Submitted:
27 January 2024
Posted:
29 January 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
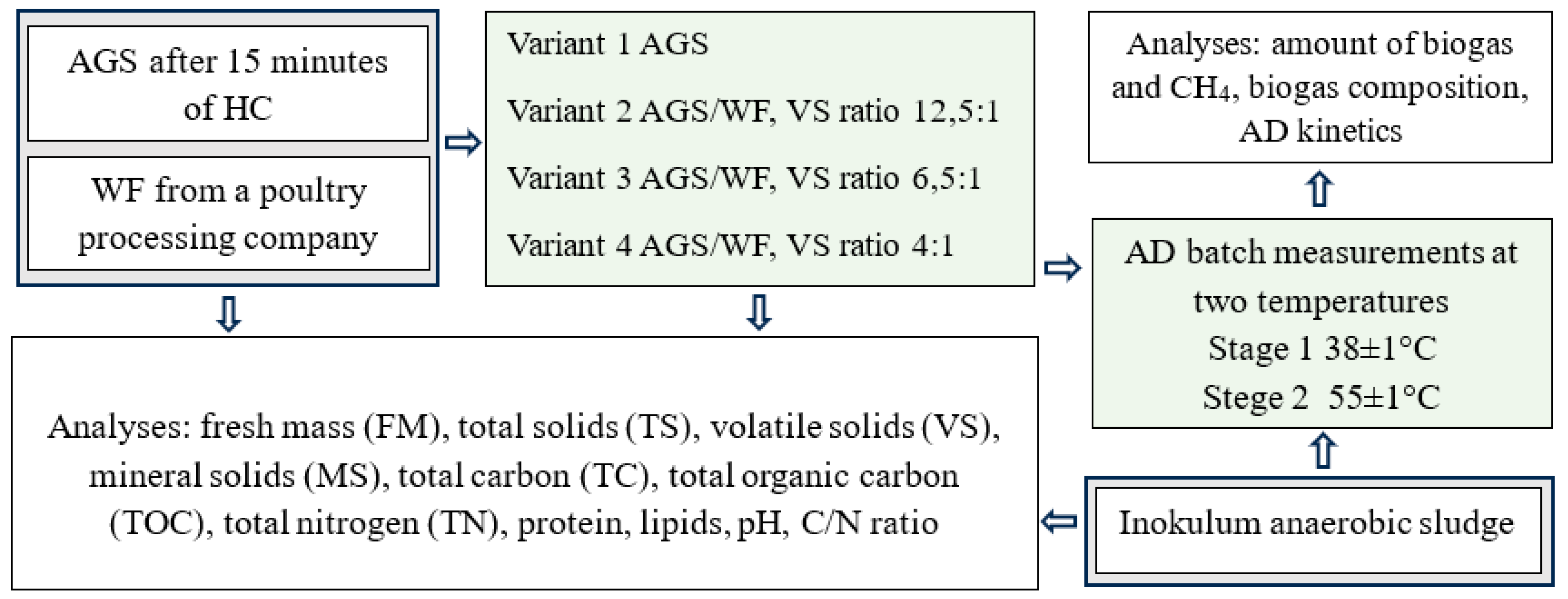
2.1. Organisation of the experiment
2.2. Materials
2.2.1. Aerobic granular sludge (AGS)
2.2.2. Waste fat (WF)
2.2.3. Anaerobic sludge inoculum (AS)
2.3. Research station
2.4. Analytical methods
2.5. Calculation and statistical methods
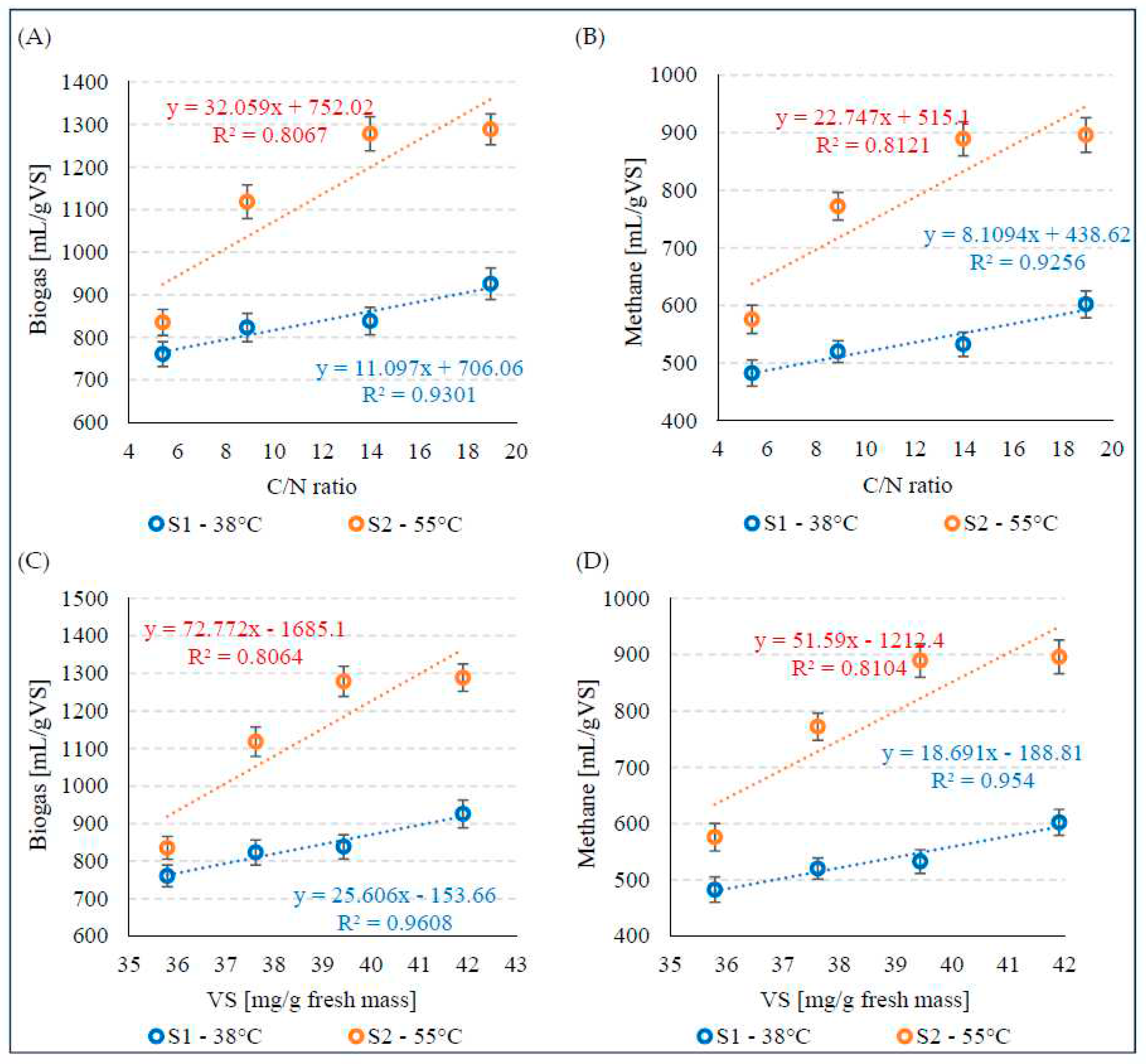
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Characterisation of the substrates
3.2. Anaerobic digestion
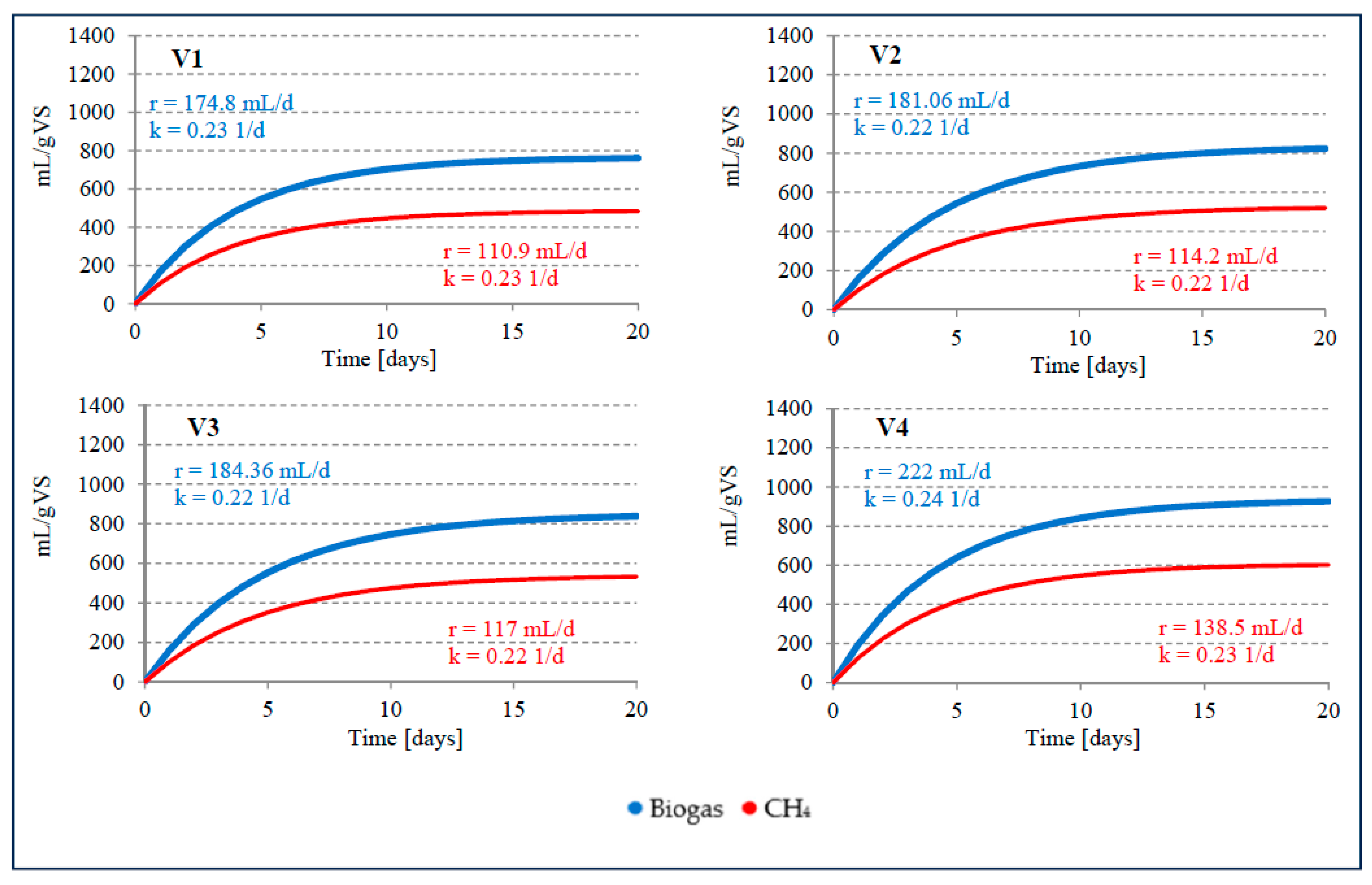
| Variant | Production efficiency | Main components of biogas | ||||||
| Biogas | Methane | |||||||
| mL/gFM | mL/gTS | mL/gVS | mL/gFM | mL/gTS | mL/gVS | CH4 [%] | CO2 [%] |
|
| S1V1 | 27.23±1.1 | 554.5±22.3 | 760.5±29.3 | 17.28±0.6 | 351.8±15.5 | 482.5±22.6 | 63.4±1.1 | 36.1±1.3 |
| S1V2 | 62.1±1.6 | 697.5±31.3 | 823.1±33.4 | 39.21±1.3 | 440.6±21.6 | 519.9±18.8 | 63.2±1.3 | 30.1±1.1 |
| S1V3 | 96.8±2.8 | 748.5±33.5 | 838.3±32.3 | 61.49±1.6 | 475.5±20.5 | 532.5±21.1 | 63.5±1.1 | 29.5±1.3 |
| S1V4 | 128.5±2.5 | 826.6±35.4 | 925.8±36.8 | 98.37±1.5 | 537.5±22.4 | 602.0±23.2 | 65.0±1.2 | 28.9±1.2 |
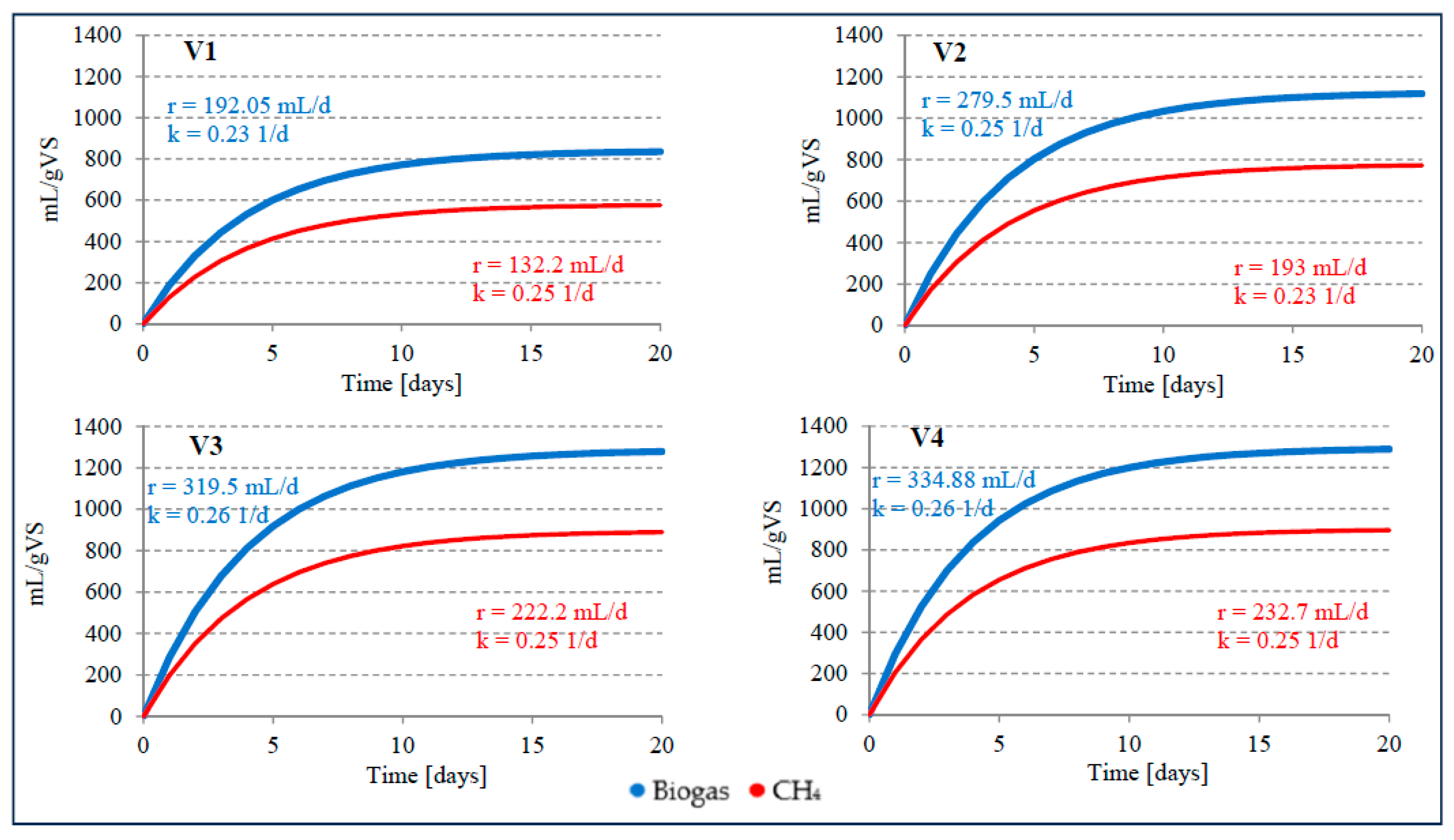
| Variant | Production efficiency | Main components of biogas | ||||||
| Biogas | Methane | |||||||
| mL/gFM | mL/gTS | mL/gVS | mL/gFM | mL/gTS | mL/gVS | CH4 [%] | CO2 [%] |
|
| S2V1 | 29.90±1.2 | 609.0±24.4 | 835.2±30.3 | 20.62±0.8 | 419.9±19.6 | 575.9±24.6 | 68.9±1.2 | 30.6±1.1 |
| S2V2 | 81.3±1.9 | 1016.8±36.2 | 1118.5±39.3 | 126.2±2.1 | 702.1±25.8 | 772.3±24.1 | 69.0±1.3 | 30.0±1.3 |
| S2V3 | 130.0±2.6 | 1083.2±32.3 | 1278.2±40.2 | 67.07±1.4 | 753.7±29.6 | 889.4±29.7 | 69.6±1.3 | 29.1±1.2 |
| S2V4 | 148.8±2.1 | 1150.4±31.1 | 1288.4±36.4 | 103.4±1.7 | 799.9±28.7 | 895.8±30.1 | 69.5±1.2 | 29.2±1.1 |
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Woo, D. C. Y.; Goh, Q. H.; Poh, P. E.; Chew, I. M. L. A Technoeconomic Analysis of Sewage Sludge Valorization for Carbon Emission Reduction. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2023, 13, 13591–13604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almansa, X. F.; Starostka, R.; Raskin, L.; Zeeman, G.; De Los Reyes, F.; Waechter, J.; Yeh, D.; Radu, T. Anaerobic Digestion as a Core Technology in Addressing the Global Sanitation Crisis: Challenges and Opportunities. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 19078–19087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Wang, J.; Liu, W. A View of Anaerobic Digestion: Microbiology, Advantages and Optimization. Acad. J. Environ. Earth Sci. 5, 1–8. [CrossRef]
- Hallaji, S. M.; Torabian, A.; Aminzadeh, B.; Zahedi, S.; Eshtiaghi, N. Improvement of Anaerobic Digestion of Sewage Mixed Sludge Using Free Nitrous Acid and Fenton Pre-Treatment. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2018, 11, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Guo, L.; Zheng, Y.; Yu, D.; Jin, C.; Zhao, Y.; Yao, Z.; Gao, M.; She, Z. Effect of Mixed Primary and Secondary Sludge for Two-Stage Anaerobic Digestion (AD). Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 343, 126160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaveli, F.; Petala, M.; Tsiridis, V.; Darakas, E. Enhanced Mesophilic Anaerobic Digestion of Primary Sewage Sludge. Water 2021, Vol. 13, Page 348 2021, 13, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannacharaju, M.; Natarajan, P.; Villalan, A. K.; Jothieswari, M.; Somasundaram, S.; Ganesan, S. An Innovative Approach to Minimize Excess Sludge Production in Sewage Treatment Using Integrated Bioreactors. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 67, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Capua, F.; Spasiano, D.; Giordano, A.; Adani, F.; Fratino, U.; Pirozzi, F.; Esposito, G. High-Solid Anaerobic Digestion of Sewage Sludge: Challenges and Opportunities. Appl. Energy 2020, 278, 115608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmegeed, M. N. M. Optimisation of Sludge Management in EThekwini Municipality, College of Agriculture, Engineering and Science, University of KwaZulu-Natal, 2022.
- Reysset, M. Comprehensive Overview of Biogas for Sanitation Options – Training of Trainers. Gates Open Res. 2021 526 2021, 5, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Dai, X.; Chai, X. Critical Review on Dewatering of Sewage Sludge: Influential Mechanism, Conditioning Technologies and Implications to Sludge Re-Utilizations. Water Res. 2020, 180, 115912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azarmanesh, R.; Zonoozi, M. H.; Ghiasinejad, H. Characterization of Food Waste and Sewage Sludge Mesophilic Anaerobic Co-Digestion under Different Mixing Ratios of Primary Sludge, Secondary Sludge and Food Waste. Biomass and Bioenergy 2020, 139, 105610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazimierowicz, J.; Dębowski, M. Aerobic Granular Sludge as a Substrate in Anaerobic Digestion—Current Status and Perspectives. Sustain. 2022, 14, 10904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, R.; Rabii, A.; Ezzahraoui, F. zahra; Morgan, G.; Iorhemen, O. T. A Review of the State of Development of Aerobic Granular Sludge Technology over the Last 20 Years: Full-Scale Applications and Resource Recovery. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2022, 5, 100173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazimierowicz, J.; Dębowski, M.; Zieliński, M. Microbial Granule Technology—Prospects for Wastewater Treatment and Energy Production. Energies 2023, Vol. 16, Page 75 2022, 16, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaegi, R.; Gogos, A.; Voegelin, A.; Hug, S. J.; Winkel, L. H. E.; Buser, A. M.; Berg, M. Quantification of Individual Rare Earth Elements from Industrial Sources in Sewage Sludge. Water Res. X 2021, 11, 100092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa-Masegosa, A.; Muñoz-Palazon, B.; Gonzalez-Martinez, A.; Fenice, M.; Gorrasi, S.; Gonzalez-Lopez, J. New Advances in Aerobic Granular Sludge Technology Using Continuous Flow Reactors: Engineering and Microbiological Aspects. Water 2021, Vol. 13, Page 1792 2021, 13, 1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Val Del Río, Á.; Palmeiro-Sanchez, T.; Figueroa, M.; Mosquera-Corral, A.; Campos, J. L.; Méndez, R. Anaerobic Digestion of Aerobic Granular Biomass: Effects of Thermal Pre-Treatment and Addition of Primary Sludge. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2014, 89, 690–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ping, Q.; Li, D.; Dai, X.; Li, Y. Comprehensive Insights into the Impact of Pretreatment on Anaerobic Digestion of Waste Active Sludge from Perspectives of Organic Matter Composition, Thermodynamics, and Multi-Omics. Water Res. 2022, 226, 119240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myszograj, S.; Płuciennik-Koropczuk, E. Thermal Disintegration of Sewage Sludge as a Method of Improving the Biogas Potential. Energies 2023, 16, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dababat, S.; Enaime, G.; Wichern, M.; Lübken, M. Aerobic Granular Sludge: Perspectives for Excess Sludge Management and Resource Recovery. Chemie Ing. Tech. 2023, 95, 1881–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, R.; Thakur, R. Valorizing Sludge: A Biorefinery Perspective Prospecting for Sustainable Development. Clean Energy Resour. Recover. Wastewater Treat. Plants as Biorefineries 2022, 2, 435–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, A.; Banerjee, A.; Bhaskar, T.; Bhaskar, T.; Ghosh, D.; Ghosh, D. A Biorefinery Approach for Sewage Sludge. Waste Biorefinery Integr. Biorefineries Waste Valoris. 2020, 393–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zieliński, M.; Dębowski, M.; Kazimierowicz, J.; Nowicka, A.; Dudek, M. Application of Hydrodynamic Cavitation in the Disintegration of Aerobic Granular Sludge—Evaluation of Pretreatment Time on Biomass Properties, Anaerobic Digestion Efficiency and Energy Balance. Energies 2024, 17, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llabrés-Luengo, P.; Mata-Alvarez, J. Kinetic Study of the Anaerobic Digestion of Straw-Pig Manure Mixtures. Biomass 1987, 14, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiśniowska, E.; Janosz-Rajczyk, M. Effect of Chemically Conditioned FOG Fraction on Methane Co-Fermentation with Excess Sewage Sludge with Regard to Heavy Metals Concentration. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 1525–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagos, K.; Zong, J.; Li, D.; Liu, C.; Lu, X. Anaerobic Co-Digestion Process for Biogas Production: Progress, Challenges and Perspectives. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 76, 1485–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestre, G.; Illa, J.; Fernández, B.; Bonmatí, A. Thermophilic Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Sewage Sludge with Grease Waste: Effect of Long Chain Fatty Acids in the Methane Yield and Its Dewatering Properties. Appl. Energy 2014, 117, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamantis, V.; Eftaxias, A.; Stamatelatou, K.; Noutsopoulos, C.; Vlachokostas, C.; Aivasidis, A. Bioenergy in the Era of Circular Economy: Anaerobic Digestion Technological Solutions to Produce Biogas from Lipid-Rich Wastes. Renew. Energy 2021, 168, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidsson, Å.; Lövstedt, C.; la Cour Jansen, J.; Gruvberger, C.; Aspegren, H. Co-Digestion of Grease Trap Sludge and Sewage Sludge. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 986–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqaralleh, R. M.; Kennedy, K.; Delatolla, R.; Sartaj, M. Thermophilic and Hyper-Thermophilic Co-Digestion of Waste Activated Sludge and Fat, Oil and Grease: Evaluating and Modeling Methane Production. J. Environ. Manage. 2016, 183, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.; Liu, R.; Cheng, Y.; Stanisavljevic, N.; Li, L.; Djatkov, D.; Peng, X.; Wang, X. Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Food Waste and Sewage Sludge under Mesophilic and Thermophilic Conditions: Focusing on Synergistic Effects on Methane Production. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 301, 122765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, W.; He, Y.; Zhang, R.; Liu, G. Effect of Ammonia on Methane Production, Methanogenesis Pathway, Microbial Community and Reactor Performance under Mesophilic and Thermophilic Conditions. Renew. Energy 2018, 125, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sulaimi, I. N.; Nayak, J. K.; Alhimali, H.; Sana, A.; Al-Mamun, A. Effect of Volatile Fatty Acids Accumulation on Biogas Production by Sludge-Feeding Thermophilic Anaerobic Digester and Predicting Process Parameters. Ferment 2022, 8, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Jang, H. M.; Shin, S. G.; Kim, Y. M. Thermophilic Anaerobic Digestion: Effect of Start-up Strategies on Performance and Microbial Community. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 687, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seneesrisakul, K.; Sutabutr, T.; Chavadej, S. The Effect of Temperature on the Methanogenic Activity in Relation to Micronutrient Availability. Energies 2018, 11, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banach, A.; Ciesielski, S.; Bacza, T.; Pieczykolan, M.; Ziembińska-Buczyńska, A. Microbial Community Composition and Methanogens’ Biodiversity during a Temperature Shift in a Methane Fermentation Chamber. Environ. Technol. 2019, 40, 3252–3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, M.; Yılmaz, C. Thermodynamic Optimization and Thermoeconomic Evaluation of Afyon Biogas Plant Assisted by Organic Rankine Cycle for Waste Heat Recovery. Energy 2022, 248, 123487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazimierowicz, J.; Dzienis, L.; Dębowski, M.; Zieliński, M. Optimisation of Methane Fermentation as a Valorisation Method for Food Waste Products. Biomass and Bioenergy 2021, 144, 105913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Parliament and of the Council. Regulation (EC) No 1069/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 21 October 2009 Laying down Health Rules as Regards Animal by-Products and Derived Products Not Intended for Human Consumption and Repealing Regulation (EC) No 1774/2002 (Animal; 2009.
- Bernat, K.; Cydzik-Kwiatkowska, A.; Wojnowska-Baryła, I.; Karczewska, M. Physicochemical Properties and Biogas Productivity of Aerobic Granular Sludge and Activated Sludge. Biochem. Eng. J. 2017, 117, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazimierowicz, J.; Dębowski, M.; Zieliński, M. Technological, Ecological, and Energy-Economic Aspects of Using Solidified Carbon Dioxide for Aerobic Granular Sludge Pre-Treatment Prior to Anaerobic Digestion. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Heal. 2023, 20, 4234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luiz de Sousa Rollemberg, S.; Queiroz de Oliveira, L.; Nascimento de Barros, A.; Igor Milen Firmino, P.; Bezerra dos Santos, A. Pilot-Scale Aerobic Granular Sludge in the Treatment of Municipal Wastewater: Optimizations in the Start-up, Methodology of Sludge Discharge, and Evaluation of Resource Recovery. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 311, 123467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mkruqulwa, U.; Okudoh, V.; Oyekola, O. Optimizing Methane Production from Co-Digestion of Cassava Biomass and Winery Solid Waste Using Response Surface Methodology. Waste and Biomass Valorization 2020, 11, 4799–4808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kainthola, J.; Kalamdhad, A. S.; Goud, V. V. Optimization of Process Parameters for Accelerated Methane Yield from Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Rice Straw and Food Waste. Renew. Energy 2020, 149, 1352–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, P.; Yang, X.; Lin, P.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, M.; Ren, L. Process Performance and Microbial Communities in Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Sewage Sludge and Food Waste with a Lower Range of Carbon/Nitrogen Ratio. Bioenergy Res. 2022, 15, 1664–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arelli, V.; Mamindlapelli, N. K.; Begum, S.; Juntupally, S.; Anupoju, G. R. Solid State Anaerobic Digestion of Food Waste and Sewage Sludge: Impact of Mixing Ratios and Temperature on Microbial Diversity, Reactor Stability and Methane Yield. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 793, 148586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadi-Pirlou, M.; Mesri Gundoshmian, T. The Effect of Substrate Ratio and Total Solids on Biogas Production from Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Municipal Solid Waste and Sewage Sludge. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2021, 23, 1938–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestre, G.; Rodríguez-Abalde, A.; Fernández, B.; Flotats, X.; Bonmatí, A. Biomass Adaptation over Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Sewage Sludge and Trapped Grease Waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 6830–6836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cydzik-Kwiatkowska, A.; Bernat, K.; Zielińska, M.; Gusiatin, M. Z.; Wojnowska-Baryła, I.; Kulikowska, D. Valorization of Full-Scale Waste Aerobic Granular Sludge for Biogas Production and the Characteristics of the Digestate. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 135167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazimierowicz, J.; Dębowski, M.; Zieliński, M.; Bartkowska, I.; Wasilewski, A.; Łapiński, D.; Ofman, P. The Use of Solidified Carbon Dioxide in the Aerobic Granular Sludge Pre-Treatment before Thermophilic Anaerobic Digestion. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 7864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Liu, H.; Chen, S.; Dichtl, N.; Dai, X.; Li, N. Effects of Thermal Hydrolysis on Organic Matter Solubilization and Anaerobic Digestion of High Solid Sludge. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 264, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosser, A.; Neczaj, E. Sewage Sludge and Fat Rich Materials Co-Digestion - Performance and Energy Potential. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 198, 1076–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, E. J.; Gil, M. V.; Fernandez, C.; Rosas, J. G.; Gómez, X. Anaerobic Codigestion of Sludge: Addition of Butcher’s Fat Waste as a Cosubstrate for Increasing Biogas Production. PLoS One 2016, 11, e0153139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabouris, J. C.; Tezel, U.; Pavlostathis, S. G.; Engelmann, M.; Dulaney, J. A.; Todd, A. C.; Gillette, R. A. Mesophilic and Thermophilic Anaerobic Digestion of Municipal Sludge and Fat, Oil, and Grease. Water Environ. Res. 2009, 81, 476–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Parameter | Unit | AGS | WF | AS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total solids (TS) | mg/gFM | 49.1±1.8 | 101±5.4 | 47.8±1.3 |
| %FM | 4.91±0.18 | 10.10±0.54 | 4.78±0.13 | |
| Mineral solids (MS) | mg/gFM | 13.3±1.2 | 10.6±0.5 | 14,7±0.3 |
| %TS | 27.1±0.9 | 9.44±0.91 | 30.7±0.2 | |
| Volatile solids (VS) | mg/gFM | 35.8±1.2 | 90.3±1.6 | 33.5±1.4 |
| %TS | 72.9±1.1 | 90.6±1.3 | 69.3±0.8 | |
| Total nitrogen (TN) | mg/gTS | 40.2±5.8 | 95.11±9.6 | 45.3±3.1 |
| Total carbon (TC) | mg/gTS | 297.2±4.5 | 9149±52.6 | 384.4±19.2 |
| Total organic carbon (TOC) | mg/gTS | 216.7±4.1 | 6164±44.4 | 319.7±21.6 |
| Total inorganic carbon (IC) | mg/gTS | 80.5±1.1 | 2985±16.4 | 64,7±20.5 |
| pH | - | 7.31±0.07 | 7.01±0.12 | 7.43±0.06 |
| Lipid | mg/gTS | 4.2±1.2 | 775.5±22.7 | 1.9±0.4 |
| Protein | mg/gTS | 251.3±12.5 | 594.4±110.2 | 283.1±19.4 |
| C/N (TOC/TN) | - | 5.39±1.1 | 64.8±4.4 | 7.06±0.7 |
| Parameter | Unit | Variant 1 | Variant 2 | Variant 3 | Variant 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total solids (TS) | mg/gFM | 49.1±1.8 | 50.8±2.5 | 52.6±2.3 | 54.3±1.9 |
| %FM | 4.91±0.18 | 5.08±0.25 | 5.26±0.23 | 5.43±0.19 | |
| Mineral solids (MS) | mg/gFM | 13.3±1.2 | 13.2±1.6 | 13.1±1.4 | 12.4±1.5 |
| %TS | 27.1±0.8 | 25.98±0.9 | 24.90±0.8 | 22.83±0.7 | |
| Volatile solids (VS) | mg/gFM | 35.8±1.2 | 37.6±1.6 | 39.4±1.4 | 41.9±1.5 |
| %TS | 72.9±1.1 | 74.02±1.9 | 75.10±2.0 | 77.17±1.8 | |
| Total nitrogen (TN) | mg/gTS | 40.2±5.8 | 42.0±3.8 | 43.9±4.4 | 46.3±6.5 |
| Total carbon (TC) | mg/gTS | 297.2±4.5 | 592.3±28.4 | 887.3±21.5 | 1280±42.2 |
| Total organic carbon (TOC) | mg/gTS | 216.7±4.1 | 415±15.2 | 613.2±20.3 | 877±22.3 |
| Total inorganic carbon (IC) | mg/gTS | 80.5±1.1 | 177.3±9.5 | 274.1±8.8 | 403±9.7 |
| pH | - | 7.31±0.07 | 7.27±0.06 | 7.19±0.11 | 7.11±0.07 |
| Lipids | mg/gTS | 4.2±1.2 | 29.9±2.1 | 55.6±4.8 | 89.9±4.2 |
| Proteins | mg/gTS | 251.3±12.5 | 262.7±13.3 | 274.1±14.6 | 289.4±18.4 |
| C/N (TOC/TN) | - | 5.39±1.1 | 9.88±1.9 | 13.96±2.2 | 18.94±2.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





