Submitted:
29 January 2024
Posted:
30 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- A wearable device, which centered around a microcontroller, that utilizes 4G network and IMU sensors to perceive and analyze the posture and behavioral states of horses.
- A real-time horse behavior recognition method which uses resultant acceleration thresholds that achieves behavior classification in horses through interval counting and statistical analysis of variance parameters between segments.
- The effectiveness of the proposed method is demonstrated through experimental verification.
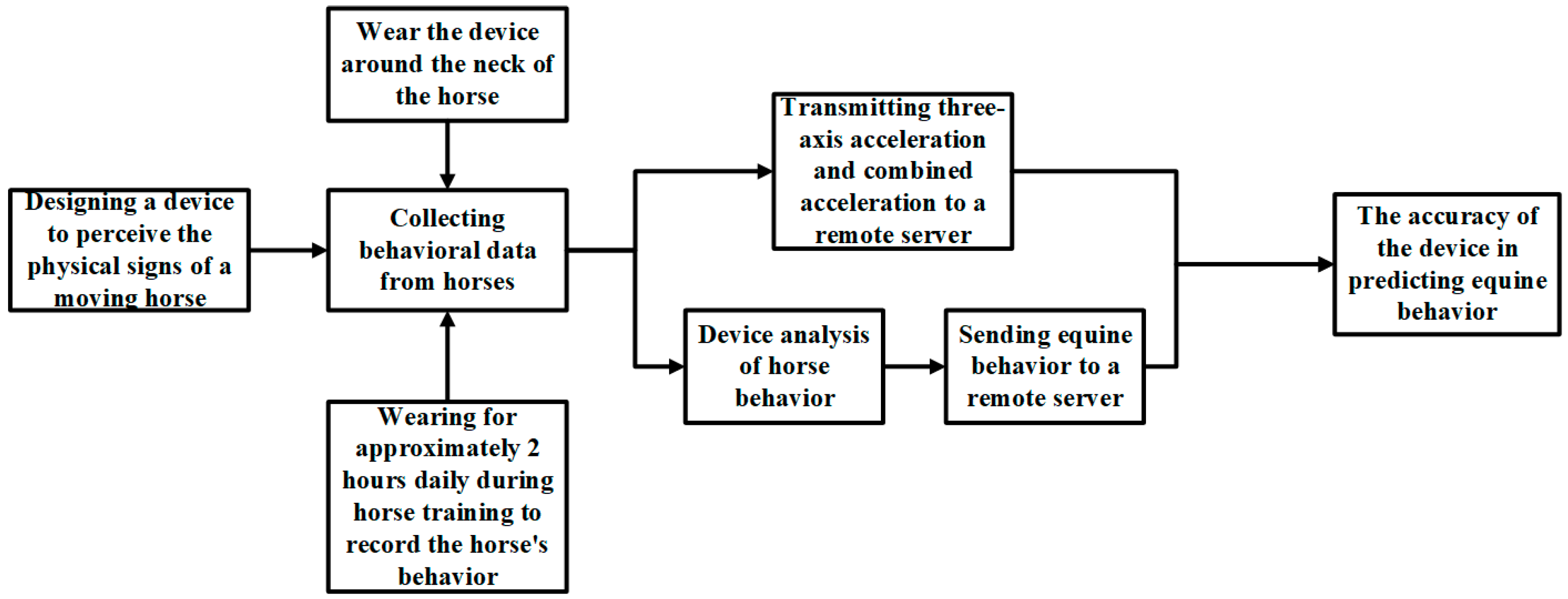
2. Materials and Methods
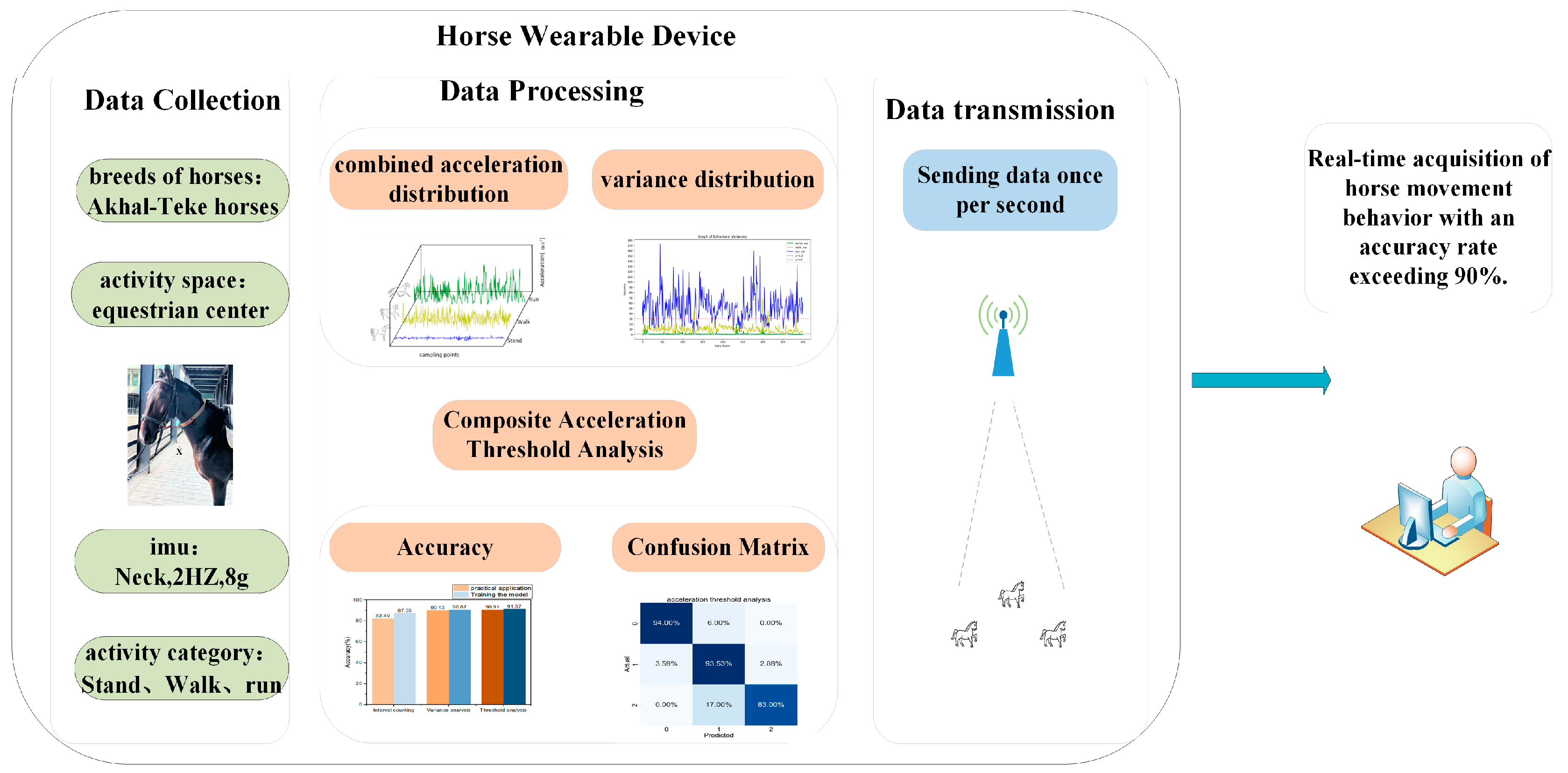
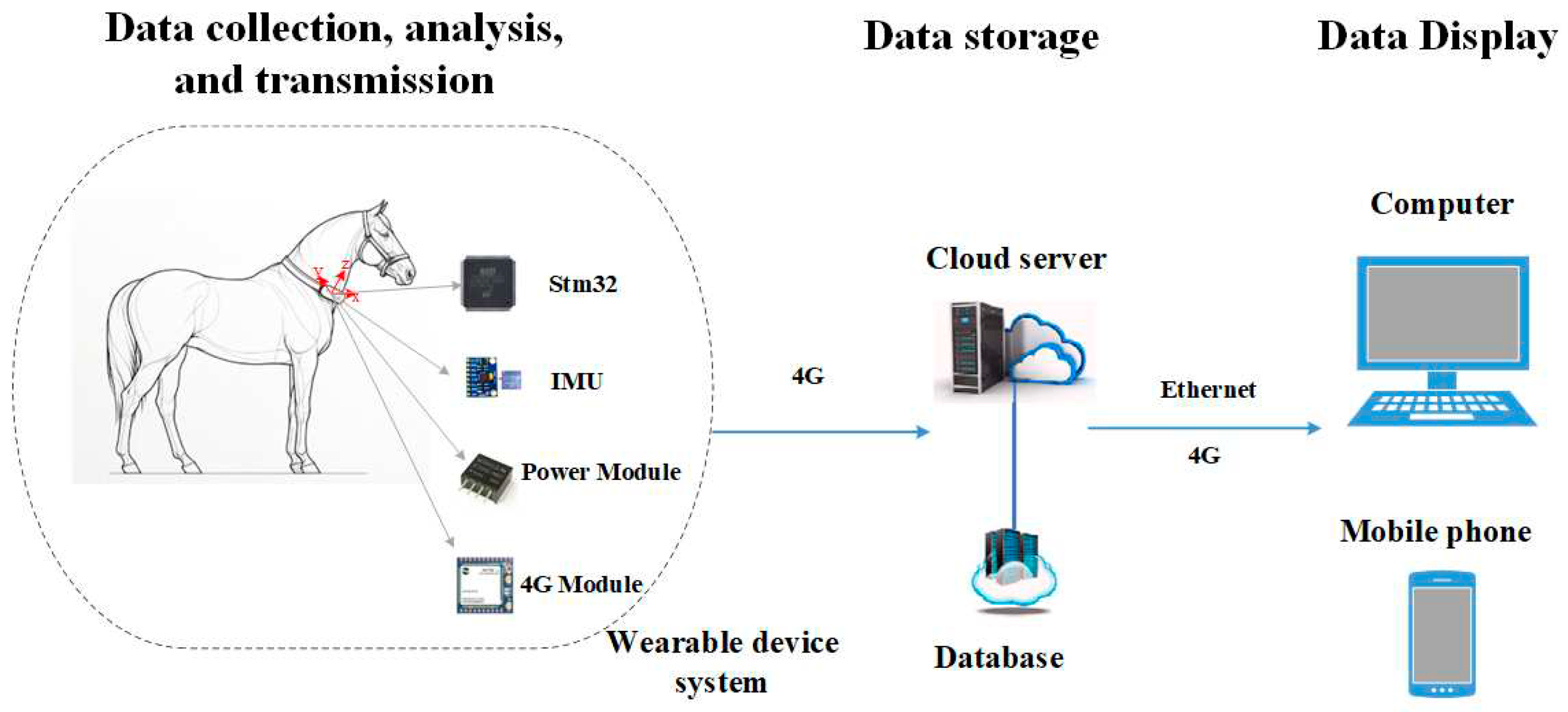
2.1. System Architecture
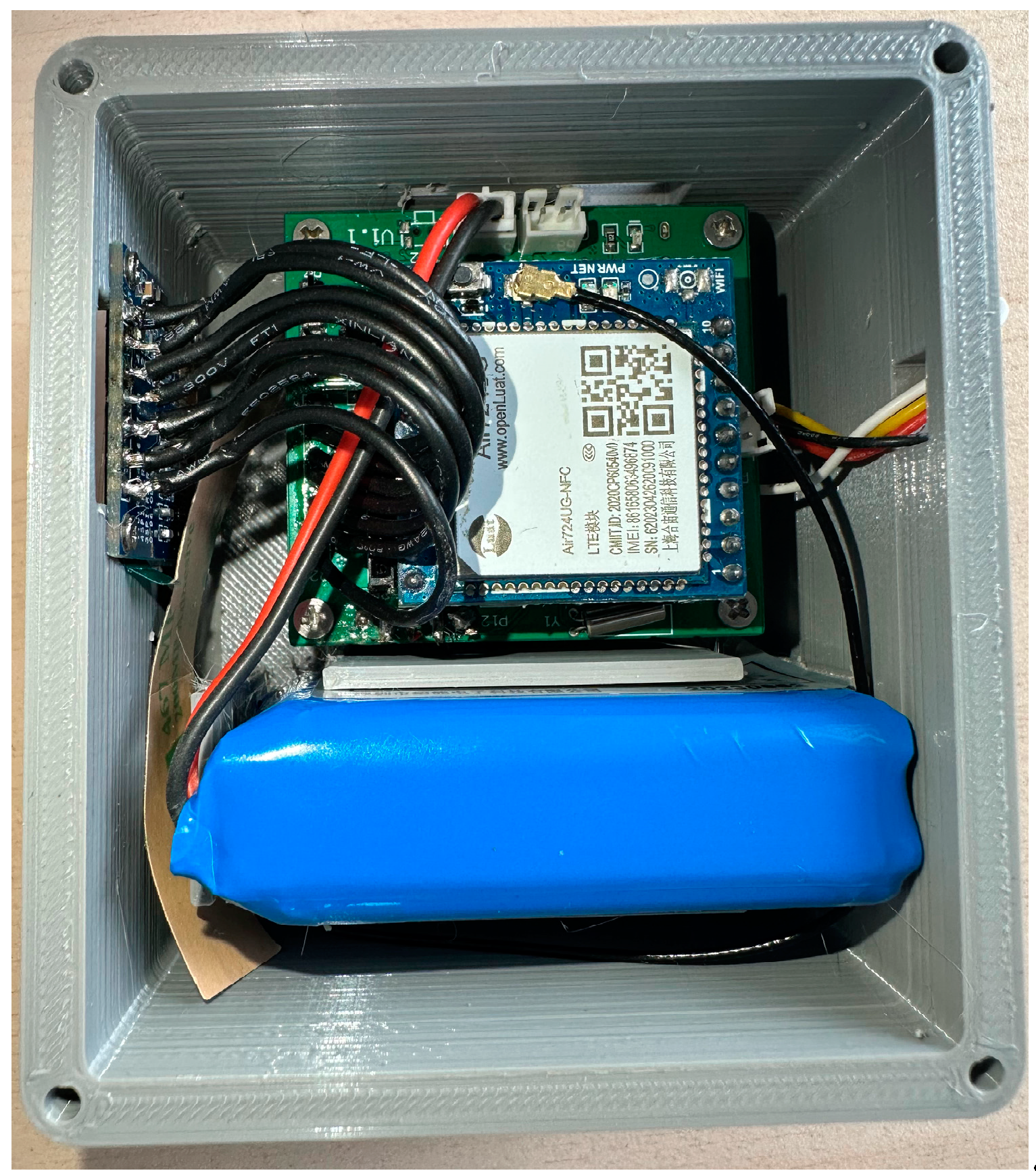
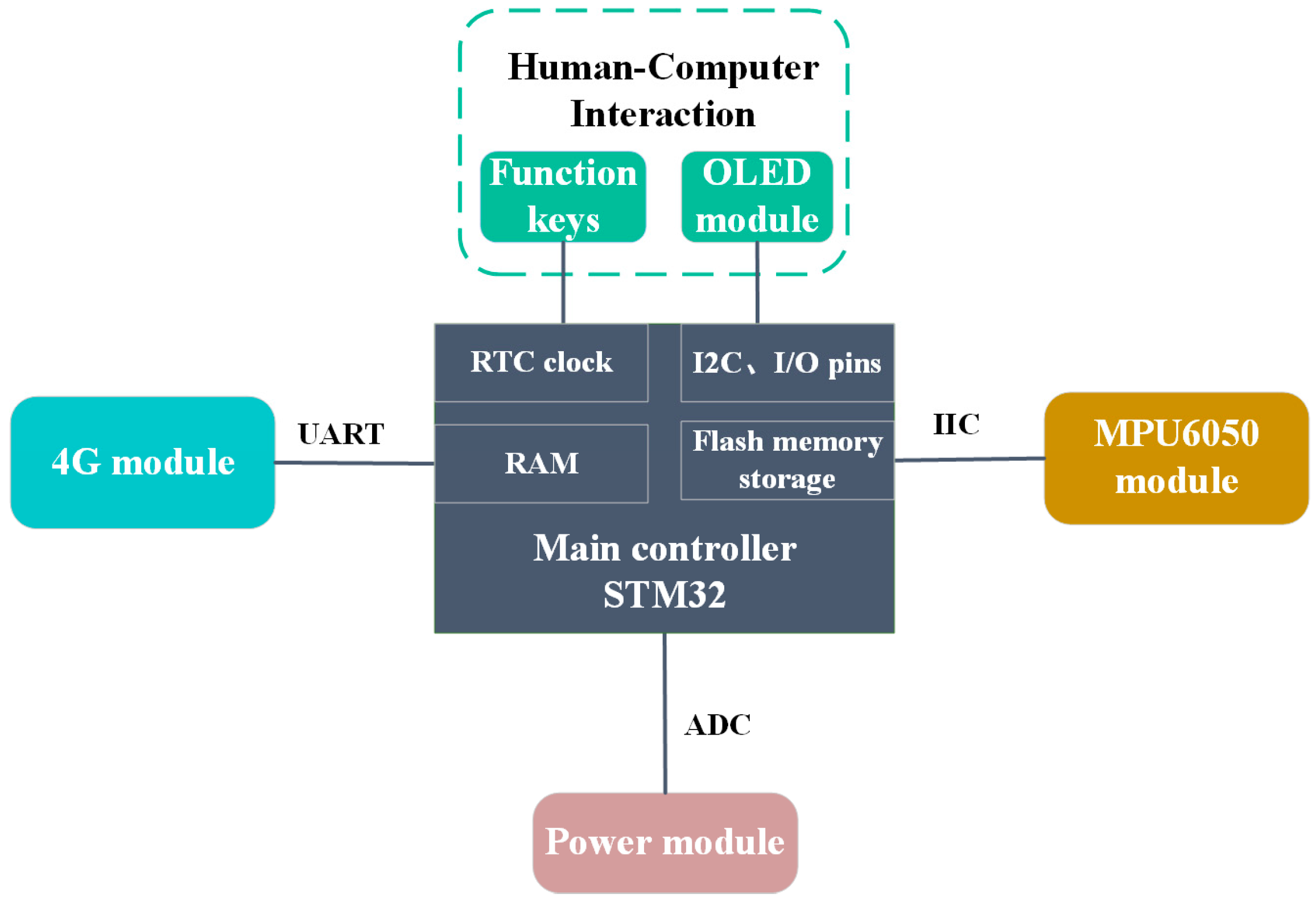
2.1.1. Hardware Design
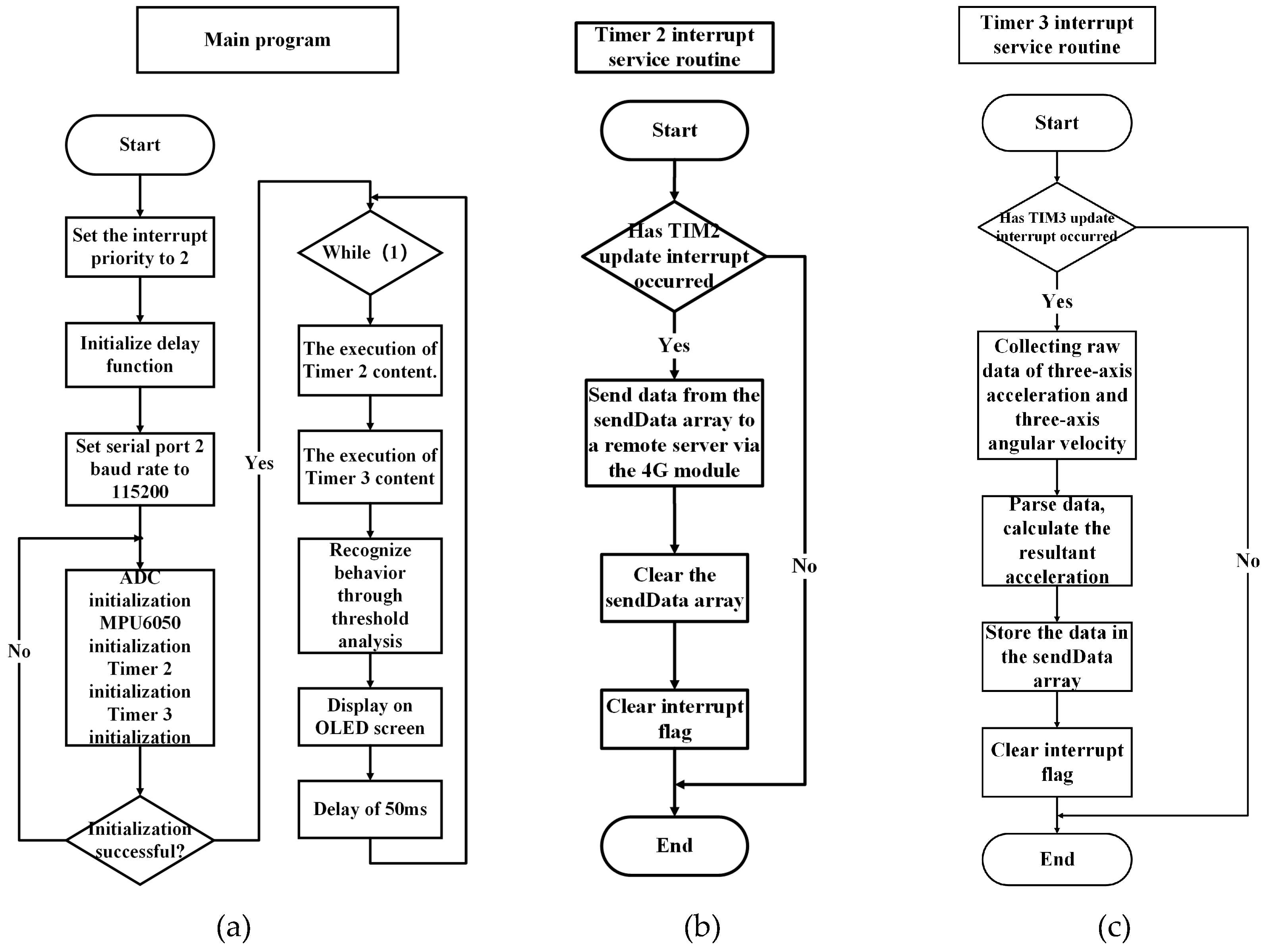
2.1.2. Software and Algorithm Design
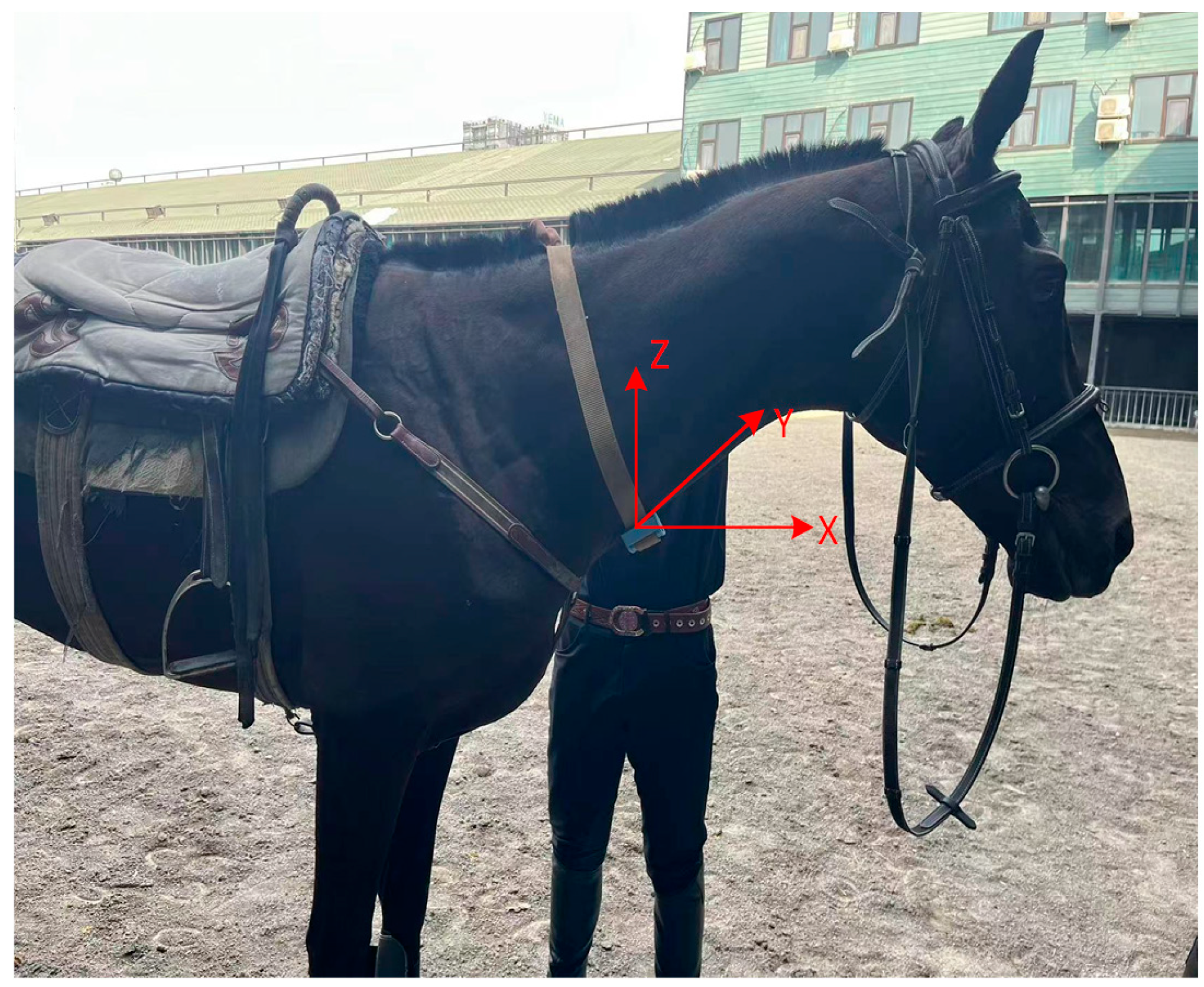
2.2. Data Acquisition
2.3. Data Processing
2.4. Algorithm Design
2.4.1. Stage 1: Cumulative Acceleration Interval Counting Method
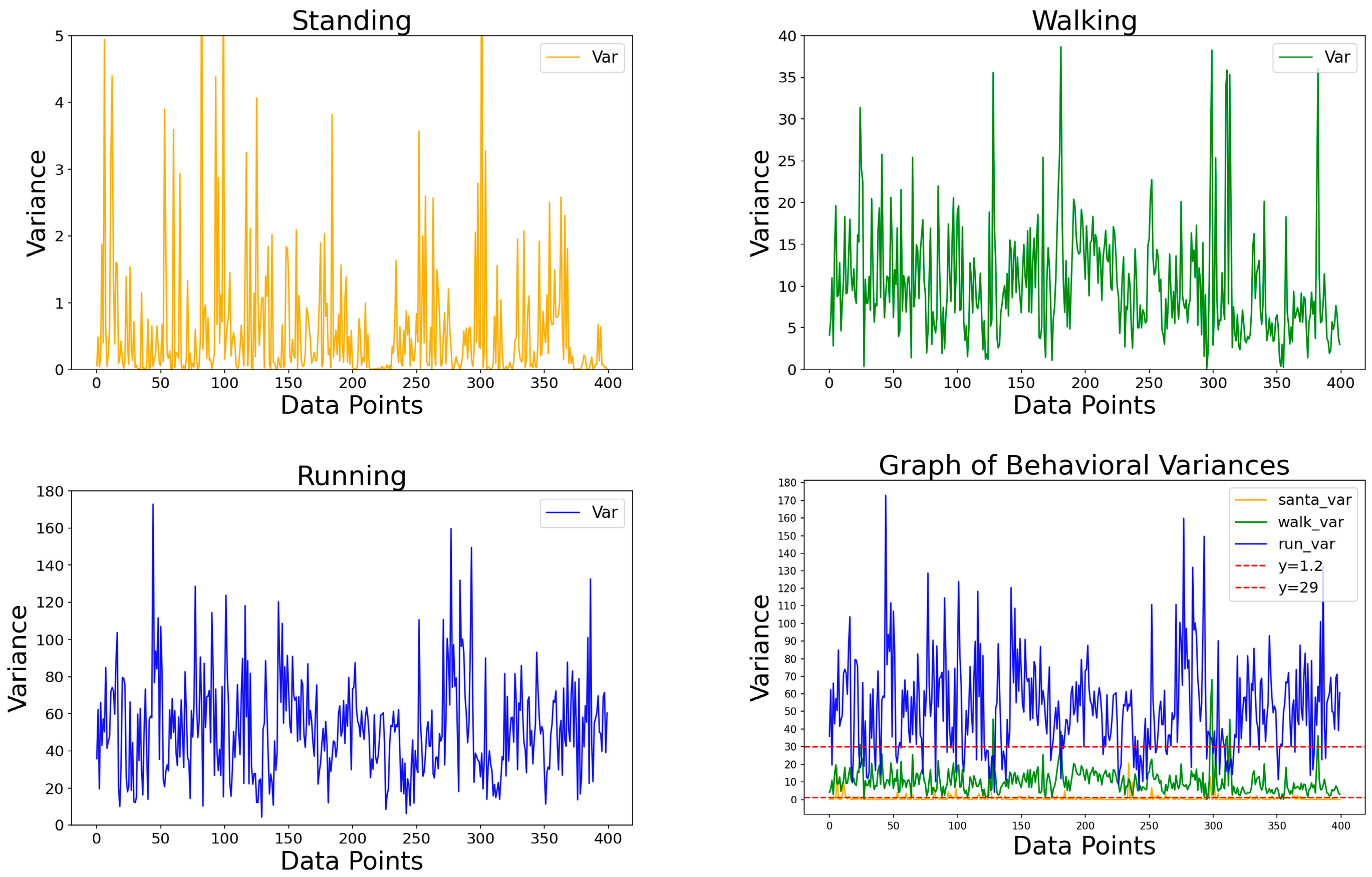
2.4.2. Stage 2: Combined Acceleration Variance Analysis Method
-
Periodically collecting combined accelerometer data via a timer.is a set of combined acceleration values, where represents the nth combined acceleration.
-
Calculate the variance with a data collection window size of N.represents the variance, stands for the mean, calculated as .
2.4.3. Threshold Analysis of Combined Acceleration
-
The combined acceleration set with a data collection window size of N.
-
Count the data volume for standing behavior., is the indicator function.
- Calculate the variance within the interval.
| Algorithm 1: Combined Acceleration Threshold Analysis |
| acc_data:Array of combined accelerations samplingQuantity:Window size function main() { if (Interval_notation (acc_data) == 0) { // Interval counting method for behavior analysis return 0 //stand } mean = calculate_mean(acc_data, samplingQuantity) variance = calculate_variance(acc_data, samplingQuantity, mean) return determine_behavior(variance) } // Variance analysis method for behavior analysis function determine_behavior(variance) { if (variance <= 1.2) { return 0 // stand } else if (variance <= 29) { return 1 // walk } else return 2 // run } |
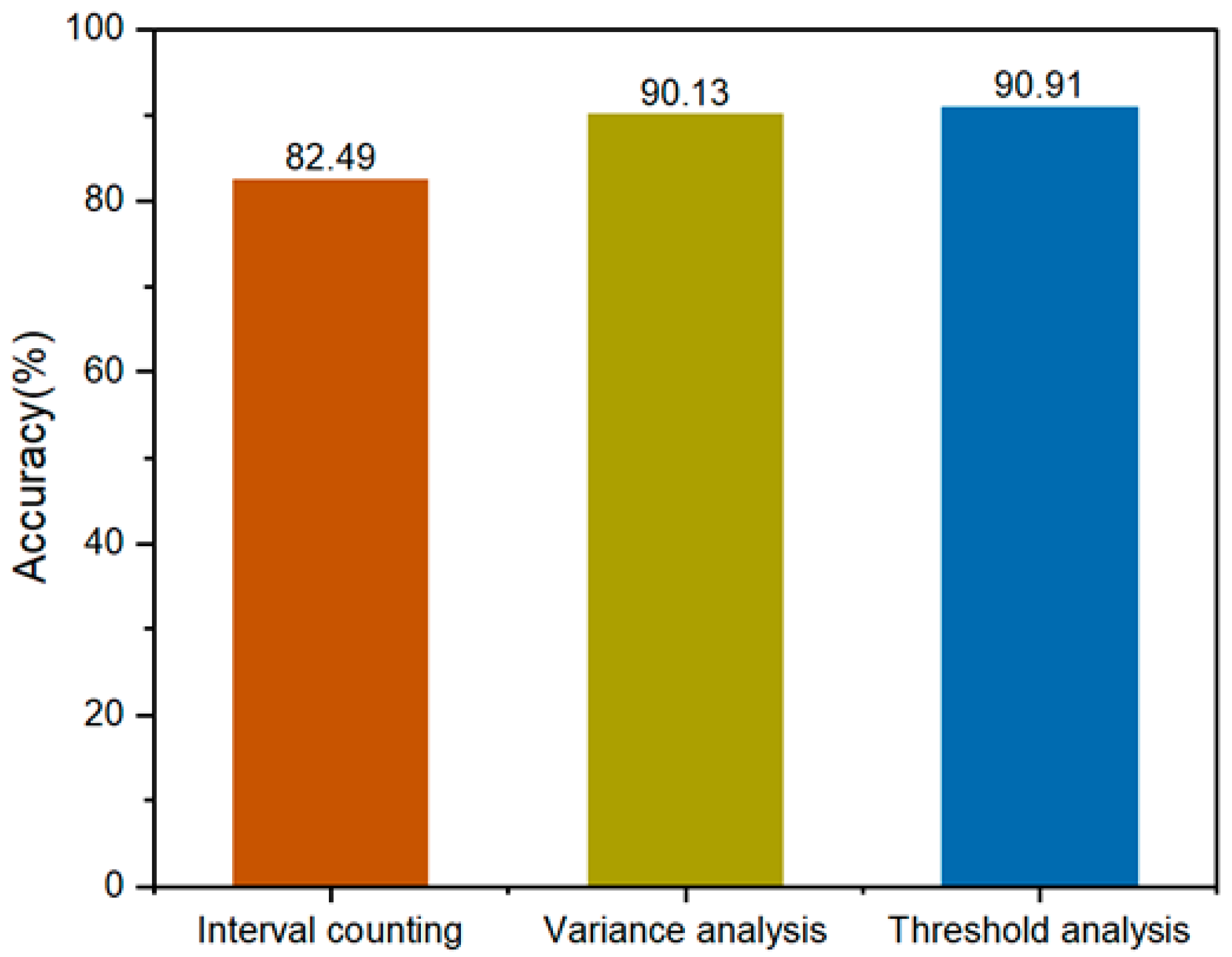
3. Results
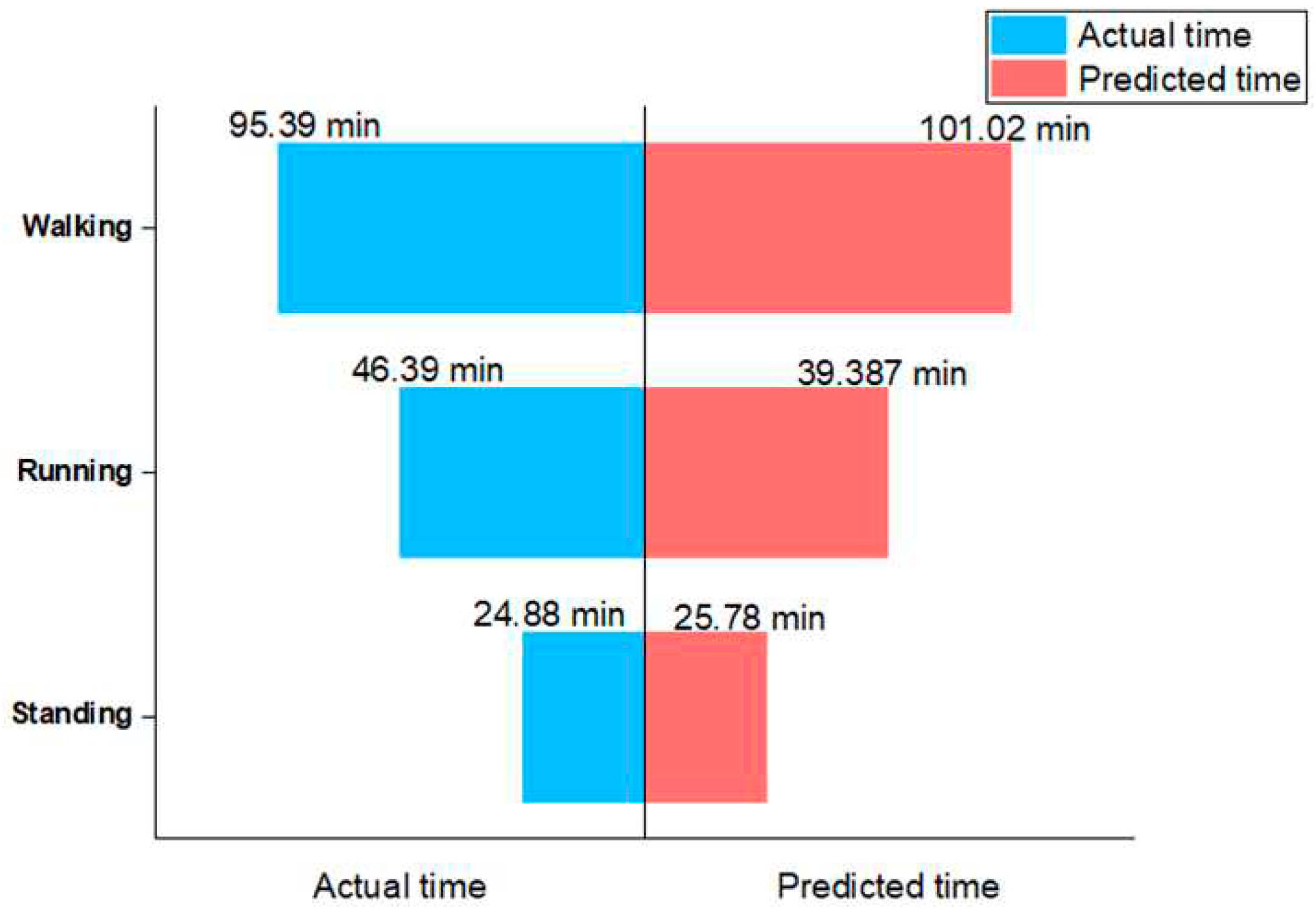
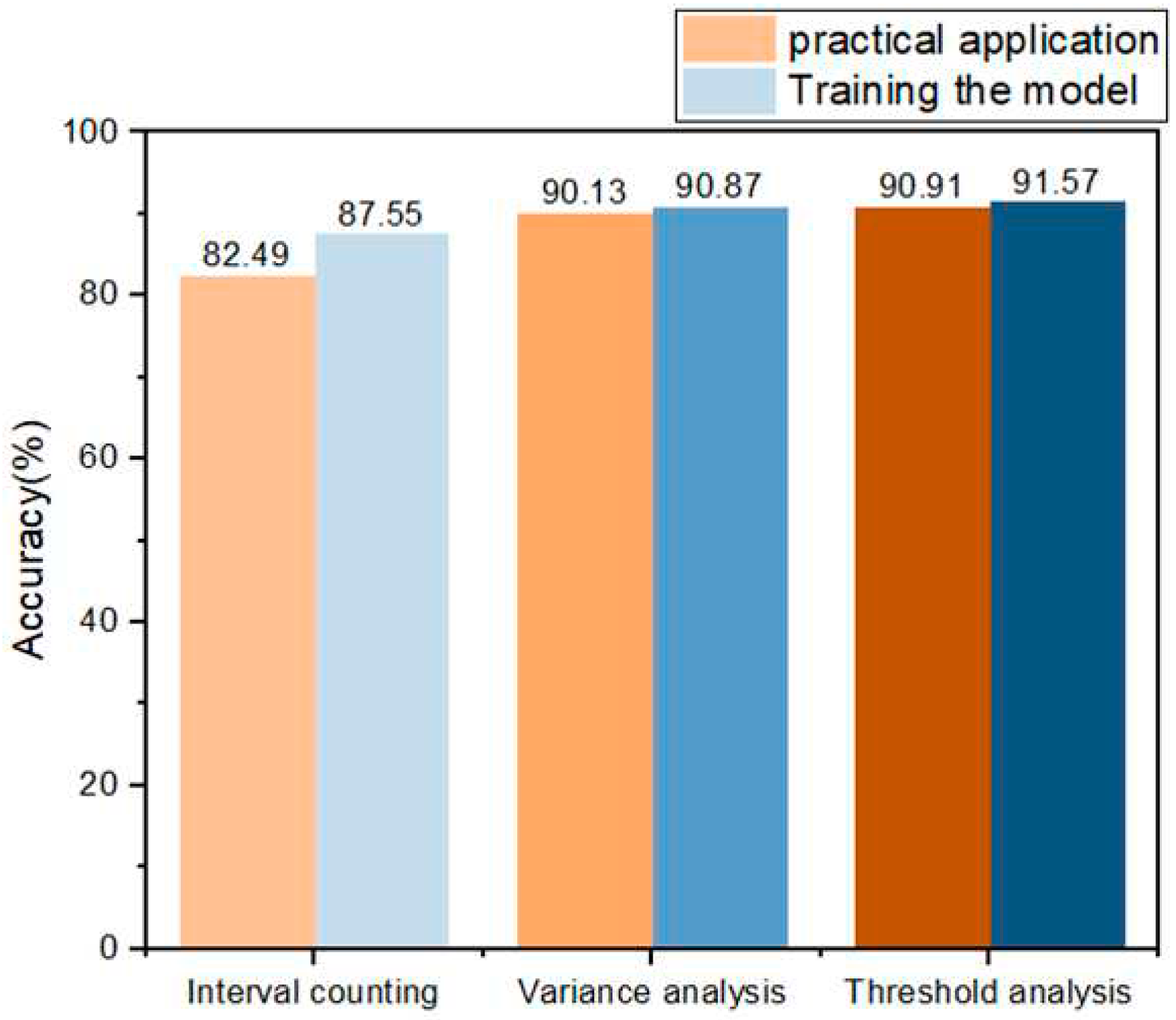
3.1. Model Training Results
3.2. Model Application
4. Discussion
4.1. Device and Algorithm
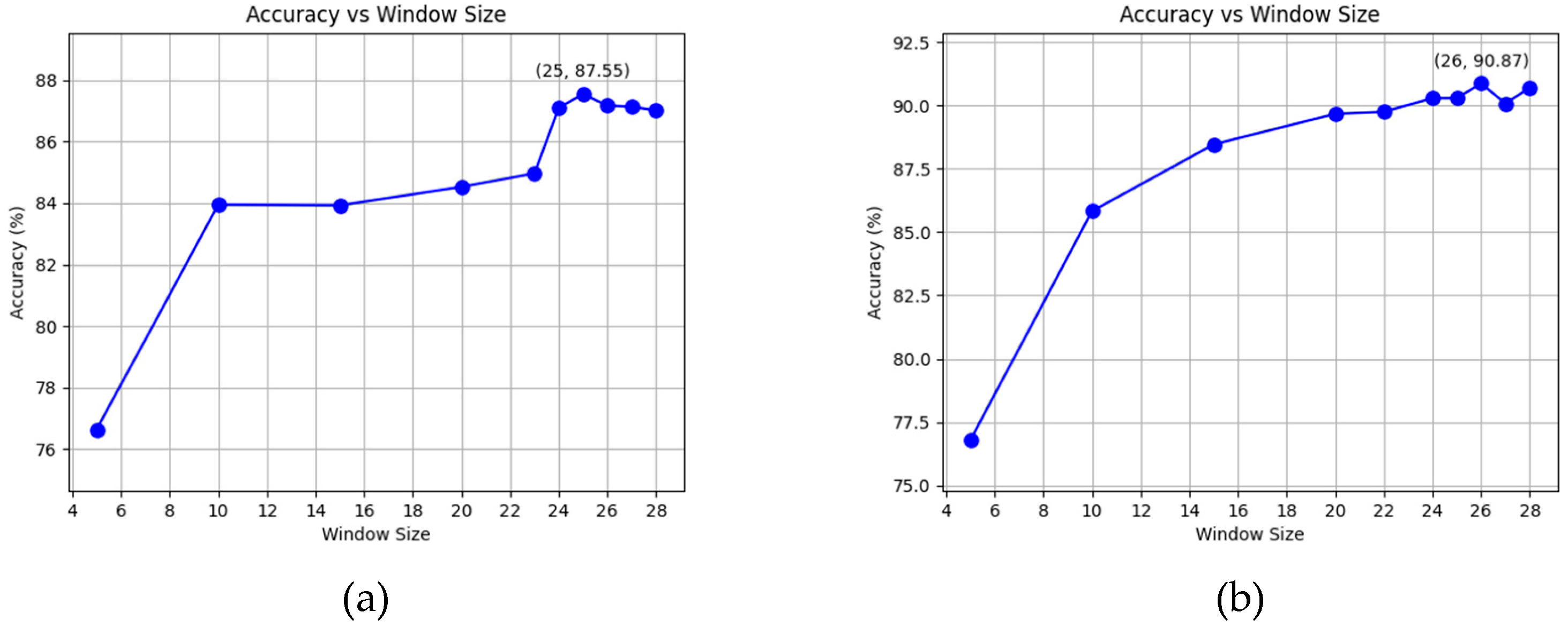
4.2. Data Collection Window
4.3. Classification Algorithm
4.4. Conclusions and Future Work
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McGreevy, P.; Berger, J.; De Brauwere, N.; et al. Using the five domains model to assess the adverse impacts of husbandry, veterinary, and equitation interventions on horse welfare. Animals 2018, 8, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesimple, C. Indicators of horse welfare: State-of-the-art. Animals 2020, 10, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Borstel, U.K.; Pasing, S.; Gauly, M. Towards a more objective assessment of equine personality using behavioural and physiological observations from performance test training. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2011, 135, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, A.N.; Christensen, J.W. The application of learning theory in horse training. Appl. Anim. Behav. Sci. 2017, 190, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eerdekens, A.; Deruyck, M.; Fontaine, J.; et al. Automatic equine activity detection by convolutional neural networks using accelerometer data. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 168, 105139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauwelaerts, S.; Zarski, L.; Aerts, P.; et al. Effects of acceleration on gait measures in three horse gaits. J. Exp. Biol. 2015, 218, 1453–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serra Bragança, F.M.; Broomé, S.; Rhodin, M.; et al. Improving gait classification in horses by using inertial measurement unit (IMU) generated data and machine learning. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, C.J.; Luck, L.M.; Keshwani, J. Location on the body of a wearable accelerometer affects accuracy of data for identifying equine gaits. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2018, 63, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogarty, E.S.; Swain, D.L.; Cronin, G.M. Behaviour classification of extensively grazed sheep using machine learning. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 169, 105175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Guo, L.; Shu, H.; et al. Behavior Classification and Analysis of Grazing Sheep on Pasture with Different Sward Surface Heights Using Machine Learning. Animals 2022, 12, 1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, K.; Karlsson, J.; Liuska, M.; et al. A sensor-fusion-system for tracking sheep location and behaviour. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2020, 16, 1550147720921776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benaissa, S.; Tuyttens, F.A.M.; Plets, D.; et al. On the use of on-cow accelerometers for the classification of behaviours in dairy barns. Res. Vet. Sci. 2019, 125, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Shu, H.; Bindelle, J.; et al. Classification and analysis of multiple cattle unitary behaviors and movements based on machine learning methods. Animals 2022, 12, 1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; He, Z.; Ji, J. IoT-based measurement system for classifying cow behavior from tri-axial accelerometer. Ciência Rural. 2019, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casella, E.; Khamesi, A.R.; Silvestri, S. Smartwatch application for horse gaits activity recognition[C]//2019 IEEE International Conference on Smart Computing (SMARTCOMP). IEEE, 2019; 409-416.
- Barwick, J.; Lamb, D.W.; Dobos, R.; et al. Categorising sheep activity using a tri-axial accelerometer. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 145, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, D.N.; Nguyen, T.N.; Khanh, P.C.P.; et al. An iot-based design using accelerometers in animal behavior recognition systems. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 22, 17515–17528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casella, E.; Khamesi, A.R.; Silvestri, S. A framework for the recognition of horse gaits through wearable devices. Pervasive Mob. Comput. 2020, 67, 101213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, D.S.; Nankervis, K.J. Equine behaviour: principles and practice; John Wiley & Sons, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- The domestic horse: the origins, development and management of its behaviour; Cambridge University Press, 2005.
- Larson, M.G. Analysis of variance. Circulation 2008, 117, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerioli, M.R.; de, S. Oliveira F, Szwarcfiter J L. The interval count of interval graphs and orders: a short survey. J. Braz. Comput. Soc. 2012, 18, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Qi, J.; Hu, T.; et al. Research on Six-Axis Sensor-Based Step-Counting Algorithm for Grazing Sheep. Sensors 2023, 23, 5831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barwick, J.; Lamb, D.W.; Dobos, R.; et al. Identifying sheep activity from tri-axial acceleration signals using a moving window classification model. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervantes, I.; Gutiérrez, J.P.; García-Ballesteros, S.; et al. Combining threshold, thurstonian and classical linear models in horse genetic evaluations for endurance competitions. Animals 2020, 10, 1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Zhou, C. Equestrian sports posture information detection and information service resource aggregation system based on mobile edge computing. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2021, 2021, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranciaro, M.; Santos, E.L.; Vara, M.F.F.; et al. Kinematic analysis of the evaluation of equine therapy patients with actimeter[C]//2018 Global Medical Engineering Physics Exchanges/Pan American Health Care Exchanges (GMEPE/PAHCE). IEEE, 2018: 1-5.
- Walton, E.; Casey, C.; Mitsch, J.; et al. Evaluation of sampling frequency, window size and sensor position for classification of sheep behaviour. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2018, 5, 171442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansbridge, N.; Mitsch, J.; Bollard, N.; et al. Feature selection and comparison of machine learning algorithms in classification of grazing and rumination behaviour in sheep. Sensors 2018, 18, 3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neethirajan, S. Transforming the adaptation physiology of farm animals through sensors. Animals 2020, 10, 1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Tocco, J.; Raiano, L.; Sabbadini, R.; et al. A wearable system with embedded conductive textiles and an imu for unobtrusive cardio-respiratory monitoring. Sensors 2021, 21, 3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Category | Body Type | Wearing Location | Device ID | Time | Behavior | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standing | walking | Running | |||||
| Akhal-Tekehorses | Light Horse | Neck | 17 | 10:38 - 10:43 | √ | ||
| 10:43 – 10:46 | √ | ||||||
| 10:46 – 11:10 | √ | ||||||
| ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ⋮ | ||||
| 12:11 – 12:19 | √ | ||||||
| X-axis | Y-axis | Z-axis | ACC |
|---|---|---|---|
| -4.46 | 8.27 | -5.96 | 11.12 |
| -4.85 | 7.43 | -5.55 | 10.46 |
| -4.6 | 6.27 | -6.7 | 10.26 |
| -4.92 | 7.51 | -4.22 | 9.92 |
| -4.93 | 5.99 | -5.3 | 9.39 |
| -5.89 | 6.8 | -4.5 | 10.05 |
| -4.68 | 7.48 | -5.73 | 10.52 |
| -4.81 | 9.27 | -4.39 | 11.32 |
| -5.56 | 7.94 | -6.89 | 11.89 |
| -5.79 | 12.75 | -6.55 | 15.45 |
| -4.79 | 9.06 | -3.81 | 10.93 |
| -5.87 | 10.5 | -7.49 | 14.17 |
| -5.52 | 8.12 | -7.12 | 12.12 |
| -0.62 | 9.54 | -8.24 | 12.62 |
| -6.27 | 8.76 | -10.6 | 15.11 |
| -0.89 | 6.29 | -4.66 | 7.87 |
| -6.69 | 7.48 | -3.06 | 10.49 |
| -3.51 | 9 | -6.77 | 11.79 |
| -3.8 | 7 | -9.31 | 12.25 |
| -8.46 | 5.1 | -6.62 | 11.89 |
| -5.49 | 3.56 | -5.71 | 8.68 |
| Horse Behavior | Behavior Definition |
|---|---|
| Standing | The horse stops moving, stands with all four hooves on the ground, and maintains a stationary posture. |
| Walking | The horse maintains a lower speed and rhythm in its gait. Movement of the forelegs and hind legs is slower, and the body posture remains relatively stable. |
| Running | The horse displays increased movement in both forelegs and hind legs, showing a rocking motion in the body, often characterized by substantial lateral and longitudinal movements while running. |
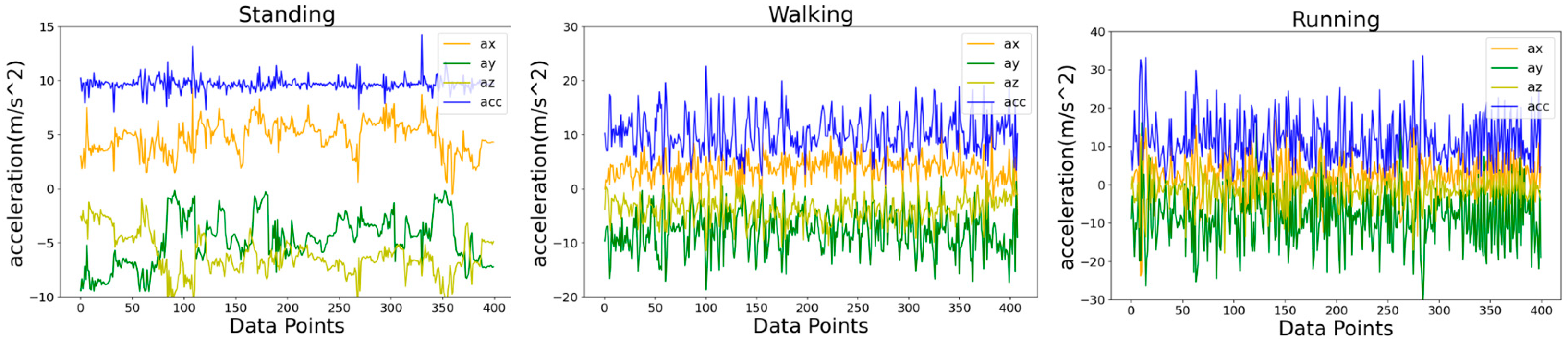
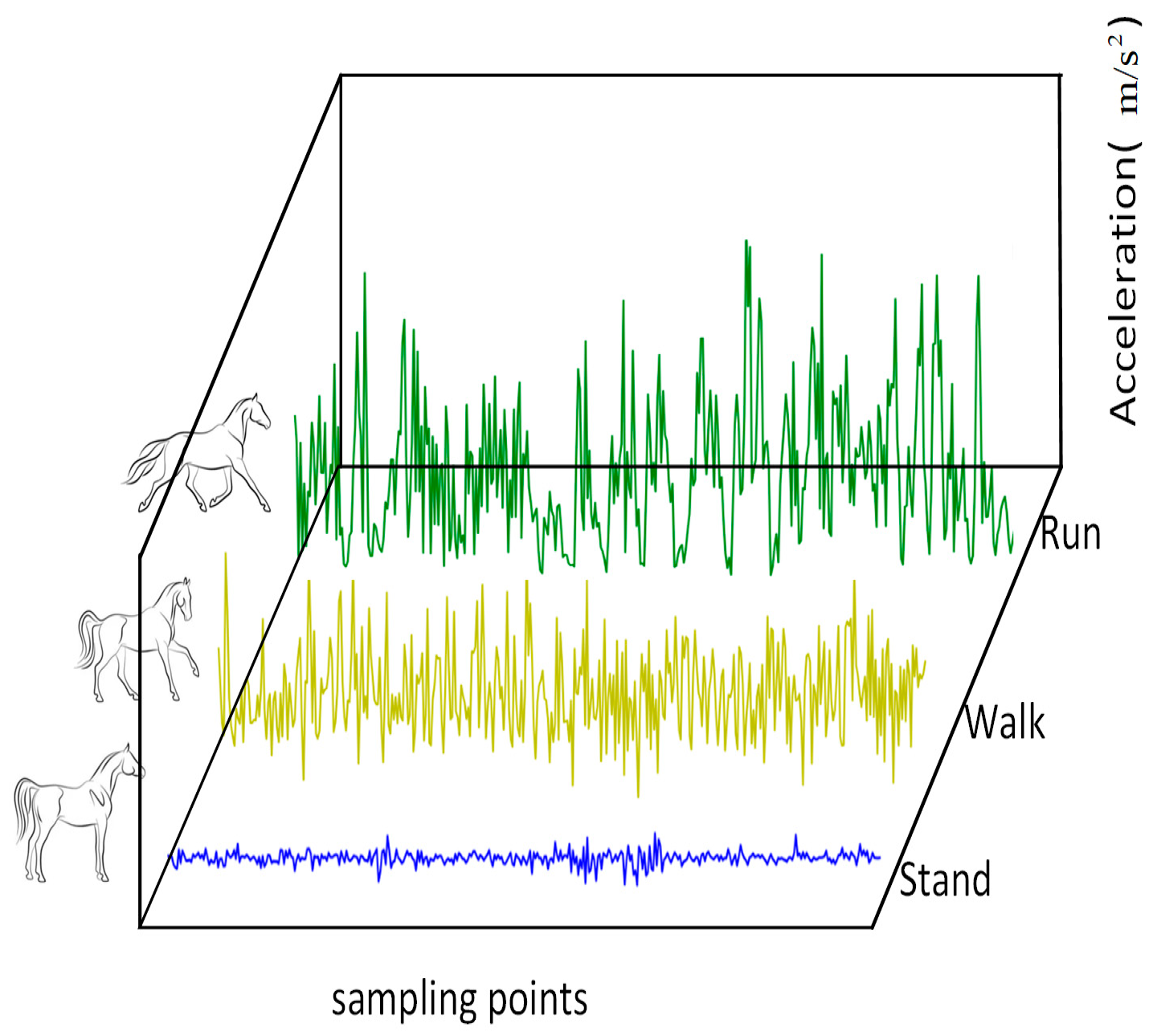
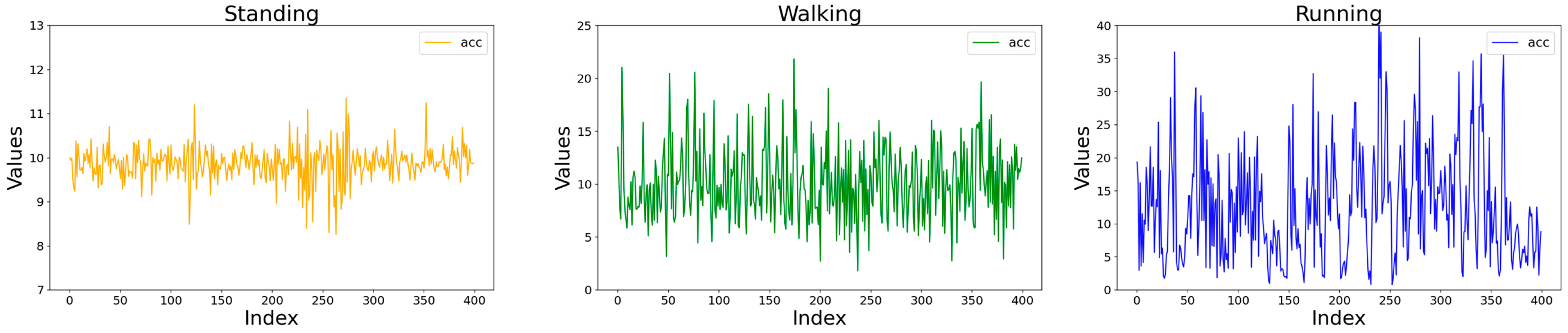
| Standing Behavior | The cumulative acceleration mainly falls within the range of [9.0, 10.5]. |
| Walking Behavior | The combined acceleration data range is mainly distributed within the interval [7.0, 15.0]. |
| Running Behavior | The combined acceleration data range is primarily distributed within the interval [2.0, 40.0]. |
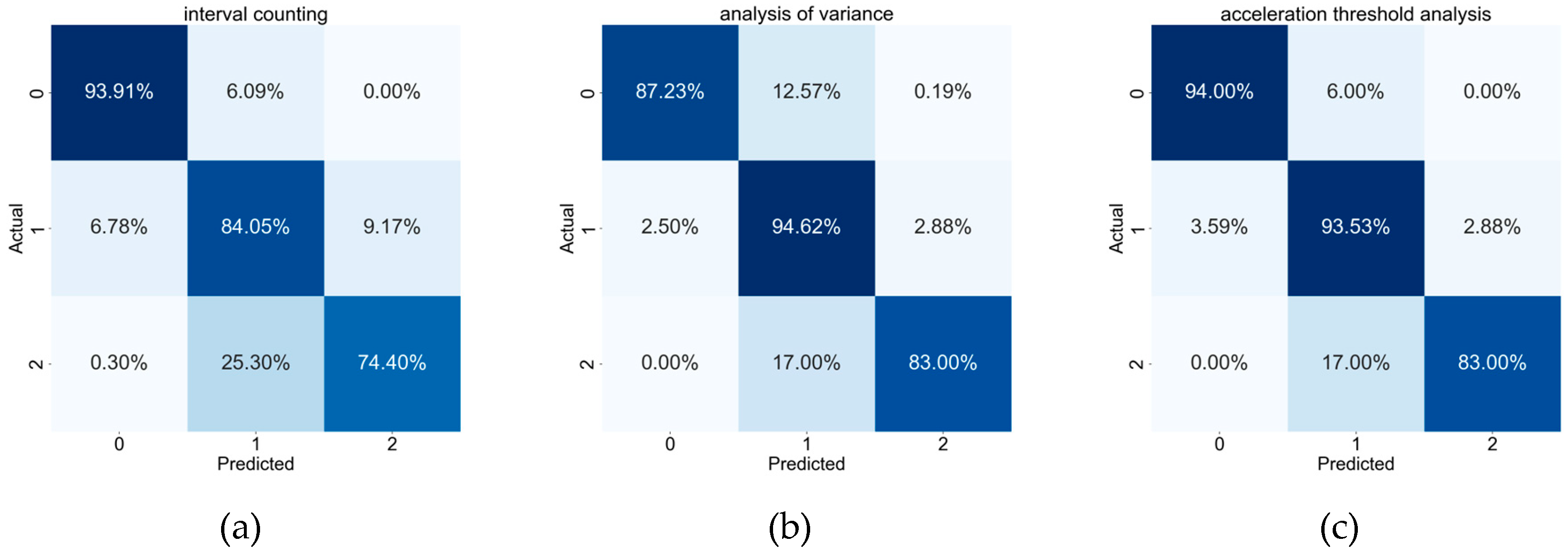
| Interval Analysis Threshold | Behavior Classification Accuracy |
|---|---|
| 86.92% | |
| 87.19% | |
| 78.92% | |
| 74.13% |
| Variance Boundary Value | Behavior Classification Accuracy |
|---|---|
| 1.0 | 90.56% |
| 1.1 | 90.68% |
| 1.2 | 90.72% |
| 1.3 | 90.52% |
| 1.4 | 90.64% |
| 1.5 | 90.44% |
| 1.6 | 90.41% |
| Variance Boundary Value | Behavior Classification Accuracy |
|---|---|
| 20 | 87.23% |
| 25 | 89.83% |
| 27 | 90.37% |
| 28 | 90.79% |
| 29 | 90.87% |
| 30 | 90.72% |
| 31 | 90.68% |
| 32 | 90.60% |
| Standing/Count | Walking /Count | Running /Count | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Actual value | 2986 | 11447 | 5567 |
| Predicted values using Combined Acceleration Interval Counting Method | 3068 | 7236 | 7696 |
| Predicted values using Combined Acceleration Variance Analysis Method | 2678 | 12538 | 4784 |
| Predicted values using Combined Acceleration Threshold Analysis Method | 3094 | 12122 | 4784 |
| Threshold Analysis Model | Interval Counting Model | Variance Analysis Model |
|---|---|---|
|
represents a set containing the interval counting model and the variance analysis model. denotes evaluating the model’s performance through experimentation. |
, represents the data point. N represents the number of data points that meet the condition. represents the threshold adjusted based on the scaling factor. |
represents data points, where L represents the lower threshold and U represents the upper threshold. represents the mean |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





