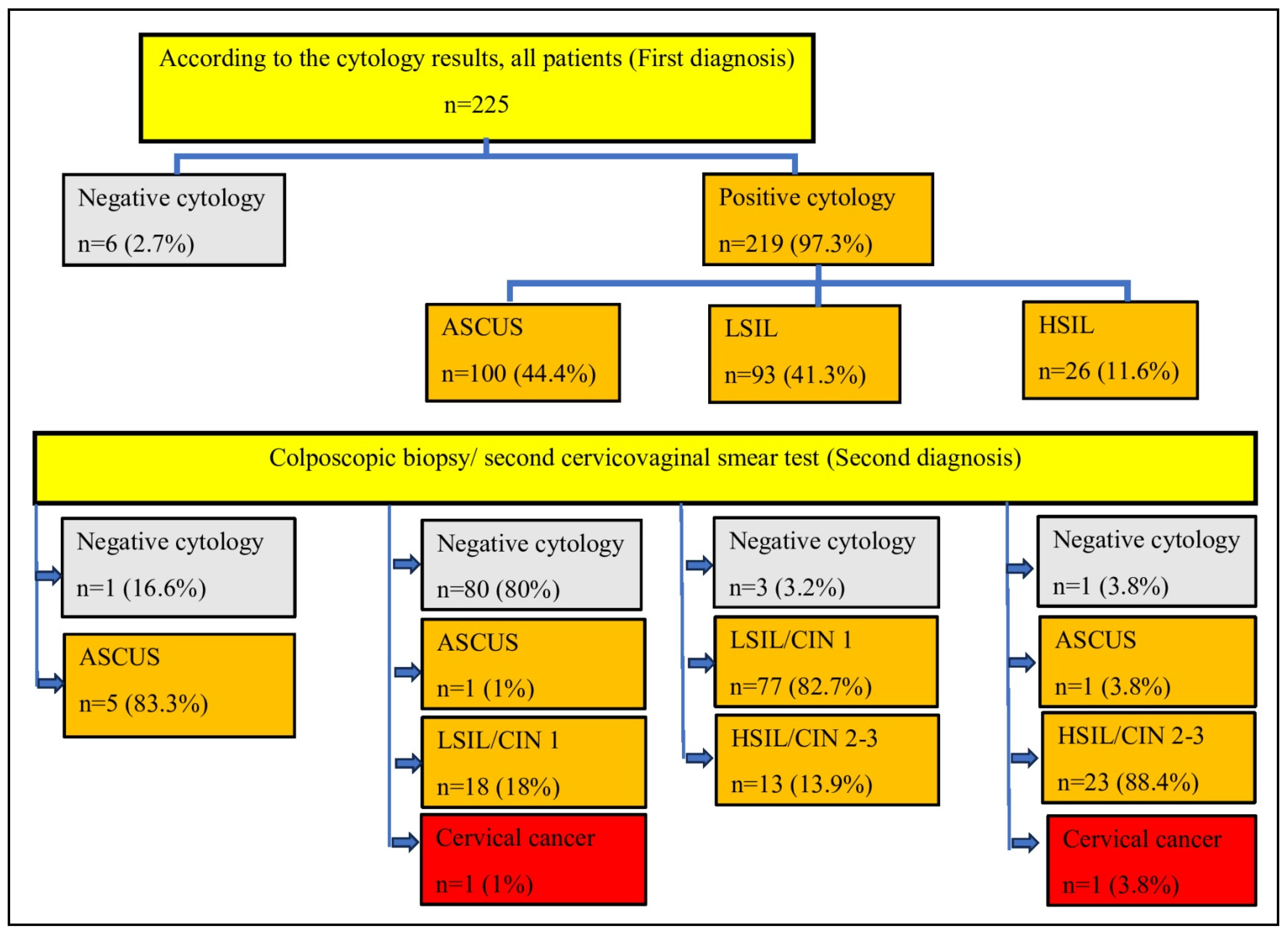
Data on the initial diagnosis by CVS test and subsequent colposcopic biopsy/ second CVS test results are shown in
Figure 2. Microscopic photographs of the sample cases are shown in
Figure 3.
When we examined the concordance of the first diagnosis with the second diagnosis in the whole patient group; the kappa value and intraclass correlation coefficient were 0.31 and 0.64 (95% CI 0.54-0.71), respectively. Among the diagnoses, the highest accuracy rate between the second diagnosis and the first diagnosis was LSIL (81.1%), while the lowest accuracy rate was found in the negative result in terms of intraepithelial lesion.
ASCUS was detected in 93.8% of the patients in whom no intraepithelial lesion was detected by CVS and in whom smears were taken for the second time. CIN 2 and CIN 3 were detected in 30% and 2.7% of the patients who were diagnosed with ASCUS by CVS and who had positive HPV-DNA test at the same time.
Most of the patients diagnosed with HSIL by smear were also diagnosed by biopsy (88.4%). There were two cases in which invasive cancer was detected on biopsy after a negative smear test.
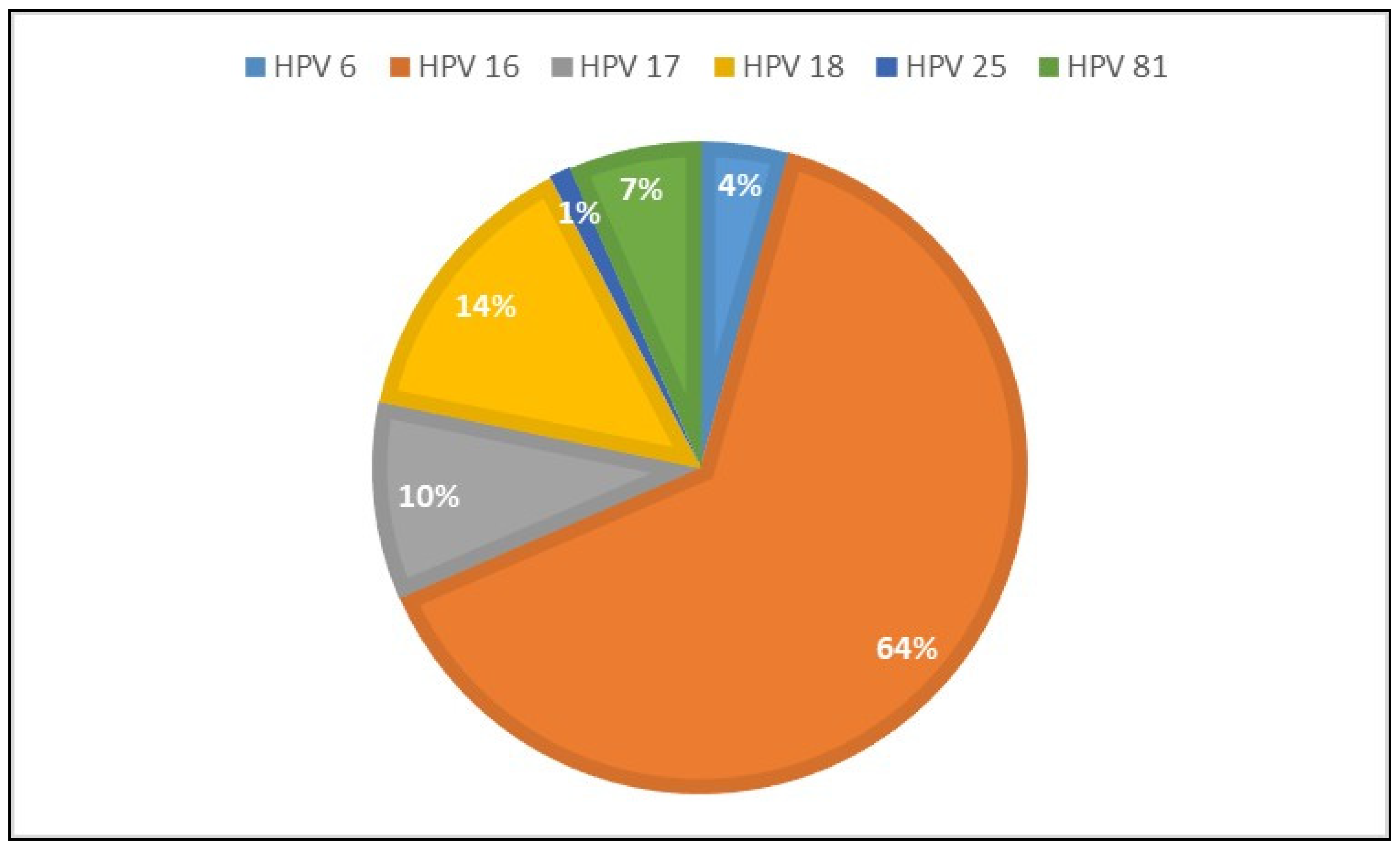
With the simultaneous HPV-DNA test, 186 patients were examined, and HPV-DNA was found to be positive in half of the patients (n=92, 49.4%). HPV DNA types 6, 16, 17, 18, 25, 81 were observed [
Figure 4] and the most common types were type 16 and type 18 (64.1% and 14.1%, respectively).
In our investigation, the sensitivity and specificity of HPV testing for detecting CIN 2 were determined to be 67.8% and 67.9%, respectively, in biopsy. In comparison, the corresponding figures for cytology testing were 73.5% and 71.7%, respectively. The PPV for CIN 2 was 64.1%, and the NPV for CIN 2 was 71.4% in biopsy, while the PPV for CIN 2 was 70.3%, and the NPV for CIN 2 was 75.6% in CVS [
Table 1].
Regarding the detection of CIN 3, the sensitivity and specificity of HPV testing were found to be 81.8% and 58.5%, respectively, in biopsy. On the other hand, the sensitivity and specificity of cytology testing for CIN 3 were 63.6% and 52.4%, respectively. The PPV for CIN 3 was 29.3%, and the NPV for CIN 3 was 93.8% in biopsy, while the PPV for CIN 3 was 15.2%, and the NPV for CIN 3 was 91.4% in CVS [
Table 1].
Intraepithelial lesions were detected in the CVS cytology of all patients with positive HPV-DNA test results and there was a statistically significant correlation (p=0.0003). HPV-DNA was positive in the most of the cases cytologically diagnosed as LSIL and HSIL (73.6% and 63.6%, respectively). In the cytologic examination of HPV-DNA negative cases, ASCUS was the most common diagnosis (67%). CVS LSIL diagnosis was significantly correlated with HPV 16 (p=0.0001).
LSIL in 91.1% of HPV 16 positive cases and HSIL in 40.9% of HPV 18 positive cases were significantly correlated (Fisher’s exact test, p=0.006).
Regarding the correlation between cervical biopsy and HPV, intraepithelial lesions were detected by biopsy in most of the HPV positive cases, but no pathology was observed in 5 cases (7.9%). There was a significant correlation between HPV test and histopathologic result of cervical biopsy (p=0.0002).
HSIL diagnosis by CVS became more frequent with increasing age (51.1 ± 10.6), although no statistically significant correlation was found (p=0.058). CIN2-3 and cancer diagnosed by cervical biopsy were significantly more common at older age (p=0.001).
Among women over 40 years of age, 25.7% had ASCUS, 27.1% had LSIL and 9.7% had HSIL. Compared to women under 40 years of age, significantly more intraepithelial lesions were diagnosed (p<0.005). The proportion of patients with HPV subtypes other than HPV16 and HPV18 was higher in older patients than in younger patients (84.6% vs. 51.4%, p = 0.037).
4. Discussion
Within the framework of our study, a cohort comprising 225 cases underwent dual screening with cotest cervicovaginal smear (CVS) and Human Papillomavirus DNA (HPV-DNA) testing, followed by subsequent colposcopic biopsy and diagnostic evaluation in the pathology laboratory.
Noteworthy is our alignment with the observations made by Aydogan et al.15, whereby our study echoed the significantly high sensitivity in detecting intraepithelial lesions through cervical smears, regardless of whether the liquid-based cytologic or conventional cytologic method was employed. This consistency in findings reaffirms the efficacy of the conventional method of cervical cytology in the identification of intraepithelial lesions, validating its continued relevance in contemporary diagnostic practices.
It is imperative to acknowledge that while colposcopy is a widely employed diagnostic tool, certain limitations persist in its ability to comprehensively detect high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN 2-3) or cervical cancer lesions. This assertion aligns with the findings reported by Zuchaa et al., who documented a sensitivity of 66.2% for CIN 2 lesions when comparing colposcopy to the gold standard of at least three biopsies of the cervix. Despite these recognized limitations, colposcopy remains a primary diagnostic modality for cervical dysplasia, emphasizing the need for a nuanced understanding of its strengths and weaknesses within the broader context of cervical health assessment15.
The findings from our study contribute to the ongoing discourse surrounding cervical cancer screening methodologies, particularly by corroborating the effectiveness of conventional cytologic methods in lesion detection. As we navigate the landscape of cervical health diagnostics, it becomes imperative to integrate multiple screening modalities judiciously to ensure a comprehensive and accurate assessment of cervical abnormalities. Future research endeavors should continue to refine our understanding of the strengths and limitations of each diagnostic tool, paving the way for optimized screening protocols and improved patient outcomes.
Nonetheless, it is imperative not to overshadow the merits of liquid-based cytology in relation to conventional smears. Primarily, the utilization of the same collected sample for both HPV testing and cytological examination constitutes a dual advantage, yielding economic efficiencies and mitigating patient discomfort6. Additionally, the microscopic scrutiny of liquid-based cytology slides proves to be notably more straightforward, and expeditious results are attainable in comparison to conventional smears16,17. Presently, numerous regions still rely on conventional smear cytology, particularly in cases where Italian guidelines mandate primary cytomorphological assessment for women below 30 years of age, eschewing molecular HPV testing. While acknowledged as a cost-effective approach, this practice is lamentable, as it foregoes the inherent advantages associated with liquid-based cytology5.
Cervicovaginal HPV testing exhibits a sensitivity of 90% in the identification of precancerous conditions. In the general population, the cumulative risk of encountering precancer over a 5-year period subsequent to obtaining a negative HPV test result is less than 0.15%. Individuals with prevailing precancer risks below 4% are advised to undergo repeat HPV testing at intervals of 1, 3, or 5 years, contingent upon the 5-year precancer risk. For those with current precancer risks ranging from 4% to 24%, including individuals with low-grade cytology test outcomes such as ASC-US or LSIL coupled with an undetermined-duration positive HPV test, colposcopy is recommended18. Conversely, individuals exhibiting current precancer risks within the range of 25% through 59%, such as those with high-grade cytology results denoting ASC-H or HSIL alongside positive HPV test results, are advised to undergo management procedures involving colposcopy accompanied by biopsy or excisional treatment. This nuanced stratification ensures tailored and evidence-based approaches to the management of cervical precancerous conditions based on individual risk profiles18.
In our investigation, the diagnostic process entailed either colposcopic biopsy or a second CVS following an initial abnormal CVS result. Comparable to certain studies in the existing literature, a notable association between CVS findings and biopsy results was not observed, as evidenced by a kappa value of 0.31. Among the various diagnostic categories, the highest degree of correlation was noted in cases classified as LSIL at 81.1%.
The profound interconnection between HPV and cervical dysplasia is prompting a paradigm shift in conventional screening approaches. ASCCP advocates for the adoption of Co-Test screening, involving the combined utilization of HPV-DNA testing and CVS examination, specifically for women within the age range of 30 to 64 years. The Co-Test methodology exhibits a higher likelihood of detecting abnormal cervical cells or cervical cancer compared to cervicovaginal smear screening in isolation. Furthermore, the Co-Test offers enhanced feasibility in diverse healthcare settings, making it more accessible than colposcopy19.
Within the purview of our investigation, the diagnostic trajectory encompassed either a colposcopic biopsy or a secondary CVS following an initial abnormal CVS result. In consonance with certain extant studies, our findings revealed a discernable lack of a robust association between CVS outcomes and biopsy results, as underscored by a kappa value of 0.31. This observation implies a modest agreement between the two diagnostic modalities, emphasizing the need for a nuanced interpretation of screening results. Intriguingly, among the various diagnostic categories, a comparatively higher degree of correlation was discerned in cases classified as LSIL at 81.1%, shedding light on potential variations in diagnostic accuracy across distinct pathological classifications.
The pivotal nexus between HPV and cervical dysplasia is reshaping conventional screening paradigms. The American Society for Colposcopy and Cervical Pathology champions the adoption of Co-Test screening, wherein both HPV-DNA testing and CVS examination are employed in tandem, particularly for women aged 30 to 64 years. This strategic amalgamation is driven by the heightened sensitivity of the Co-Test methodology in detecting abnormal cervical cells or cervical cancer when compared to isolated cervicovaginal smear screening. Moreover, the Co-Test approach offers augmented practicality across diverse healthcare settings, rendering it more accessible than colposcopy, thereby aligning with the imperative of enhancing screening reach and efficacy19.
As our study contributes to the growing body of knowledge in cervical health diagnostics, it underscores the intricate relationship between screening modalities and emphasizes the evolving landscape of cervical dysplasia detection. The insights garnered from this investigation not only contribute to the academic discourse but also hold practical implications for refining screening strategies, ultimately contributing to improved patient outcomes. Future research endeavors should continue to explore innovative approaches and technologies to further enhance the precision and accessibility of cervical cancer screening in diverse clinical contexts.
In our study, similar to the study by Kussaibi H. et al.20, a high correlation was found between HPV-DNA test and positive cytology and biopsy. There was a significant correlation between HPV-DNA test and cervicovaginal smear result and cervical biopsy (p=0.0003, p=0.0002, respectively). This result emphasizes that HPV-DNA testing should be included in cervical cancer screening methods.
Numerous studies have proven that HPV infection is a precursor virus for the development of cervical precancerous lesions and cervical cancer21,22. Moreover, the temporal progression from HPV infection to the manifestation of cervical carcinoma in situ typically spans a duration of approximately 7 to 12 years, as corroborated by various clinical studies. Consequently, the timely identification and prompt management of CIN 2 and higher-grade lesions assume paramount significance in the context of cervical cancer screening efforts21.
ASCUS represents the most common abnormal diagnostic result encountered in CVS screening tests and is characterized by cell abnormalities that are more prominent than reactive changes but do not reach the threshold of a squamous intraepithelial lesion. Yarandi F et al.23 found the rate of detection of higher intraepithelial lesions in CVS screening in patients diagnosed with ASCUS to be 3-10%. In addition, Li X. et al.24 reported a CIN II detection rate of 13.55% in 251 ASCUS cases, while Li SR. et al.24 reported a CIN2-3 detection rate of 7.3% in 463 ASCUS cases. Furthermore, existing literature reports high rates of HPV positivity and the association of lesions with CIN 2-3 among patients with ASCUS, standing at 6.8%, 11%, and 14.3%24-26.
Similarly, in our study, cases with ASCUS identified through CVS and concomitant HPV-DNA positivity exhibited cervical biopsy results indicating CIN 2 in 30% of cases and CIN 3 in 2.7% of cases. This finding suggests that HPV-DNA testing is a test that should be performed in women with ASCUS. Hence, ASCUS represents a lesion warranting thorough evaluation through colposcopy, particularly when HPV-DNA testing yields a positive result.
According to the literature, around 13% of women diagnosed with LSIL through CVS screening tests are likely to progress to HSIL within a 3-year period13. In our study, all patients with LSIL underwent colposcopy-guided biopsy, and 13 of them were subsequently diagnosed with a higher-stage lesion, specifically CIN2-3. This finding aligns with previous reports that indicate such progression rates to range from 12% to 20%27-29. These results emphasize the crucial role of colposcopic evaluation as an essential step to be undertaken in cases of LSIL for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management.
In our study, a statistically significant difference was observed in the diagnosis of intraepithelial lesions between women aged over 40 years and those under 40 years (p<0.005). Specifically, a higher proportion of intraepithelial lesions was detected in women over 40 years of age compared to their younger counterparts. This finding contrasts with the findings reported by Louro et al.30, where they reported a lower likelihood of detecting clinically significant lesions in the subsequent histologic follow-up of patients aged 40 years and older, as opposed to patients younger than 40 years.
In our study, HPV-DNA testing in combination with CVS cytology yielded a diagnosis of LSIL/CIN1 with higher sensitivity and specificity than colposcopic cervical biopsy. In contrast, a study conducted by Wang et al.21 reported lower sensitivity and specificity between LSIL and HPV with cytologic evaluation compared to biopsy. Similar trends were observed in the evaluation of HSIL/CIN3 in our study, where the sensitivity and specificity between cytology and HPV were lower than those of biopsy (81.8% and 58.5% sensitivity and specificity in biopsy, 63.6% and 52.4% in cytology, respectively).
The severity of cervical lesions may vary according to HPV types. Notably, a progressive escalation in cervical lesion grades is observed with higher viral loads of HPV16 and HPV18, and a robust correlation exists between these viral loads and the severity of the cervical lesions21. Depuydt et al.31 further bolstered this concept, suggesting that the pathological changes observed in CIN 3 may be attributed to a steady increase in the specific HPV type and viral load. Consequently, detection of specific HPV load can be used to predict the risk of CIN 3 occurrence.
Another study emphasized that high-risk HPV types other than HPV16 and 18 can also predict high-risk lesions such as CIN 2 and CIN 332. In our study, we identified a noteworthy association between HPV 16 and LSIL, and between HPV 18 and HSIL. HPV16/18 viral load increased in proportion to the severity of cervical lesions (p=0.006).
5. Conclusions
While our study provided valuable insights, it is imperative to acknowledge certain limitations that may influence the interpretation of results. Notably, the inclusion of cytologic evaluation utilizing the conventional method, deemed an older technique, introduces a potential source of variability in histologic diagnosis when compared to contemporary liquid-based cytology. The literature emphasizes the impact of diverse cervical cytology evaluation techniques on result comparisons, highlighting the need for caution in extrapolating findings across different methodologies. A prospective study design, incorporating a larger sample size, would have bolstered the robustness, reliability, and generalizability of our findings.
Despite these limitations, our study revealed that the conventional smear technique, while considered older, remained a reliable tool in the detection of high-grade cervical lesions. This underscores the importance of continuous patient follow-up, recognizing that diagnostic outcomes may evolve upon biopsy, necessitating vigilant monitoring for accurate clinical management.
Furthermore, the incorporation of HPV-DNA studies in all cytologic examinations was deemed indispensable, particularly in specific patient subsets. This precautionary measure aimed to avoid unnecessary interventions and contribute to the precision of diagnostic assessments. The accurate detection of cervical lesions through this comprehensive approach holds significance not only in preventing unwarranted surgical procedures but also in empowering clinicians to devise tailored and appropriate follow-up strategies for improved patient management.
While these limitations underscore the need for caution in interpreting our findings, the study underscores the ongoing relevance and reliability of the conventional smear technique in certain diagnostic scenarios. It emphasizes the pivotal role of patient follow-up and the integration of advanced molecular techniques, such as HPV-DNA studies, in refining diagnostic accuracy and optimizing clinical decision-making. Future endeavors in this field should consider adopting a prospective study design with an expanded sample size to further elucidate the nuances of cervical pathology assessment and enhance the applicability of study outcomes to broader clinical contexts.
Funding
There is no financial support.
Informed Consent Statement
All patients provided informed consent.
Data Availability Statement
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of ÇANAKKALE 18 MART ÜNİVERSİTESİ KLİNİK ARAŞTIRMALAR ETİK KURULU(approval code, 2023/05-12; approval date, 22/03/2022)).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
References
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018 Nov;68(6):394-424. Epub 2018 Sep 12. Erratum in: CA Cancer J Clin. 2020 Jul;70(4):313. [CrossRef]
- Brian Wasita, Suyatmi, Riza Novierta Pesik, Ratih Dewi Yudhani, Nanang Wiyono, Rachmi Fauziah Rahayu, & Kristanto Yuli Yarso. (2023). High-risk human papillomavirus prevalence among patients with cervical cancer at Moewardi General Hospital in Surakarta, Indonesia. Bali Medical Journal, 12(2), 1918–1921. Retrieved from https://www.balimedicaljournal.org/index.php/bmj/article/view/3782.
- Höhn AK, Brambs CE, Hiller GGR, May D, Schmoeckel E, Horn LC. 2020 WHO Classification of Female Genital Tumors. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd. 2021 Oct;81(10):1145-1153. [CrossRef]
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 2023 Jan;73(1):17-48. [CrossRef]
- Caputo A, Macrì L, Gibilisco F, Vatrano S, Taranto C, Occhipinti E, Santamaria F, Arcoria A, Scillieri R, Fraggetta F. Validation of full-remote reporting for cervicovaginal cytology: the Caltagirone-Acireale distributed lab. J Am Soc Cytopathol. 2023 Sep-Oct;12(5):378-385. [CrossRef]
- Swid MA, Monaco SE. Should screening for cervical cancer go to primary human papillomavirus testing and eliminate cytology? Mod Pathol. 2022;35:858e864. [CrossRef]
- Schiffman M, Doorbar J, Wentzensen N, et al. Carcinogenic human papillomavirus infection. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16086.
- Perkins, R. B., Guido, R. S., Castle, P. E., Chelmow, D., Einstein, M. H., Garcia, F., Huh, W. K., Kim, J. J., Moscicki, A. B., Nayar, R., Saraiya, M., Sawaya, G. F., Wentzensen, N., Schiffman, M., & 2019 ASCCP Risk-Based Management Consensus Guidelines Committee (2020). 2019 ASCCP Risk-Based Management Consensus Guidelines for Abnormal Cervical Cancer Screening Tests and Cancer Precursors. Journal of lower genital tract disease, 24(2), 102–131. [CrossRef]
- Ronco G, Confortini M, Maccallini V, Naldoni C, Segnan N, Sideri M, Zappa M, Zorzi M, Calvia M, Giorgi Rossi P. Health Technology assessment Report. Uso della citologia in fase liquida nello screening dei precursori del cancro del collo uterino [Health technology assessment report. Use of liquid-based cytology for cervical cancer precursors screening]. Epidemiol Prev. 2012 Sep-Oct;36(5 Suppl 2):e1-e33.
- Schiffman M, Yu K, Zuna R, et al. Proof-of-principle study of a novel cervical screening and triage strategy: Computer-analyzed cytology to decide which HPV-positive women are likely to have ≥CIN2. Int J Cancer. 2016;140:718e725. [CrossRef]
- Walboomers JM, Jacobs MV, Manos MM, Bosch FX, Kummer JA, Shah KV, Snijders PJ, Peto J, Meijer CJ, Muñoz N. Human papillomavirus is a necessary cause of invasive cervical cancer worldwide. J Pathol. 1999 Sep;189(1):12-9. [CrossRef]
- de Martel C, Plummer M, Vignat J, Franceschi S. Worldwide burden of cancer attributable to HPV by site, country and HPV type. Int J Cancer. 2017 Aug 15;141(4):664-670. [CrossRef]
- Pangarkar MA. The Bethesda System for reporting cervical cytology. Cytojournal. 2022 Apr 30;19:28. [CrossRef]
- LeBreton, James. (2010). Book Review: Von Eye, A., & Mun, E. Y. (2005). Analyzing Rater Agreement: Manifest Variable Methods. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum. Organizational Research Methods - ORGAN RES METHODS. 13. 207-209. [CrossRef]
- Aydogan Kirmizi D, Baser E, Demir Caltekin M, Onat T, Sahin S, Yalvac ES. Concordance of HPV, conventional smear, colposcopy, and conization results in cervical dysplasia. Diagn Cytopathol. 2021 Jan;49(1):132-139. [CrossRef]
- Lee RE, McClintock DS, Laver NM, Yagi Y. Evaluation and optimization for liquid-based preparation cytology in whole slide imaging. J Pathol Inform. 2011;2:46. [CrossRef]
- Lew M, Wilbur DC, Pantanowitz L. Computational Cytology: Lessons Learned from Pap Test Computer-Assisted Screening. Acta Cytol. 2021;65(4):286-300. [CrossRef]
- Perkins RB, Wentzensen N, Guido RS, Schiffman M. Cervical Cancer Screening: A Review. JAMA. 2023 Aug 8;330(6):547-558. [CrossRef]
- Practice Bulletin No. 168: Cervical Cancer Screening and Prevention. Obstet Gynecol. 2016 Oct;128(4):e111-e130. [CrossRef]
- Kussaibi H, Al Dossary R, Ahmed A, Muammar A, Aljohani R. Correlation of High-Risk HPV Genotypes with Pap Test Findings: A Retrospective Study in Eastern Province, Saudi Arabia. Acta Cytol. 2021;65(1):48-55. [CrossRef]
- Wang M, Hou B, Wang X, Han L, Shi Y, Zhang Y, Zhang L, Liu L, Jin F, Zhang Y. Diagnostic value of high-risk human papillomavirus viral load on cervical lesion assessment and ASCUS triage. Cancer Med. 2021 Apr;10(7):2482-2488. [CrossRef]
- Pham TH, Nguyen TH, Herrero R, Vaccarella S, Smith JS, Nguyen Thuy TT, Nguyen HN, Nguyen BD, Ashley R, Snijders PJ, Meijer CJ, Muñoz N, Parkin DM, Franceschi S. Human papillomavirus infection among women in South and North Vietnam. Int J Cancer. 2003 Mar 20;104(2):213-20. [CrossRef]
- Yarandi F, Shojaei H, Eftekhar Z, Izadi-Mood N. Comparison of three management strategies for patients with atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance, after six months delay: a three-year experience in an Iranian university hospital. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 2009 Apr;49(2):207-10. [CrossRef]
- Li X, Jiang XJ, Zhou XH. Discussion on treatment of atypical squamous cell of undetermined significance. Chinese J Wom Child Health Res. 2013;24(3):436-438.
- Li SR, Wang ZM, Wang YH, Wang XB, Zhao JQ, Xue HB, Jiang FG. Value of PAX1 Methylation Analysis by MS-HRM in the Triage of Atypical Squamous Cells of Undetermined Significance. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2015;16(14):5843-6. [CrossRef]
- Molijn A, Jenkins D, Chen W, Zhang X, Pirog E, Enqi W, Liu B, Schmidt J, Cui J, Qiao Y, Quint W; Chinese HPV Typing Group. The complex relationship between human papillomavirus and cervical adenocarcinoma. Int J Cancer. 2016 Jan 15;138(2):409-16. [CrossRef]
- Kabaca C, Sariibrahim B, Keleli I, Karateke A, Cesur S, Cetiner H. The importance of immediate verification of a cervical cytological abnormality with histology. Indian J Cancer. 2013 Oct-Dec;50(4):292-6. [CrossRef]
- Chute DJ, Covell J, Pambuccian SE, Stelow EB. Cytologic-histologic correlation of screening and diagnostic Papanicolaou tests. Diagn Cytopathol. 2006 Jul;34(7):503-6. [CrossRef]
- Pothisuwan M, Pataradool K, Tangjitgamol S, Srijaipracharoen S, Manusirivithaya S, Thawaramorn T. Visual inspection with acetic acid for detection of high grade lesion in atypical squamous cells and low grade squamous intraepithelial lesions from cervical Pap smear. J Gynecol Oncol. 2011 Sep;22(3):145-51. [CrossRef]
- Louro AP, Roberson J, Eltoum I, Chhieng DC. Atypical squamous cells, cannot exclude high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion. A follow-up study of conventional and liquid-based preparations in a high-risk population. Am J Clin Pathol. 2003 Sep;120(3):392-7. [CrossRef]
- Depuydt CE, Criel AM, Benoy IH, Arbyn M, Vereecken AJ, Bogers JJ. Changes in type-specific human papillomavirus load predict progression to cervical cancer. J Cell Mol Med. 2012 Dec;16(12):3096-104. [CrossRef]
- Li J, Jinghe L, Youfang W, et al. Grading relationship between high-risk human papillomaviral load and cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. J Reprod Contracep. 2006;07:422-425.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).